Neuro
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
MidBrain
(Mesencephalon): Small structure connecting hindbrain and forebrain
Interconnects with some cranial nerves
Red nucleus: coordinates muscles signals
Reticular formation: works with medulla, regulates sleep, temperature, arousal
Tectum (Major Structures along it)
Superior colliculi: integrates visual information, coordinates eye movement with attention
Inferior colliculi: Integrates auditory information, coordinates head movement with attention
Forebrain
(prosencephalon): ?
Diencephalon
Thalamus : Major relay center
Hypothalamus : Interface with endocrine system
Telencephalon
Limbic System: Emotion, memory formation
Amygdala
Mammillary bodies - connected to the hypothalamus, processing emotions related to hormones in the body
Hippocampus
Fornix
Septal nuclei - pleasures/reward systems
Cingulate gyrus - coordinate activity
Olfactory bulb - process smell
Stria terminalis - Two lines that run along thalamus and connect to amygdala, simply discomfort of uncertainty
Basal Ganglia
Reciprocates activity with cortex
Caudate nucleus
Putamen
Globus Pallidus
Substantia nigra (midbrain)
Cerebral Cortex
Long-term memories, perception ( (Make note of basal ganglia and limbic system and know where they are located within the brain, check textbook)
Know different lobes: occipital, temporal, parietal, frontal
Occipital lobe processes vision
Temporal -
Parietal lobe
Frontal lobe- planning, forward thinking things
Sulci
folds in, fissure
Sylvian fissure: Dividing line of frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
Central sulcus: Dividing line of frontal and parietal lobes
Gyri
folds out, raised portions
Postcentral gyrus: location of somatosensory cortex
Precentral gyrus: location of motor cortex
Support system (Two)
Meninges
Dura mater: tough outer shell
Pia mater: softer inner shell
Subarachnoid space: between dura and pia mater, filled with csf. Made of arachnoid “web-like” matter
Ventricular system: Fluid-filled cavities in brain
Lateral ventricle
Choroid plexus: produces CSF
Third ventricle
4th ventricle
Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
Filtered blood, helps clear nervous system of debris. Mild shock absorber
Vascular System (Two main arteries)
Anterior and middle cerebral arteries
supply blood to front ⅔ of brain. Supplied by carotid arteries
Posterior cerebral arteries
supply blood to rear ⅓ of brain. Supplied by vertebral arteries, then basal artery.
All converge at Circle of Willis
Works with glymphatic system
Neuroimaging: Structure
Computerized axial tomography (CAT)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
Fractional anisotrophy (FA)
DTI tractography
Neuroimaging: Activity
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
Optical imaging
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Electroencephalography (EEG)
(Training needed in interpretation of neuroimaging
Can easily get the wrong idea)
Neurophysiology: Neuronal Biophysics
Resting potential
Nernst Equation
Action Potential
Neurophysiology: Neurotransmission
Presynaptic membrane
Exocytosis
Receptors
Circuits
Neurophysiology: Information Processing
Summation
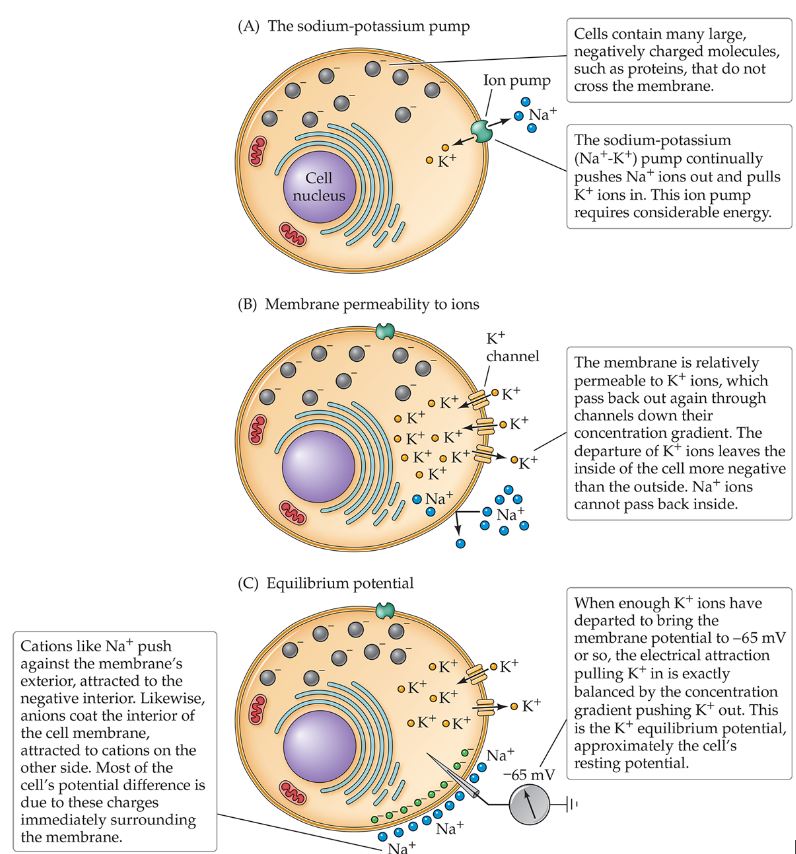
Neuronal Biophysics: Resting membrane potential
Resting potential: the difference in electrical charge between the inside voltage and the outside voltage
Not receiving signals
Not sending signals
Typically, -65mV
- -50 to -80mV
- “Polarized”
Neuronal Biophysics: Ions within “cellular” fluids
Ions within intracellular and extracellular fluids
Potassium
Sodium
Calcium
Chloride
Equilibrium potential
the difference in charge between inside and outside of the neuron after balancing several other factors
Electrostatic pressure
The anti attraction of like charged particles
The attraction of oppositely-charged particles
Diffusion
Entropic movement of particles from high densities to low densities
Concentration gradient: density as a function of location
Concentration gradient
density as a function of location
Selectively permeable membrane
boundary of neuron allows passage of some ions and not others
Ion channels
specialized proteins, pores in the membrane
Sodium-Potassium pumps: energetically-expensive active enzymes
Exchange 3 intracellular na+ for 2 extracellular k+
Net negative intracellular space
Nernst Equation Theory
Can predict the equilibrium potential for a permeable membrane given a specific ion
Expressed in terms of extracellular voltage, but can easily refer to the inside voltage
An approximate predictor. Assumes only one ion influences potential and the membrane is perfectly permeable.
