BIOL 1021: Lab Final
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
hydroxyl group
Name this functional group.

carbonyl group
Name this functional group.
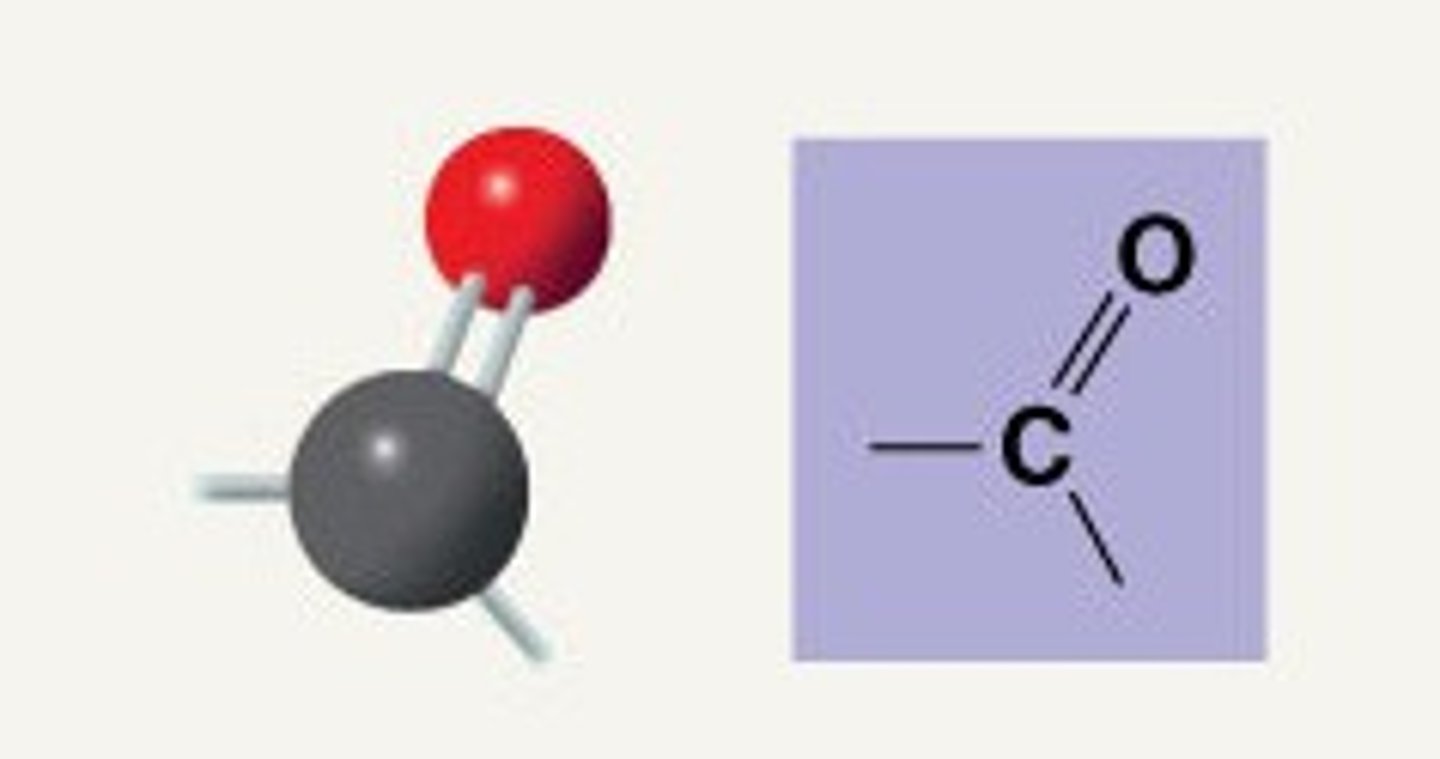
carboxyl group
Name this functional group.

