Digital Forensics Quiz 1
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1 (Introduction to Forensics) & Chapter 2 (Overview of Computer Crime)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Computer Forensics
The use of analytical and investigative techniques to identify, collect, examine, and preserve evidence/information that is magnetically stored or encoded
Objective: recover, analyze, and present computer-based material in such a way that it can be used as evidence in a court of law
7 Domains of a typical IT Infrastructure
User Domain
Workstation Domain (User’s computer)
LAN Domain (server, hub)
LAN-to-WAN Domain (router, firewall)
WAN Domain
Remote Access Domain (broadband internet)
System/Application Domain
Three Ways of Using Scientific Knowledge
Collecting → How you collect evidence determines if that evidence is permitted in a court
Analyzing → Putting together the data you have and finding out what sort of picture is revealed
Presenting → The expert report, expert testimony
Expert Report
Formal document that lists what tests you conducted, what you found, and your conclusions
Includes your curriculum vitae (CV)
Support every conclusion with at least two to three reputable references that either agree with that conclusion or provide support for how you came to that conclusion
Must be very thorough, complete, and error free
Expert Testimony
Deposition—testimony taken from a witness or party to a case before a trial: Less formal and is typically held in an attorney’s office
Sworn testimony—lying under oath is perjury, which is a felony
U.S. Federal Rule 702 defines what an expert is and what expert testimony is
Digital Evidence
Information that has been processed and assembled so that it is relevant to an
investigation and supports a specific finding or determination
Raw information is not, in and of itself, evidence
Data must be relevant to a case in order to be evidence
Types of Evidence
Real → can be physically touched or inspected, e.g., laptop, USB drive, or smartphone
Documentary → written or recorded materials, e.g., emails, system logs, chat transcripts
Testimonial → statements made under oath by a witness or expert, helps to support technical evidences
Demonstrative → explain, or clarify other evidences, e.g., charts containing technical concepts
Scope-Related Challenges to System Forensics
Volume of data to be analyzed
Complexity of the computer system
Size and character of the crime scene (e.g., distributed, geographically dispersed)
Size of the caseload and resource limitations
Types of Digital System Forensics Analysis
Physical storage media / Disk
Email
Network
Internet
Software
Live system
Cell phone / mobile
General Guidelines
Maintain chain of custody
Do not touch suspect drive [exception, e.g., live forensics in cloud environment]
Create a document trail (document everything)
Secure evidence (preserve the integrity, locked room with limited access)
Knowledge Needed for Computer Forensic Analysis
Hardware (e.g., RAM, ROM)
Software (e.g., OS, File System)
Networks
Addresses (e.g., MAC, IP, Port)
File Systems
FAT
NFTS
EXT
APFS
Networking: Addressing
Physical ports
MAC address
IP address
IPv4 example: 192.2.132.8
Logical port numbers
Uniform resource locator (URL)
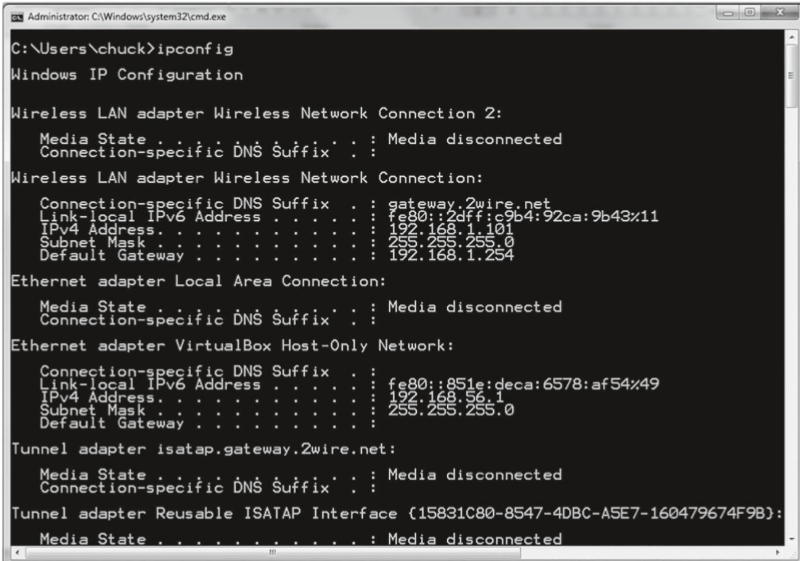
