The output gap
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
When does a negative an output gap occur?
If there is a difference between actual and potential output in the economy.
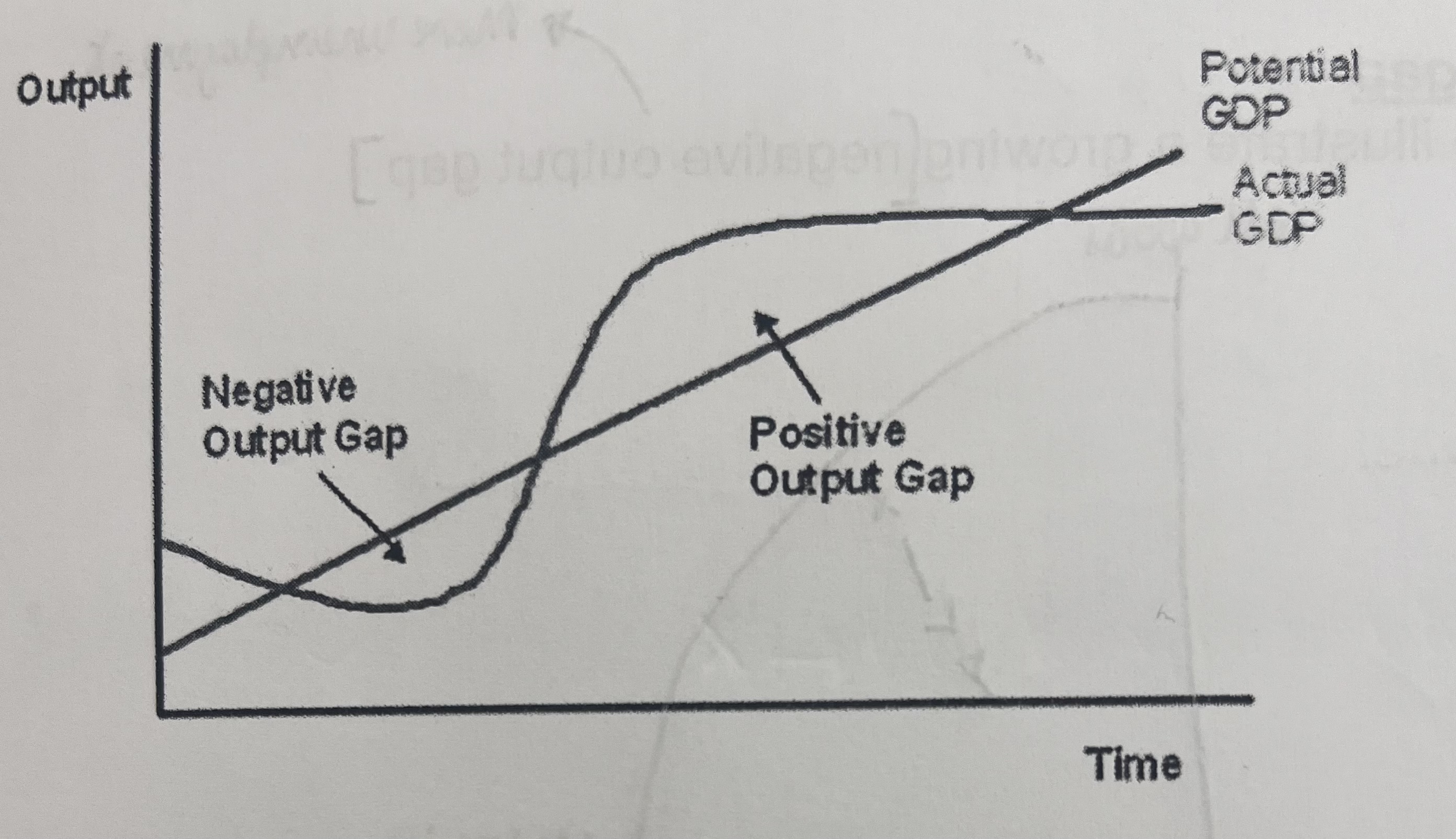
When is there a negative output gap?