Goldman Equation
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz voltage (GHK) equation
An update to Nernst Equation which accounts for multiple ions and multiple levels of permeability
Nernst Equation
Ex = (58/Ax)MV * log10(Cout x/Cin x)
X: A specified ion
Ax : The ion valence
Cout x : The ion concentration on the outside o fthe neuron
Cin x: The ions concentration on the inside of the neuron
58: An approximated constant
Goldman equation would tell the charge of the whole neuron
Action Potential
Action Potential: Brief, but intense change in polarization which regenerates in nearby membrane
Essential for neural communication
Occurs when cell membrane is depolarized to threshold level
Depolarization: Reducing the potential voltage difference towards zero
Hyperpolarization: Increasing the potential away from zero
Ion concentrations are frequently in flux, perturbed
opening/closing of ion channels
Red nucleus
coordinates muscles signals
Reticular formation
works with medulla, regulates sleep, temperature, arousal
Superior colliculi
integrates visual information, coordinates eye movement with attention
Inferior colliculi
Integrates auditory information, coordinates head movement with attention
Thalamus
Major relay center in the Diencephalon
Hypothalamus
Interface with endocrine system in the Diencephalon
Limbic System
Emotion, memory formation
Mammillary bodies
connected to the hypothalamus, processing emotions related to hormones in the body
Septal nuclei
pleasures/reward systems
Cingulate gyrus
coordinate activity
Olfactory bulb
Process smell
Stria terminalis
Two lines that run along thalamus and connect to amygdala, simply discomfort of uncertainty
Occipital lobe
processes vision
Frontal lobe
planning, forward thinking things
Sylvian fissure
Dividing line of frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
Central sulcus
Dividing line of frontal and parietal lobes
Gyri
folds out, raised portions
Postcentral gyrus
location of somatosensory cortex
Precentral gyrus
location of motor cortex
Dura mater
tough outer shell
Pia mater
softer inner shell
Subarachnoid space
between dura and pia mater, filled with csf. Made of arachnoid “web-like” matter
Ventricular system
Fluid-filled cavities in brain
Choroid plexus
produces CSF
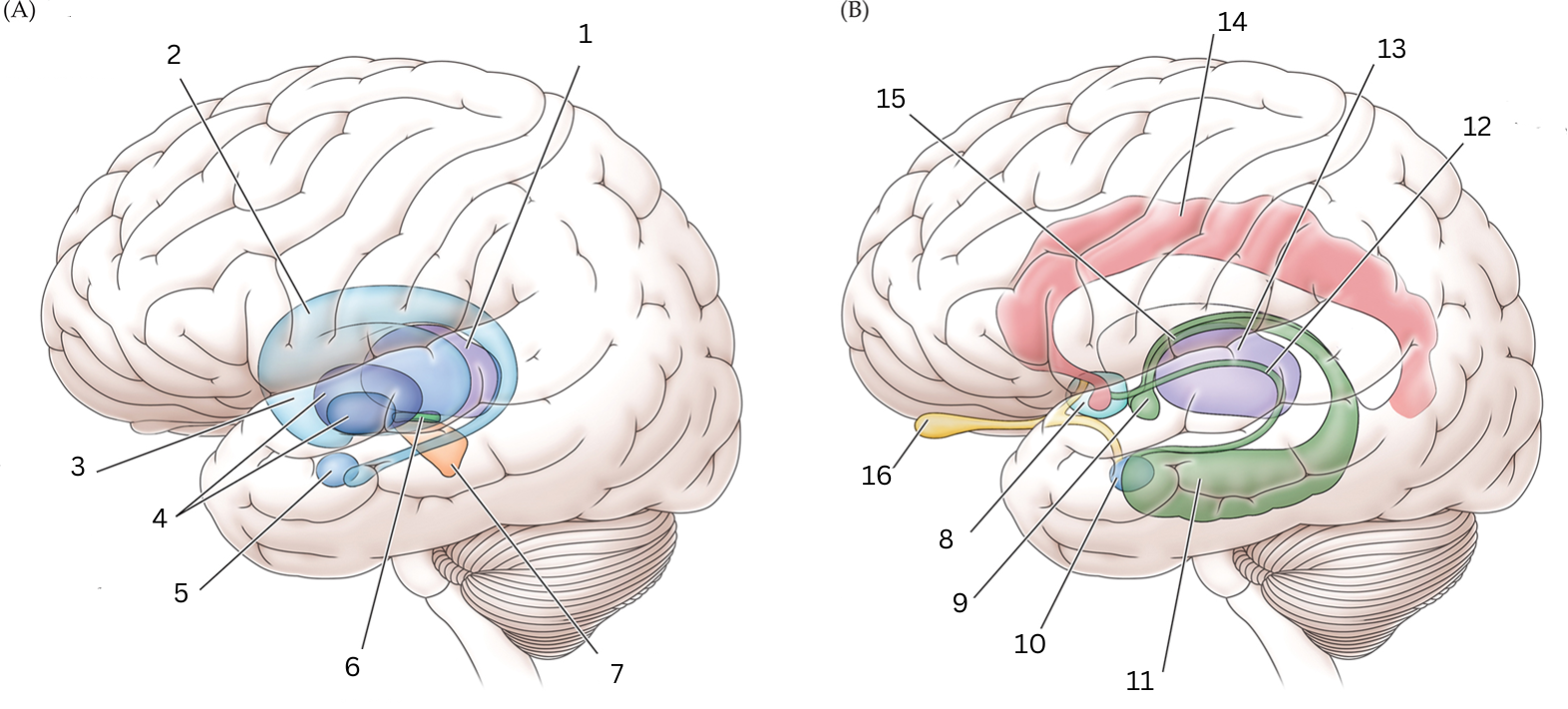
What is 1
Thalamus: Relays sensory/motor signals from various locations to cerebral cortex. It helps with alertness, sleep, consciousness, learning and memory.
What is 2
Caudate nucleus: Processes visual info, control movement, working memory, cognitive function and emotions.
What is 3
Putamen: The putamen is involved in learning and motor control, including speech articulation, language functions, reward, cognitive functioning, and addiction
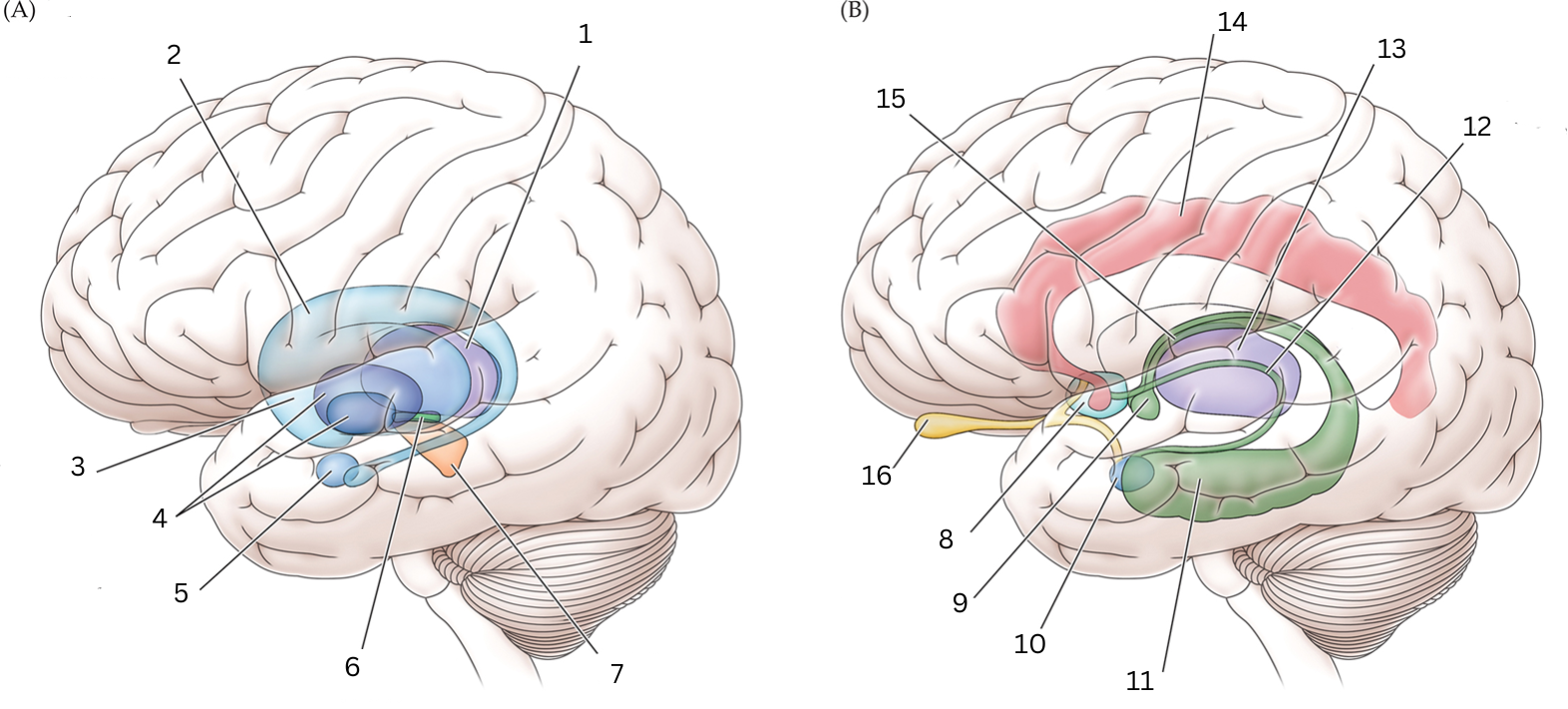
What is 4
Globus Pallidus: helps with movement, cognitive/emotional functions. Inhibits undesired movements
What is 5
Amygdala: helps assess/respond to threats and challenges by evaluating emotional importance of sensory info.
