ch. 24, section 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/23
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
what marks the branching points on the evolutionary tree?
animal’s anatomical features
2
New cards
relationships on the evolution tree are inferred by what?
studies of similarities in embryological development and shared anatomic features
3
New cards
what was the first major change in body plan?
the development of tissues
4
New cards
what is symmetry:
the balance or similarity of an organism’s structure and the next branching point after tissues
5
New cards
what are the different types of symmetry?
asymmetry, radial symmetry, and bilateral symmetry
6
New cards
asymmetry:
irregular shape, no symmetry or balance (example: sponge)
7
New cards
radial symmetry:
can be divided along any plane, through a central axis (example: jellyfish)
8
New cards
bilateral symmetry:
* can be divided into mirror-image halves along only one plane (example: bird)
* animals with bilateral symmetry also have an anterior and posterior end
* animals with bilateral symmetry also have an anterior and posterior end
9
New cards
what is cephalization?
a tendency to concentrate nervous tissue and sensory organs at the anterior end of the animal
10
New cards
anterior:
head
11
New cards
posterior:
tail
12
New cards
ventral:
belly side
13
New cards
dorsal:
backside
14
New cards
animals with bilateral symmetry have a gut, which is:
either a sac inside the body or a tube that runs through the body, where food is digested
15
New cards
how many openings does a sac-like gut have?
one
16
New cards
how many openings does a tube-like gut have?
two
17
New cards
name the types of body cavities:
1. coelomates
2. pseudocoelomates
3. acoelomates
18
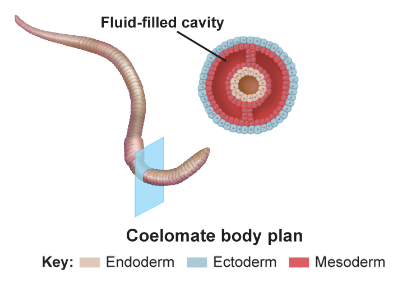
New cards
coelomates:
mesoderm-lined, fluid-filled cavity between gut and outside wall (example: mollusks)
19
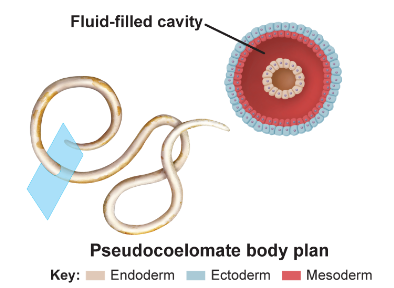
New cards
pseudocoelomates:
(false cavity) one partially-lined, fluid-filled body develops between mesoderm and endoderm (example: roundworms)
20
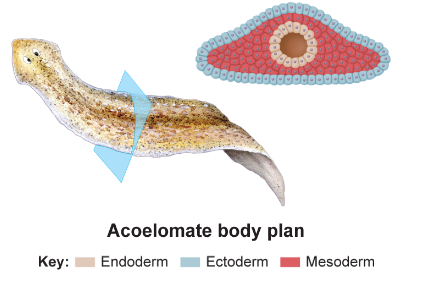
New cards
acoelomates:
no coelom, have solid bodies without fluid-filled body, and no circulatory system (example: sponges)
21
New cards
protosomes:
coelomate animals that develop mouths from the first opening in the gastrulas and the anus from the second opening
22
New cards
deuterostomes:
coelomate animals that develops the anus from the first opening in the gastrulas and mouths from the second opening
23
New cards
segmentation:
evolutionary development which allows segmented animals to be “put together”
24
New cards
animals advantages of segmentation:
* can survive damage to one segment because the other segments can carry out the functions of the damaged
* movement is more effective
* movement is more effective