Alkene Addition Reactions
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
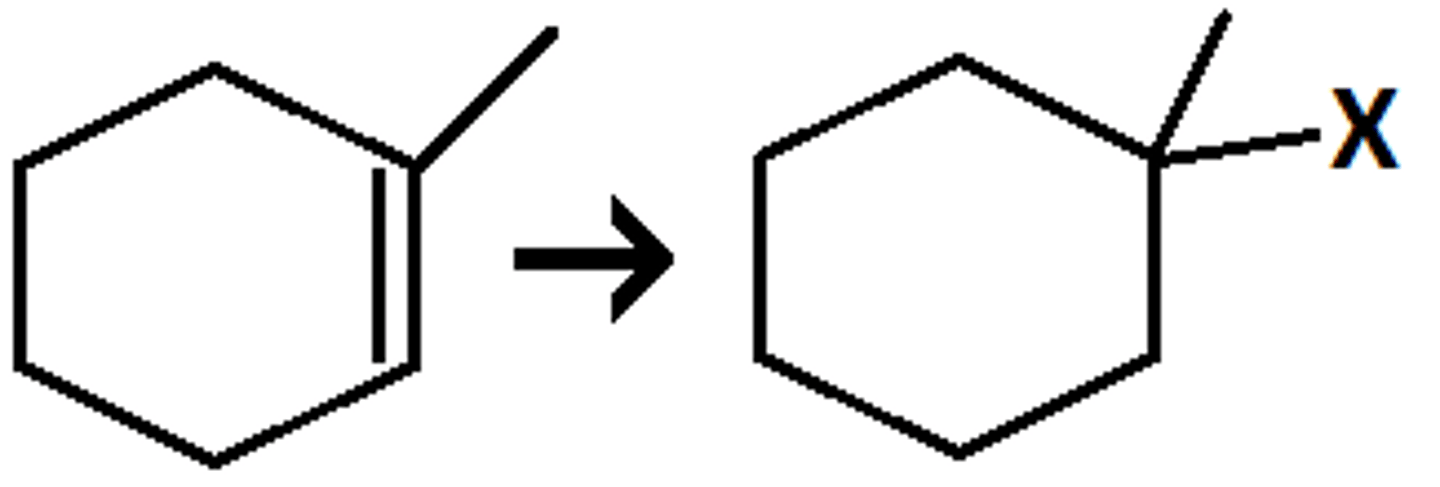
Hydrohalogenation
(Requires a strong acid) - HCl, HBr, HI
Markovnikov
No stereochemical control (racemic mixture)
Attaches a hydrogen and a halogen
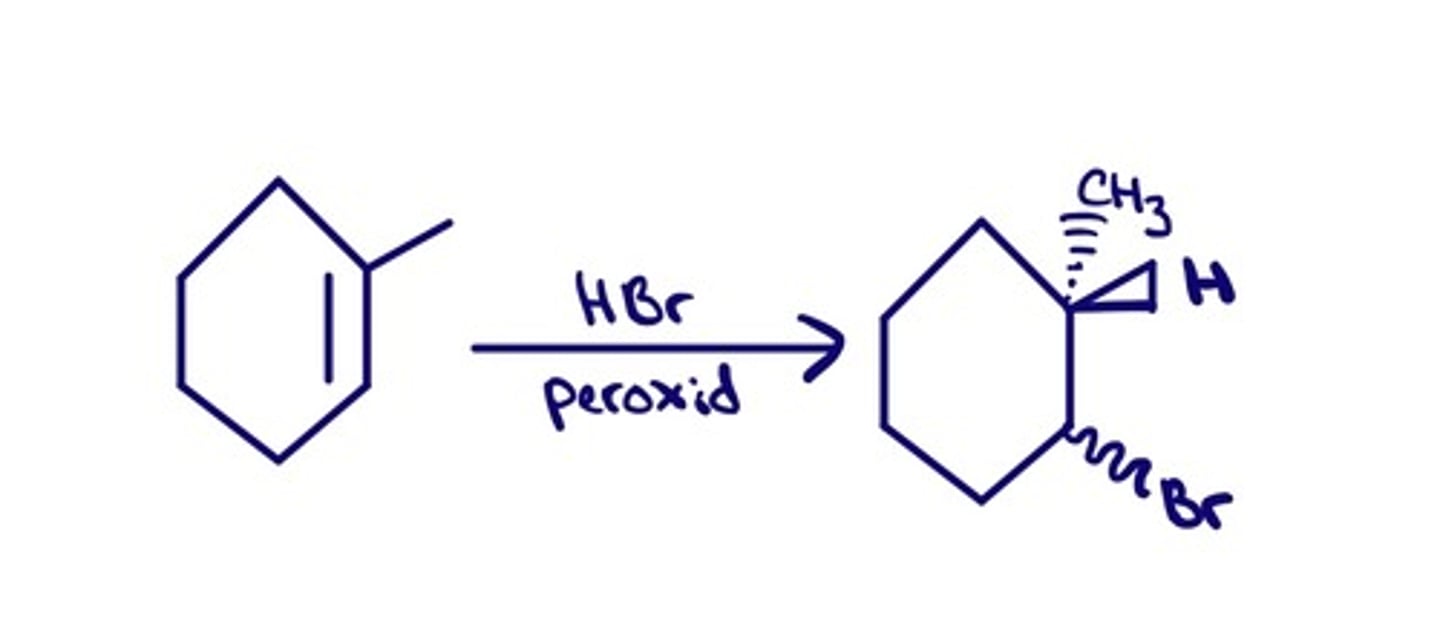
Hydrohalogenation (In Peroxide RO-OR)
(Requires Strong Acid) - HCl, HBr, HI
Anti-Markovnikov
No stereochemical control
Attaches a hydrogen and a halogen
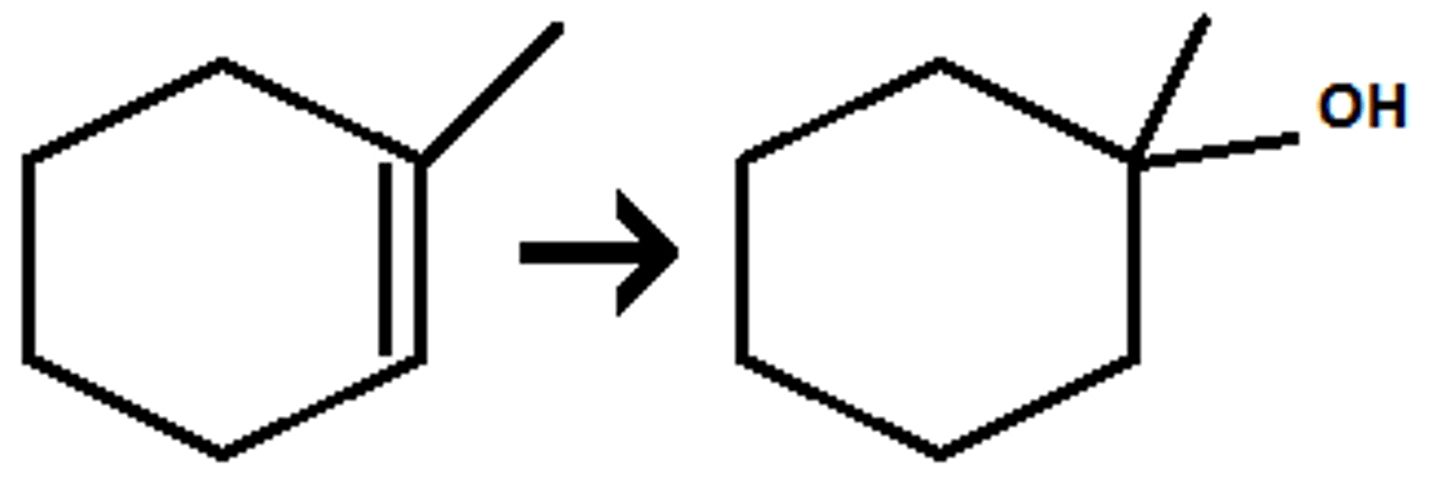
