MIDI II: Module 3 Exam Study
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
What is anisotrophy?
property of tendons, nerves, and muscles to appear different on US depending on angle
What is the minimum optimal vein diameter for a PICC line?
4 mm
Cephalic vein is ______ to biceps brachii and is very _______, seen within a fat pad
lateral; superficial
Basilic vein is ______ to biceps brachii and brachial a/v, it _______ than cephalic
medial; deeper
What vessels disappear with pressure on US?
veins
What determines the direction of the probe in MSK US?
direction of muscle fibers
POCUS has largely replaced procedures once performed with _______ identification and ______ landmarks
tactile; anatomical
The technique of ________ needle insertion has been vastly replaced with US
blind
List some procedures that have been enhanced by use of POCUS:
venous and arterial cannulation
lumbar puncture
thoracentesis
fine needle aspiration
needle biopsy
arthrocentesis
paracentesis
What are the indications for DIAGNOSTIC arthrocentesis of the knee?
septic arthritis, crystalloid arthritis, and traumatic effusion
What are the indications for THERAPEUTIC arthrocentesis of the knee?
Aspiration of large effusion or hemarthrosis
Injection of intraarticular lidocaine or steroids
What are the ABSOLUTE contraindications of knee arthrocentesis?
infection of skin or deeper tissues at site of interest (UNLESS septic arthritis is strongly suspected)
What are the relative contraindications of knee arthrocentesis?
supra-therapeutic anticoagulation
presence of prosthetic joint (increases susceptibility to infection)
What are the potential complications of knee arthrocentesis
iatrogenic infection due to improper sterile technique
tendon, nerve, cartilage, or BV damage
What is the post-procedure care for knee arthrocentesis?
RICE --> rest, ice, compression, elevation
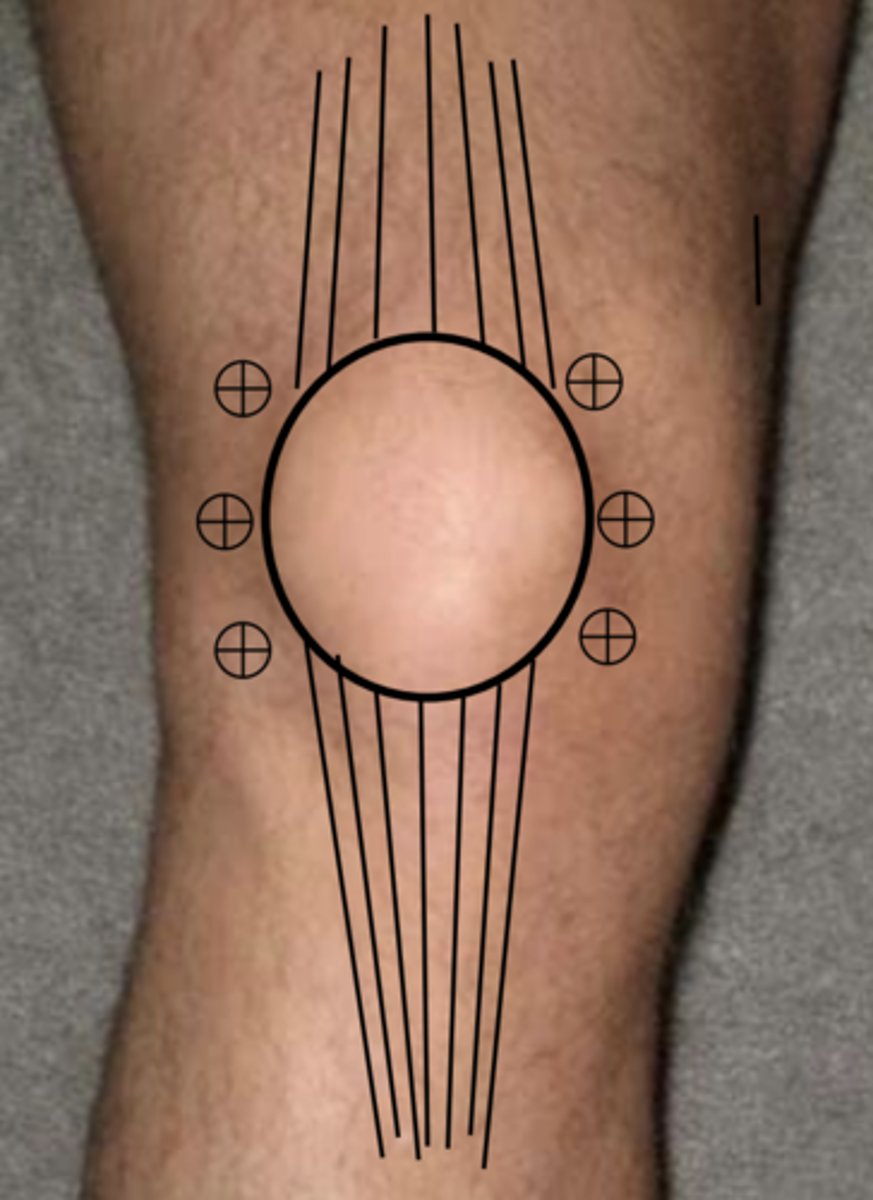
1. palpate knee to ID patella
2. rest knee and prepare with antiseptic --> then remove with alcohol pad
3. place wheal of local anesthetic over entry site w/ 25 gauge needle
4. inject deeper anesthetic along needle path do not enter joint space
5. aspirate joint with 18/20 gauge needle on 20-60 mL syringe
6. enter skin in perpendicular fashion and direct needle posteriorly behind patella toward intercondylar notch
7. pull back on plunger while you advance, synovial fluid will enter once in joint space
8. if you hit bone, retract almost to skin surface and try different angle
9. if unsuccessful, can flex knee slightly and try OR try on opposite side of knee
10. aspirate as much fluid as possible (apply gentle pressure to suprapatellar region to help drain extra fluid)
11. in large effusions, second syringe may be required
12. inject medication if needle
13. after injecting med, move joint through full ROM
General procedure for knee aspiration
What are some lab tests that can be done on synovial fluid?
