OPT 221 Final Part 1 (Iris & CB)
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
What are the 3 iris regions?
1. iris root = peripheral region of iris that is continuous with CB
2. pupillary margin = free edge of the iris, rests on the lens
3. collarette = circular, jagged ridge 1.5 mm from the pupillary margin = attachment site for the fetal pupillary membrane
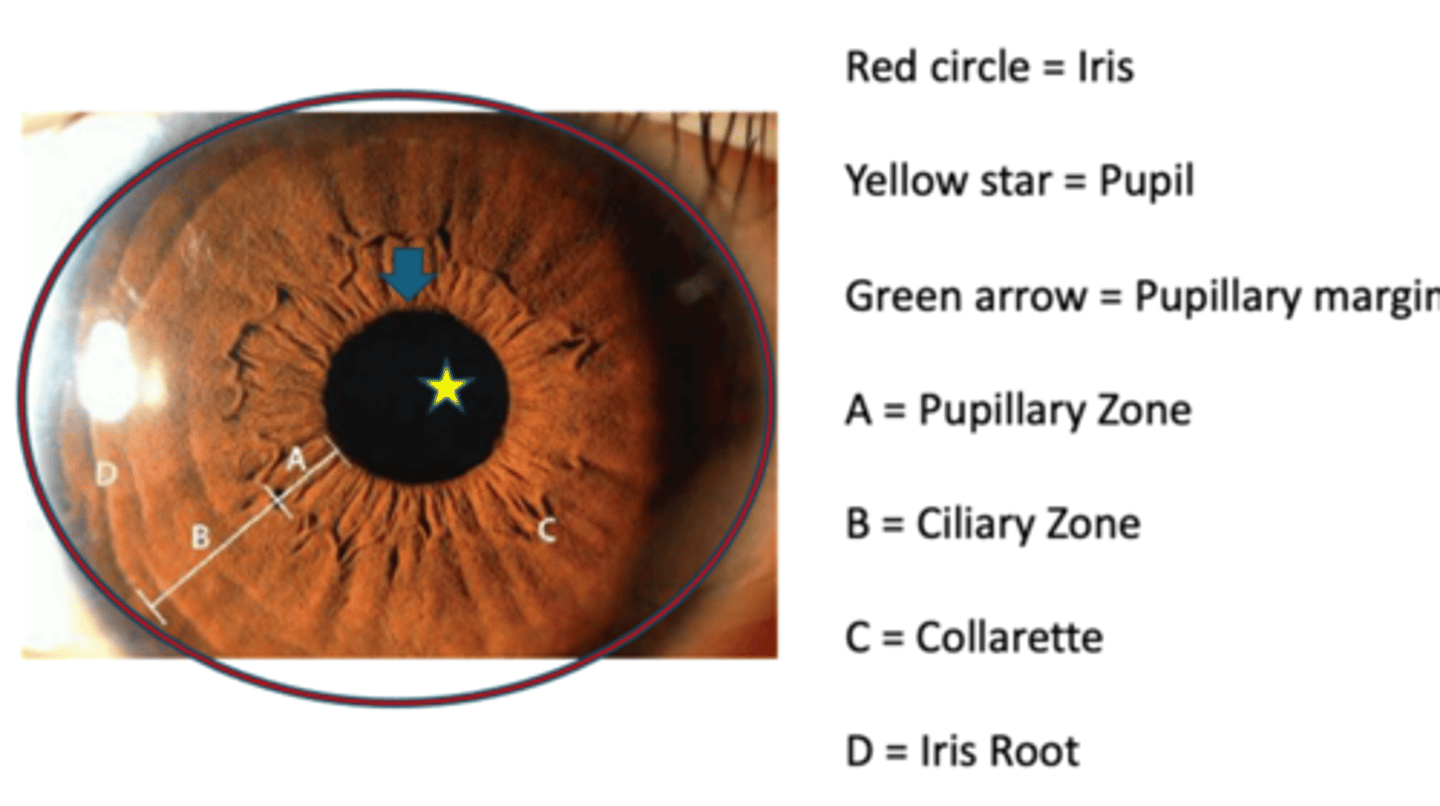
What divides the iris into the pupillary zone and ciliary zone?
collarette
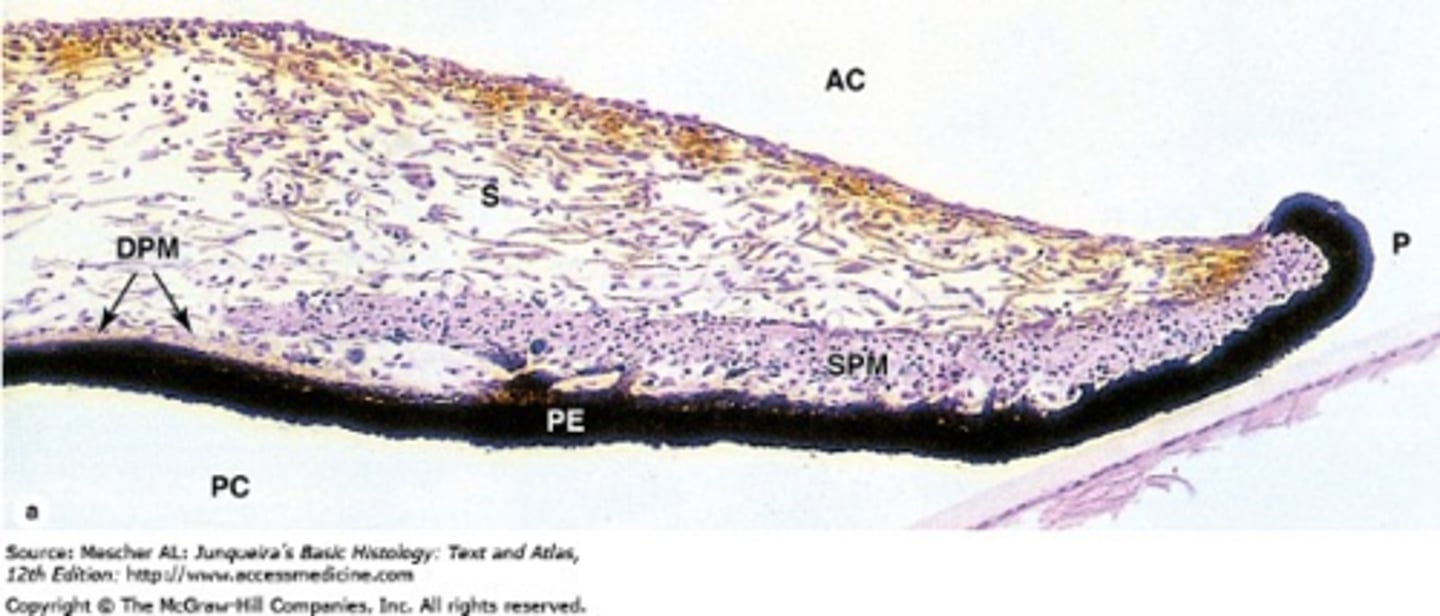
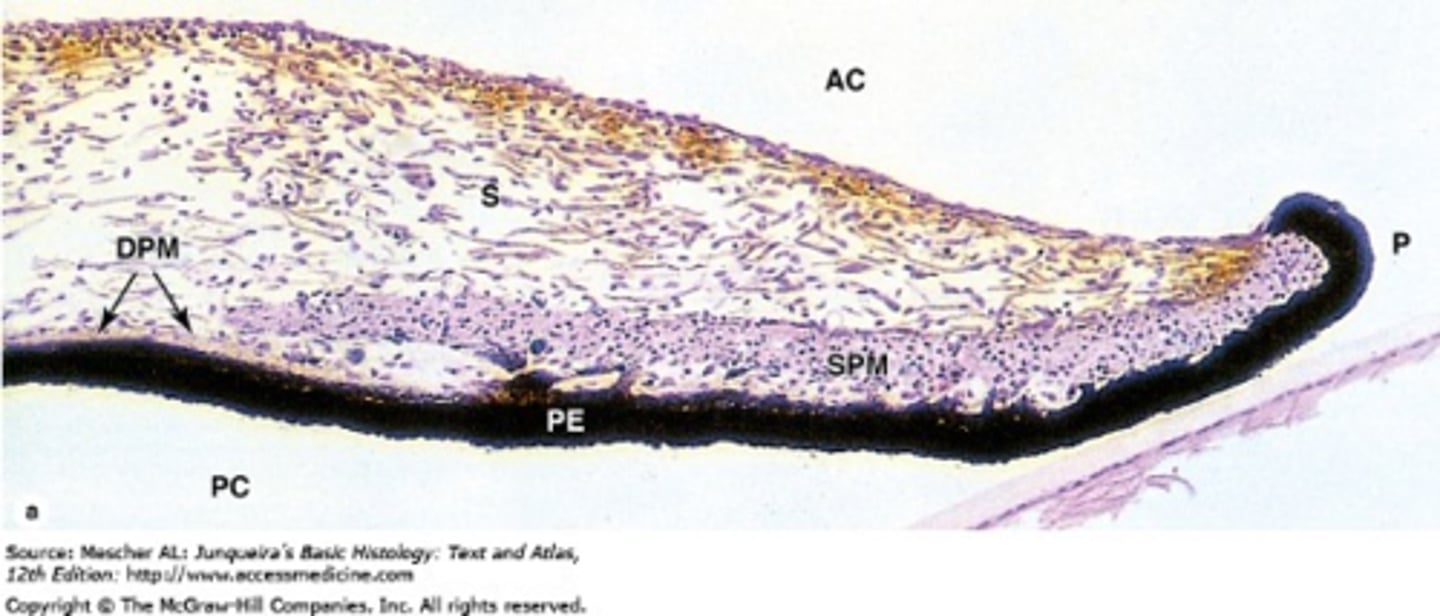
What are the 3 iris layers from anterior to posterior?
ANTERIOR
stroma
ant pigmented epithelium
post pigmented epithelium
POSTERIOR
What makes up the iris stroma?
loose CT = fibroblasts, radial collagen, radial anchor BV
pigmented cells = melanocytes, clump cells (macrophages)
WBCs
sphincter muscle = circular
dilater muscle extensions
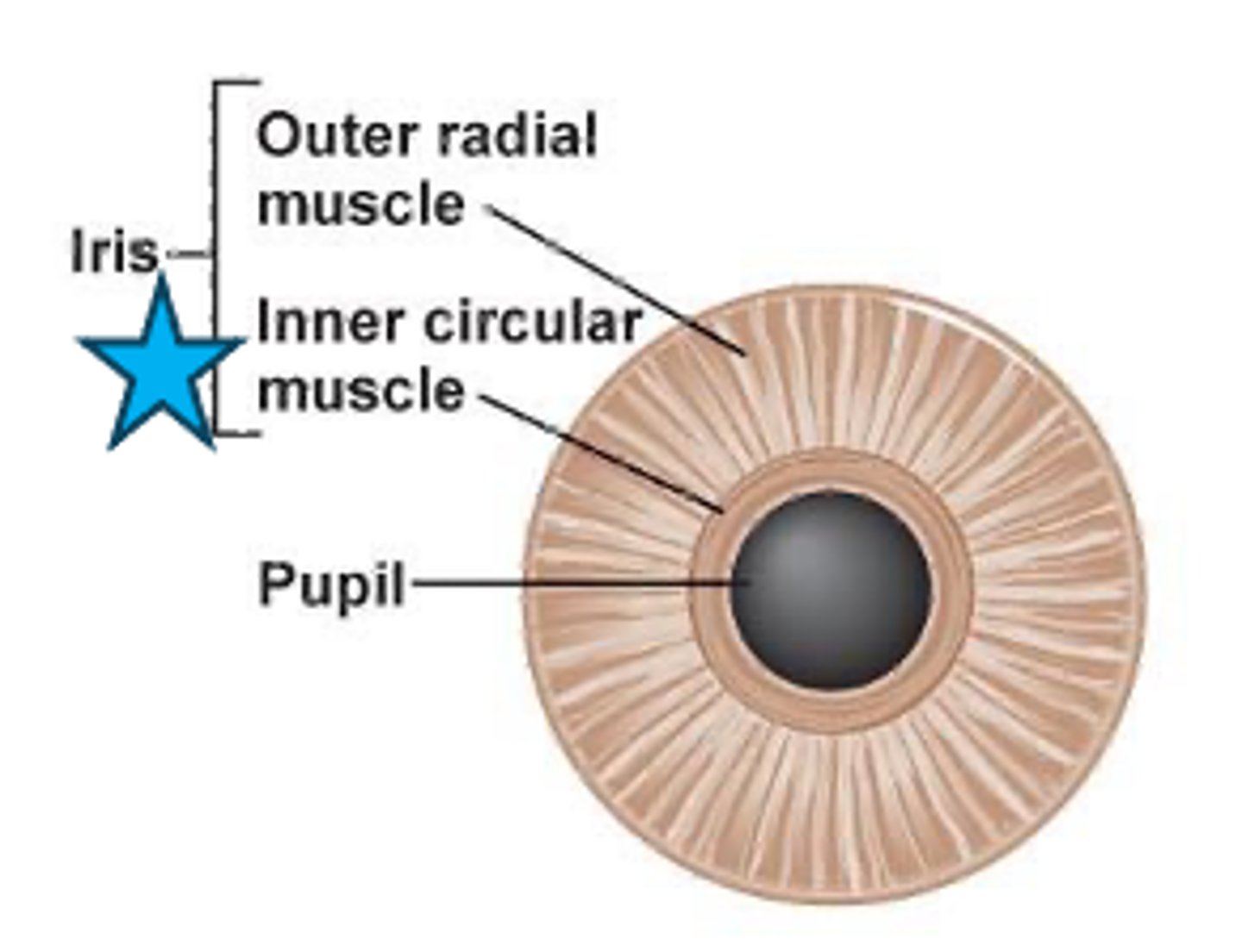
What makes up the ant pigmented epithelium?
dilator muscle = radial smooth mm
tight junctions to regulate aqueous humor flow
pigmented myoepithelial cells
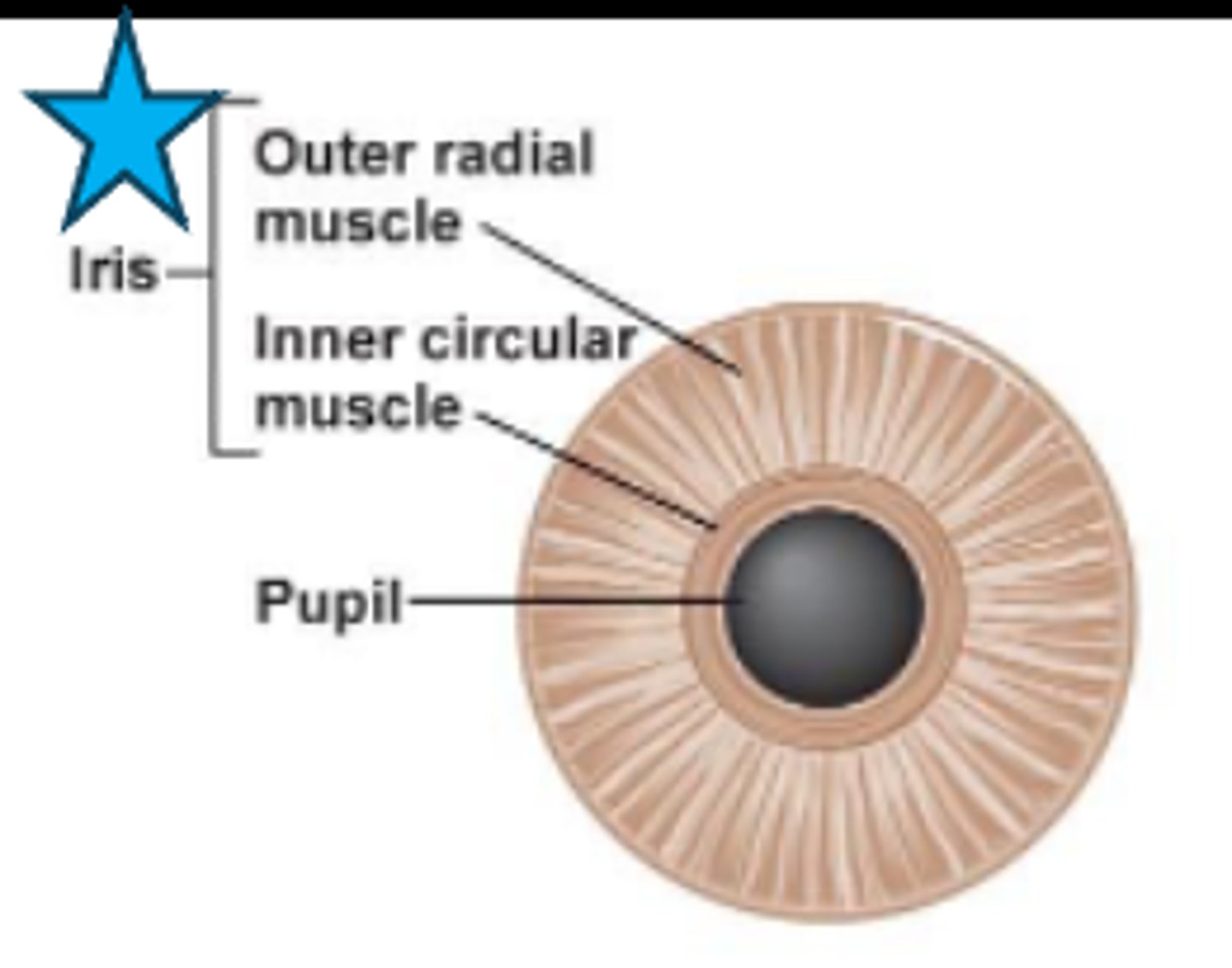
What makes up the post pigmented epithelium?
tight junctions to regulate aqueous humor flow
pigmented epithelial cells
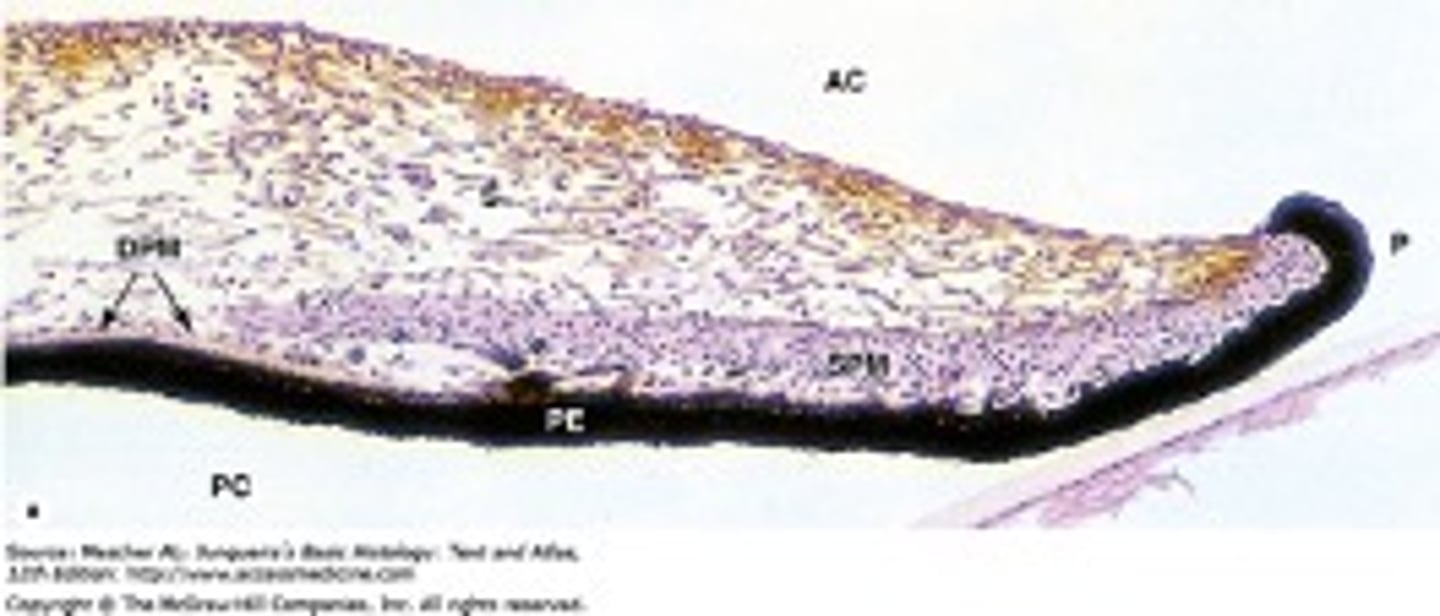
What makes up the pupillary ruff?
anterior and posterior pigmented epithelium layers
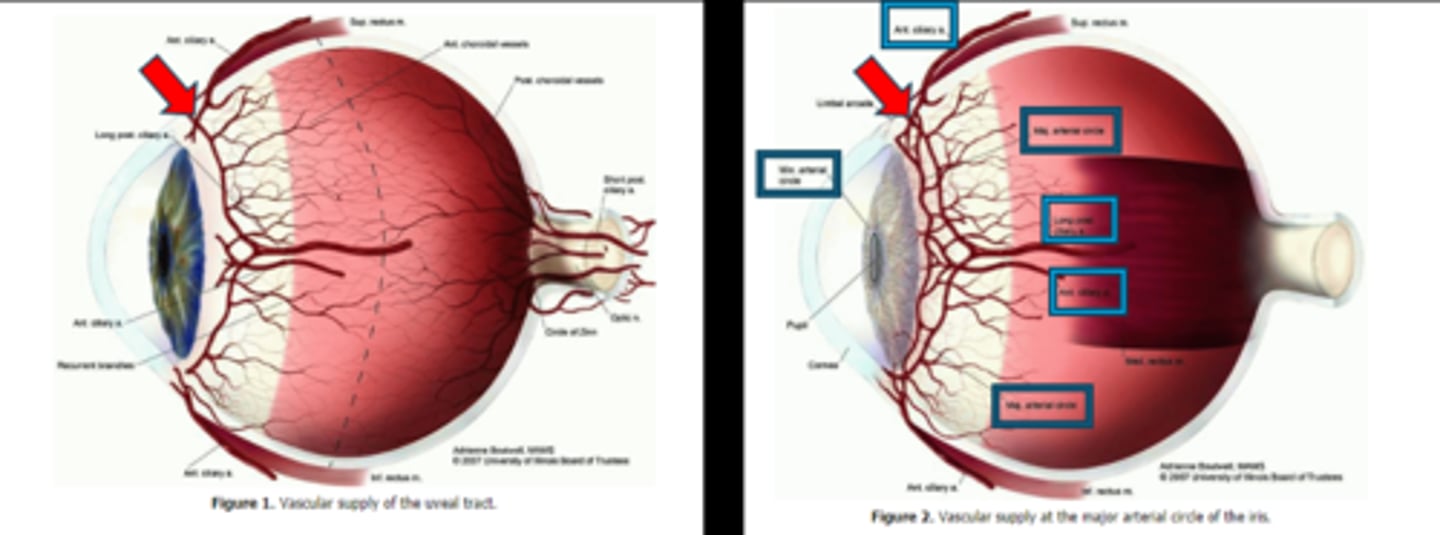
What supplies the iris and CB with blood?
major and minor arterial circle of the iris
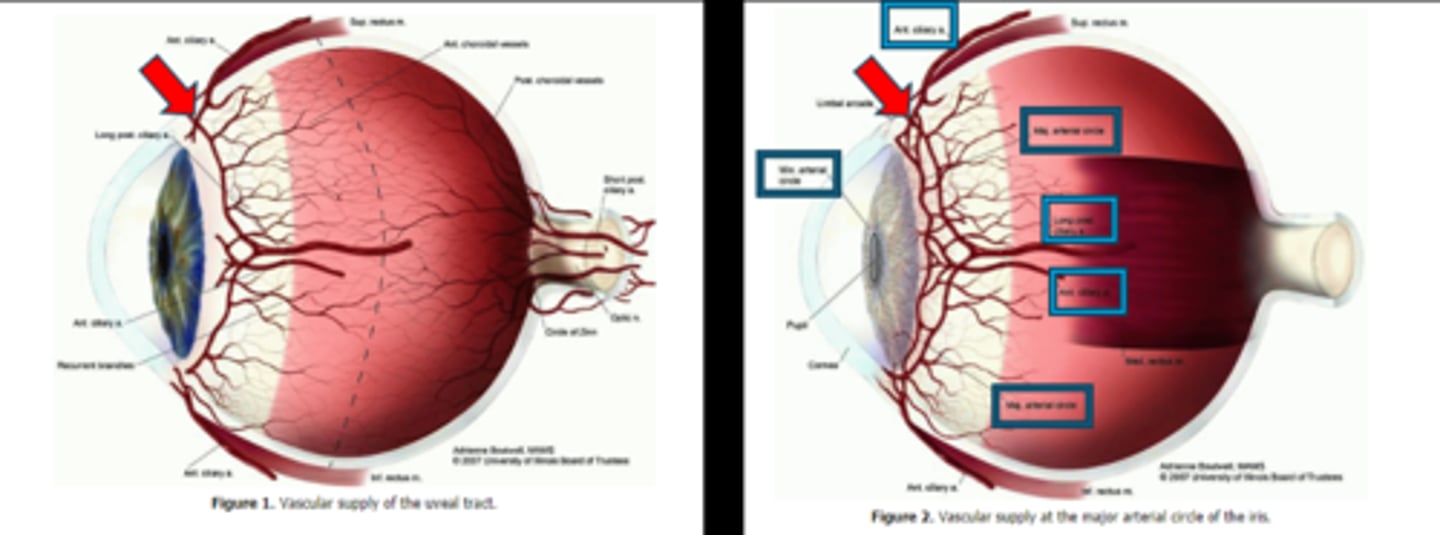
How do the iris capillaries contribute to the BAB?
capillaries lack fenestrations
AND
endothelial cells joined by tight junctions
to create a tight barrier
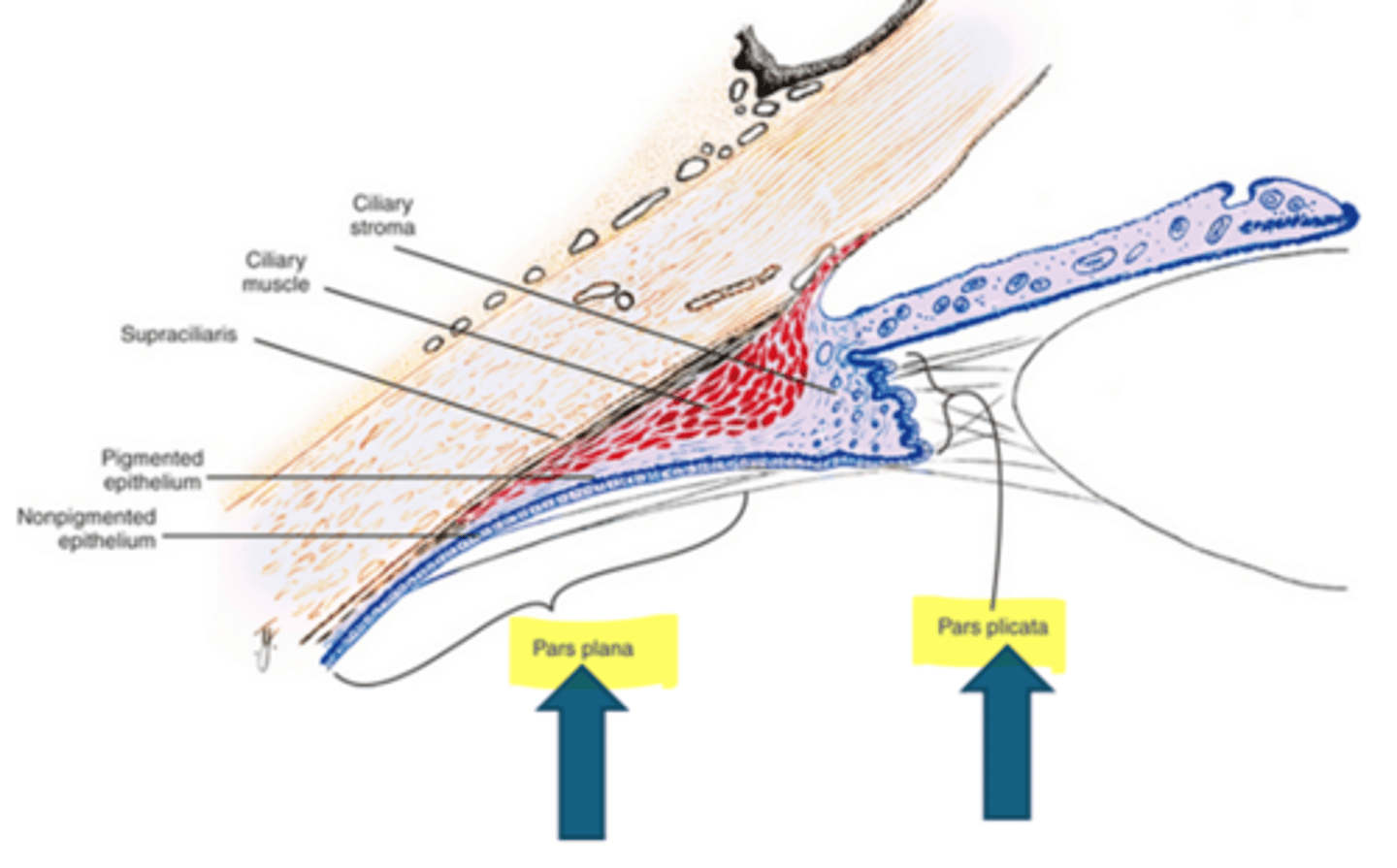
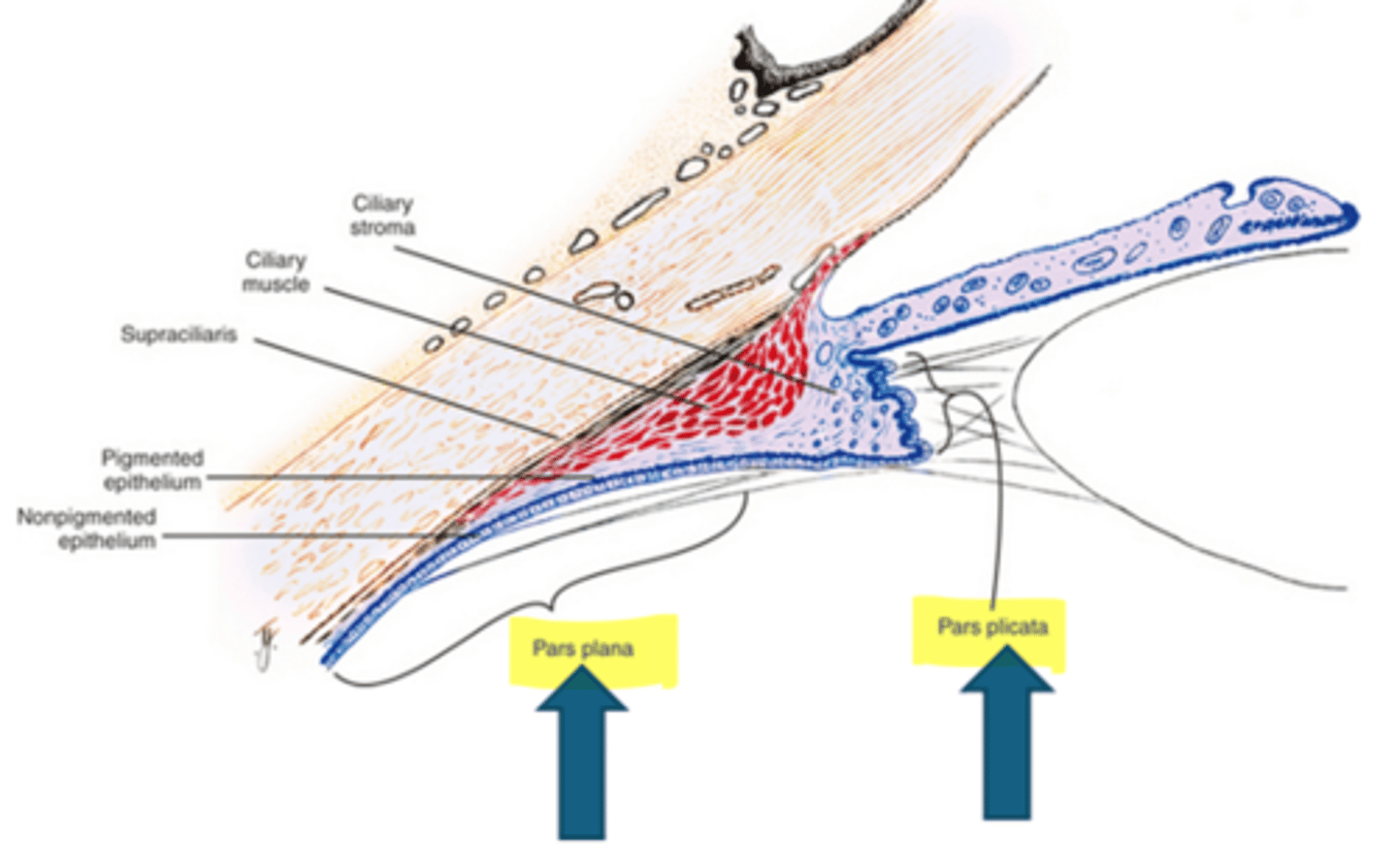
What are the 2 regions of the ciliary body?
pars plicata = wider, anterior, projections of stroma w/ pigment and nonpigment epithelium
pars plana = thinner, flatter, posterior, serrated with the ora serrata
Which portion of the ciliary body produces aqueous?
anterior nonpigmented epithelium on the pars plicata (ciliary processes)
What are the 5 layers of the ciliary body?
nonpigmented epithelium = zonules, aqueous production, tight junctions form a complete BAB = things must pass through cells
pigmented epithelium = gap junctions
ciliary stroma = loose CT, melanocytes, WBCs
ciliary mm = longitudinal, radial circular orientations
supraciliaris = potential space between CB and sclera
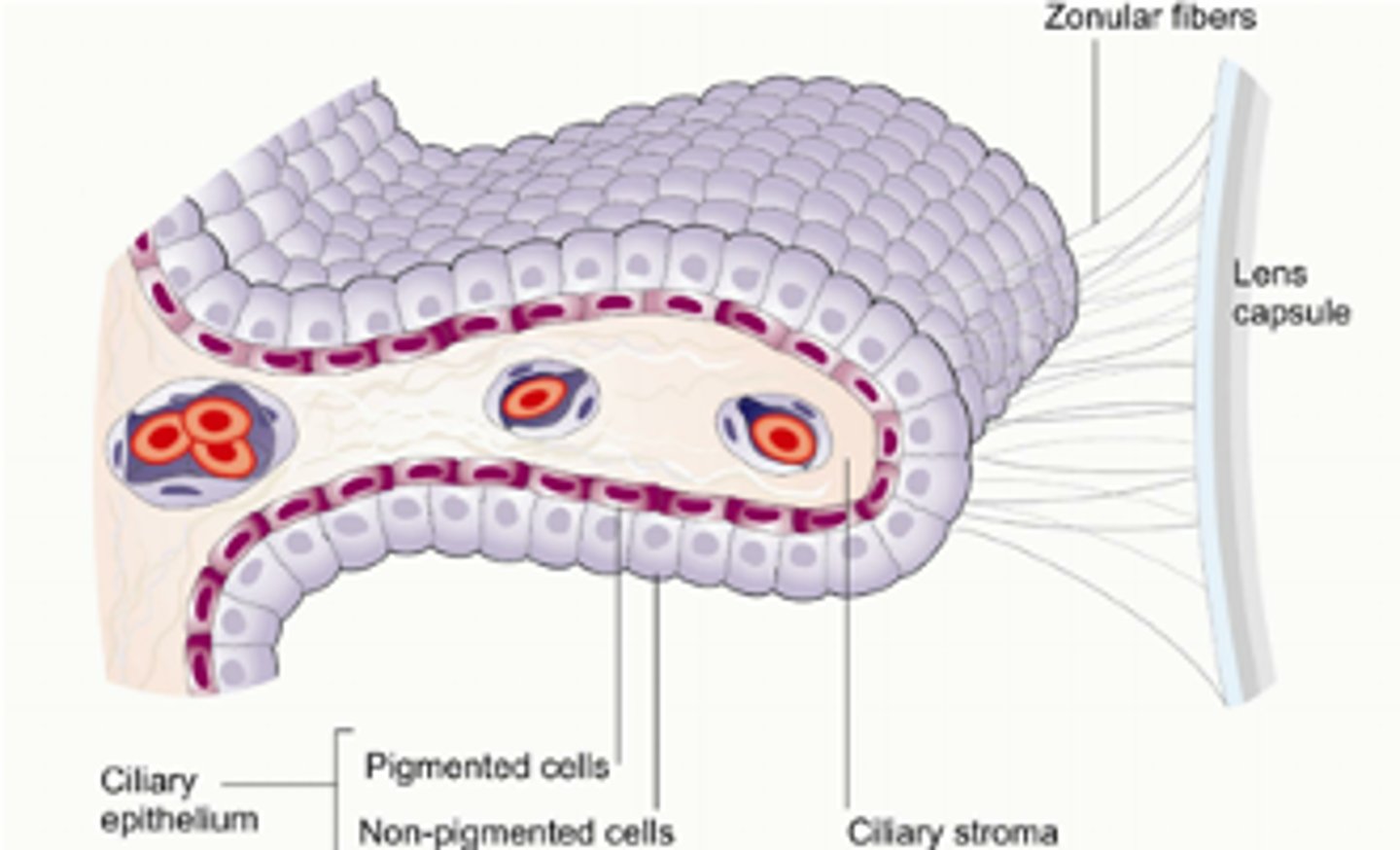
How do the capillaries differ in the ciliary body?
highly fenestrated = allows water, molecules, ions to enter stroma
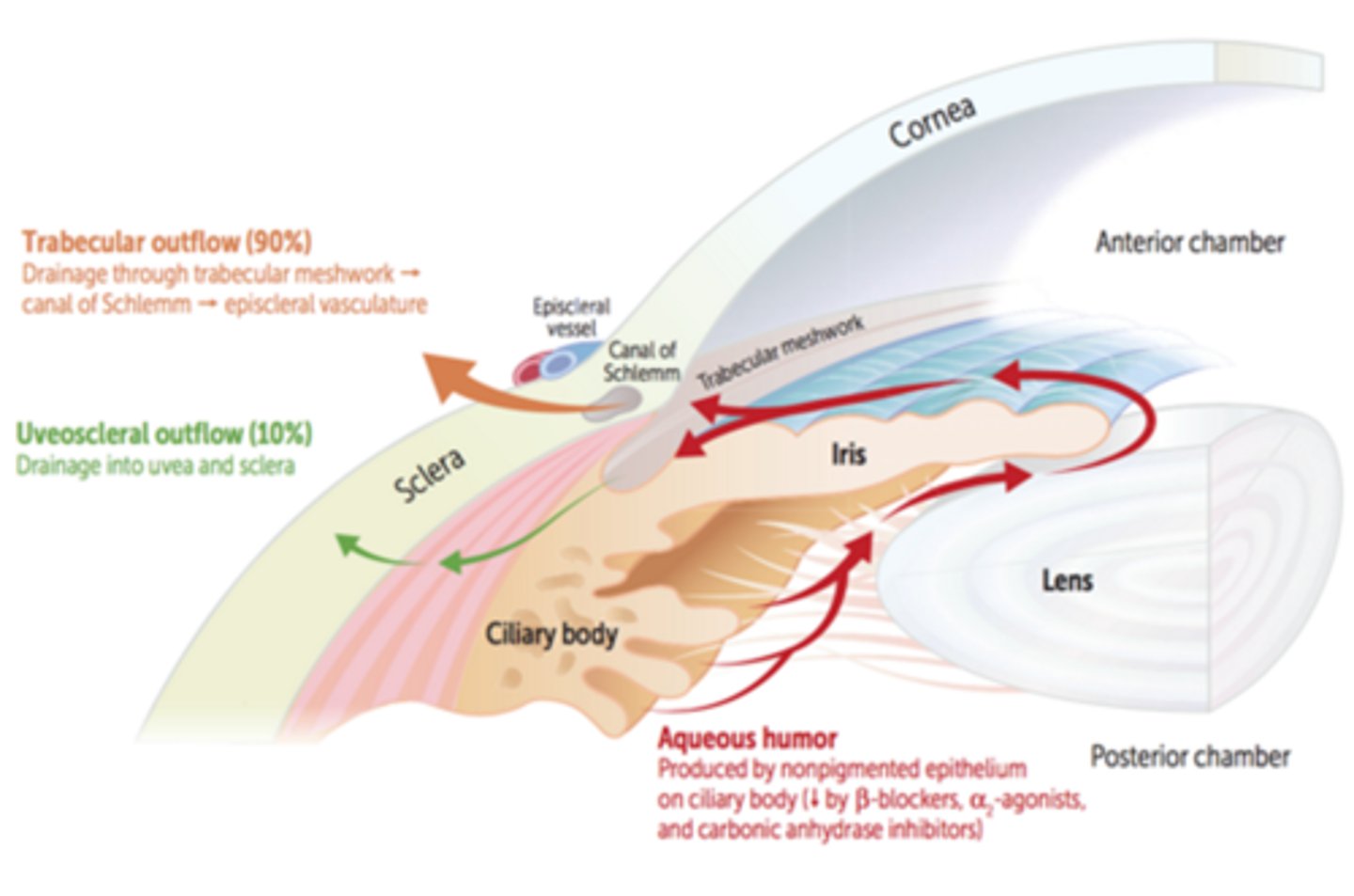
Explain the trabecular route (70-90%) of aqueous humor drainage.
