Horseshoe, Hydronephrosis, Renal Cystic Diseases, Renal Vascular Disease
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Congenital and Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and Urinary Tract (CAKUT)
Renal tract abnormalities are common, and included abnormalities of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and/or urethra - occurs in 4% of infants, comprises 20-30% of all prenatal congenital anomalies
Pronephros, Mesonephros, Metanephros
Stages of kidney development
Pronephros
Which stage of kidney development is characterized by transient and non-functional kidneys
Mesonephros
Which stage of kidney development is characterized by temporary kidneys
Metanephros
Which stage of kidney development is characterized by Metanephric blastema (baby nephrons) and the ureteric buds (forms the collecting ducts, calyces, renal pelvis, and ureter) kissing 😗
Renal agenesis renal hypoplasia, renal dysplasia, polycystic kidney disease, ectopic kidney, horseshoe kidney, ureteropelvic junction (UPJ), Ureterovesical junction (UVJ), Posterior urethral valve (PUV), megaureter, Vesicoureteral reflux, bladder exstrophy, hypospadias/epispadias
Types of CAKUTs
Horseshoe kidney, hydronephrosis, duplication of kidney, duplication of ureters, ectopic kidney
Abnormalities of the collecting systems
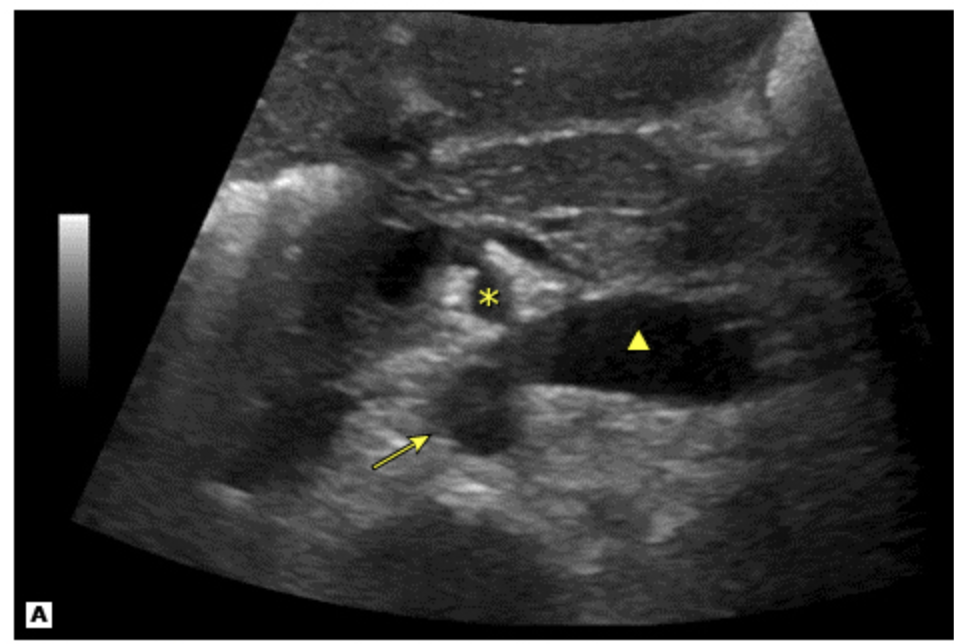
Horseshoe kidney
Which CAKUT is characterized by the kidneys getting trapped under the INFERIOR mesenteric artery (one of the common fusion anomalies that affects 1/400-800 births)
UTIs, UPJ obstruction, hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, renal stones
While horseshoe kidney patients are usually asymptomatic having a kissing kidney can but them at an increased risk of what?