cell count, gram stain, leukocyte differential, culture/sensitivity, microscopic wet prep (for crystals)
What are the most common crystals seen in synovial fluid in a patient with gout?
monosodium urate, negatively birefringent needle shaped crystals
calcium pyrophosphate arthritis appears as
rhomboid or rod shaped crystals that are positively birefringent or not
If crystals appear atypical on wet prep, they may be one of the following less common crystals:
cholesterol, liquid lipid, oxalate, cryoglobulins or artifacts
What is an example of an artifact crystal?
depot corticosteroid crystal
What could cause marrow spicules or fat globules to appear in synovial fluid?
fracture
What stain is used to ID amyloid fragments in synovial fluid?
congo red stain
What does the workup result for NORMAL synovial fluid look like?
clear, negative culture, PMNs <25%, WBCs < 200/mcL
What does the workup result of hemorrhagic synovial fluid look like?
bloody, negative culture, WBC affected by amount of blood
What does the workup result of infectious synovial fluid look like?
turbid or purulent, culture often positive, PMNs>85%, WBCs 5K- >100K /mcL
What does the workup result of inflammatory synovial fluid look like?
yellow/cloudy, negative culture, PMNs>50% WBCs 1K-50K / mcL
What does the workup result of non-inflammatory synovial fluid look like?
straw colored/clear, culture negative, PMNs <25%, WBCs 200-1000 / mcL
What is the LAB ORDER for analysis of synovial fluid?
(clinical PEARL)
1. CBC w/ diff
2. Gram stain
3. C/S
4. Crystals w/ polarized light microscopy
WBC count and PMN % in infectious arthritis are lower if the organism is _________ OR _________
less virulent; partially treated
Some effusions in systemic lupus erythematosus and other CT diseases are only ______ w/ WBC count of ________
inflammatory; 500-2000 mcL
Noninfectious effusions rarely have up to _______ WBC /mcL
100,000
What position should the knee be in when scanning QT and patellar tendon?
flexed 30 degrees
What area near the QT is clinically significant for tendon tears and joint effusion?
suprapatellar bursa
What view is this?
LAX QT

What view is this?
SAX Quad muscles

What is large and fills the space deep to the patellar tendon?
infrapatellar fat pad
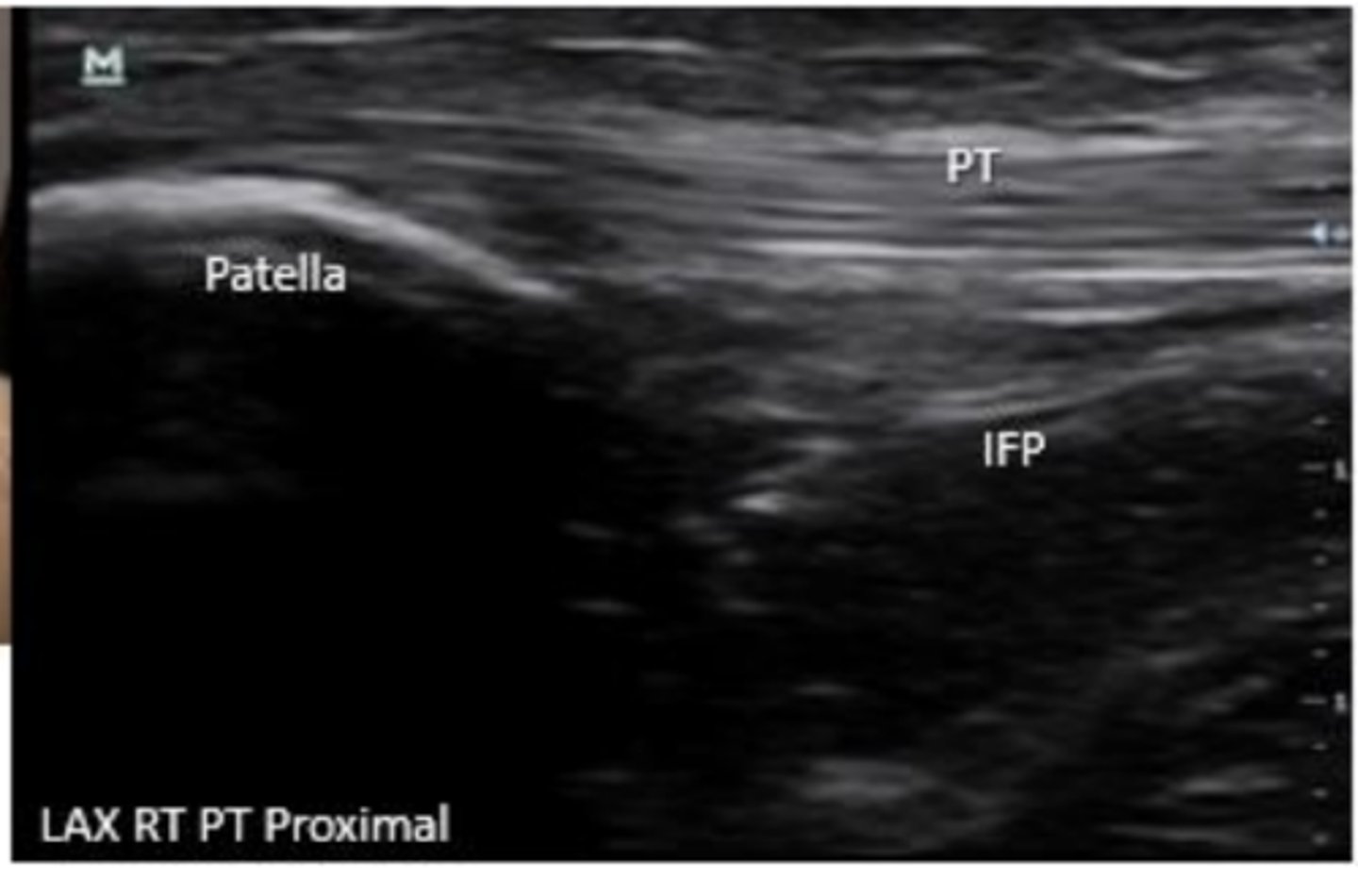
The infrapatellar fat pad is prone to what?
