Protists and Endosymbiosis - Egan 120
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
When were the first eukaryotes?
~1.8 billion years ago
What do eukaryotic cells have?
a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles
What does the cytoskeleton do?
provides the cell shape and anchoring points for organelles within a eukaryote
What does evidence suggest about mitochondria?
Mitochondria evolved before plastids as the ancestral host was an archaean ancestor with membrane bound-nucleus and cytoskeleton
How did plastids arise?
when a heterotrophic eukaryote engulfed a photosynthetic cyanobacterium
What does the phylogeny of photosynthesis say?
there’s been a discontinuous presence of photosynthesis throughout the eukaryotic tree
What do protists refer to?
it refers to all eukaryotes not within the kingdom plantae, Animalia, and fungi
What are the four supergroups?
excavata, archaeplastida, SAR, and unikonta
What are excavata characterized by?
its cytoskeleton
Excavata include what three monophyletic groups?
diplomonads, parabasalids, and euglenozoans
What organisms make of euglenozoans, and what is their main feature?
predatory heterotrophs, parasites, mixotrophs, photosynthetic autotrophs; they feature a spiral or crystalline rod inside each flagella
What does SAR represent acronym wise?
stramenopiles, alveolates, and rhizarians.
What is a feature most stramenopiles have, and what are some groups in the clade?
They feature a hairy flagellum paired with a smooth flagellum; diatoms and brown algae
What are diatoms?
diatoms are unicellular algae with a unique two-part, glass-like wall (called frustule) composed of silicon dioxide; they’re photosynthetic and planktonic
Why are brown algae notable of the stramenopiles?, and what produces its color?
They are the largest and most complex multicellular algae; carotenoids in plastids give it brown color
Brown algae evolved a life cycle highlighted by alternation of generations. What describes alternation of generations?
Haploid and diploid stages are multicellular.
A diploid generation, sporophytes, produce haploid spores.
These haploid spores develop into haploid gametophytes, producing haploid gametes.
Fertilization results in a diploid zygote, which develops into a sporophyte.
Brown algae are a foundational species. What do they contribute? (4 contributions)
Ecosystems: Kelp create complex underwater forests that provide food, shelter, and nursing habitat
Drivers of ecosystem dynamics: Kelp regulate structure from trophic cascades
Primary producers
Fuel coastal food webs and supports biodiversity all around
What main feature do alveolates have?
they have membrane-enclosed sacs (alveoli) just under the plasma membrane
What are dinoflagellates?
They are alveolates that have two flagella housed in the grooves of armor-like cellulose plates that surround the cell
Why do dinoflagellates spin moving through water?
the beating of the spiral flagella causes them to spin.
What are red tides, and why are they harmful?
Red tides are dinoflagellate blooms and are red due to carotenoids; they are toxic and can kill large numbers of invertebrates and fishes
What do archaeplastids consist of?
red algae, green algae, and plants
Why are red algae red?
phycoerythrin masks the color of chlorophyll
What two groups make up green algae?
chlorophytes and charophytes
What is the supergroup unikonta made up of?
animals, fungi, choanoflagellates
Opithokonts includes what?
animals and fungi
How do opithokonts propel itself?
with a single posterior flagellate cell (sperm of most animals, spore of the chytrid fungi)
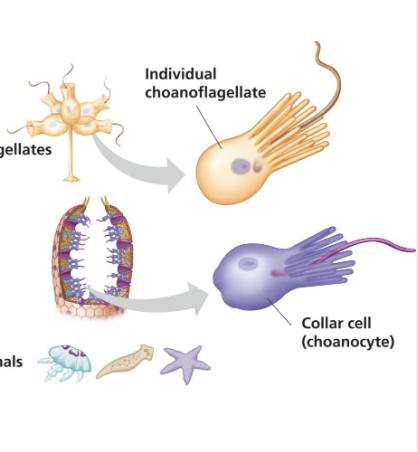
what are choanoflagellates?
free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes
What do choanoflagellates look like?
an ovoid/spherical cell body 3-10 micrometers in diameter with a single apical flagellum surrounded by a collar of 30-40 microvilli