A&P Lecture Unit 4 Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
1
New cards
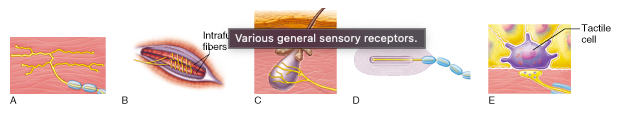
Which of these receptor types functions as an exteroceptor?
All of the listed are correct
2
New cards
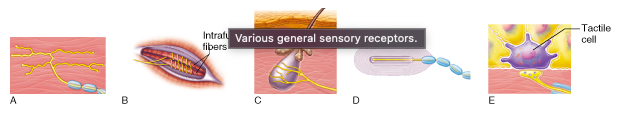
Which of the receptor types pictured functions exclusively as a proprioceptor?
B.
3
New cards
__________ are receptors that can respond to painful stimuli.
Nociceptors
4
New cards
__________ do NOT exhibit the property of adaptation.
Tonic receptors
5
New cards
Which of the following characteristics is representative of receptor-level processing, NOT perceptual-level processing?
Transduction
6
New cards
Three main levels of neural integration operate in the somatosensory system. Which level involves the spinal cord?
Circuit Level
7
New cards
Which of the following is NOT correct concerning nerves?
Nerves are collection of axons of either sensory or motor neurons but not both.
8
New cards
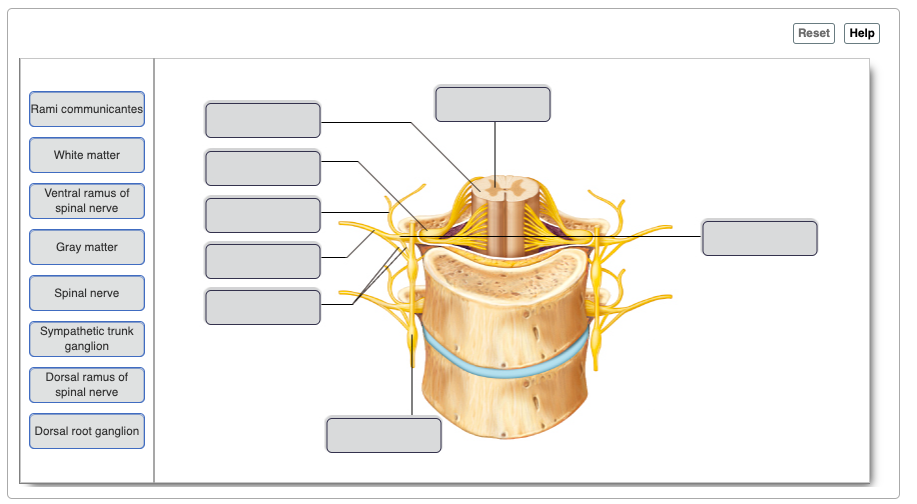
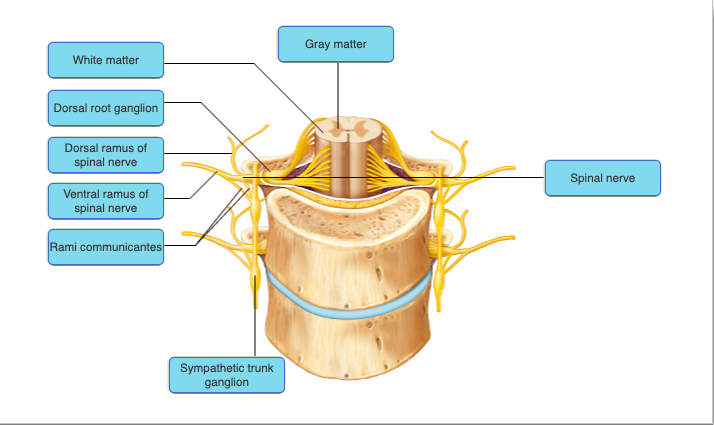
9
New cards
Spinal nerves are all classified as __________.
Mixed nerves
10
New cards
A knee-jerk reflex that is unusually strong may be caused by ______.
transmission of excitatory signals from the brain to the neurons that form the femoral nerve
11
New cards
What is a benefit of a nerve plexus?
Damage to one single branch of a plexus does not necessarily disrupt all motor information sent to a region.
12
New cards
What motor structure inhibits the motor cortex at rest?
basal nuclei
13
New cards
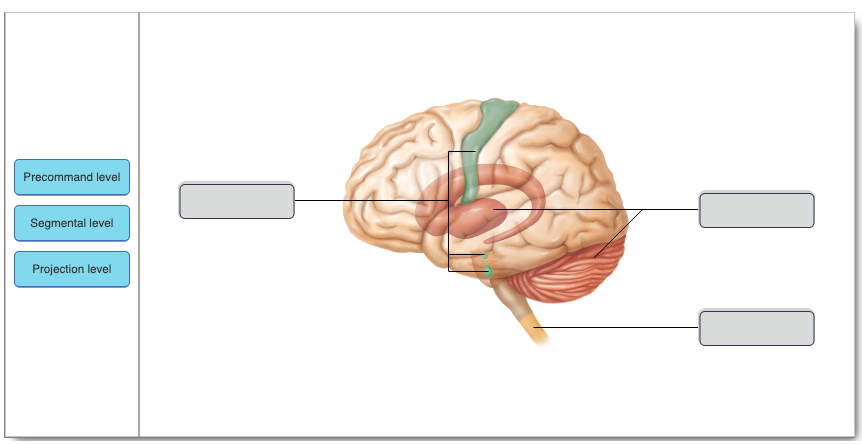
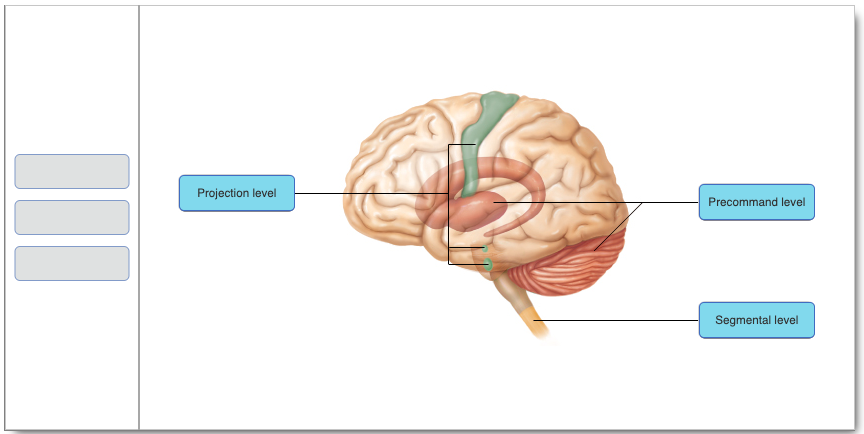
Which of the following lists the hierarchy of motor control from lowest to highest level of control?