AC = posterior TM = Schlemm's canal = aqueous veins and intrascleral collector channels = episcleral veins and intrascleral venous plexus
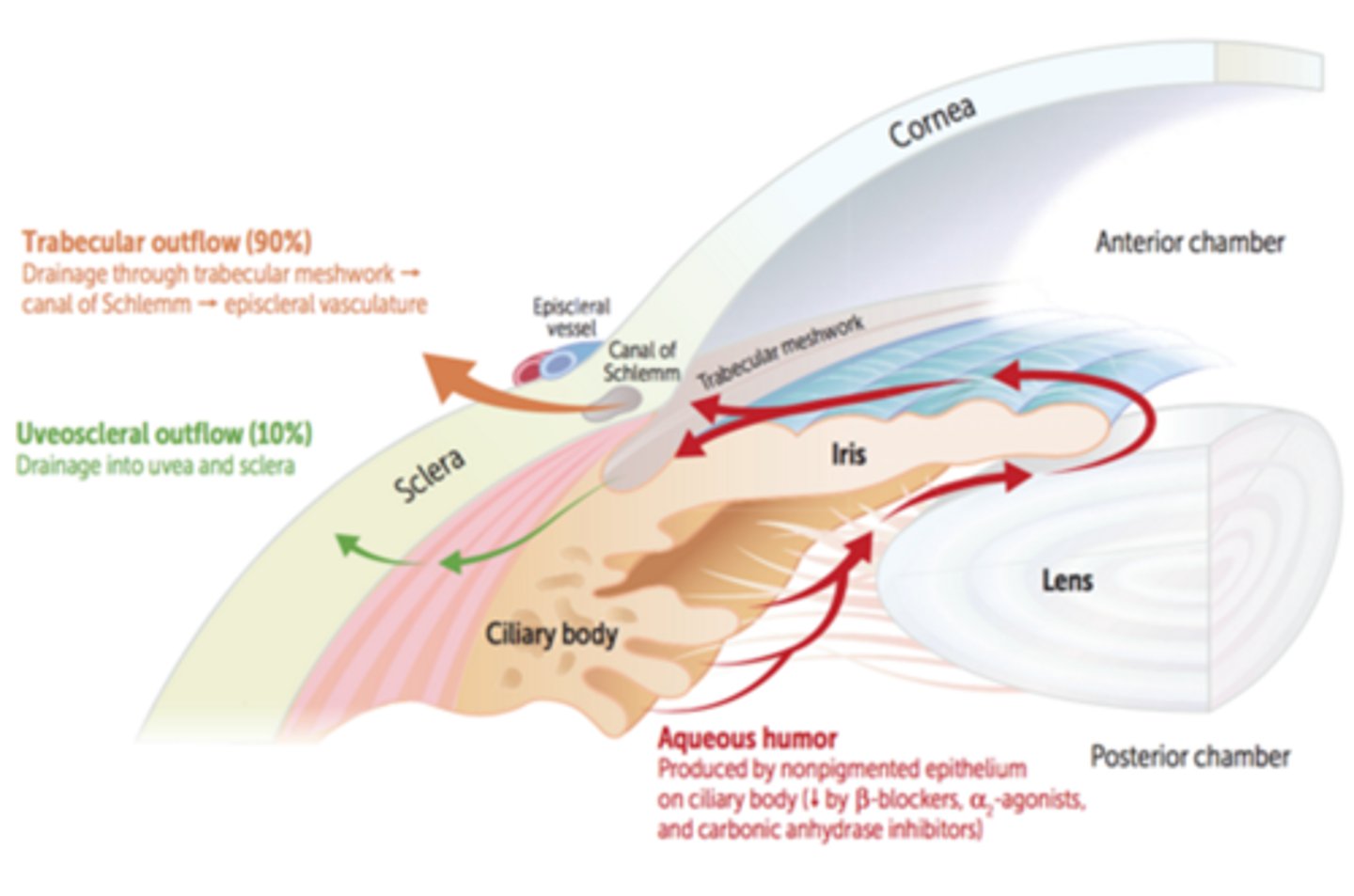
Explain the uveoscleral route (10-30%) of aqueous humor drainage.
AC = iris root = CB = supraciliaris = suprachoroidal space = vortex veins
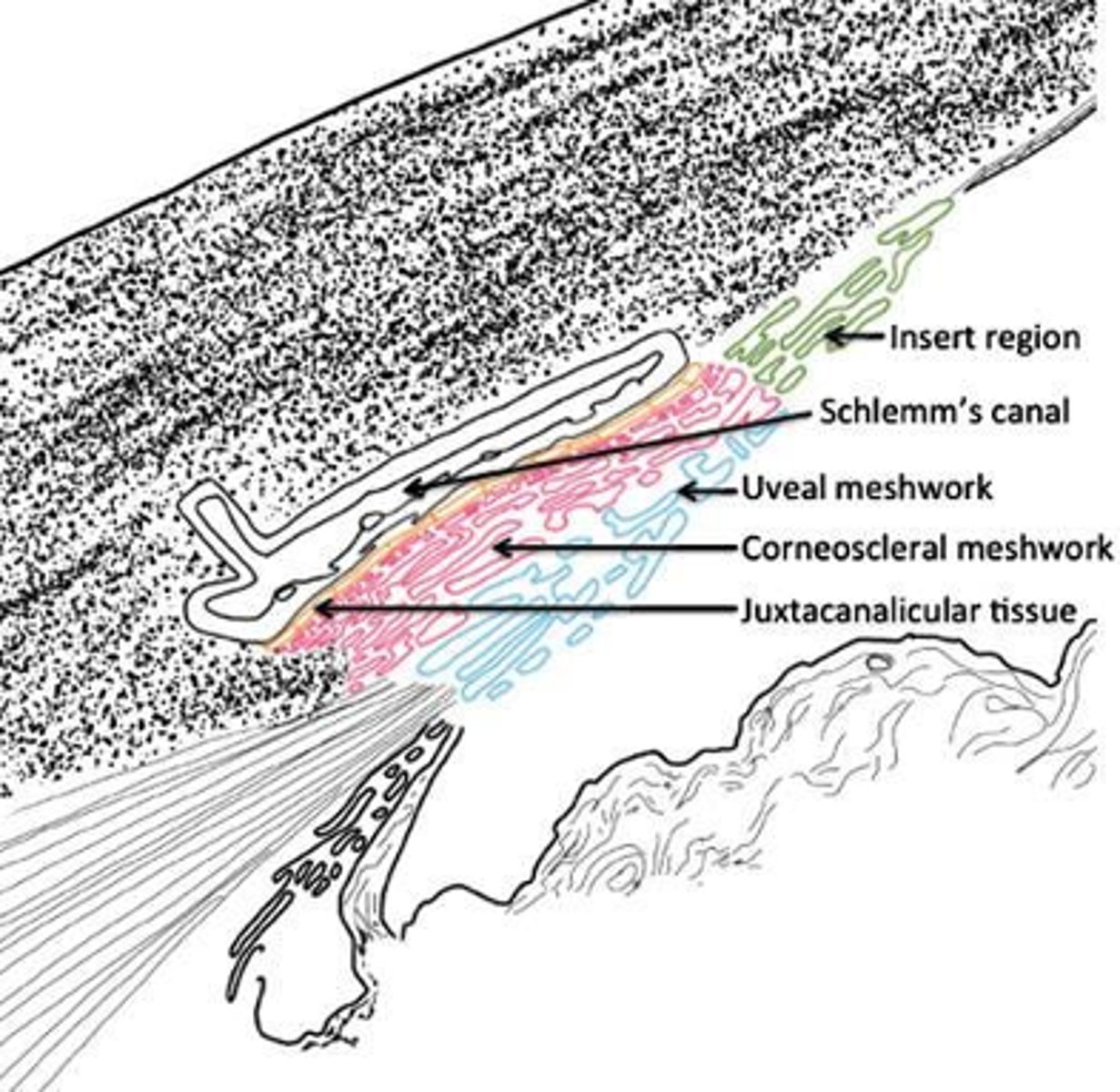
What is the order of structures in the angle from posterior to anterior?
“I Can See The Line”
Iris
Ciliary Body
Scleral Spur
Trabecular Meshwork
Schwalbe’s Line
What is pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
liberation of pigment from the iris with subsequent accumulation on anterior segment structures
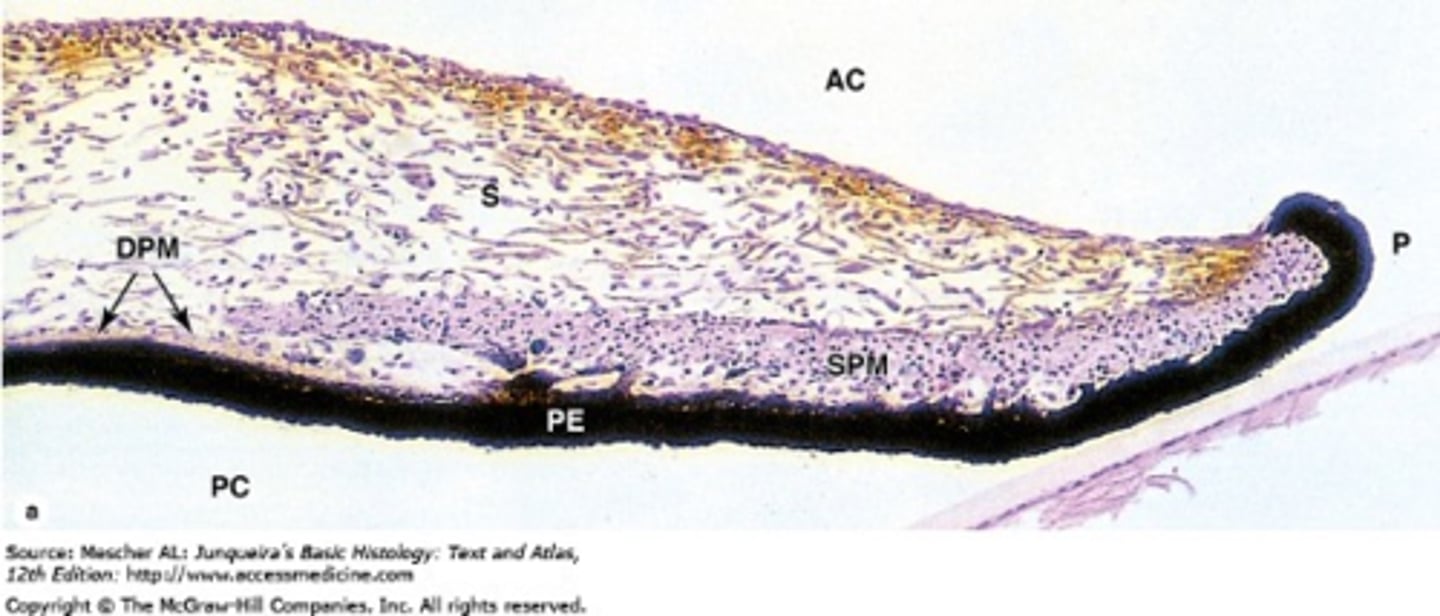
What is the etiology of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
increased AC pressure relative to PC pressure = posterior bowing of midperipheral iris = iris epithelium rubs on zonules = pigment released
What are 4 common demographic groups we see pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
age 20-50
Caucasian men
myopes
lattice degeneration
What is the laterality of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
bilateral
While mostly asymptomatic, what are some symptoms of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
blurred vision, eye pain, and halos around lights after exercise or pupillary dilation (can cause pigment release with acute elevation of IOP)
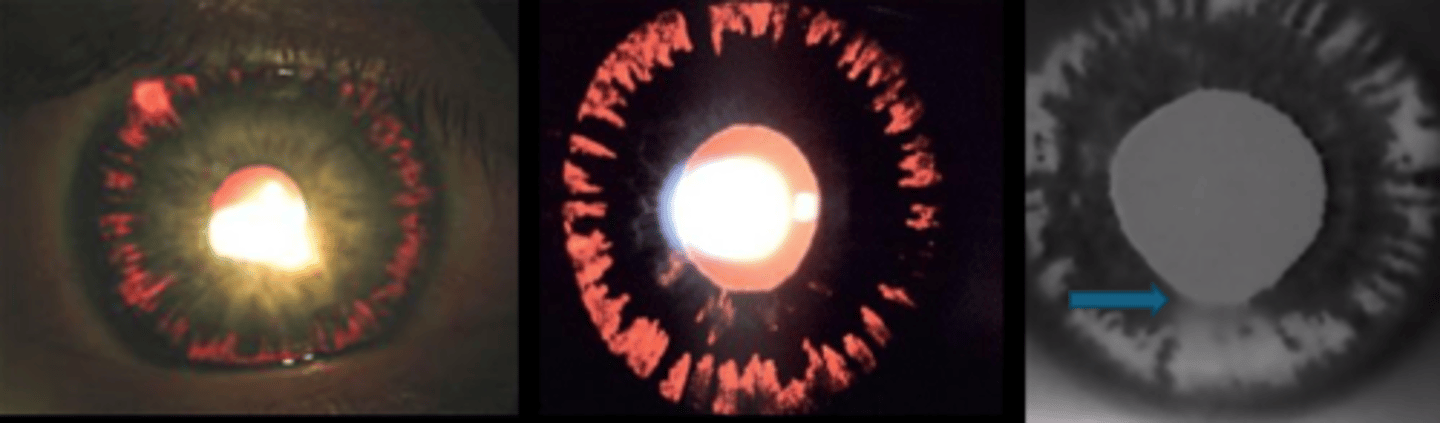
What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
posterior bowing of midperipheral iris = AC appears deep on gonio, ASeg-OCT, UBM

What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
midperipheral, spoke-like iris TIDs usually 360 deg = seen on retroillumination = can progress with disease
What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS) that the blue arrow is pointing to?
Sampaolesi line = pigment deposition at or anterior to Schwalbe's line
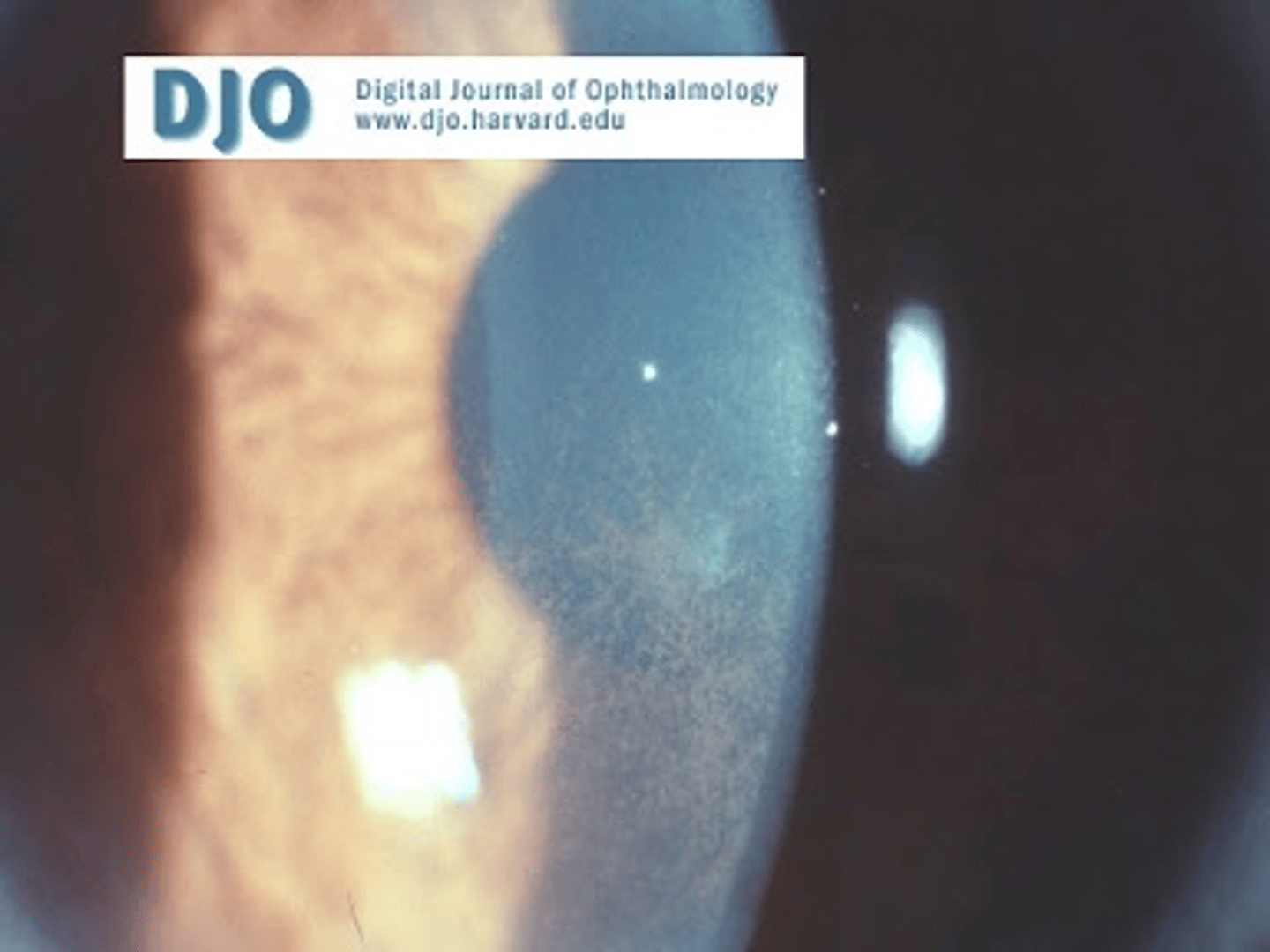
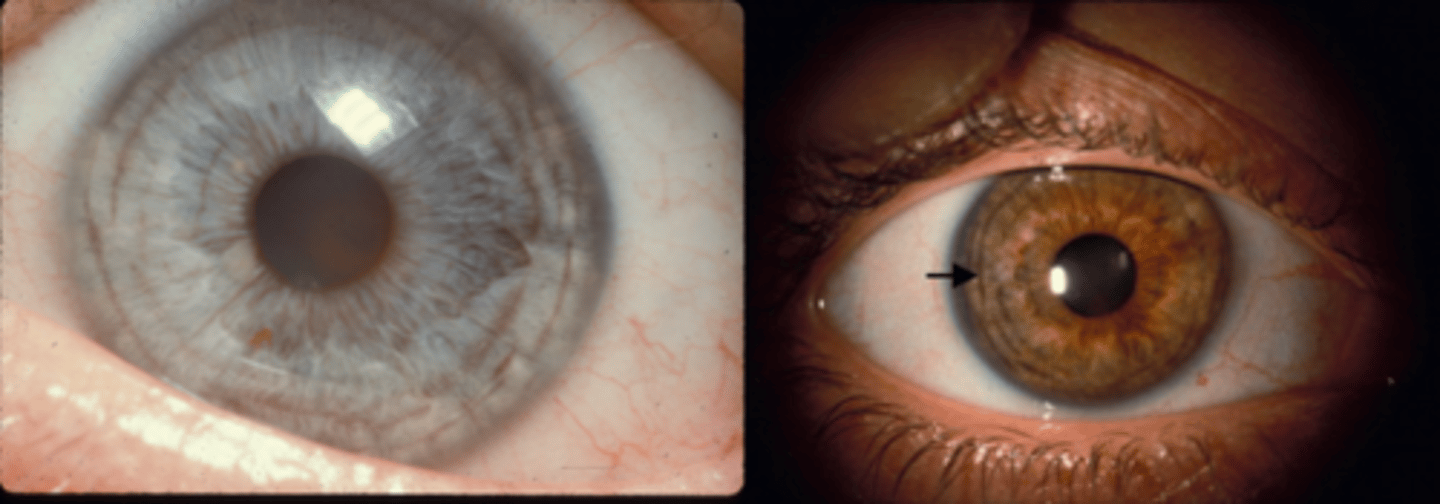
What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
Krukenberg spindle = vertical band of pigment deposition on K endothelium
What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
Scheie line/stripe = pigment deposition on posterior equatorial lens surface (between post lens capsule and zonules = pathognomonic for PDS
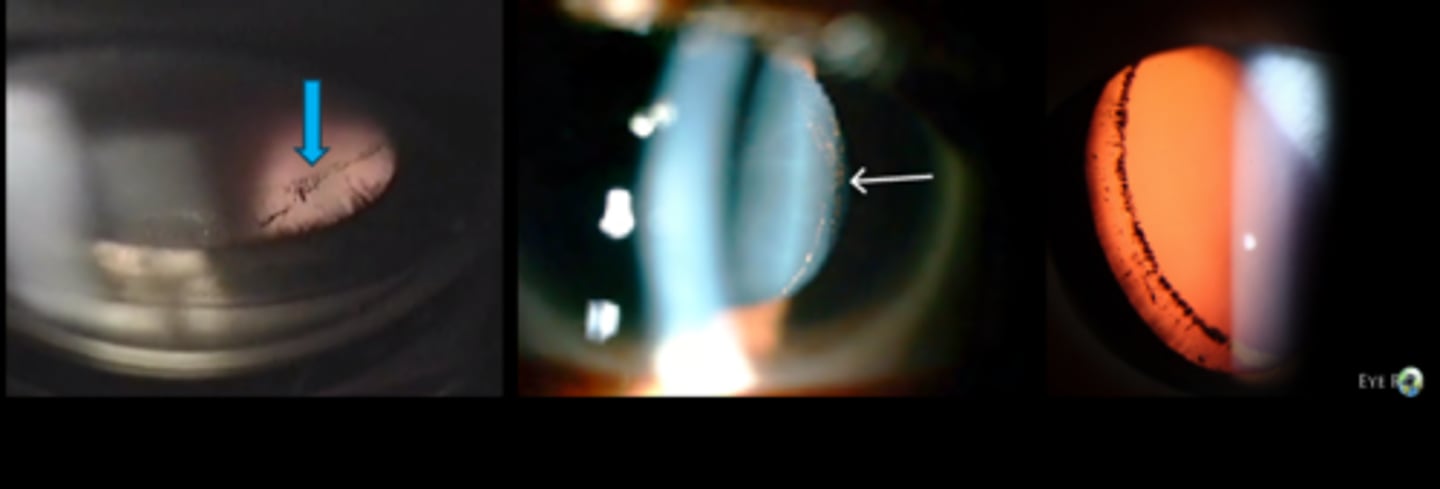
How can we best assess the Scheie line/stripe and zonules?
view the lens equator on SL exam by angling the slit beam nasally and having the patient look temporally
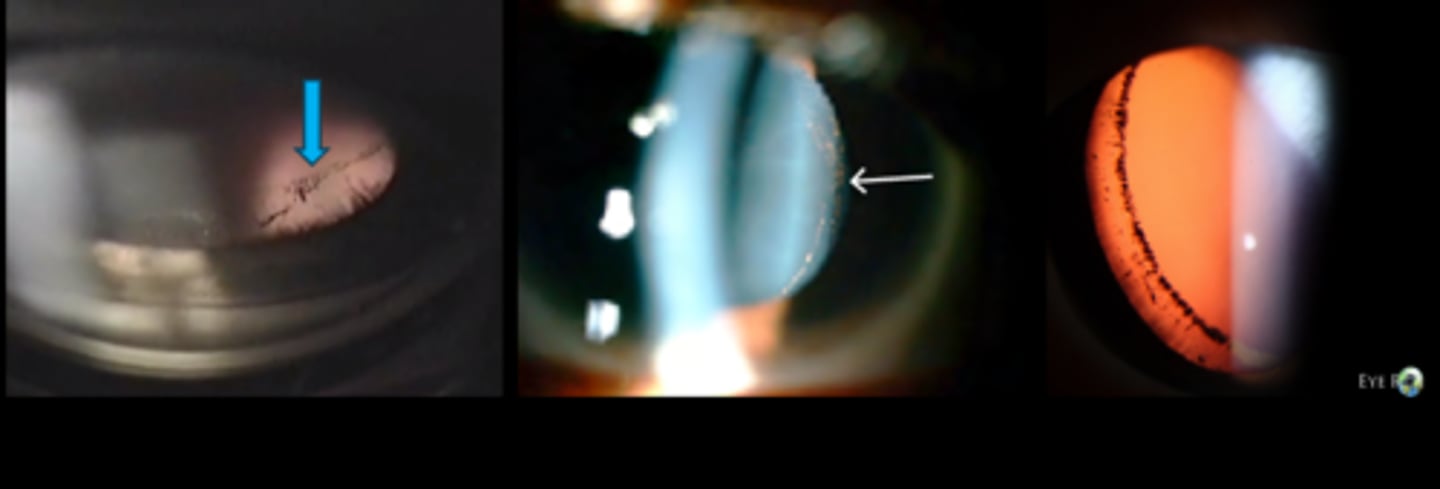
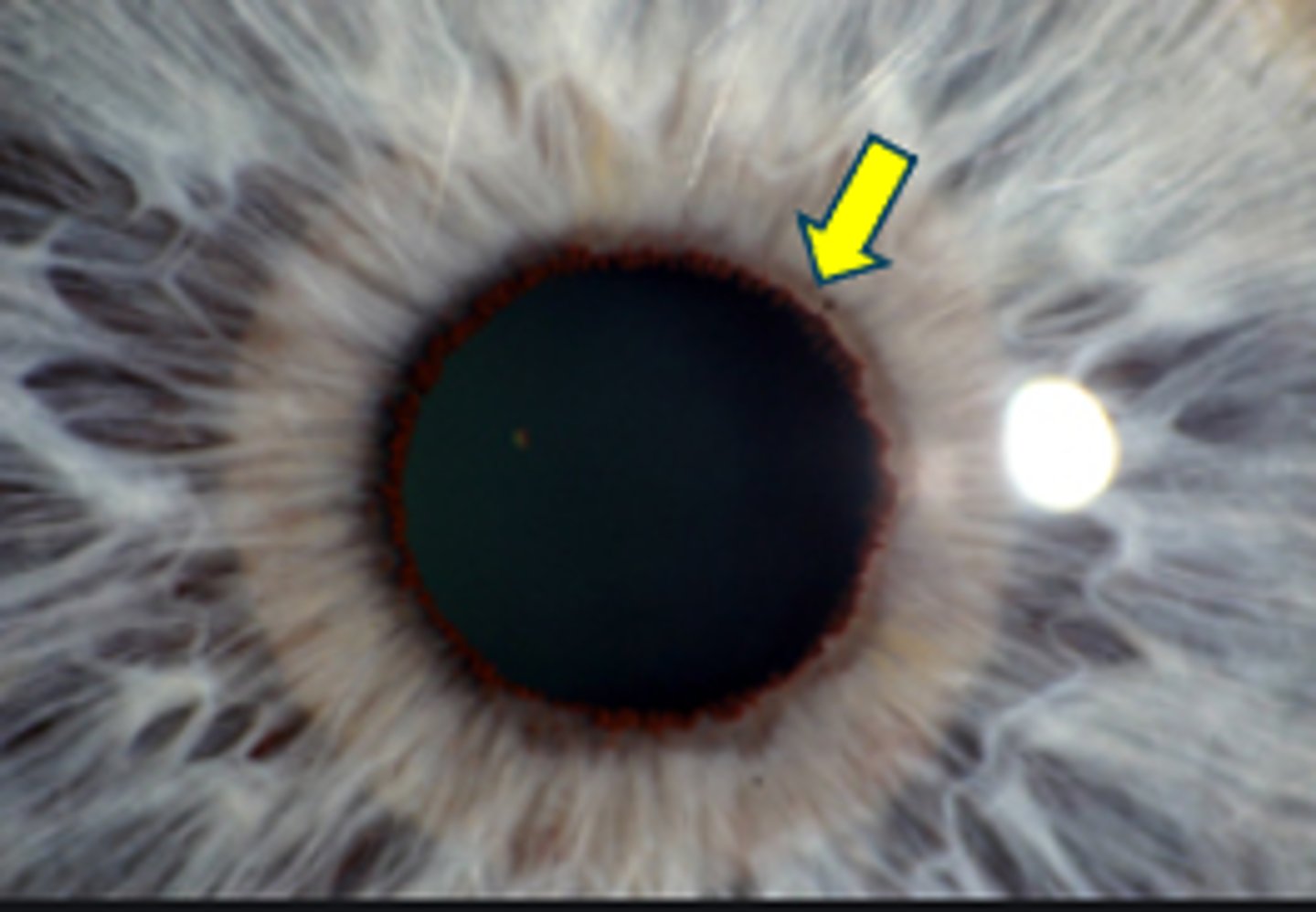
What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
pigment deposition on...