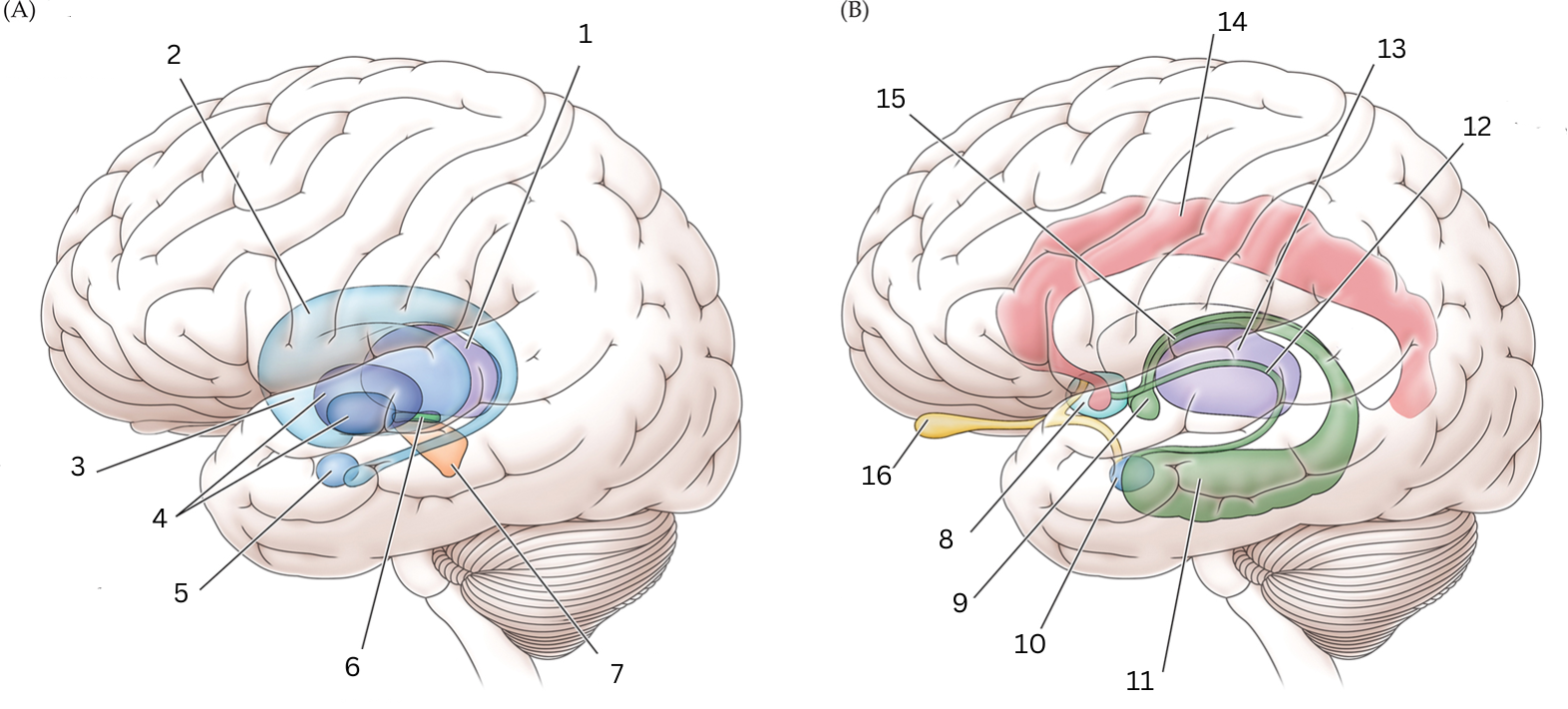
What is 6
Subthalamic nucleus: performs action selection, implement “hyperdirect pathway” of motor control.
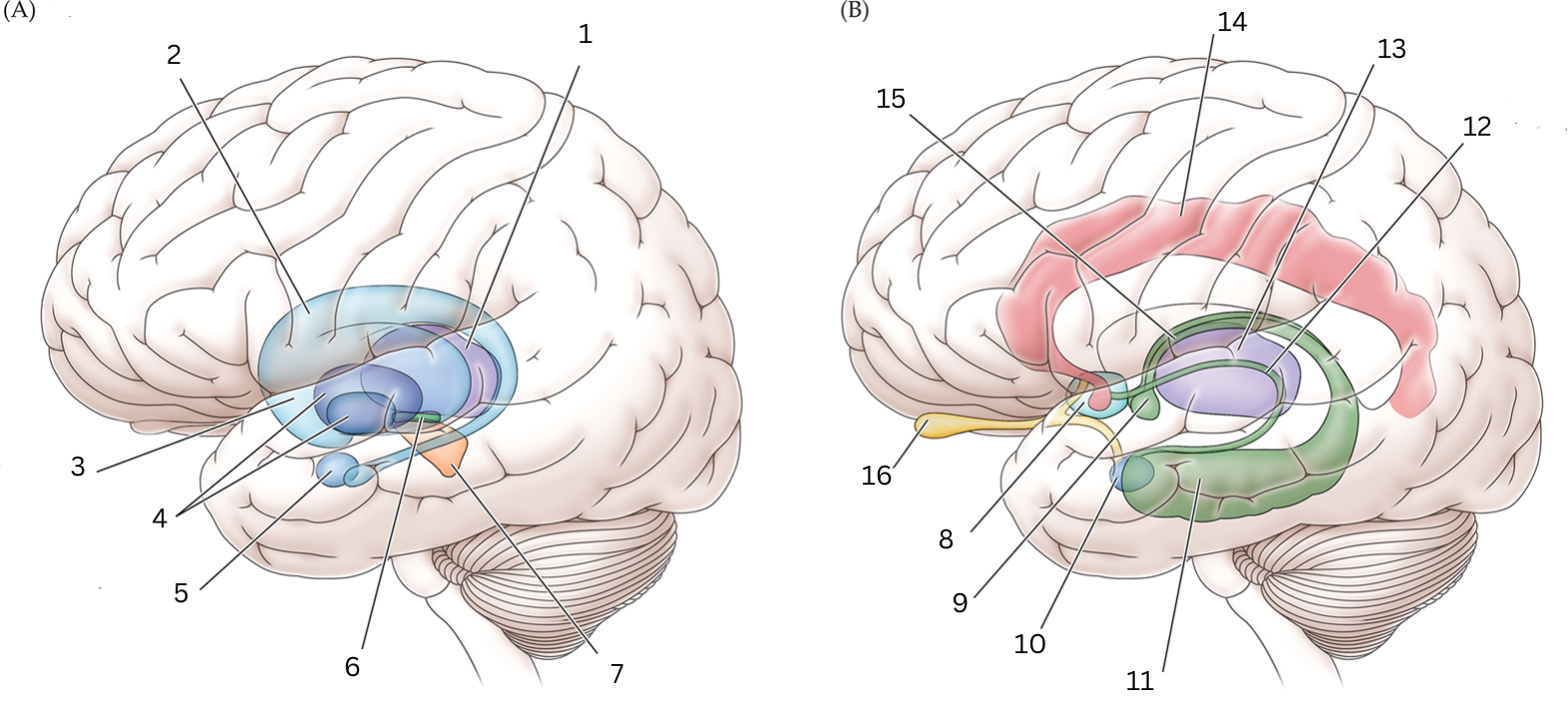
What is 7
Substantia nigra:
Reticulata: helps with eye movements with eyes, ability to learn/think