When GDP falls below its potential level leaving spare capacity in the economy
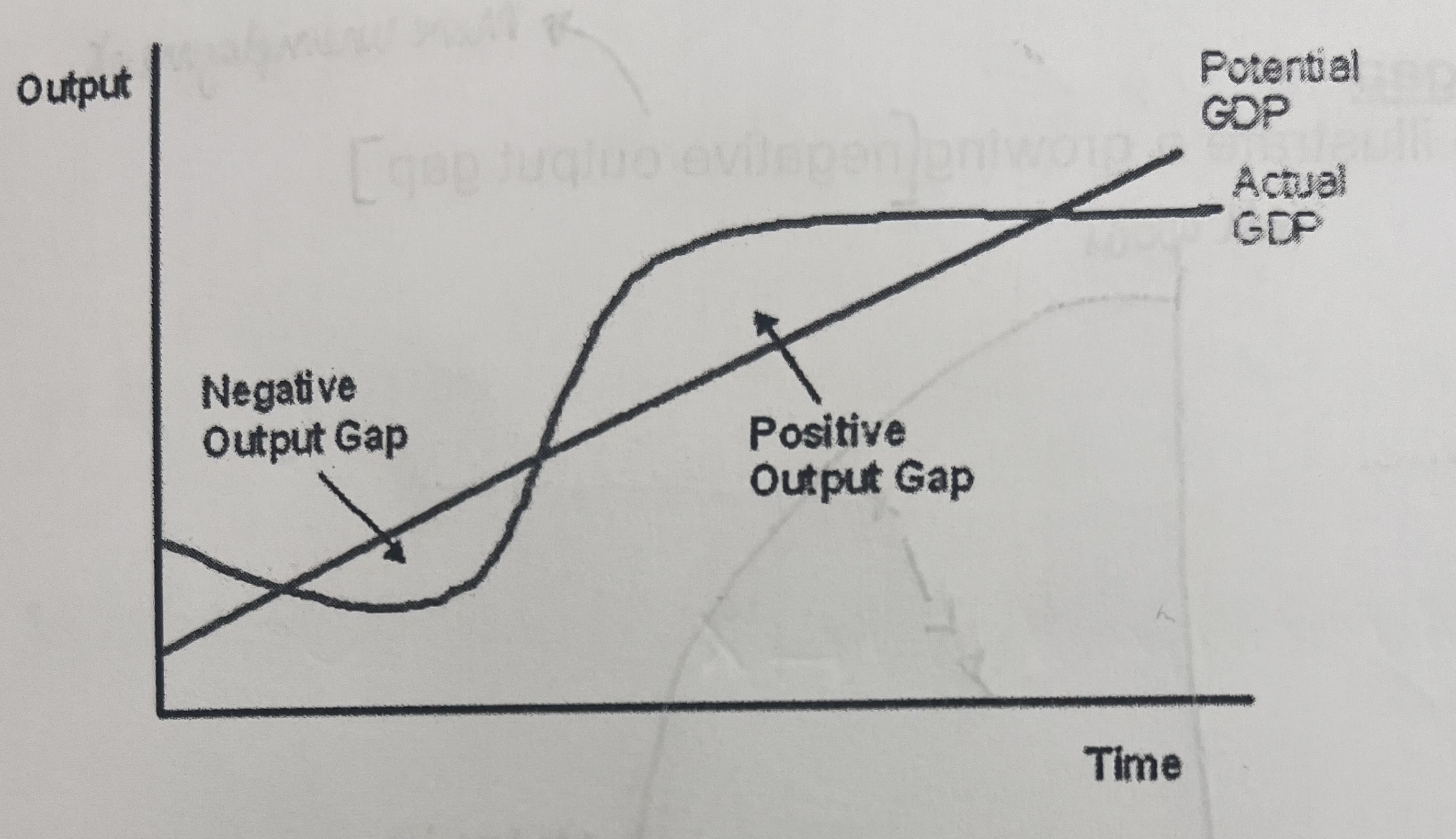
What are the effects on the increase in the negative output gap?
falling rates of inflation or deflation
A fall in the current account deficit
Rising unemployment
Business failures
When is there a positive output gap?
