BILD 3 Midterm Study Guide: Key Biology Terms
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
3 domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaraya
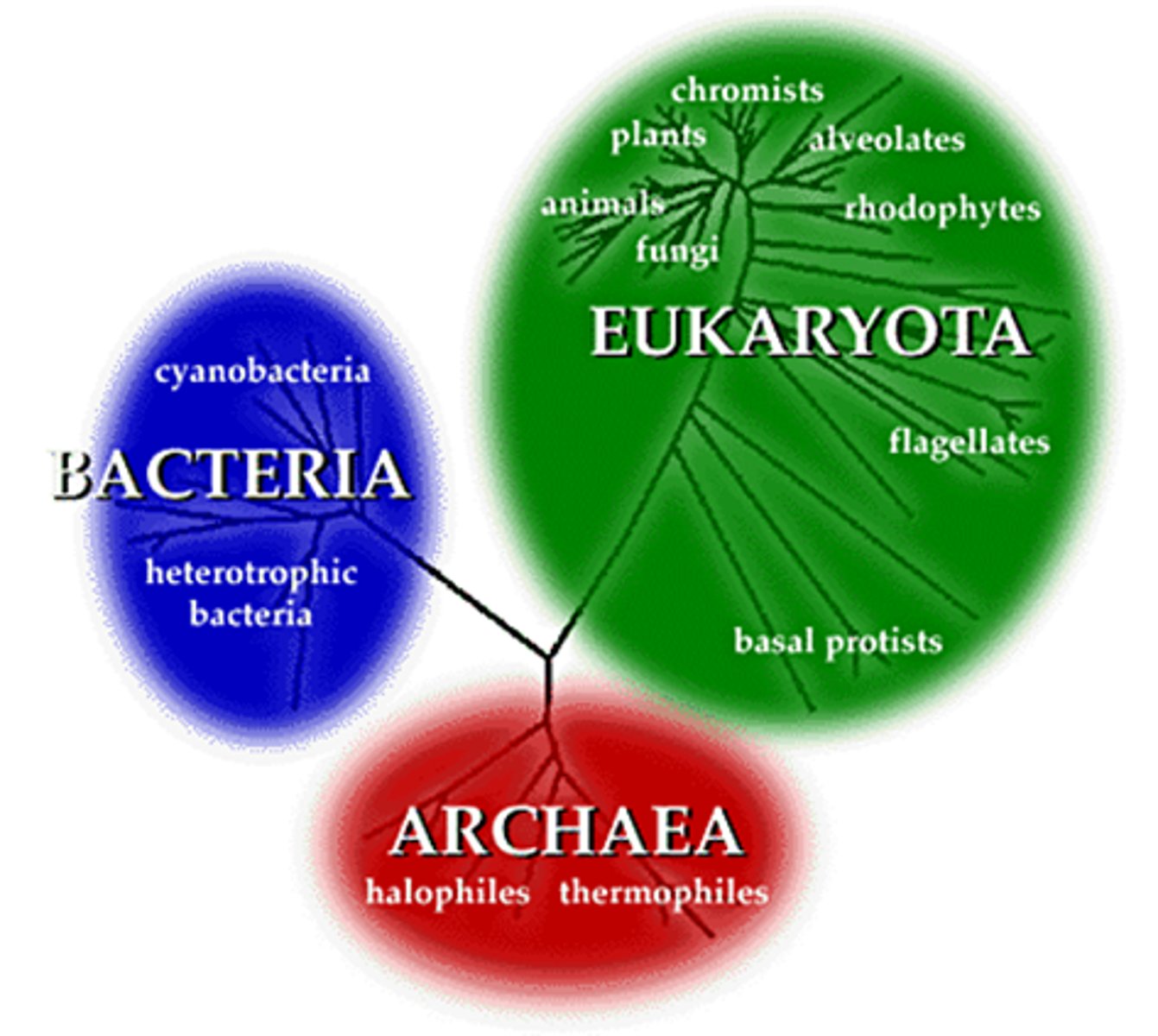
3 multicellular kingdom within Eukaraya
Fungi, Animalia, Plantae
Darwin's Theory of Evolution
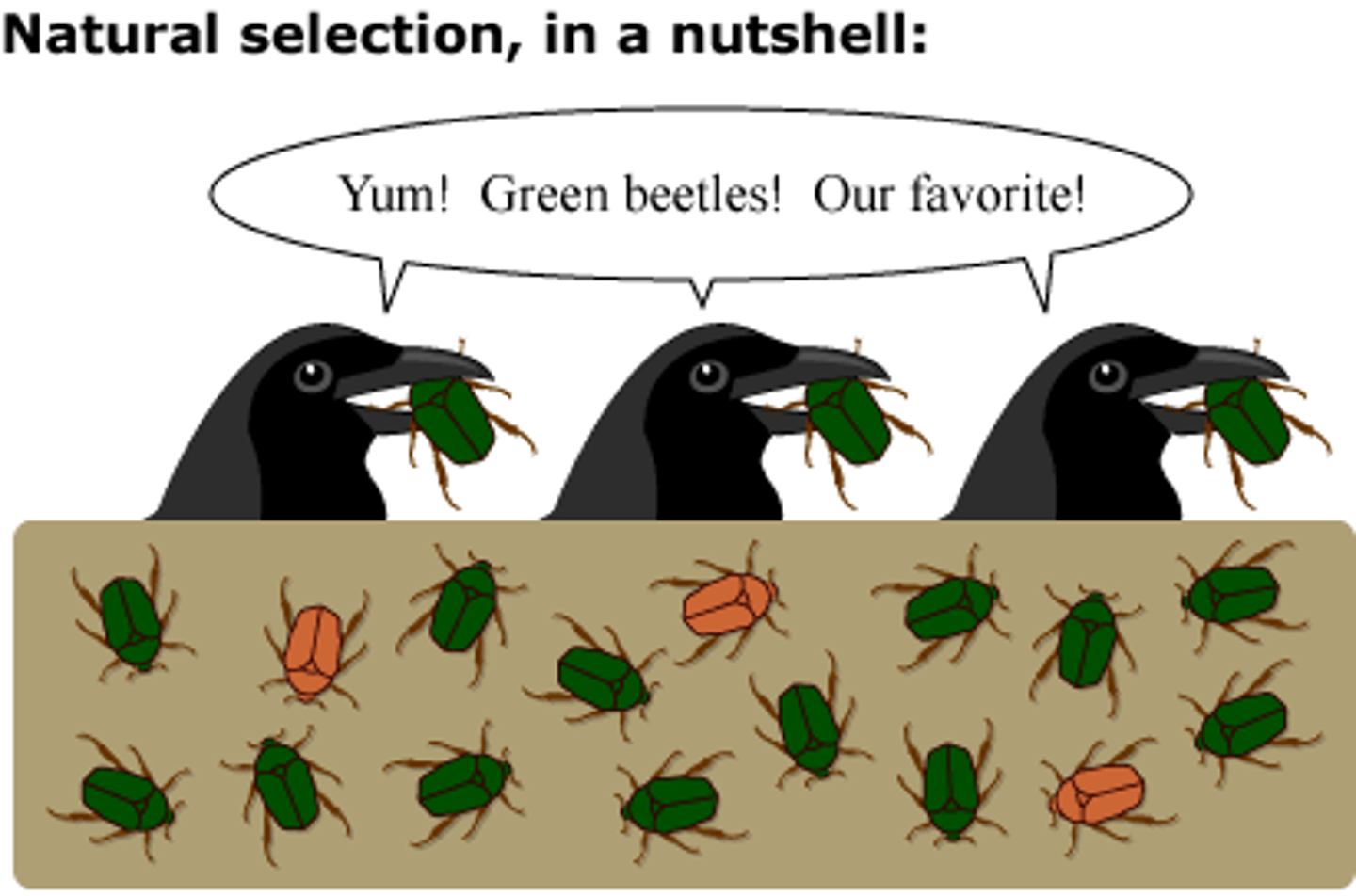
Individuals that are best adapted to the environment will survive and reproduce; their advantageous traits help them. This is called natural Selection.
natural selection
(Not Random) A natural process resulting in the evolution of organisms best adapted to the environment.
Hypothesis
an explanation that is based on prior scientific research or observations and that can be tested
deductive reasoning
reasoning in which a conclusion is reached by stating a general principle and then applying that principle to a specific case (The sun rises every morning; therefore, the sun will rise on Tuesday morning.)
Homologous trait
trait shared between 2 species b/c both species inherited from shared ancestor
Convergent trait
trait shared between 2 species b/c it evolved multiple times
Hutton
Gradualism. earth is millions of years old, major changes are caused by small changes over time
Cuvier
catastrophism: believed that the extinction of species was caused by catastrophic events such as floods
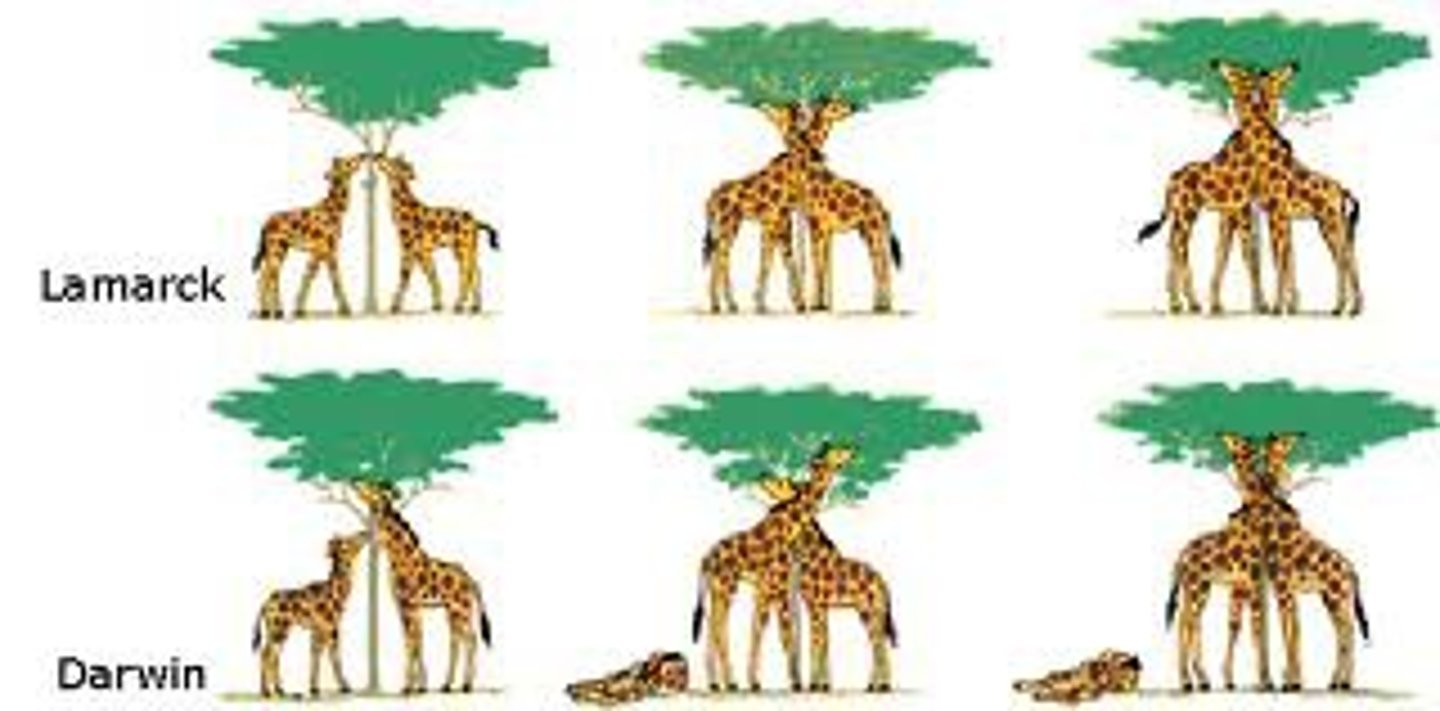
Lamarck
Proposed theory that organisms pass on traits they acquire in their lifetime. Ex. giraffe necks
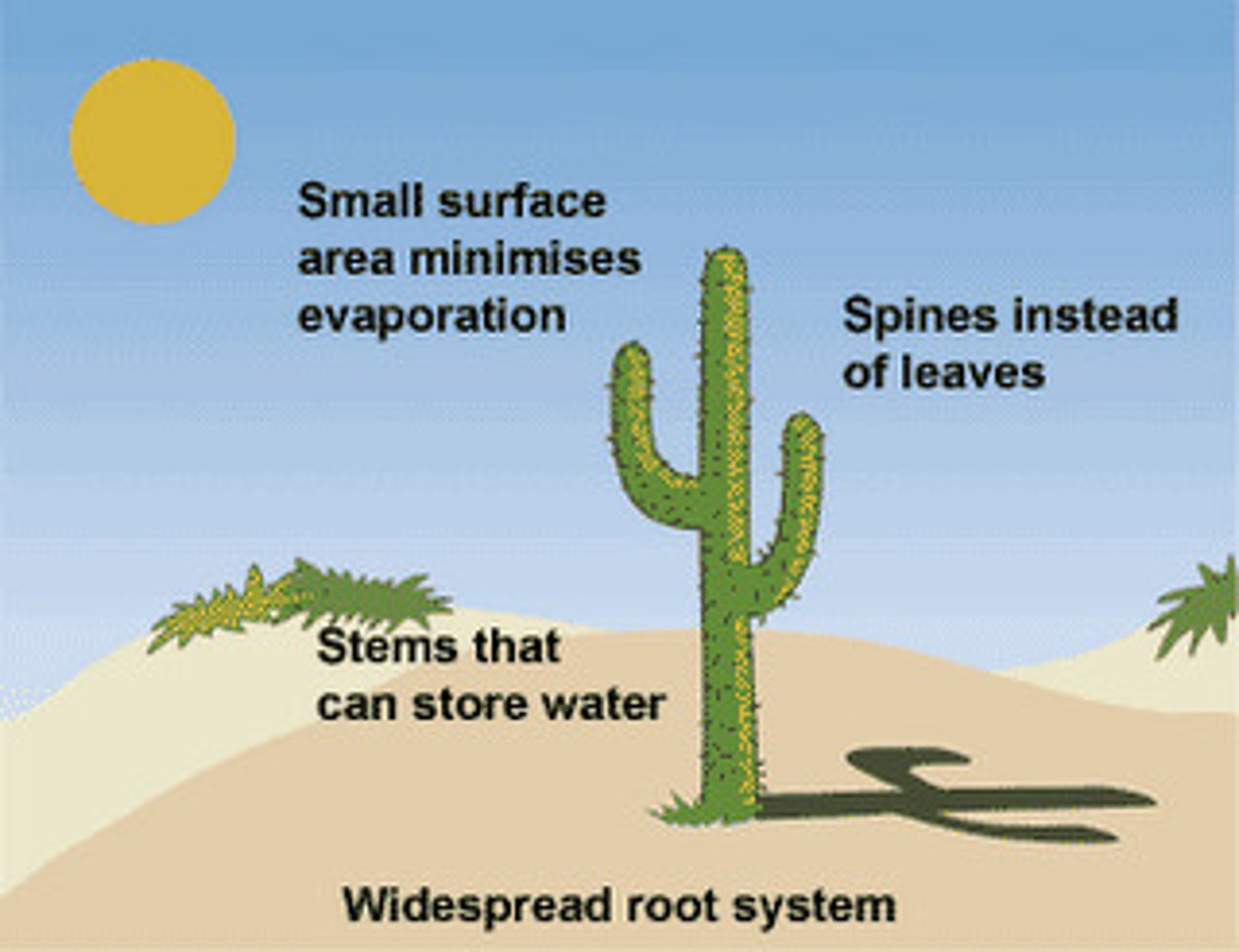
Adaptation
inherited characteristic that increases an organism's chance of survival and reproduction to a specific environment
artificial selection
selective breeding of plants and animals to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in offspring
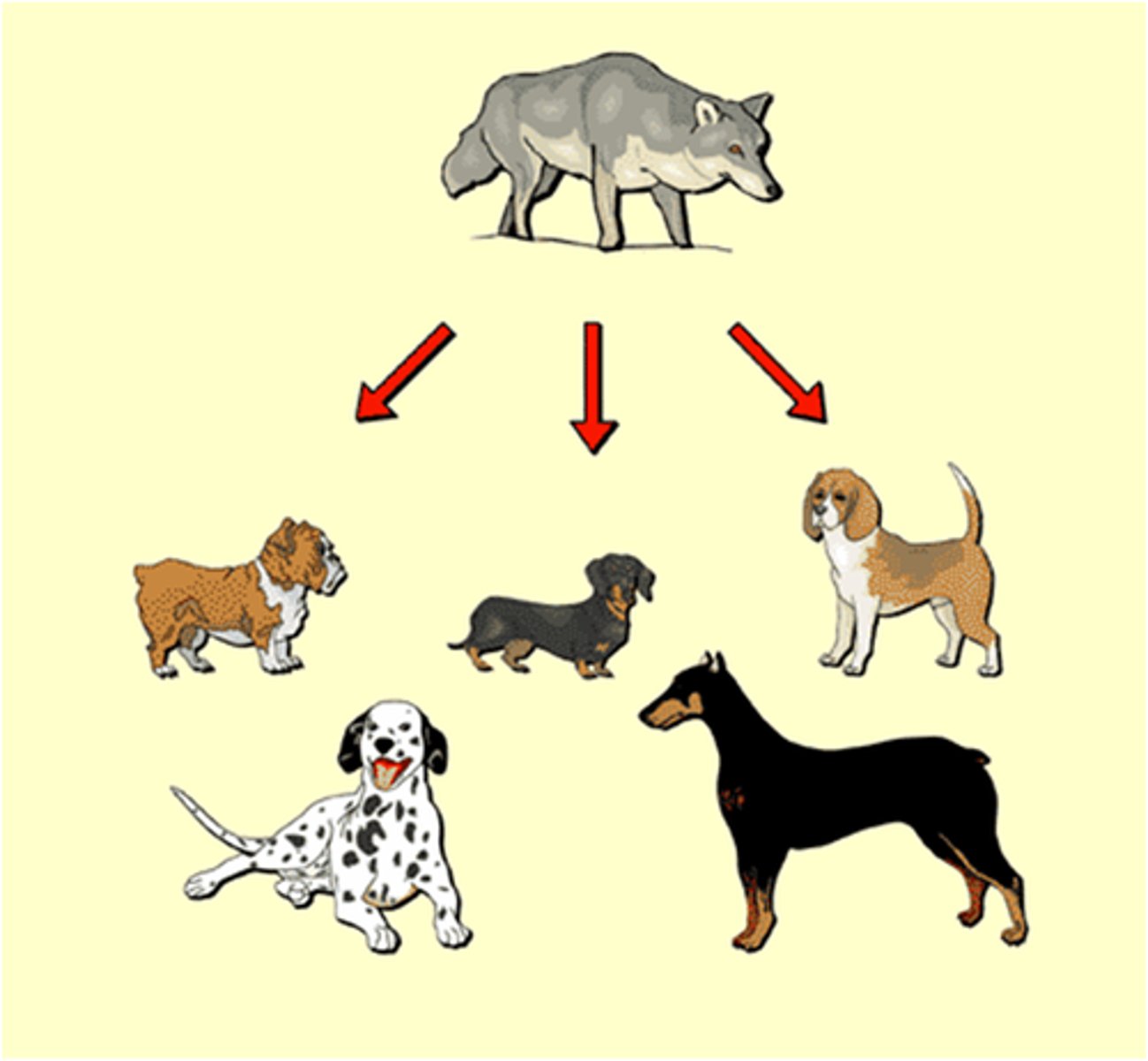
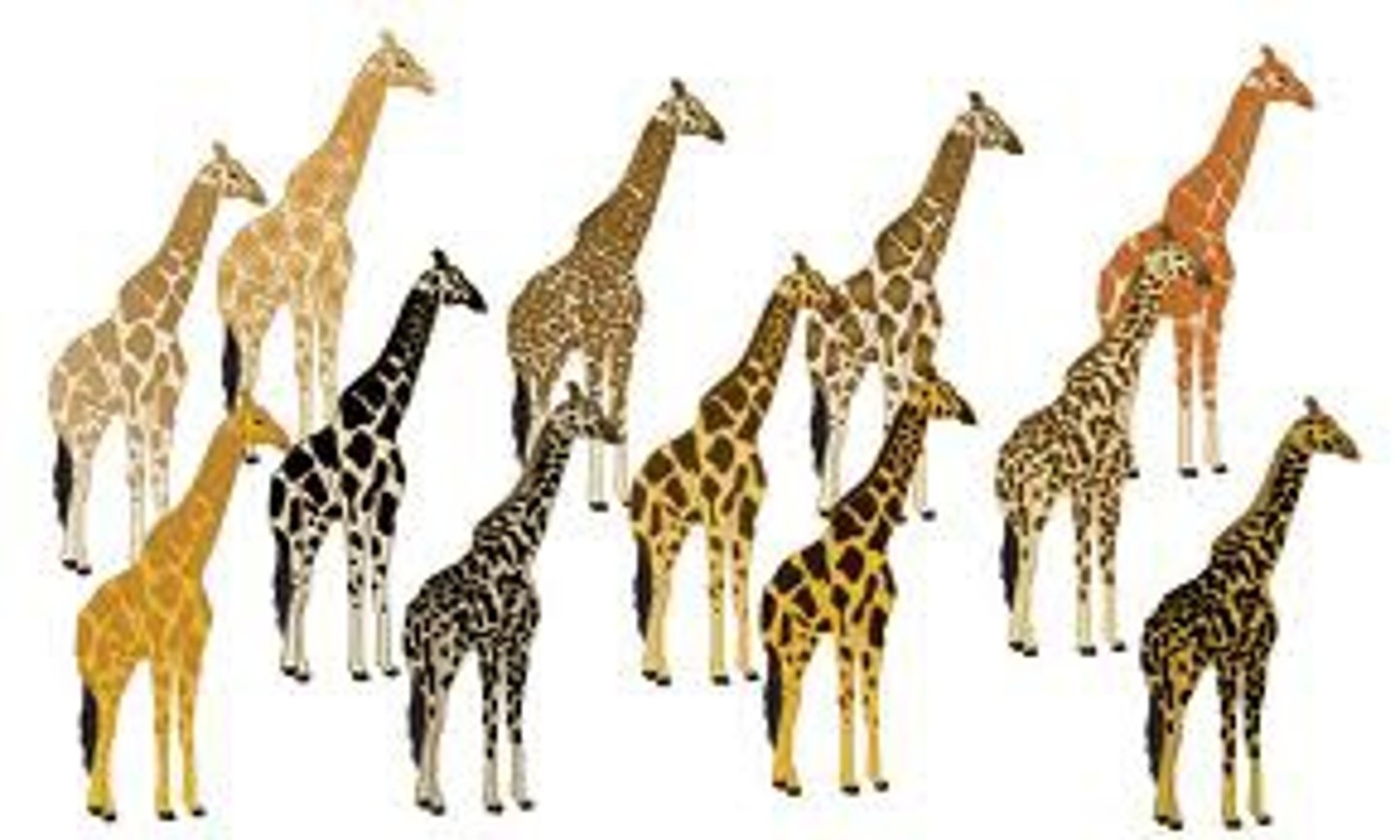
Variation