ipconfig
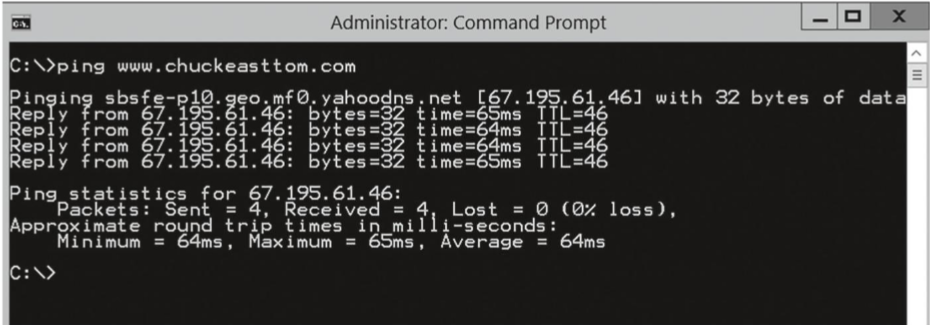
ping
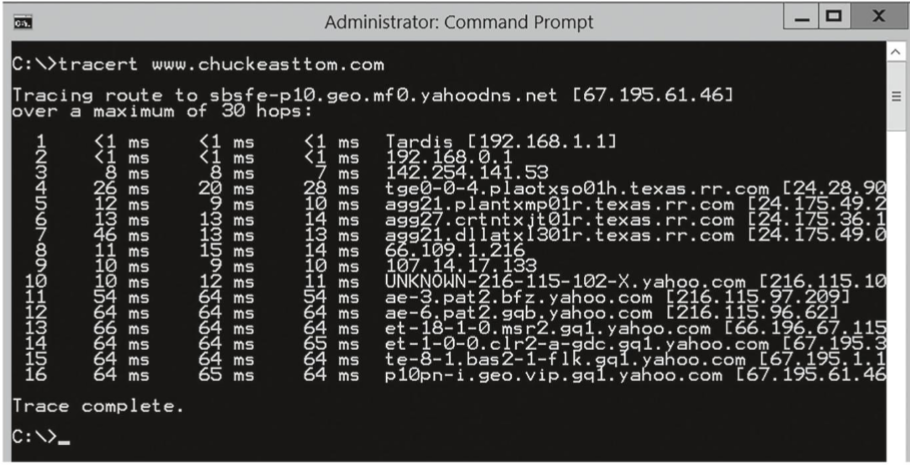
tracert
Obscured information
May be secured by encryption, hidden using steganographic software, compressed, or in a proprietary format
Cybercriminals sometimes obscure information to deter forensic examination
Anti-forensics
Attackers may use techniques to intentionally conceal their identities, locations, and behavior
Examples:
Data destruction
Data hiding
Data transformation
File system alteration
A computer or another device can play one of three roles in a computer crime…
Target of the crime
Instrument of the crime
Evidence repository that stores valuable information about the crime
Identity Theft
Use of another person’s identity
Typically performed for economic gain, e.g., credit card information
Common methods: phishing, spyware, discarded information
Phishing
An attempt to trick a victim into giving up personal information
Usually done by emailing the victim and claiming to be from an organization the victim would trust
Generally, a process of reaching out to as many people as possible, hoping enough people respond
EX: fake email pretending to be from IRS
More-targeted attacks: spear phishing (specific group) and whaling (specific high-value target)
Spyware
Software that can monitor activity on a computer
May involve taking screenshots or perhaps logging keystrokes
Can have legal or illegal applications
Example: malicious cookies (programmer designed, website may be legal)
Discarded Information
Another method that allows a hacker to gather information about a person’s identity
Often referred to as dumpster diving
Shred documents before throwing them out to avoid identity theft
Hacking via SQL Injection
Typical SQL statement:
SELECT * FROM tblUsers WHERE USERNAME = '" + txtUsername.Text +' AND PASSWORD = '" + txtPassword.Text +" 'Specific username and password:
SELECT * FROM tblUsers WHERE USERNAME = 'thisuser' AND PASSWORD = 'letmein'SQL injection example:
SELECT * FROM tblUsers WHERE USERNAME = '' or '1' = '1' AND PASSWORD = '' or '1' = '1'→ RETURNS ALL RECORDSHow it affects forensics:
Look in firewall logs
Search database logs
Hacking via Cross-Site Scripting
Perpetrator seeks out someplace on target website that allows end users to post text that other users will see, such as product reviews
Instead of posting a review or other text, the attacker posts JavaScript
If website does not filter user input before displaying, other users navigate to this review and script executes
EX: redirect users to the phishing site (may look similar to the original site and capture the login information of the users)
Look for scripts in the website; search the web server’s logs for redirect messages
Hacking via Ophcrack
When Windows boots up, system locks the SAM (Security Account Manager)
file so it cannot be copied or edited
Passwords are stored using hash computation
A hacker can use Ophcrack to:
Boot to a Linux Live CD
Compares rainbow table (precomputed table) against SAM file, searching for matching passwords
Ophcrack displays all the passwords it finds
Fraud
Any attempt to gain financial reward through deception
Investment offers, e.g., pump and dump of stock through false rumours
Data piracy, e.g., illegal copies of software, games, and movies etc.
