4. Population Ecology (Population Dynamics, Human Population Growth)
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
the study of population dynamics
focuses on the complex interactions between biotic and abiotic factors that cause variation in population sizeq
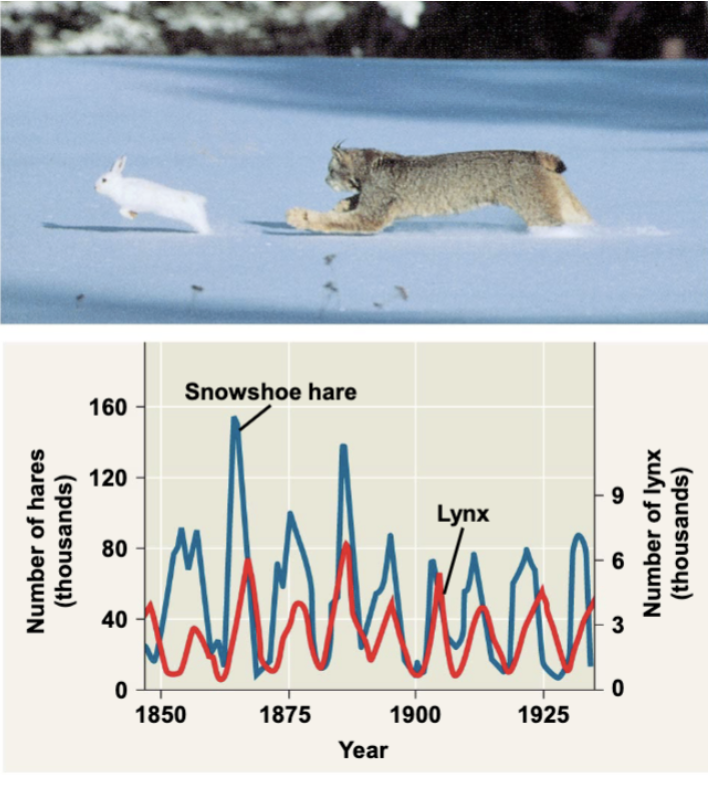
examples of a boom-and-bust cycle
hare populations
3 hypotheses proposed to explain the hare’s 10 year interval
Hypothesis I: hare pop cycle follows a cycle of winter food supply
if correct, cycles should stop if the food supply is increased
study provided additional food and the pop increased in size
no hares appeared to have died of starvation
Hypothesis II: hare pop cycle is driven by pressure from other predators
study conducted, 90% of the hares were killed by predators
data support this hypothesis
Hypothesis III: hare pop cycle is linked to sunspot cycles
sunspot activity affects light quality, which in turn effects the quality of the hares food
there is good correlation between sunspot activity and hare pop size
both predation and sunspot activity regulate hare numbers and that food availability plays less important roles
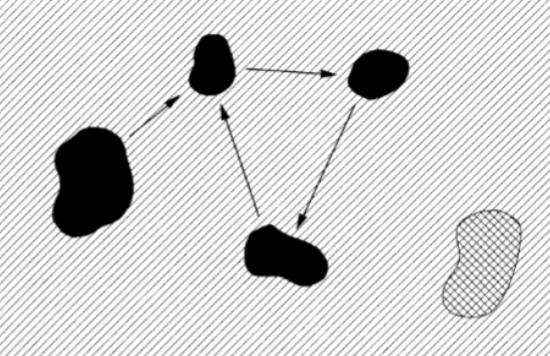
metapopulations
groups of populations linked by immigration and emigration
metapopulation in theory
patch- matrix view
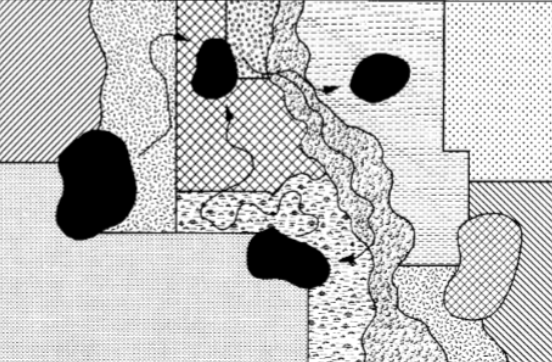
metapopulations in reality
patch-mosaic view
can a population grow indefinitely
no
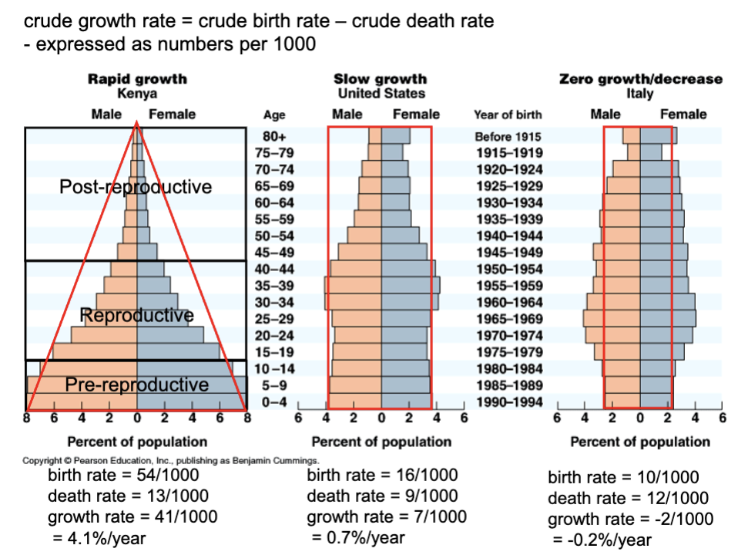
one important demographic factor in present and future growth trends is a countries age structure
which is the relative number of individuals at each age
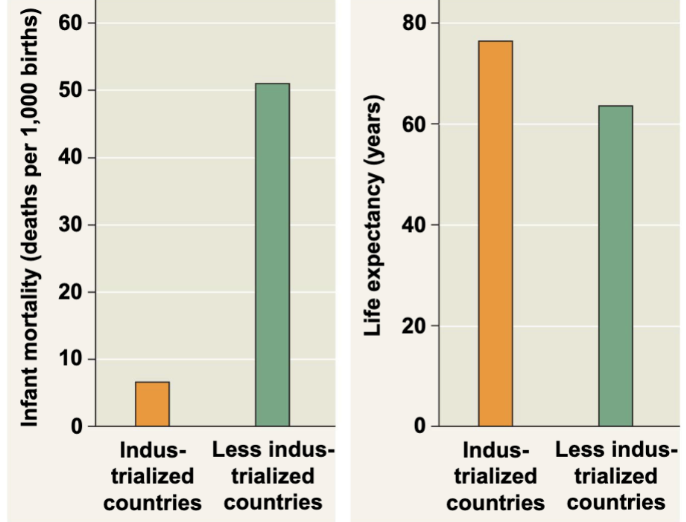
infant mortality and life expenctancy at birth vary greatly among developed and developing countries but do not capture the wide range of the human condition
(pic)
global carrying capacity
how many humans can the biosphere support?
10-15 billion
limited by food, space, nonrenewable resources, buildup of wastes