differences in physical traits of an individual from the group to which it belongs

Heritability
the ability of a trait to be passed down from one generation to the next
Principles of Succession
living organisms are similar to the fossils in their region because they are descended from those ancestors with modification
Lyell
The theory that the earth has been formed over long periods of time with the geological features
evolutionary change (modification)
happens when groups of organisms encounter new environments and over time adapt to those environments via natural selection
descended with modification
according to the theory of evolution, species alive today have a common ancestor from species that lived in the past.
adaptive radiation
An evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species
Biogeography
Study of past and present distribution of organisms
Two structures shared by all vertebrate embryos
post-anal tail & pharyngeal arches (throat)
Tetrapods
vertebrate animals having four feet, legs or leg-like appendages. Ex. (amphibians, mammals, and reptiles)
homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
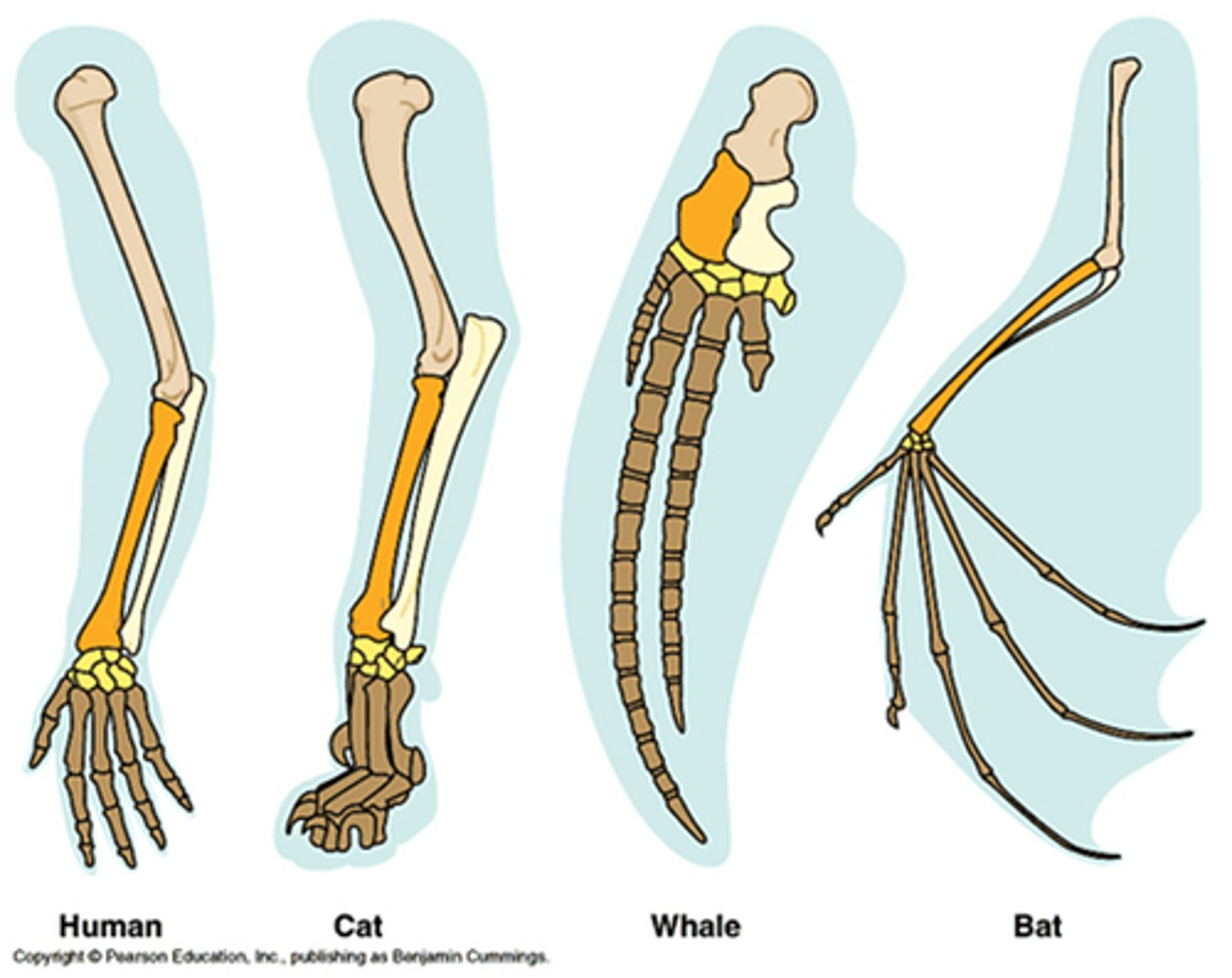
vestigial structures
remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species.
Microevolution
evolutionary change within a species or small group of organisms, especially over a short period.
Macroevolution
large-scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time
Evolution (Micro and Macro)
change in heritable traits (gene pool) over time. Ex. (Mutation, gene flow, genetic drift, natural selection)
Tiktaalik
supposed link between fish and tetrapods (vertebrates with four legs)
Archaeopteryx
supposed link between birds and reptiles and dinosaurs
Extinction
A term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
Homology
A trait that two species share because both species inherited it from their common ancestor.