How it affects forensics:
Trace the communications
Follow the money
Non-Access Computer Crimes
Crimes that do not involve an attempt to actually access the target (The attacker doesn’t need to log into the victim’s computer)
EX: Denial of service (DoS) attacks, viruses, logic bombs
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Three-way handshake:
Client machine sends TCP packet to server with synchronize (SYN) flag turned on
Server acknowledges the request to synchronize by sending back a TCP packet with two flags turned on: acknowledgment (ACK) flag and the SYN flag
Client responds with a single ACK flag and communications begin
SYN flood attack:
Attacker keeps sending SYN packets but never responds to the SYN/ACK it receives from the server
Eventually, the server has so many open connections it can no longer respond to legitimate users
Viruses
Any software that self-replicates, like a human or animal virus (malware, e.g., viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, etc and virus are related, but not the same thing
Categories:
Macro (infect the macros in documents)
Memory-resident (persistent even after shut down)
Multi-partite (attack computer in multiple ways)
Armored (hard to analyze, e.g., due to encryption)
Sparse infector (malicious activities sporadically)
Polymorphic (can change forms time to time)
How it affects forensics:
Easy to locate, but difficult to trace back to the creator
Document the particulars of the virus
Identify commonality among infected computers, such as a visit to the same website
Logic Bombs
Malware designed to harm a system when some logical condition is reached
Often triggered based on a specific date and time
Possible to distribute a logic bomb via Trojan horse (appears as something useful/harmless, but when activated perform malicious activities)
Cyberterrorism
The use of the internet to perform terrorist activities
Can include large-scale disruption of computer networks
Attacks on national power grids
Investigate as you would any other cybercrime, difference lies in the jurisdiction
Cyberterrorism and cyberespionage are referred to the FBI
Which of the following is not true of computer forensics
The objective is to recover, analyze, and present computer-based material
The emphasis is on the volume of evidence.
A forensic specialist must adhere to stringent guidelines.
Any device that can store data is potentially the subject of forensics.
The emphasis is on the volume of evidence.
__________ is the continuity of control of evidence that makes it possible to account for all that has happened to evidence between its original collection and its appearance in court, preferably unaltered.
Consistent scientific manner
Demonstrative evidence
The chain of custody
Documentary evidence
The chain of custody
Ed is an expert witness providing testimony in court. He uses high-tech computer animation to explain a technical concept to the judge and jury. What type of evidence is Ed using?
Real
Documentary
Demonstrative
Testimonial
Demonstrative
Tonya is an attorney. She is preparing evidence to be presented in a court trial. Her exhibits include several photographs, printouts of email messages, and printouts of text messages. What type of evidence is Tonya preparing?
Documentary evidence
Real evidence
Testimonial evidence
Demonstrative evidence
Documentary evidence
Which of the following is the process of examining data traffic, including transaction logs and real-time monitoring using sniffers and tracing?
Network forensics
Live system forensics
Software forensics
Email forensics
Network forensics
Which of the following is not true of random access memory (RAM)?
It is volatile memory.
It stores programs and data that are currently open.
It cannot be changed.
It retains items in memory for as long as the computer has power supplied to it.
It cannot be changed.
Arturo is a digital forensics specialist. He is investigating the computer of an identity theft victim. Which of the following is an attack vector that cannot be investigated on the victim’s machine?
Spyware
Dumpster diving
SQL injection
Phishing email
Dumpster diving
The main purpose of ____ is to prevent legitimate users from being able to access a give computer resource.
a logic bomb
a phishing attack
a denial of service (DoS) attack
identity theft
a denial of service (DoS) attack
Attackers leveraging Structured Query Language (SQL) injection can be thwarted using proper programming techniques that:
force applications to consistently read true statements as false.
bypass validation to allow for stronger security controls.
force applications to return all records where the username and password are blank.
disallow the use of additional characters to “escape” an application reading them as text and instead process them as an instruction.
disallow the use of additional characters to “escape” an application reading them as text and instead process them as an instruction.
Bill is an accountant for a construction firm. He receives an urgent email at 5:30 p.m. on Friday that appears to be from his company's chief financial officer. The email is approving a request for funds to be moved from a corporate account to a personal account for the construction manager. The request is for the funds to be moved immediately so that the manager can purchase equipment needed for a project to be completed over the weekend. Bill notices that the sender's actual email account is from a domain that is not affiliated with the company. What type of attack is likely underway?
A SQL injection attack
Phishing
A denial of service (DoS) attack
Spyware
Phishing
What is the name of a type of targeted phishing attack in which the criminal targets a high-value target, such as a senior company executive?
C-Suite attack
Spoofing
Whaling
Denial of service attack
Whaling
Window passwords are hashed and then stored in the ___ on the local machine.
/domain/password file
PSDW store
Windows Registry
SAM file
SAM file