segmental level, projection level, precommand level
14
New cards
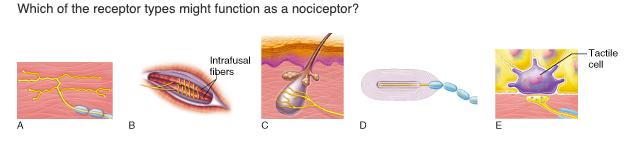
Which of the receptor types might function as a nociceptor?
A
15
New cards
Which type of sensory receptor allows us to feel an insect landing on our skin?
mechanoreceptor
16
New cards
Classify the neuron at A.
afferent sensory neuron
17
New cards
What is the specific function of the structure labeled F?
determination of muscle length
18
New cards
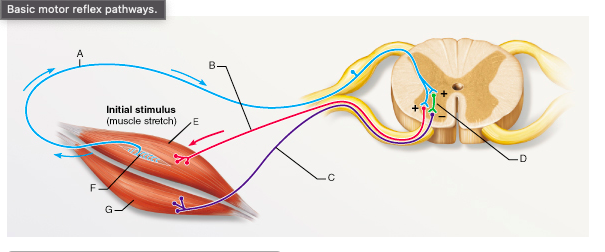
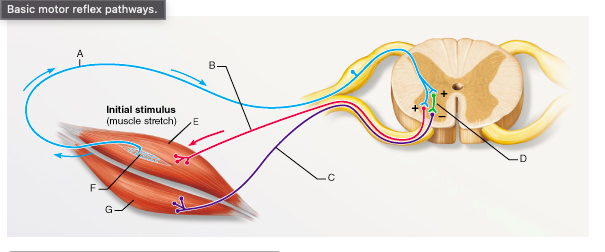
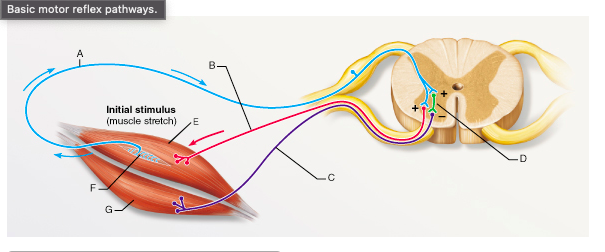
The synapse between which of the following two neurons is a part of a monosynaptic reflex arc?
A and B
19
New cards
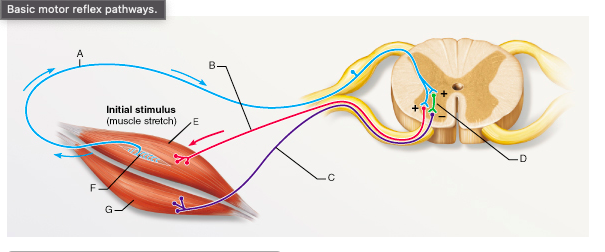
What is the type of reflex represented by the pathway that includes A, D, and C?
reciprocal inhibition
20
New cards
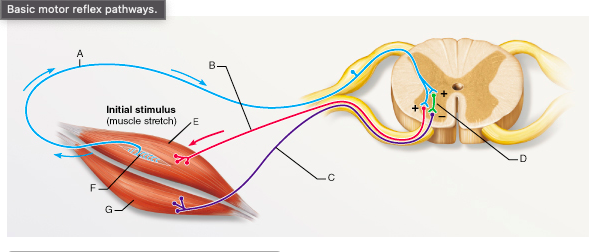
The letter E would represent which of the following muscles during the knee-jerk reflex?
rectus femoris
21
New cards
The knee-jerk reflex is an example of a __________.
stretch reflex
22
New cards
Which reflex is triggered when a stranger suddenly grasps your arm?
crossed-extensor reflex
23
New cards
24
New cards
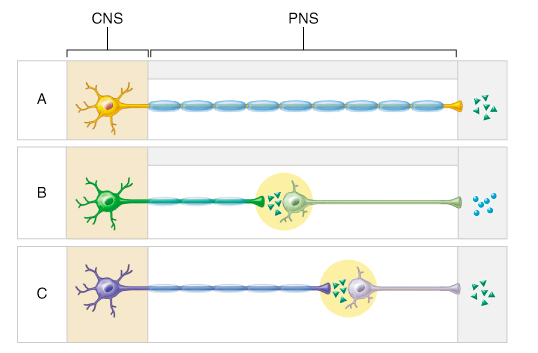
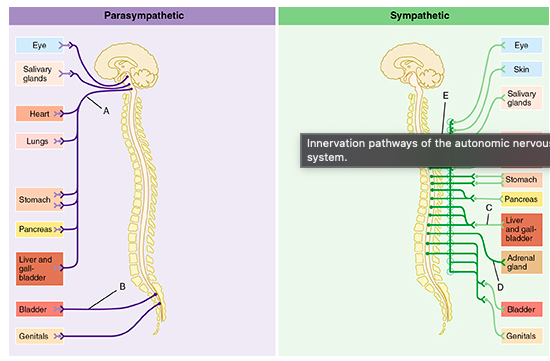
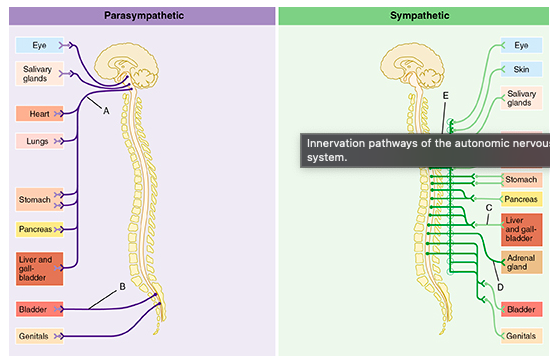
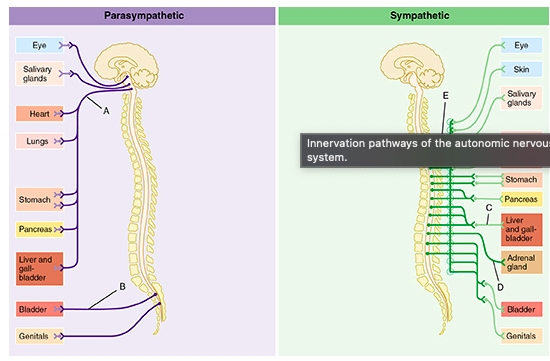
Which of the following best describes the effect on the heart of neurotransmitters released from the postganglionic neurons of B and C?