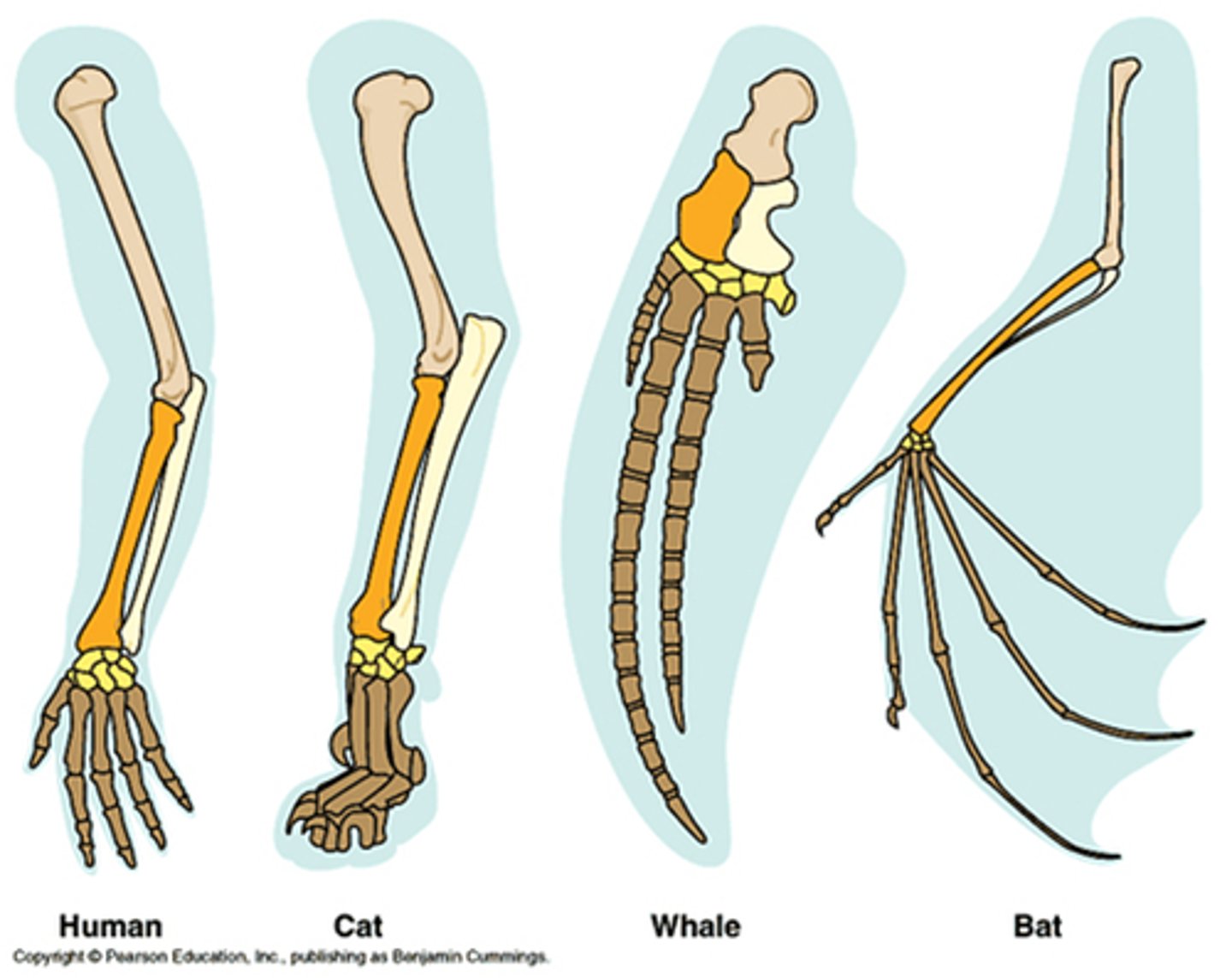
analogous structures
structures that do not have a common evolutionary origin but are similar in function
structural homology
The study of similar structures in different species
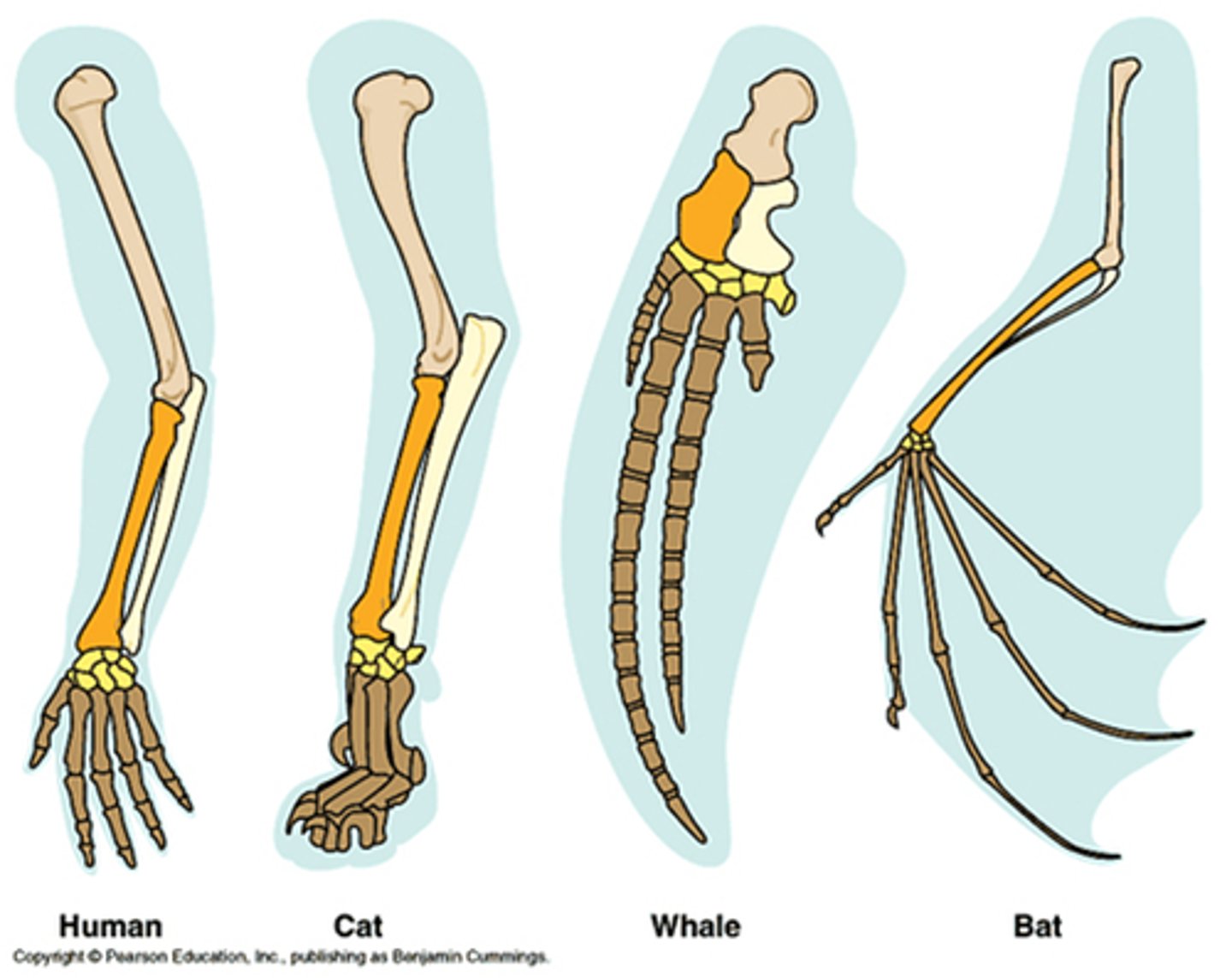
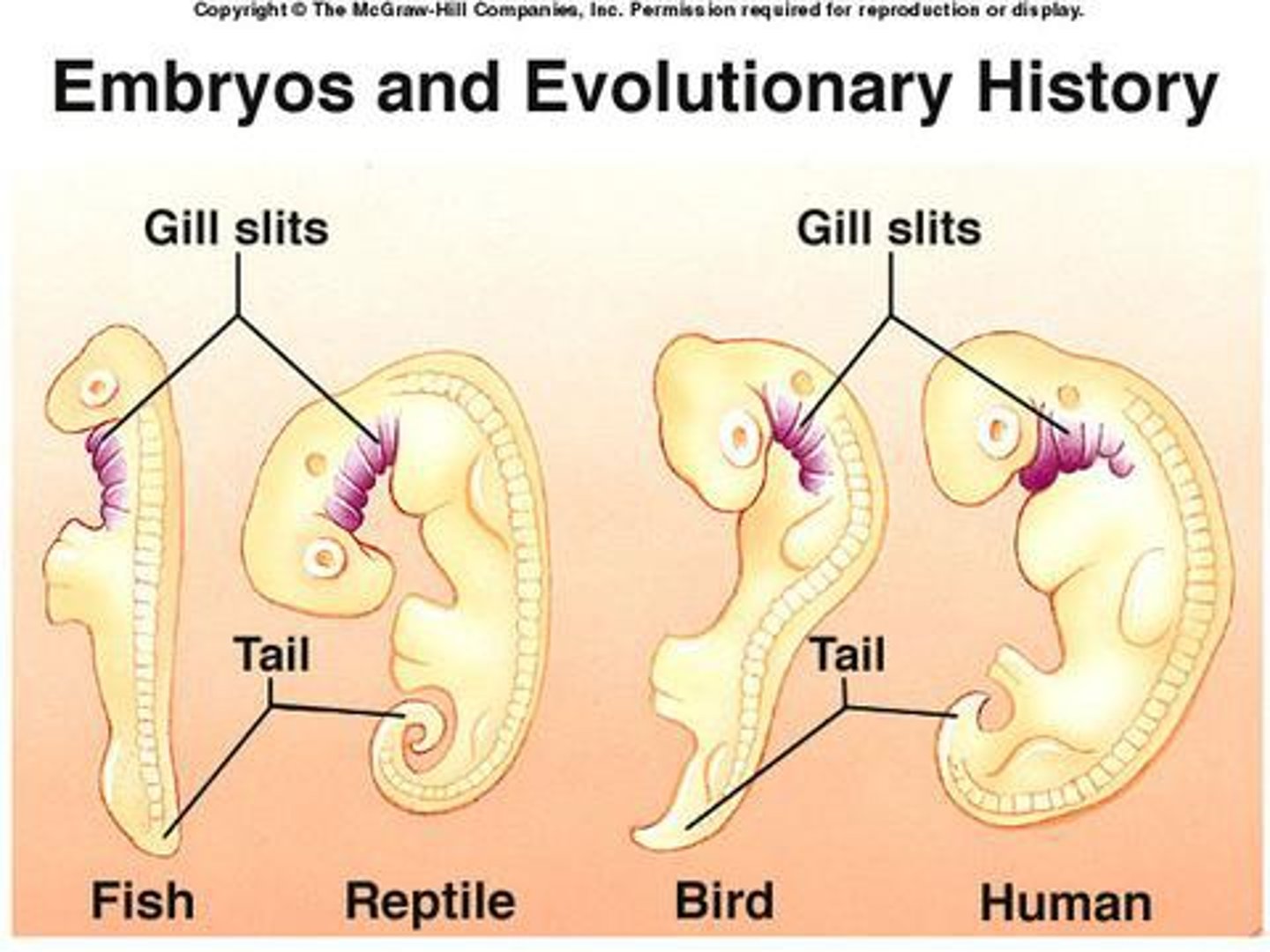
developmental homology
Species that differ as adults but bear striking similarities during embryonic stages
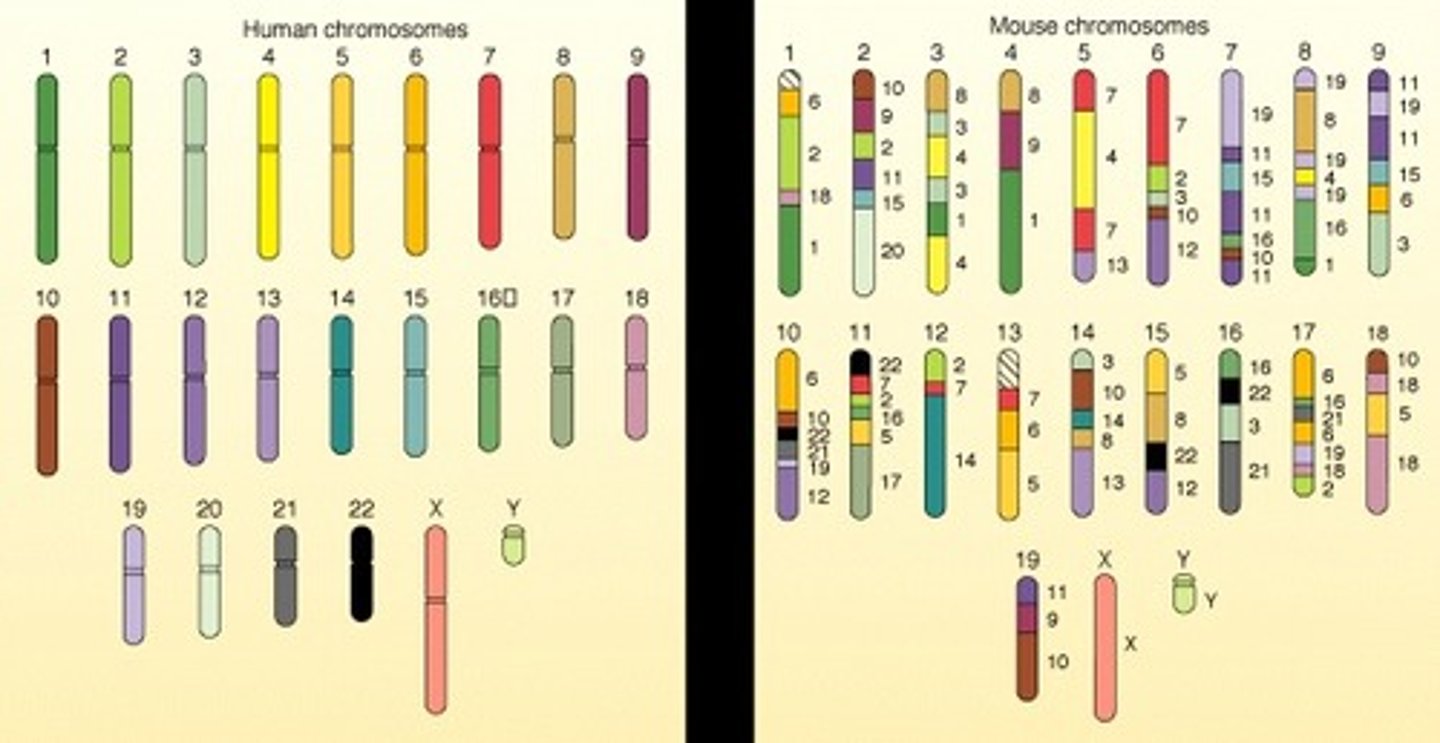
molecular homology
similar DNA (amino acid sequences) among different species from a common ancestor
Phenotypes can be determined by _____.