Compacta: helps with learning, judging risks/reward, motivations
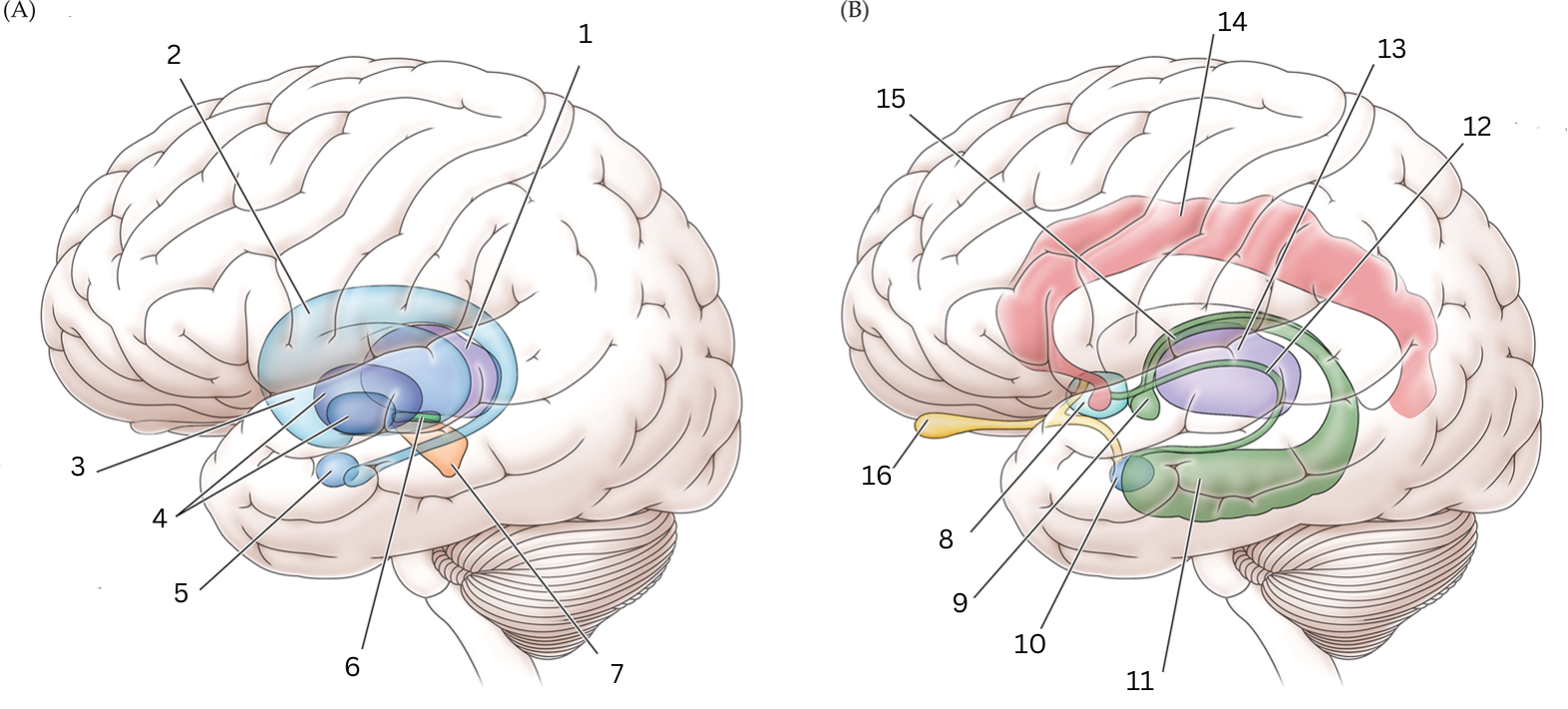
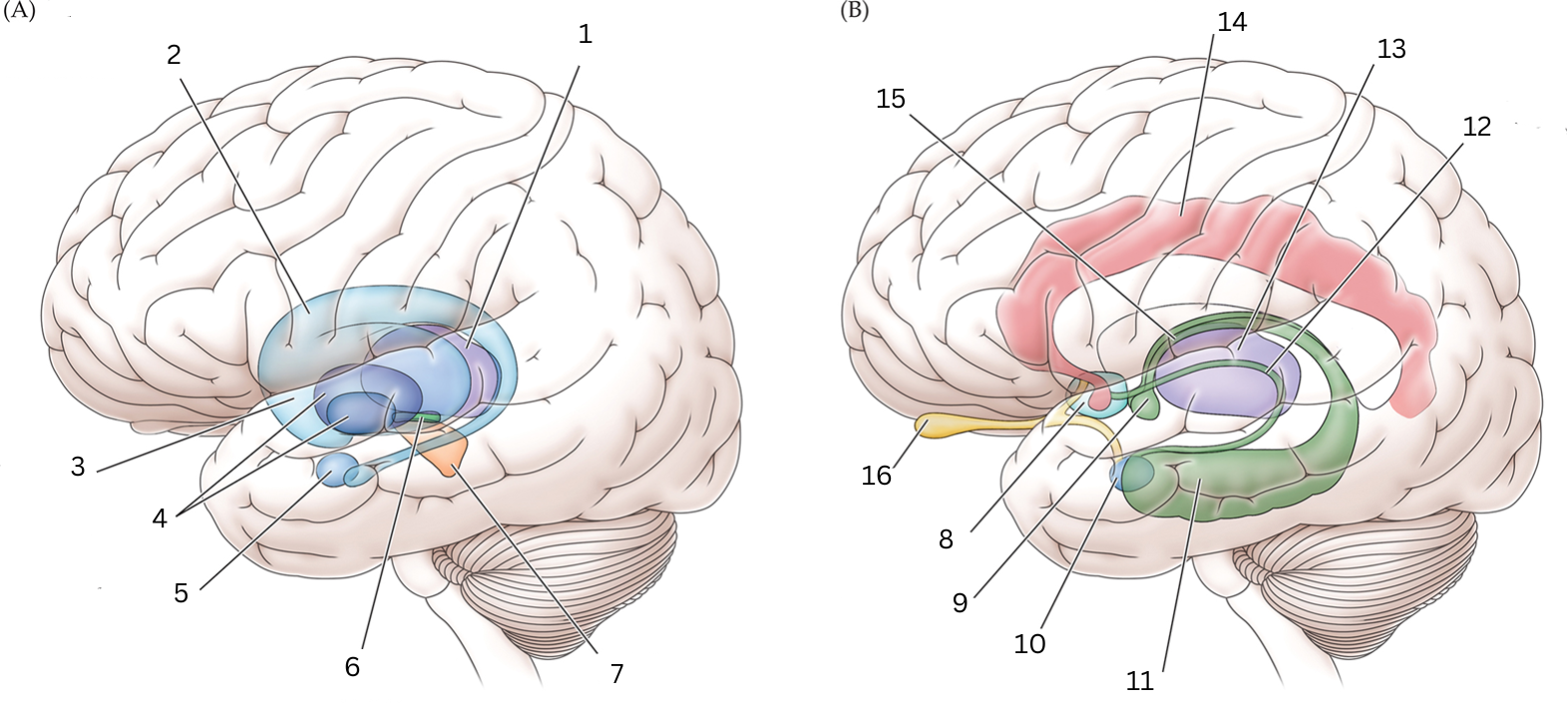
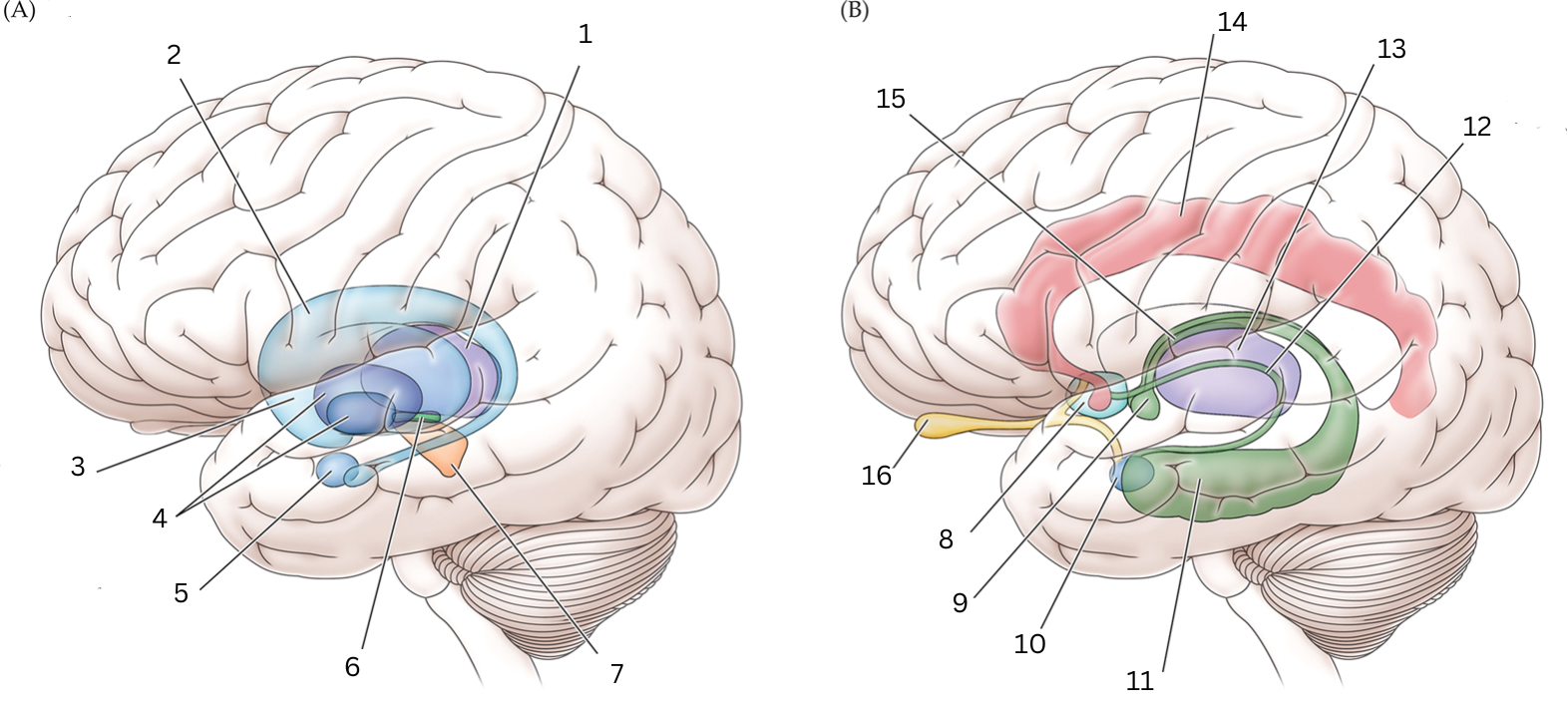
What is 8
Septal nuclei: involved with experience of pleasure
