Mod 13: Mixtures and Solutions
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
solution
another name for a **homogeneous mixture.**
the result when you mix a solvent and solute
the result when you mix a solvent and solute
2
New cards
solute
what dissolves in a substance
3
New cards
miscible
meaning (liquids) soluble in each other in __any proportion__
4
New cards
insoluble
doesn’t dissolve in substance. leads to a **heterogeneous mixture**
5
New cards
immiscible
two (liquids) that can be mixed, but separate after
6
New cards
suspensions
contain **large-sized particles** that __settle out__ if left undisturbed.
7
New cards
colloids
**medium-sized particles** that __doesn’t settle out__
*particles stay within substance + can’t be filtered out*
*particles stay within substance + can’t be filtered out*
8
New cards
Brownian motion
jerky random movements of particles in a liquid colloid from the results of particle collisions
9
New cards
Tyndall effect
scattering of light by dispersed colloid/suspension particles
10
New cards
concentration
measure of how much solute dissolved in a specific solvent/solution
11
New cards
diluted
small concentration of solute
12
New cards
concentrated
large concentration of solute
13
New cards
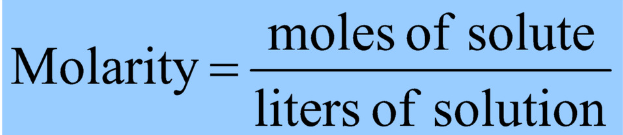
molarity
number of moles of a solute dissolved per liter of a solution
14
New cards
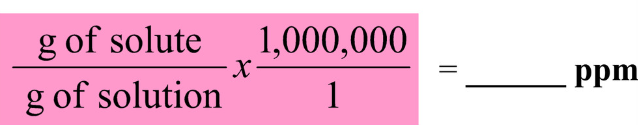
parts per million
**ppm**. used to express extremely small concentrations
15
New cards
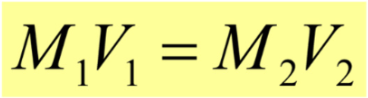
dilutions
the adding of more solvent in ____ **doesn’t change the solute’s amount of moles**
16
New cards
solvation
the **dissolving process**. called *hydration* within water.
\
the surrounding of solute particles with solvent particles, forming a solution. __breaks apart__
\
the surrounding of solute particles with solvent particles, forming a solution. __breaks apart__
17
New cards
heat of solution
overall energy change that occurs during solution formation process
\
either warmer or cooler __depending on the solution dissolved__
\
either warmer or cooler __depending on the solution dissolved__
18
New cards
agitation
stirring or shaking. __increases the rate of solvation__
19
New cards
surface area
more particles broken from dissolving = more ____. allows more collision between particles + __increases rate of solvation__
20
New cards
temperature
increases kinetic energy in particles, and __increases solubility.__
\
**does the opposite for gases** → gases are less soluble at higher __.
\
**does the opposite for gases** → gases are less soluble at higher __.
21
New cards
solubility
describes the ability to dissolve in a substance.
\
depends on __nature of solution__ and __temperature__
\
depends on __nature of solution__ and __temperature__
22
New cards

Henry’s Law
solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to pressure
\
S = g/L
\
S = g/L
23
New cards
unsaturated
When a solution contains less dissolved solute than what can dissolve for a given temperature and pressure, it is called a ____ solution.
\
**more solute can be dissolved**
\
**more solute can be dissolved**
24
New cards
saturated
When a solution has the maximum amount of dissolved solute for a given amount of solute at a specific temperature and pressure, it is called a ___ solution
\
**no more solute can be dissolved**
\
**no more solute can be dissolved**
25
New cards
supersaturated
When a solution contains more dissolved solute than a saturated solution, it is called a ___ solution.
\
**formed at high temperatures then slowly cooled**
(unstable) → forms a crystal
\
**formed at high temperatures then slowly cooled**
(unstable) → forms a crystal
26
New cards
colligative properties
physical properties of solutions affected by number of particles but not by the identity of dissolved solute particles
27
New cards
electrolyte
ionic compounds that **dissociate** (not dissolve).
\
produces more mols of each element involved in substance
“strength” is determined by **how many particles dissociate**
\
produces more mols of each element involved in substance
“strength” is determined by **how many particles dissociate**
28
New cards
nonvolatile solute
a solute that has little tendency to become a gas.
\
*When added to a solvent, creates colligative properties*
\
*When added to a solvent, creates colligative properties*
29
New cards
vapor pressure lowering
the lowering of a solvent’s vapor pressure due to __interference from a nonvolatile solute__
30
New cards
boiling point elevation
the temperature difference between a solution’s boiling point and a pure solvent’s boiling point
31
New cards
freezing point depression
difference in temperature between a solution’s freezing point and its pure solvent’s freezing point