genes, the environment or both
Modes of Selection
directional, stabilizing, disruptive
directional selection
occurs when natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of a trait
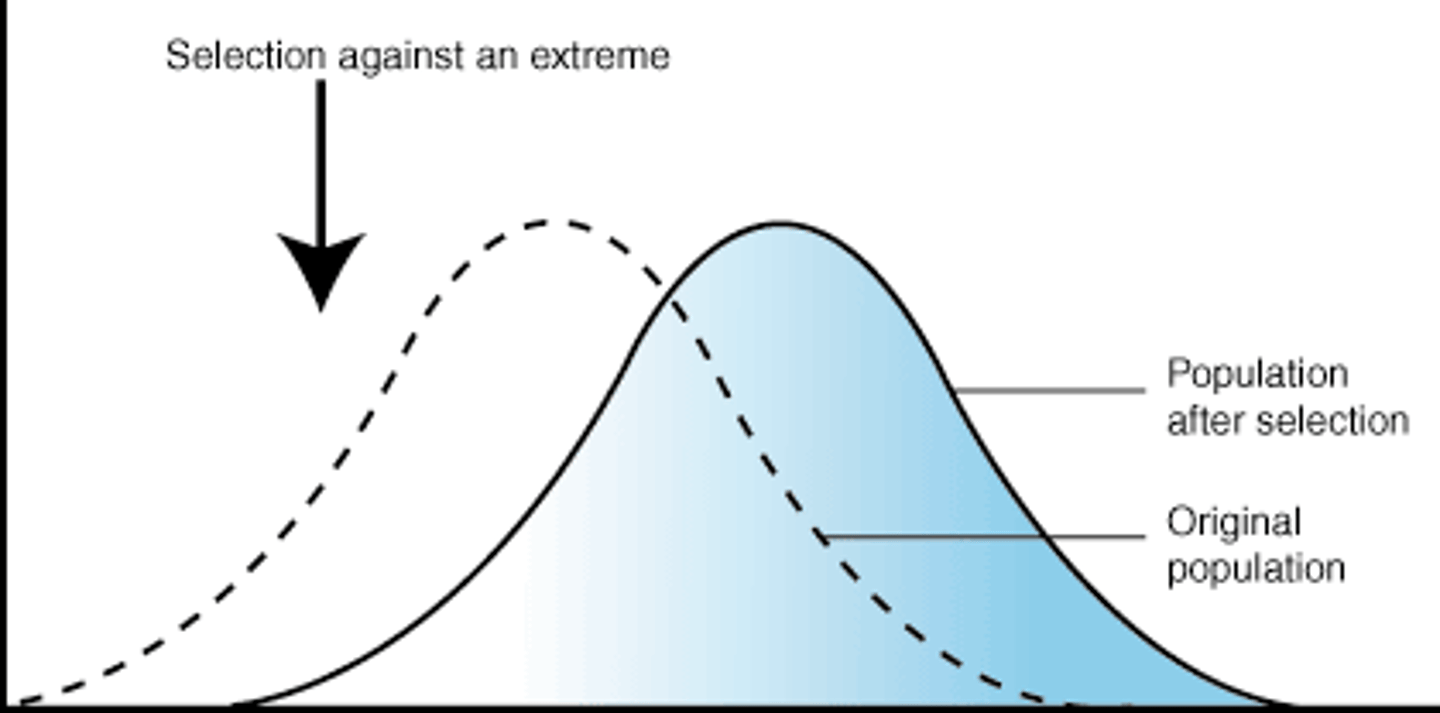
directional selection effect
population mean: changes
population variation: decreases
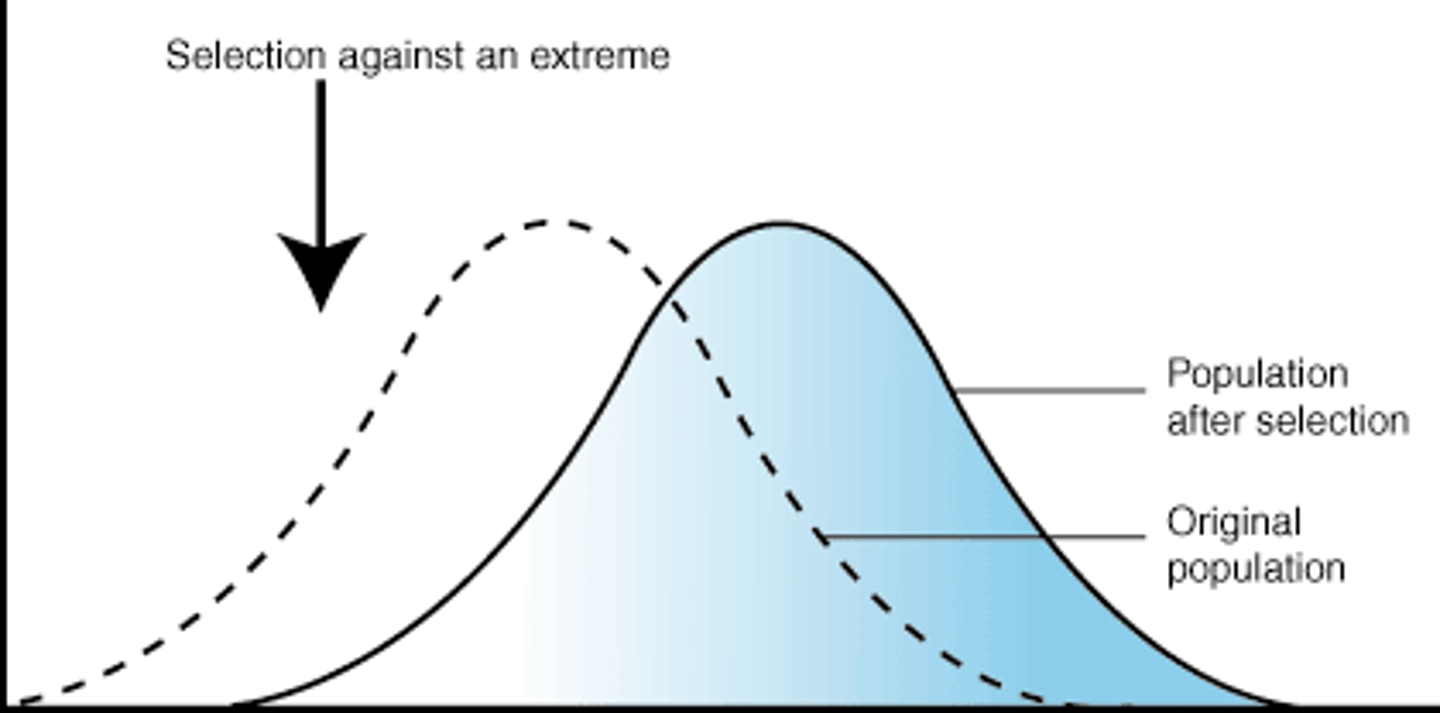
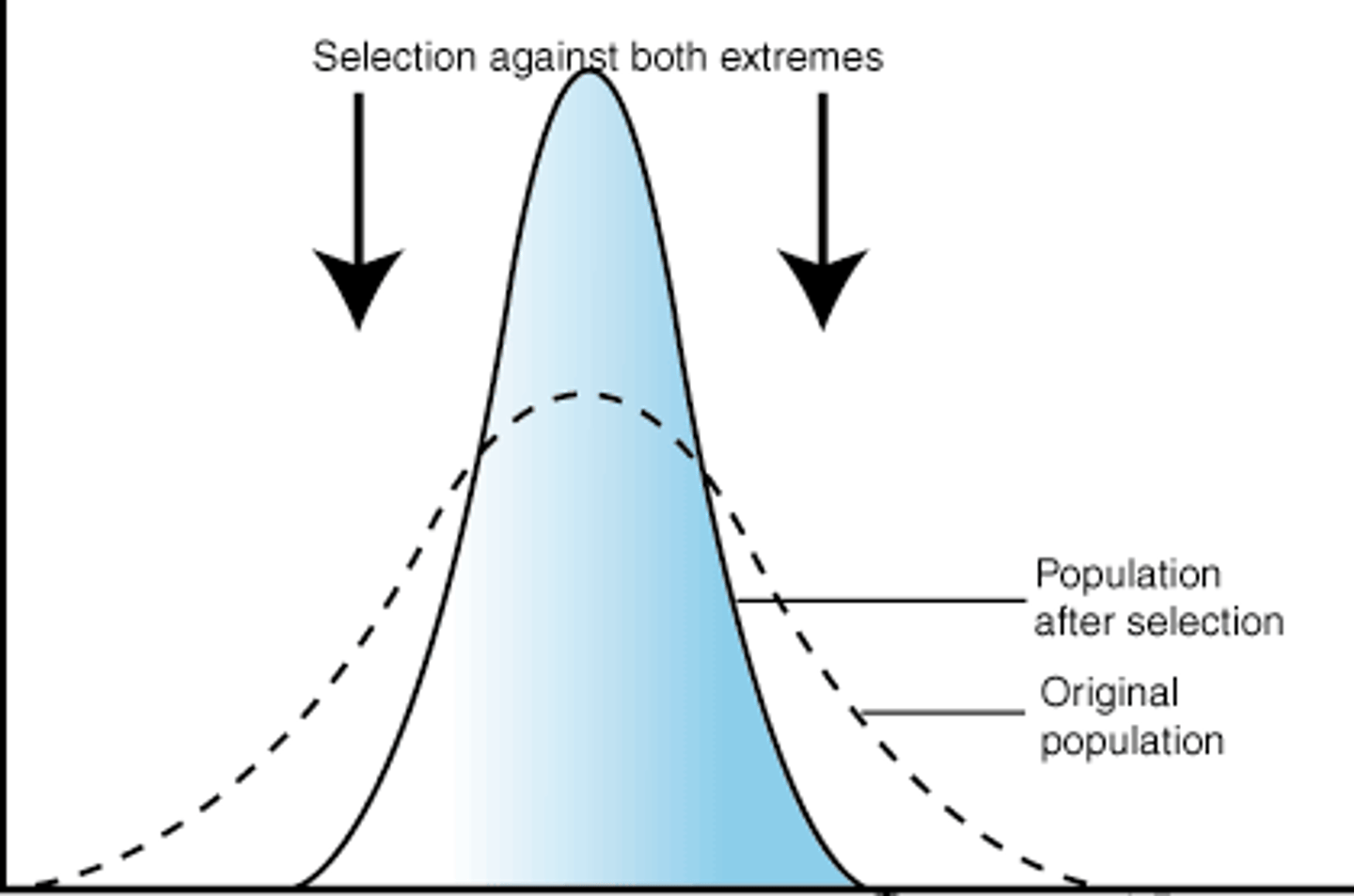
stabilizing selection
natural selection that favors average individuals in a population; results in a decline in population variation
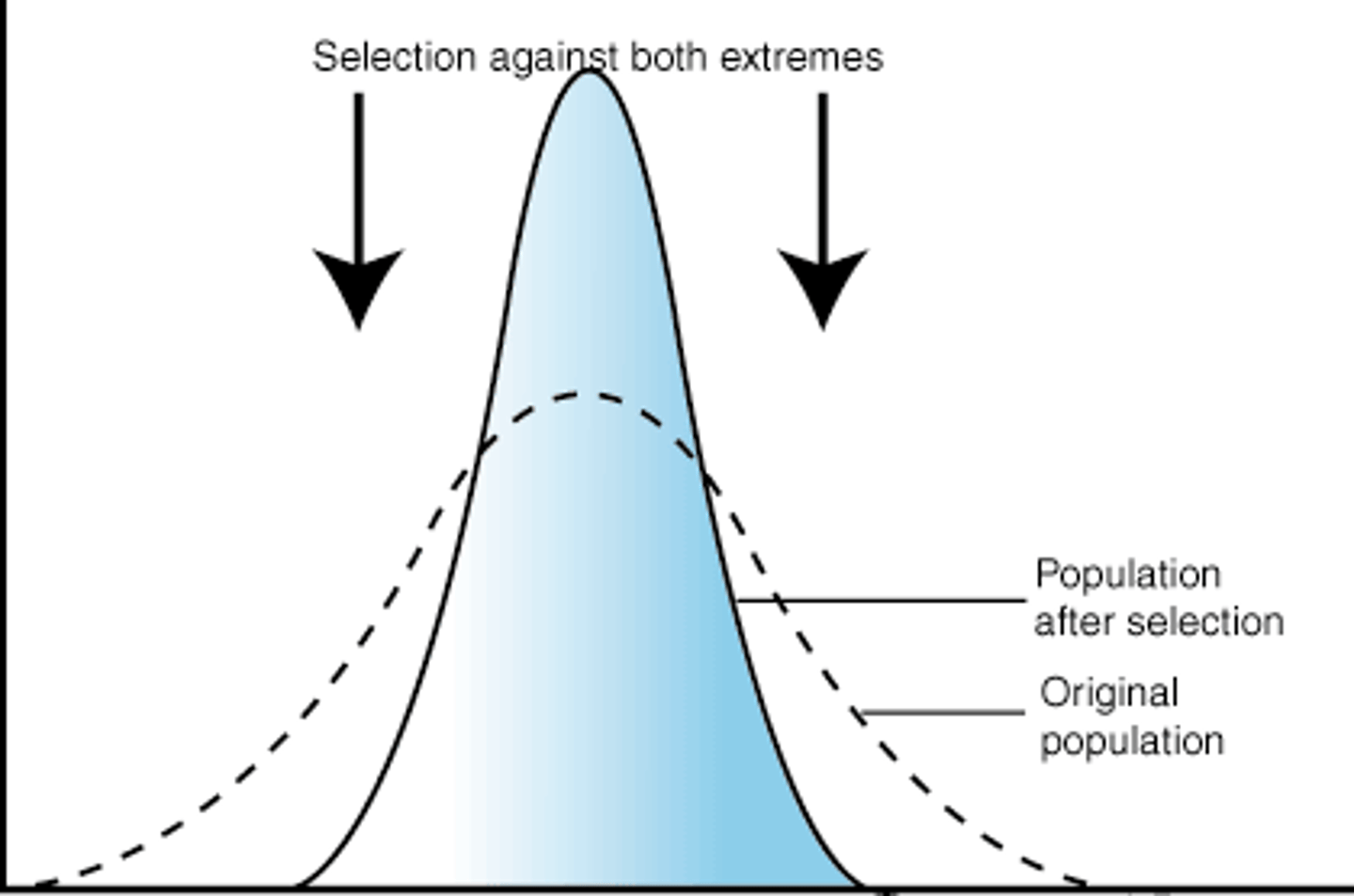
stabilizing selection effect
population mean: stays
population variation: decreases
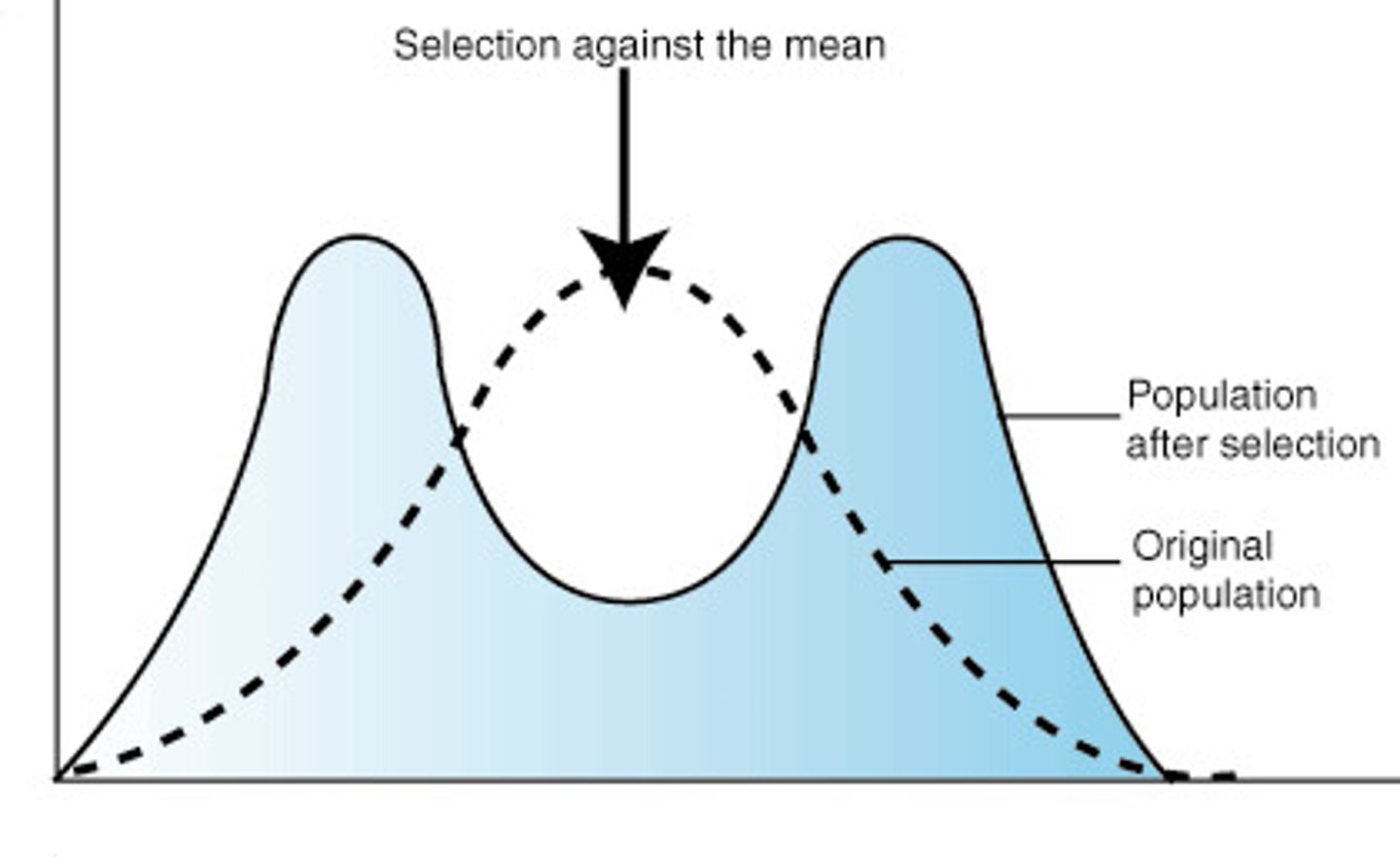
disruptive selection
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotype range
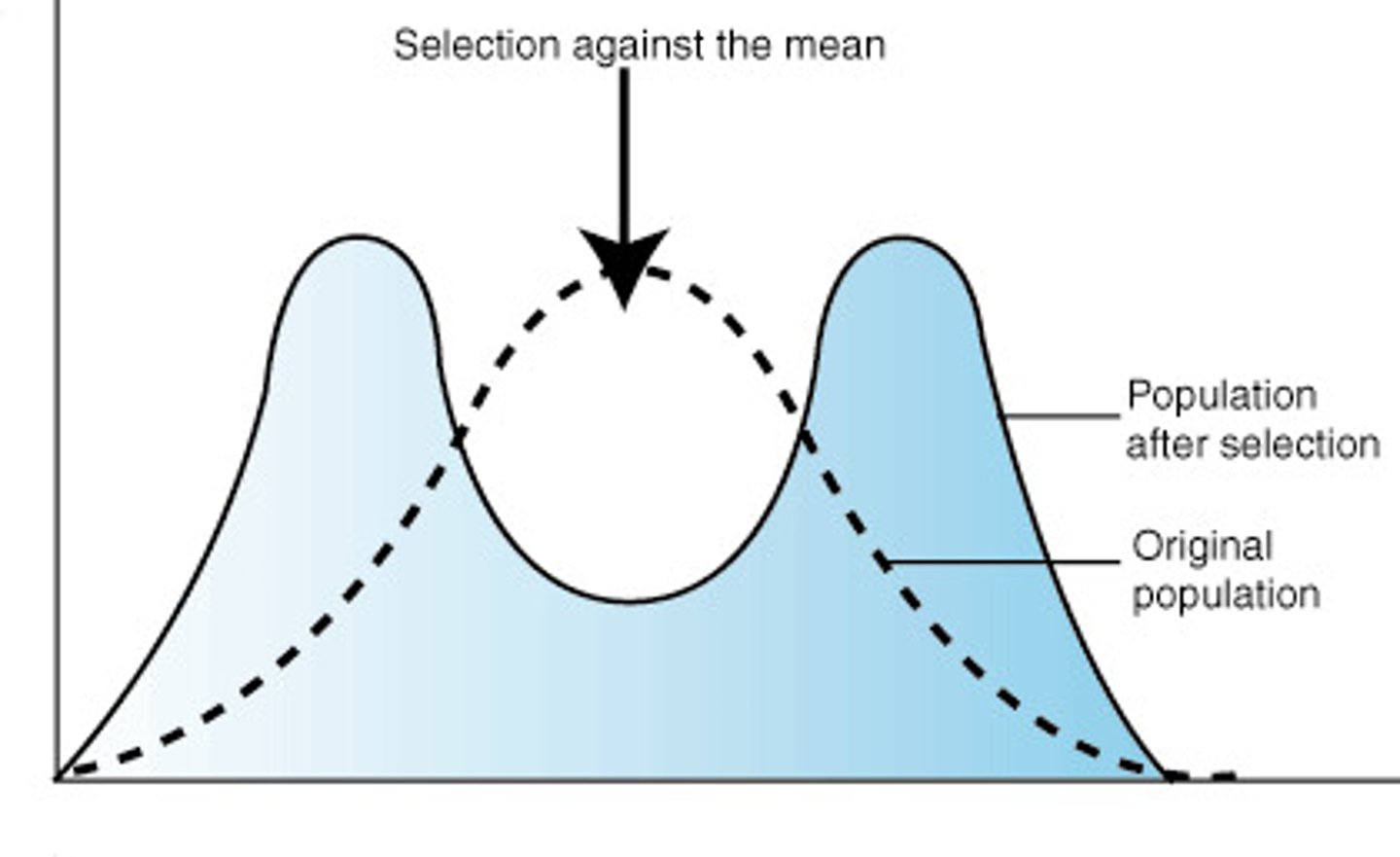
disruptive selection effect
population mean: stays
population: increases
relative fitness
The contribution of one genotype to the next generation compared to that of alternative genotypes for the same locus.
sexual selection
A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates.
sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species.
intrasexual selection
competition among individuals of one sex (often males) for mates of the opposite sex
balancing selection
Natural selection that maintains stable frequencies of two or more phenotypic forms in a population.