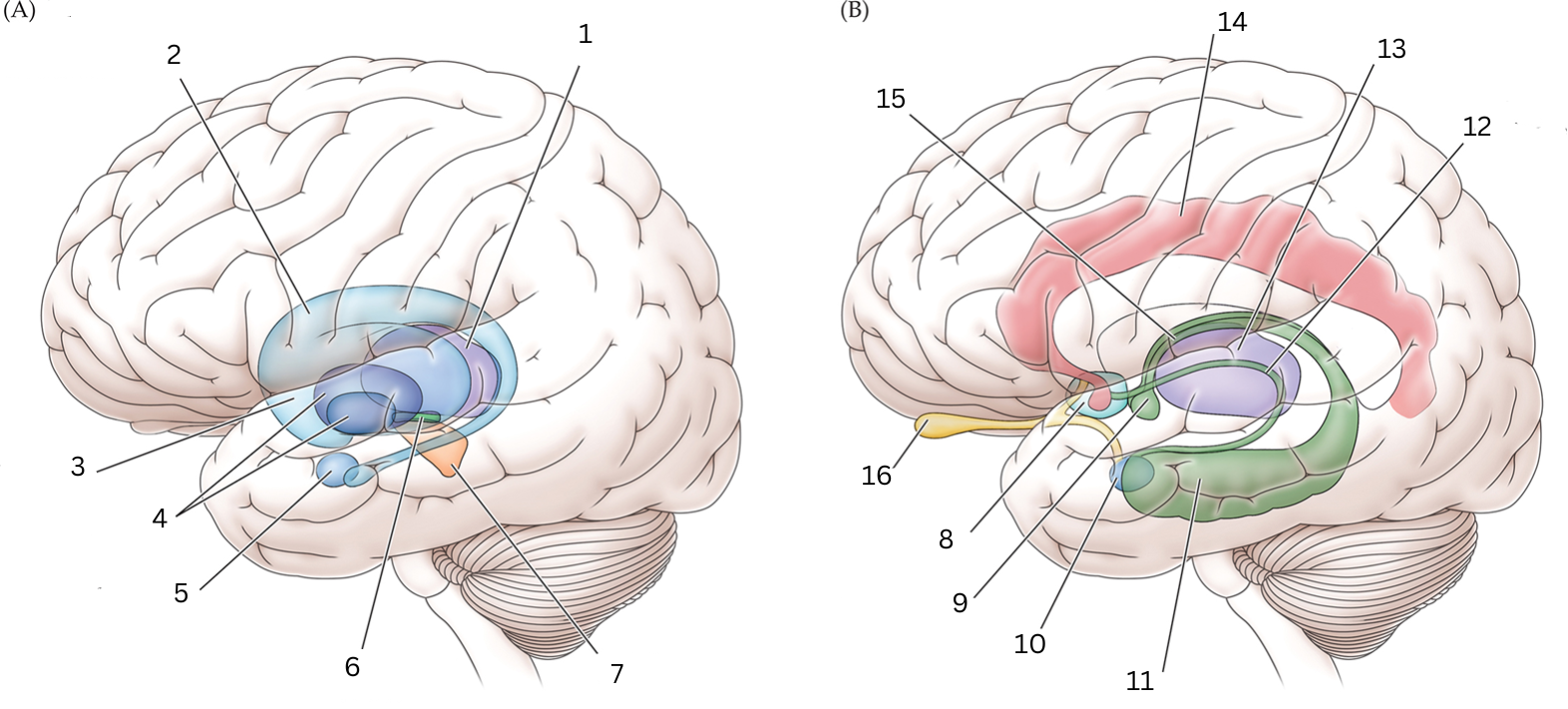
What is 9
Mammillary body: helps with recollective memory
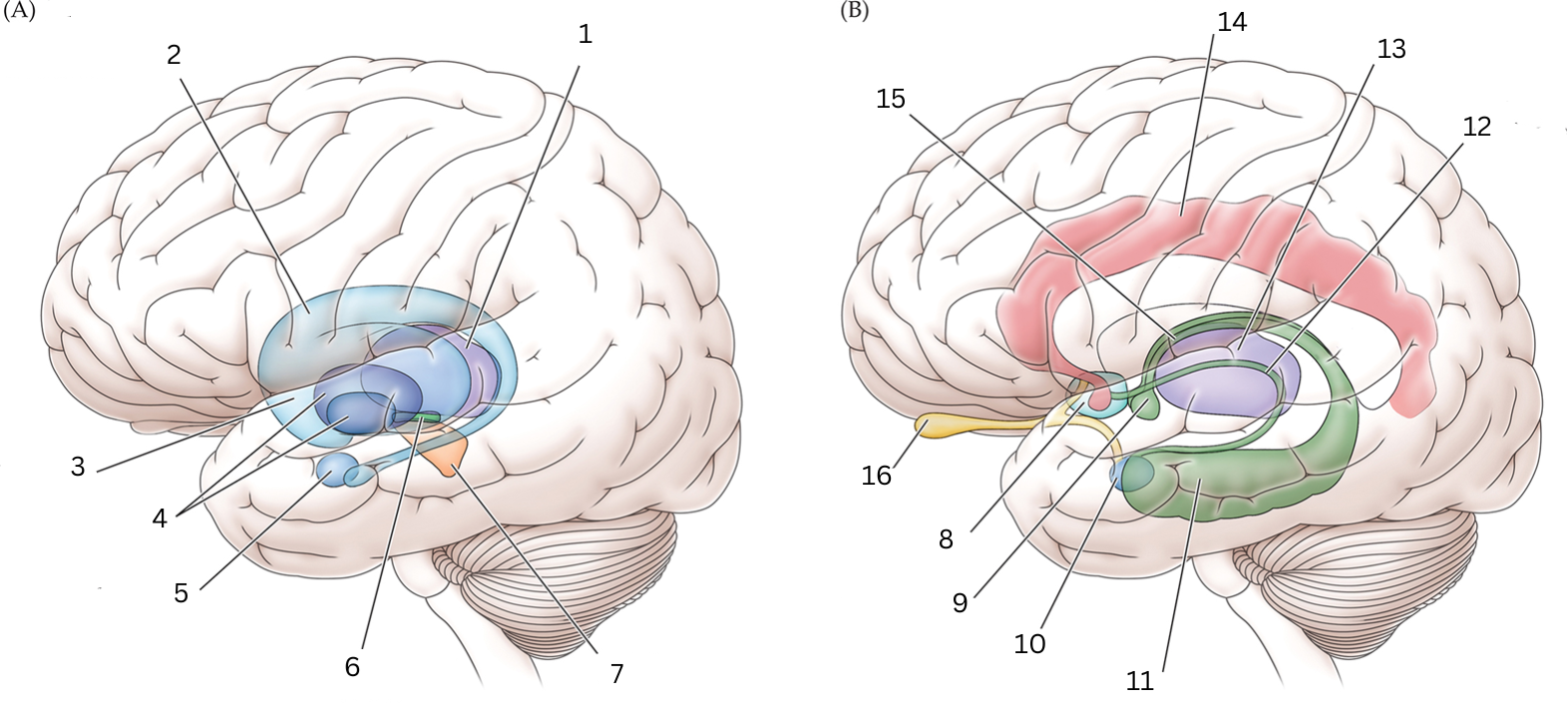
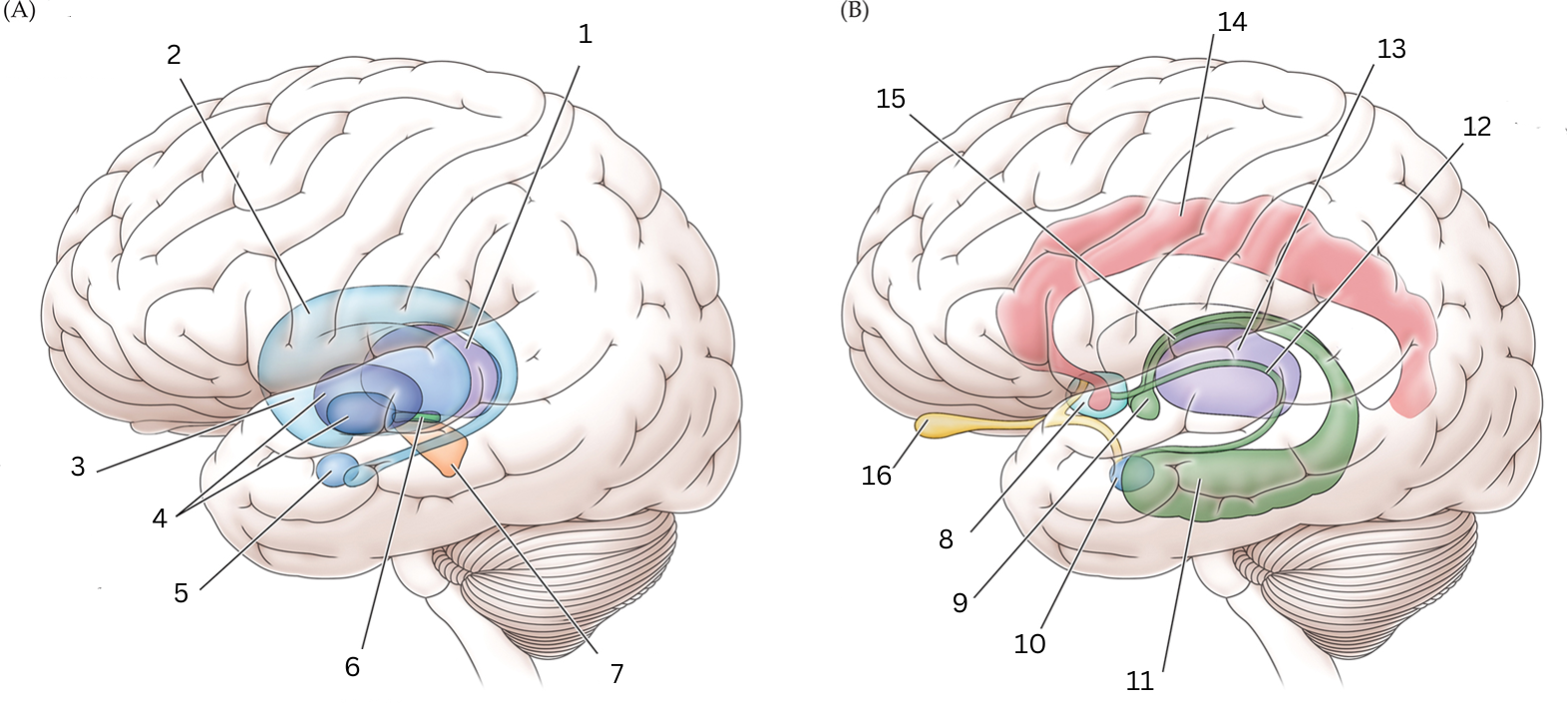
What is 10
Amygdala: Controls fear, processes what you