Aggregate demand and supply
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Define aggregate demand
Total quantity of aggregate output , or rGDP, that all buyers in the economy want to buy at different possible price levels.
Consists of: demand of consumers, demand of business, demand of government, and ned demand of foreigners
What causes change in consumption spending (6)
Change in consumer confidence (degree of optimism of consumers about future income and economy): Positive feedback
Changes in interest rate: Negative feedback
Changes in wealth: positive feedback
Changes in income tax: Negative feedback
Expectations of future price levels: Positive feedback
Changes in level of household indebtedness: Negative feedback
Causes of changes in investment spending (6)
Changes in business confidence (Degree of optimism among firms about future performance): Positive feedback
Changes in interest rates: Negative feedback
Changes in tech: Positive feedback
Changes in business tax: Negative feedback
Level of corporate indebtedness: Negative feedback
Legal/institutional changes: depends
Causes of change in government spending (2)
Changes to political priority
Changes in economic priorities (deliberate efforts to influence AD
Causes of changes in export spending - import spending (3)
Changes in national income abroad: Positive feedback
Changes in exchange rate: Negative feedback
Changes in trade policies
Why do wages not change a lot in short term
Labour contract fix wage rate
Minimum wage legislation
workers and labour unions resist wage cuts
Wage cuts leads to low morale, inefficiency
Define aggregate supply
Total quantity of goods and services produced in an economy (rGDP) over particular amount of time
Causes in changes in SRAS (5)
Changes in wage: Negative feedback (assuming PL is constant)
Changes in non-labour resource price: Negative feedback
Changes in indirect taxes: Negative feedback
Changes in subsidy: Positive feedback
Supply shock