B would increase heart rate, while C would decrease it.
25
New cards
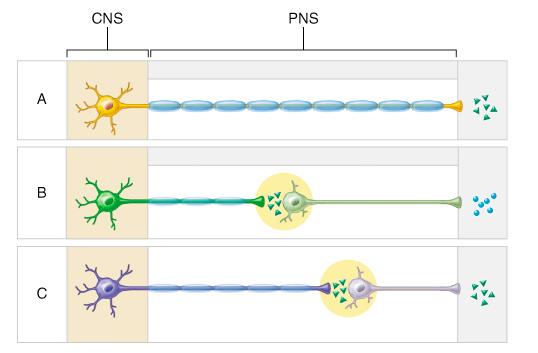
The circular structures shown within pathways B and C represent which of the following?
ganglia
26
New cards
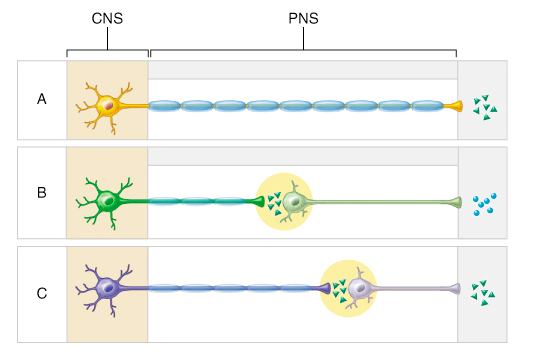
Which of the following releases the neurotransmitter norepinephrine?
terminus of a sympathetic postganglionic neuron
27
New cards
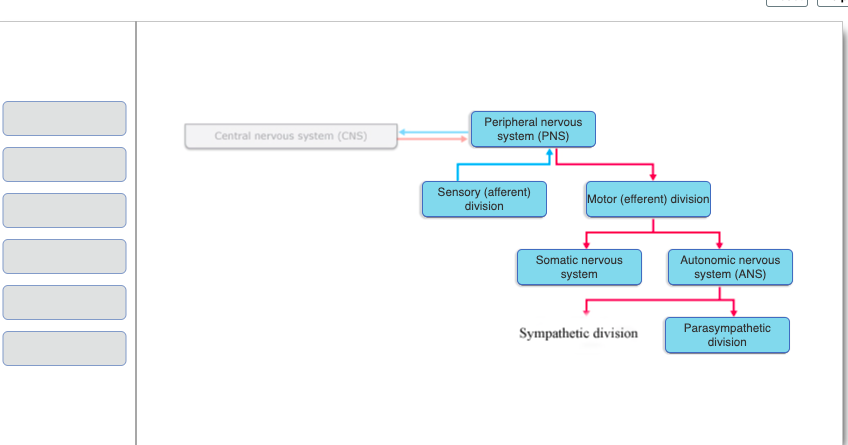
28
New cards
Where are ganglia of the parasympathetic division located?
in or near effector organs
29
New cards
Outflow of the sympathetic division occurs from which regions of the CNS?
thoracic and lumbar
30
New cards
Which organ receives major input from the sympathetic, but not parasympathetic, division?
skin
31
New cards
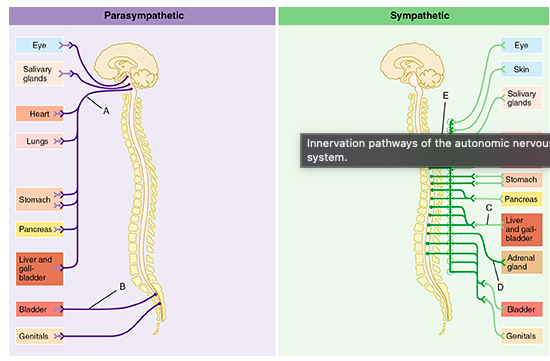
Which of the letters in the figure indicates the vagus nerve?
A
32
New cards
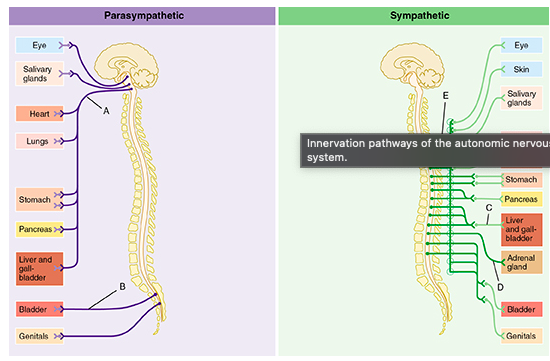
The group of fibers indicated by E represents which of the following?
white rami communicantes
33
New cards
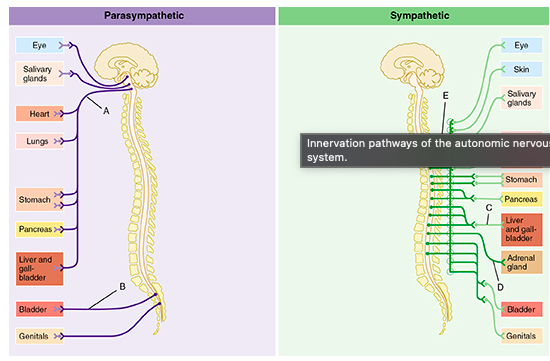
Which of the following statements is true of the group of fibers indicated by the letter D?
