Microbiology quiz 1
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
what is a Pathogen
organisms that cause infections and disease'
what is pathogenicity
the ability to cause disease
what is virulence
the degree/severity of pathogenicity
what are overt pathogens
pathogens that can cause disease in healthy people
what are opportunistic pathogens
pathogens that will cause disease of given the opportunity
what kind of opportunities do opportunistic pathogens take advantage of
immunocompromised, immunosuppression, poor health, age, invasive procedures
what are virulence factors
characteristics that allow pathogens to cause disease
what is infective dosage
the number of organisms required to cause infection
what are capsules
evades the host’s immune system by inhibiting phagocytosis and mimicking of human antigens
what are examples of adhesions
Pili, flagella
what do pili do
allows the pathogen to attach to the host
what do flagella do
gives the pathogen the ability to move
what are toxins
biochemically active substances that have a particular effect on the host
what are endotoxins
gram negative organisms that are released when a cell is destroyed
what are exotoxins
gram positive organisms that are produced in the infectious cell and secreted out
what are enterotoxins
toxins affecting the GI tract that causes diarrhea and vomiting
who has normal flora
everyone
what is normal flora
microbes that are present on our body and supposed to be there
what type of person is more likely to get infections from normal flora
immunocompromised individuals
normal flora are mostly gram __________
positive
what parts of the body are considered sterile and have no normal flora
blood and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
what are the types of normal flora
resident and transient
what is resident normal flora
long term flora that is long term and well adapted to live, LOVES living on you
what is transient normal flora
temporary flora that lasts just a few hours or months. “just passing through” tries to settle in but is pushed out by resident flora
what are biofilms
communities of organisms that live together
what are biofilms held together by
pili and exopolysaccharide structural glue
biofilms are typically antibiotic __________
resistant
what is a transient carrier
a host who harbors a pathogen for a short period of time and does not get an infectious disease from it
what is a chronic carrier
a host who harbors a pathogen for a long time and does not get an infectious disease from it
what is mutualism
a relationship where both members benefit
what is commensalism
a relationship where one member benefits but the other is unharmed
what is parasitism
a relationship where one member lives at the expense of the other
what are the benefits of normal flora
keeps the neighborhood crowded and unfriendly so no new microbes can join, produces vitamin B and K
What is the normal flora of the skin
staphylococcus epidermidis
The lower respiratory tract is __________________
sterile
the upper respiratory tract is ______________
highly colonized, over 100 species
primarily home to streptococcus viridians
staphylococcus aureus is found in the _______________ of the upper respiratory tract
nose
Neisseria meningitidis is found in the _____________ of the upper respiratory tract
nasopharynx
why is there very little natural flora in the upper GI tract
due to high HCl concentrations
what are exogenous infections
infections that do not come from normal flora, comes from outside the body
the lower GI tract is ____________________
highly colonized
examples of bacteria found in the lower GI tract include
anaerobes, Enterobacteriaceae , Enterococcus
in the genitourinary tract, the bladder and above is__________
sterile
in males ____________________ is sterile
above the urethra
in females __________________ is sterile
above the cervix
the bacteria in the urethra is
a combination of skin flora and GI flora
in the vaginal tract, the predominant organism is
lactobacillus acidophilus
what immune system has characteristics fast, responds in the same way, response does not change with repeated exposure, no prior exposure is needed and born with