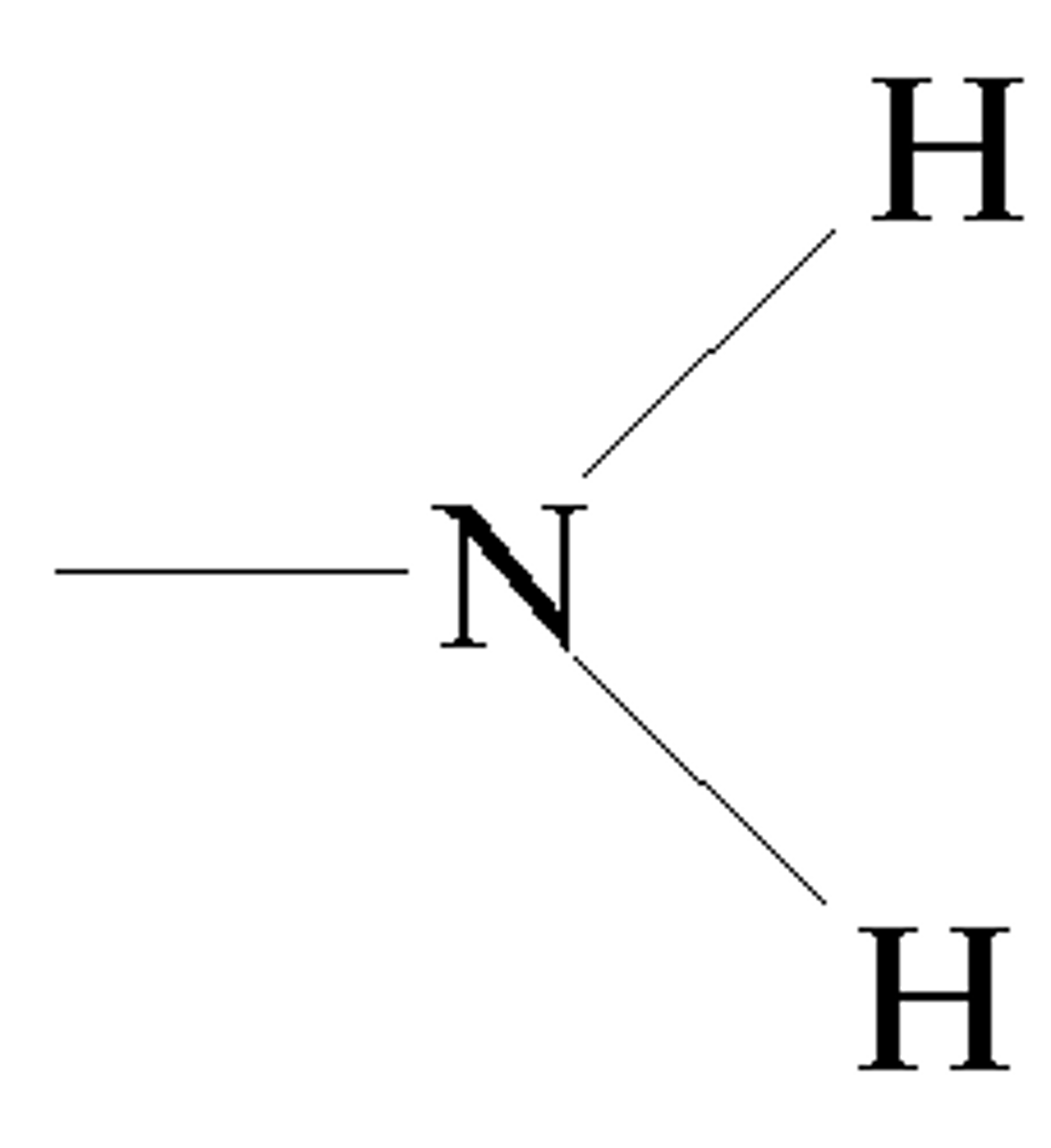
amino group
Name this functional group.