AC
anterior iris = peripheral segmented pigment rings (esp in chronic LT disease)
CB
zonules
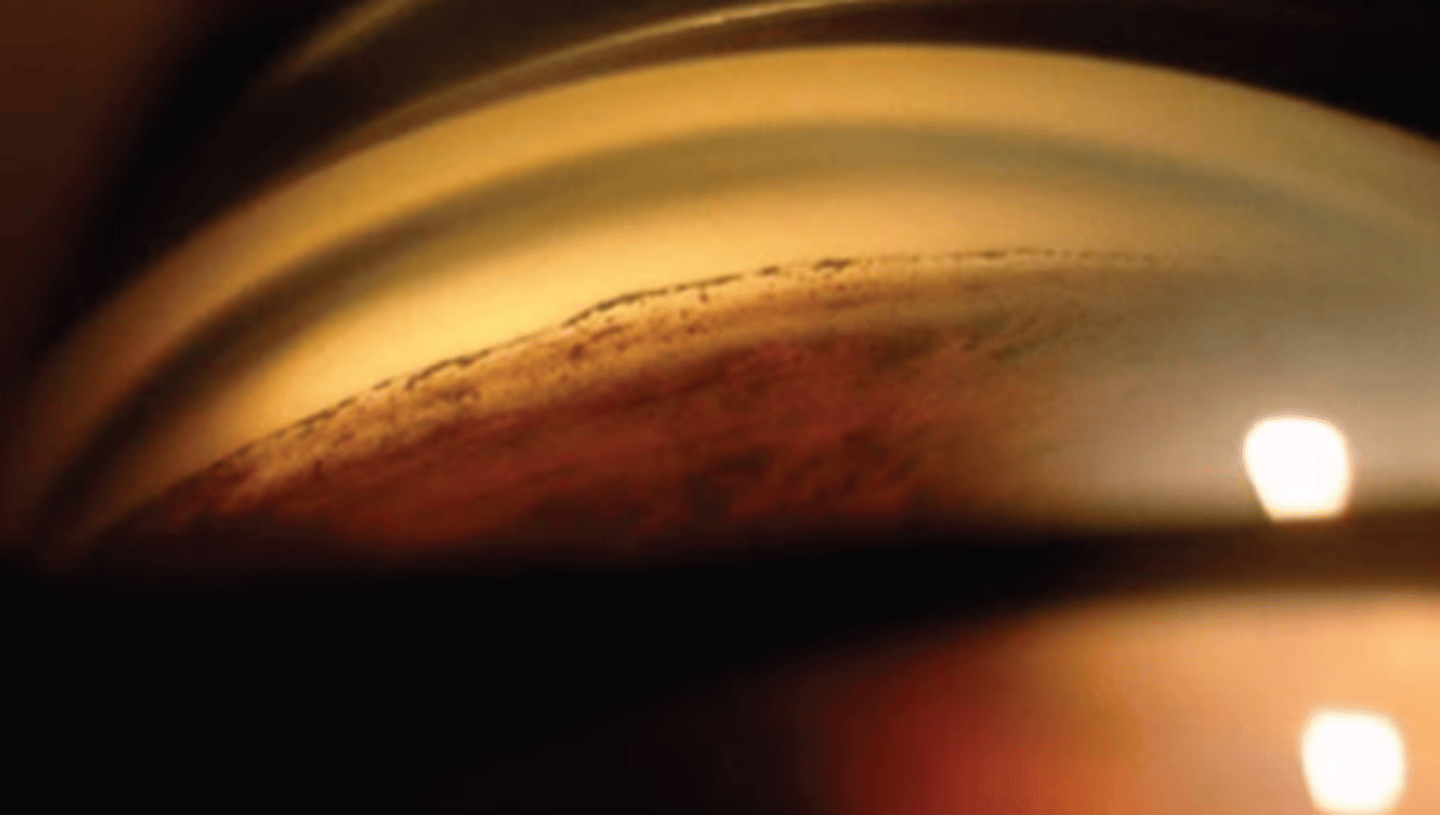
What is this sign of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
thick, homogenous line of pigment deposition in the pigmented TM = ONLY observable by gonio
becomes more clumpy in end stage of disease
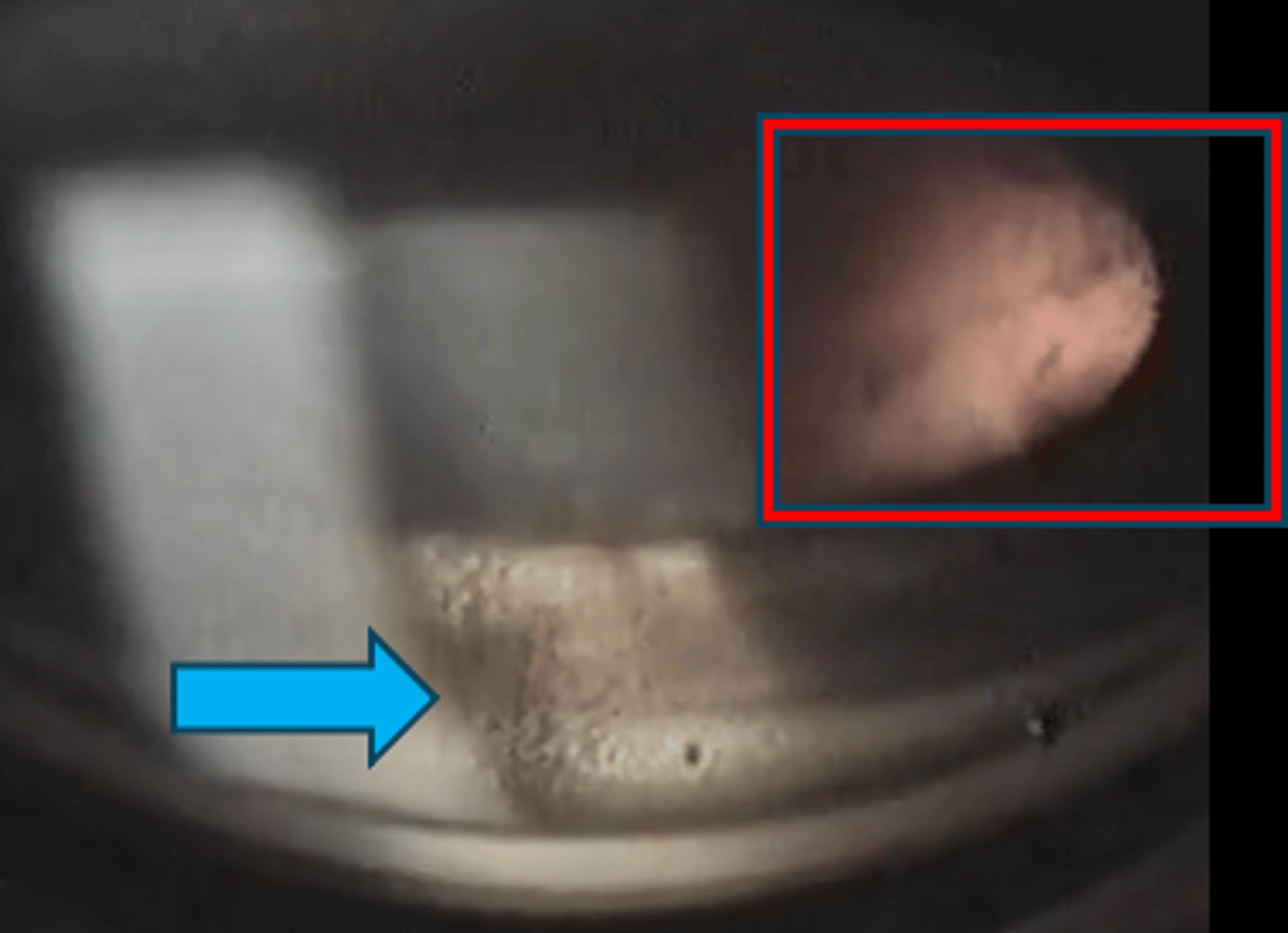
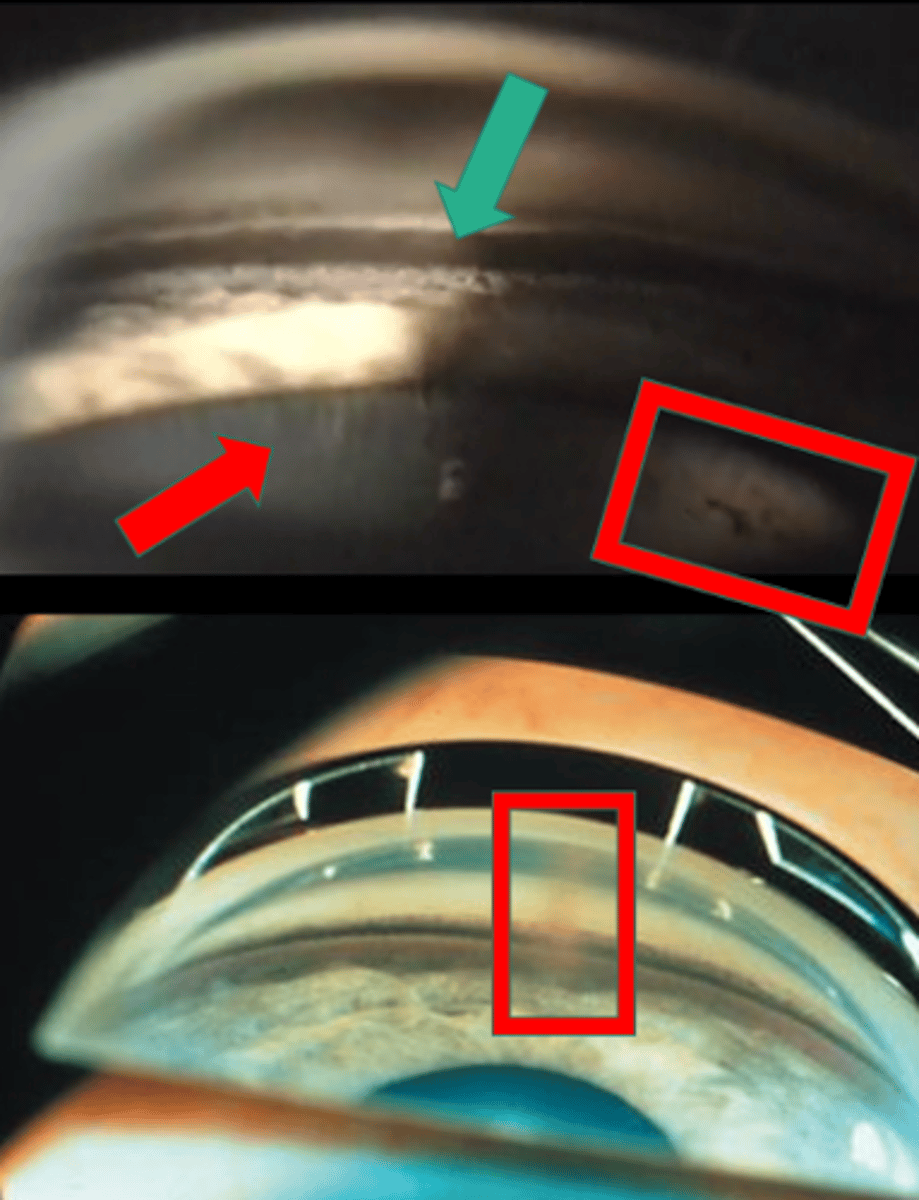
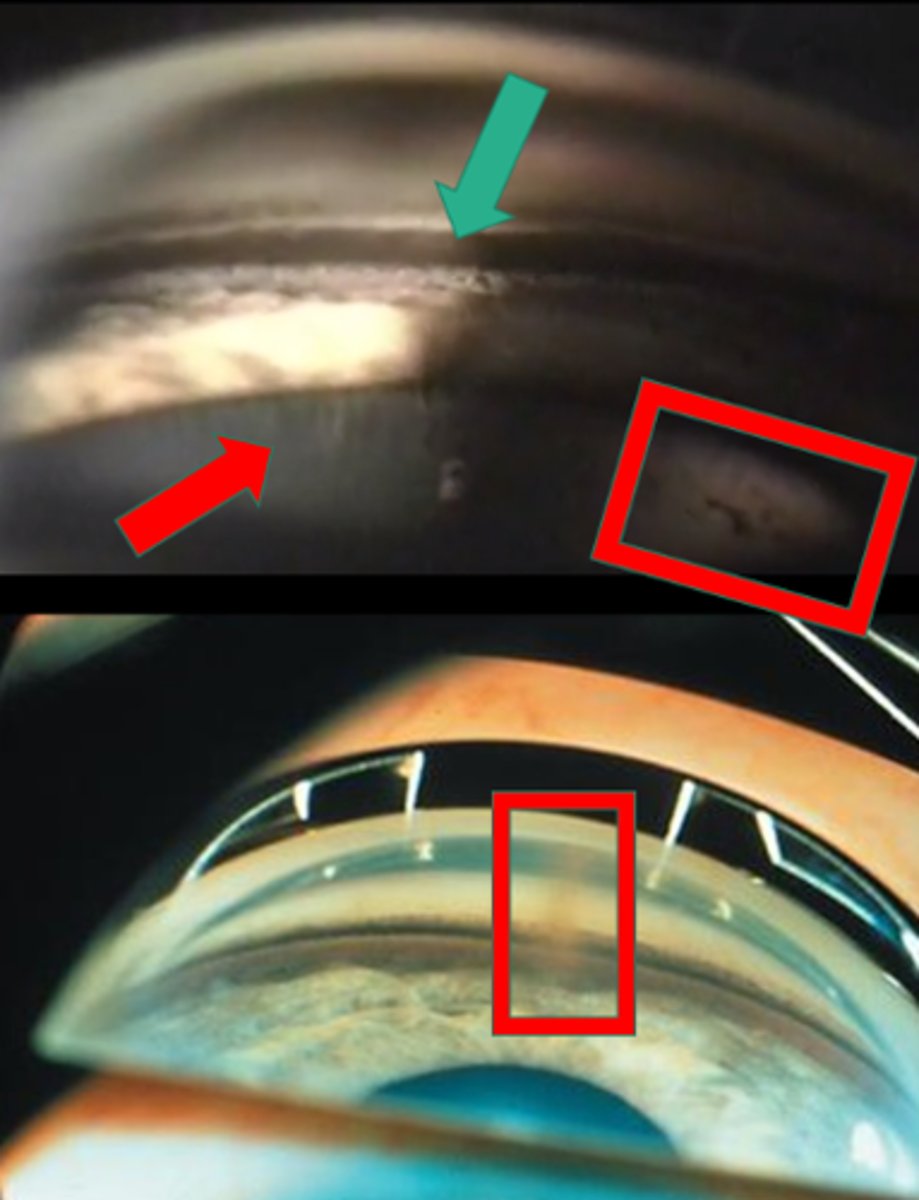
What sign of PDS is indicated by the green arrow?
thick, dense pigment in posterior TM
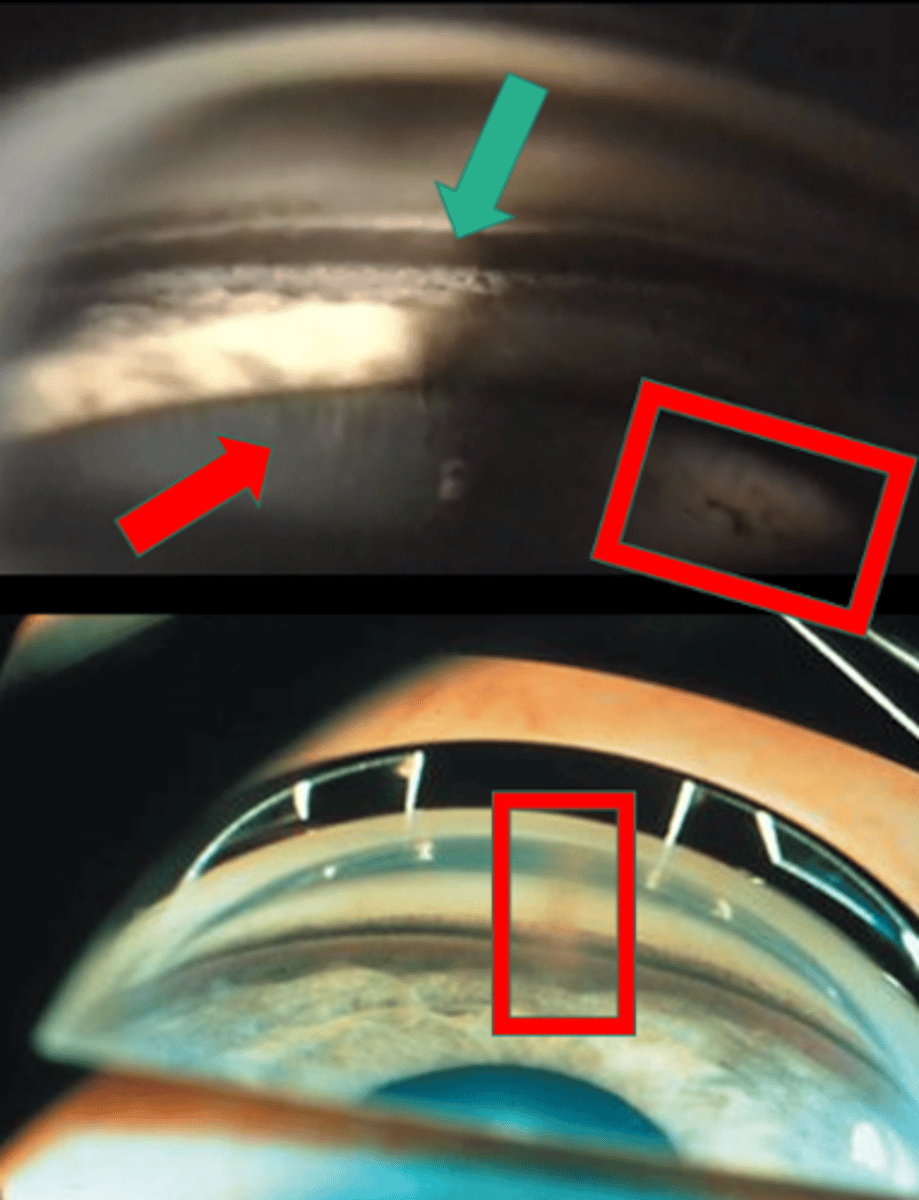
What sign of PDS is indicated by the red arrow?
zonules
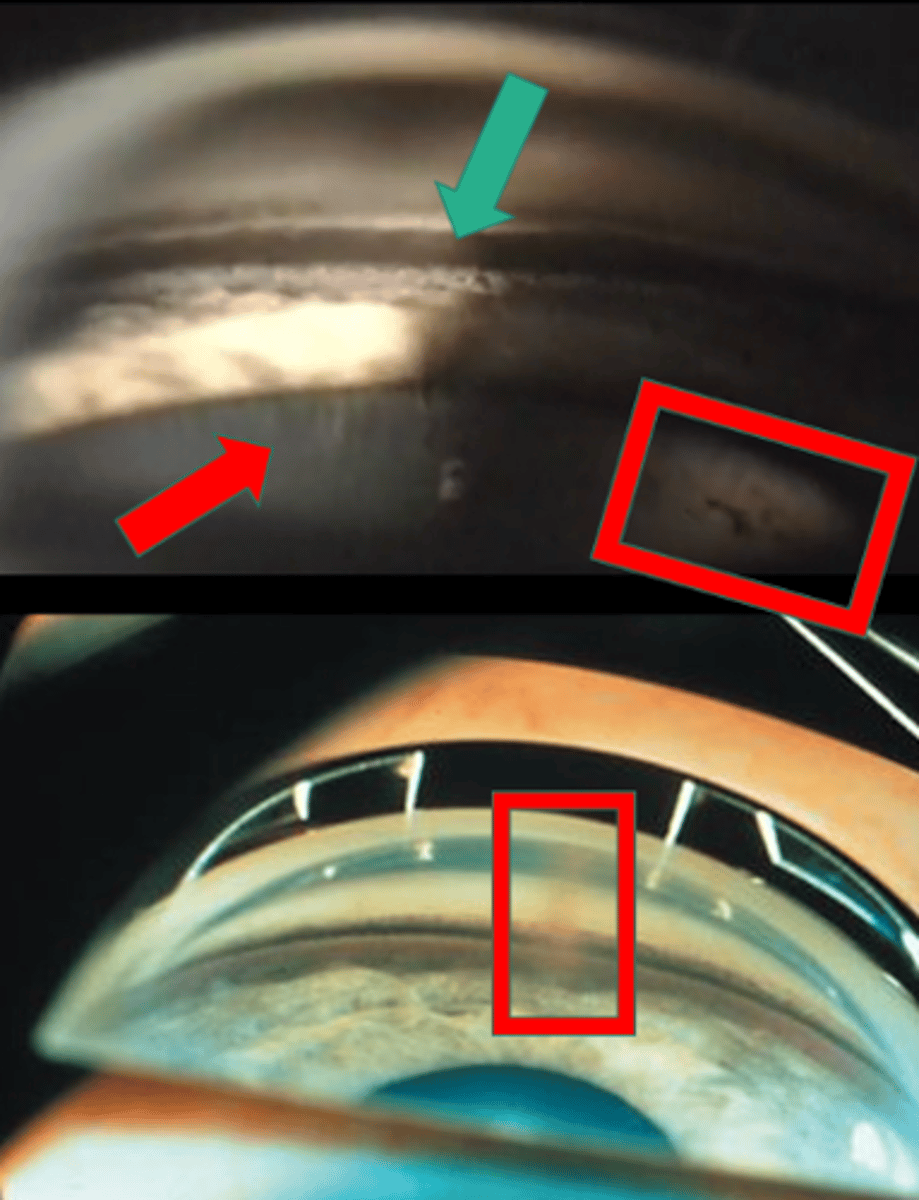
What sign of PDS is indicated by the upper red box?
Scheie stripe/line
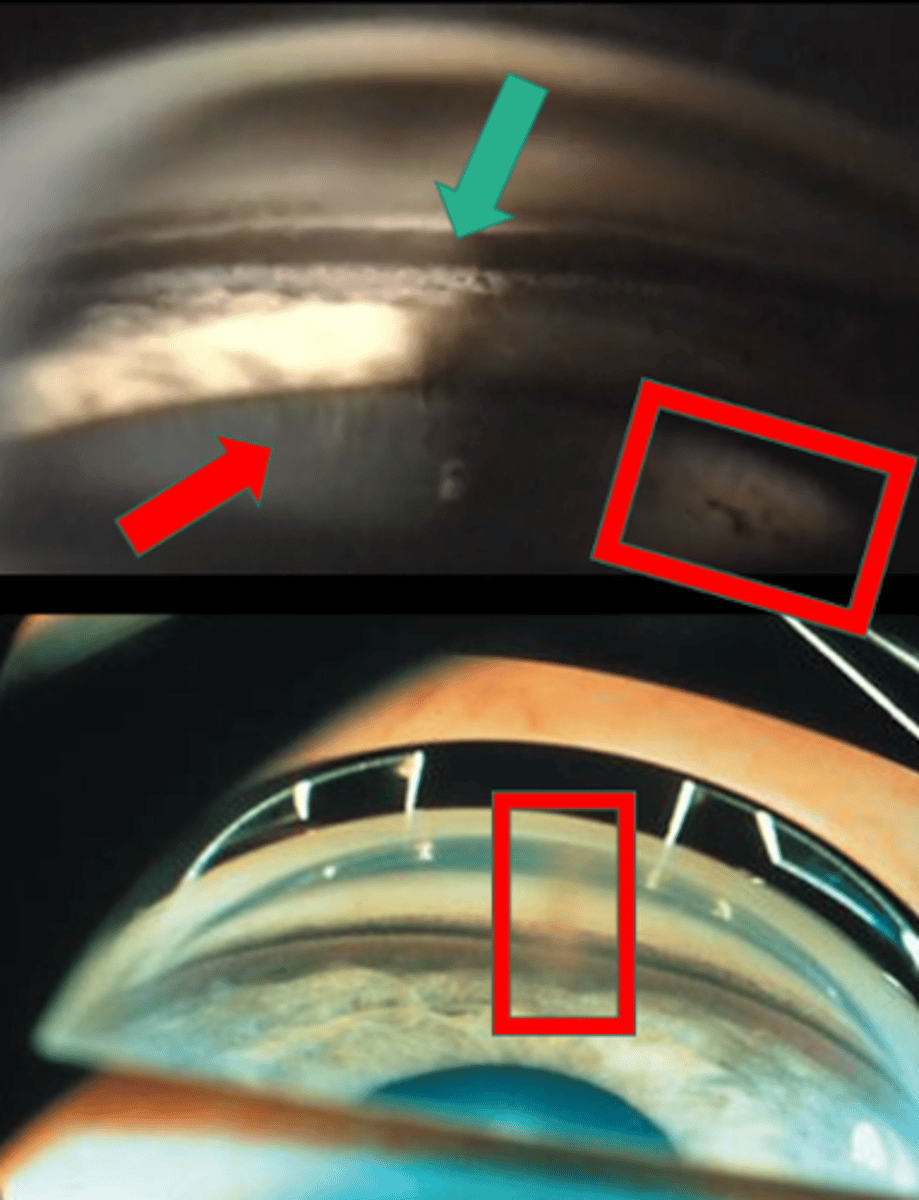
What sign of PDS is indicated by the lower red box?
Krukenberg spindle
Recall: in what 3 conditions can we see Sampaolesi's line?
PXF
PDS
pigment dispersion glaucoma
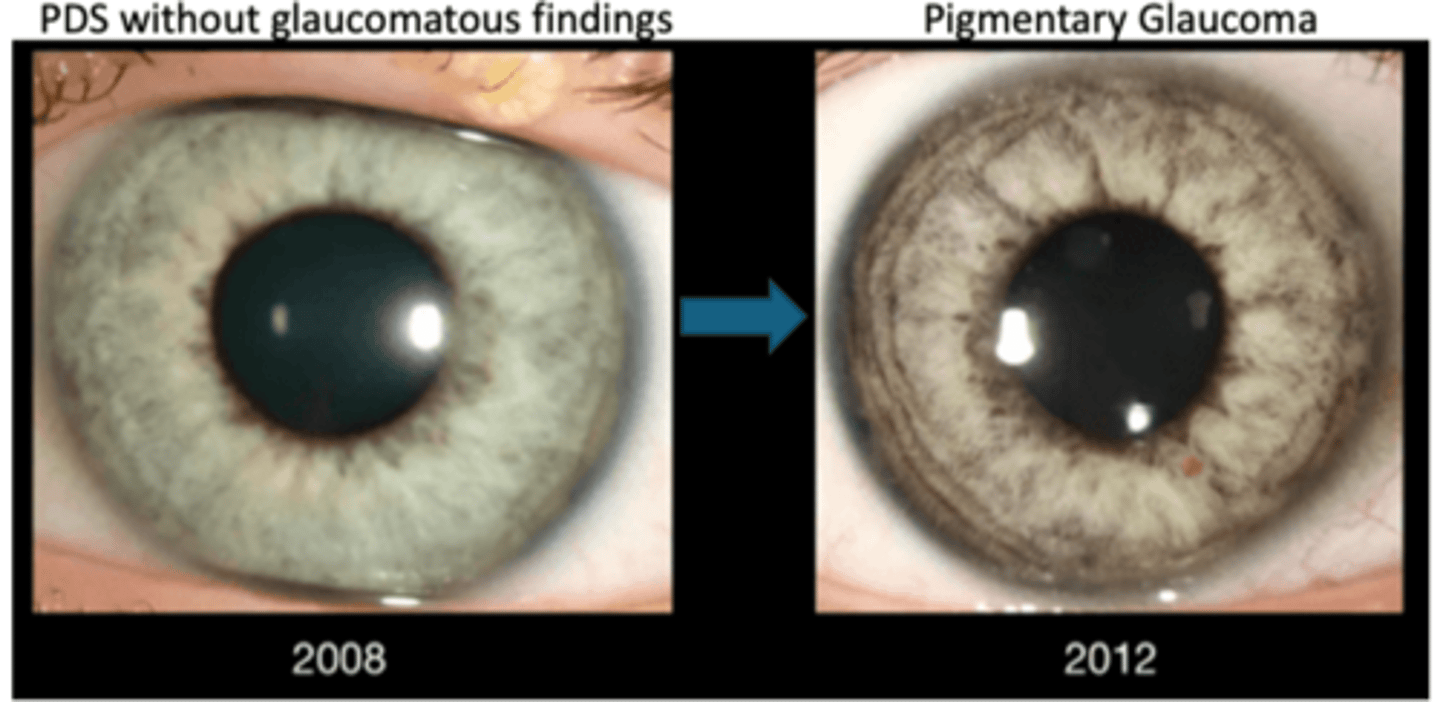
What is the main complication seen in pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
secondary open angle glaucoma / pigmentary glaucoma:
too much TM pigment = TM endothelial cells cannot phagocytize = cells disintegrate = pigment may obstruct TM = aqueous cannot flow out = increased IOP
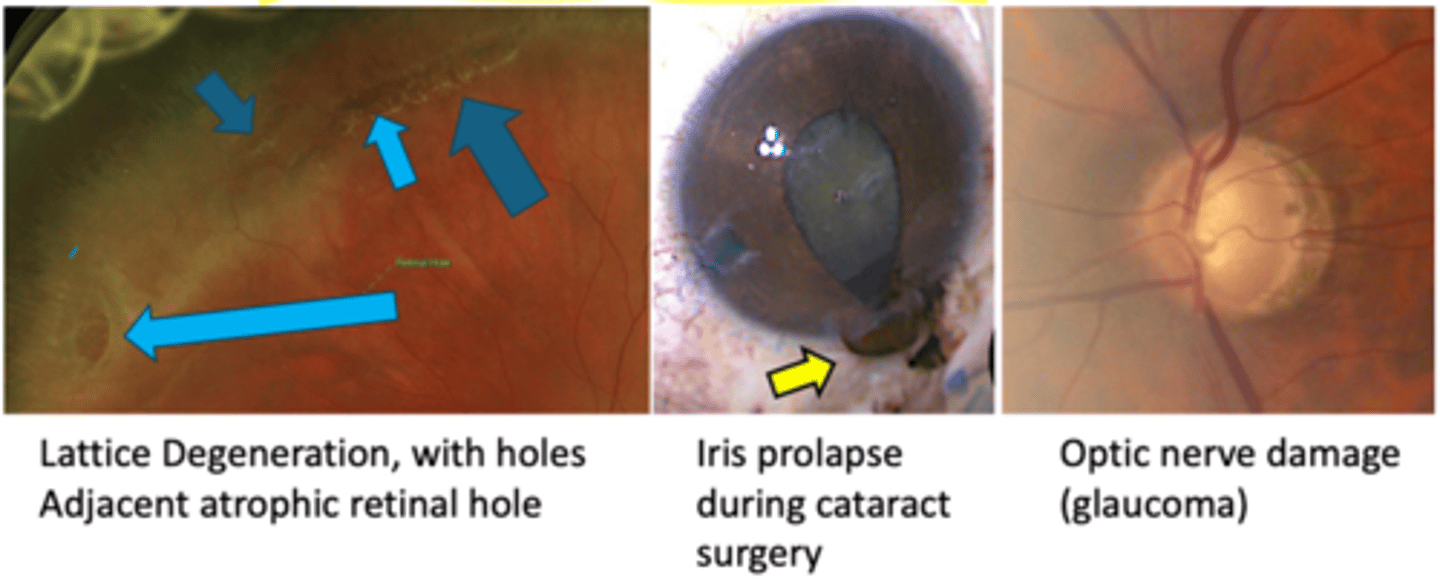
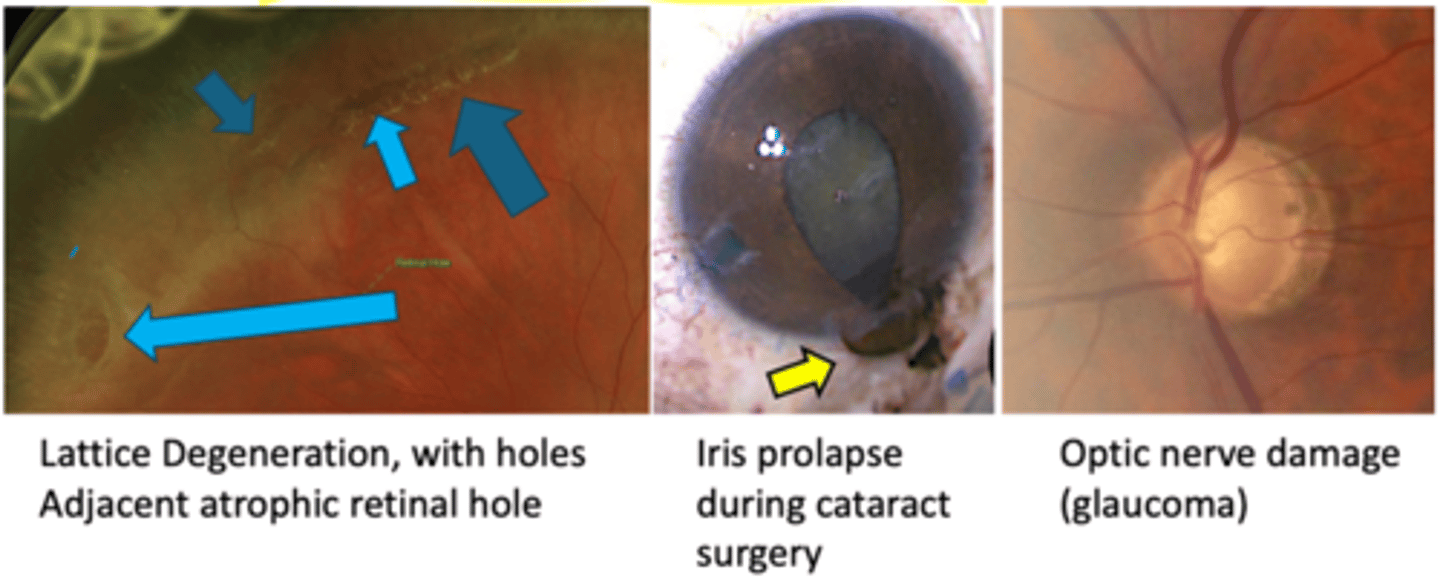
What are 3 other complications of pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
iris cyst formation
lattice degeneration
iris prolapse during CAT Sx
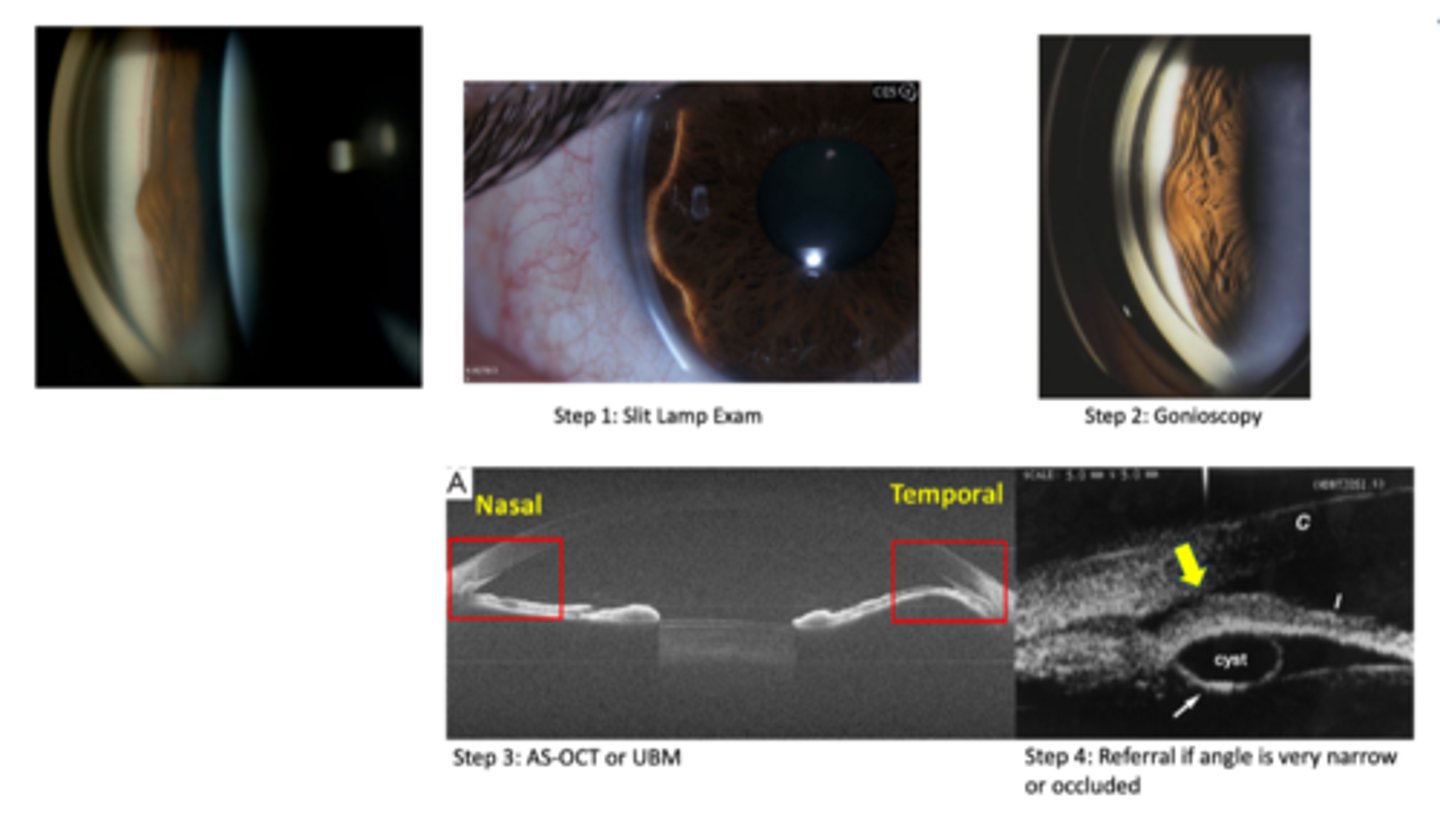
How do we monitor pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
SL exam with retro
check IOP
gonio
A Seg photos
monitor 6-12 mos
How do we tx pigment dispersion syndrome (PDS)?
miotics like pilocarpine help minimize iridozonular contact
LPI surgery = equalize ant and post chamber pressures = iris flattens = minimize iridozonular contact
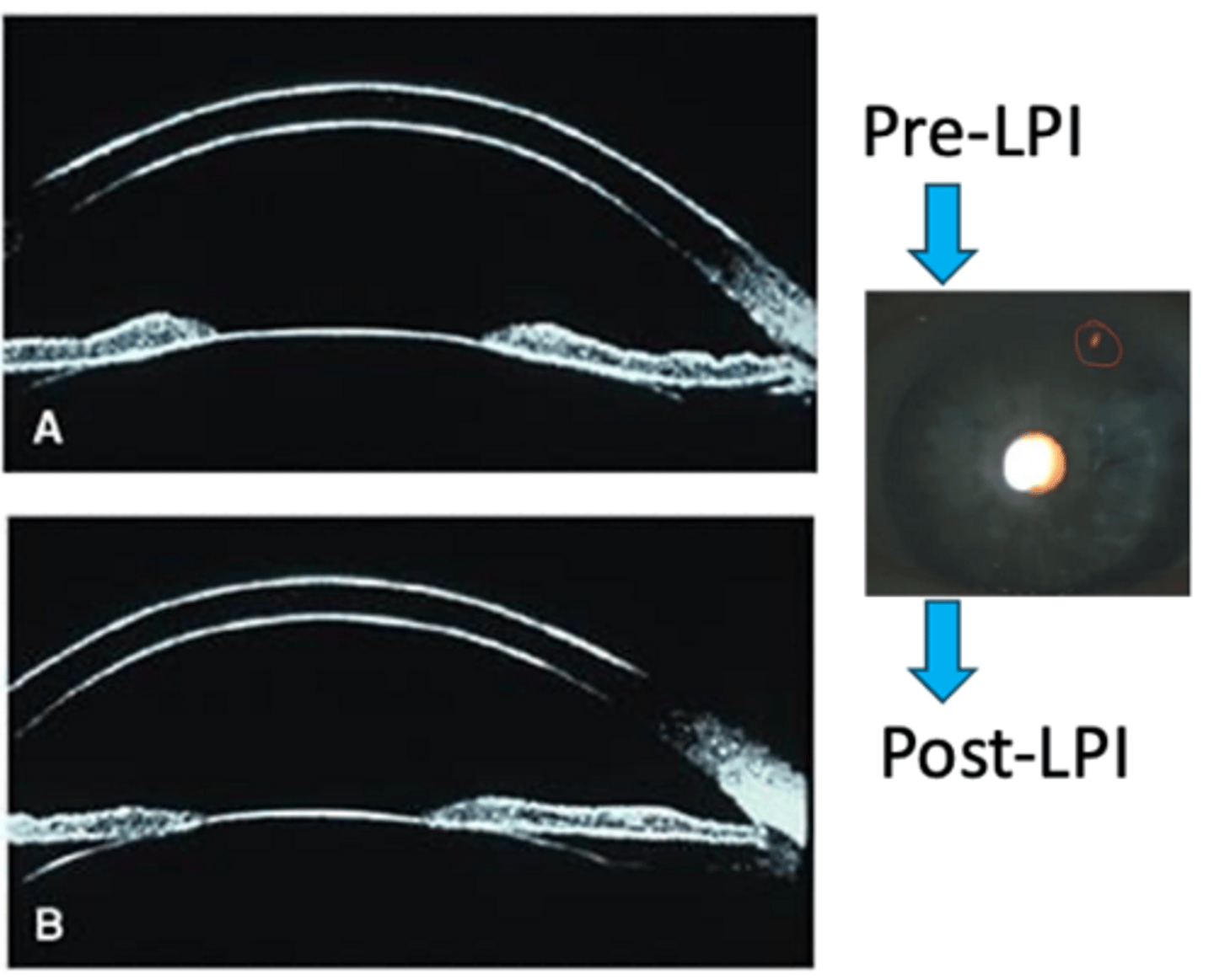
How do we evaluate for pigmentary glaucoma?