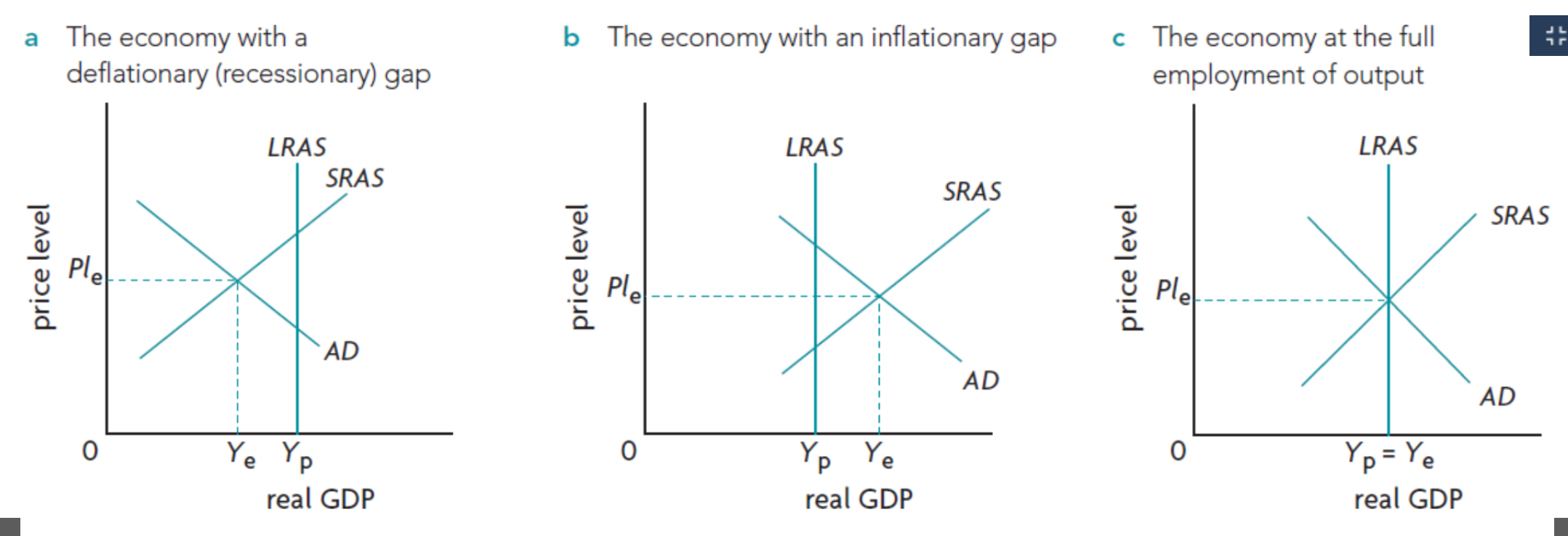
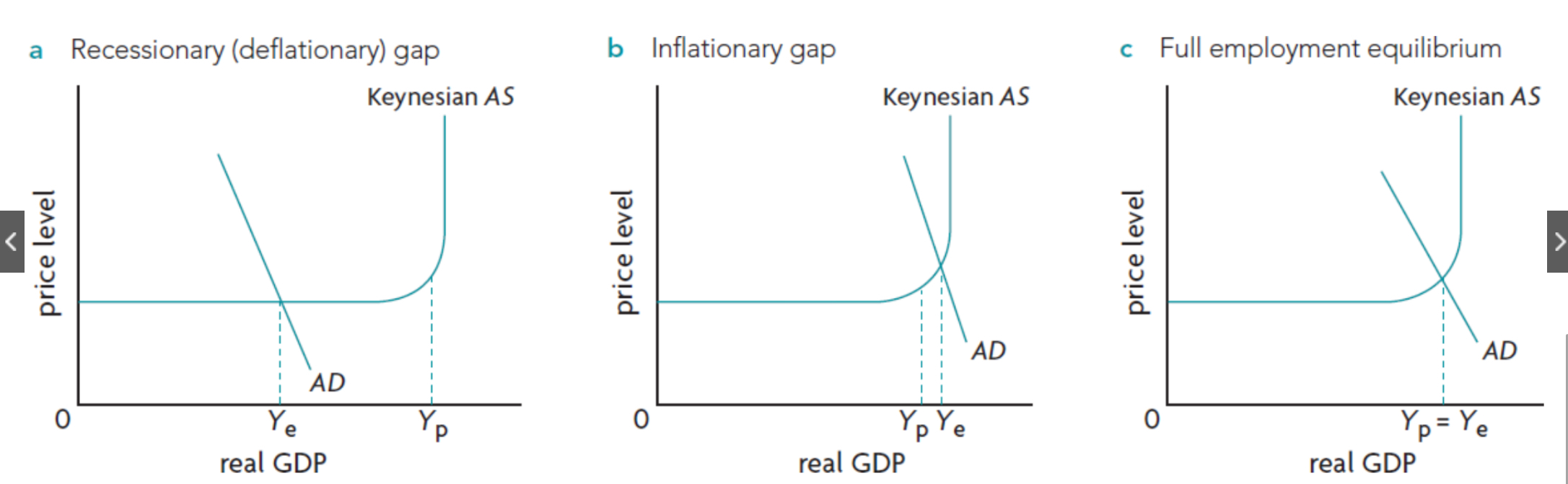
Draw and label Recessionary gap (keynsian + monetarist)
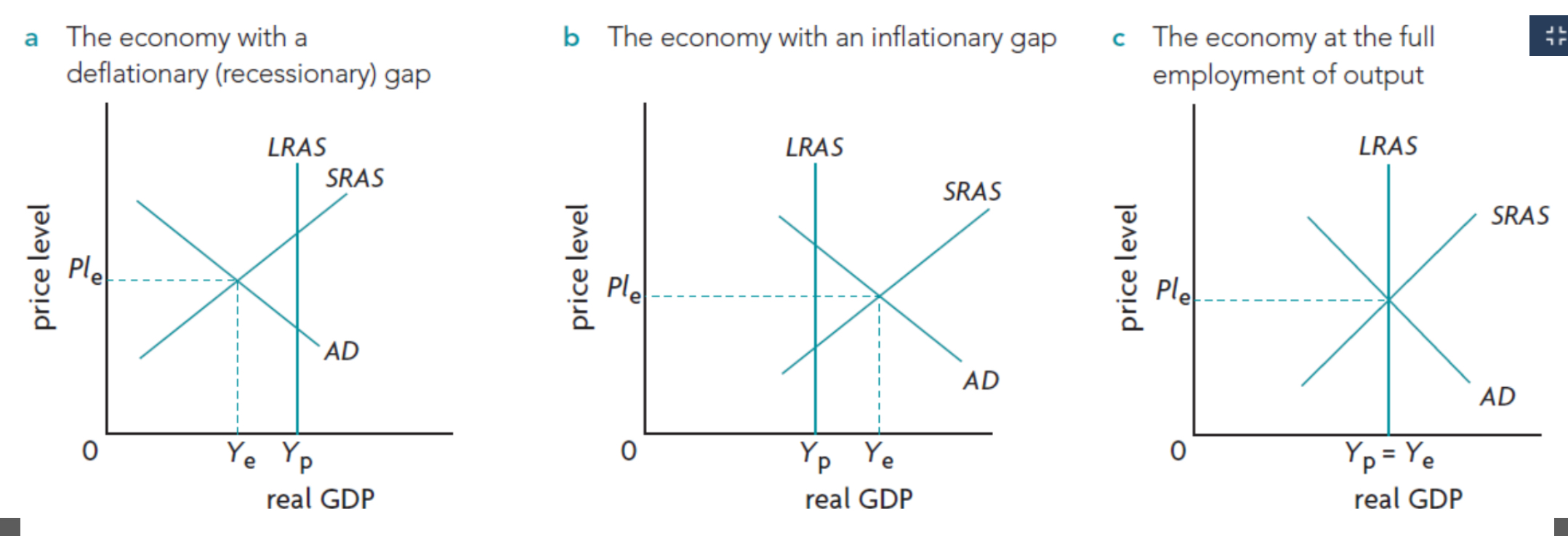
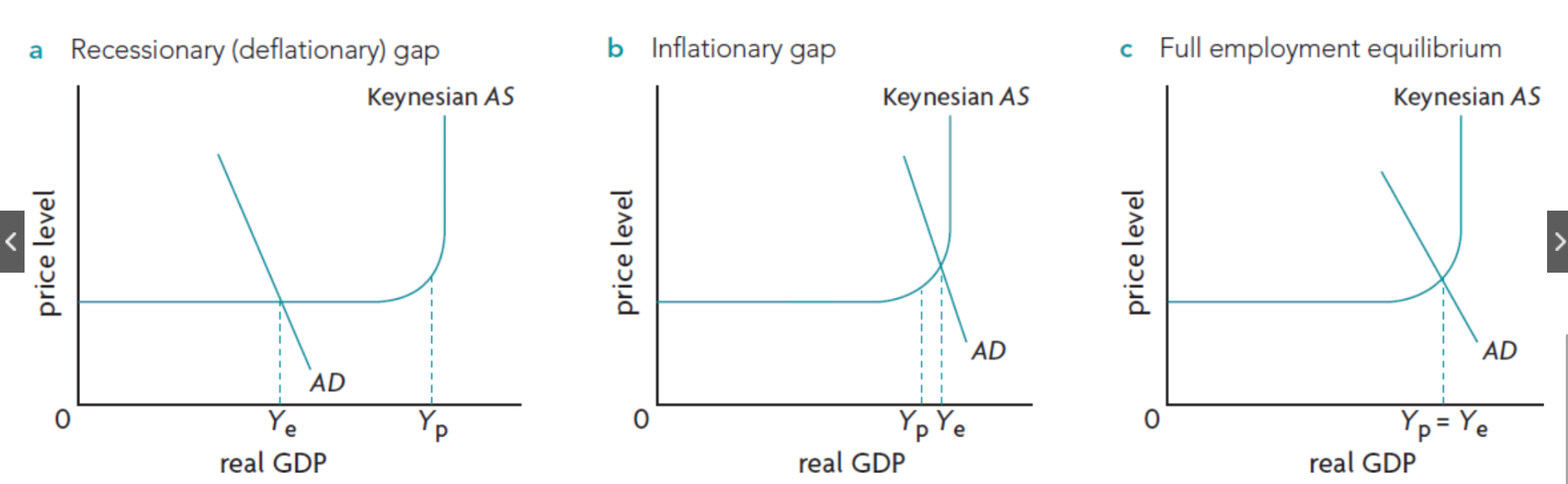
Draw and label Inflationary gap (keynsian + monetarist)
Draw and label potential output (keynsian + monetarist)
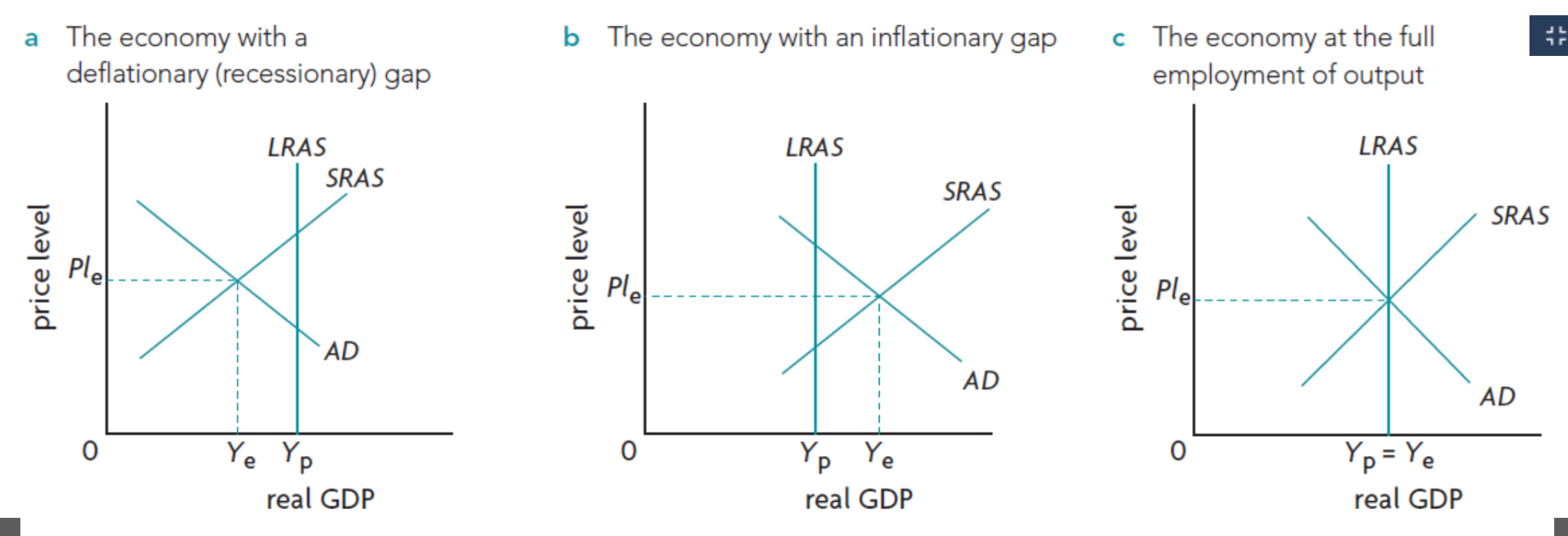
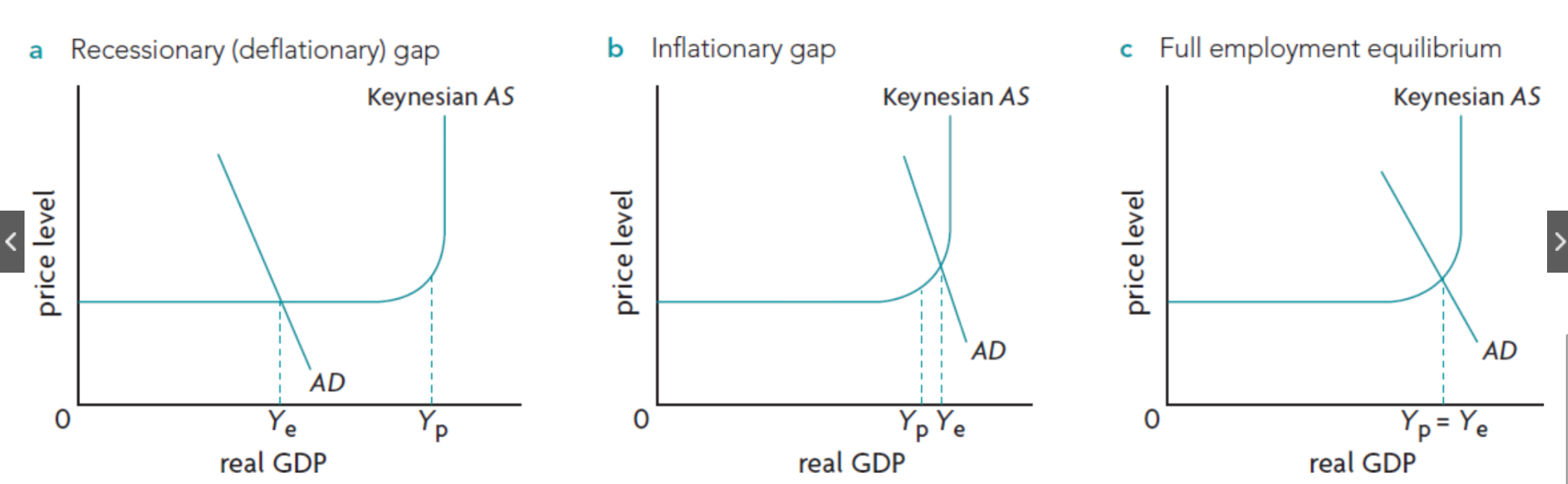
Causes of change in LRAS (6)
Quantity of FOP: Positive feedback
Quality of FOP: Positive feedback
Tech improvement: Positive feedback
Efficiency: Positive feedback
Institutional changes: eg privatisation
Rate in natural rate of unemployment: Negative feedback