D indicates fibers that bypass collateral ganglia and terminate within the adrenal gland
34
New cards
Which of these activities is most likely driven by parasympathetic innervation?
resting and digesting
35
New cards
Which of the following is NOT an autonomic nervous system (ANS) function?
reflex of skeletal muscle
36
New cards
Which division of the nervous system has long preganglionic neurons?
parasympathetic
37
New cards
Which target organ is NOT affected by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
adrenal medulla
38
New cards
Which set of details correctly identifies a series of events in a sympathetic pathway?
thoracolumbar origin, short preganglionic fiber, ACh release at ganglion, long postganglionic fiber, NE release at effector
39
New cards
What differentiates an autonomic reflex from a somatic reflex?
a two-neuron motor pathway
40
New cards
Which receptor paring below is correct?
nicotinic; acetylchline
41
New cards
The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine during sympathetic stimulation. Which of the following statements describes why epinephrine would increase the sympathetic response?
The same receptors that respond to norepinephrine also respond to epinephrine, increasing the action of both.
42
New cards
Which of the following target organs/systems is affected by the sympathetic nervous system but is NOT affected by the parasympathetic nervous system?
cellular metabolism
43
New cards
Which of the following is responsible for the overall integration of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
hypothalamus
44
New cards
The somatic and autonomic nervous systems differ in all of the following EXCEPT ________.
regulation of activity by higher brain centers
45
New cards
Preparing the body for the "fight-or-flight" response is the role of the ________.
sympathetic division
46
New cards
The "resting and digesting" division of the autonomic nervous system is the ________.
parasympathetic division
47
New cards
Which of the following is NOT associated with the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
emergency action
48
New cards
The parasympathetic ganglion that serves the eye is the ________
ciliary ganglion
49
New cards
The sympathetic division innervates targets with nerves that all originate from the thoracolumbar region.
True
50
New cards
Unlike the sympathetic division, the parasympathetic division synapses with the adrenal medulla.
False
51
New cards
Once a preganglionic axon reaches a trunk ganglion, one of three things can happen to the axon. Which of the following is NOT one of these three things?
The axon can course back into the spinal cord to synapse with preganglionic neurons in a different spinal segment.
52
New cards
The secretions of the adrenal medulla act to supplement the effects of ________.
sympathetic division
53
New cards
Fibers that enter and leave the sympathetic trunks without synapsing form structures called ________.
splanchnic nerves
54
New cards
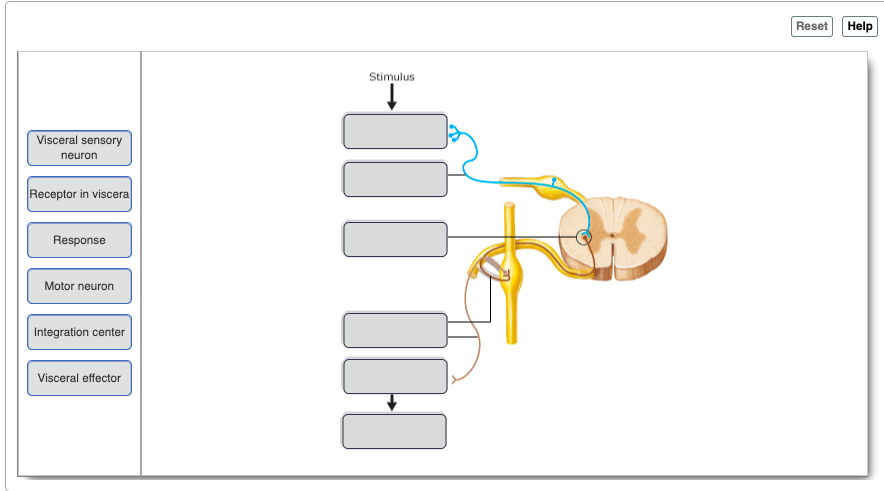
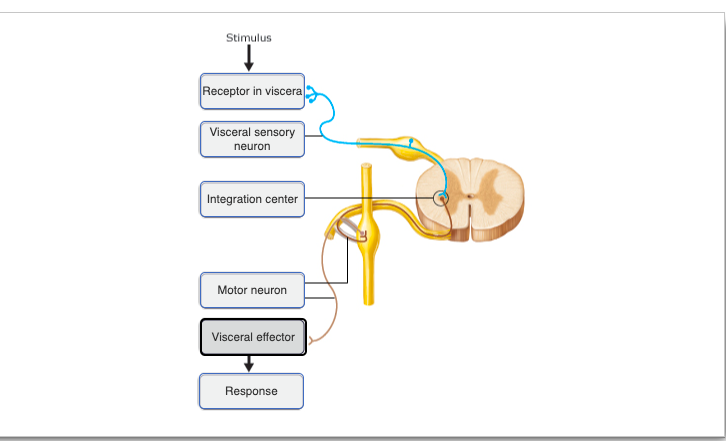
55
New cards
Where would you NOT find a cholinergeric nicotinic receptor?
all parasympathetic target organs
56
New cards
Which of the following adrenergic neurotransmitter receptors plays the major role in heart activity?
beta 1
57
New cards
Which of the following is characteristic of the parasympathetic division?
stimulates secretory activity
58
New cards
Sympathetic responses generally are widespread because ________.