DFE
ONH photos
ONH OCT of rNFL
GCC
HVF
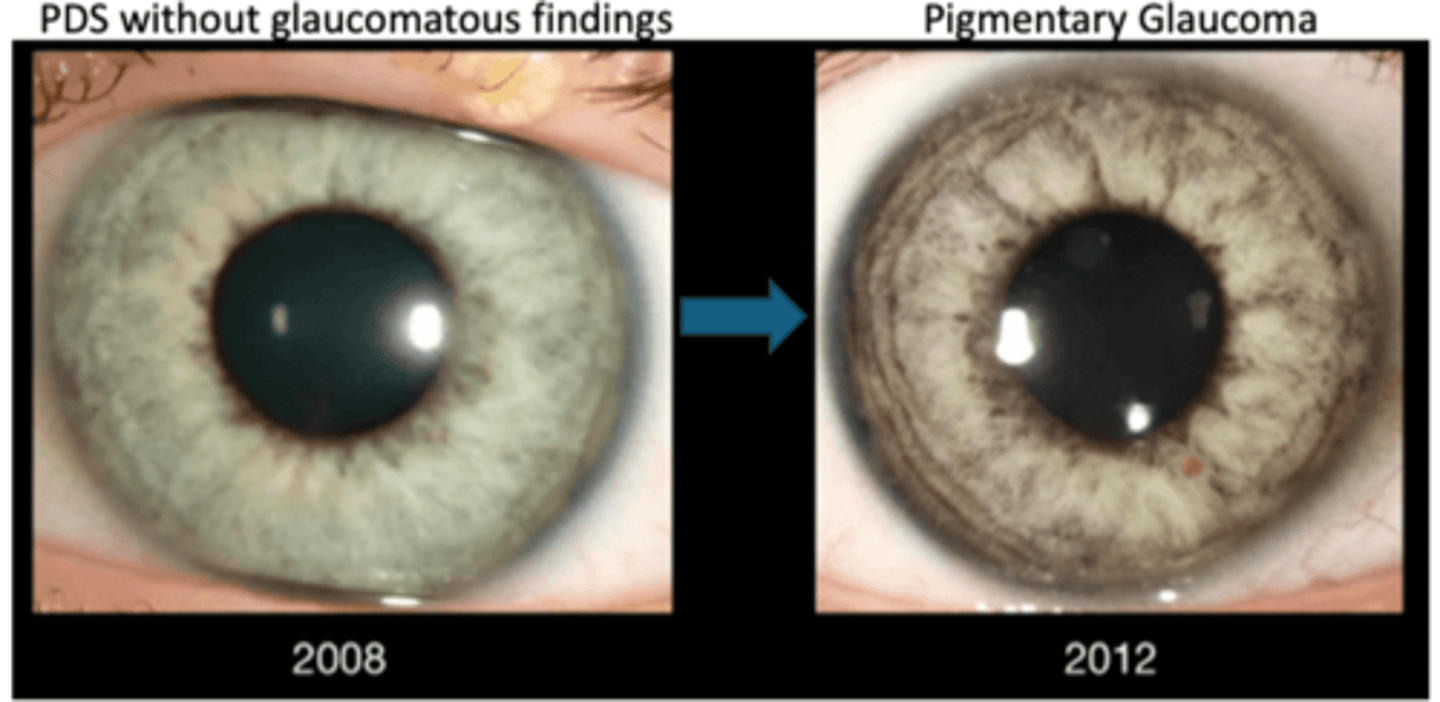
How do we tx pigmentary glaucoma?
similar to POAG...
topical eyedrops to lower IOP like beta blockers, alpha agonists, CAIs to decrease aqueous production
miotics like pilocarpine
SLT
LPI
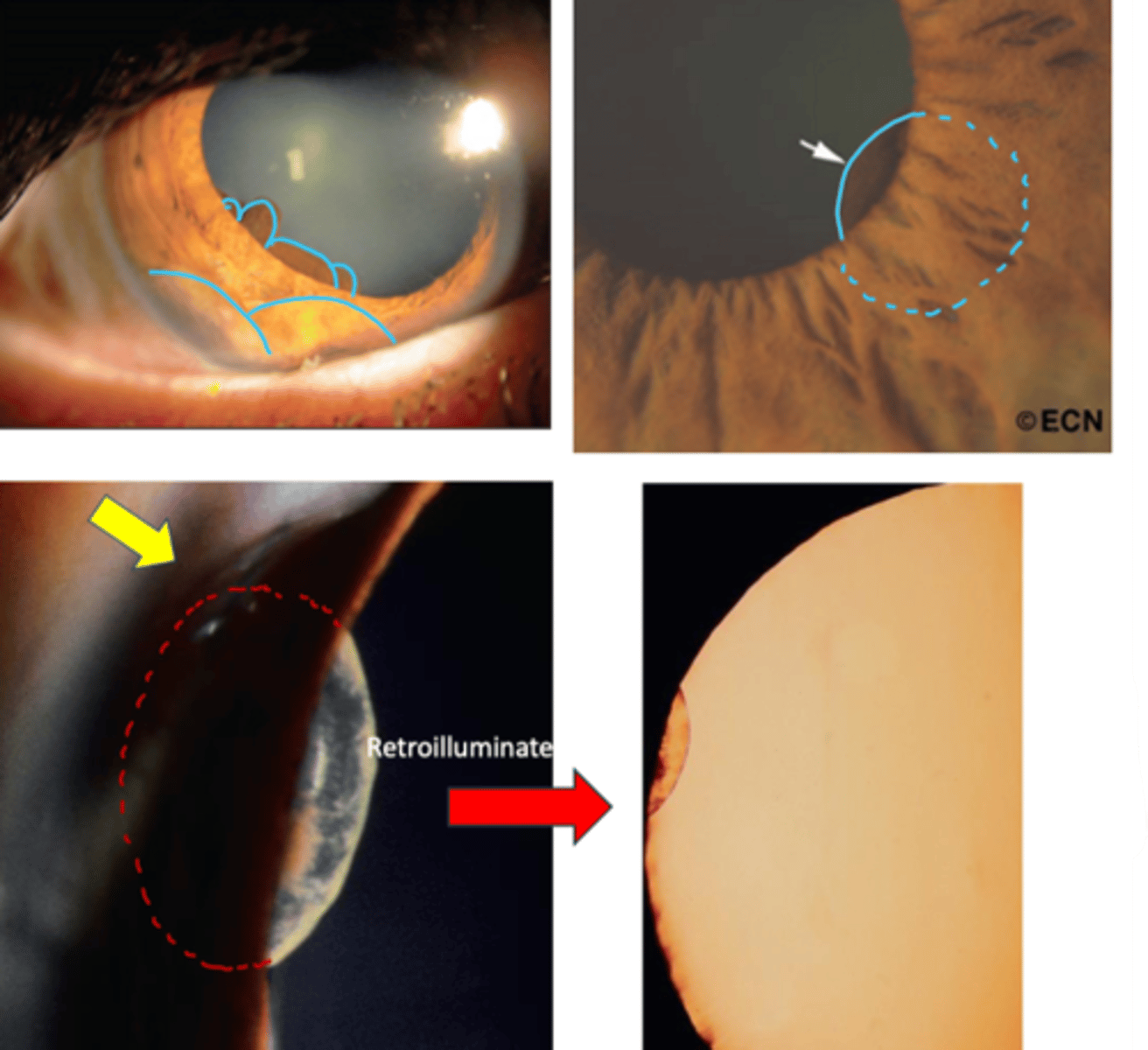
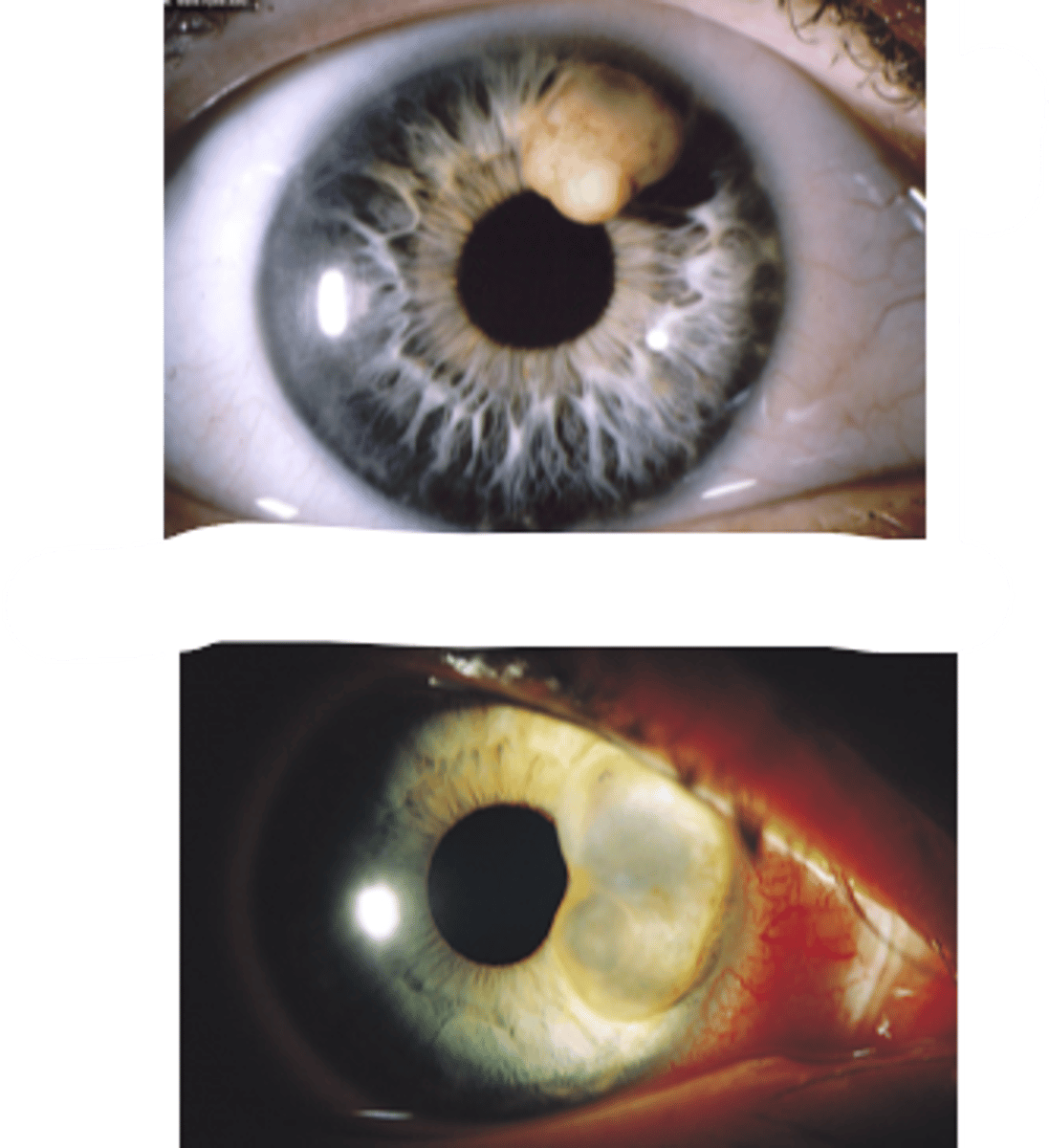
What is an iris cyst?
benign cyst originating from the iris epithelium or stroma
What are some etiologies for iris cyst?
idiopathic = most common
topical PGs or miotics
trauma/surgery
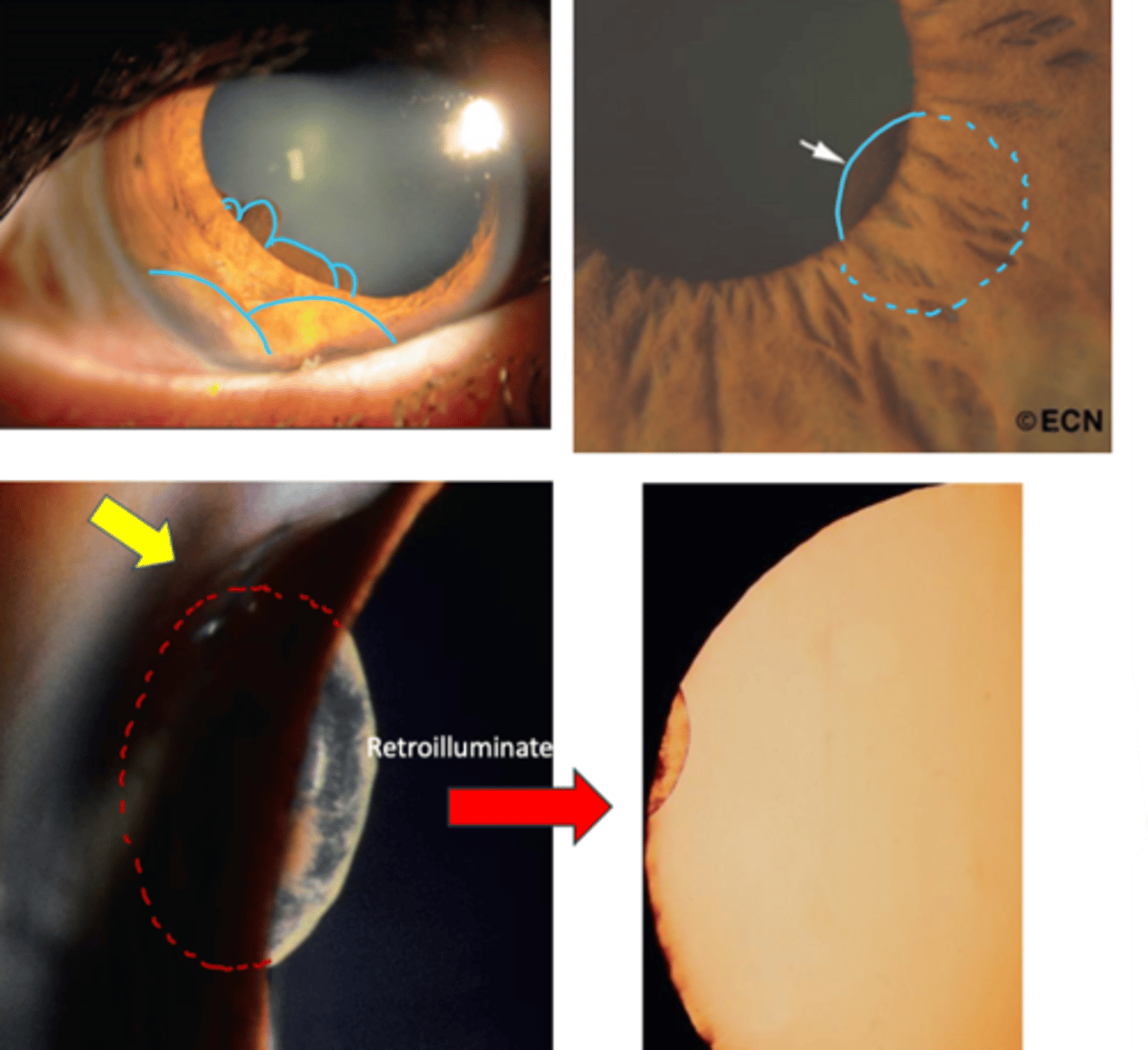
What is the laterality of iris cyst?
unilateral
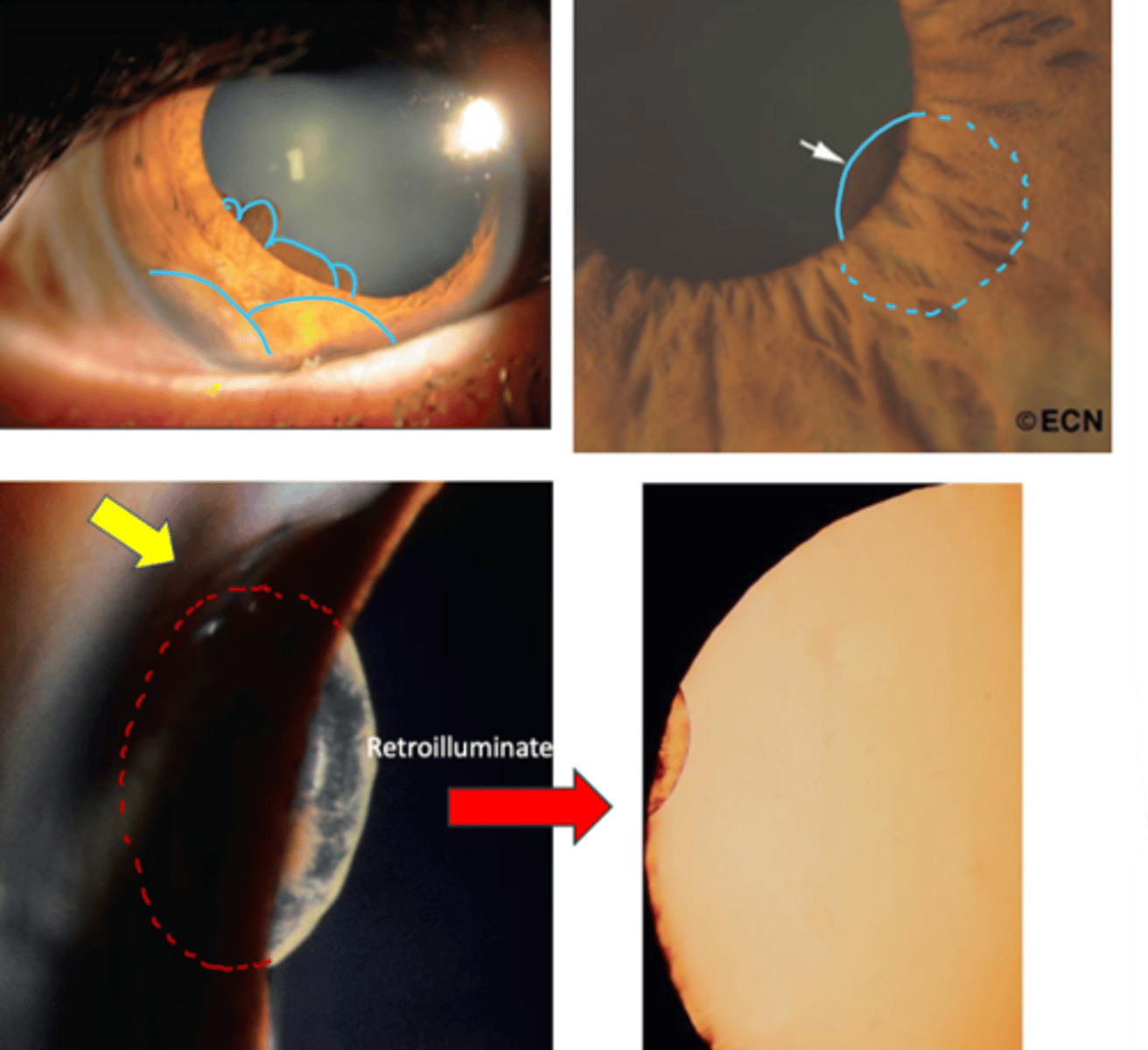
What are the symptoms of iris cyst?
asymptomatic
may be visible if stromal
blurred vision
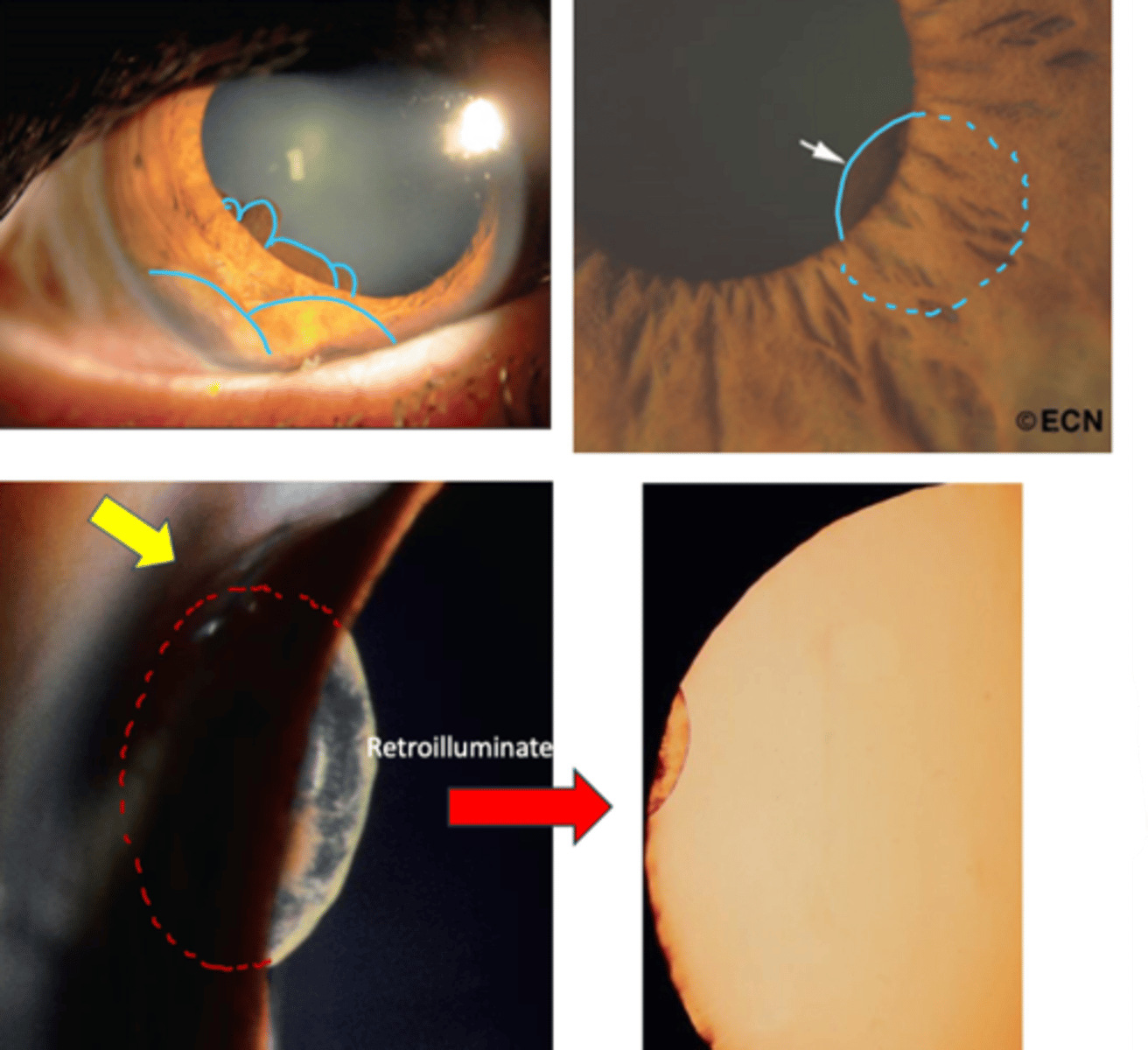
What are the clinical signs of an epithelial iris cyst?
solitary, smooth, dome-shaped elevation of the iris
unable to view cyst unless in the pupil
may extend into the pupil = pupillary distortion and occlusion of the visual axis
darkly pigmented lesion that transilluminates
may detach and float freely in the anterior or vitreous chamber
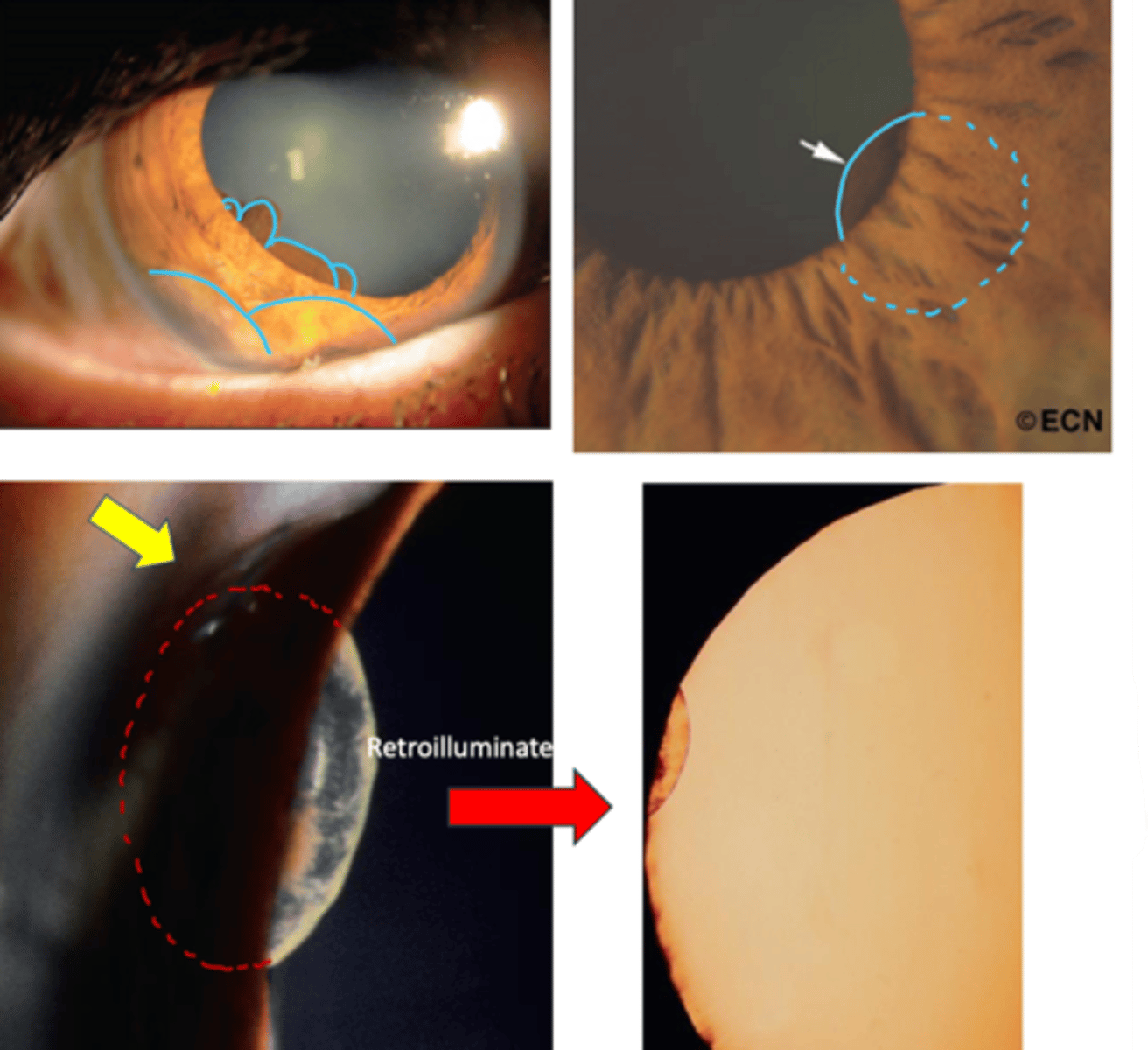
What are the clinical signs of an stromal iris cyst?
solitary, smooth, translucent lesion on the surface of the iris
transilluminates
may extend into the pupil = pupillary distortion and occlusion of the visual axis
may detach and float freely in the anterior chamber
What is the main complication of iris cyst?
secondary glaucoma if large cyst blocks the TM
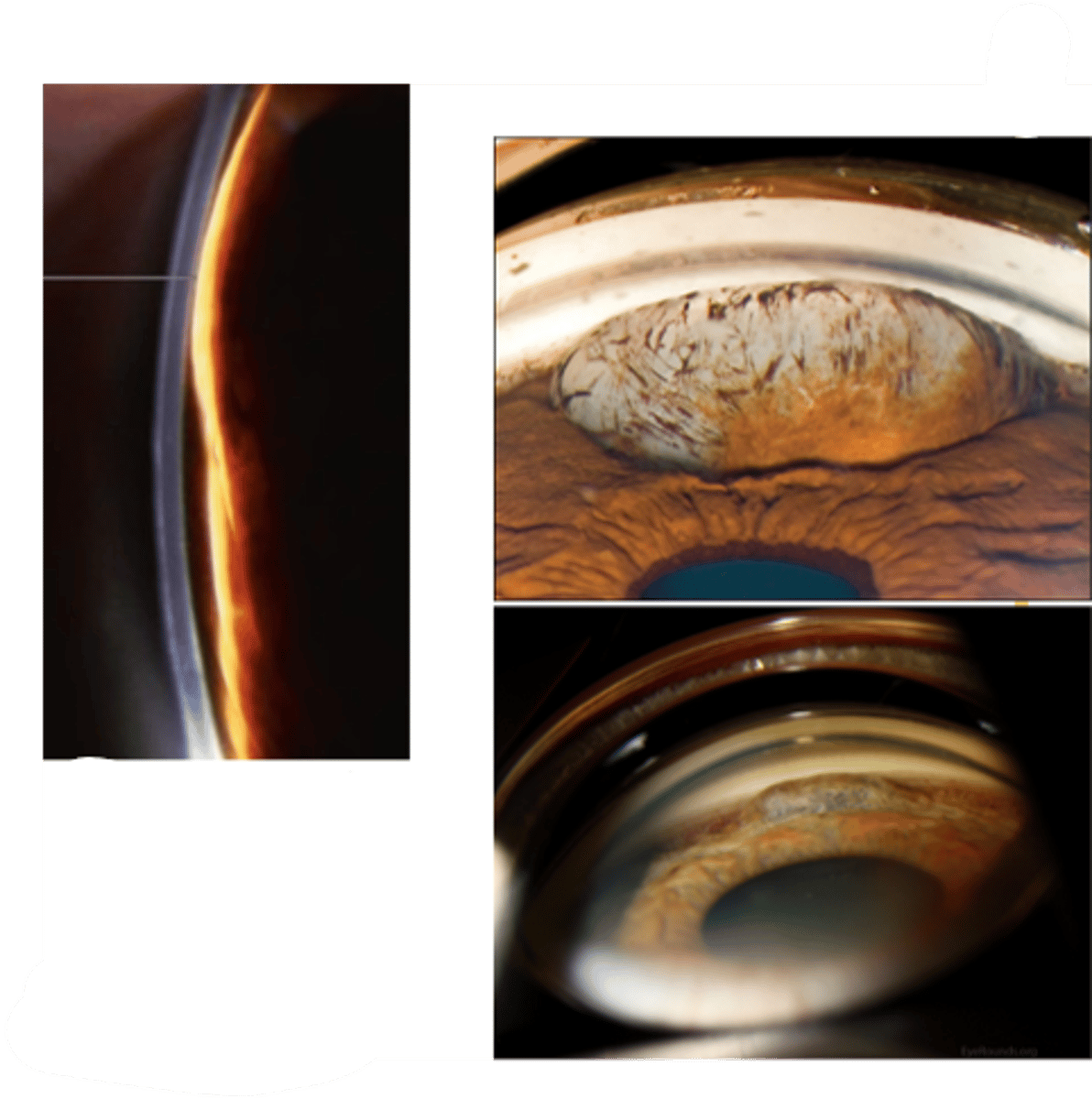
What is the management for iris cyst?
