🦠 Bacteria & Archaea
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Antibiotic Resistance
Occurs when bacteria evolve mechanisms to survive exposure to antibiotics, often via gene transfer and selection.
Natural Selection & Resistance
Antibiotic use selects for resistant strains, increasing their frequency in populations.
Binary Fission
A form of vertical gene transfer where prokaryotes replicate DNA and divide into identical cells.
Budding
Vertical gene transfer where a new organism grows from the body of the parent.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Movement of genetic material between organisms via transformation, transduction, or conjugation.
Transformation
Uptake of free DNA from the environment by a prokaryote.
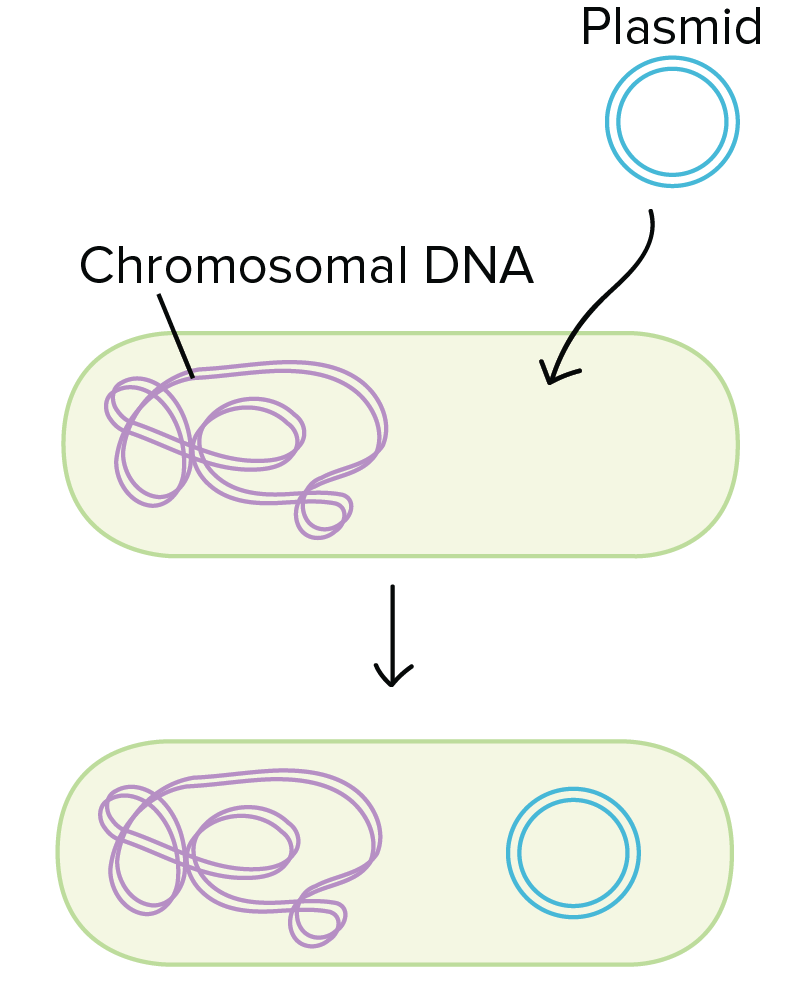