NE and epinephrine are secreted into the blood as part of the sympathetic response
59
New cards
Control of temperature, endocrine activity, and thirst are functions associated with the ________.
hypothalamus
60
New cards
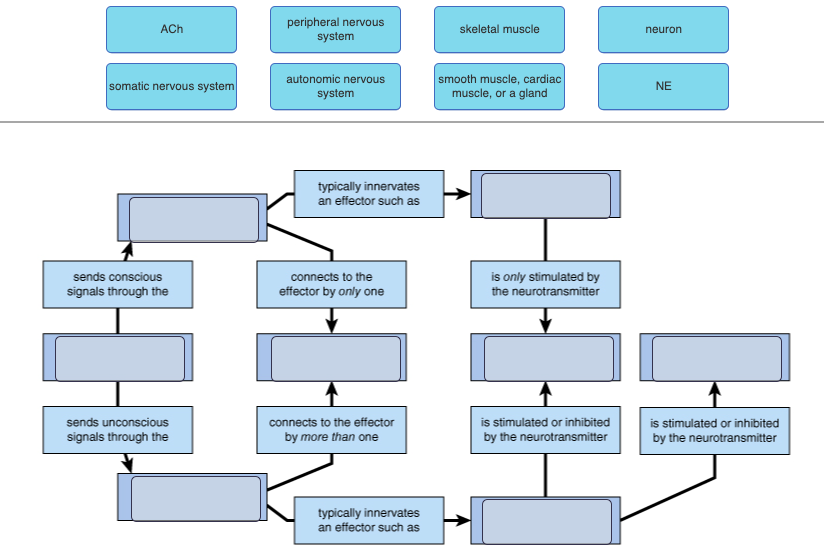
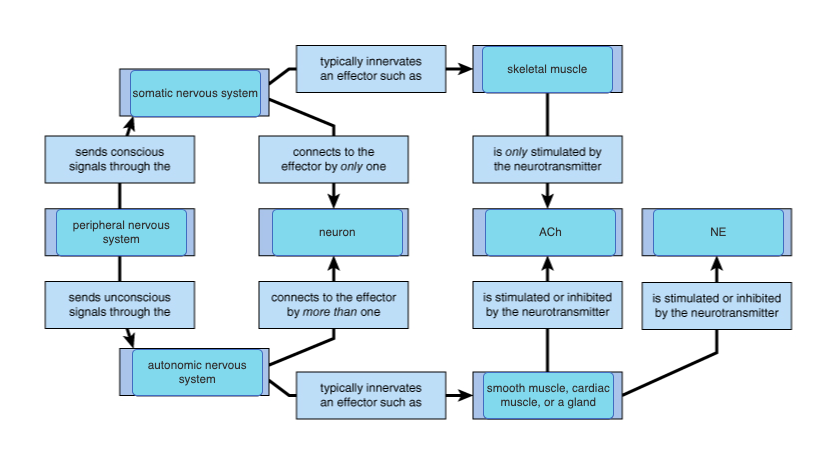
61
New cards
All somatic motor neurons produce __________.
only acetylcholine
62
New cards
Autonomic motor neurons __________.
utilize a two-neuron chain to reach their effectors
63
New cards
Autonomic nerve fibers that increase heart rate, elevate blood pressure, induce dry mouth, and increase sweating do so primarily through the secretion of __________.
norepinephrine
64
New cards
Myelination tends to be heaviest on which types of neurons?
somatic motor neurons
65
New cards
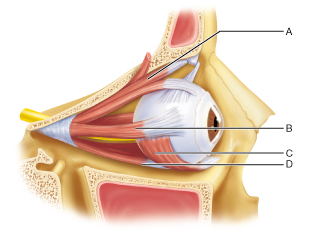
Identify the muscle responsible for depressing the eye and turning it laterally.
A
66
New cards
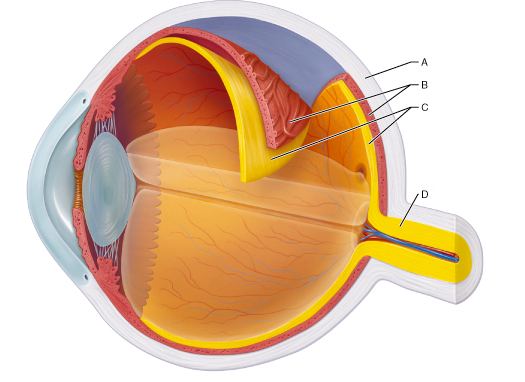
Identify the layer that contains both a single-celled pigmented layer and a neural layer.
C
67
New cards
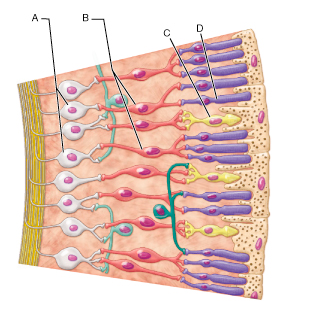
Identify the type of neuronal cell that detects bright light and provides high-resolution color vision.