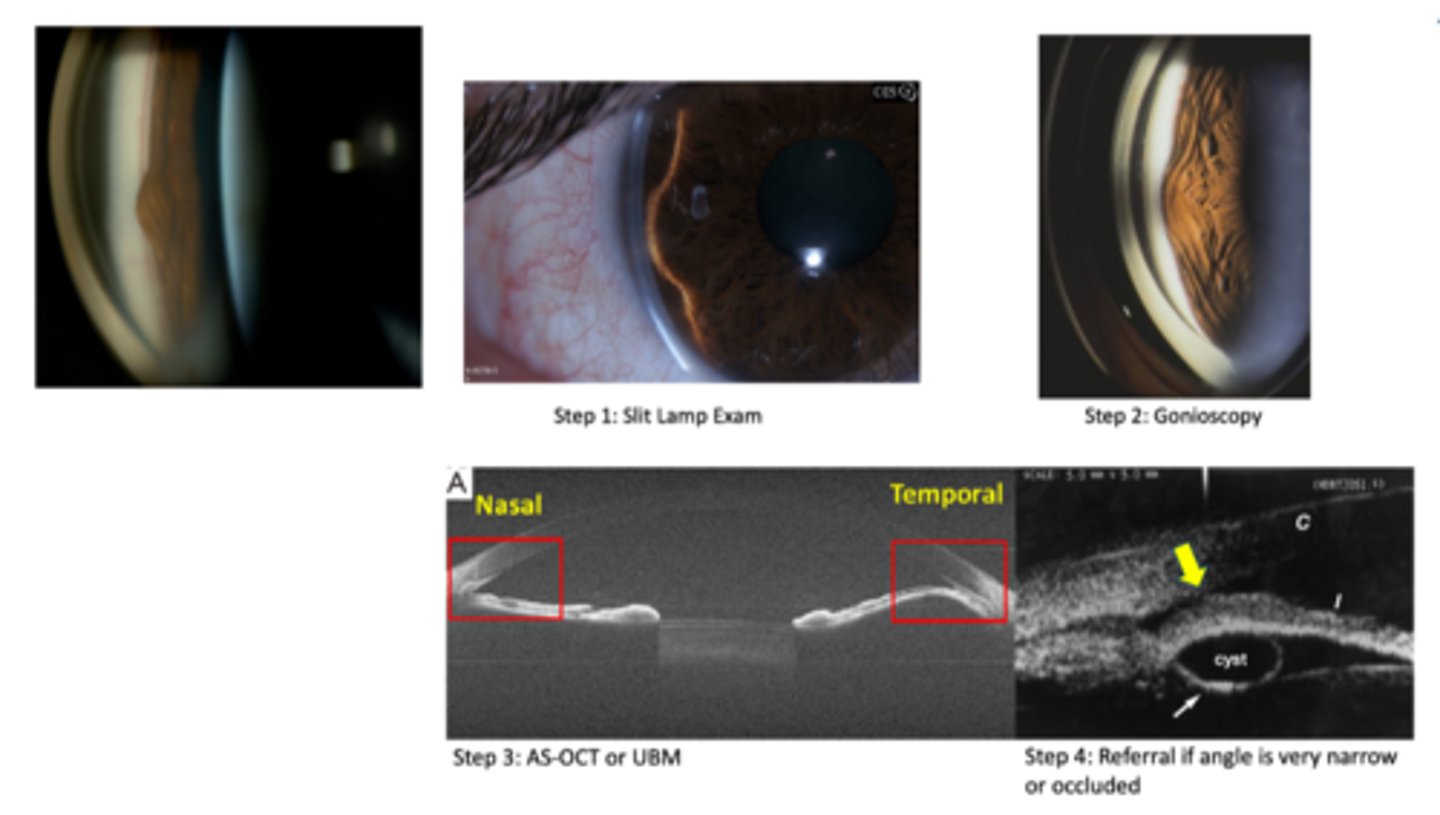
monitor annually if asymptomatic = SLE, A Seg photos, gonio, OCT, UBM
refer out if affecting vision or blocking TM
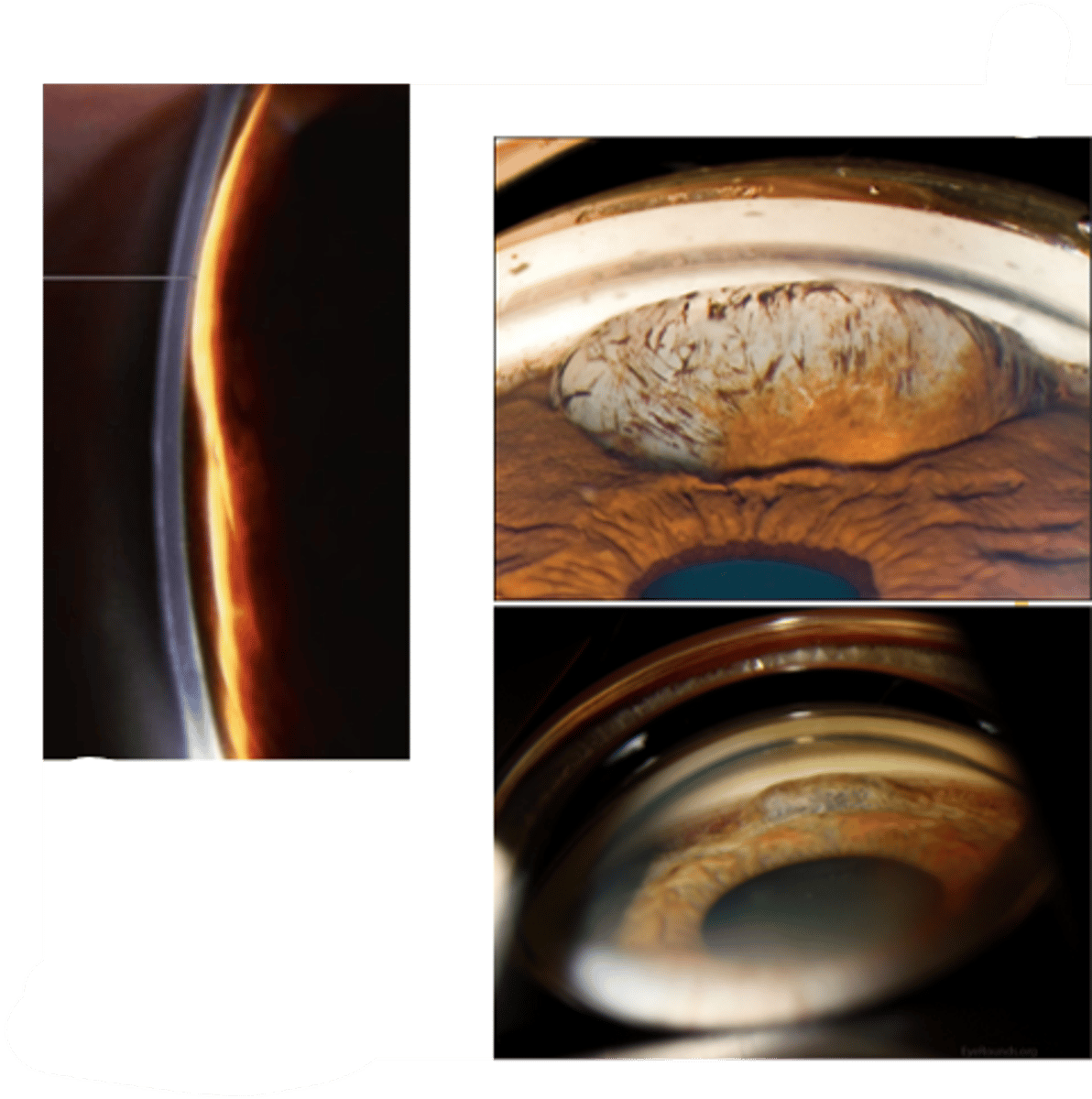
What 3 tests can differentiate between iris cyst, nevus, and malignant melanoma?
gonio
A Seg OCT
UBM
Are epithelial or stromal iris cysts more common?
epithelial cysts
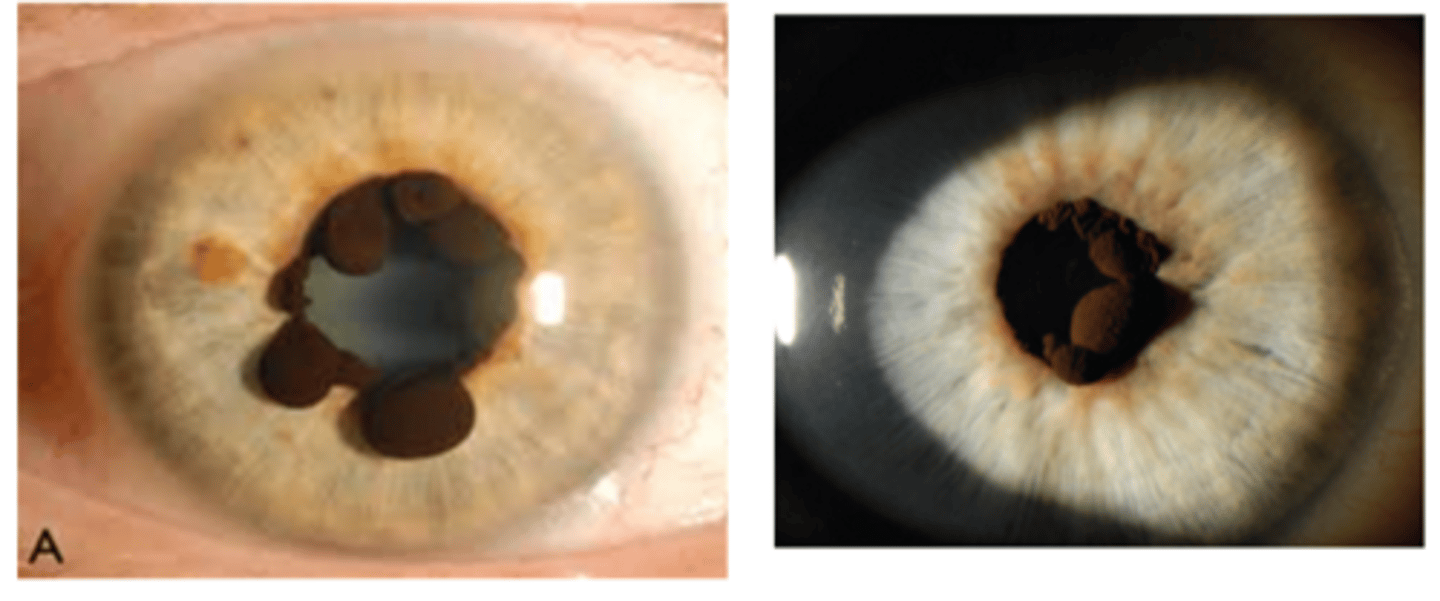
What do we call a congenital epithelial iris cyst?
iris floccule = more often bilateral, multiple at pupil margin
What is an iris ephelis (freckle)?
benign excess melanin pigmentation in iris stroma
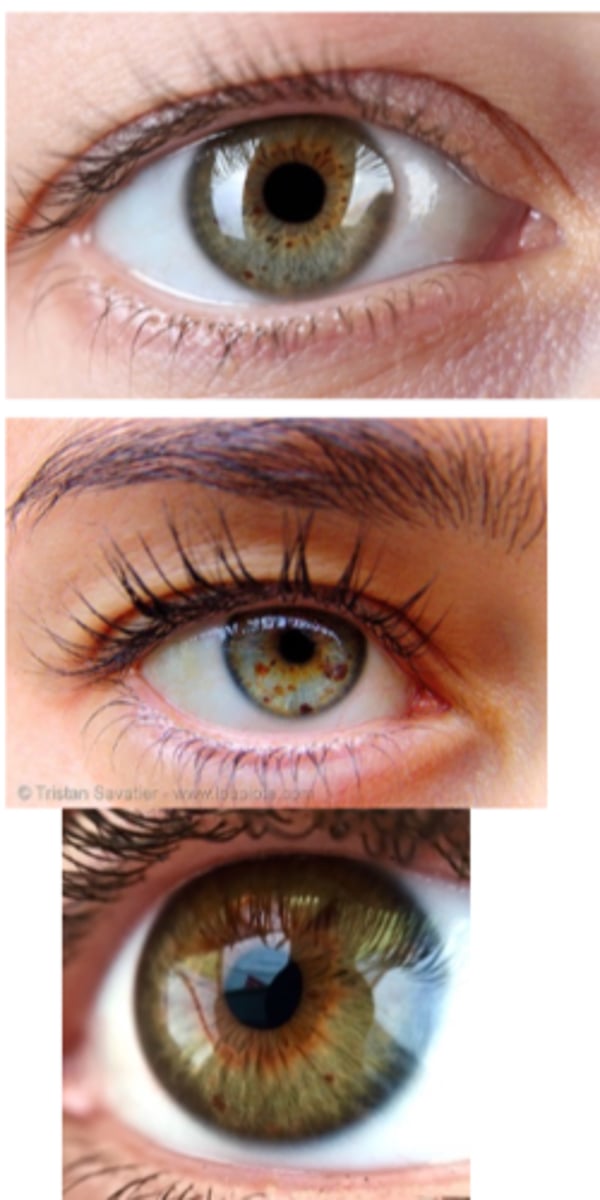
What is the etiology of an iris ephelis (freckle)?
excess melanin
chronic UV exposure
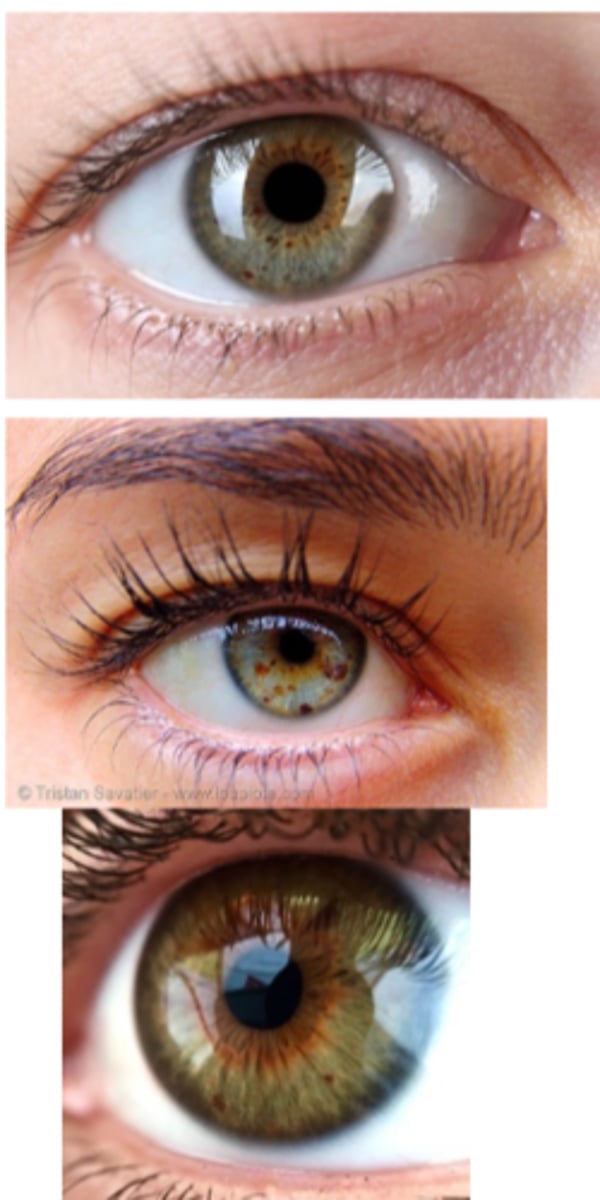
What are the demographics of an iris ephelis (freckle)?
more common in light-coloured irises
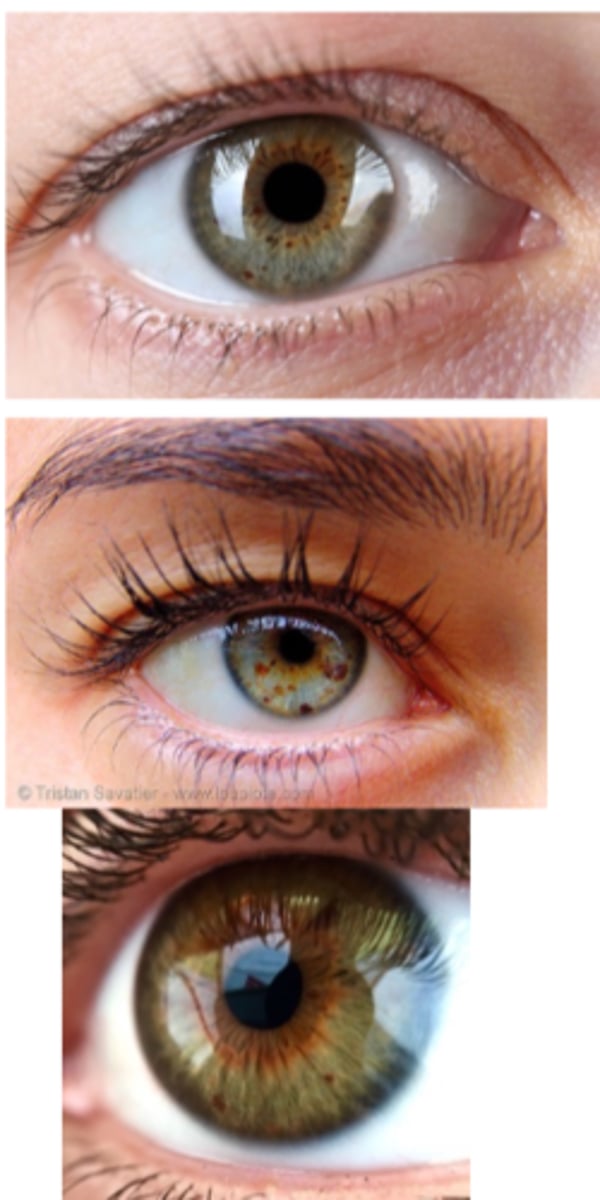
What is the laterality of an iris ephelis (freckle)?
unilateral or bilateral
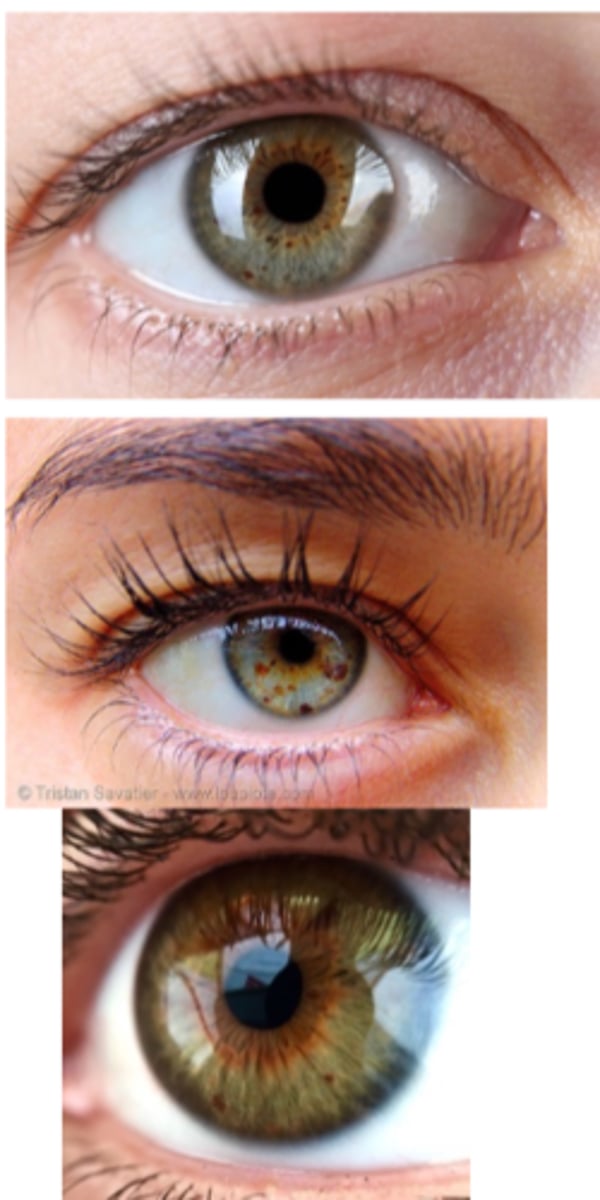
What are the S/S of an iris ephelis (freckle)?
asymptomatic
visible discoloration of the iris
tan to brown, flat circumscribed pigmentation on the anterior iris surface
may occur in one or multiple areas
typically inferior and small size
**normal iris architecture
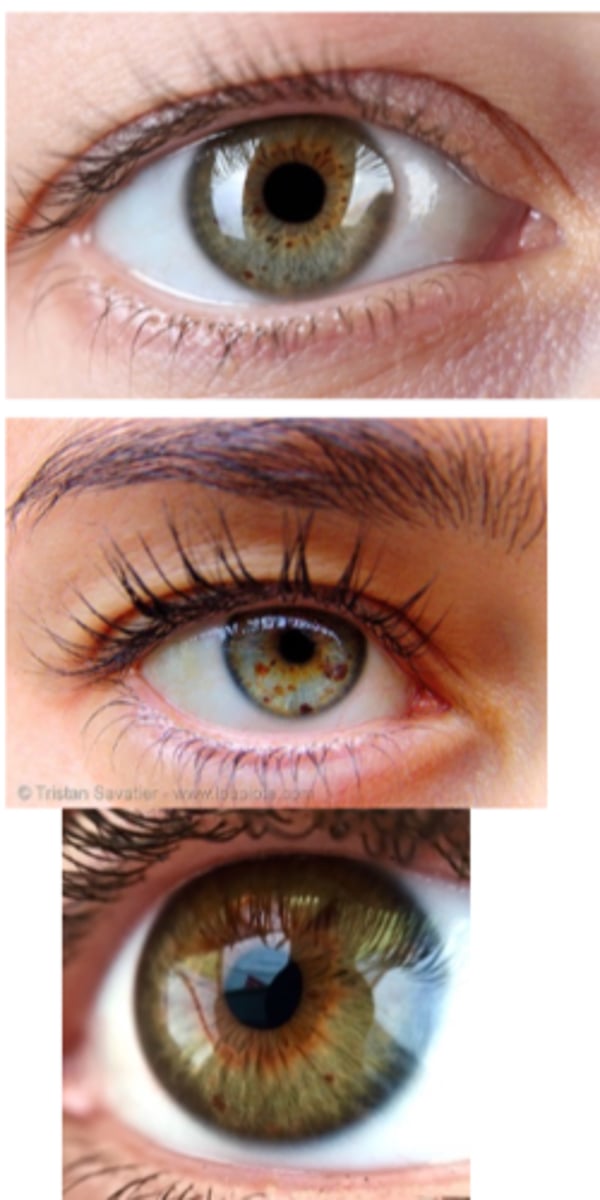
What is the management for an iris ephelis (freckle)?
monitor with routine exam
consider baseline A Seg photos
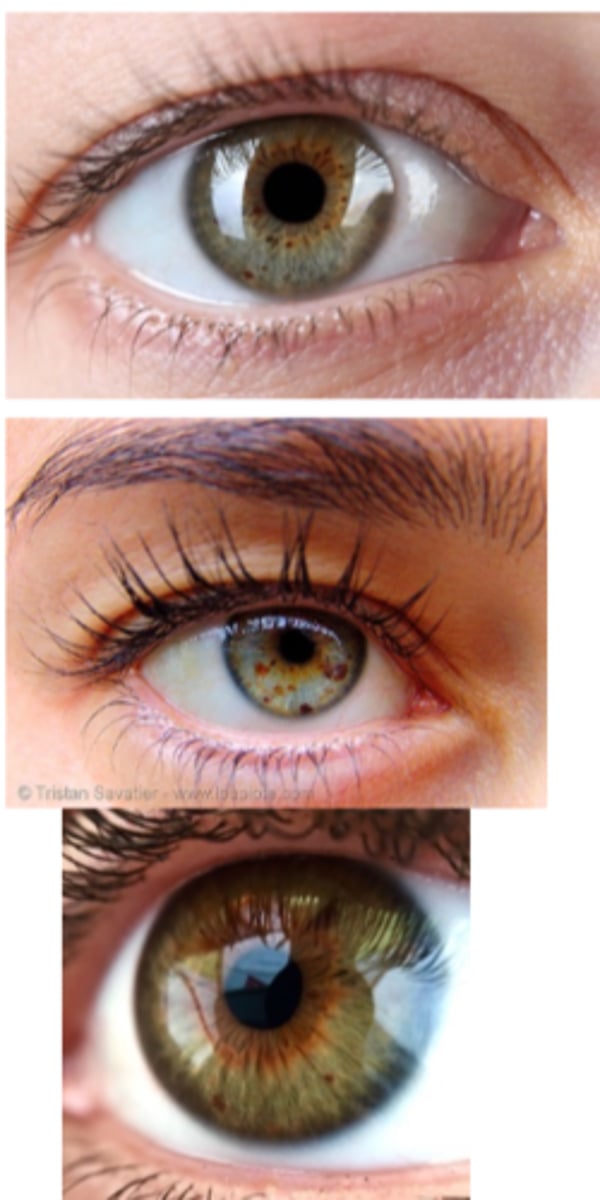
How common is an iris ephelis (freckle)?
60% of people
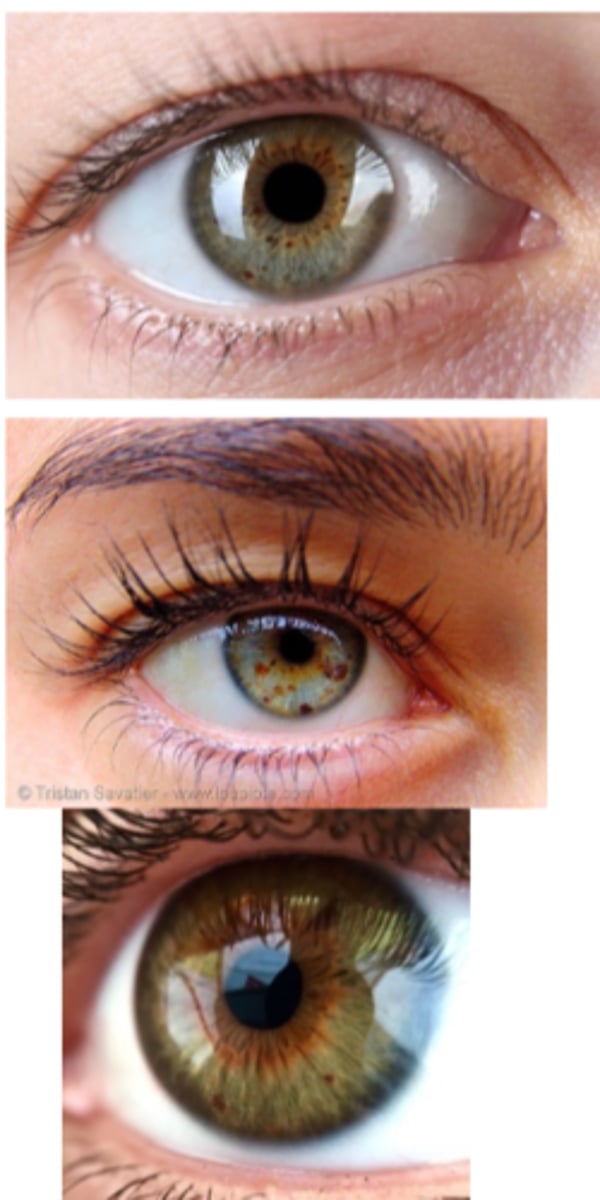
What is an iris nevus?
benign tumor of the iris stroma
What is the etiology of an iris nevus?
proliferation of melanocytes
chronic UV exposure
What is the demographics of an iris nevus?
often appear during puberty
more common in light-coloured irises
What is the laterality of an iris nevus?
unilateral or bilateral
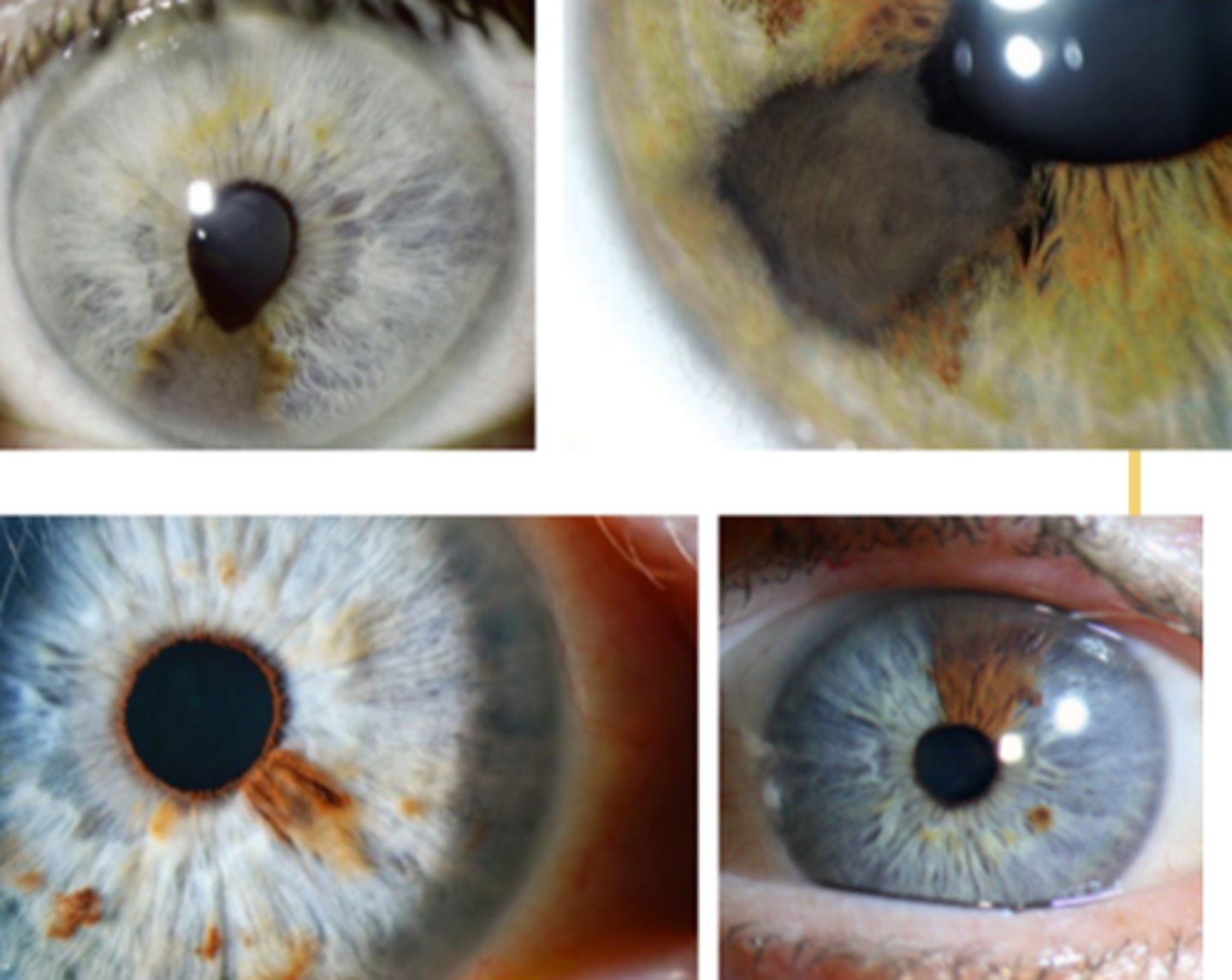
What are the S/S of an iris nevus?
asymptomatic
visible discoloration of the iris
tan to brown, flat or slightly elevated, circumscribed lesion in the iris stroma
may be amelanotic
one or multiple lesions may be present
typically inferior, <3 mm in diameter, and <1 mm thick
+/- pupillary peaking
+/- ectropion uveae
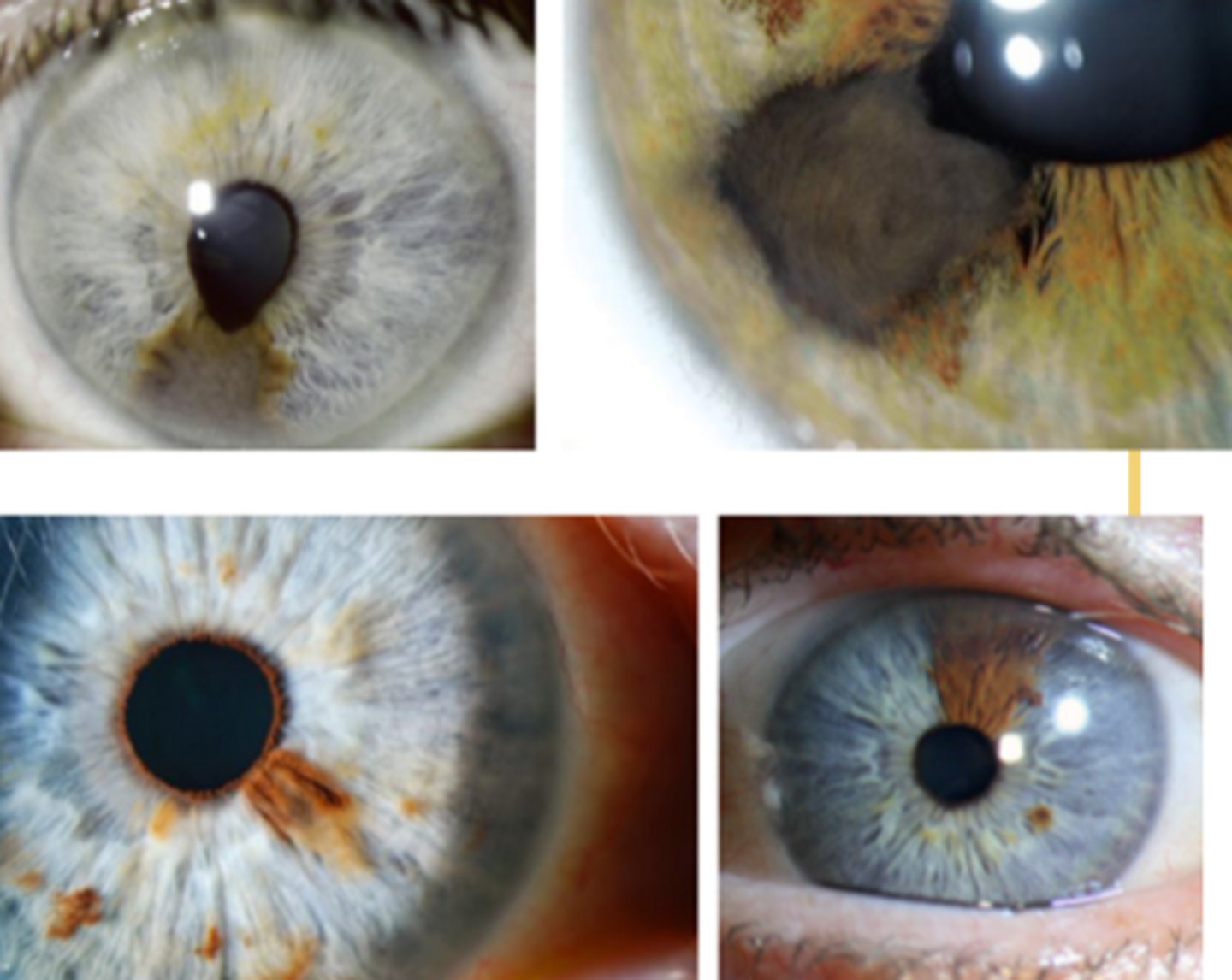
What is the main complication of an iris nevus?
malignant potential = indicated by documented growth
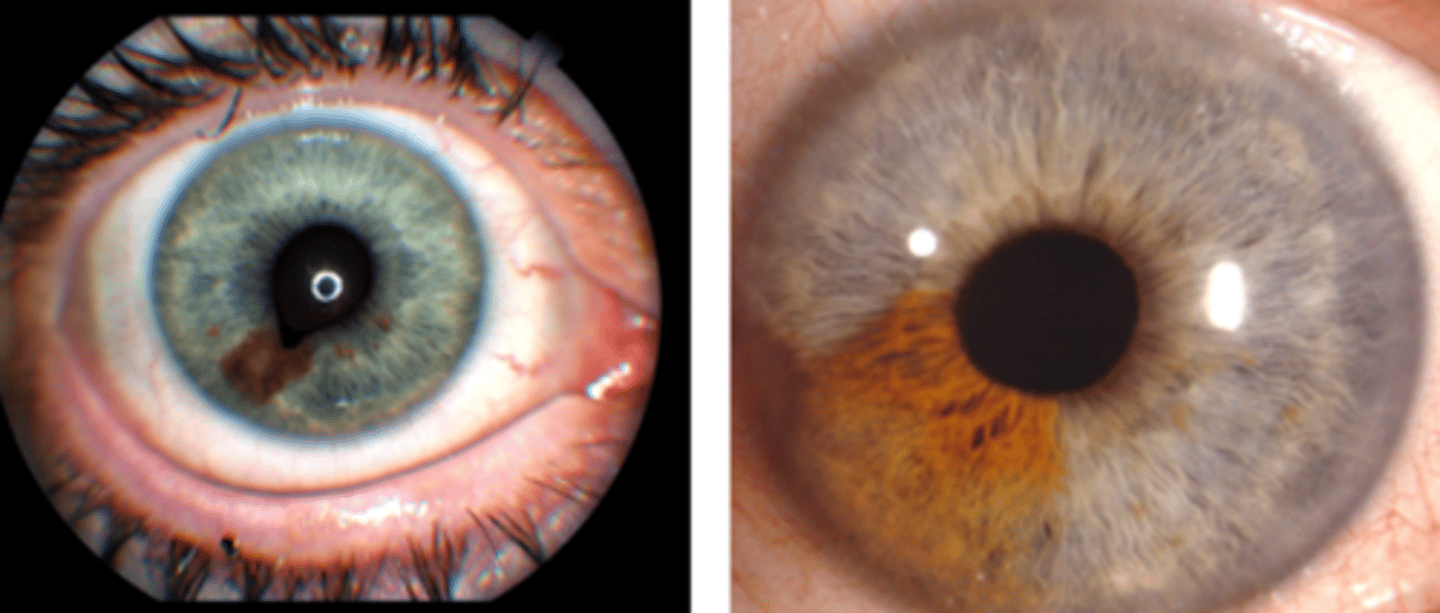
What is the management for an iris nevus?
monitor annually for growth into melanoma = SLE, A Seg photos, gonio, OCT, UBM
refer out if changes, iris/pupil deformity
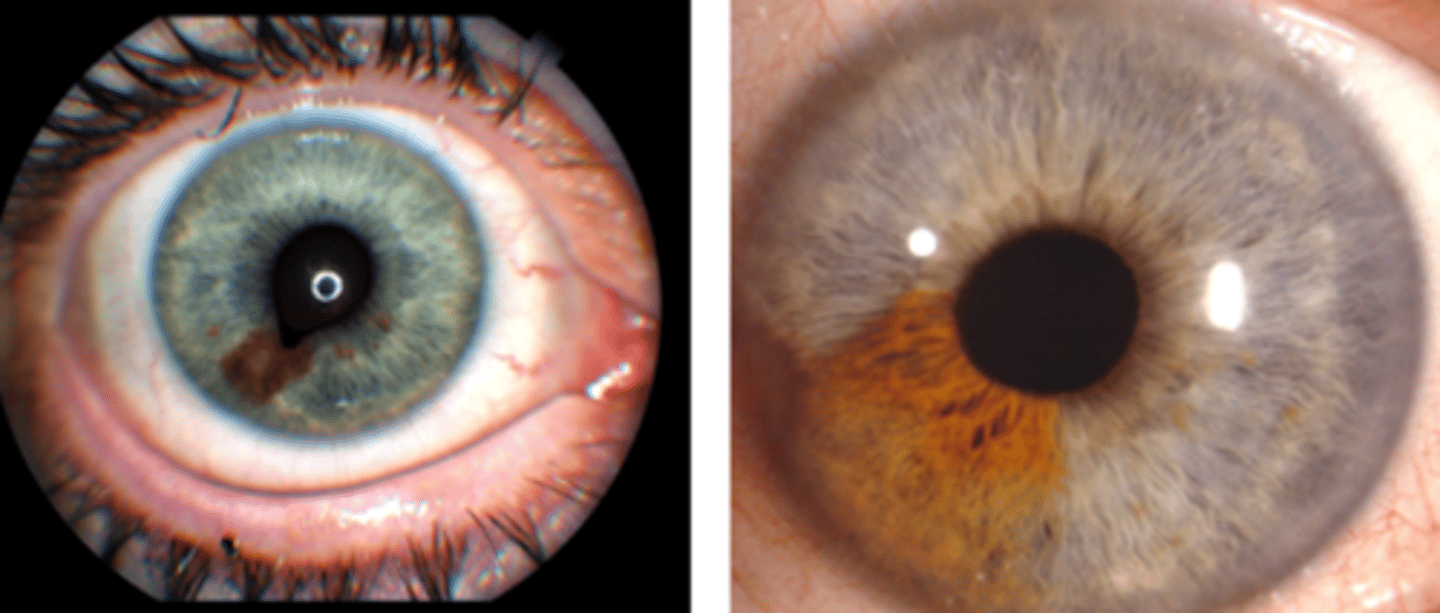
How does an iris nevus differ from an iris freckle?
larger and deeper than iris freckles
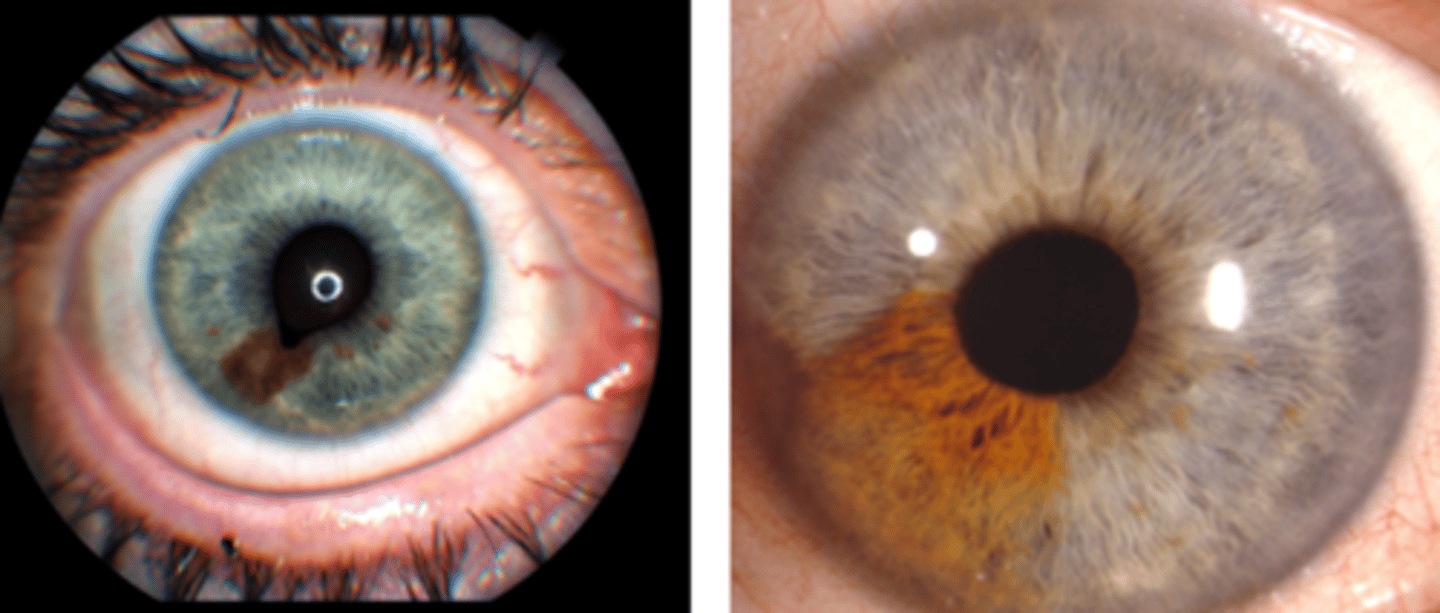
What is the ABCDEF rule for monitoring iris nevus growth into melanoma?
