Science 1.1 "What are Theories of Origins"
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
origins
the beginning
2
New cards
creationism
the idea that God created the universe and all life
3
New cards
informed interventionism
-a broader concept that also acknowledges God's intervention at other times in history
-used instead of the word "creation"
-came up by scientists
ex: the flood
-used instead of the word "creation"
-came up by scientists
ex: the flood
4
New cards
abiogenesis
-life arose spontaneously from non-living matter many millions of years ago
-made by T.H. Huxley in 1870
-people believed in the idea of it in 1600s by believing that meat made maggots
word = no life beginning or spontaneous generation
-made by T.H. Huxley in 1870
-people believed in the idea of it in 1600s by believing that meat made maggots
word = no life beginning or spontaneous generation
5
New cards
macroevolution
-all present life forms descended from a simple one-celled organism
-believed by only evolutionists
-major changes over time
-hasn't been proved
-believed by only evolutionists
-major changes over time
-hasn't been proved
6
New cards
spontaneous generation
the idea that life (living organisms) come from non-living matter
7
New cards
primoridal soup
-hypothesized that at some previous time, oceans were filled with CO2, methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and water
-term made by Alexander Oparin
-term made by Alexander Oparin
8
New cards
exogenesis
-a hypothesis that life began somewhere else such as comets and meteorites
-term started when some scientists believed life was imossible to come from non-living matter
word = outside beginning
-term started when some scientists believed life was imossible to come from non-living matter
word = outside beginning
9
New cards
fixity of species
people believed that life on Earth was exactly the same as what was created by God during creation week
10
New cards
artificial selection
-breeders purposely selected plans or animals with desireable characteristics next generation
-helps with the evolution theory
-helps with the evolution theory
11
New cards
natural selection
pattern of variation, greater survival, and successful reproduction
12
New cards
microevolution
-small changes of characteristics over time
-involves the process of evolutionary changes within populations
-leads to sorts of variation that we see within species
-believed by scientists and evolutionists
-involves the process of evolutionary changes within populations
-leads to sorts of variation that we see within species
-believed by scientists and evolutionists
13
New cards
mutation
changes that occur when a gene is altered, damaged, or lost
14
New cards
panspermia
-suggests that life is widespread throughout the universe
-some scientists believed in the hypothesis, others didn't because it still doesn't explain how life started
-some scientists believed in the hypothesis, others didn't because it still doesn't explain how life started
15
New cards
intelligent design
-not creationism
-doesn't describe origins from a religious pov
-mostly relies on scientific evidence, not scripture
-theory that states that living things + other features in the universe are best explained by a "_____ designer"
-doesn't describe origins from a religious pov
-mostly relies on scientific evidence, not scripture
-theory that states that living things + other features in the universe are best explained by a "_____ designer"
16
New cards
Biblical worldview
-a theory of origin
-viewing the world through the creation of God
-informed intervention
-can't be tested on scientifically
-believed only in faith
-many belief its a myth
-many believe these accounts were borrowed from famous myths
-viewing the world through the creation of God
-informed intervention
-can't be tested on scientifically
-believed only in faith
-many belief its a myth
-many believe these accounts were borrowed from famous myths
17
New cards
worldview
-collection of attitudes, values, stories, + expectations about the world around us
-it informs our every action (influences us)
-ex: all scientists are influenced by this
-it informs our every action (influences us)
-ex: all scientists are influenced by this
18
New cards
Naturalistic worldview
-a theory of origin
-belief in abiogenesis + evolution
-doesn't believe that a higher being created the world
-belief in abiogenesis + evolution
-doesn't believe that a higher being created the world
19
New cards
study of origin
when scientists develop theories on how life began by looking through evidence
20
New cards
theory
-wide acceptance based on scientific evidence
-proven to be true due to perfomed experiments by scientists
-proven to be true due to perfomed experiments by scientists
21
New cards
scientific process
-observations that are made + experiments are performed
-ex: helps scientists study how life began on earth