Non specific
what are other names for the non specific immune system
Natural, innate, non-adaptive, constitutive, nonimmune, native
the specific immune response is part of the ___________
adaptive immune system
characteristics of the adaptive immune system include
slow, response is specific to the invader, requires prior exposure to the pathogen, response is improved with repeated exposure
what are the body’s 3 main lines of defense
Non-specific surface defenses, non-specific interior defenses, specific immune defenses
The skin is an example of
a non specific surface defense
the eyes are an example of
a non specific surface defense
goblet cells are an example of
a non specific surface defense
goblet cells provide defense by
secreting mucous to trap bacteria and producing substances that are toxic to bacteria
the skin provides defense by
being a physical barrier, shedding to dislodge organisms, containing organisms that help defend
the eyes provide defense by
producing tears, having lysosomes that destroys the cell wall in bacteria, blinking
phagocytosis is an example of
non specific interior defenses
inflammation is an example of
a non specific interior defense
the complement system is an example of
a non specific interior defense
interferons are an example of
a non specific interior defense
b cells (antibodies) are an example of
specific immune defense
t lymphs (killer cells) are an example of
specific immune defenses
the humoral immune response
follows the primary immune response to an antigen
the anamnestic humoral response
is a memory formed after repeated exposure to an antigen
microorganisms use humans for
food, shelter and reproduction
a carrier is
a person who harbors organisms but shows no sign of infection
an infection
the human host is sick because of the organism
nosocomial acquired infection
a hospital acquired infection
the place of origin of an infecting agent is referred to as
a reservoir
microbial reservoirs include:
humans
animals
water
food
soil
air
what is direct transmission
host contacts the reservoir directly
what is indirect transmission
an additional agent such as a vector or a vehicle introduces the organism to the host
what is a vector
a living mode of transport for an organism
what is a vehicle
a non living mode of transport for an organism
what are the 3 types of infection
acute, chronic, latent
what is an acute infection
an infection that develops quickly from the time of exposure
what is a chronic infection
an infection that develops slowly from the time of exposure
what is a latent infection
an infection that can live in your body inactive, and flare up when your immune system is weak
what is a sign of infection
measurable indications or physical observations
what is a symptom of infection
what is described by the host
what is active immunization
the bacteria is introduced to the body which creates antibodies
what is passive immunization
the antibodies from the bacteria are introduced in hopes of creating more
what is epidemiology
the science of infectious diseases and the effects they have on public health
bacteria are
prokaryotic
what does prokaryotic mean
they lack organelles
bacteria contain a cell wall made of
peptidoglycan
what bacteria is shaped like balls
cocci
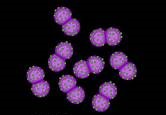
what bacteria is this
diplococci (2 balls)
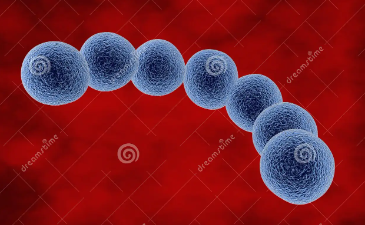
what bacteria is this
streptococci ( chain of balls)
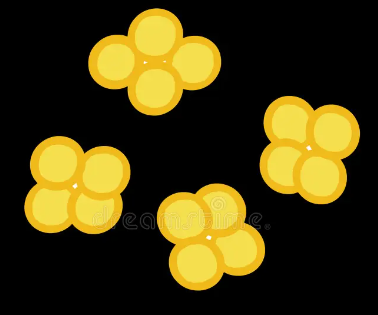
what bacteria is this
tetrad (4 cocci)
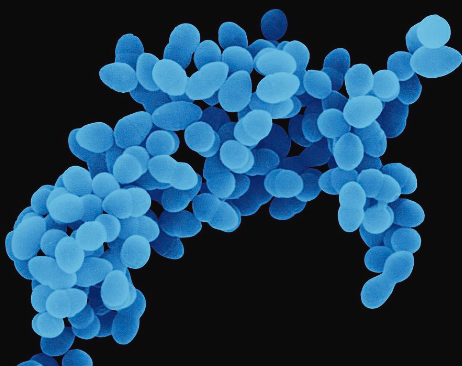
what bacteria is this
staphylococci ( grape cluster)
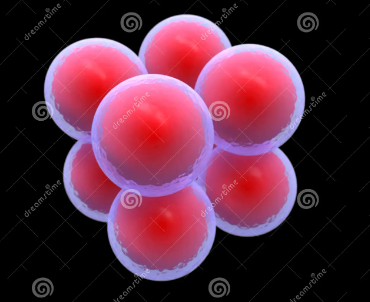
what bacteria is this
sarcina (8 or 2 tetrads)

what bacteria is this
chain of bacilli (elongated chain)

what bacteria is this
flagellate rods (elongated and has legs)
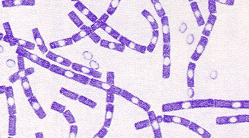
what bacteria is this
spore former

what kind of bacteria is this
vibrios (has a tail and able to move)

what bacteria is this
spirilla ( has multiple tails and able to move)

what bacteria is this
spirochaetes (worm)