A = age (young)
B = blood (hyphema, feeder)
C = clock hour (inferior)
D = diffuse configuration
E = ectropion (of iris or uvea)
F = feathery margin
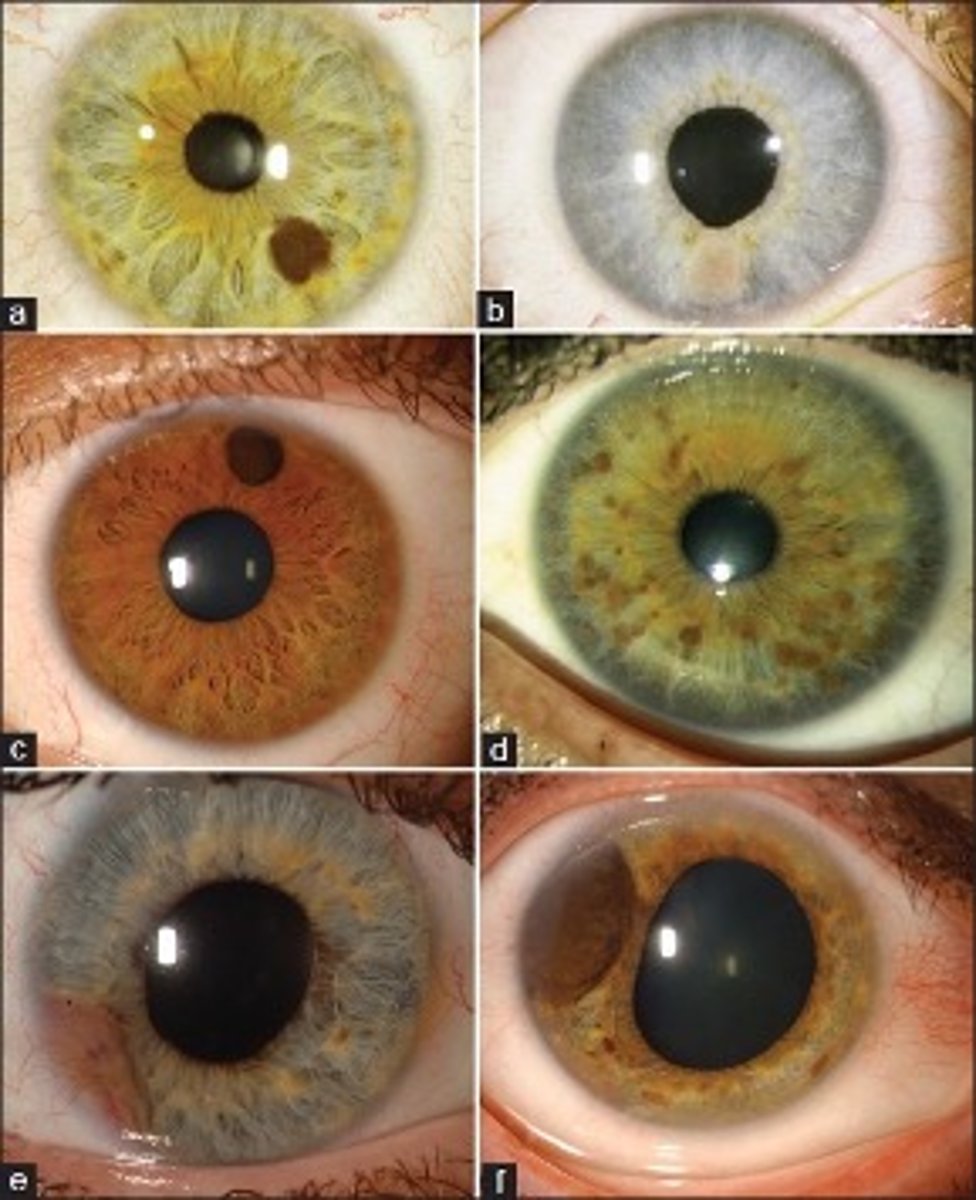
What is a diffuse iris nevus, one uncommon variant of iris nevi?
flat with distinct margins, often in congenital ocular melanocytosis
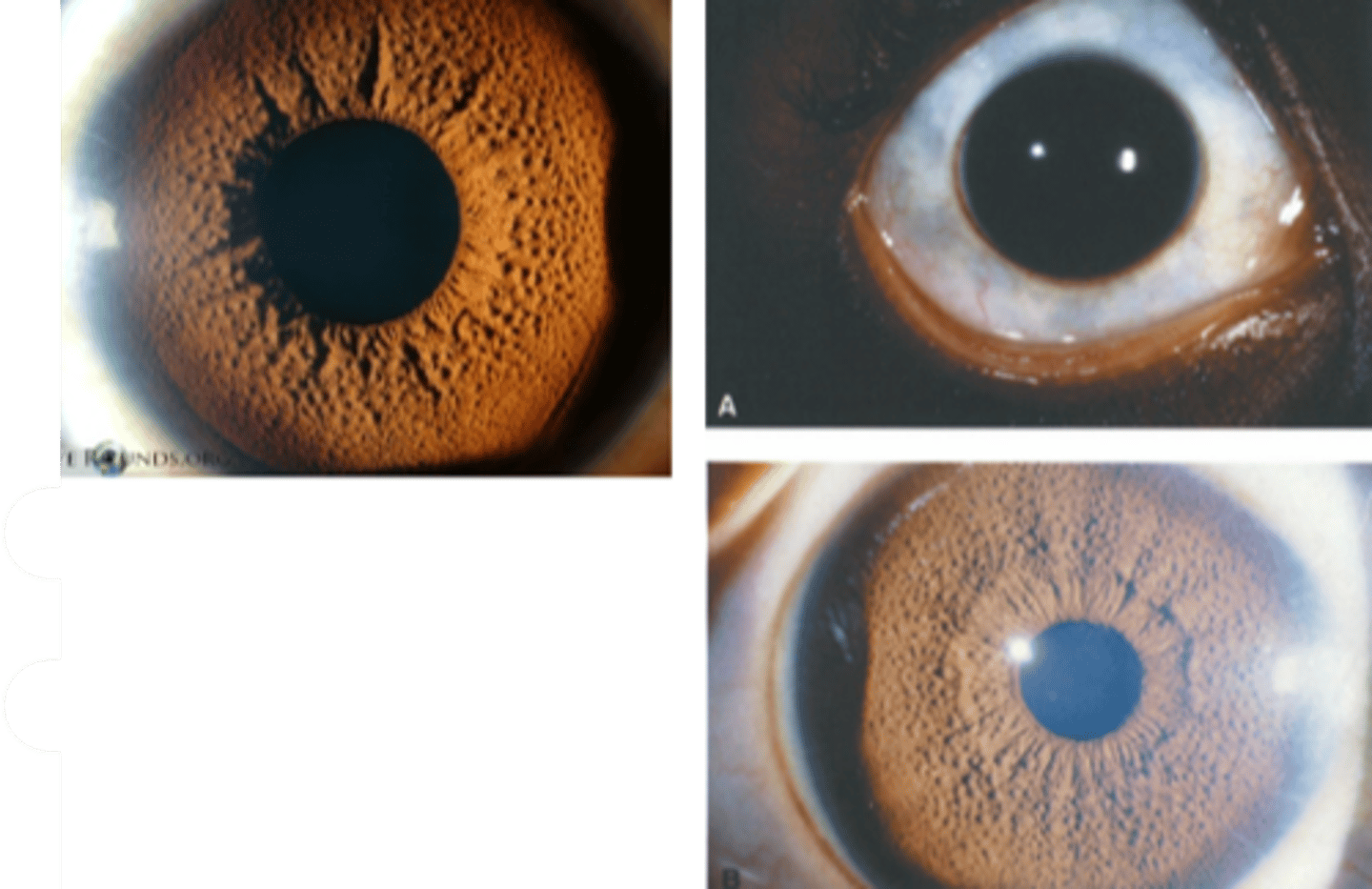
What are the iris findings seen in ocular melanocytosis?
iris mammillations: distinct villiform protruberances covering the iris
blue nevus
diffuse iris nevus
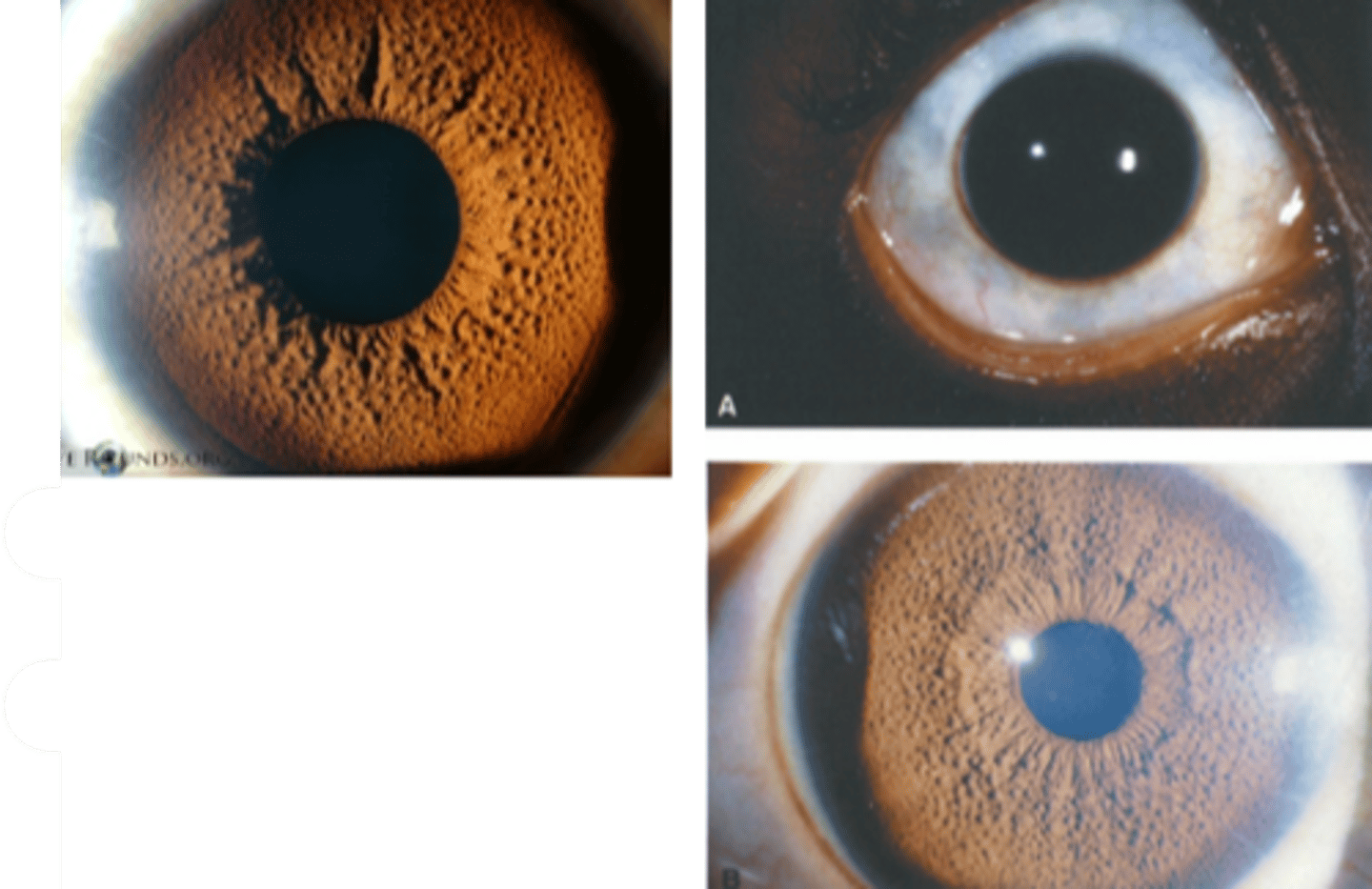
What are some complications of ocular melanocytosis?
choroidal melanoma
glaucoma
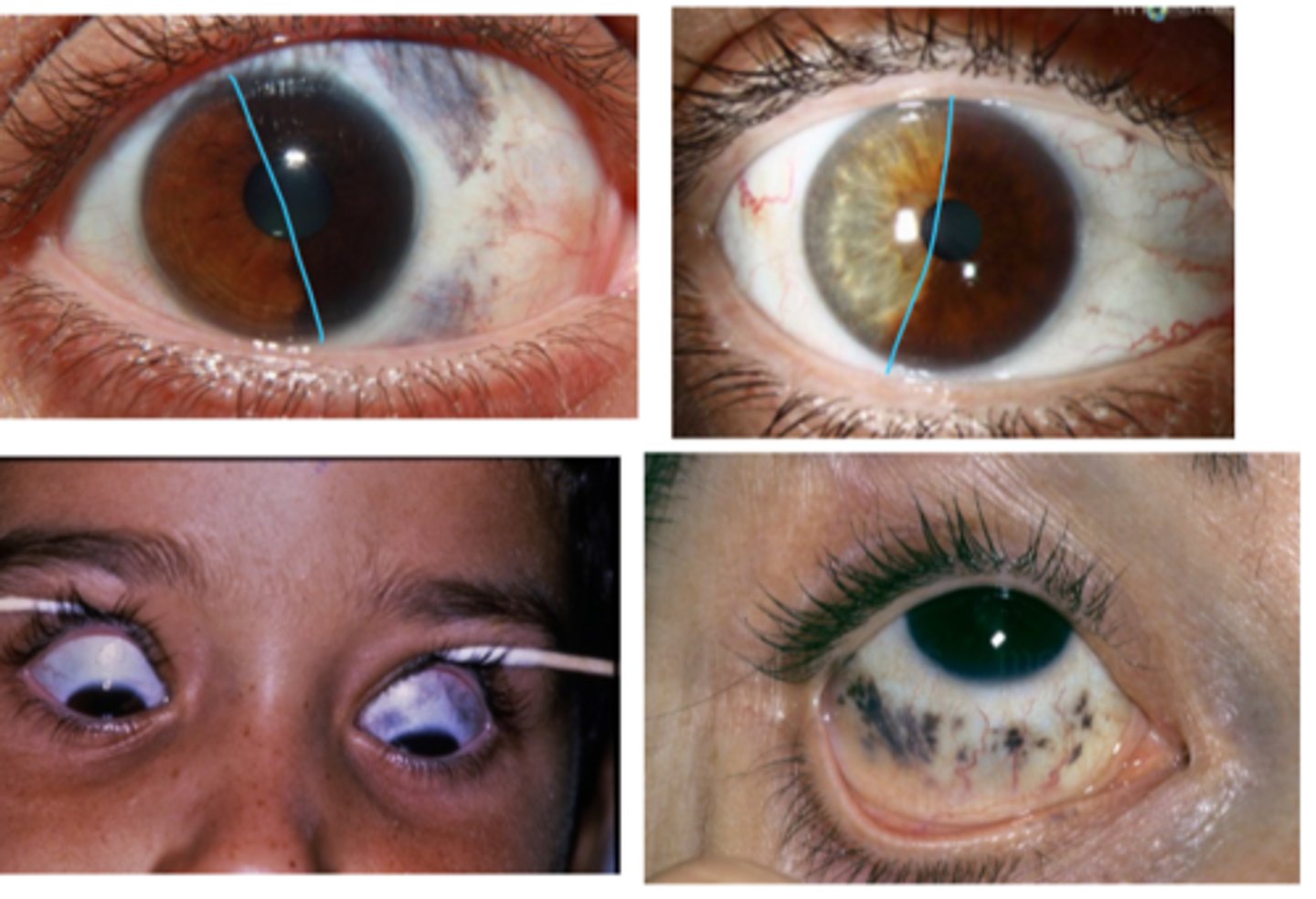
What is a Lisch nodule, one uncommon variant of iris nevi?
small bilateral iris nevi in pt's with neurofibromatosis-1 (NF1)
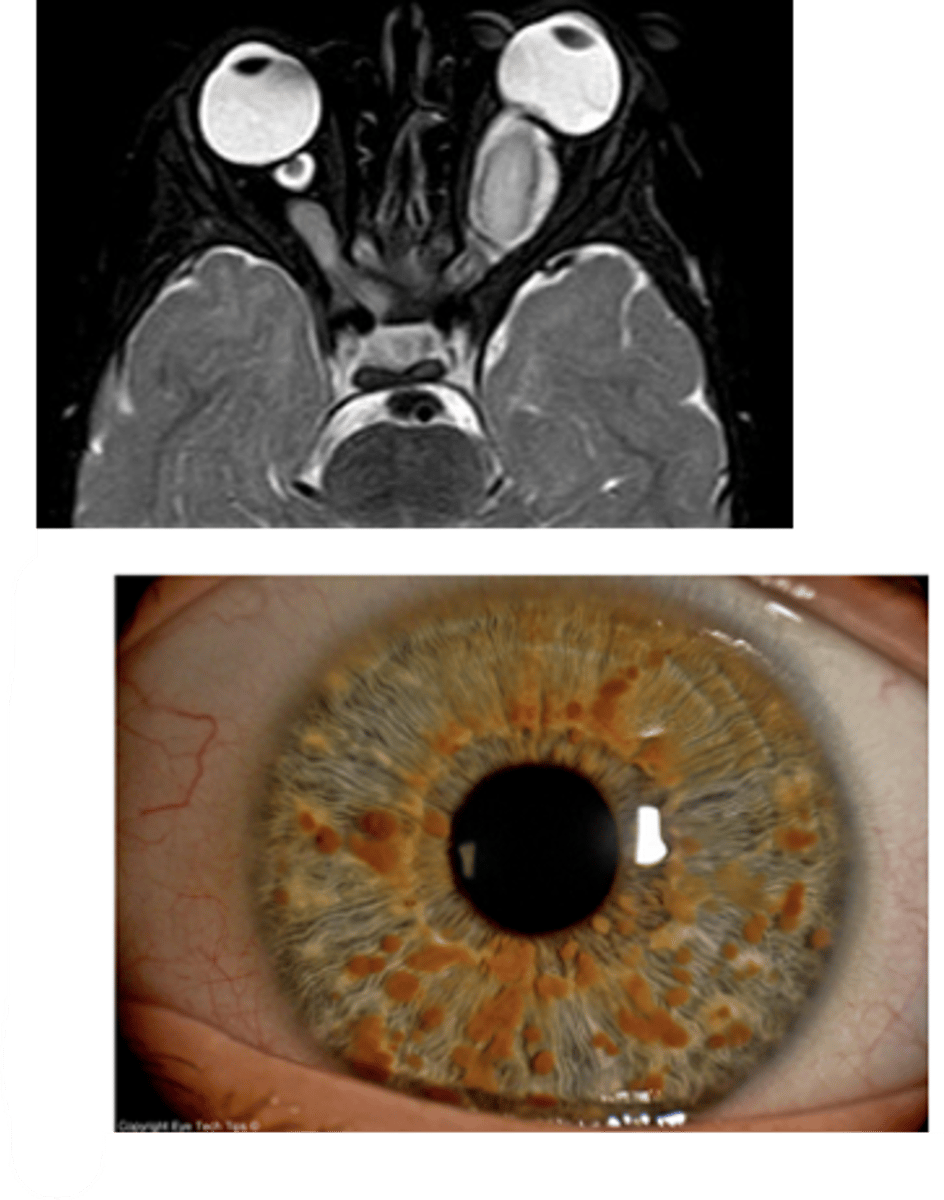
What is another ocular findings seen in NF-1?
ON glioma = may cause proptosis
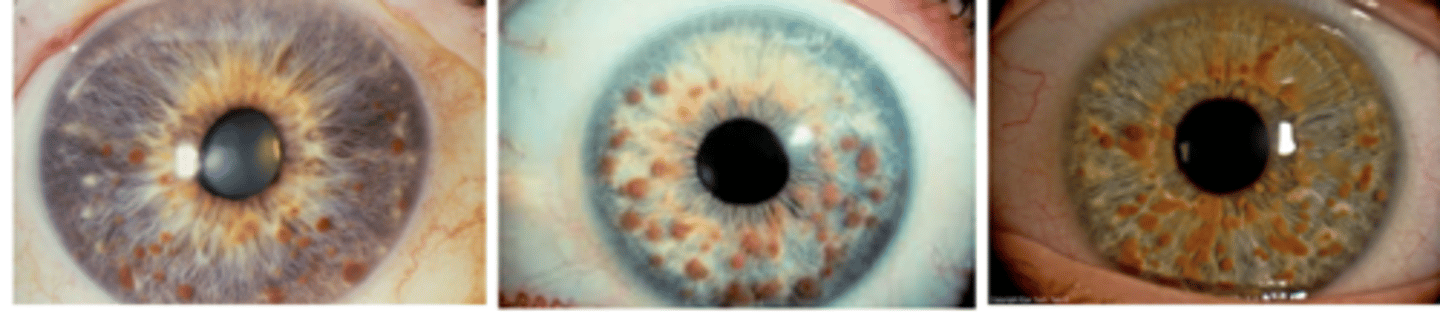
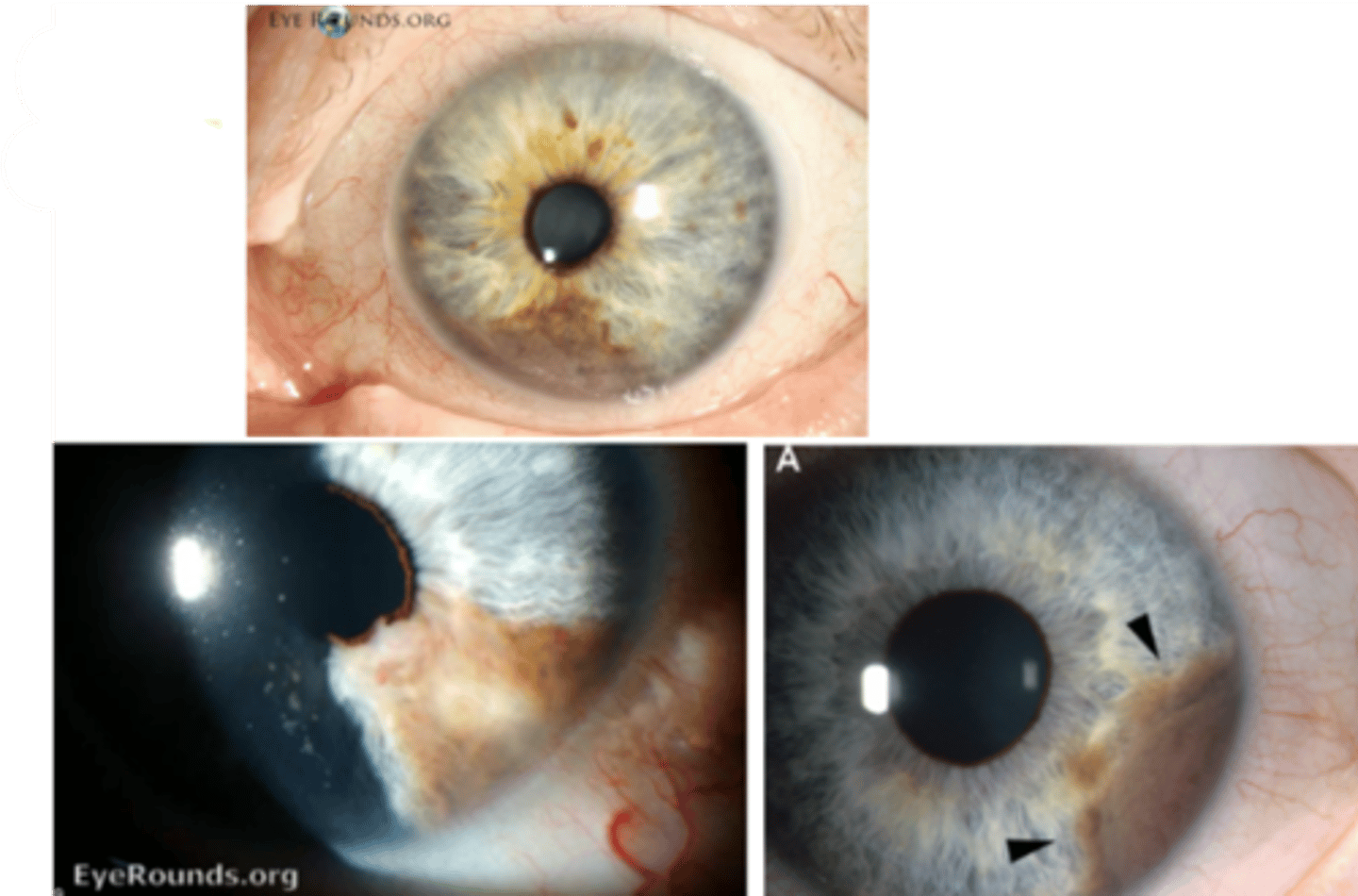
What is the most common solid iris tumor in all age groups?
melanocytic iris nevus
occurs in 4-6% of people
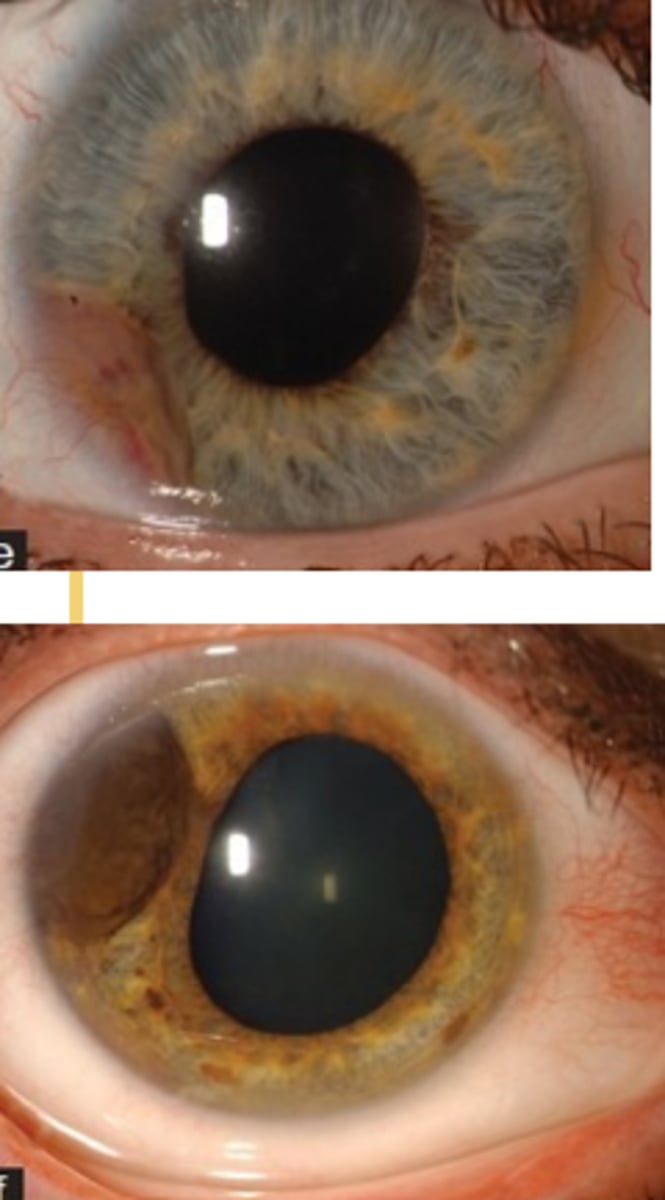
What is an iris melanoma?
malignant tumor of the iris stroma
What is the etiology of iris melanoma?
proliferation of atypical melanocytes, stemming from changes to iris nevus
chronic UV exposure
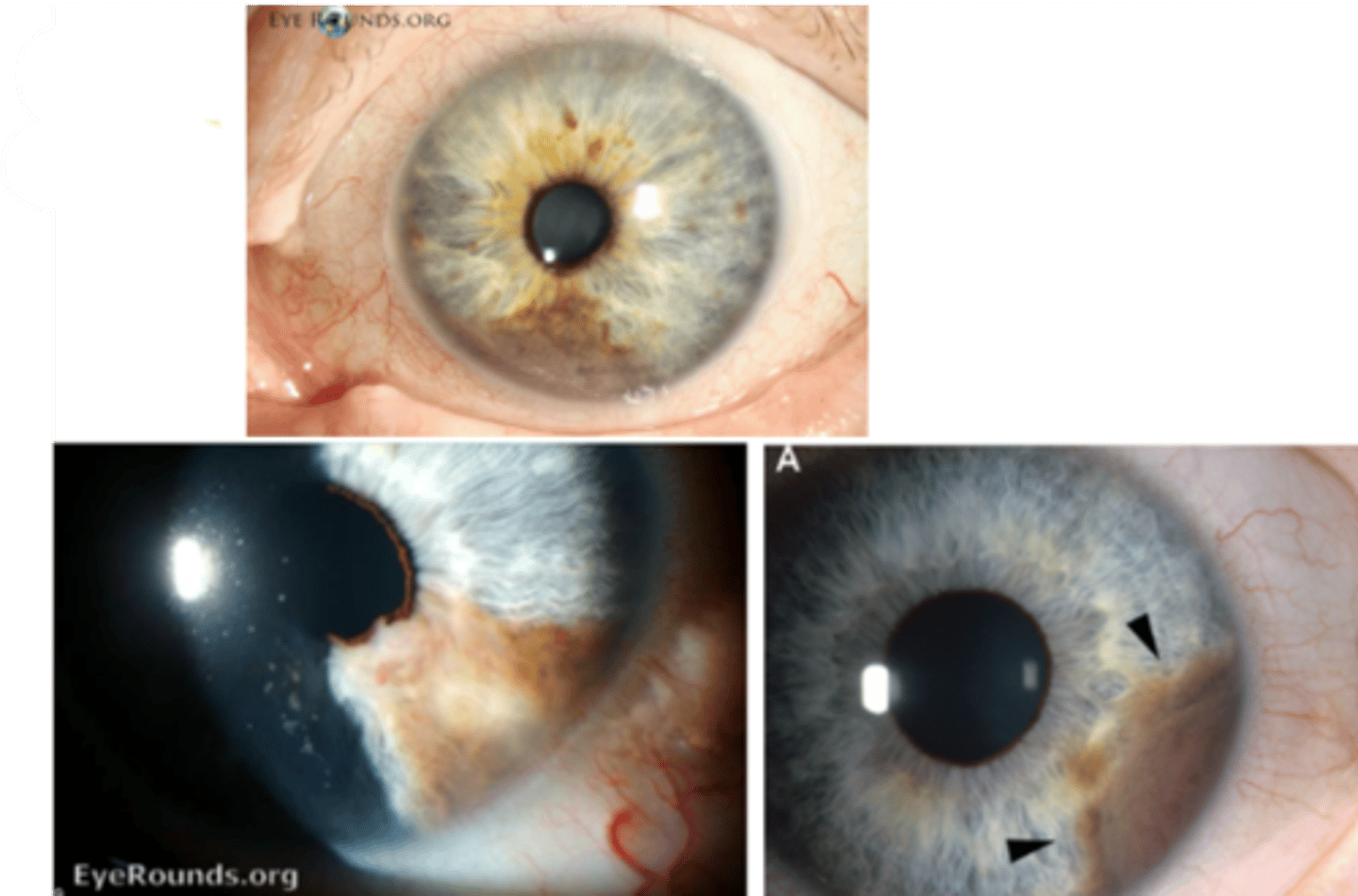
What are the main demographics of iris melanoma?
age 50-60
Caucasians w/ light-coloured irises
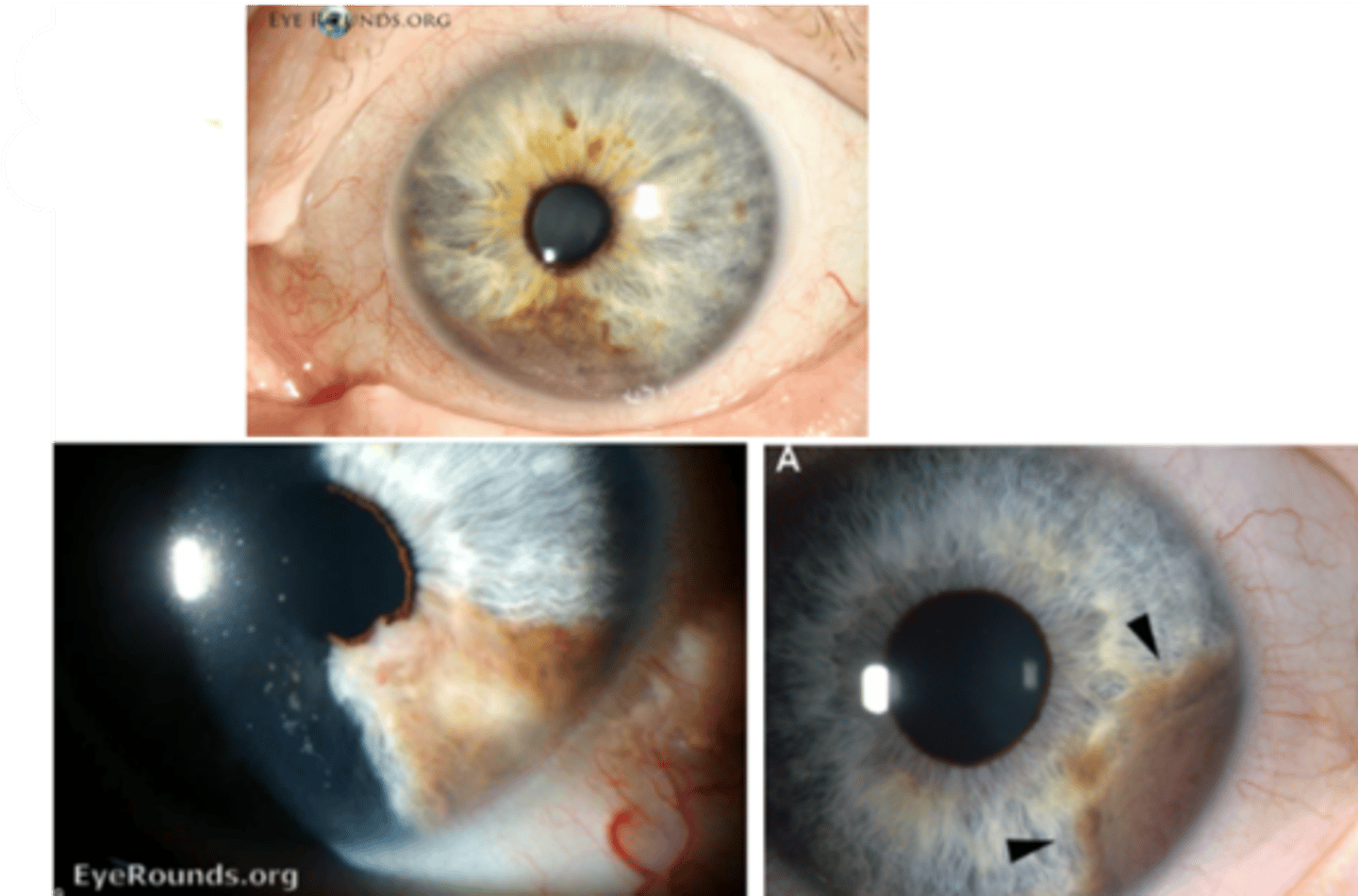
What is the laterality of iris melanoma?