CT/MRI, diuretic renogram, voiding cystourethrography (VCUG), labs are usually normal
Diagnosis of Horseshoe Kidney - usually an incidental finding
Treat the complications (infection, stones, obstruction), refer to nephrology/urology for vesicoureteral reflux OR recurrent infections
Treatment for kidney horseshoe
Hydronephrosis
Dilation of the ureters and kidney swelling due to persistent pressure from an obstruction
Kidneys producing more urine in utero (antenatal), Obstructions (VUR, UPJ, PUV, ureterocele), BPH, stones, tumors, cancers, neurogenic bladder
Etiologies of hydronephrosis
Prune Belly
A group of birth defects that results in poor development of the abd muscles, enlargement of the ureters and bladder, bilateral UDT and VUR
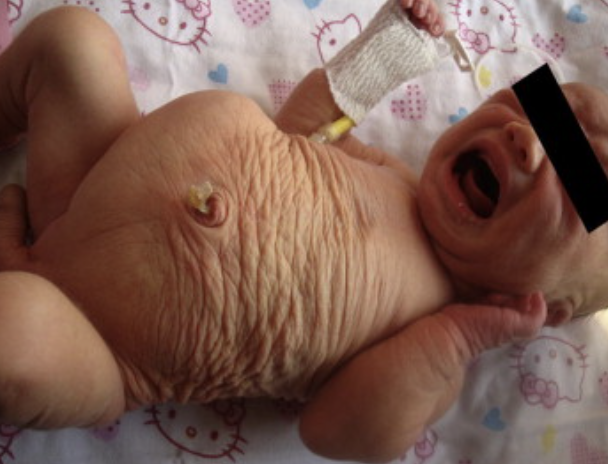
cryptorchidism, Dilated ureters, GU reflux, hydronephrosis, cystic dysplasia, absent abd wall muscles, pulmonary hypoplasia
What are the anomalies in Prune Belly syndrome?
UTI, hemature, renal colicky pain, back pain that radiates to the groin, N/V, sweating
Acute symptoms of hydronephrosis (depends on severity)