-ex: helps scientists study how life began on earth
22
New cards
Doctors Gerhard + Michael Hasel
who found out that
myths: creation happened through struggle
Bible: creation happened through love
myths: creation happened through struggle
Bible: creation happened through love
23
New cards
Francesco Redi
-Italian physician + biologist
-experimented with abiogenesis in 1668
-experimented with abiogenesis in 1668
24
New cards
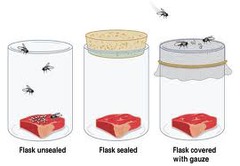
Redi's experiment
-experimented to prove that abiogenesis is false
-life doesn't start from non-living matter
-the source of the maggots were from flies laying tiny eggs that we can't see
-life doesn't start from non-living matter
-the source of the maggots were from flies laying tiny eggs that we can't see
25
New cards
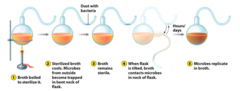
Louis Pasteur
-a scientist who later updated Redi's experiment with a special flask in the 1800s
-even with enough oxygen, no live beings came out of the non-living matter
-even with enough oxygen, no live beings came out of the non-living matter
26
New cards
20th century
when scientists started investigating where molecules came from
27
New cards
Alexander Oparin
-believed life came from the ocean
- made the term "primordial soup" for it
- made the term "primordial soup" for it
28
New cards
Stanley Miller + Harold Urey
-experimented on abiogenesis by sealing in a container: water, methane, ammonia, CO2, + hydrogen (to resemble earth's atmosphere)
-the theory was true back then, but is now false
-the theory was true back then, but is now false
29
New cards
Miller-Urey Experiment
experiment:
-boiled water + several gases in a flask
-sent electrical charges to it
results:
-several types of amino acids in mix
-its possible for molcules (organic model)
-some amino formed weren't ones found in living organisms
-boiled water + several gases in a flask
-sent electrical charges to it
results:
-several types of amino acids in mix
-its possible for molcules (organic model)
-some amino formed weren't ones found in living organisms
30
New cards
Miller-Urey Experiment issues
-some molecules created weren't useful in life
-some processes broke down amino acids and molecules too fast
-Earth's atmosphere may have been different back then
-amino acids are only right hand or only left hand seperately (mirror images). the experiment showed both right hand + left hand acids.
-some processes broke down amino acids and molecules too fast
-Earth's atmosphere may have been different back then
-amino acids are only right hand or only left hand seperately (mirror images). the experiment showed both right hand + left hand acids.
31
New cards
RNA world
-RNA = ribonucleic acid, found in living cells
-some scientists believe theres an this type of world
-suggests that life began with RNA formed molecules
-false theory
-some scientists believe theres an this type of world
-suggests that life began with RNA formed molecules
-false theory
32
New cards
Carolus Linnaeus
botanist who observed plants could become hybrids + cross between 2 species
33
New cards
evolution
-means: change over time
-occurs in populations + groups, not individually
-occurs in populations + groups, not individually
34
New cards
Charles Darwin
naturalist who made a theory that the evolution of new species occured as the result of natural selection
35
New cards
Points to Darwin's theory
-competition
-variation
-adaptation
-selection
-variation
-adaptation
-selection
36
New cards
competition
when each species produces more offspring that can actually survive
37
New cards
variation
when each indicidual within a species is slightly different so there is a variety
38
New cards
adaptation
when some variations are more advantageous than others leading to certain individuals being able to survive better in their environment
39
New cards
selection
-when those that survive + reproduce pass characteristions on to their offspring,
-making them better equipped to survive
-making them better equipped to survive
40
New cards
Microevolution examples
-differences in beaks of finches
-length of a giraffe's neck over time
-predominance of light or dark peppered moths
-length of a giraffe's neck over time
-predominance of light or dark peppered moths
41
New cards
two complex patterns of Intelligent Design
irreducible complexity + specified complexity
42
New cards
irreducible complexity
-a complex pattern of Intelligent Design
-system that doesn't work if one part is missing
ex: a mousetrap
-system that doesn't work if one part is missing
ex: a mousetrap
43
New cards
specified complexity
-a complex pattern of Intelligent Design
-a system w/ a specific sequence to work
ex: a sentence - "esleap sasp eht eanmleond" = "please pass the lemonade"
-a system w/ a specific sequence to work
ex: a sentence - "esleap sasp eht eanmleond" = "please pass the lemonade"