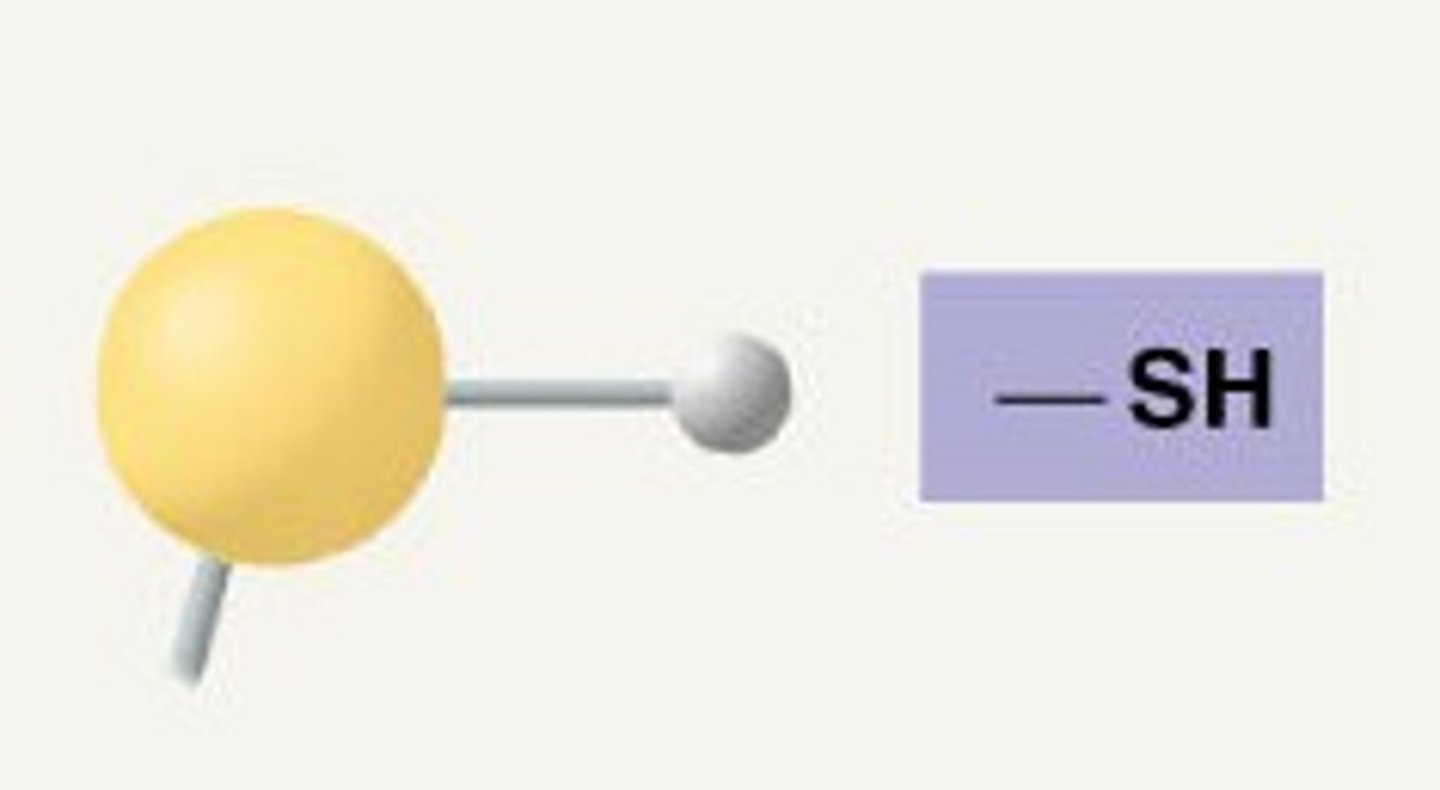
sulfhydryl group
Name this functional group.
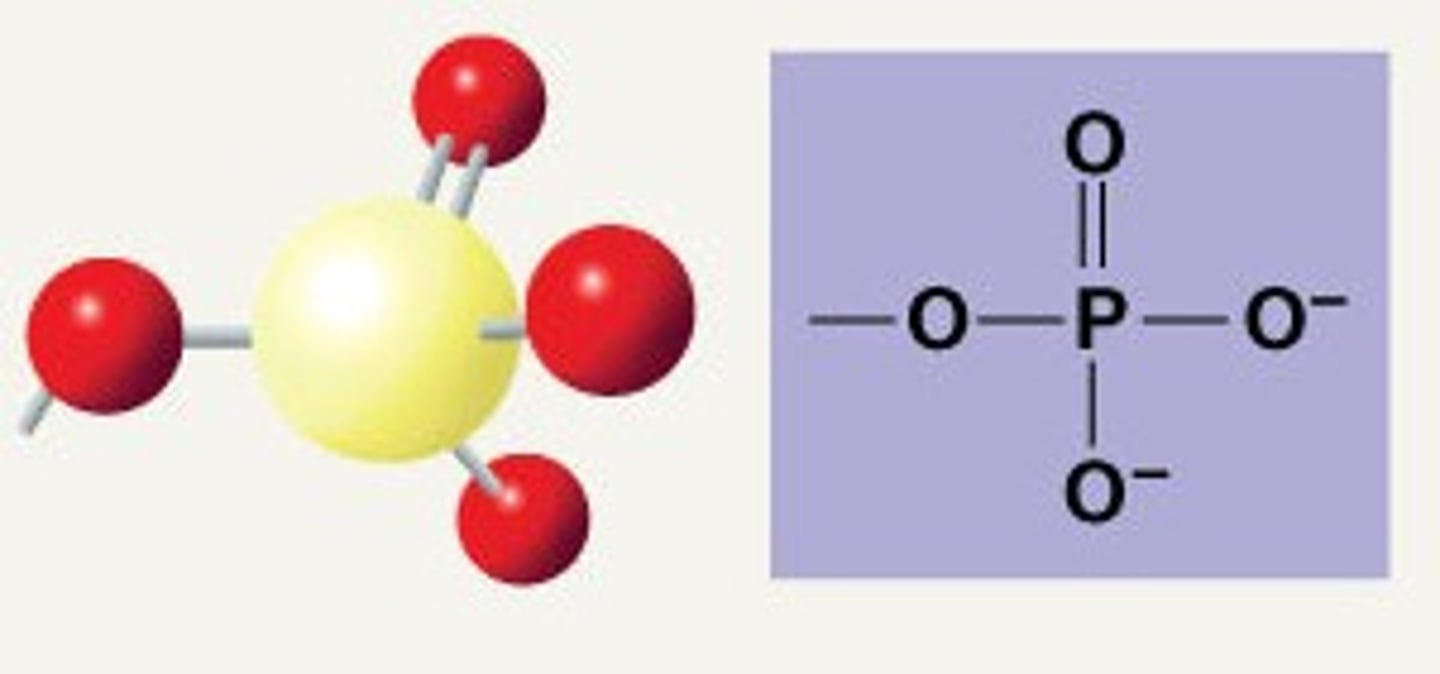