Asymptomatic, then progresses to renal failure; weakness, malaise, chest pain, SOB, leg swelling, N/V, electrolyte abnormalities, arrhythmias, muscle spasm
Chronic symptoms of hydronephrosis
UA, BUN/Cr, CMP, Renal U/S 🏆 (in children), VCUG (shows degree of VUR), Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) renal scan, US or CT (stones)
Diagnosis of Hydronephrosis
In utero (they are benign, so repeat the prenatal U/S later); Percutaneous nephrostomy tubes (acutely), ureteric stent/pyeloplasty (chronic)
Treatment plan for hydronephrosis
Simple retention cysts, polycystic kidney disease (dominant and recessive), medullary sponge kidney, renal dysplasia, renal agenesis
Which CAKUTs are renal malformations?
echo-free/hypoechoic, sharp demarcated smooth walls, and enhanced back wall (U/S); sharp demarcated thin wall with no enhancement with contrast (CT)
Simple renal cyst findings on U/S and CT
Thick walls, calcifications, mixed echogenecity with fluid and solid components
Complex renal cyst findings on U/S and CT
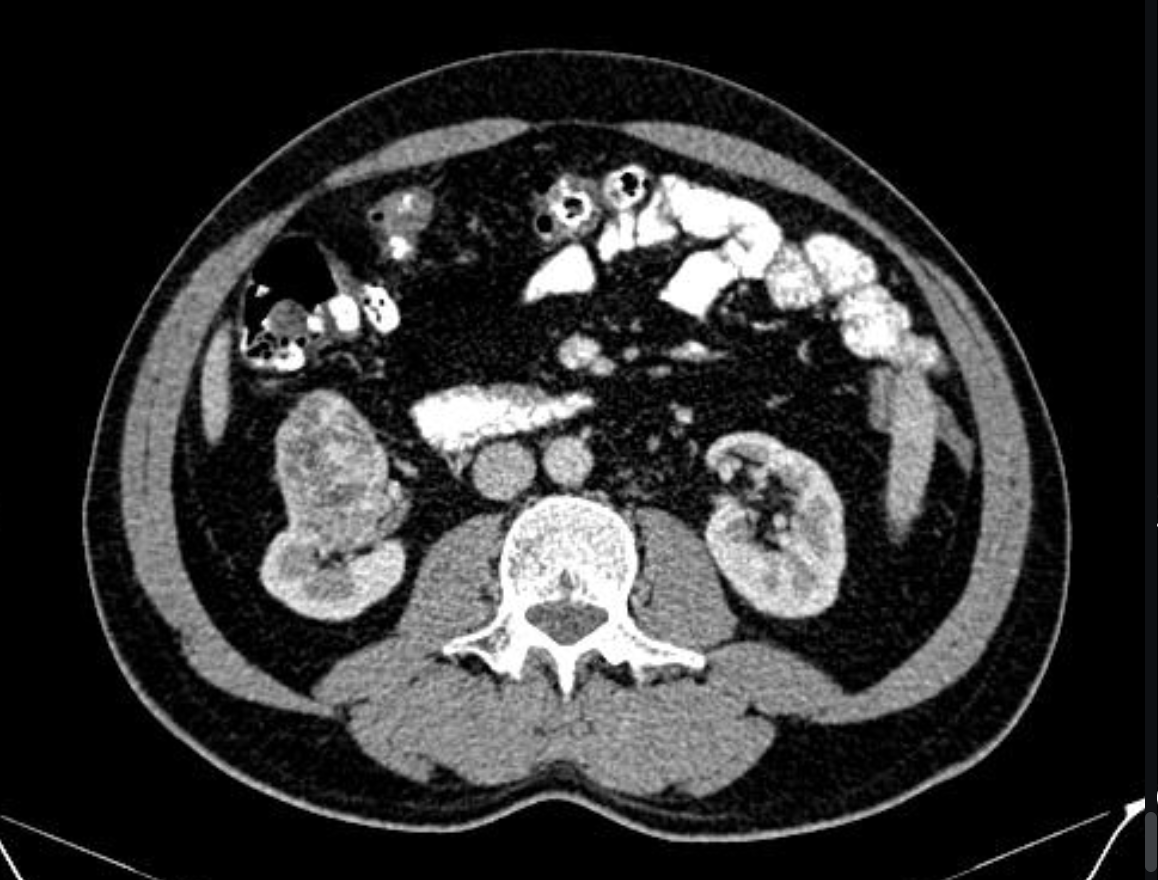
Nothing (simple 👍), Surgical removal (complex)
Treatment plan for Renal Cysts
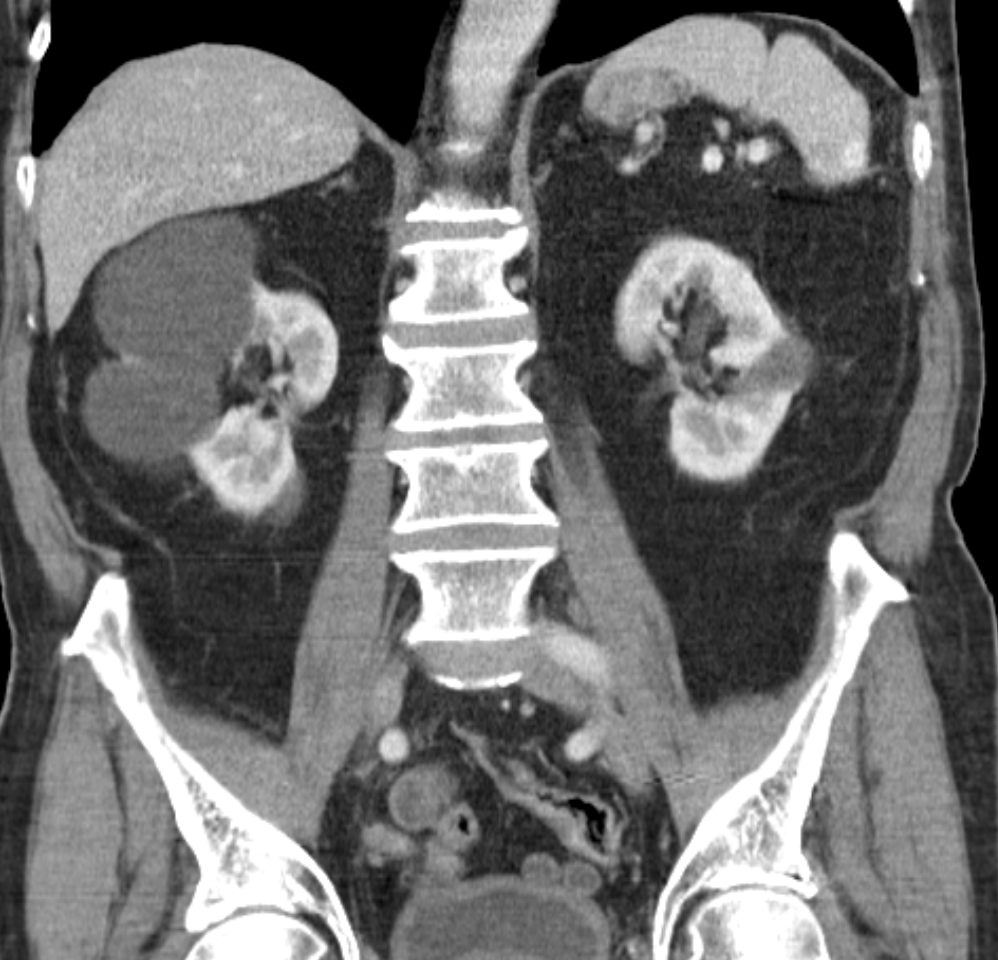
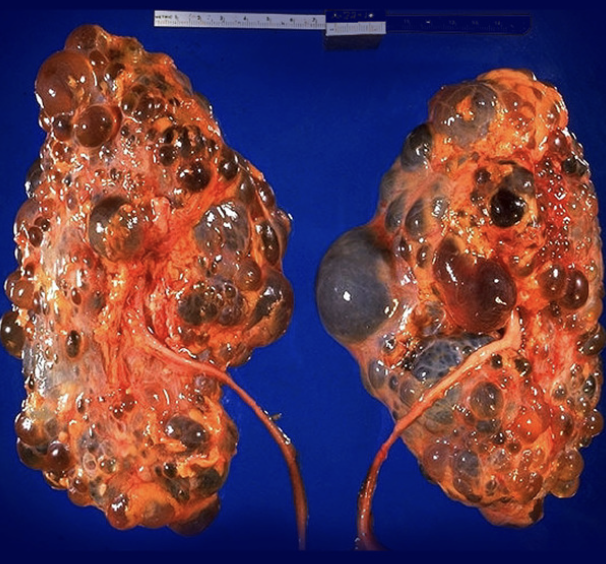
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
The most common inherited kidney disease that is characterized by cyst growth on the kidneys, damaging the parenchyma and disturbing renal function
chromosome 16 (type 1), Chromosome 4 (type 2)
Defect location in ADPKD
Loss of the protective polycystin 1 and 2 proteins in cilia, tubular epithelial cells proliferate into cyst which damage the interstitium - if 1 parent has it, 50% shot for kids
Pathophys for ADPKD
Obstruction of tubules by interstitial fibrosis (seen with dialysis)
How can PKD be acquired?
UA, CBC, CMP, U/S, CT, MRA (maybe)
21 y/o female presents to the ED for bilateral flank pain. She states that she thinks her mom had a kidney problem, but she doesn’t know what it is. Vitals are stable with the exception of 150/95. On physical exam you note a mid systolic click and hepatomegaly. What diagnostics do you want?