inflammation, injury, and impingement
What area of the patellar tendon is clinicallly significant for tendinopathy?
proximal PT
What area of the PT is significant for deep infrapatellary bursitis?
distal attachment of PT to tibial tuberosity
What are not seen in normal knees, but can be seen in cases of bursitis?
prepatellar and superficial infrapatellar bursae
When scanning the vasculature in the posterior knee, what position should the patient be in?
prone with rolled towel under ankle OR with foot hanging off bed
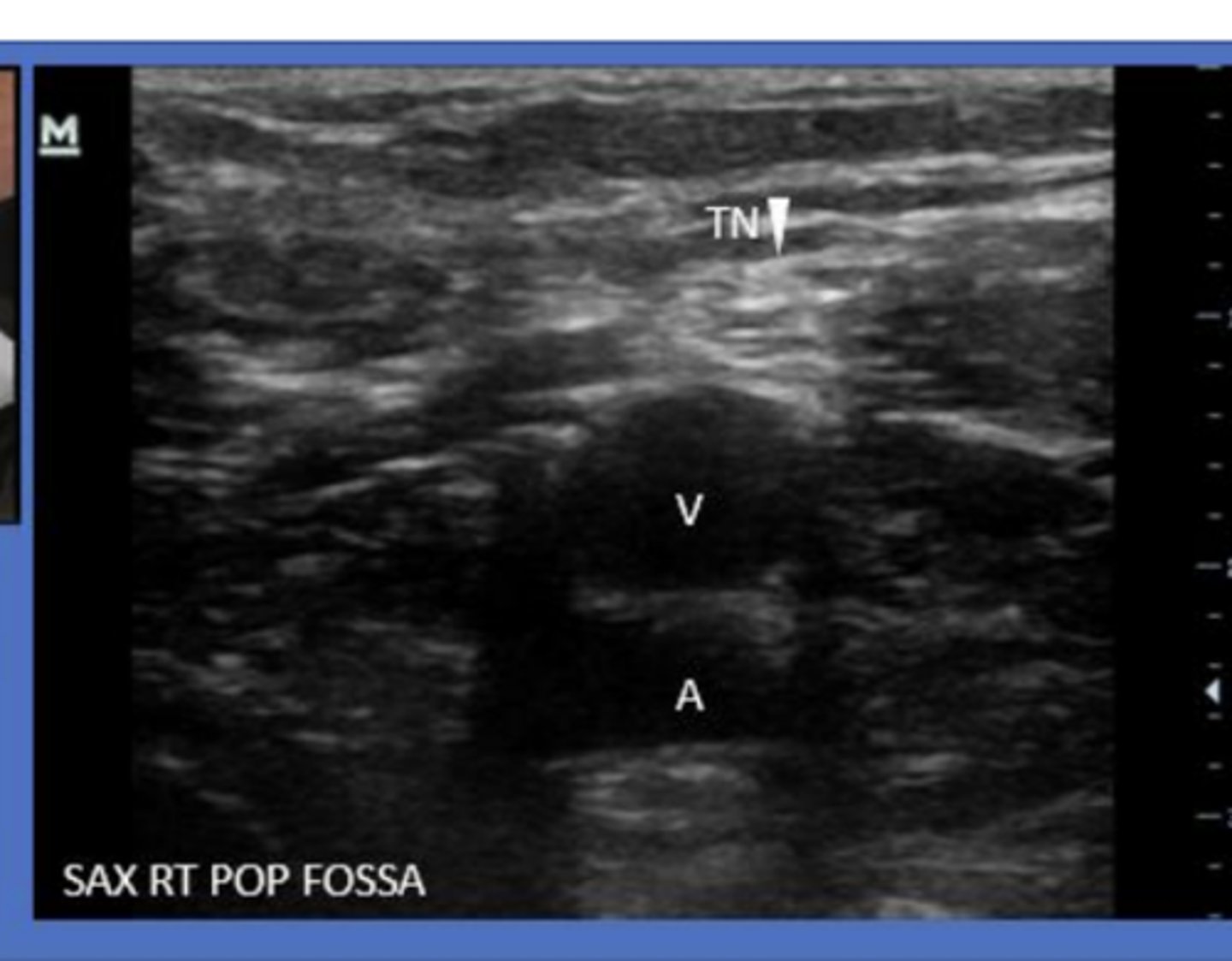
What comprises the neurovascular bundle posterior to the knee?