phosphate group
Name this functional group.
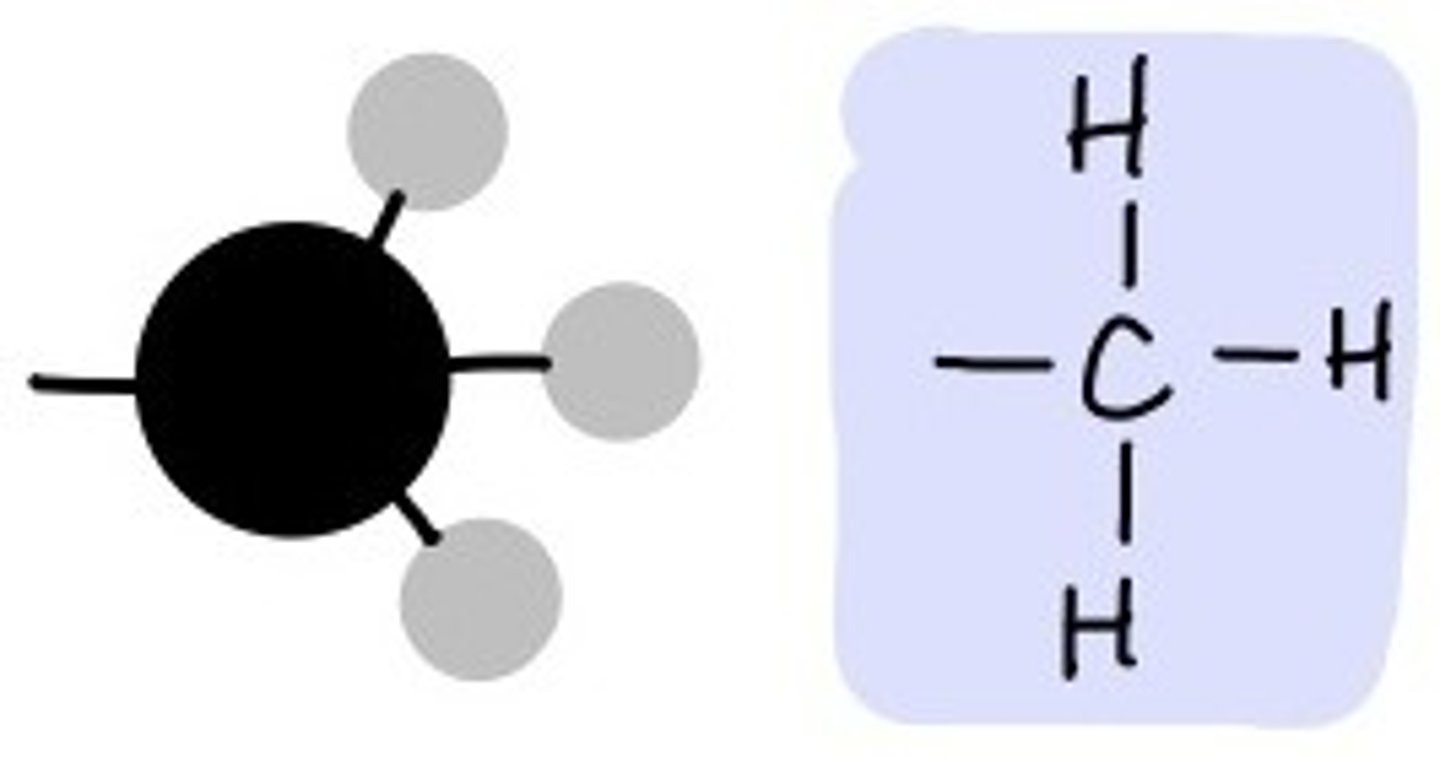
methyl group
Name this functional group.