68
New cards
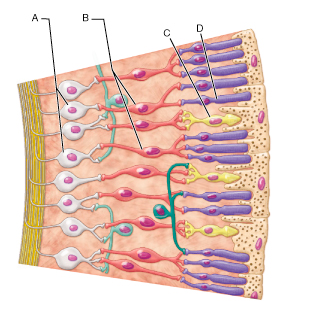
Identify the type of neuron that would be secreting neurotransmitter in the light
A and B
69
New cards
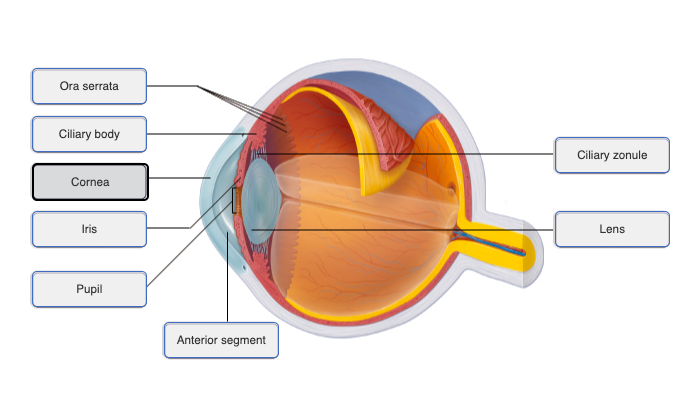
70
New cards
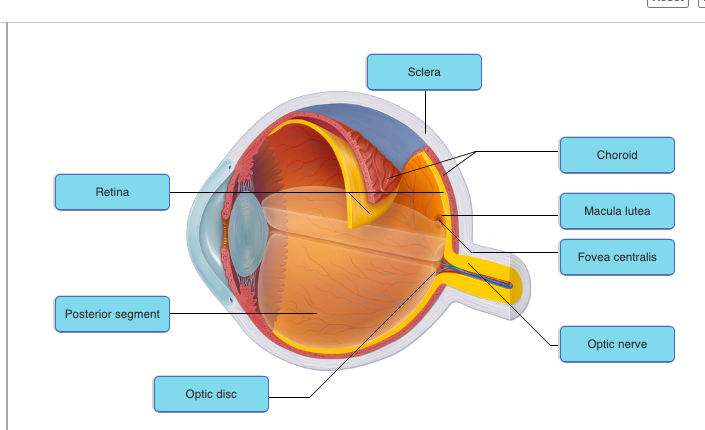
71
New cards
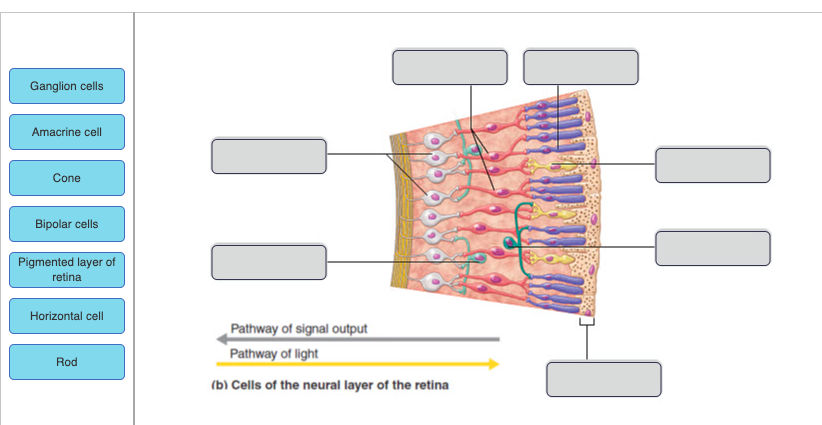
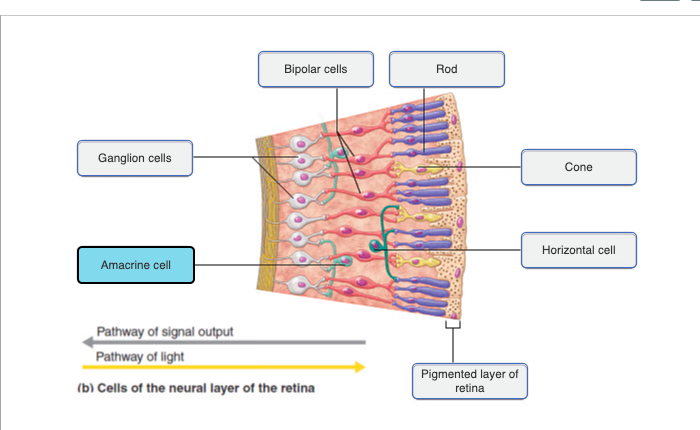
72
New cards
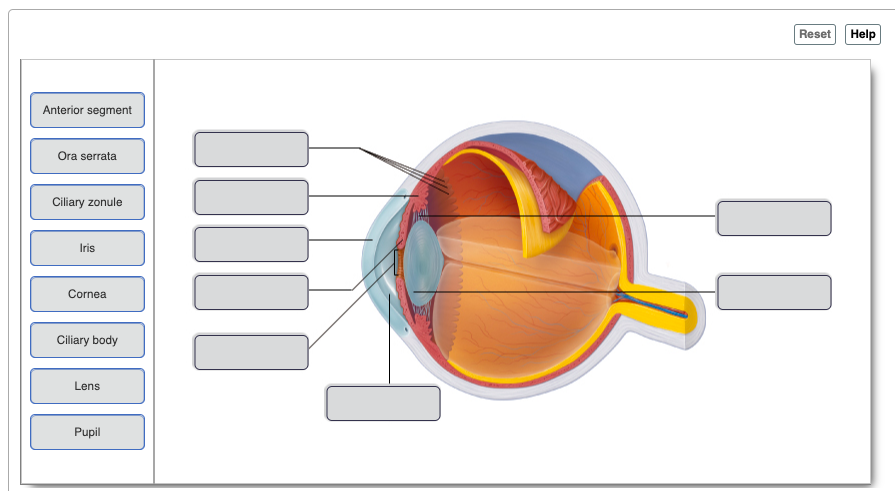
Which structure is NOT matched with its function?
ciliary body: focus the pupil
73
New cards
You want to look up and to your right. Which extrinsic eye muscles would be the most active in each eye?
right eye: inferior oblique left eye: superior rectus
74
New cards
Aqueous humor forms during capillary filtration in the __________?
ciliary body
75
New cards
If retinal detachment occurs in the macula lutea, one can predict that there would be a significant loss of ______.
color vision
76
New cards
Which structure provides the vascular support for the eye?
the choroid
77
New cards
What structure in the eye creates a visual blind spot?
optic disc
78
New cards
What term refers to the eye’s moving medially to track items close at hand?
convergence
79
New cards
During close vision, what actions must the eye take to bring an object into focus?
contract the ciliary body
80
New cards
This image best illustrates an eyeball that is __________.
emmetropic
81
New cards
Which of the following statements is true?
Contraction of the ciliary muscles is required for hyperopic individuals to clearly see distant objects.All of the listed responses are true.