hear and see. Interacts with aggression, learning thru rewards/punishments
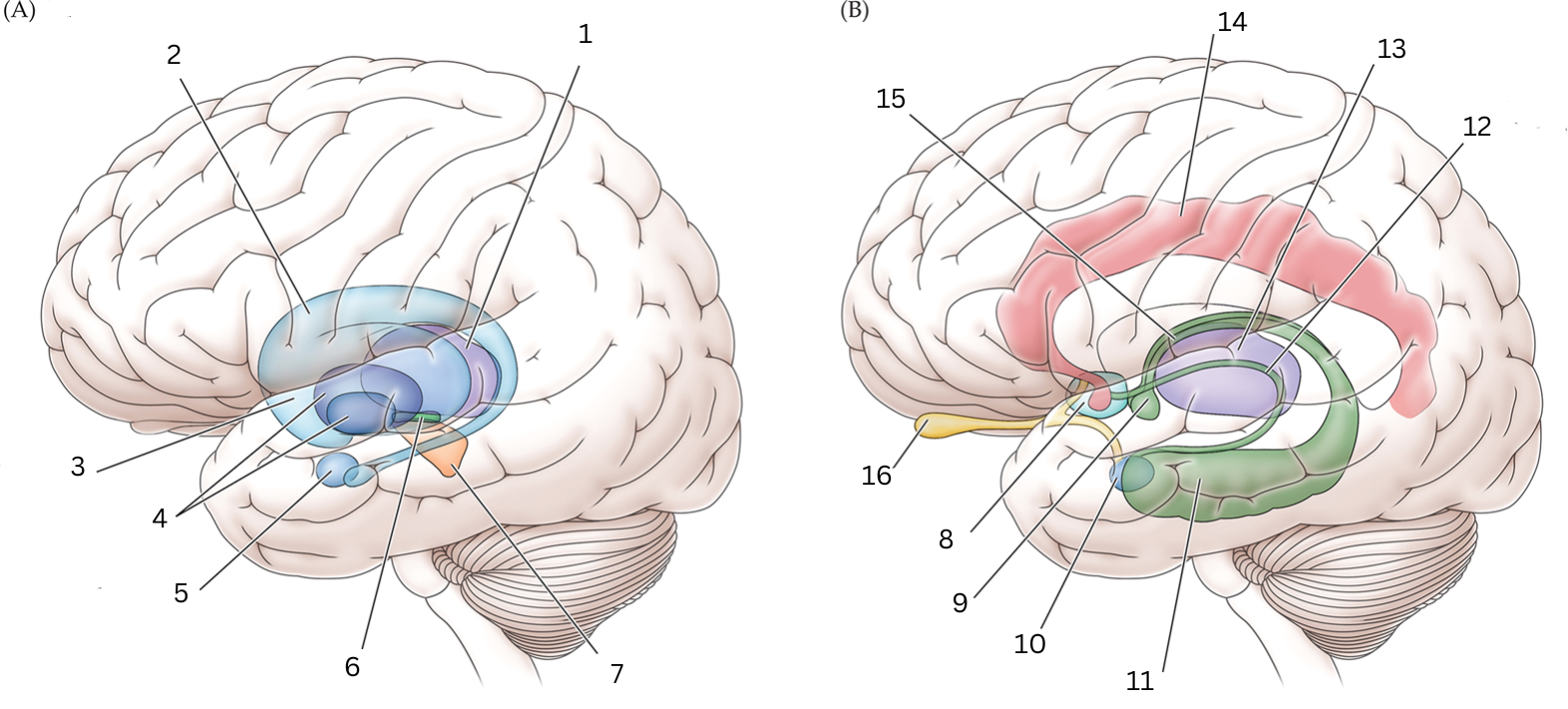
What is 11
Hippocampus: Organization/storage of new memories. Transfer center for long term memory. Helps with Spatial memory and navigation.