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
Uses H2SO4 & H2O
Markinov
No syn / Anti (Adds an alcohol and hydrogen)
Attatches an OH and H to the molecule
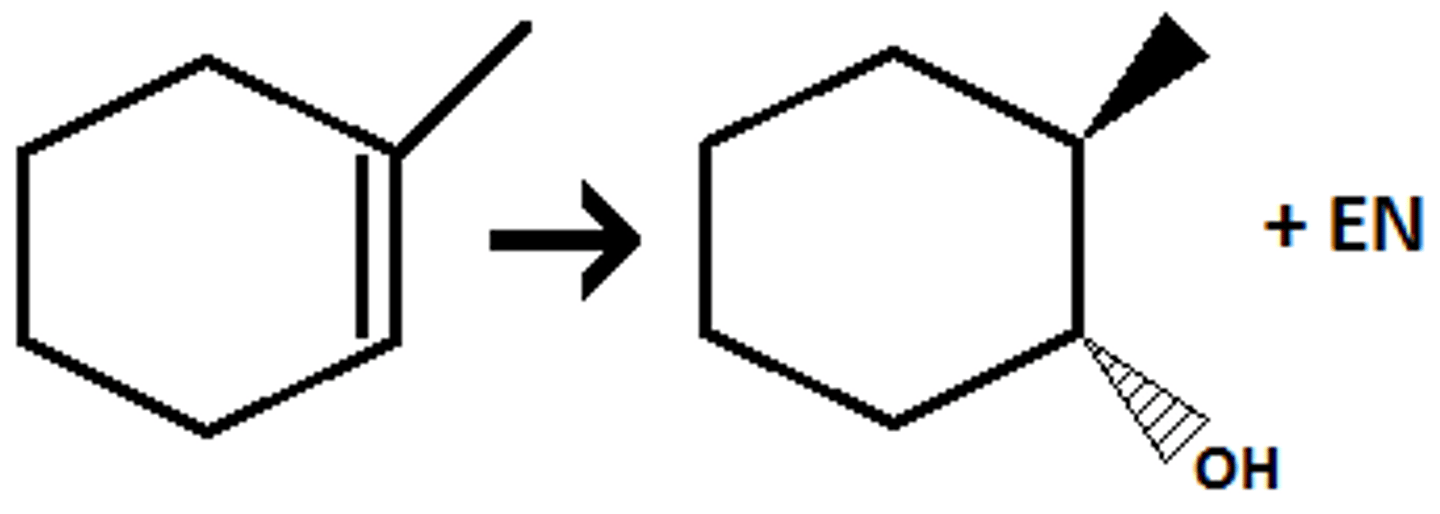
Hydroboration
Uses BH3 *THF or NaOH & H2O2
Anti-Markovnikov
Syn addition (Concerted reaction)
Attaches an OH to the alkenes
Hydrogenation
Uses H2 (Pd, Pt, Ni catalysts)
No Markovnikov / Anti-Markovnikov
Syn addition
Results in two hydrogens being added across alkene