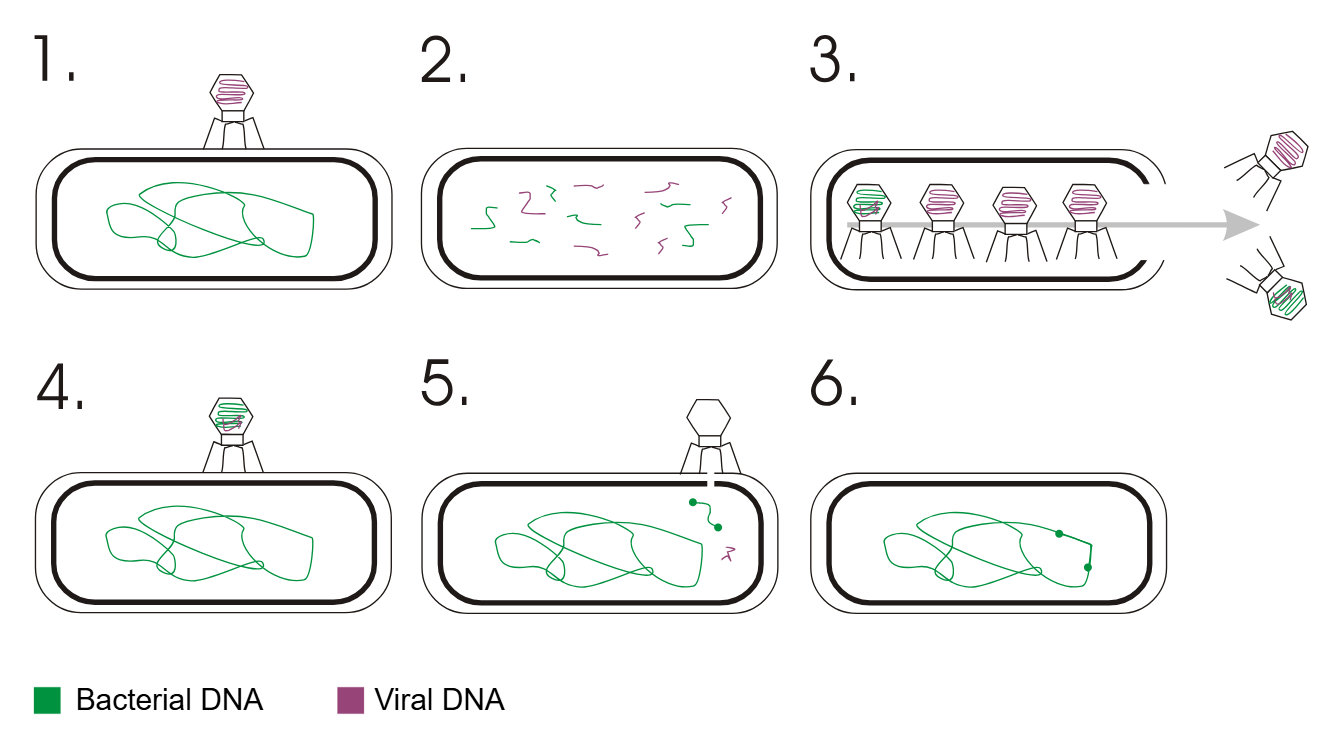
Transduction
Transfer of DNA between bacteria via bacteriophages.
Conjugation
Direct transfer of DNA between bacteria using a pilus; F+ cells donate plasmids to F- cells.
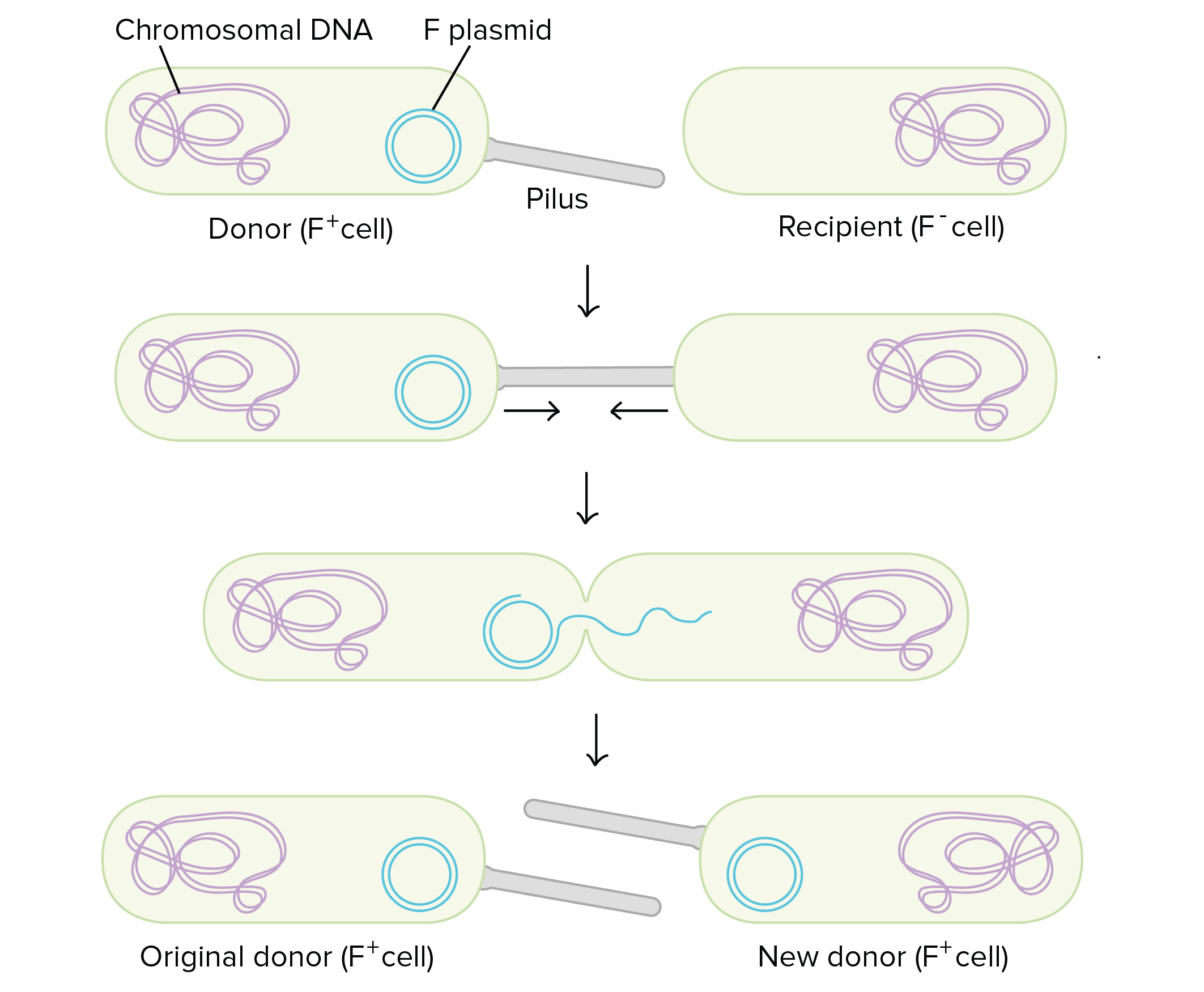
F+ vs F- Cell
F+ cells contain the fertility plasmid and can initiate conjugation; F- cells lack it.
Genetic Variation in Prokaryotes
Achieved through horizontal gene transfer, mutations, and plasmid exchange.
Acquired Genes
Can confer antibiotic resistance, virulence factors, or new metabolic capabilities.
Metabolic Diversity via Gene Transfer
Allows adaptation to diverse habitats and ecological niches.
Habitat Diversity
Includes acidophiles, halophiles, mesophiles, psychrophiles, and thermophiles.
Lateral Gene Flow
Another term for horizontal gene transfer.
Vertical Gene Flow
Transmission of genetic material from parent to offspring.
Photoautotrophs
Use light energy to synthesize organic compounds from CO₂.
Chemoheterotrophs
Obtain energy from organic molecules.
Chemolithotrophs
Use inorganic molecules for energy.
Methanogens
Produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anaerobic conditions.
Methanotrophs
Consume methane as their energy source.
Acidophile
Thrives in acidic environments.
Halophile
Thrives in high-salt environments.
Mesophile
Prefers moderate temperatures.
Psychrophile
Thrives in cold environments.
Thermophile
Thrives in high-temperature environments.
Anabaena
A genus of cyanobacteria with nitrogen-fixing heterocysts.
Heterocyst
Specialized nitrogen-fixing cell in cyanobacteria.