82
New cards
Atropine eye drops are used to temporarily paralyze the accommodation reflex and as a long-lasting pupil dilating agent, or mydriatic. What action causes the dilation effect?
blocked contraction of sphincter pupillae muscle
83
New cards
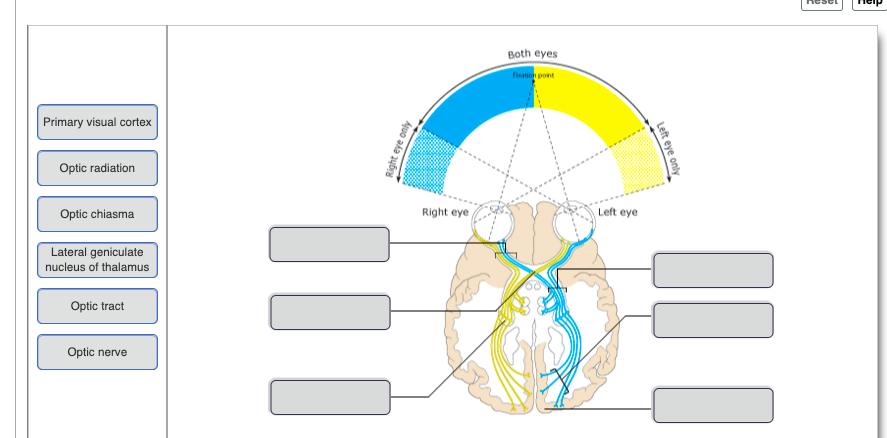
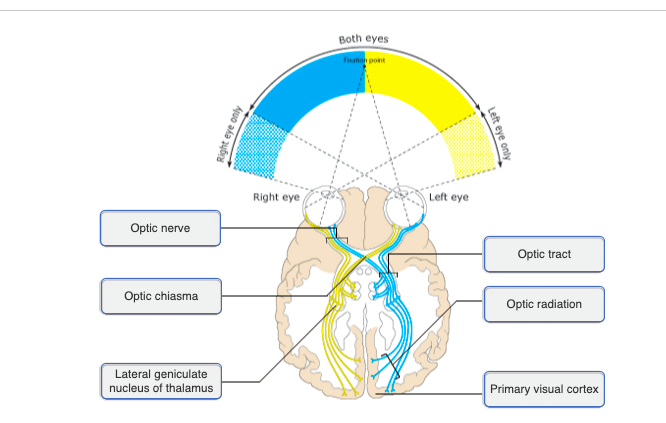
84
New cards
Damage to the medial portion of the optic chiasm, cause by a pituitary tumor, would lead to __________.
loss of peripheral vision
85
New cards
Which part of the visual pathway is responsible for our daily biorhythms?
suprachiasmatic nucleus
86
New cards
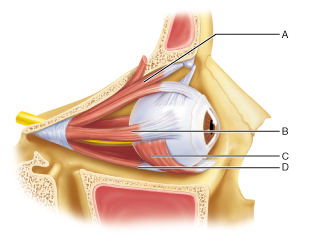
Name the muscle at D.
inferior rectus
87
New cards
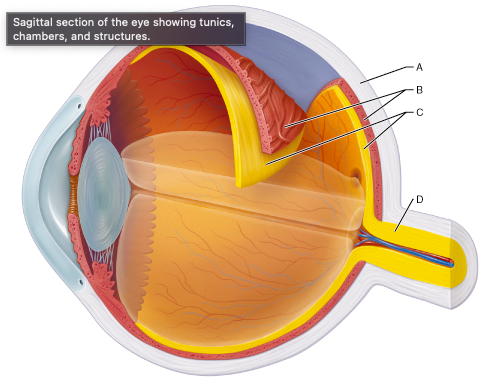
Identify the choroid.
**B**
88
New cards
As light hits the retina, the first structure the light encounters is a rod or a cone.
False
89
New cards
Which photoreceptors respond to very dim light?
Rods
90
New cards
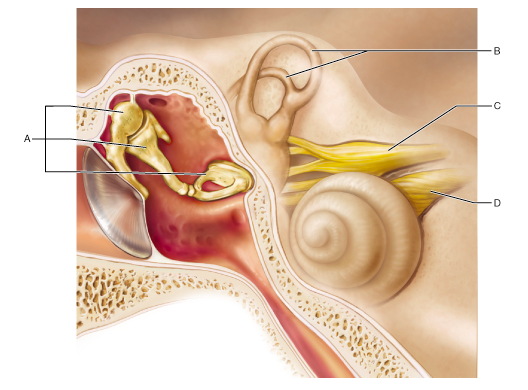
Damage to which of these structures can result in sensorineural deafness?
D
91
New cards
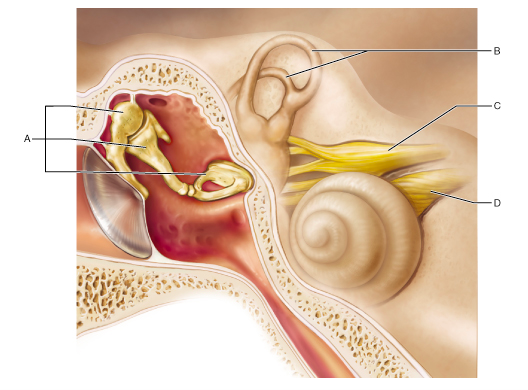
Otosclerosis, which can result in conduction deafness, affects which of these structures?
A
92
New cards
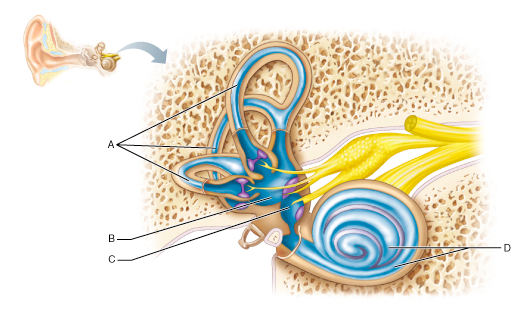
What part of the inner ear houses the receptor organ of hearing, the spiral organ (organ of Corti)?
D
93
New cards
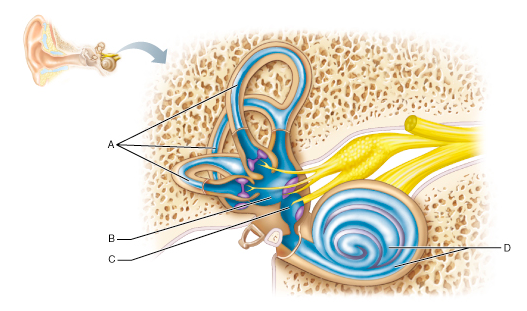
Which part of the inner ear houses receptors for rotational (angular) movement of the head?