ACEI/ARB (HTN), cyst decompression (pain/HTN), analgesics, rest/hydration (hematuria)
21 y/o female presents to the ED for bilateral 10/10 flank pain. She states that she thinks her mom had a kidney problem, but she doesn’t know what it is. Vitals are stable with the exception of 150/95. On physical exam you note a mid systolic click and hepatomegaly. Labs reveal hematuria, polycythemia vera, high phosphorus and uric acid, low vitamin D, sodium, calcium. See CT scan. What is your treatment plan?
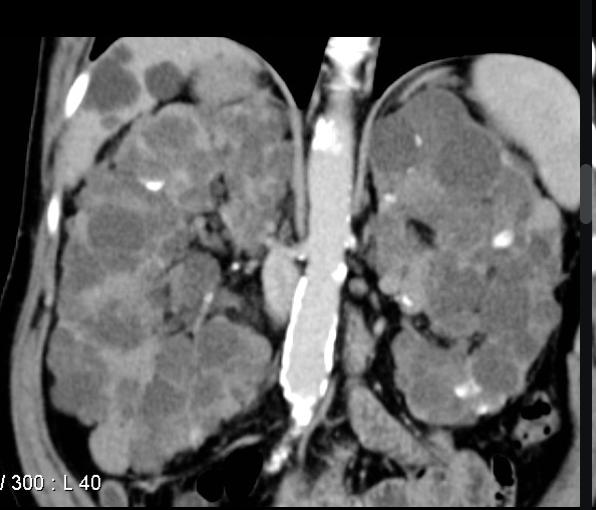
2 cysts unilateral/bilateral if under 30, 2 cysts bilaterally if 30-59, 4+ cyst bilaterally if 60+
With a family hx of ADPKD, an U/S is diagnostic IF
MVP, cysts in liver/spleen/pancreas, brain (cerebral aneurysms), thoracic abdominal aneurysms
Extrarenal manifestations of ADPKD
Non-contrast CT scans, hydration (2L/day), stone passage/removal
Treatment plan for nephrolithiasis associated with ADPKD
UA, urine/blood cultures, non-contrast CT, IV abx
Treatment plan for infected cysts/pyelonephritis associated with ADPKD
Ursodial, portocaval shunt (connects portal vein to IVC), liver transplant
Treatment plan for liver involvement associated with ADPKD

control HTN and activities
Treatment plan for cerebral aneurysm associated with ADPKD
RRT (transplanted kidney is not at risk for cysts - usually required by age 60)
Treatment plan for renal involvement associated with ADPKD
Male under 30 with hematuria, HTN before 35 y/o
Which patients with ADPKD have an increased risk of ESKD?
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
A bilateral cystic disease of the nephrons due to a mutation on the PKHD gene on chromosome 6 which codes for fibrocystin protein (affects both kidney and liver)
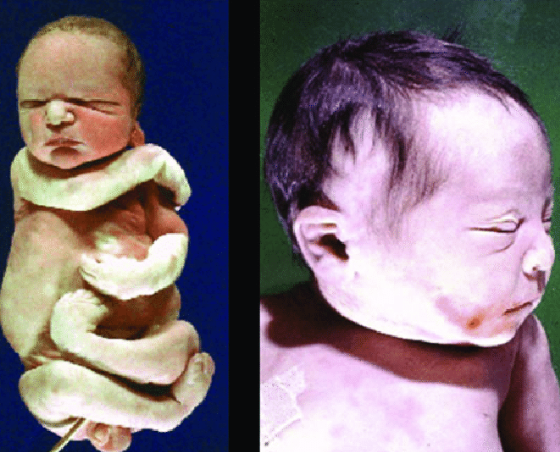
Potter’s syndrome in the 2nd and 3rd trimester, pulmonary hypoplasia (kills 30% in the first week)
In utero symptoms of ARPKD
Pulmonary hypoplasia, Oligohydramnios, Twisted skin, twisted face, extremities defect, renal agenesis
Signs and symptoms of Potter’s disease
Abdominal distention, HTN, oliguria, respiratory distress, liver cyst, hepatic fibrosis
Symptoms of ARPKD in infancy
Decreased GFR, BUN/Cr UP, maybe hyponatremia, bright cyst on enlarged kidneys and liver (U/S)
Diagnostic findings in ARPKD
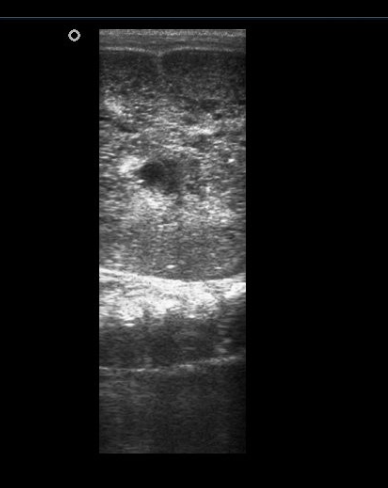
RRT with ESKD, ACEI/ARBS, respiratory and liver support, genetic counseling for parents
Treatment plan ARPKD
Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease (medullary sponge kidneys)
A congenital disorder with tiny fluid filled cyst in the medullary collecting tubules in utero due to a mutation on chromo 1 (MCKD1) or chromo 16 (MCKD2)