popliteal artery/vein and tibial nerve
BART on color doppler
BLUE AWAY RED TOWARDS (transducer)
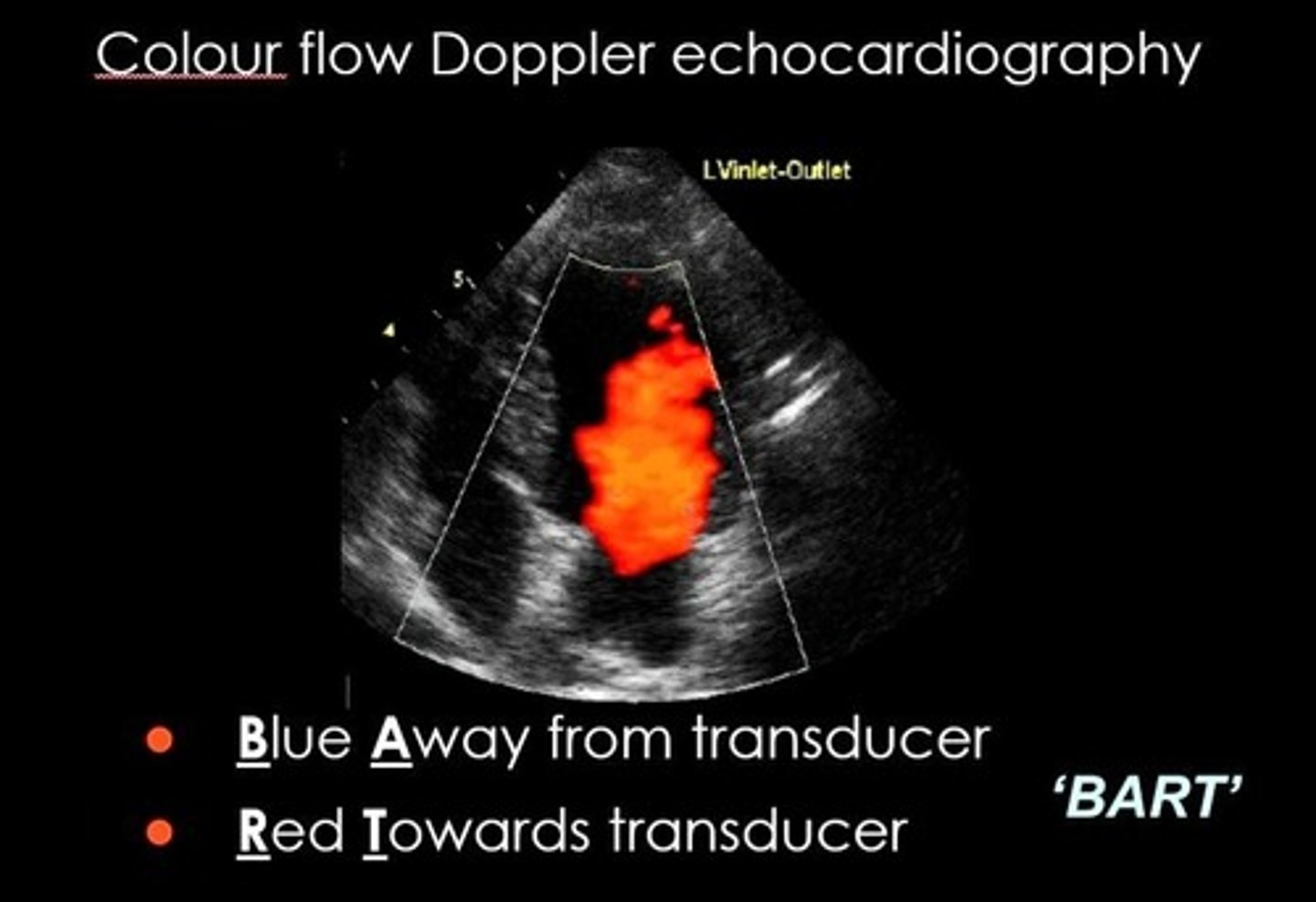
When using color flow to determine vasculature on US, what does blue mean?
the blood is moving AWAY from the probe --> if probe is pointing towards feet, this would be arterial flow
When using color flow to determine vasculature on US, what does red mean?
the blood is moving TOWARDS the probe --> if probe is pointing towards feet, this would be venous flow
What is the clinical significance of the popliteal fossa?
site of DVT
site of baker's cysts
What may indicate a DVT on US of popliteal fossa?
Inability to compress popliteal vein
Where do Baker's cysts usually originate in the popliteal fossa?
medial to vasculature with the neck of the cyst b/w medial head of gastrocnemius and semi membranous tendon
What are the 2 points we observe when performing focused 2-point DVT evaluation with US?
1) femoral vein and saphenophemoral junction
2) popliteal vein
How is the patient positioned when using US to search for DVT when using a 2-point limb evaluation?
frog leg position
What are some things we can ID/DX on US of neck and thyroid?
carotid bruits, cervical lymphadenopathy, thyroid masses
POCUS is the ONLY method currently able to determine WHAT at the bedside (regarding the thyroid)?
if the mass is solid, cystic, or homogenous
allows for rapid DX
Thyroid US is preferred DX method for the ID and eval of what?
thyroid nodules
How should the neck be positioned in order to scan the thyroid gland?
slightly hyperextended
Where should probe be placed initially when scanning thyroid?
transverse, on trachea, inferior to cricoid cartilage
What planes MUST you scan the thyroid in?
transverse and sagittal --> one is not enough
Thyroid POCUS can assist in evaluation of what?
thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, and shape/vascularity of gland
What thyroid nodules have higher risk of malignancy?
solid hypoechoic appearance, irregular margins, interrupted calcifications, and involvement of surrounding soft tissues
What is NEEDED in order to pathologically confirm malignancy of a thyroid nodule?