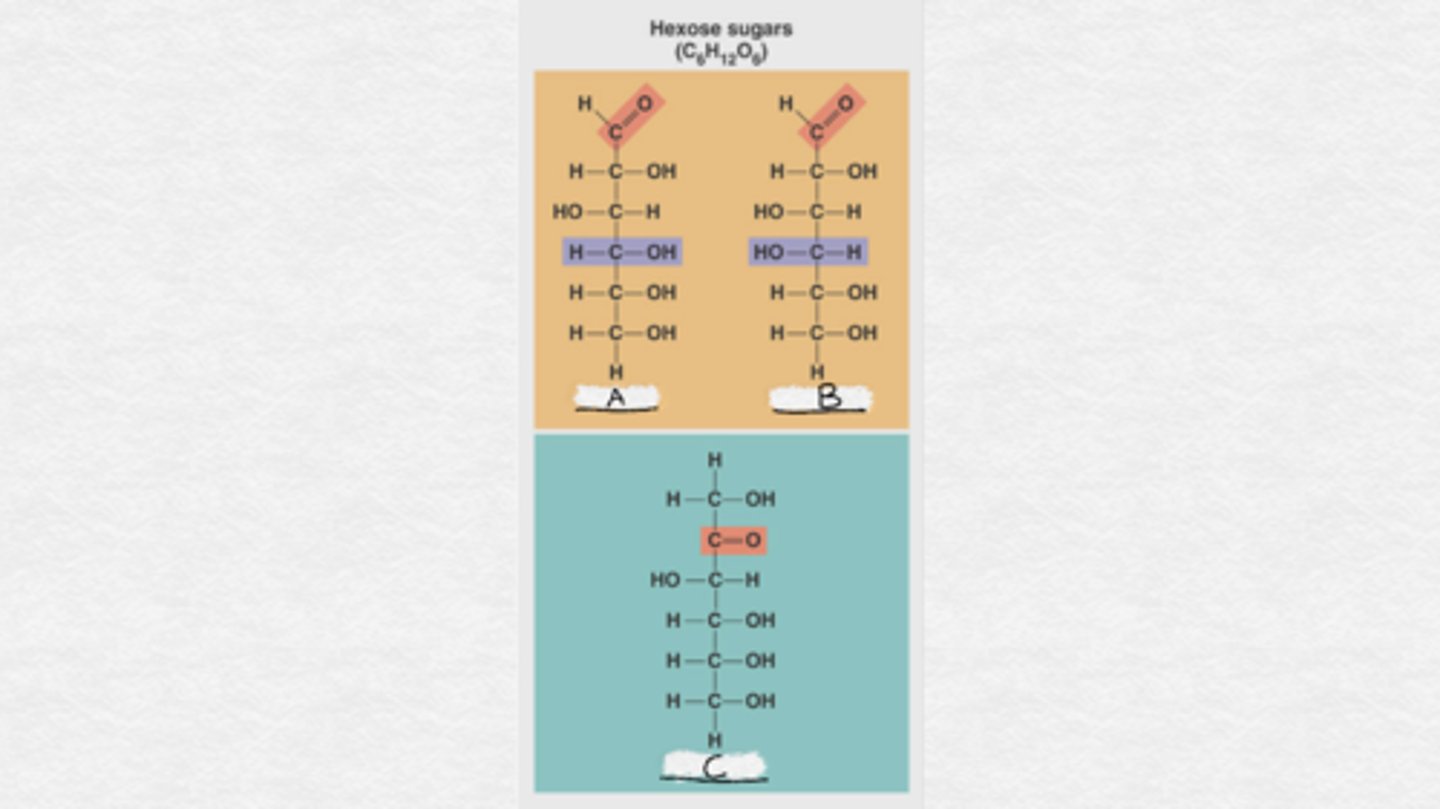
A. glucose
B. galactose
C. fructose
Label these hexose sugars in order from A to C.