recurrent stones, hematuria, UTIs, decreased ability to concentrate urine
Presentation of Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease
hematuria, pyuria, hypercalciuria, BUN/Cr will decrease over time, metabolic acidosis
Lab findings in Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease
Paintbrush appearance 🖌 on U/S (hyperdense clusters of small stones), Swish cheese 🧀 on CT (cystic dilation of distal collecting tubules)
Imaging findings in Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease
treat any stones/UTI, hypercalciuria (thiazide), metabolic acidosis (IV bicarb)
Treatment plan for Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease
Renal Dysplasia
The MOST common cystic disease in children with no inheritance pattern that presents with enlarged, irregular cystic flank mass (if bilateral may lead to renal failure)
unilateral renal agenesis
What occurs in 1/1000 infants (usually males, usually the left side) and results in the remaining kidney going beast mode (compensatory hypertrophy)?

Bilateral renal agenesis
What occurs in 1/3000 births (usually male) and is incompatible with life?
Renovascular disease
What occurs when the renal arteries or veins are blocked due stenosis or occlusion (acute or chronic) - common cause of secondary HTN?
smoking 🥇, HTN, DM, CKD, nephrotic syndrome
Risk factors for Renovascular disease
Acute renal artery stenosis (RAS)
What is caused by a thrombo-emobolic event from the heart that results in renal infarction (if longer than 30-60 min)
Atherosclerosis plaque formation (usually bilateral - 90%), fibromuscular dysplasia (10% usually in young females with refractory HTN)
Causes of Chronic RAS
UA, CMP, CBC, Doppler U/S, CTA, Abdominal U/S, Invasive Contrast renal angiography (do after the noninvasive imaging) 🏆
54 y/o male presents to the ED for severe 10/10 flank pain. He also reports that the last time he went pee it was BRIGHT red. Vitals are stable with the exception of 100.5 temp. On physical exam you note crackles/rales in the posterior lung zones, BLE edema, and papilledema on retinal exam. What do you want to order?
Fibrinolytics (streptokinase, ateplase-tPA), anticoags (DOACs, or heparin bridged warfarin), surgical/catheter based embolectomy within 3 hours, surgical revasculation for traumatic RAS
54 y/o male presents to the ED for severe 10/10 flank pain. He also reports that the last time he went pee it was BRIGHT red. Vitals are stable with the exception of 100.5 temp. On physical exam you note crackles/rales in the posterior lung zones, BLE edema, and papilledema. Labs reveal hematuria, decreased GFR and hypokalemia. The renal angiograph shows a blockage, what do you want to do?