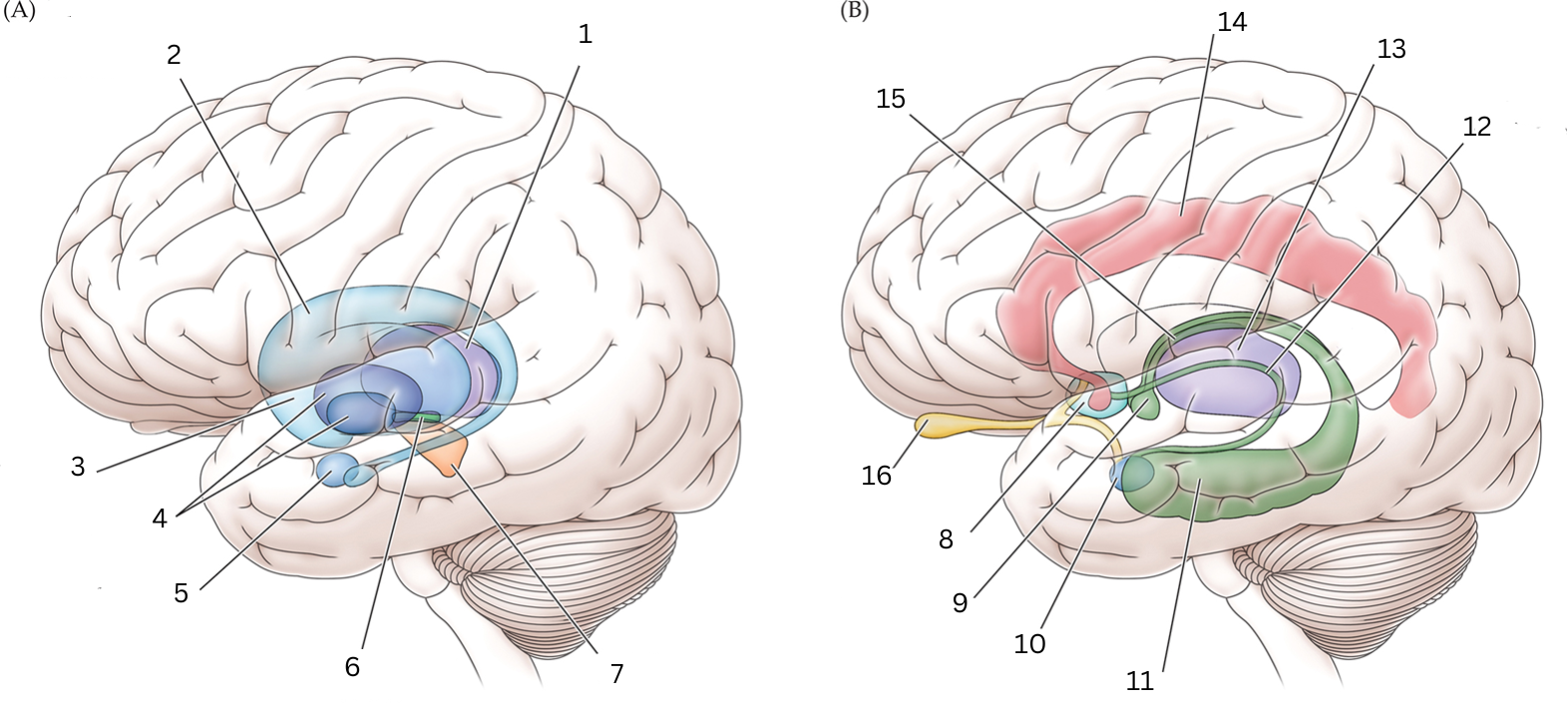
What is 12
Stria terminalis: Relays olfactory info thought to be related to reproductive behavior to the medial preoptic area and anterior nucleus of hypothalamus
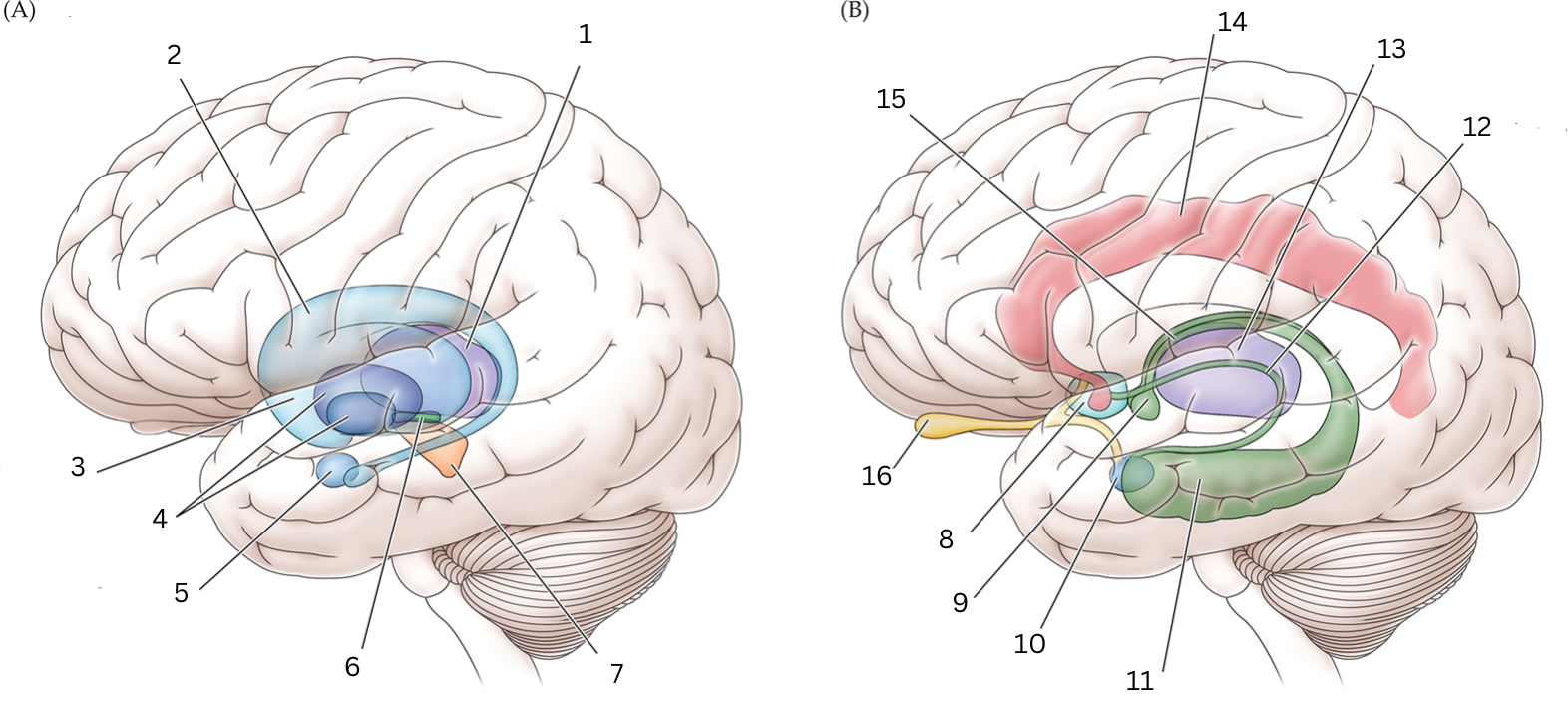
What is 13
Thalamus: Relays sensory info, relaying motor info, priortizing attention. Plays role in attention span, consciousness, memory/thinking
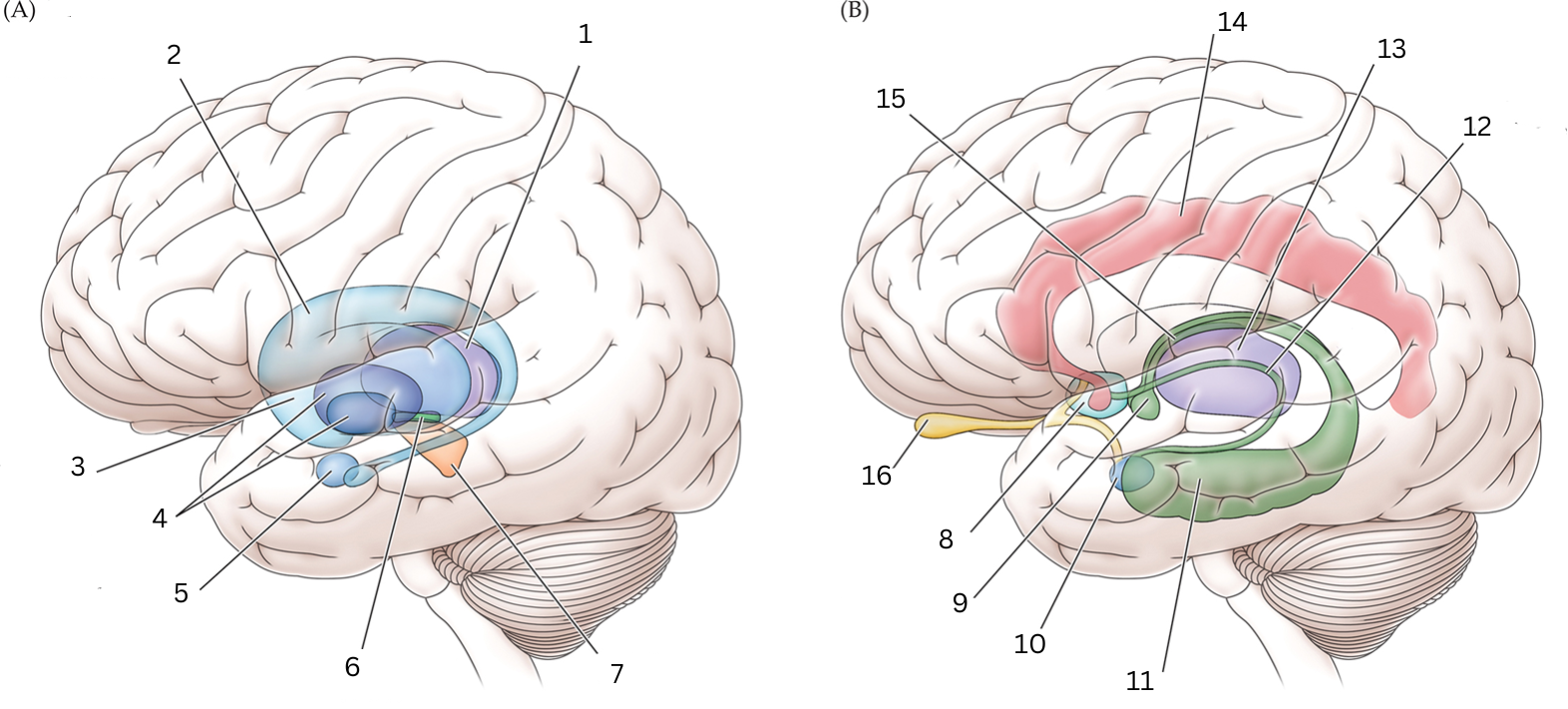