unilateral
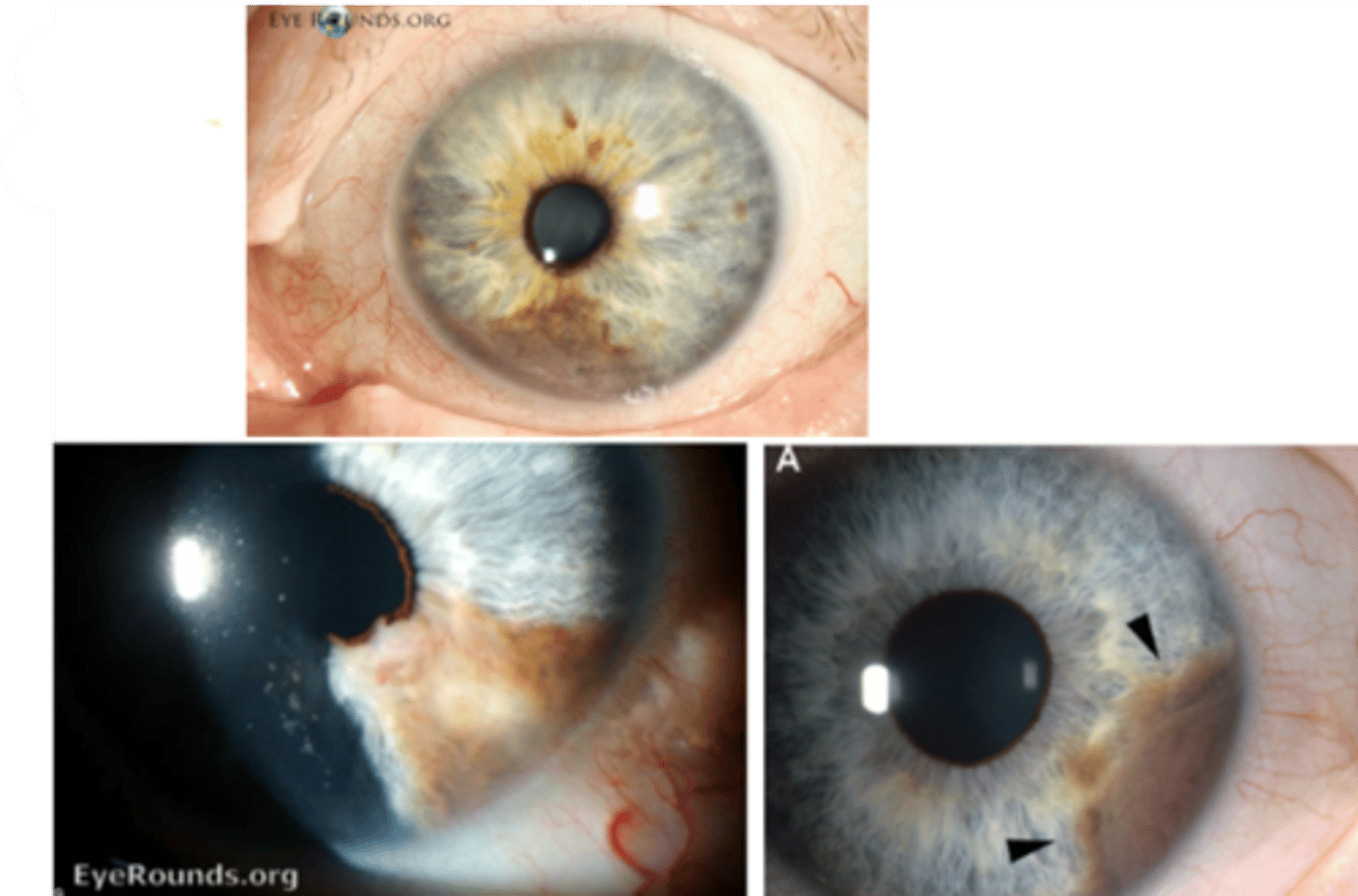
What are the S/S of iris melanoma?
asymptomatic
ocular complications
visual disturbances
visible spot or discoloration of the iris OR enlargement of a preexisting iris lesion
tan to brown, elevated lesion in the iris stroma and possibly extending to the CB
may be amelanotic
may be localized or diffuse
typically inferior, >3 mm in diameter, and >1 mm thick
often associated with intralesional feeder BV and a sectoral cataract
+/- pupillary peaking
+/- ectropion uveae
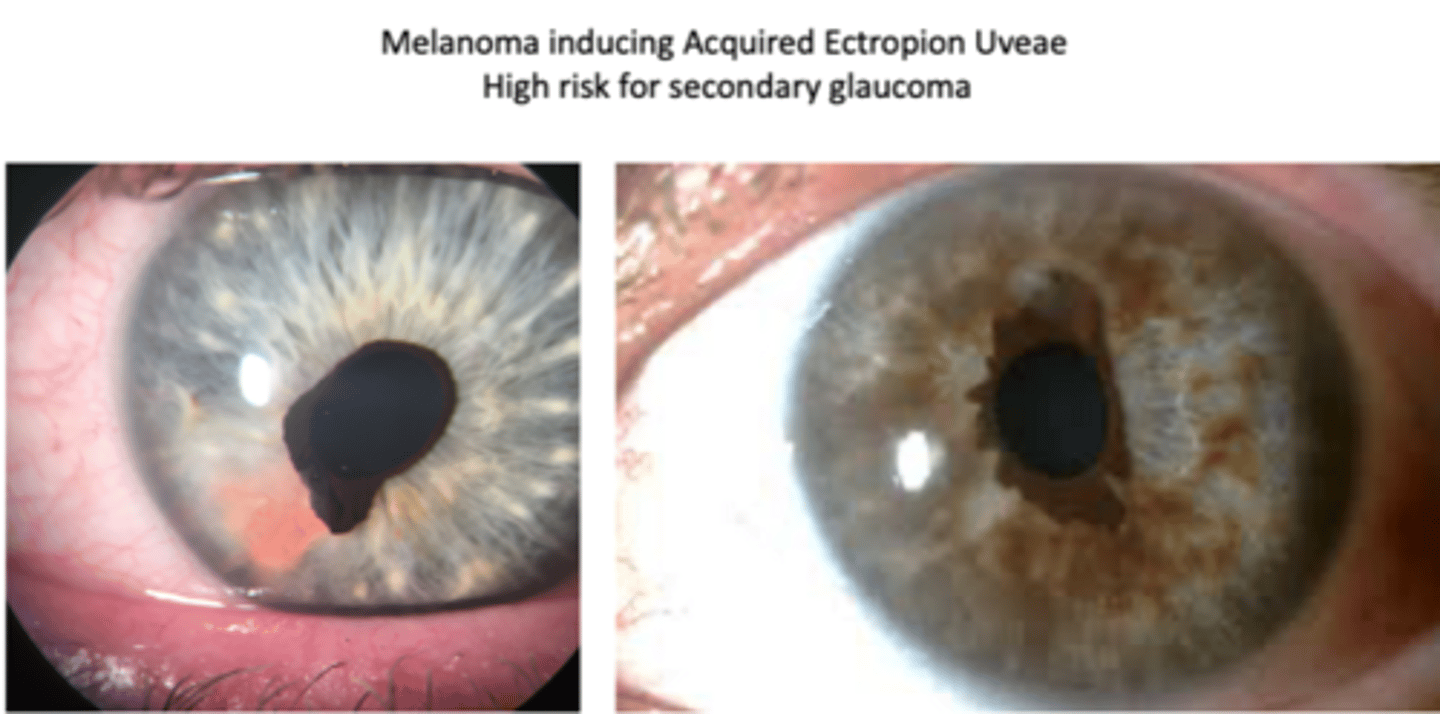
What are 4 possible complications of iris melanoma?
extension intraocularly, orbit, iris deformity
metastasis systemically
hyphema when BV leak into AC
secondary glaucoma when tumor cells or liberated pigment blocks TM
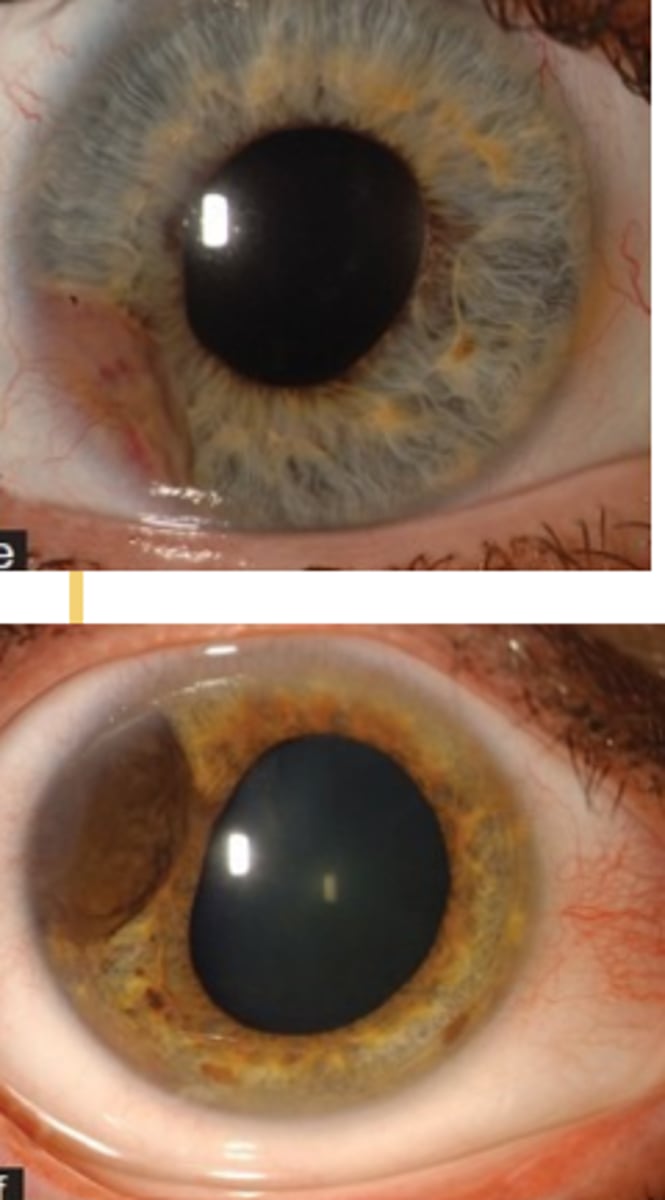
What is the survival rate if there is no metastasis of the iris melanoma?
100% if confined to iris only
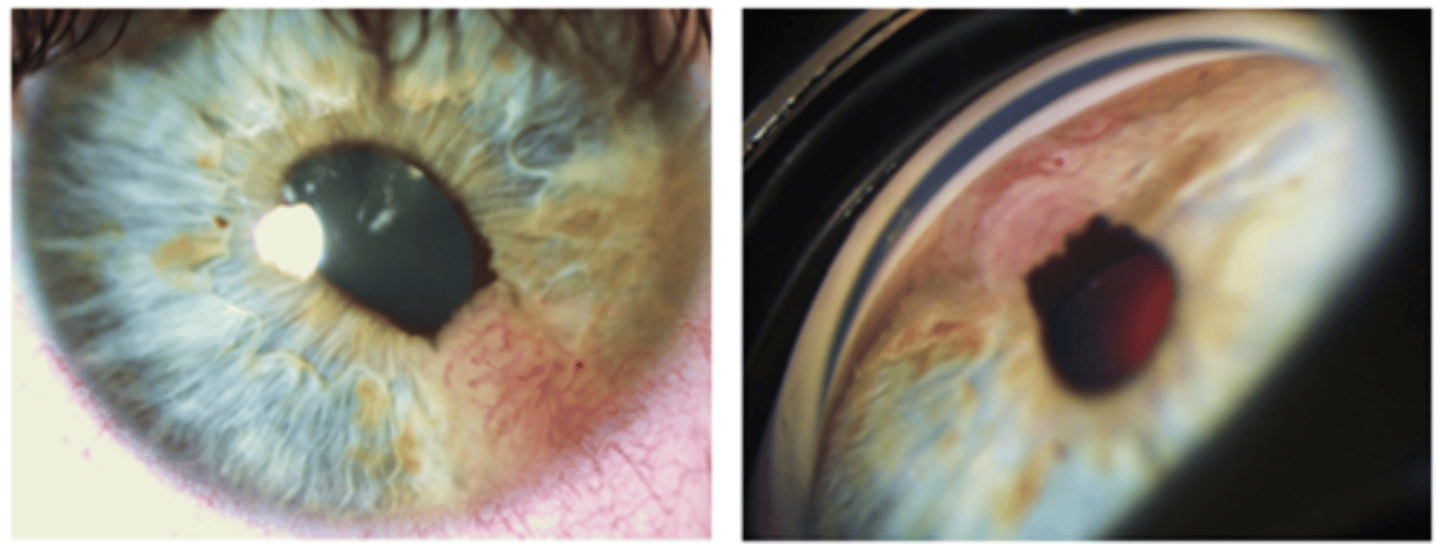
What is the management for iris melanoma?
refer out
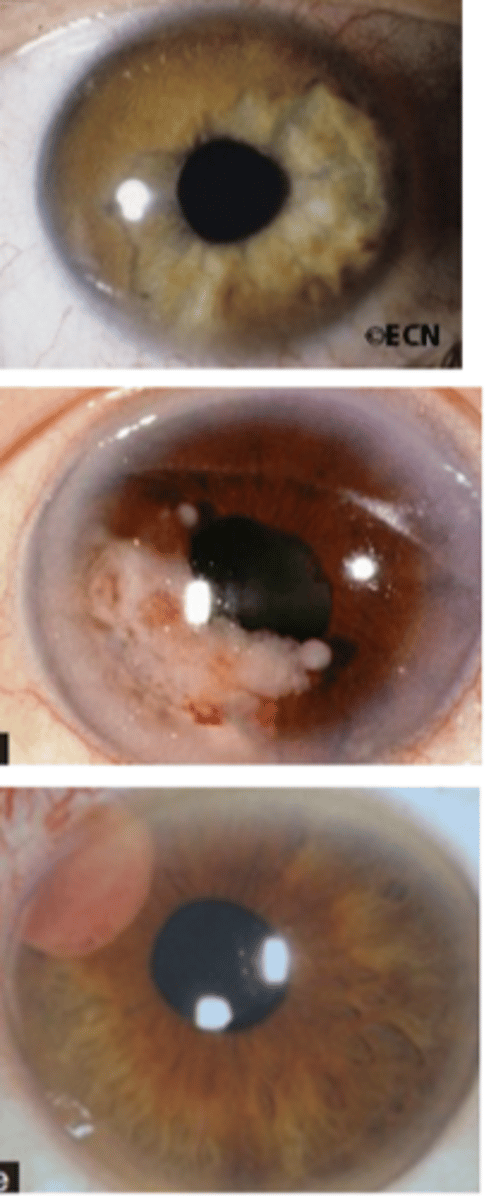
How do ocular oncologists treat iris melanoma?
iridectomy to excise small tumors 3-4 clock hours in size (-)seeding
radiotherapy with plaque or beam for large tumors > 3-4 clock hours in size (+)seeding
enucleation if diffusely growing or radiotherapy not possible
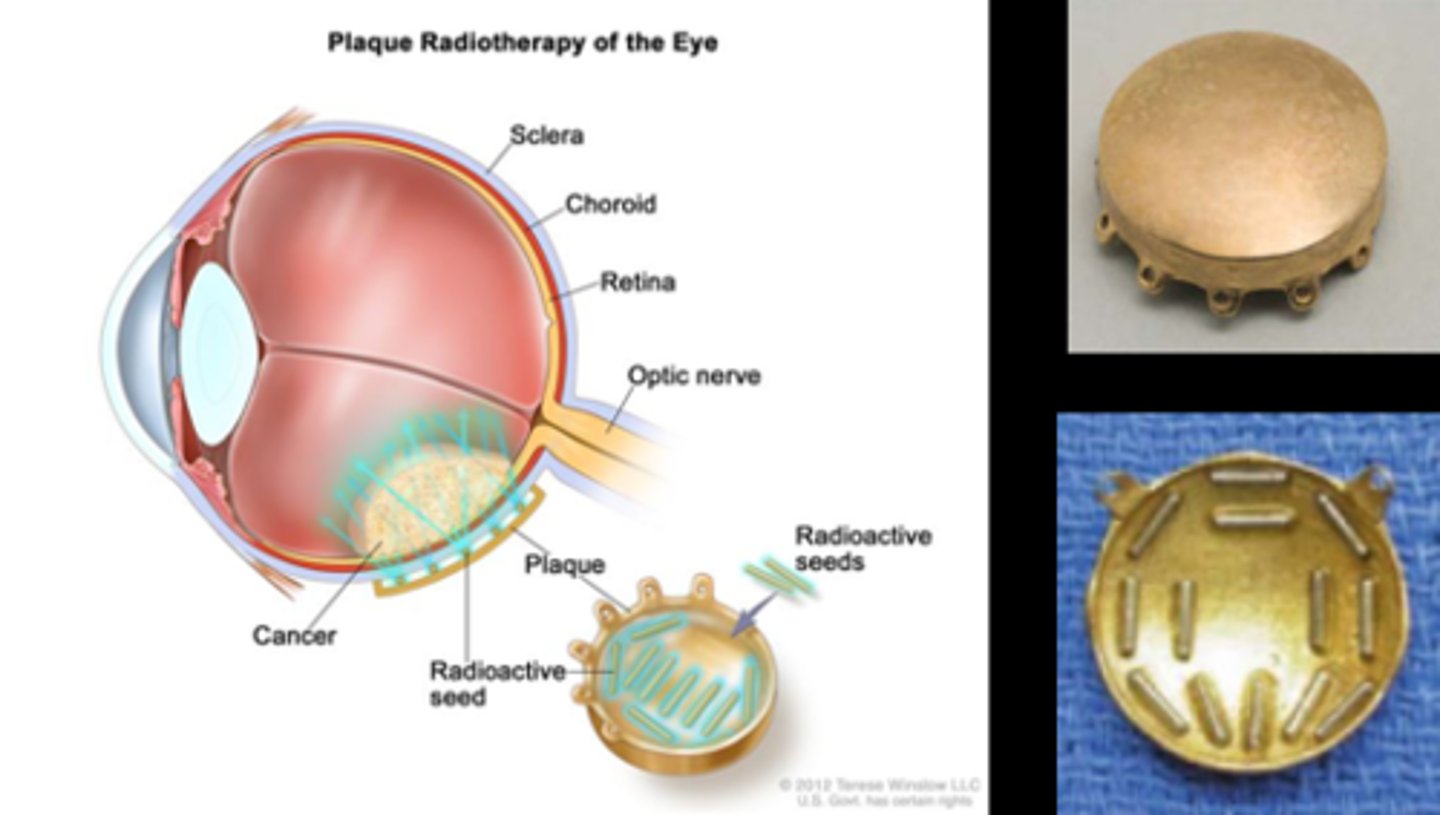
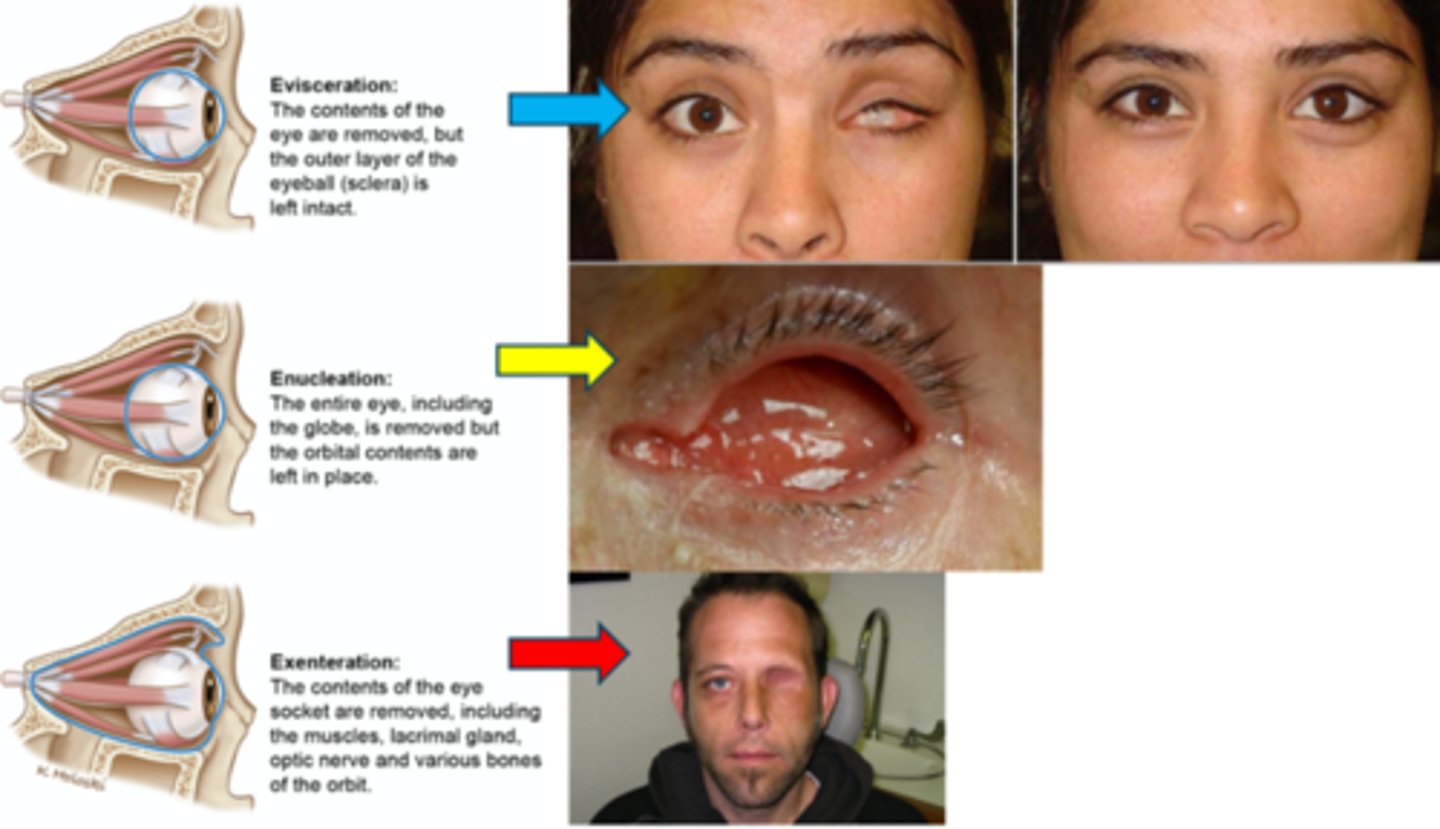
Recall: what is the difference between evisceration vs enucleation vs exenteration?
evisceration = remove contents of glove, sclera remains
enucleation = entire globe removed, orbital tissue remains
exenteration = remove globe and all orbital tissue, ON, etc.
What additional test do we perform if we suspect iris melanoma?
DFE to rule out posterior findings
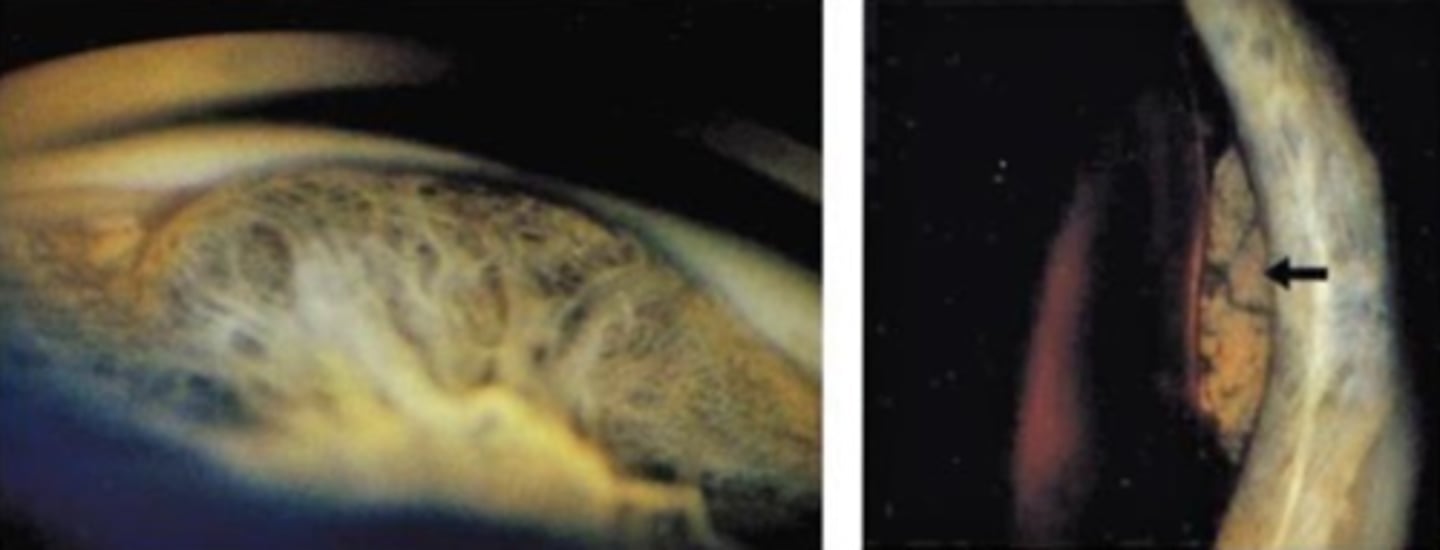
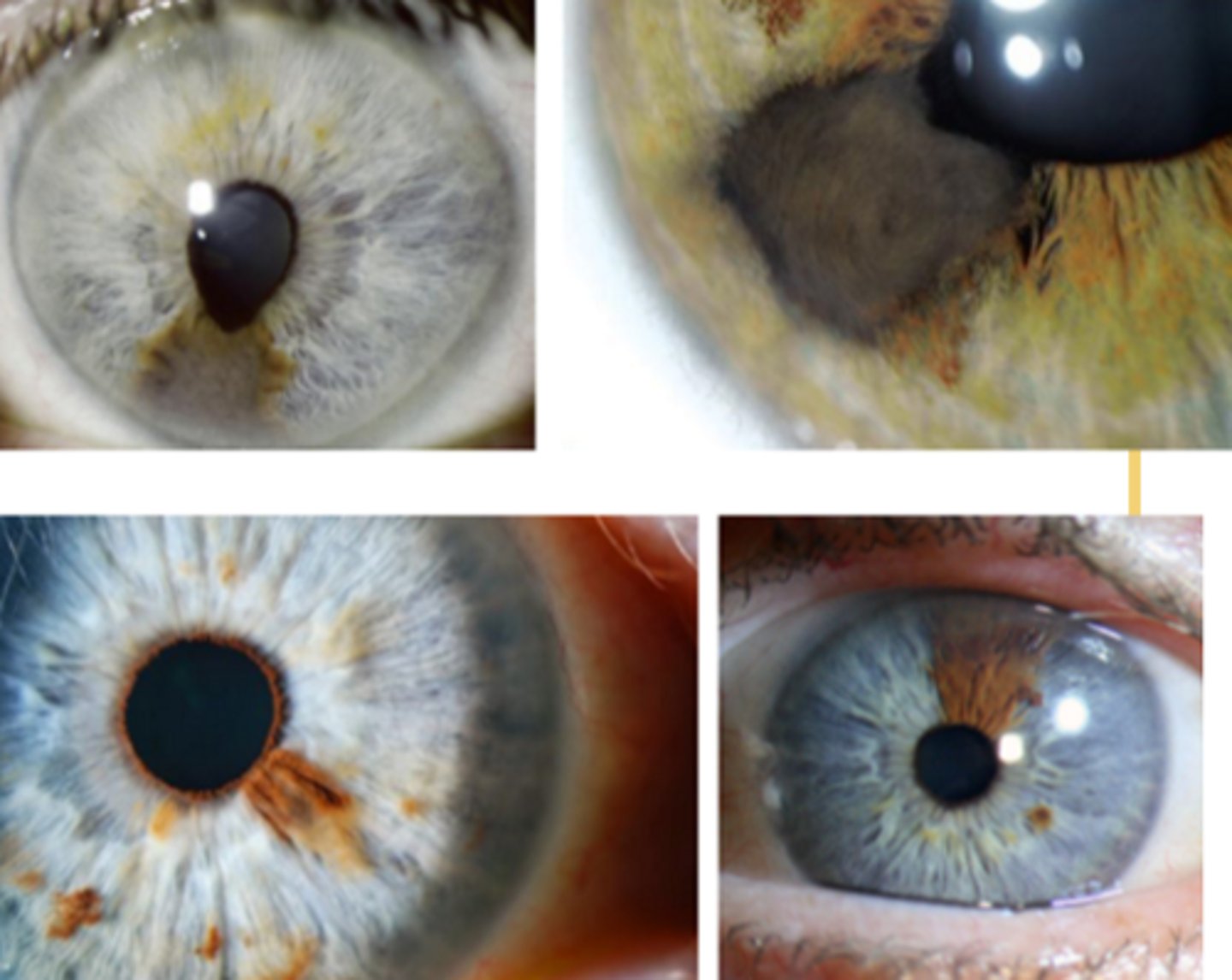
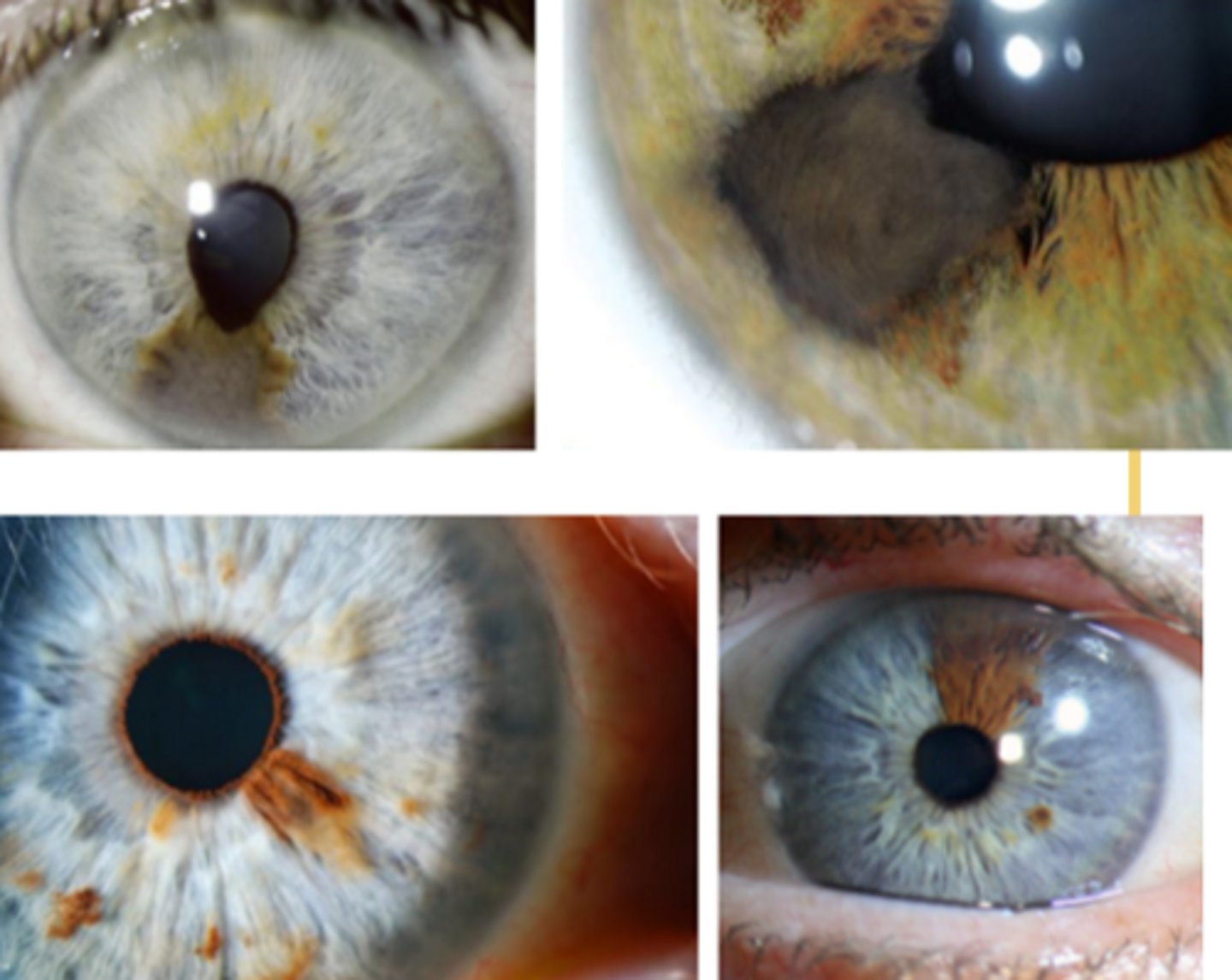
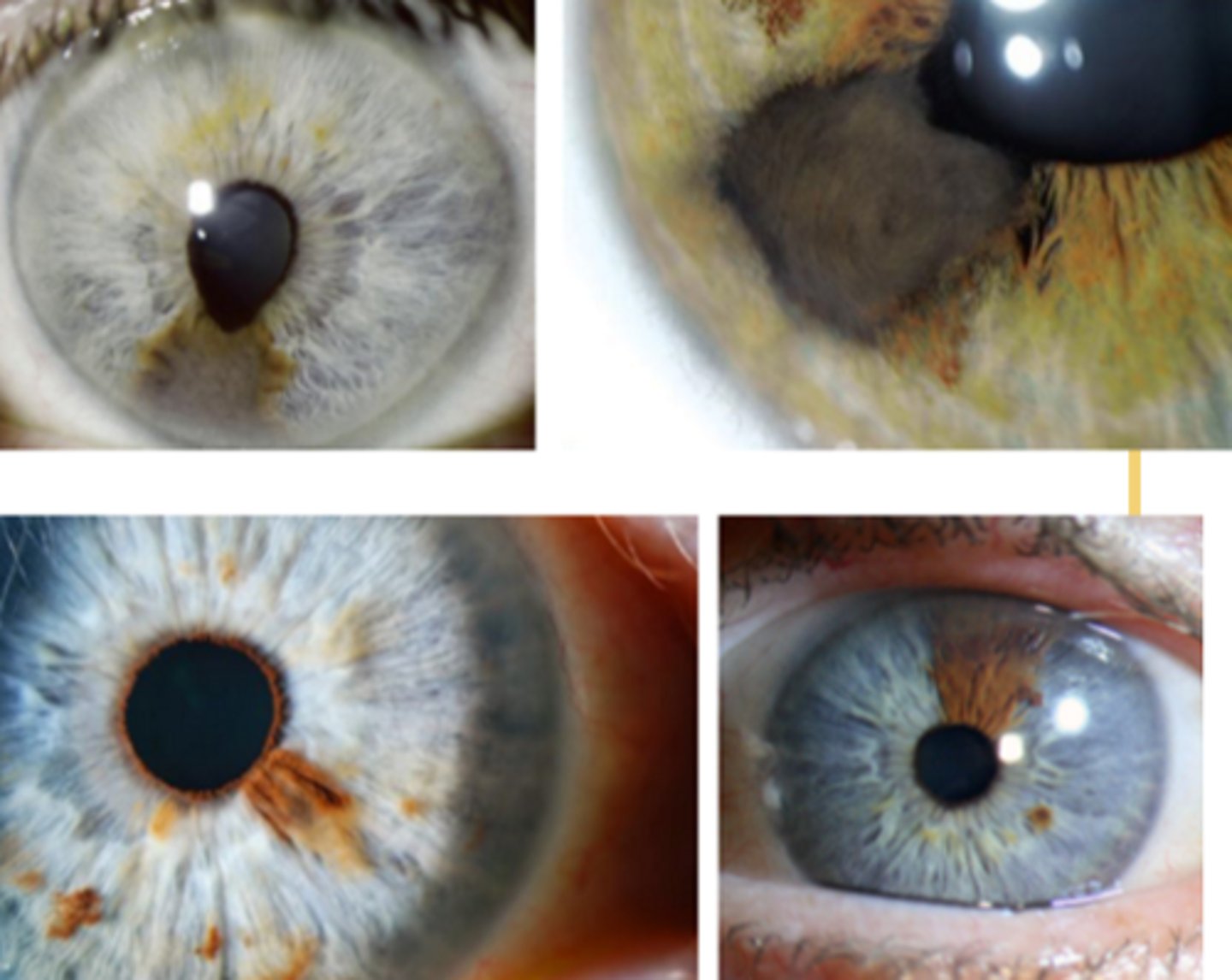
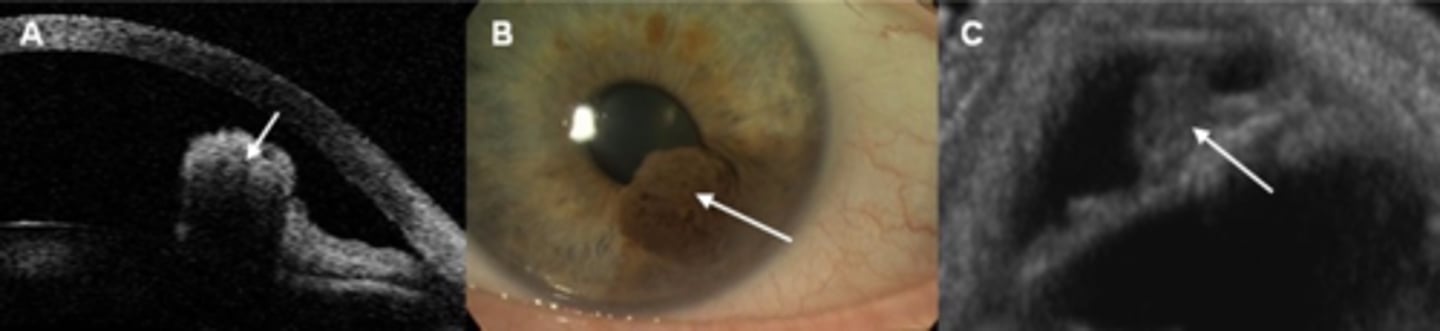
How does an iris melanoma differ from iris cyst on UBM / A Seg OCT, as seen here?