A
94
New cards
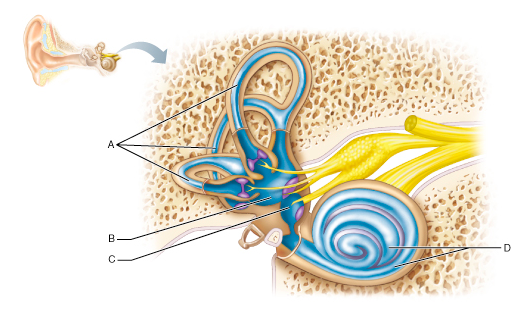
Name the enlarged swelling at the end of A that is a sensory structure.
Ampulla
95
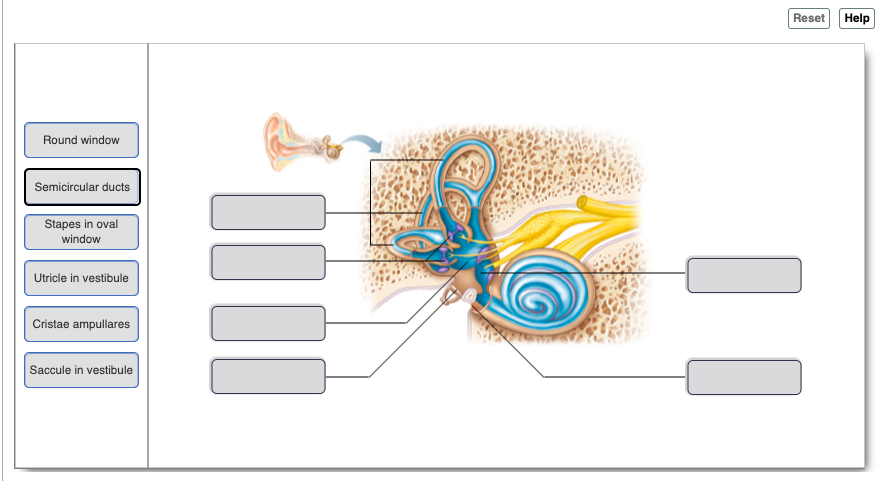
New cards
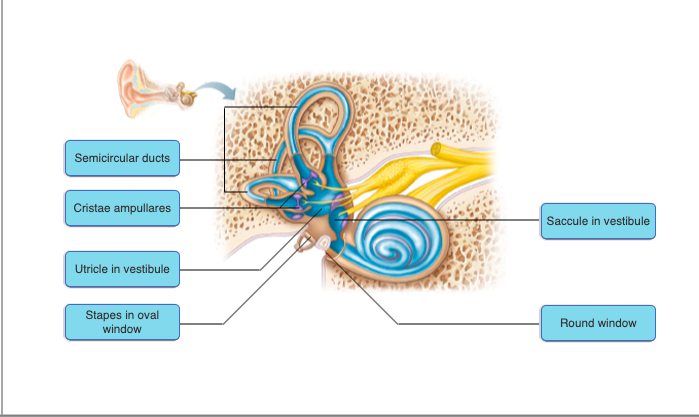
96
New cards
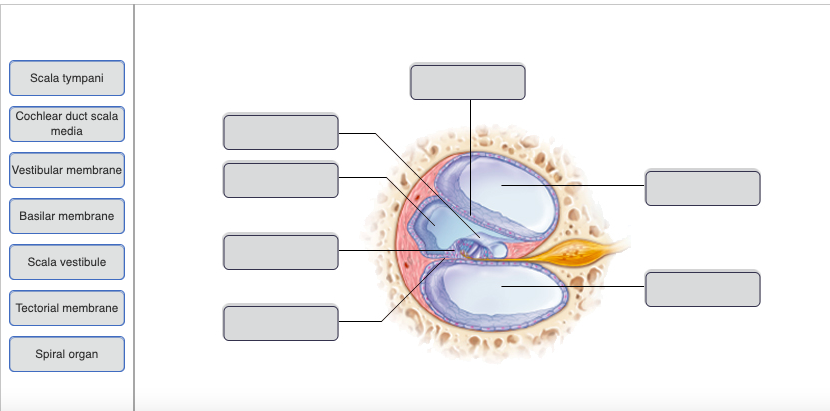
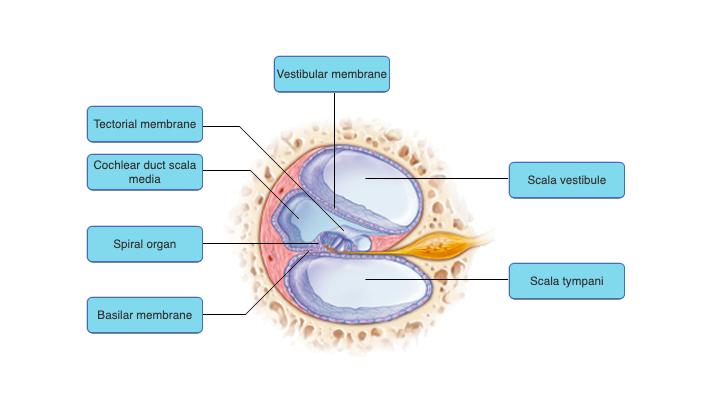
97
New cards
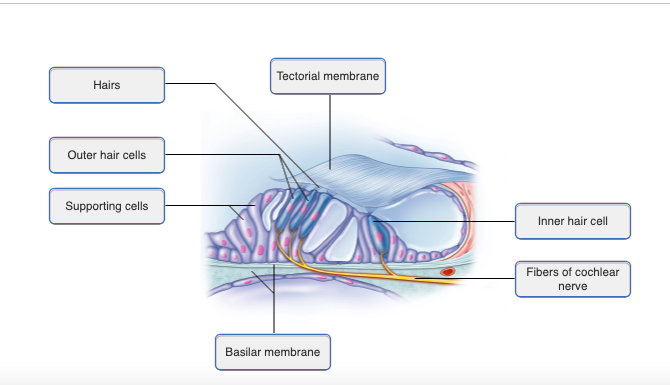
98
New cards
Which portion of the ear is responsible for sound transduction?
the cochlea
99
New cards
Transduction of lower frequency sound waves occurs at the __________ of the cochlea.
apex
100
New cards
What type of channel is responsible for the initial changes in the membrane potential of the hair cells, which ultimately determines the cochlear nerve response to sound?
mechanically gated