When GDP is above potential output or when nominal GDP continues to grow (driven by rising AD)when the economy is at full capacity- this is a classical theory that cannot be shown with a Keynesian AS curve
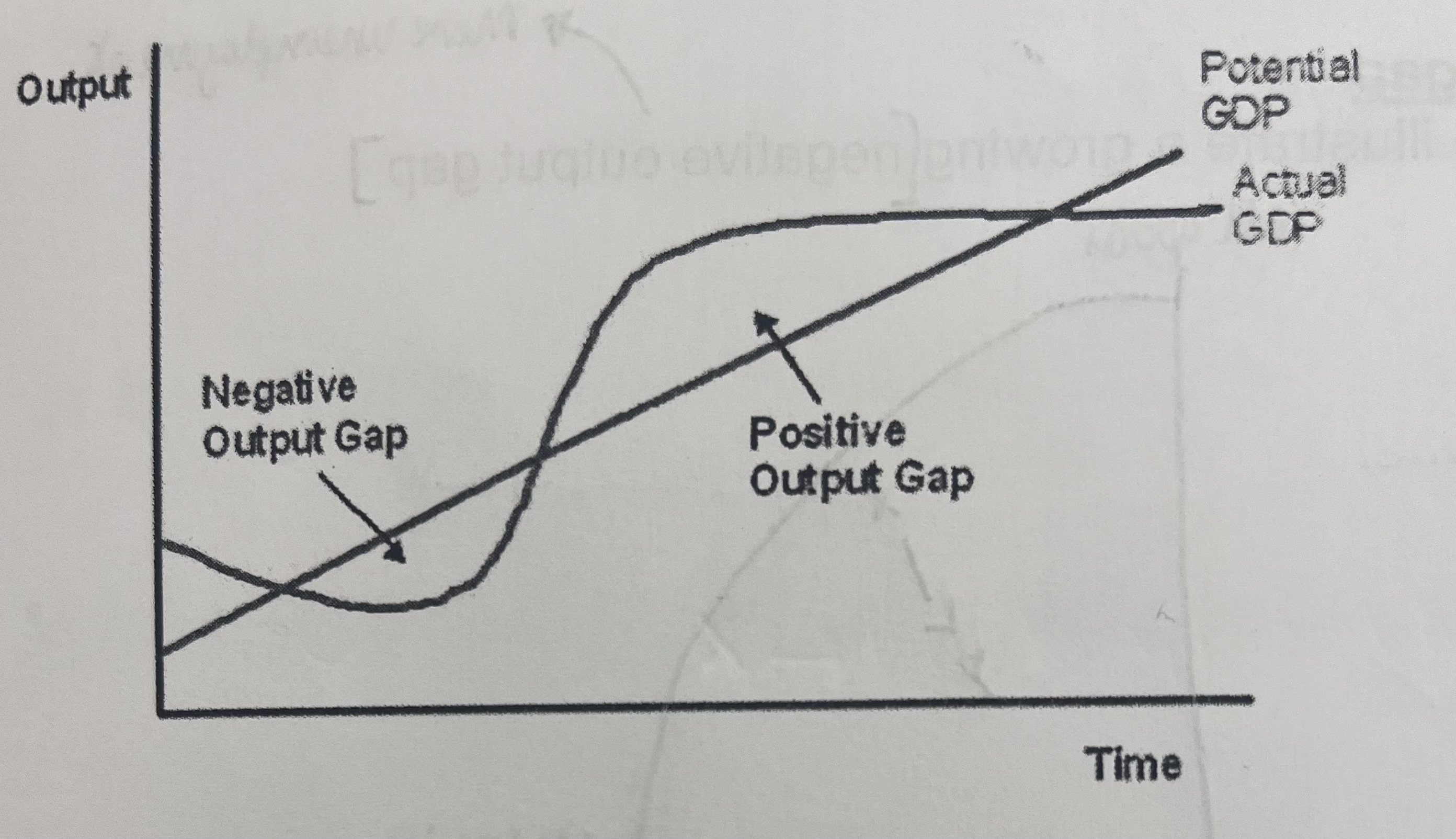
When does the positive output gap occur?