US guided fine needle aspiration
what will you see before the bifurcation into ECA and ICA
carotid bulb
ICA
internal carotid artery
ECA
external carotid artery
ECA is typically more _____ and ______
ECA is usually more anterior and medial
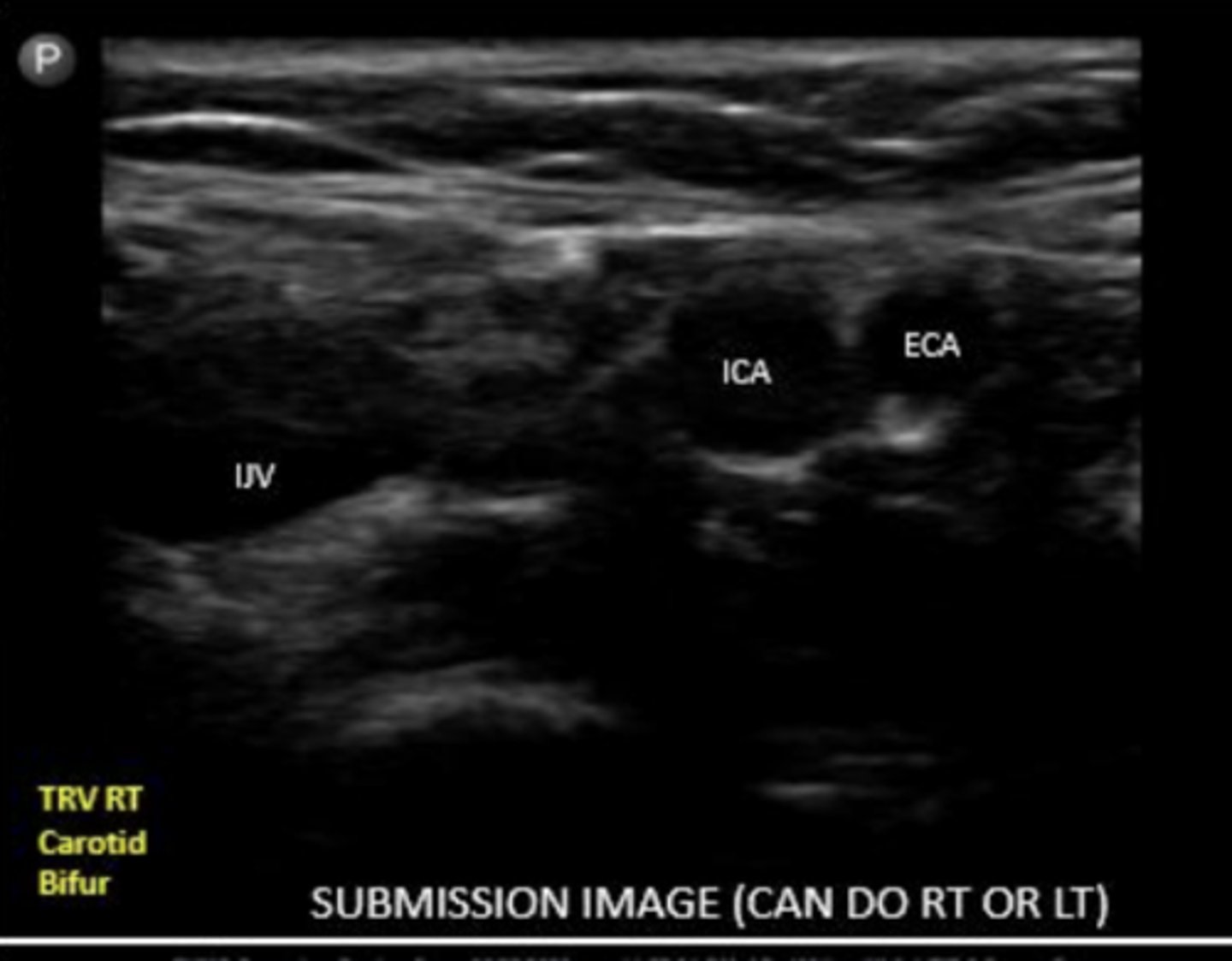
ICA is typically more ____ and _____
ICA is usually more posterior and lateral
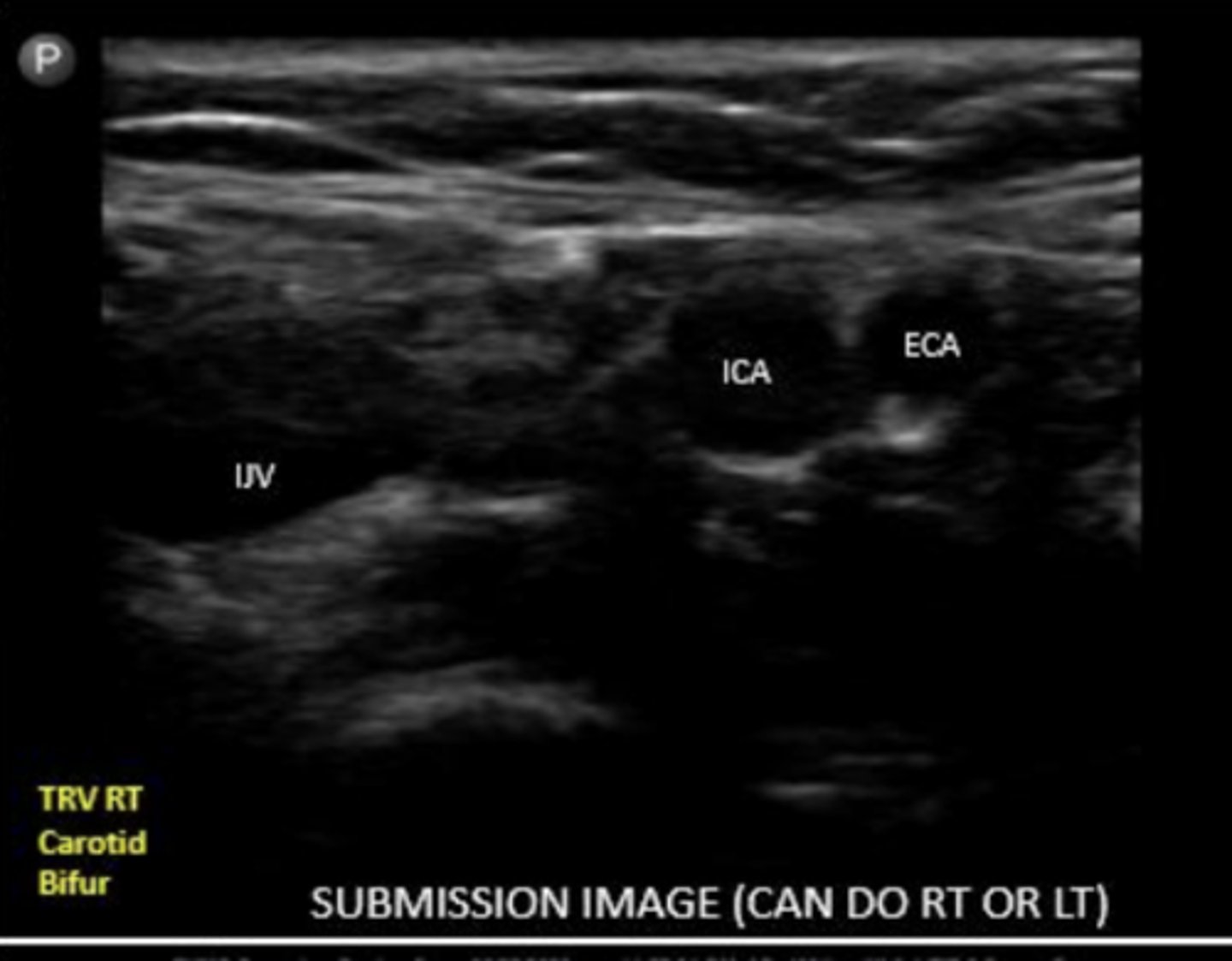
What are concerning lymph node characteristics?
hypoechoic, larger than 1 cm, irregular borders, cortical thickening, and increased vascularity