What is 14
Cingulate gyrus: coordinates sensory input with emotions, emotional responses to pain, regulates aggressive behavior, maternal bonding, language expression
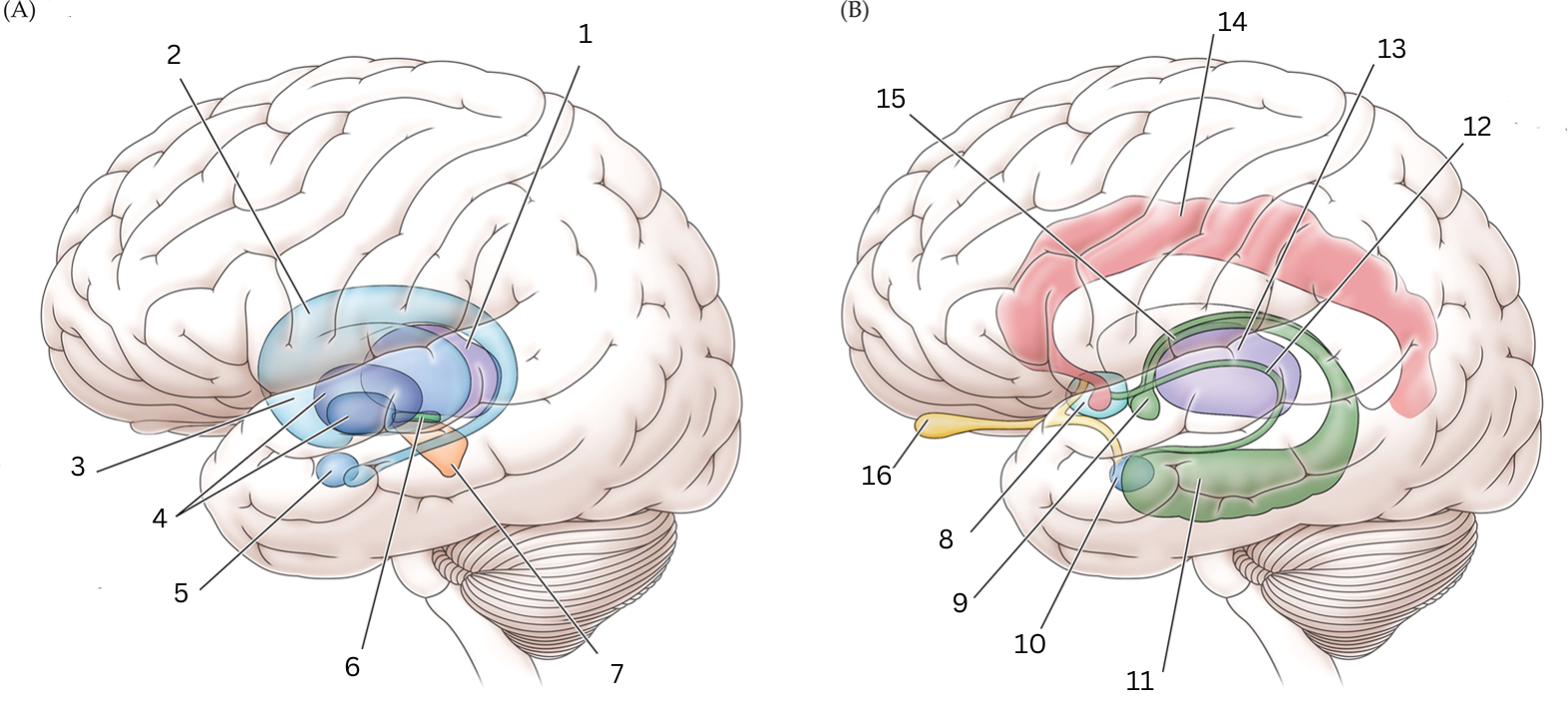
What is 15
Fornix: Deals with cognition, memory and emotions
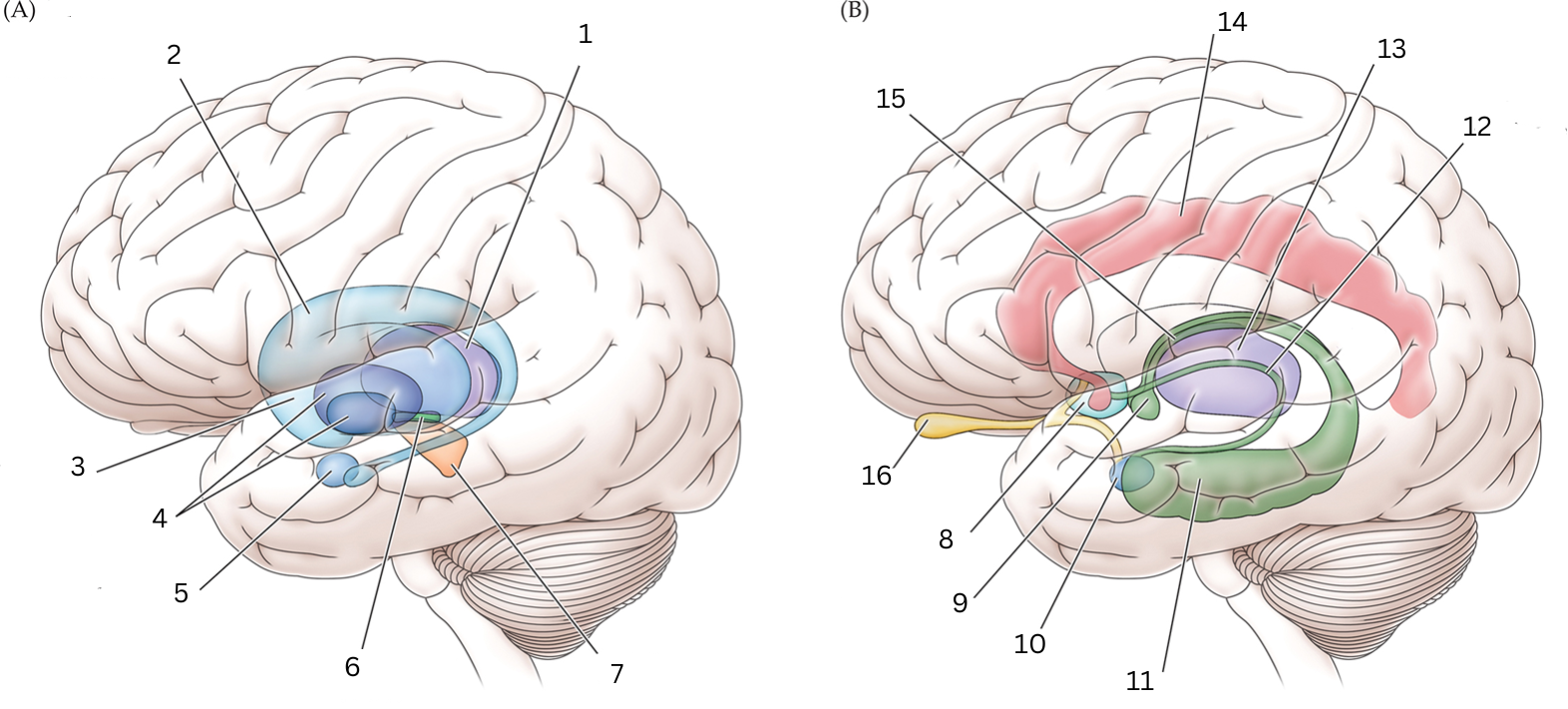
What is 16
Olfactory bulb: Acts as the main relay structure of the olfactory pathway