When actual output is more then full capacity output, this happens when demand is very high and to meet it factories and workers operate far above efficient capacity e.g working over time and longer hours then they would be willing to in the long run
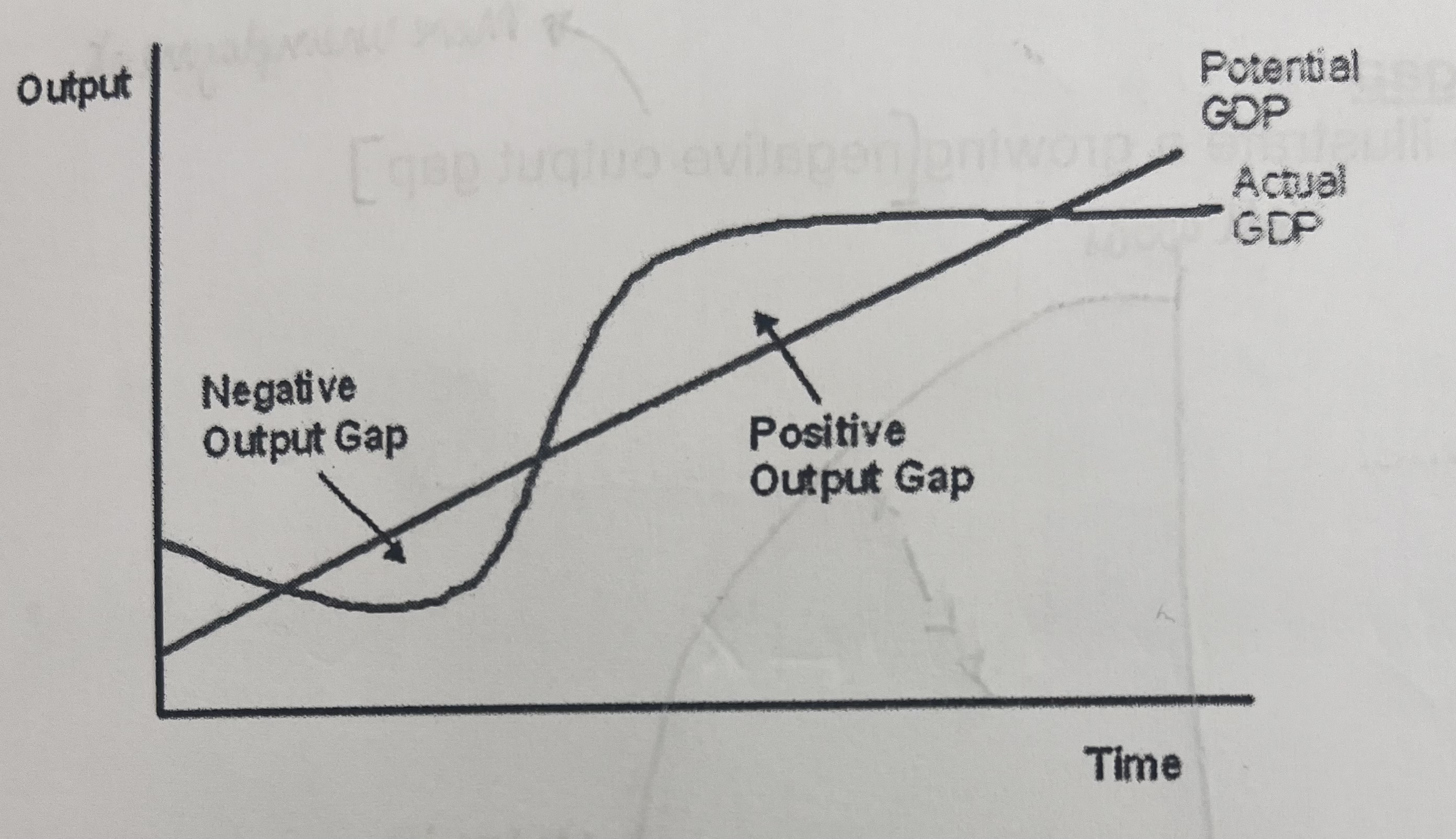
What does the classical theory believe about the long run and positive output gap?
a positive gap cannot be sustained in the long run as waves will rise, the cost of production will rise, prices will rise but real output will fall chasing the economy to return to long run potential output
What does the classical theory believe about the long run and a negative output gap?
A negative output gap cannot be sustained in the long run as wages will fall, the cost of production will fall, prices will fall and real output will rise causing the economy to return to the long run potential output
According to the classical theory, when do output gaps only exist?
In the short run- in the long run, the economy will return to potential output, therefore the trend rate of growth is the same as the growth of potential output as illustrated in the picture?