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
frequency-dependent selection
the fitness of a phenotype depends on how common it is in the population
Heterozygous advantage
Heterozygous alleles have greater selective advantage than either homozygous condition.
BEST definition of evolution
Genetic change over time
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE)
condition that occurs when the frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time
Process that violates HWE
1. Genetic Drift
2. Natural Selection
3. Gene Flow
4. Mutation
5. Non-random mating
genetic drift
A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance
gene flow
movement of alleles from one population to another
calculating OBSERVED HWE 1)Genotype
((TT or Tt or tt)/Total individuals)
To check work. All answers + together = 1

calculating OBSERVED HWE 2)Allele
(2(TT or tt)+Tt)/(2(Total individual))
To check work. All answers + together = 1

calculating EXPECTED HWE
p=Freq of T
q=Freq of t
Freq of TT= p^2
Freq of tt= q^2
Freq of Tt= 2pq
To check work. All answers + together = 1
Compare observed genotypes to predicted genotypes under HWE
Observed = expected genotype -> no evolution + random mating
Observed different from expected genotype -> may be evolving
gene pool
all copies of every type of allele at every locus in all members of the population
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
condition that occurs when the frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time
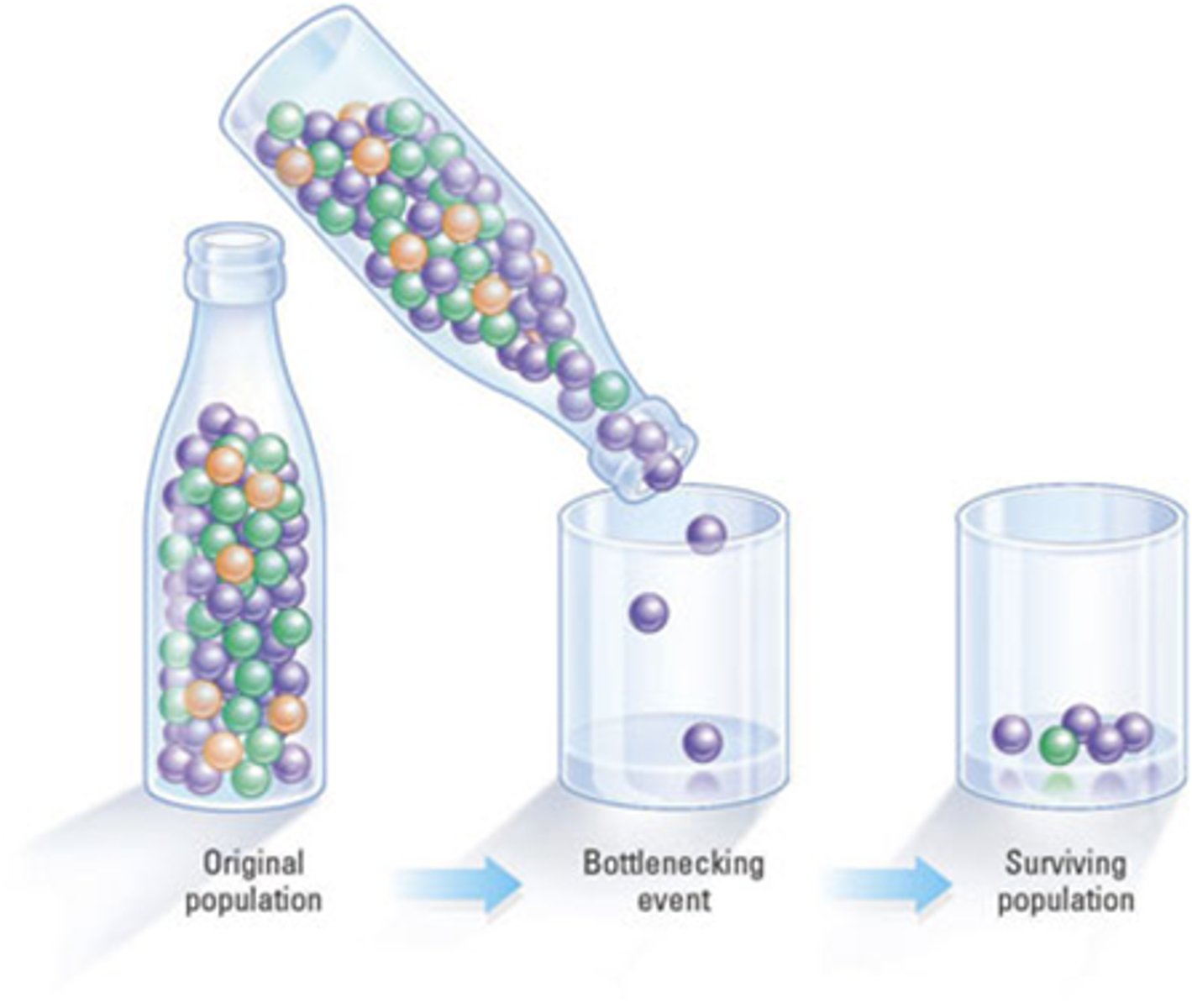
Bottleneck Effect
sudden change that drastically reduces population size, genetic diversity and allele frequencies
Ex) Natural disaster
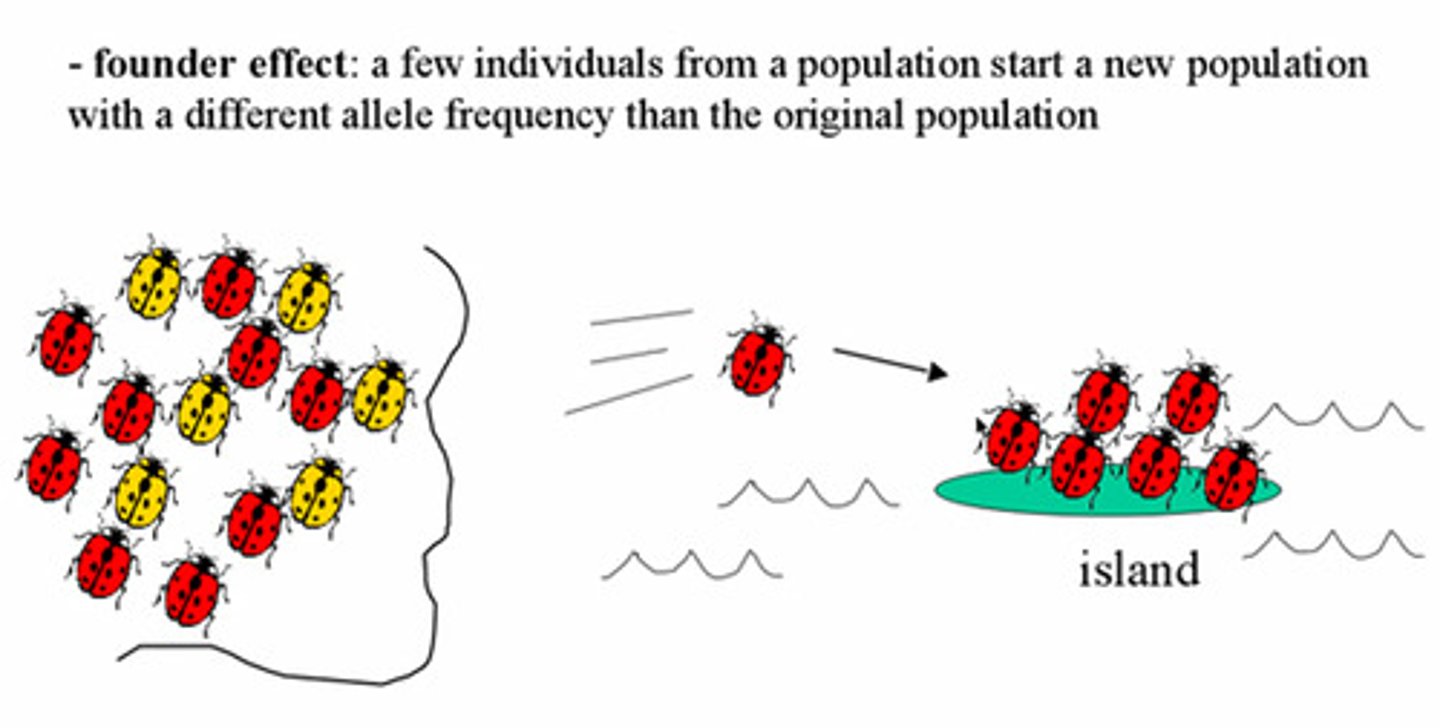
Founder Effect
small number of individuals start a new population and new allele frequences
Ex) Finches moving to a new island
adaptive evolution
a process in which traits that enhance survival or reproduction tend to increase in frequency in a population over time
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group of species.
phylogenetic tree
A family tree that shows the evolutionary relationships thought to exist among groups of organisms
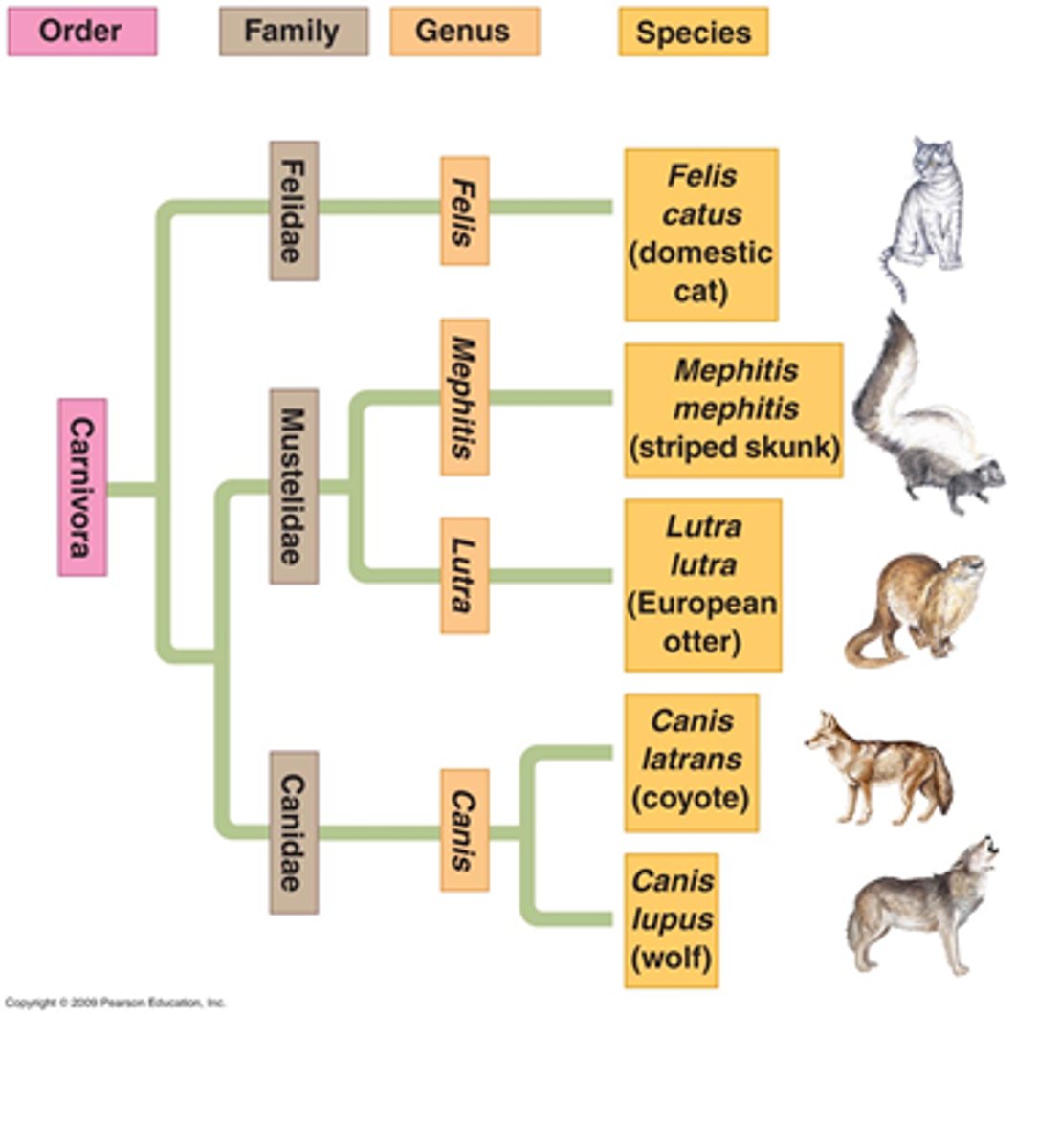
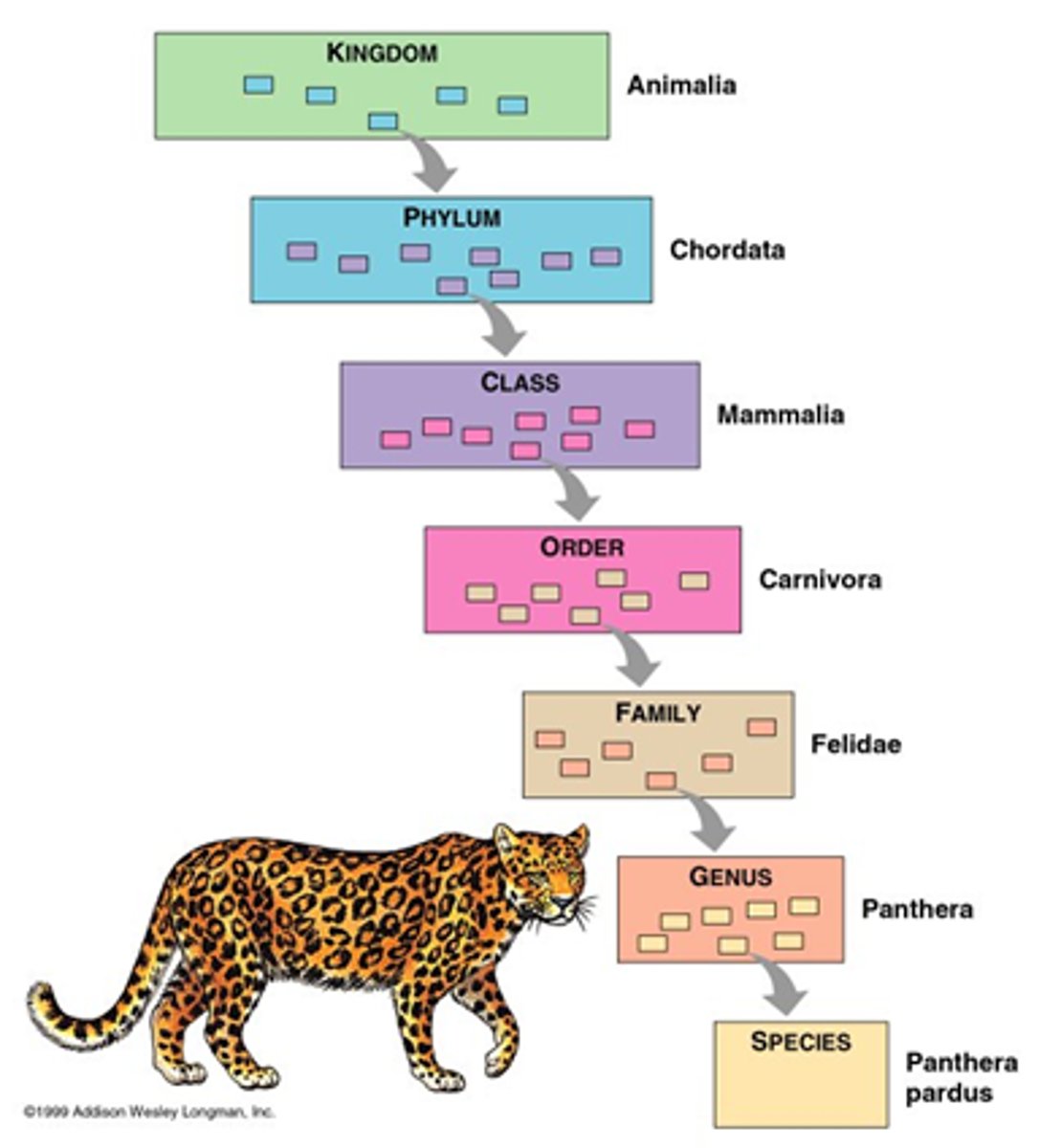
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
Binomial
A polynomial with two terms
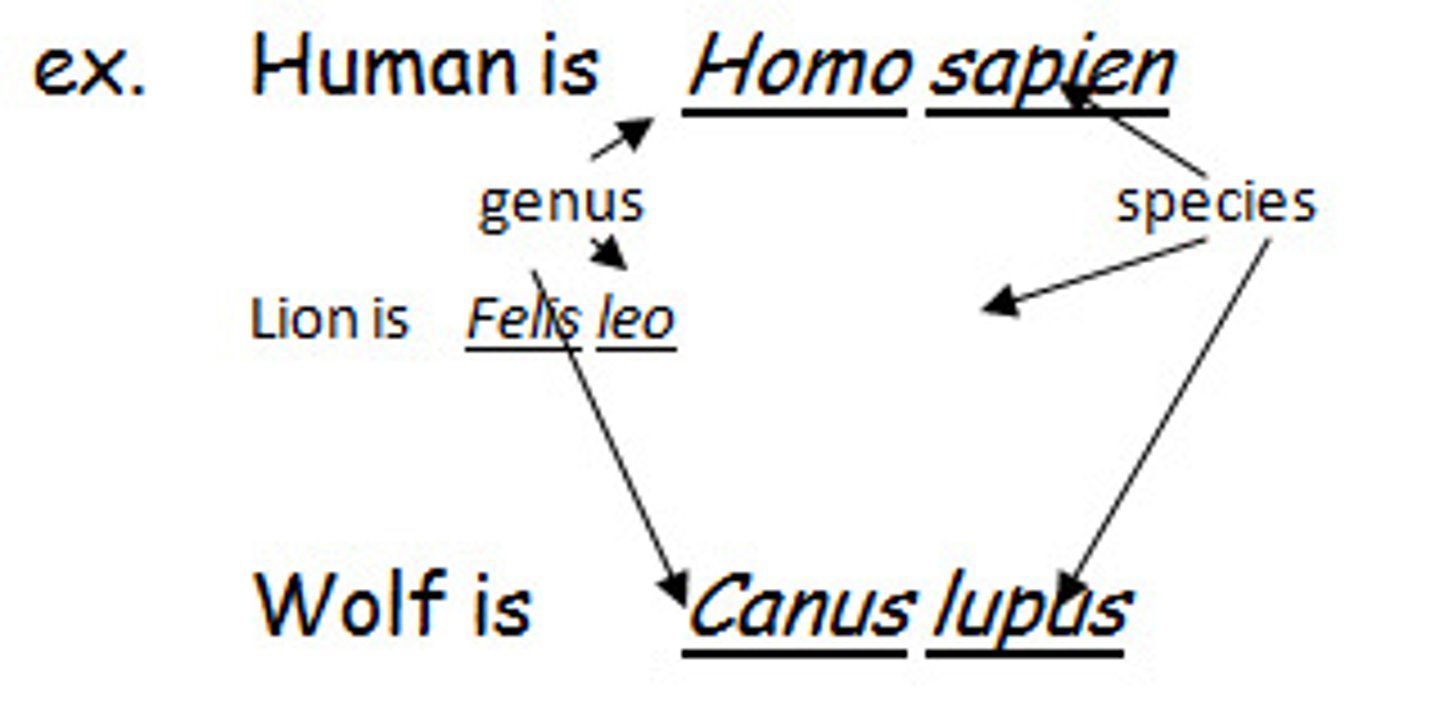
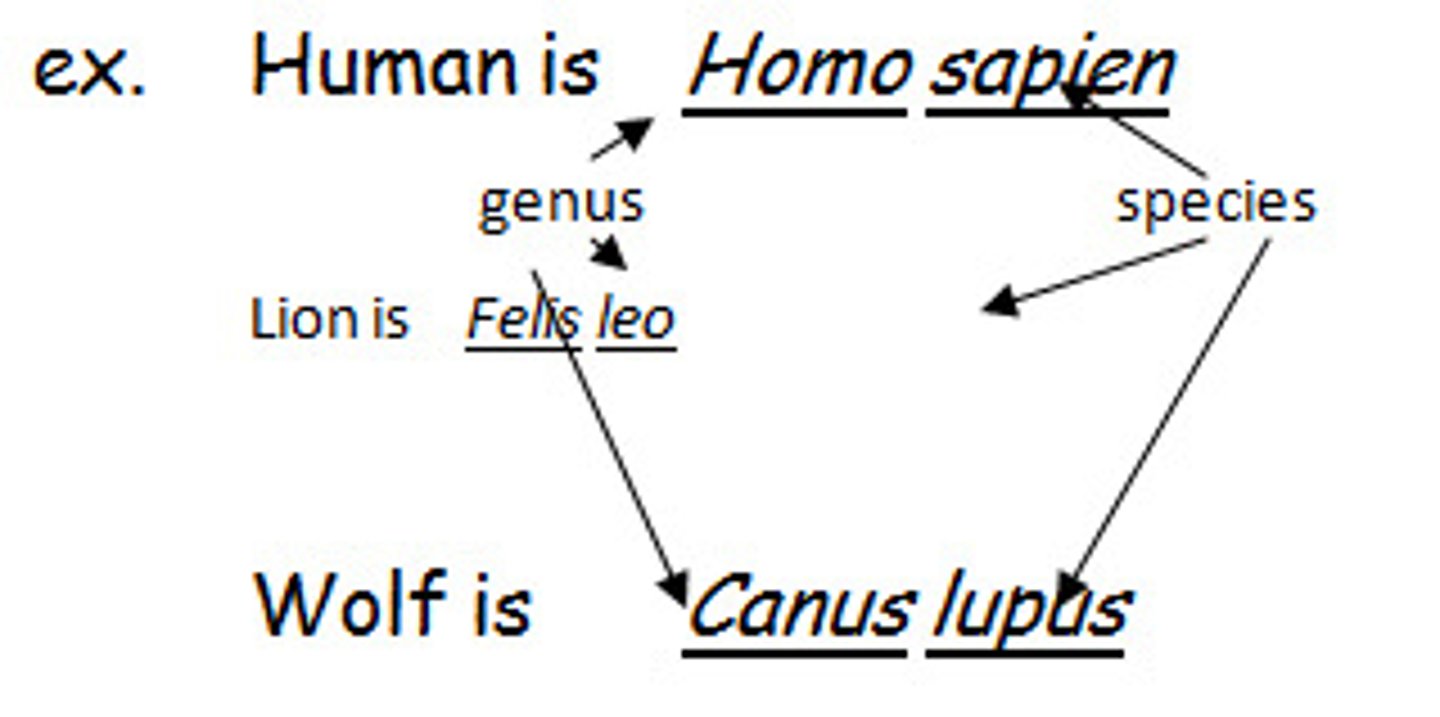
genus and species
scientific name
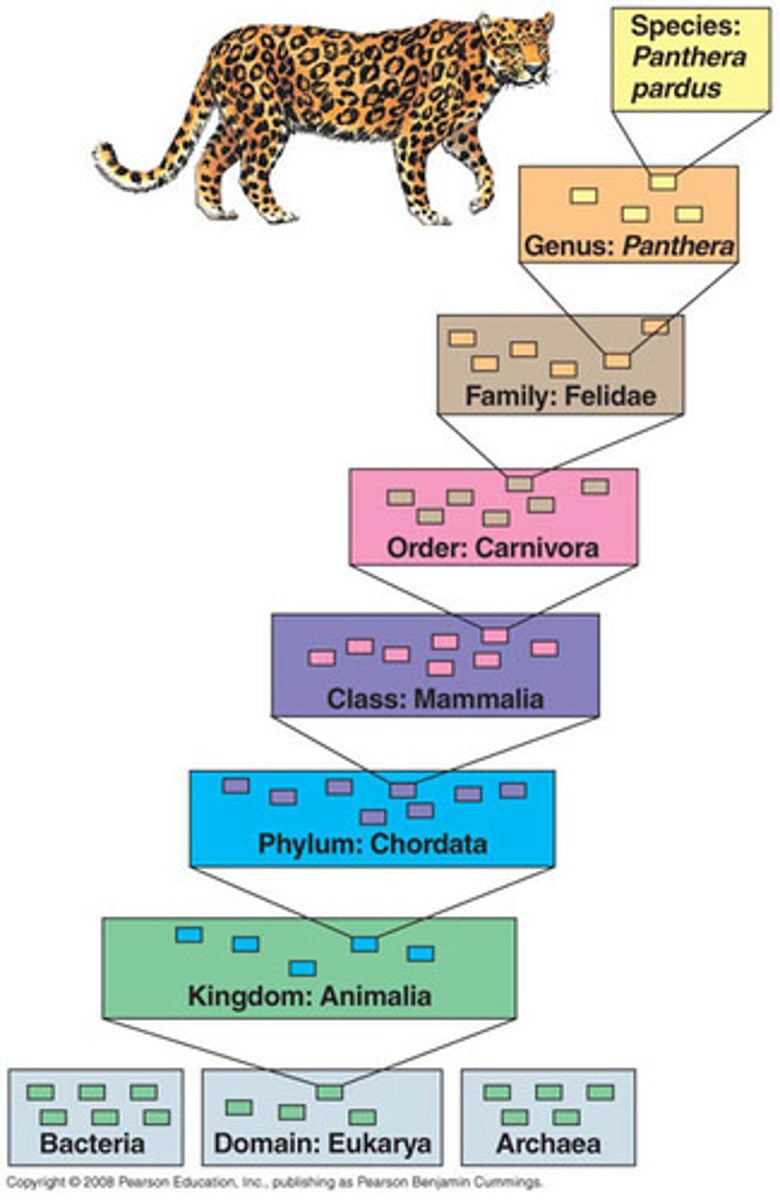
Linnaean System
Classification system useful for storing and finding information about living things
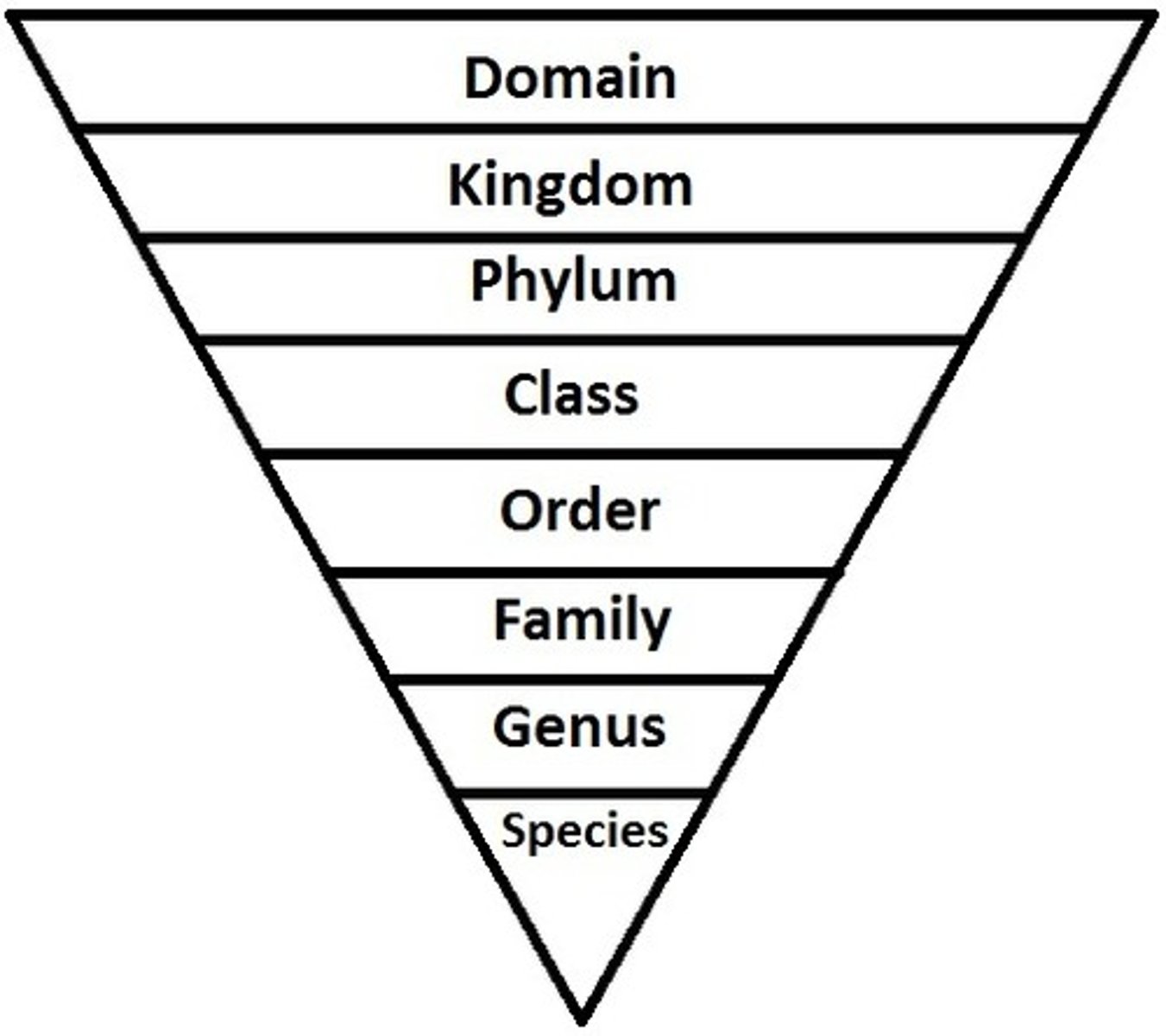
Taxon
group or level of organization into which organisms are classified
branch point
the representation on a phylogenetic tree of the divergence of two or more taxa from a common ancestor
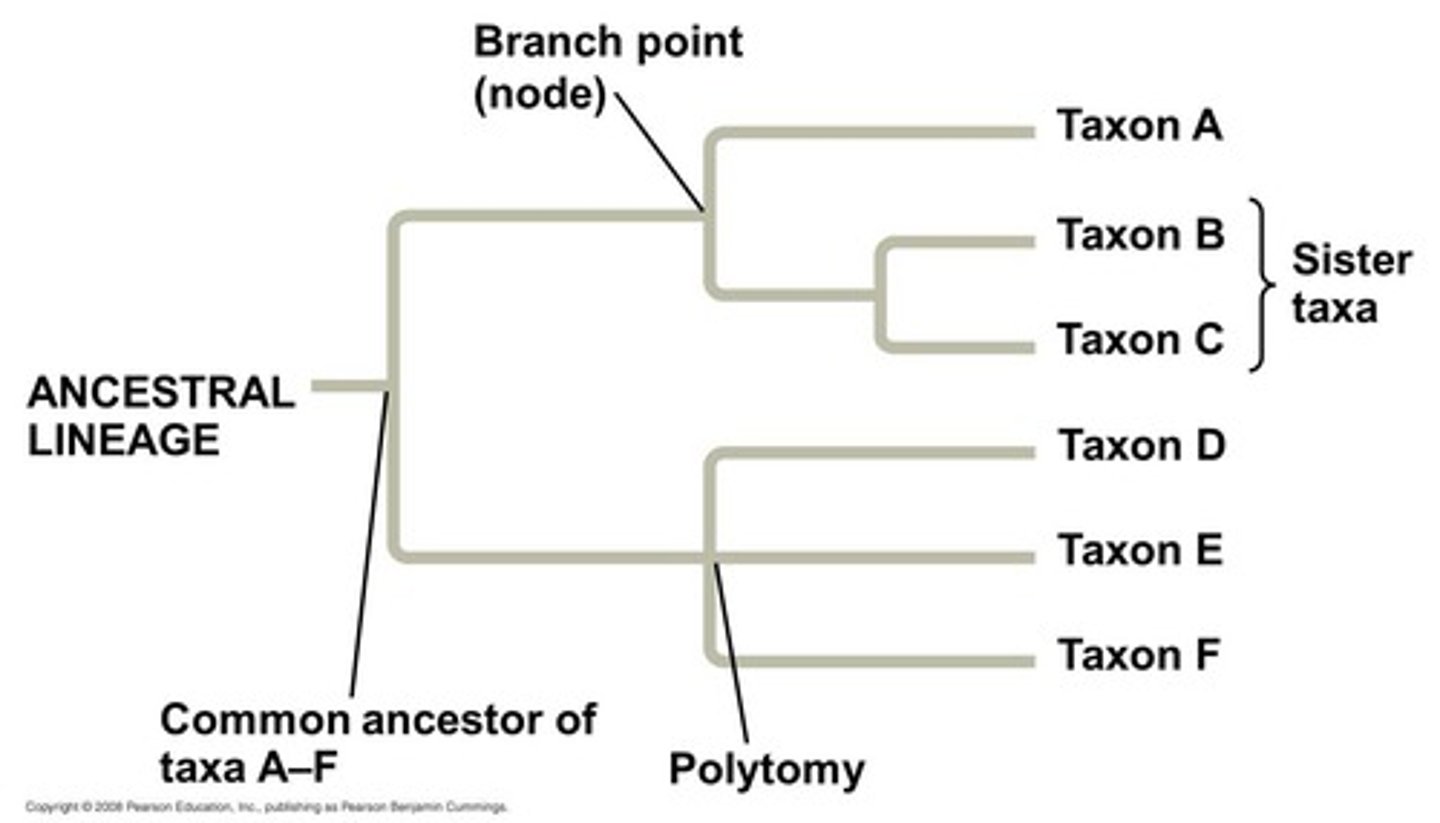
sister taxa
Groups of organisms that share an immediate common ancestor and hence are each other's closest relatives.