In order to determine lymph node differential DX, you must get ____________
tissue sample
_________ has equal value to lymph node surgical excision when evaluating a suspicious LN
US guided core-needle biopsy
US guided core-needle biopsy of lymph node is preferred over what?
FNA
When scanning the carotid bifurcation, is the IJV the most medial or lateral structure?
lateral
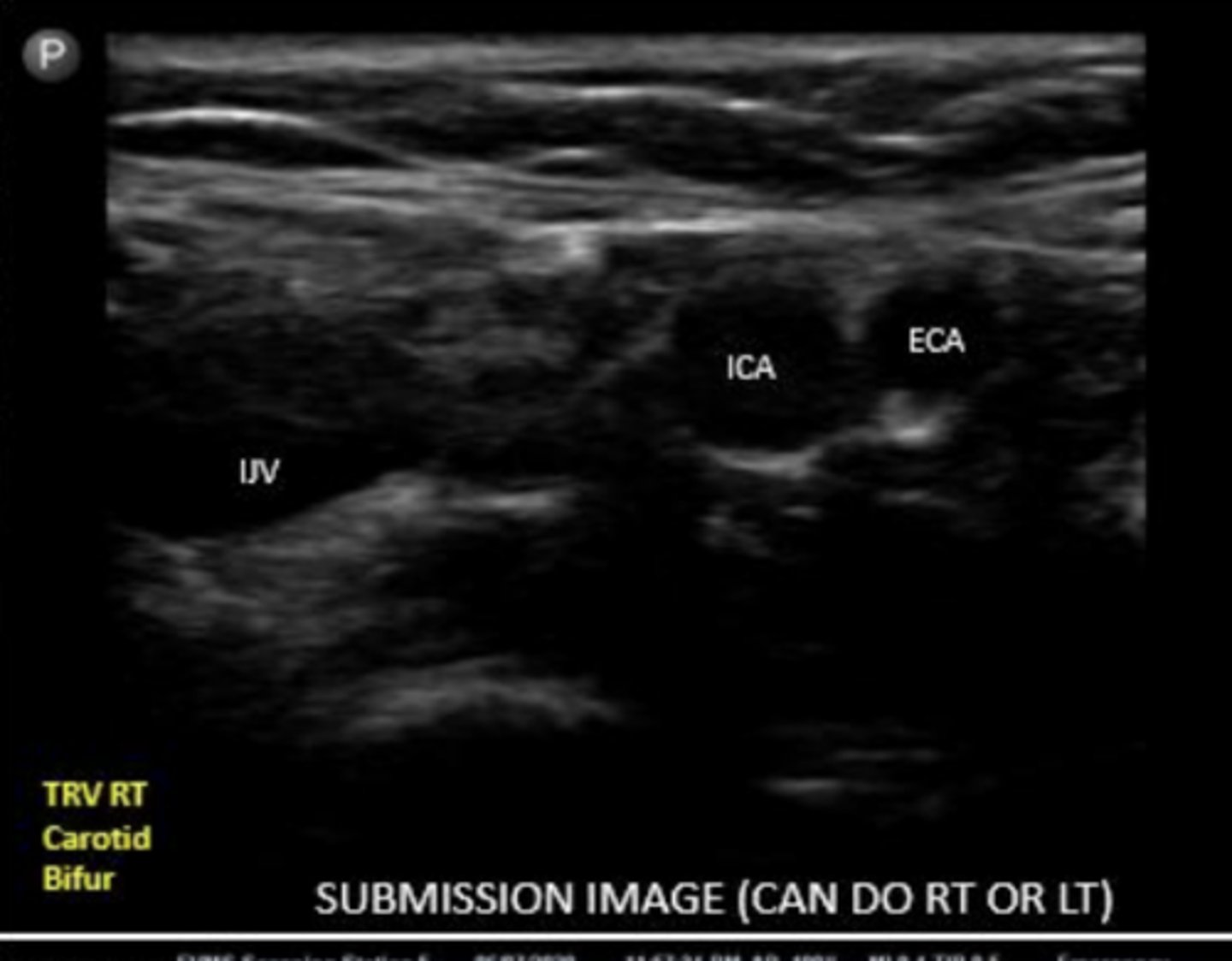
How can you distinguish between ICA and ECA on US?