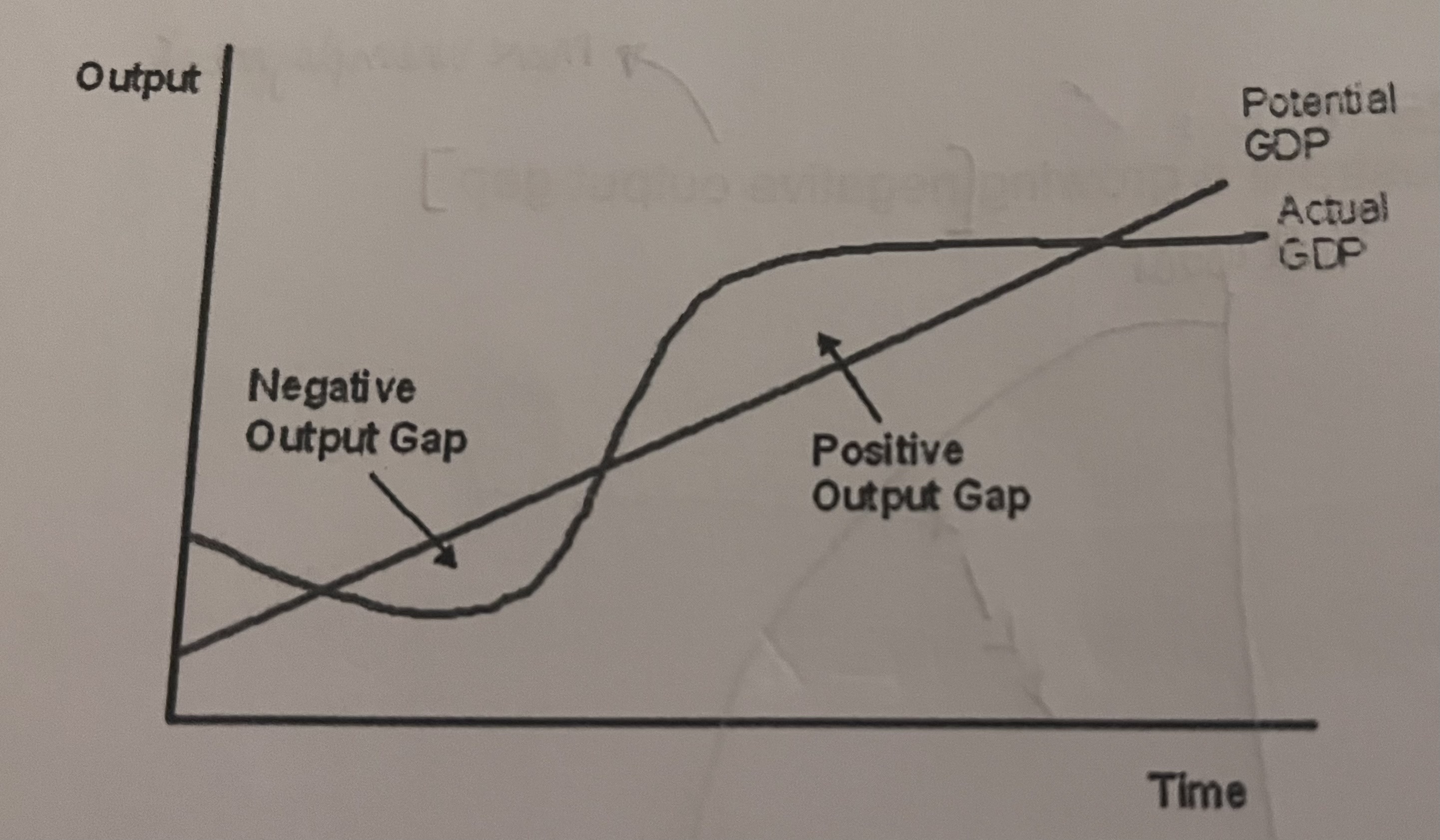
Why can it be difficult to measure the size of the output gap?
unlike actual output, potential output cannot be directly observed, only estimated
Even actual output may not be completely accurate as GDP stats are often revised
It is not always clear how much capacity may be lost during and after a recession when factors are closed and unemployed workers lose their skills
Why is it a problem if you cannot measure the output gap?
If you go beyond the full potential it cannot be sustainable
Why is it important to look at reduced labour and inflation aswell as the negative output gap?
Nobody really knows the size of the negative output gap
In a boom, will there be any spare capacity?
No