NOT hollow like an iris cyst
In all patients with a Hx of cancer (even if in remission), we should do a _______________ to assess for ocular malignancies/metastasis.
CEE with DFE
What is CB melanoma?
malignant CB tumor
What is the etiology of CB melanoma?
proliferation of atypical melanocytes
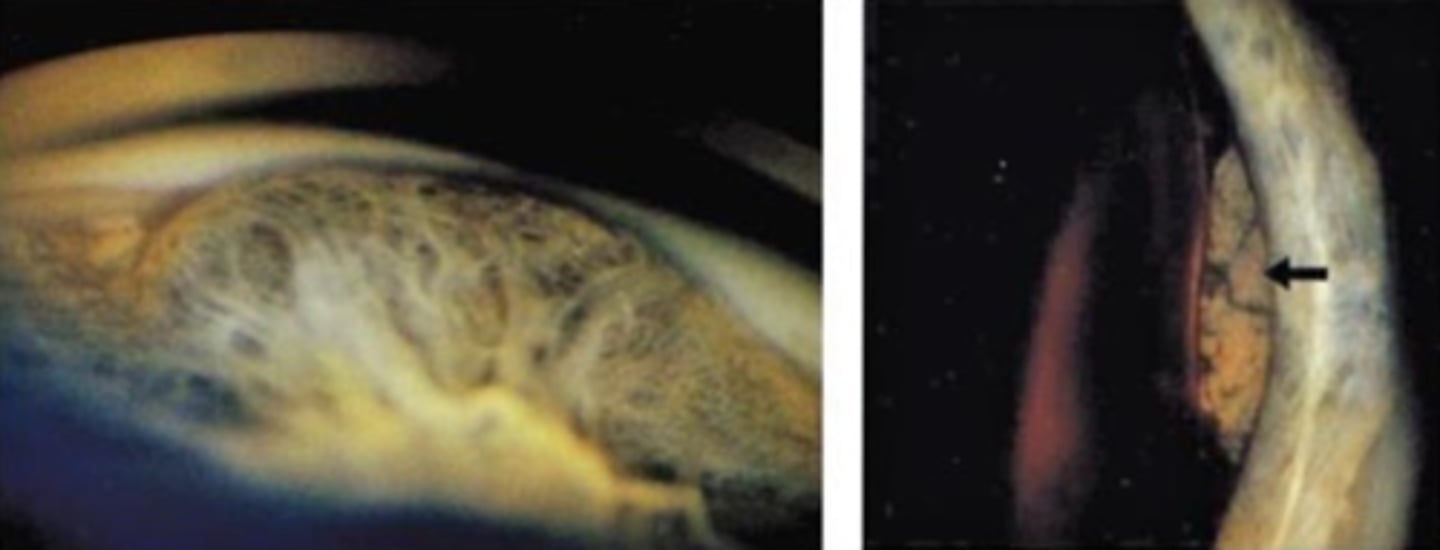
What is the demographics of CB melanoma?
age 50
Caucasians w/ light-coloured irises
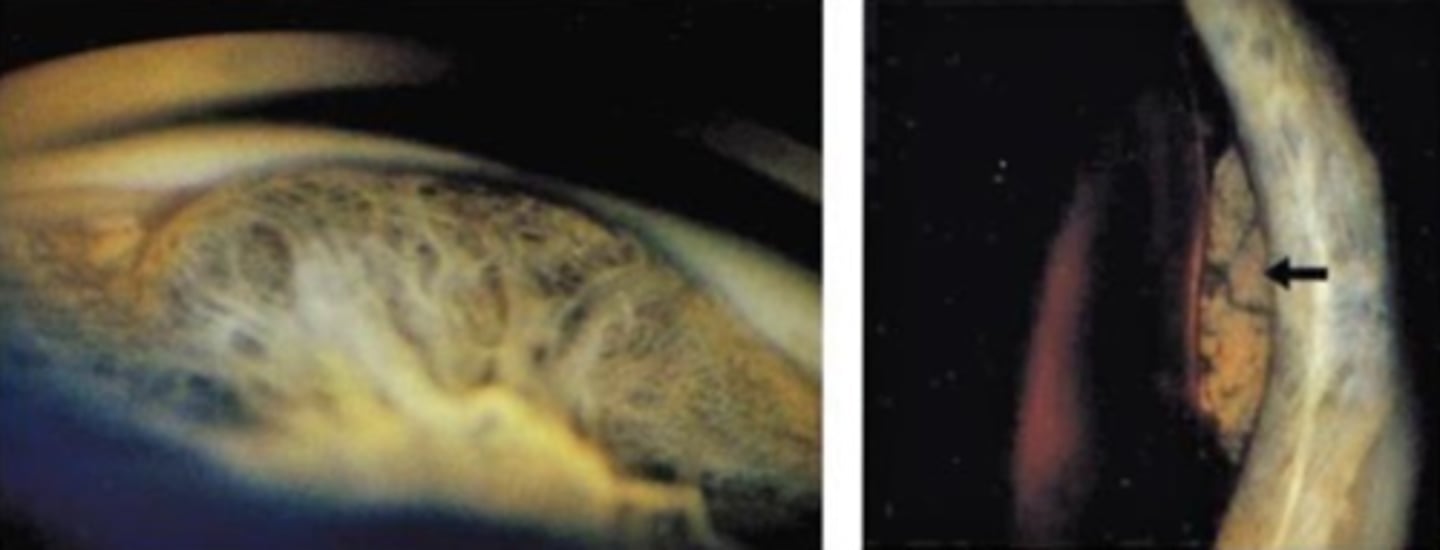
What is the laterality of CB melanoma?
unilateral
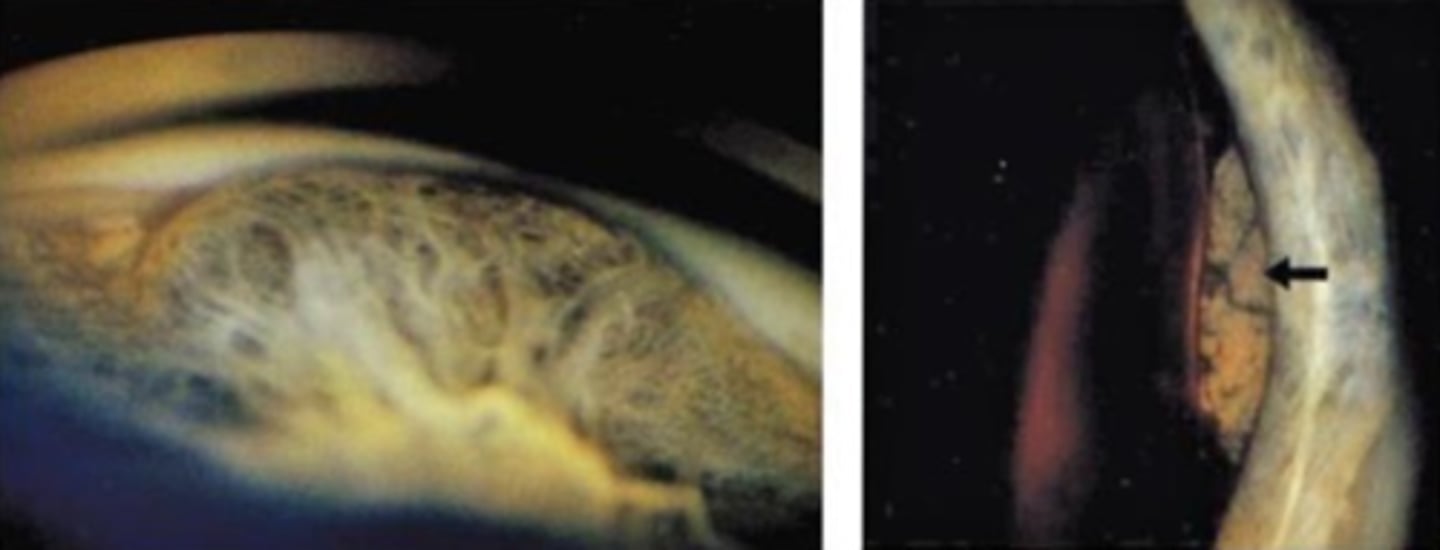
What are some symptoms of CB melanoma?
asymptomatic!
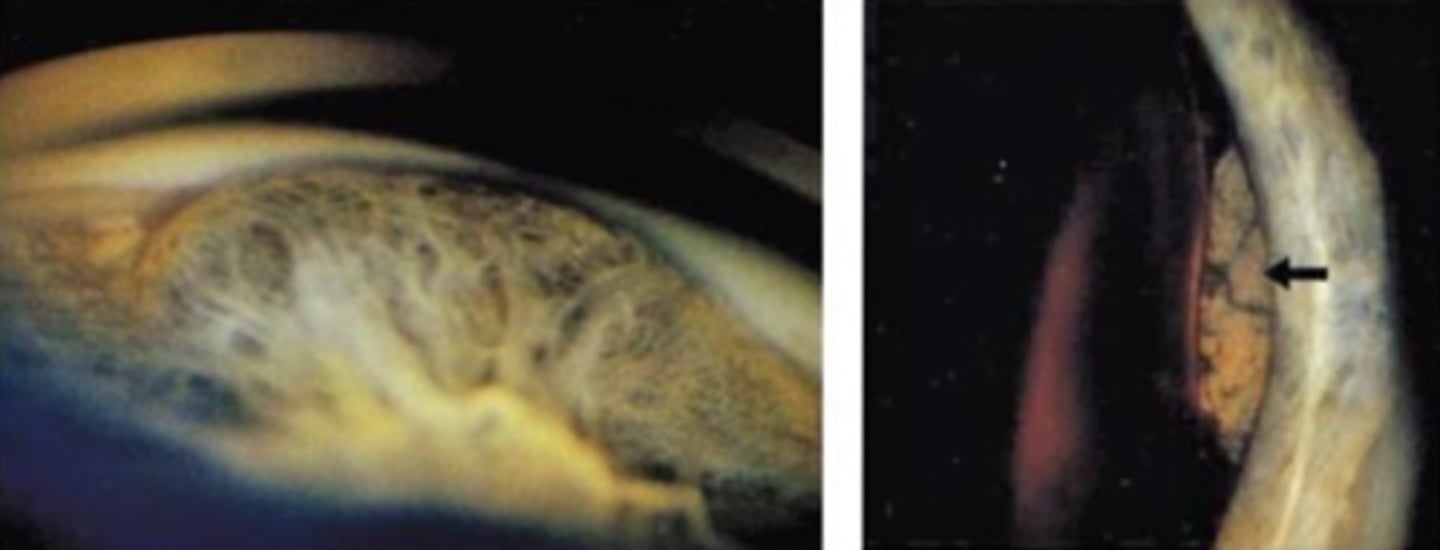
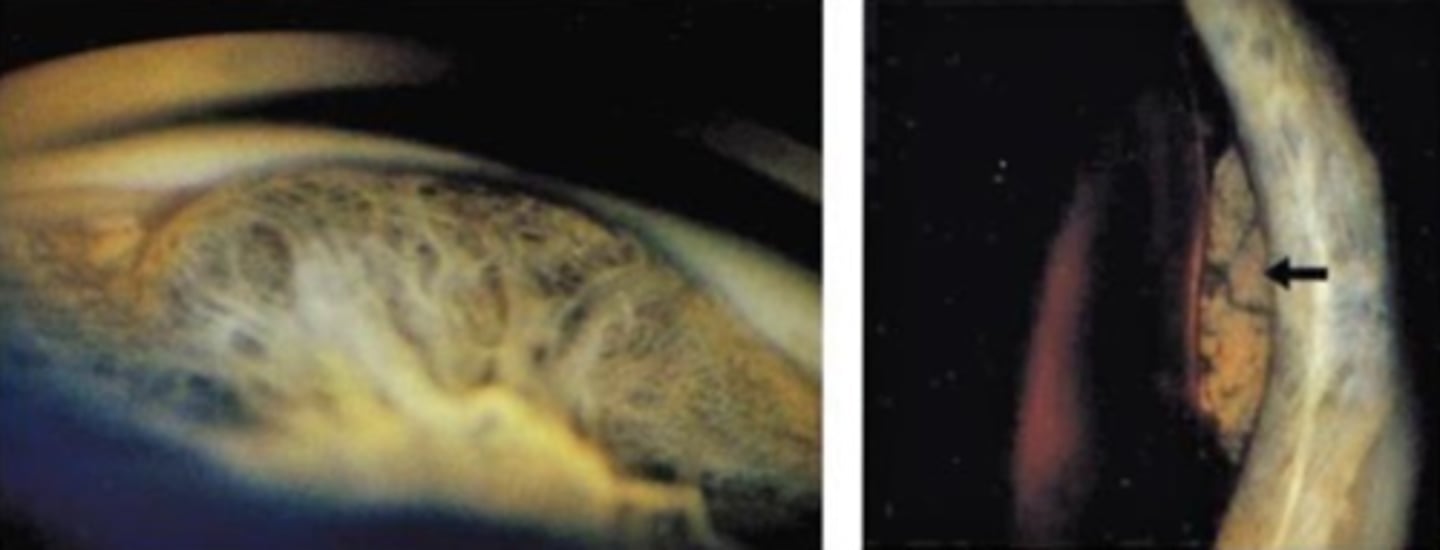
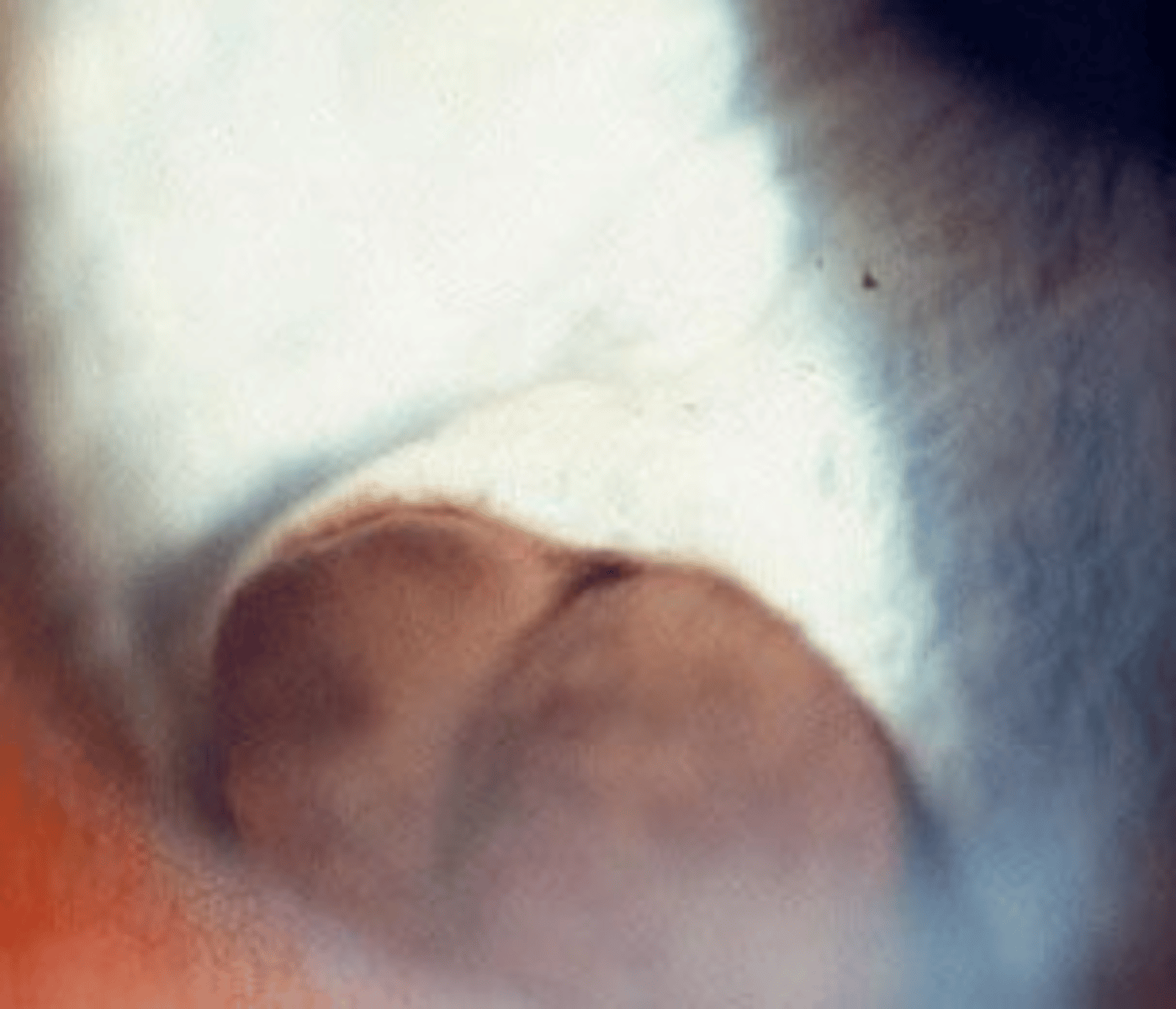
What is this sign of CB melanoma?
smooth dome-shaped elevation of the CB, pushing on the iris
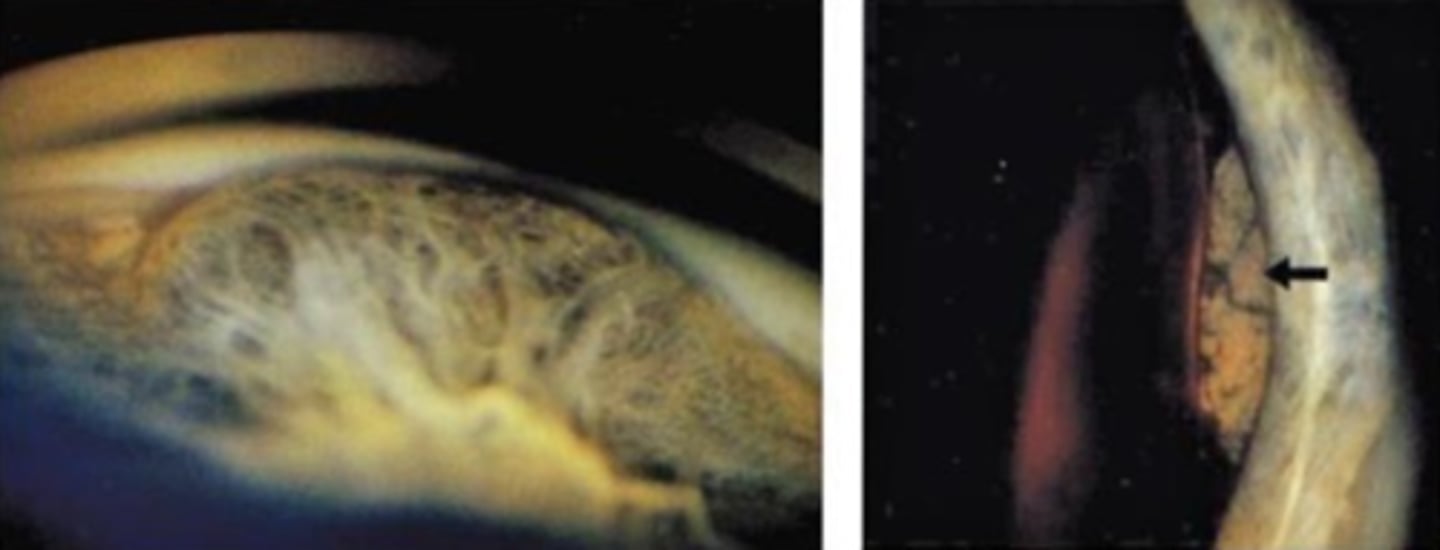
What is this sign of CB melanoma?
may be amelanotic or dark brown mass on fundo or gonio following dilation
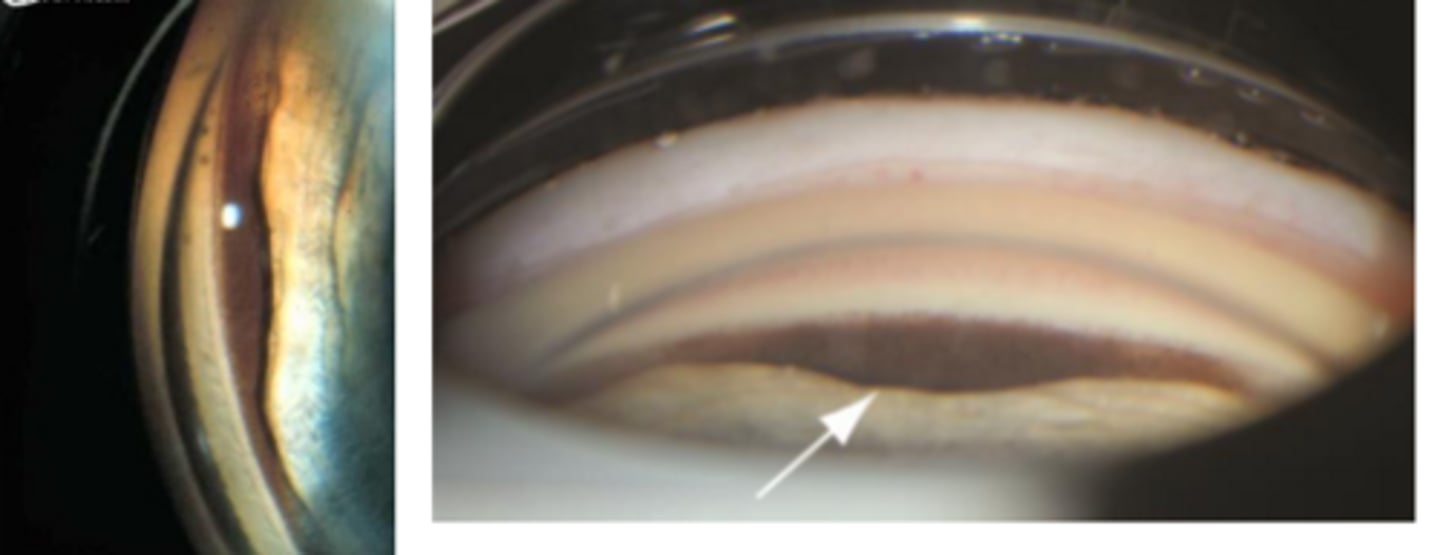
What is this sign of CB melanoma?
sentinel BV = dilated episcleral BV in the same quadrant as the tumor
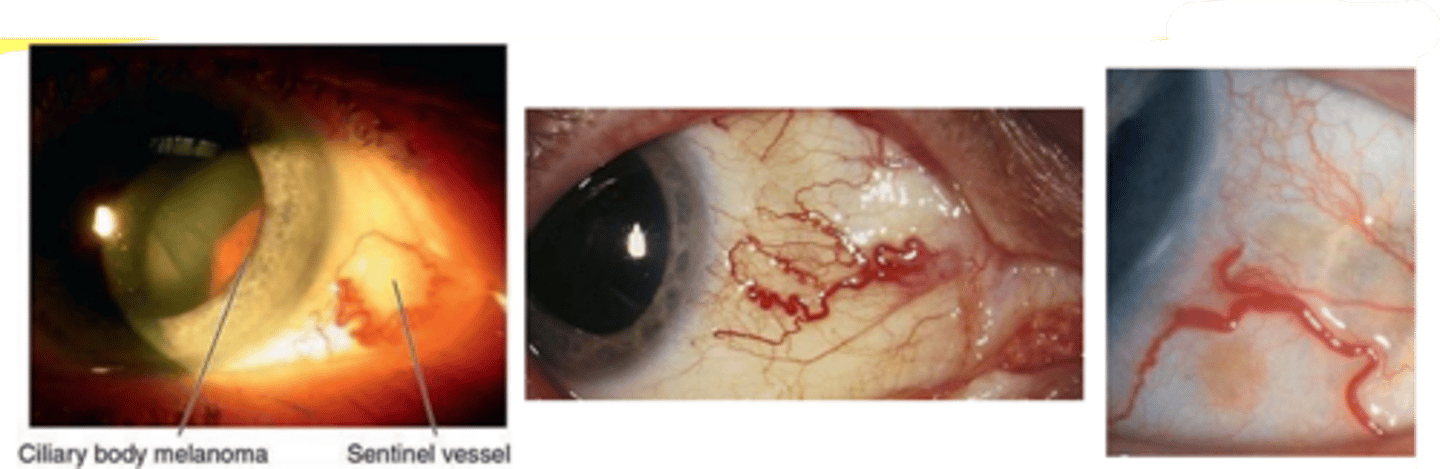
What is this sign of CB melanoma?
CB tumor extends through peripheral iris = visible as nodule mass on iris stroma
What are 2 other signs of CB melanoma?
higher IOP than fellow eye
astig, subluxation, CAT from pressure on the lens
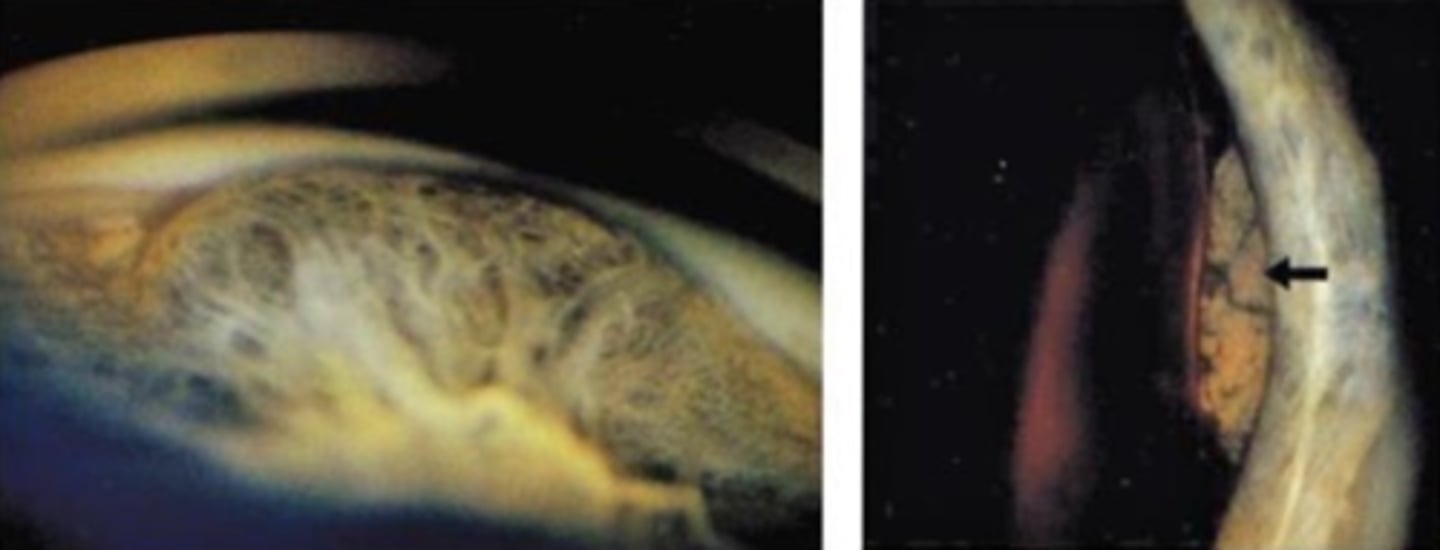
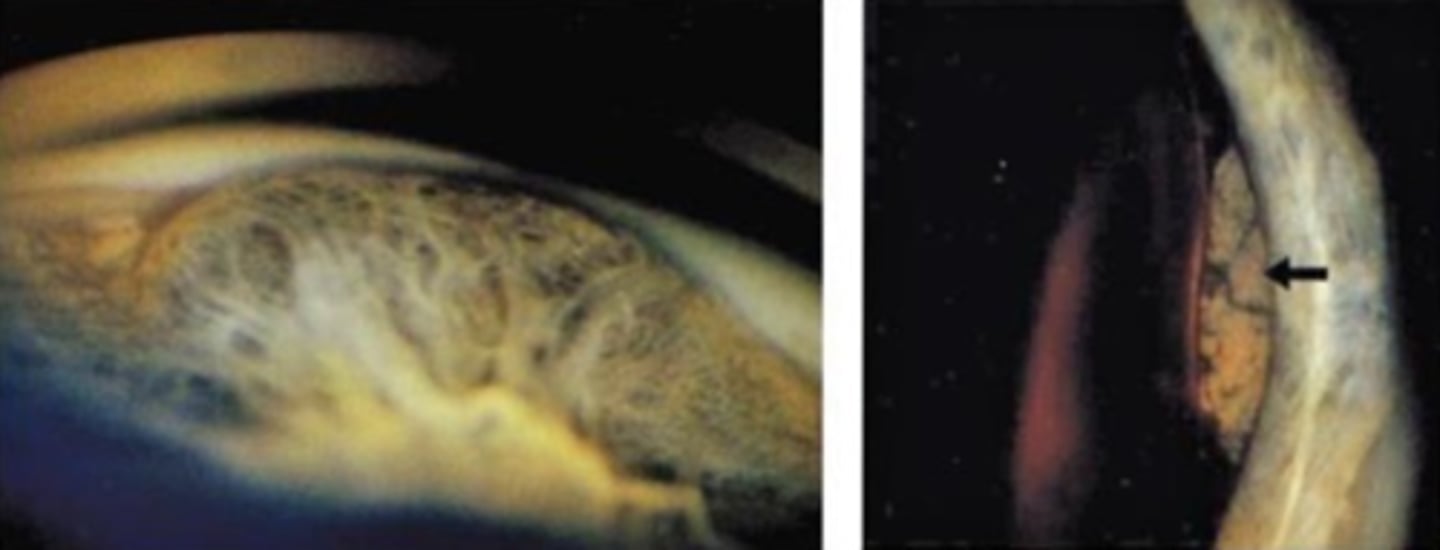
What is this sign of CB melanoma?
CB tumor extends through sclera and becomes visible as a dark epibulbar nodule
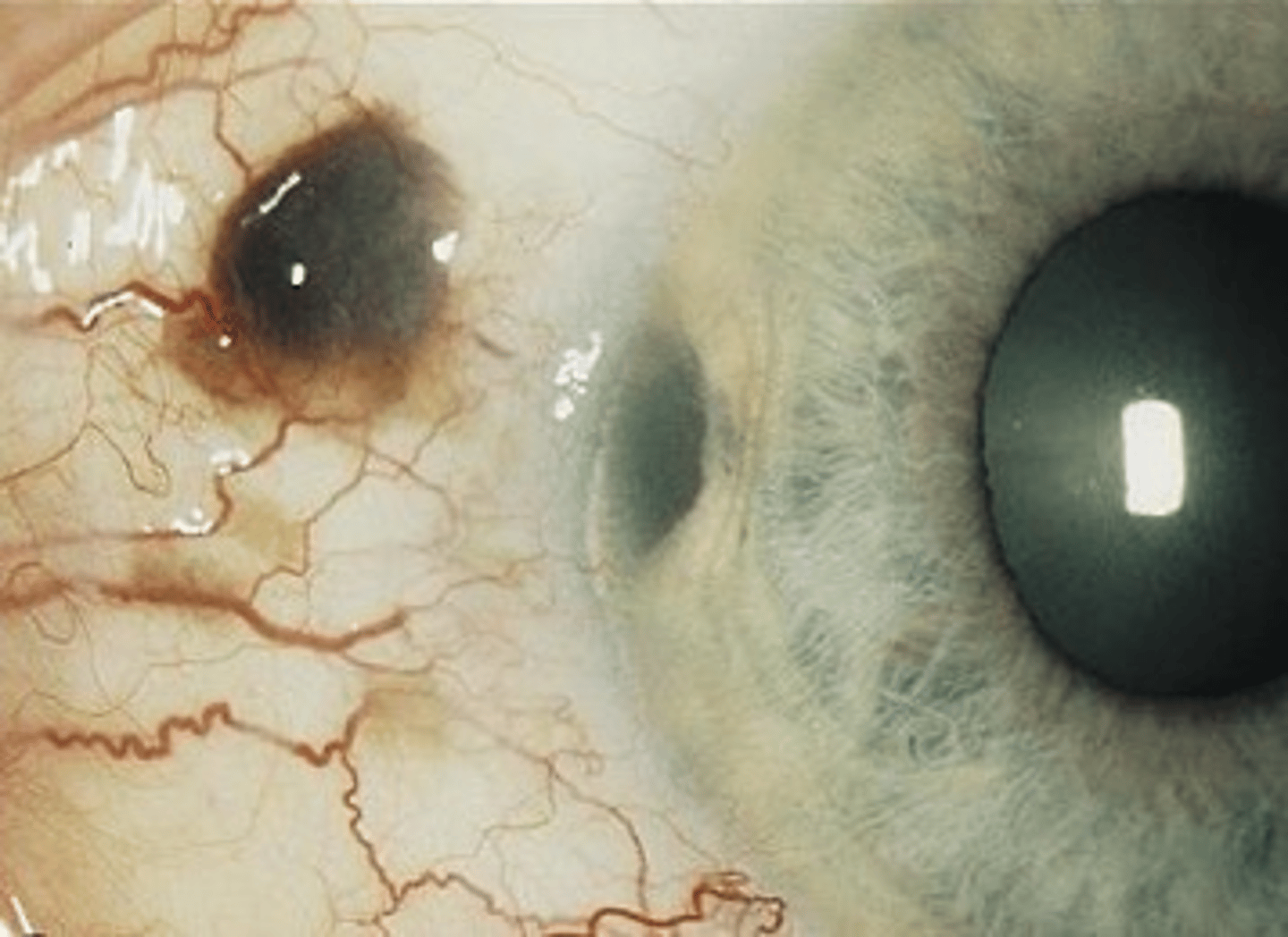
What are 3 complications of CB melanoma?
extension intraocularly, orbit, iris deformity
metastasis systemically
secondary glaucoma when tumor cells or liberated pigment blocks TM, OR if tumor pushes the iris root anterior to narrow the angle
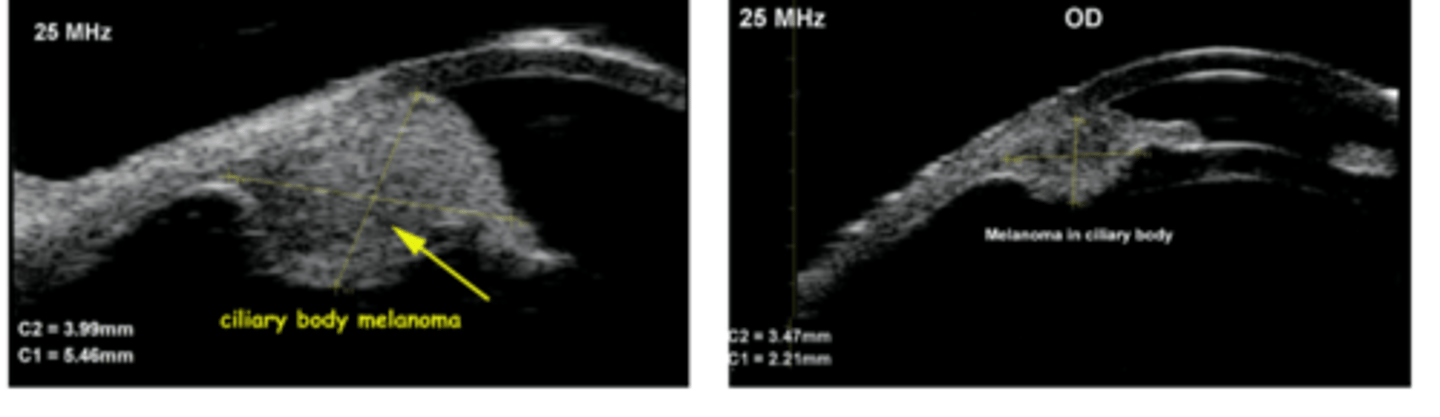
What is the management for CB melanoma?
refer out
What is the tx for CB melanoma?
iridocyclectomy to excise iris and CB if small, local tumor
radiotherapy for medium tumors, local
enucleation for large tumors
exenteration if orbit extension