use color and pulsed wave flow
ECA has ______ resistance flow
high
ICA has ______ resistance flow
low
When performing US guided procedures, your ______ hand should be holding the probe
nondominant
Needle should be advanced ______ up
bevel
how do wood, plastic and metal appear on ultrasound
typically hyperechoic
Why should you pull the syringe while advancing the needle?
so that as soon as you see fluid/blood you know to immediately stop advancing
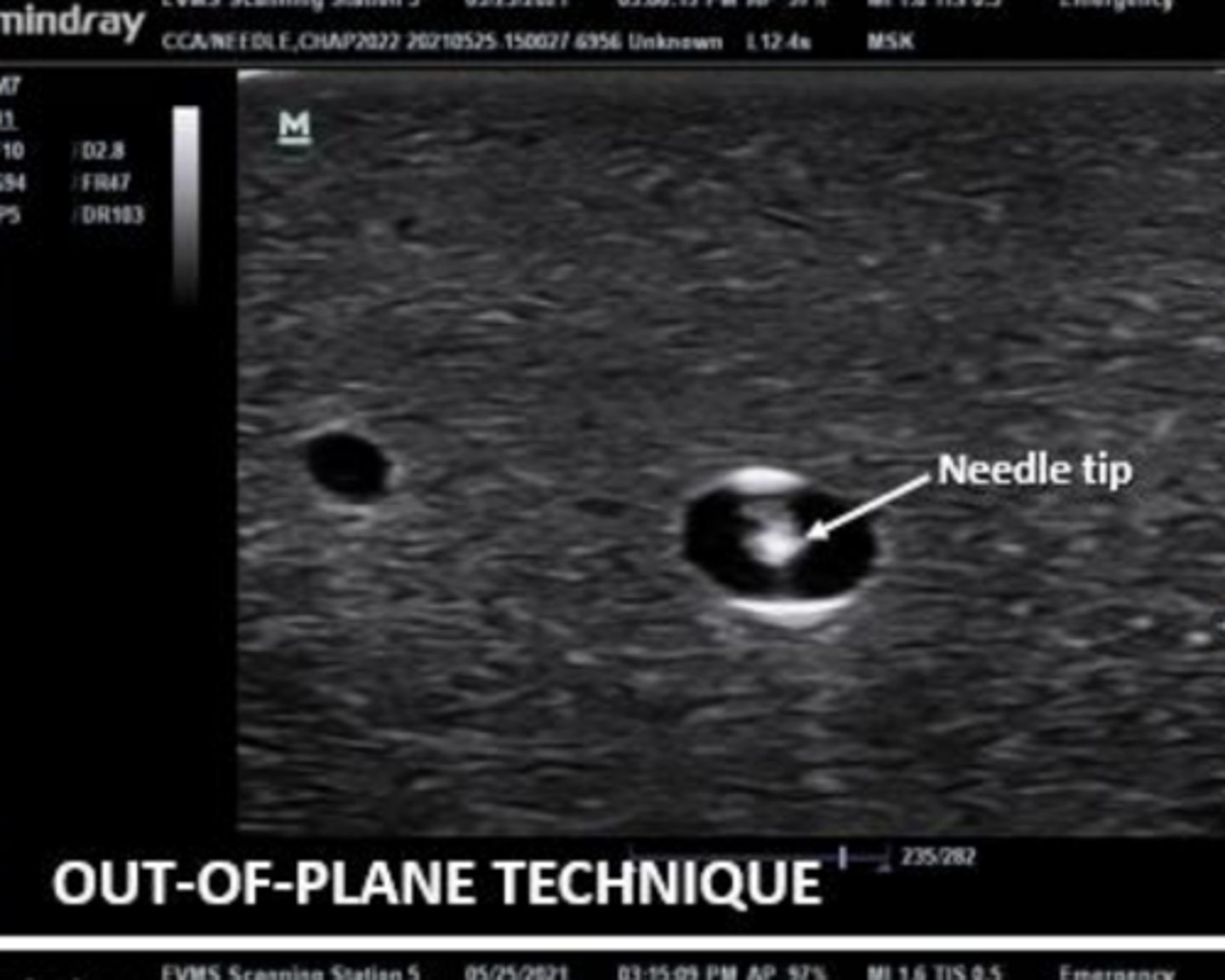
is this an out of plane or in plane view
is this an out of plane or in plane view
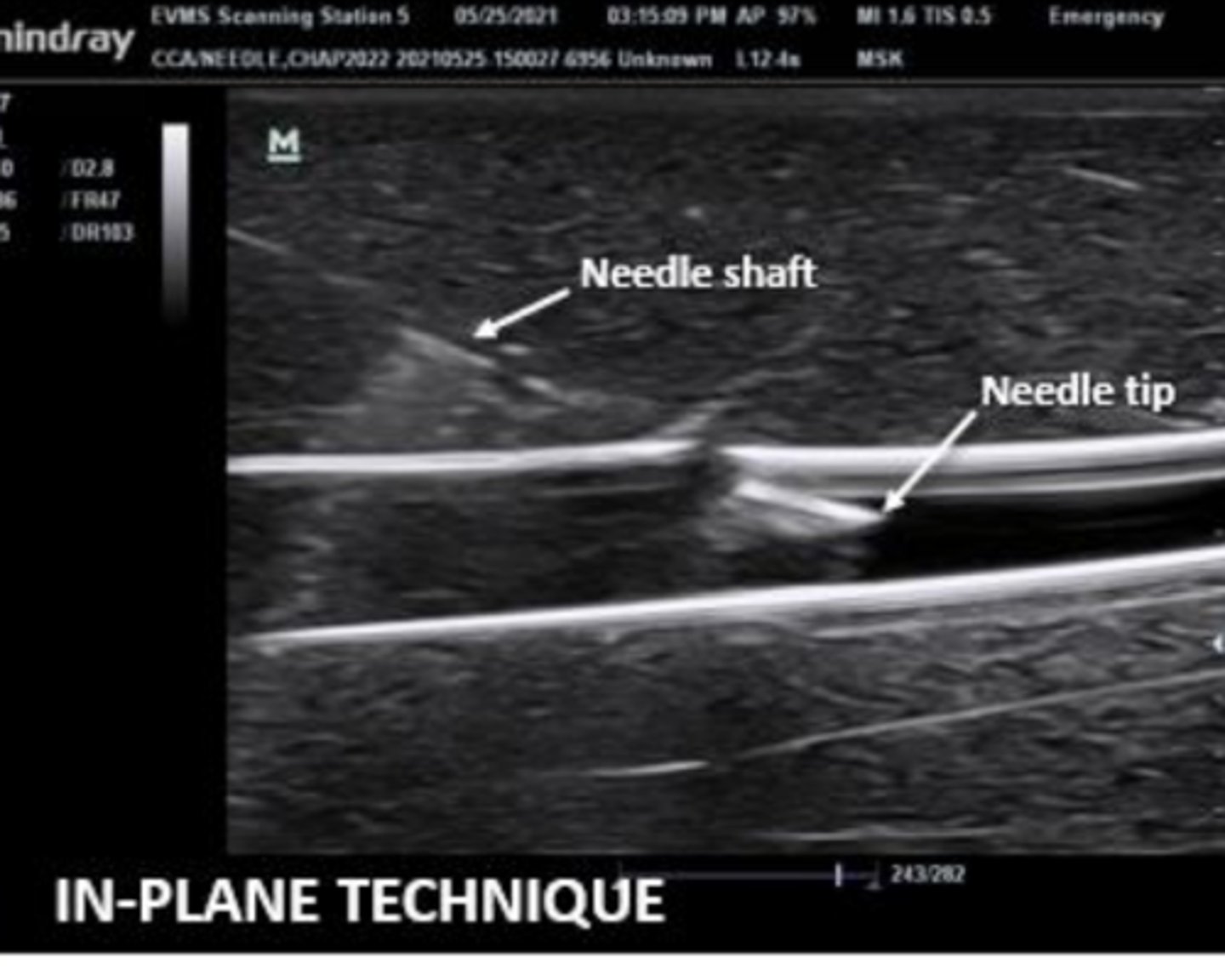
MSK imaging can be performed in both static and _____ settings
dynamic
What is the benefit of dynamic evaluation with US?
can perform ROM to better visualize internal structures during precipitation of injury or discomfort
3 things that affect ability to obtain quality MSK US images:
1) properly trained US operator
2) good quality machine and probe
3) obtaining images in at least 2 views
Clinically, MSKUS may assist in diagnosing what?
tendonitis, ligament and tendon tears, bursitis, joint effusions, and long bone fractures
Most of MSK imaging is performed with what probe?
linear (high frequency)
Clinical POCUS eval should begin at what area?
area that patient is experiencing most tenderness (determined by PE)
RUSH protocol has helped to rapidly diagnose the etiology of _______ and initiate early care of critically ill
shock
What types of shock has RUSH been shown to correctly DX etiology?
hypovolemic, cariogenic, and obstructive