Natural selection (genotype)
can select for same genotype and against others,
non-random mating (genotype)
mating between individuals of the same phenotype or by those who live nearby (excess homozygotes or heterozygotes)
non-random mating
mates chosen on basis of physical or behavioral characteristics
assortive mating (genotype)
an individual chooses mates that are similar to itself (produces excess homozygotes)
genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes or other DNA segments
neutral variation
differences in DNA sequence that do not confer a selective advantage or disadvantage
Adaptive Selection
evolution that results in a better match between organisms and their environment
root
the most ancestral branch in the tree
Analogy
phylogeny is similarity between organisms due to convergent evolution rather than to a shared ancestry (homology)
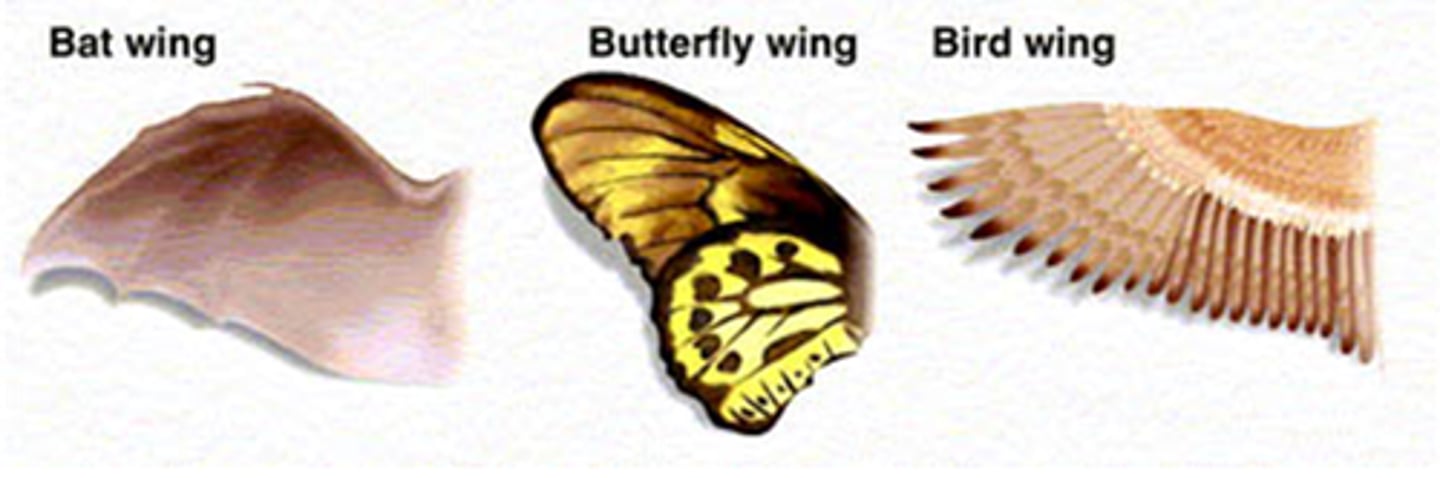
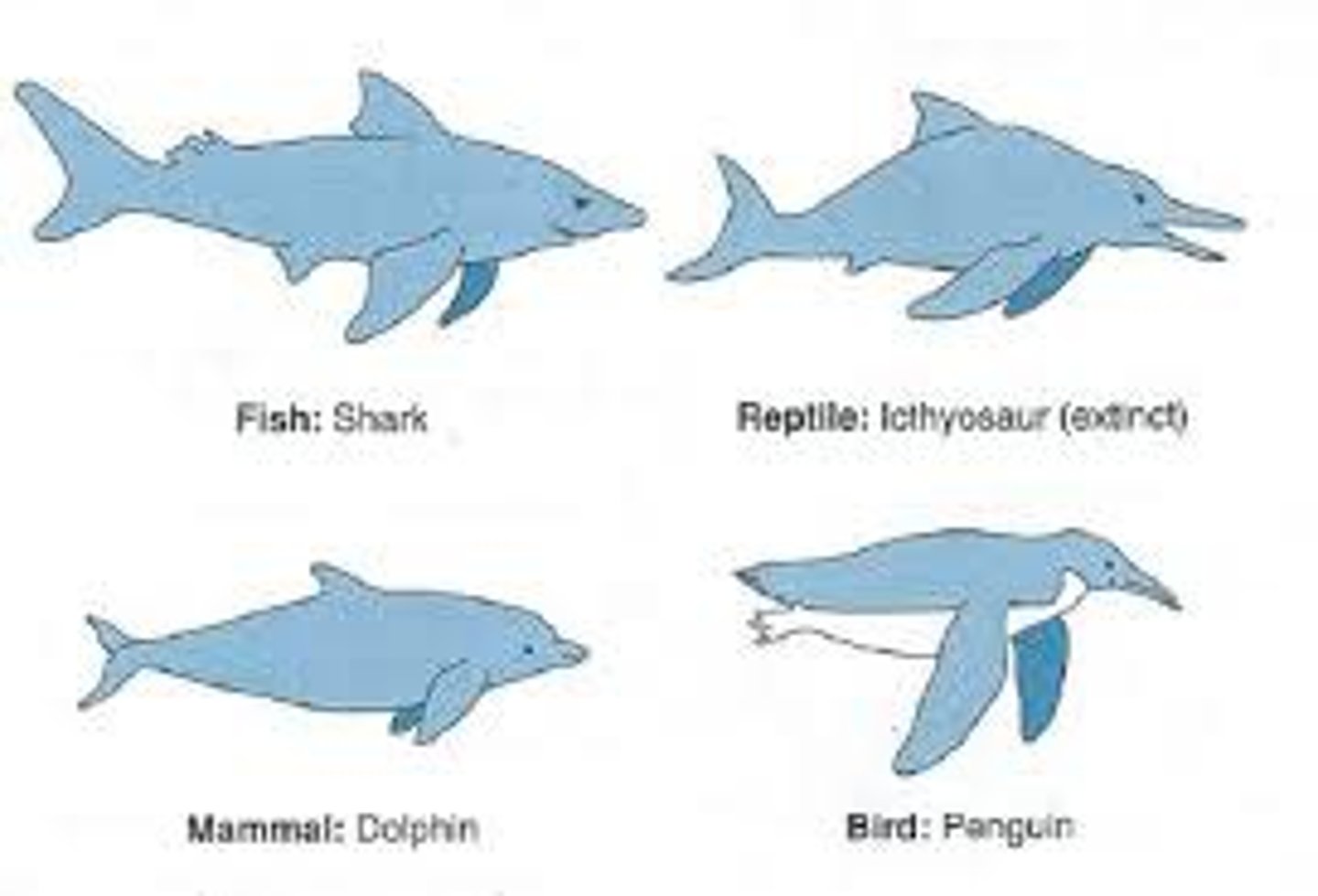
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
Cladistics
classification based on common ancestry
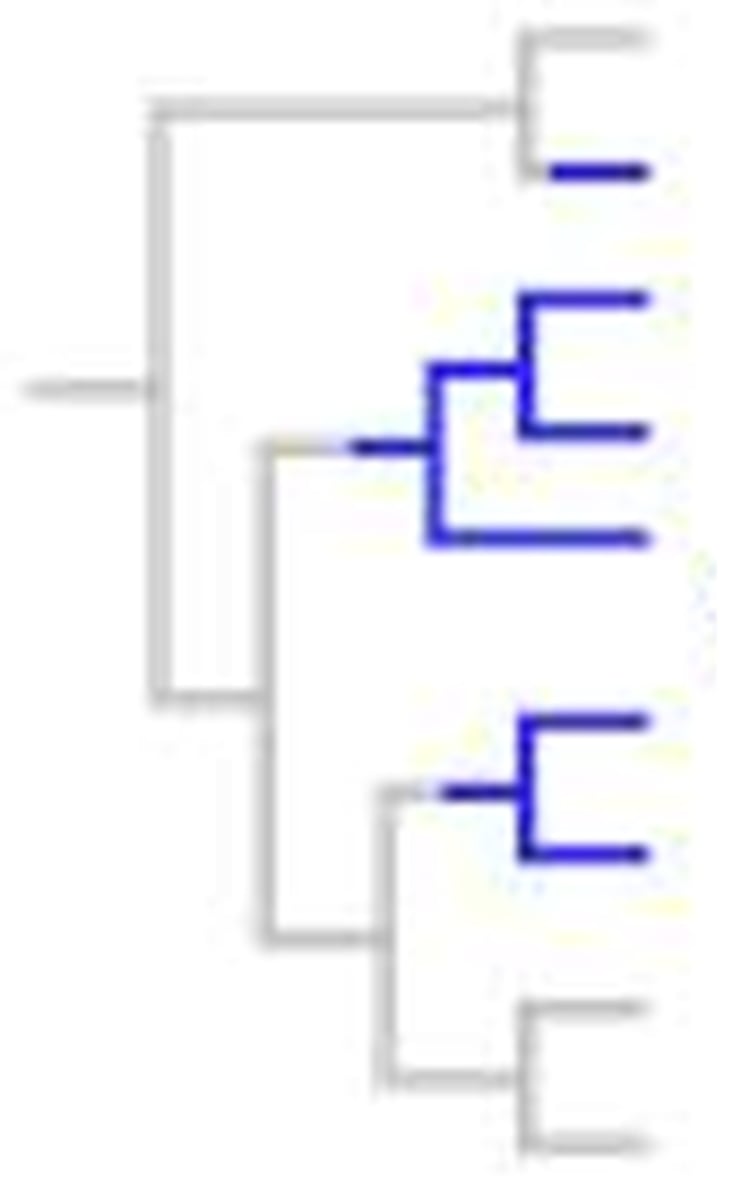
monophyletic
ALL descendants came from one common ancestor
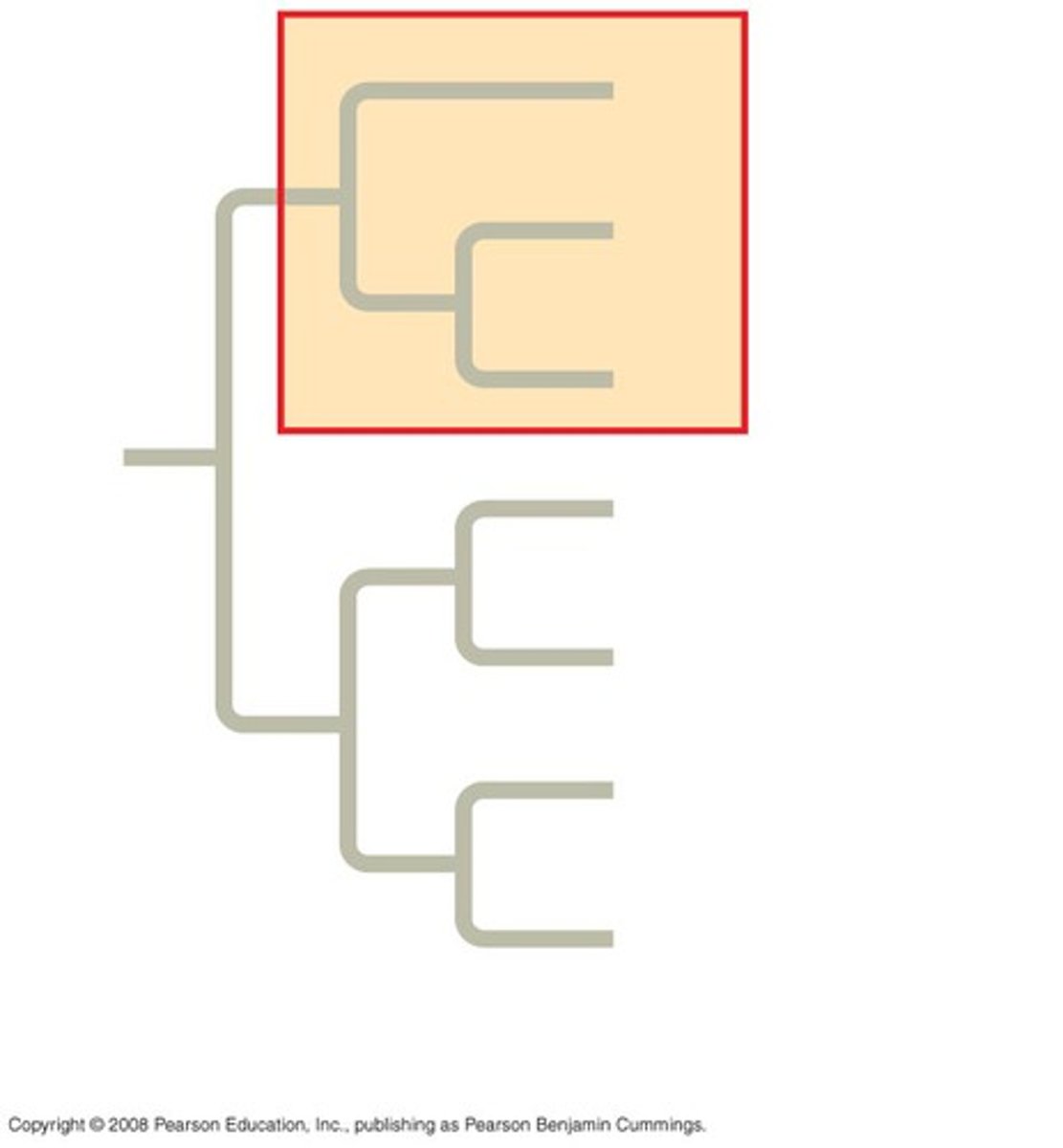
non-monophyletic
Pertaining to a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants.