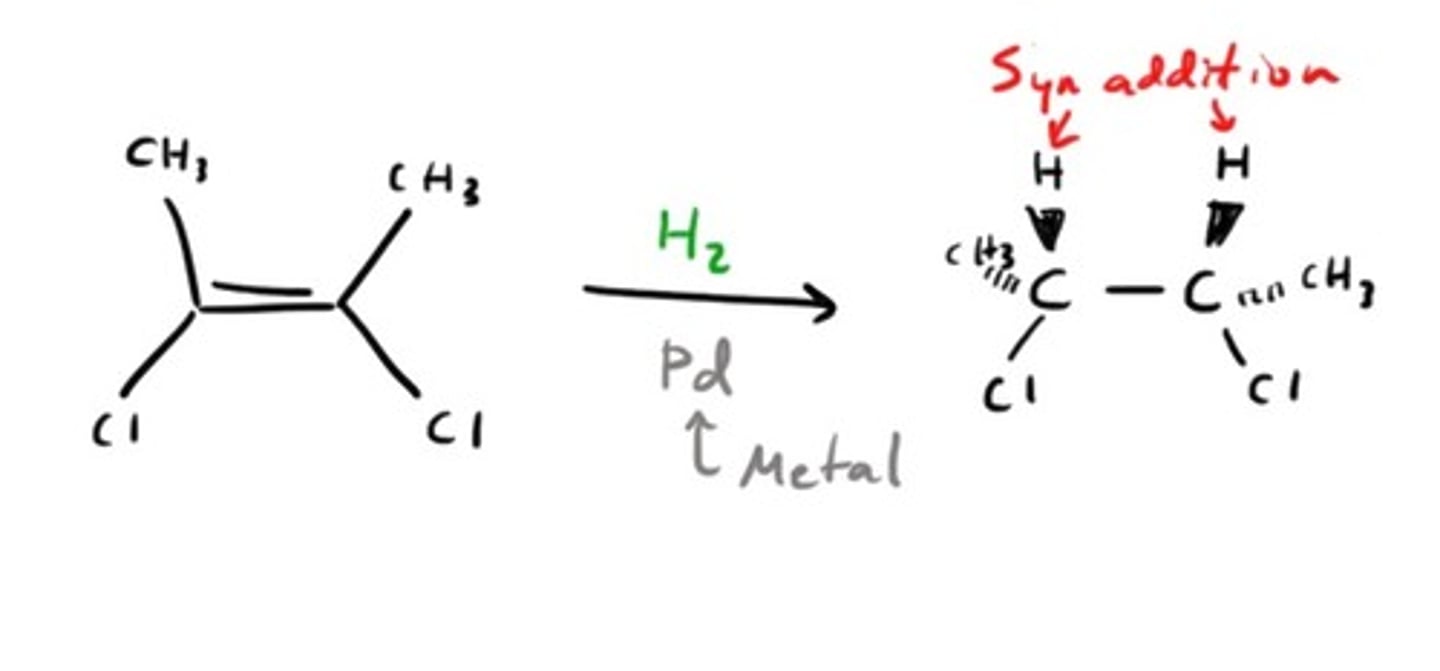
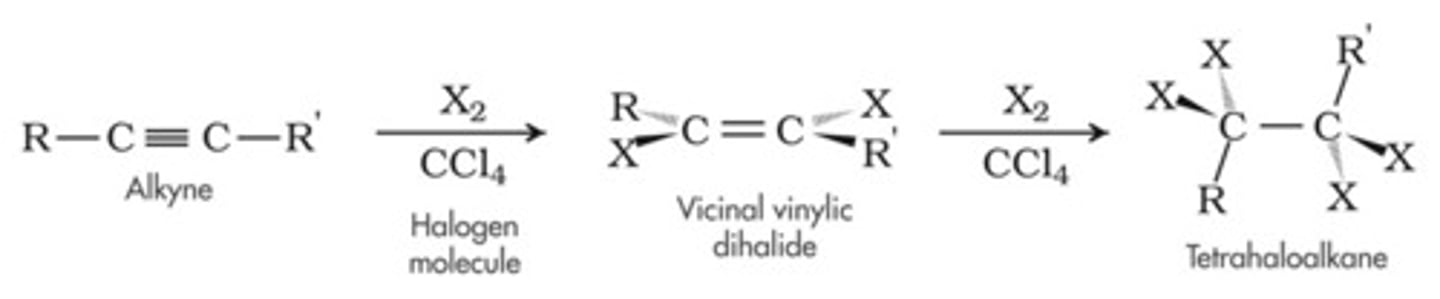
Halogenation
Uses X2 (X= Cl or Br)
No Markovnikov / Anti-Markovnikov
Anti Relationship
(Uses Halonium ion intermediate (basically just two carbons bonding to the same halogen))
Results in an addition of a halogen on both sides across an alkene
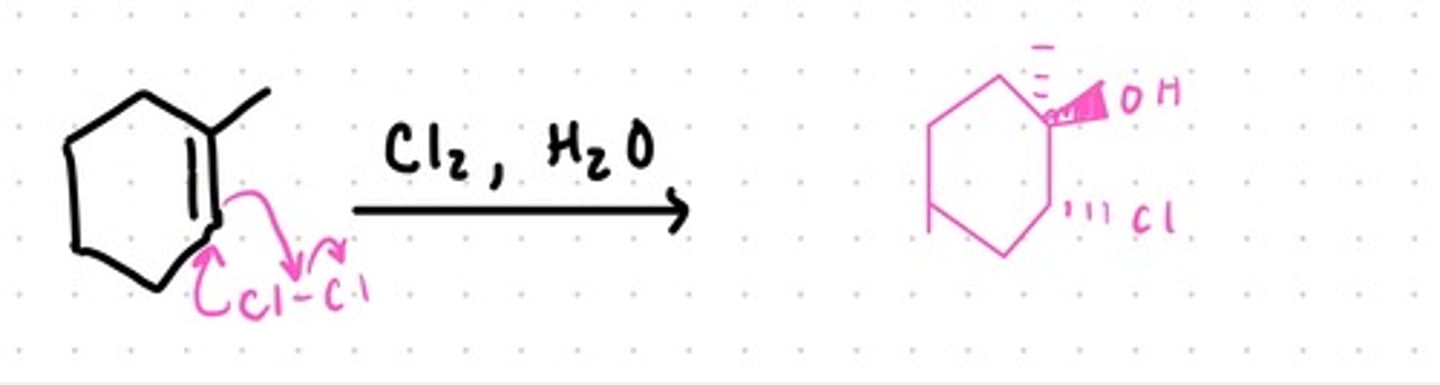
Hydroxyhalogenation
Uses Water and X (X= Cl or Br)
OH bond goes to more substituted carbon
Anti Relationship