(less sensitive for distributive and mixed etiologies, but still some benefit)
RUSH protocol order:
heart (pump) --> IVC and jugular veins (pipes) --> FAST exam (tank) --> aorta (rupture of pipes)
What are you looking for in the first step of RUSH?
Heart --> pericardial effusion, tamponade, left ventricular contractility, acute right heart strain
What are you looking for in the second step of RUSH?
IVC and jugular veins --> observe size and collapsibility with inspiration
What are you looking for in the 3rd step of RUSH?
FAST exam --> traumatic and non-traumatic intra-abdominal fluid
What are you looking for in the 4th and final step of RUSH?
Aorta --> aneurysm or dissection
Shock frequently presents with clincal features of:
tachycardia, tachypnea, oliguria, AMS, hypotension
A missed diagnosis rate of ___ is documented with FAST exams and is most commonly attributed to _________
20%; operator error
AP CXR needs a minimum of _____ of blood/fluid in order to DX PTX
200 mL
US needs a minimum of _____ of blood/fluid in order to DX PTX
50 mL
How much intraperitoneal fluid must be present to be ID by US in abdomen?
200 mL
What is the standard of care for eval of traumatically injured patients?
eFAST
What is the PROPER order of eFAST protocol?
1= RUQ
2= LUQ
3= Cardiac
4= Bladder (TRV and Long)
5= Lungs (B/L 3 intercostal spaces)
What is the clinical answer to this question: what is the proper order of the eFAST protocol?
assess the area most likely to have the most life threatening positive finding first