uncontrolled HTN, decreased renal function, pulmonary edema
Symptoms of a gradual occlusion RAS
Atherosclerosis
_______________ usually forms at the beginning of the renal artery where it branches from the aorta
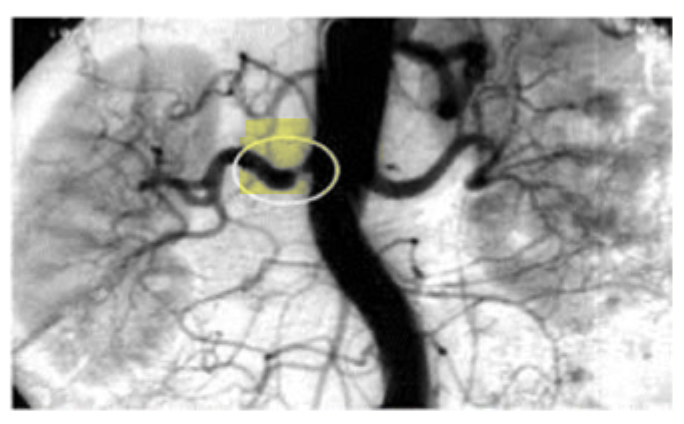
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)
____________ develops in the middle to distal end of the renal artery, closer to the kidneys with a string of pearls/beads 🦪 presentation
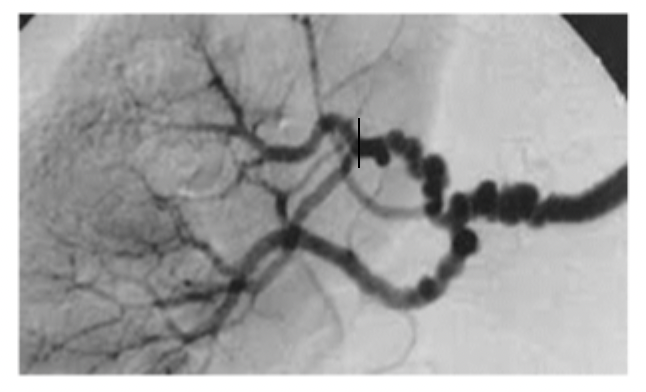
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), surgical bypass of the stenotic segment, ACEI/ARB (avoid if bilateral) or aliskiren/tekturna, CCBs, or vasodilators (minoxidil/hydralazine) for HTN
Treatment plan for chronic RAS
Renal vein thrombosis (RVT)
A formation of a clot in one or both renal veins that leads to a reduction in the blood flow from the kidney - most common cause is membranous nephropathy
endothelial damage + low blood flow + increased coaguability
Virchow’s triad (AKA the reasons for clots in a vein)
severe back/flank pain, hematuria/proteinuria, oliguria, N/V, death (if bilateral)
Acute signs and symptoms of RVT
maybe proteinuria/hematuria, patients may present with a PE or sudden decrease in urine function
Chronic signs and symptoms of RVT
renal venogram (U/S, CTA, MR venography are non invasive, CT renal angiography is the procedure of choice)
Gold standard for RVT 🏆
if in acute renal failure → tPA with/without catheter directed thrombectomy; anticoags if without AKI or chronic, nephrectomy if totally infarcted
Treatment plan for RVT
Renal Nutcracker Syndrome
Loss of the fat pad around the renal vein leading to compression by the SUPERIOR mesenteric artery - common in growth spurts or extreme weight loss
UA, U/S 🏆
12 y/o boy presents to the ED for left flank pain. His mother states that he just grew 2 inches. Vitals are stable. On physical exam you note left varicocele. What do you want to order?
Surgery with a stent in the left renal vein, weight gain
12 y/o boy presents to the ED for left flank pain. His mother states that he just grew 2 inches. Vitals are stable. On physical exam you note left varicocele. UA reveals hematuria. U/S reveal demonstrates significant narrowing between the superior mesenteric artery and the aorta. What is your treatment plan?