Results in an OH and Halogen to be added across an alkene (can form enantiomers)
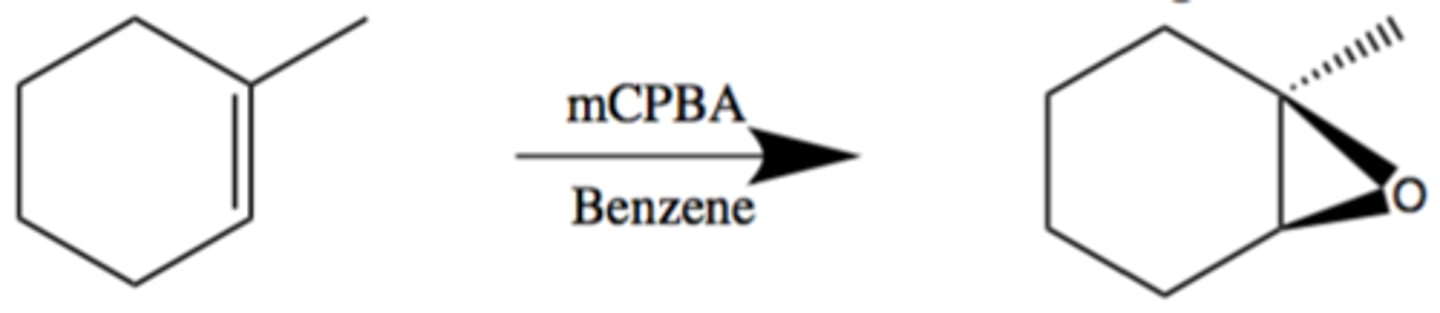
Epoxidation
Uses mCPBA
Syn Relationship
Dead giveaway is that there are a lot of oxygens attached to an group
Uses a mechanism with 4 arrows in a concerted reaction
Results in two products
(Carboxylic acid & an Epoxide)
Dihydroxylation (syn selective)
Uses OsO4
Syn relationship
No Markinov / Anti-Markovnikov
Results in a molecule with an OH added to both sides across an alkene
Dihydroxylation (anti selective)
Two steps,
First step uses mcPBA
Second step uses an OH (which opens up epoxide) and Water
Anti Relationshio
No Markovnikov / Anti-Markovnikov
Results in an an OH an being attatched across the alkene
Ozonolysis
Two step reduction
First step uses ozone to lyse (cut) a double bond
Second Step uses DMS (or ZN & H2O)
Basically turns carbons into carbonyls
Results in two separate molecules, split across the original alkene, both double bonded to an Oxygen where there was originally a double bond