Forces In Equilibrium
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is a Vector and a Scalar Quantity?
Vector - A physical quantity that has a direction as well as a magnitude (Displacement, Velocity, Weight, Acceleration)
Scalar - A physical quantity that has a magnitude but no direction (Distance, Speed, Mass, Temperature)
How can you add vectors?
If two vectors are perpendicular to each other it is best to use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the resultant vector or angle.
If the vectors are not at 90 degrees to each other, trigonometry/scale diagram will be better to use.
What is Equilibrium?
Equilibrium is the state in which an object has a resultant force and a resultant moment equal to 0, meaning it has to be either at rest or moving with a constant velocity.
What is a Moment?
The Moment (Turning Force/Torque) about a point is the perpendicular distance from the point multiplied by the distance from the point to the line of action from the force.
Moment = F x d
What is the Principle of Moments?
For an object in equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise moments must be equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments.
What is the Centre of Mass?
The point at which the whole mass of an object appears to act. If an object is described as uniform, its centre of mass is in its geometric centre.
What is a Couple?
A pair of equal and opposite forces, separated by a distance D, between the lines of action of the forces.
What is Stable and Unstable Equilibrium?
Stable Equilibrium - A state where an object returns to its equilibrium position after being displaced.
Unstable Equilibrium - A state where if an object is displaced, it does not return to its equilibrium position.
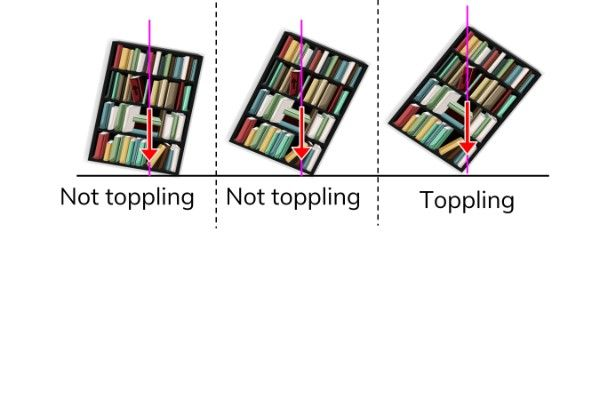
What is Tilting and Toppling?
Tilting - Where an object at rest on a surface is acted on by a force that raises it up on one side.
Toppling - Where an object on a flat surface is tilted more and more so that the line of action of its weight passes beyond the pivot.