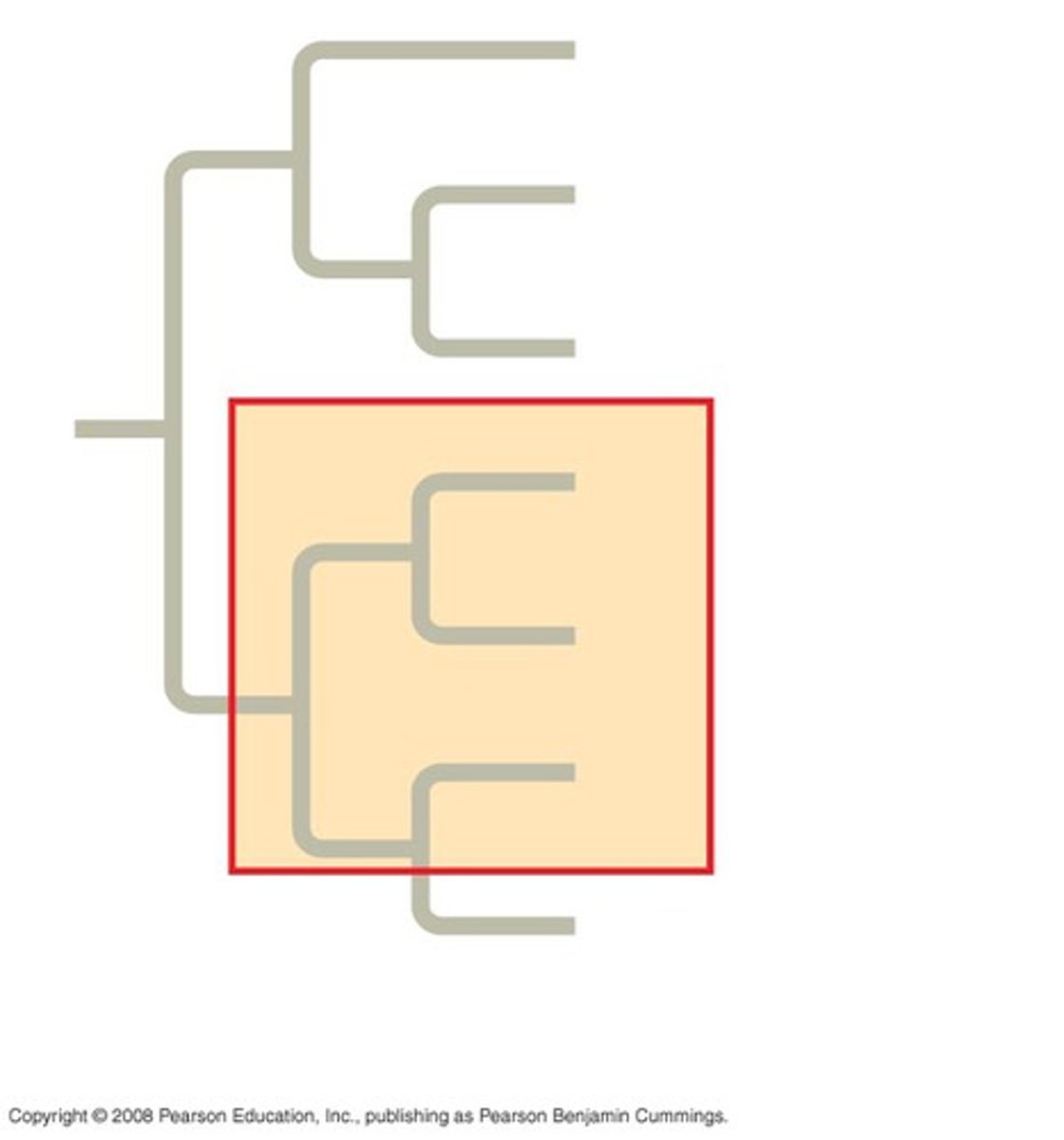
polyphyletic
pertaining to a group of taxa derived from two or more different ancestors
shared ancestral character
a character that originated in an ancestor of the taxon
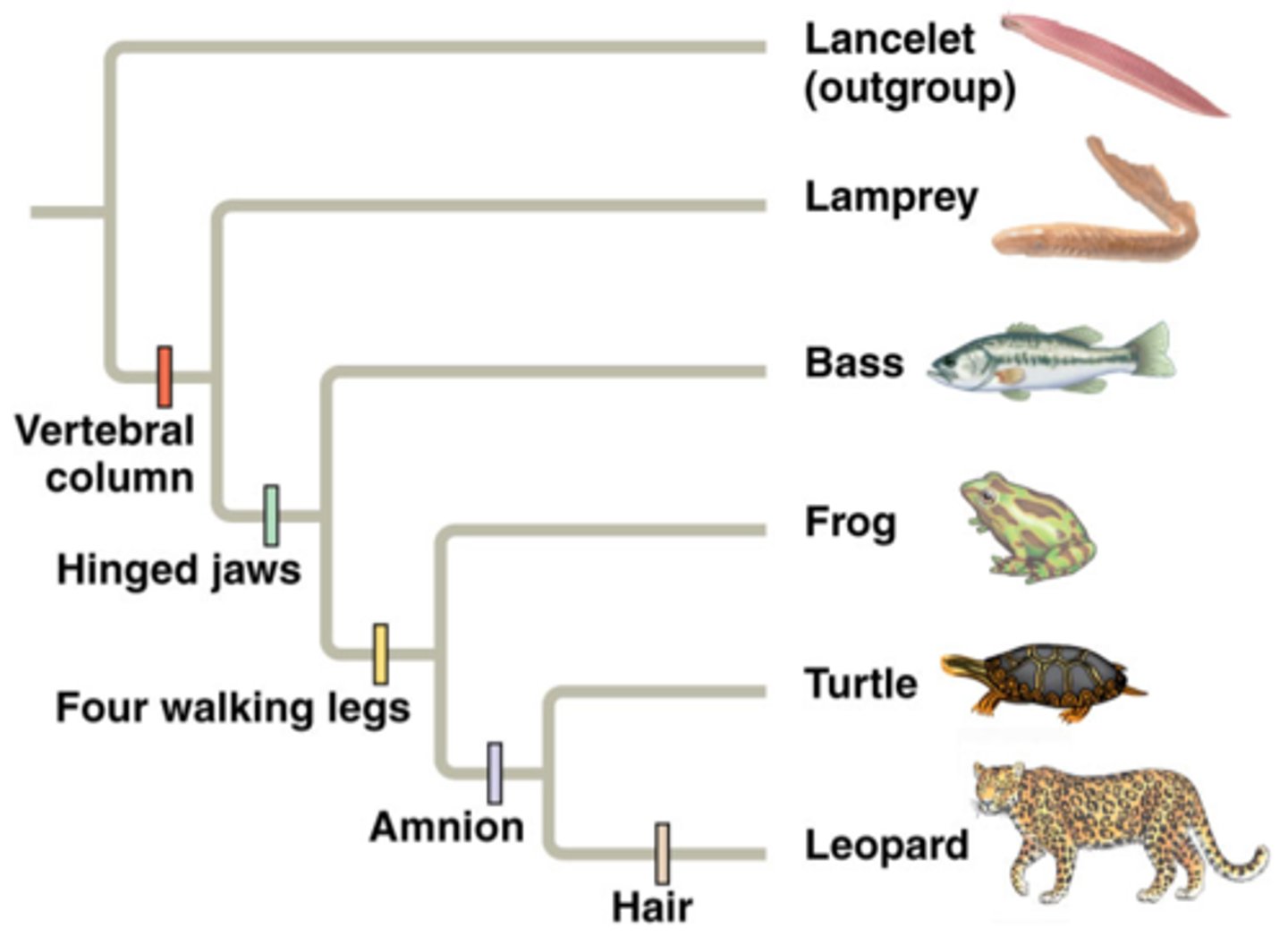
shared derived character
an evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade
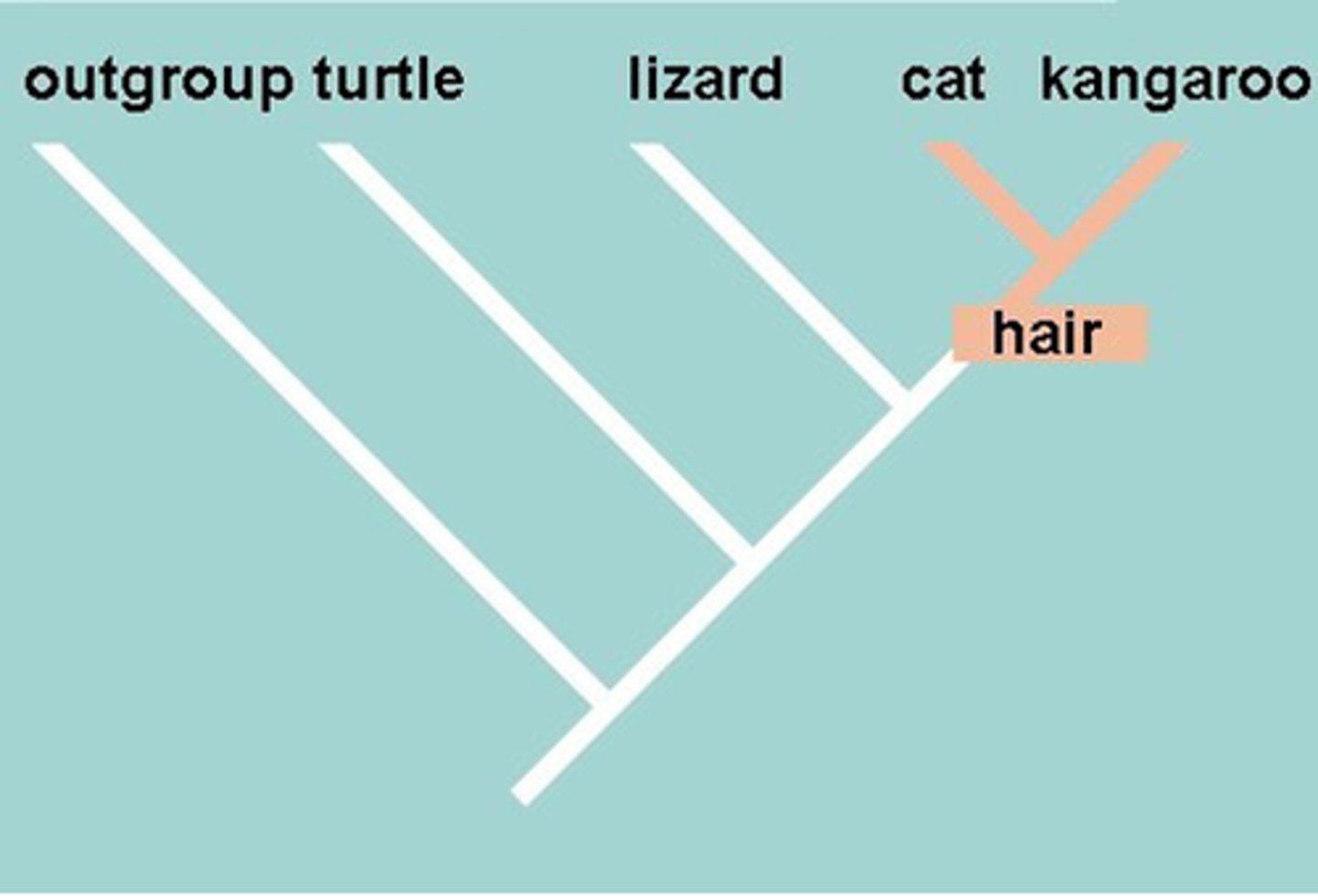
outgroup
generally, any group that one does not belong to
Write this tree as a set of nested paratheses
((A,B),C)
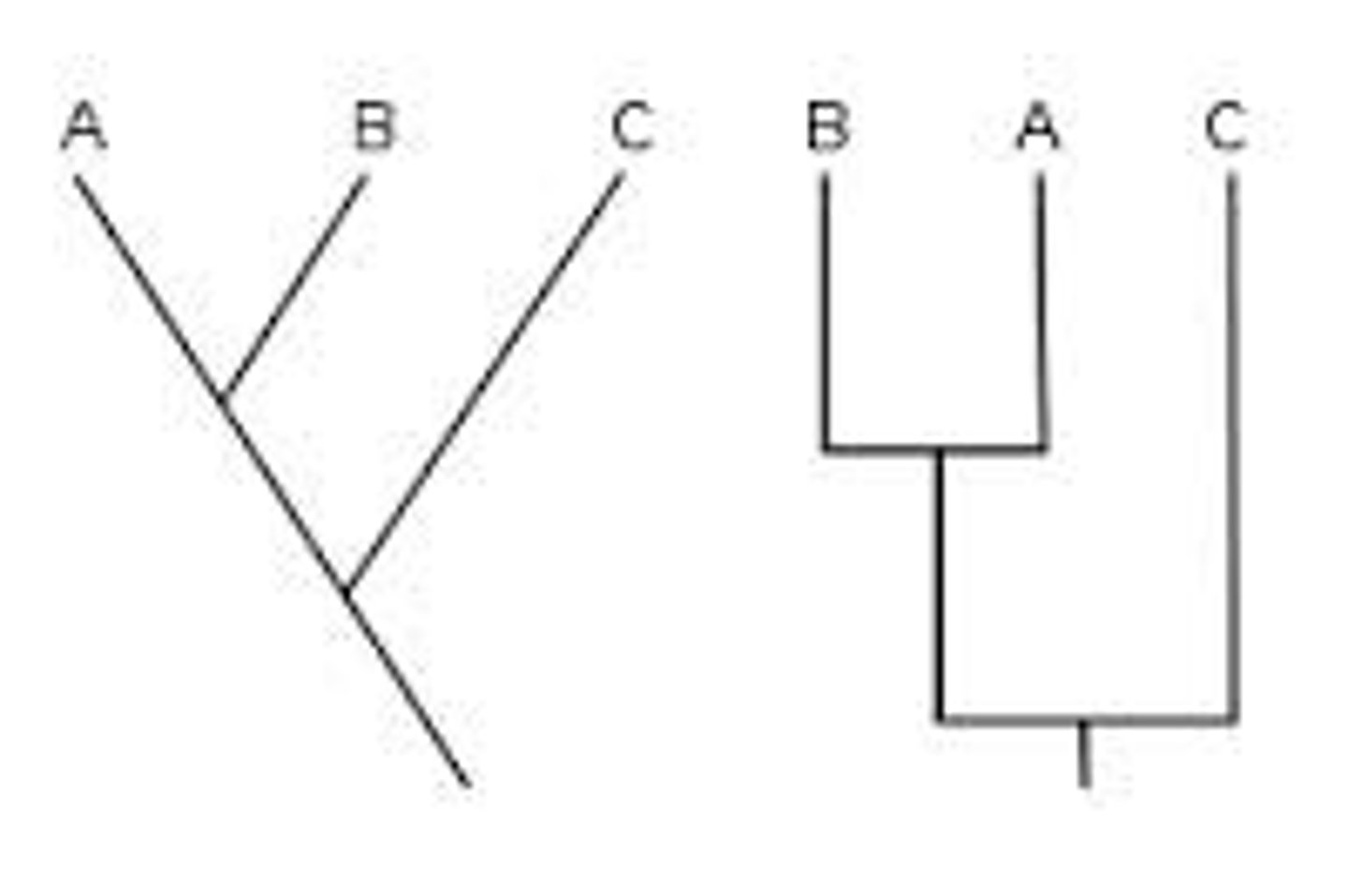
Parsimony Tree
Tree with fewest evolutionary changes is most likely to be correct