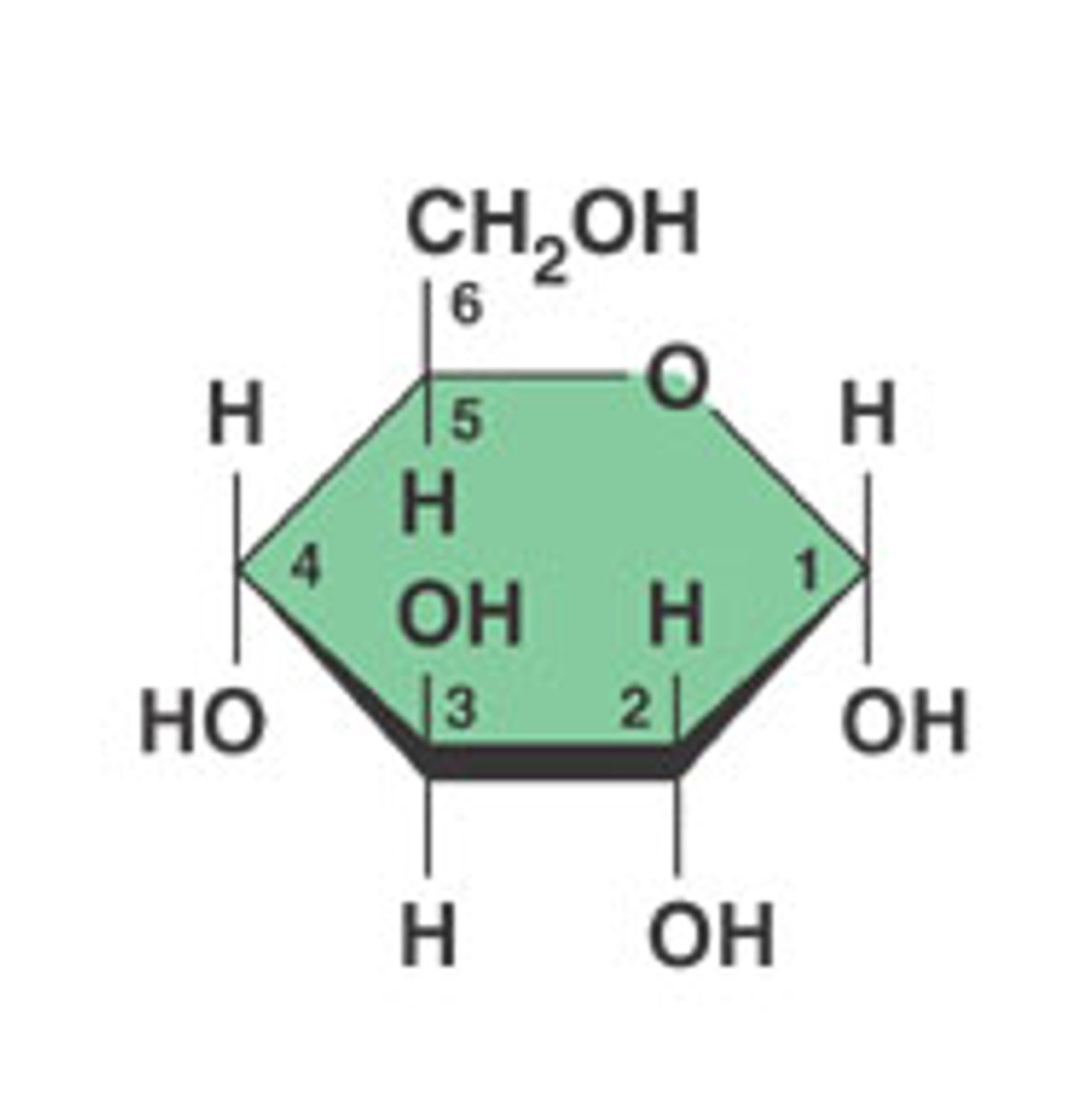
6
How many carbons does this glucose have?
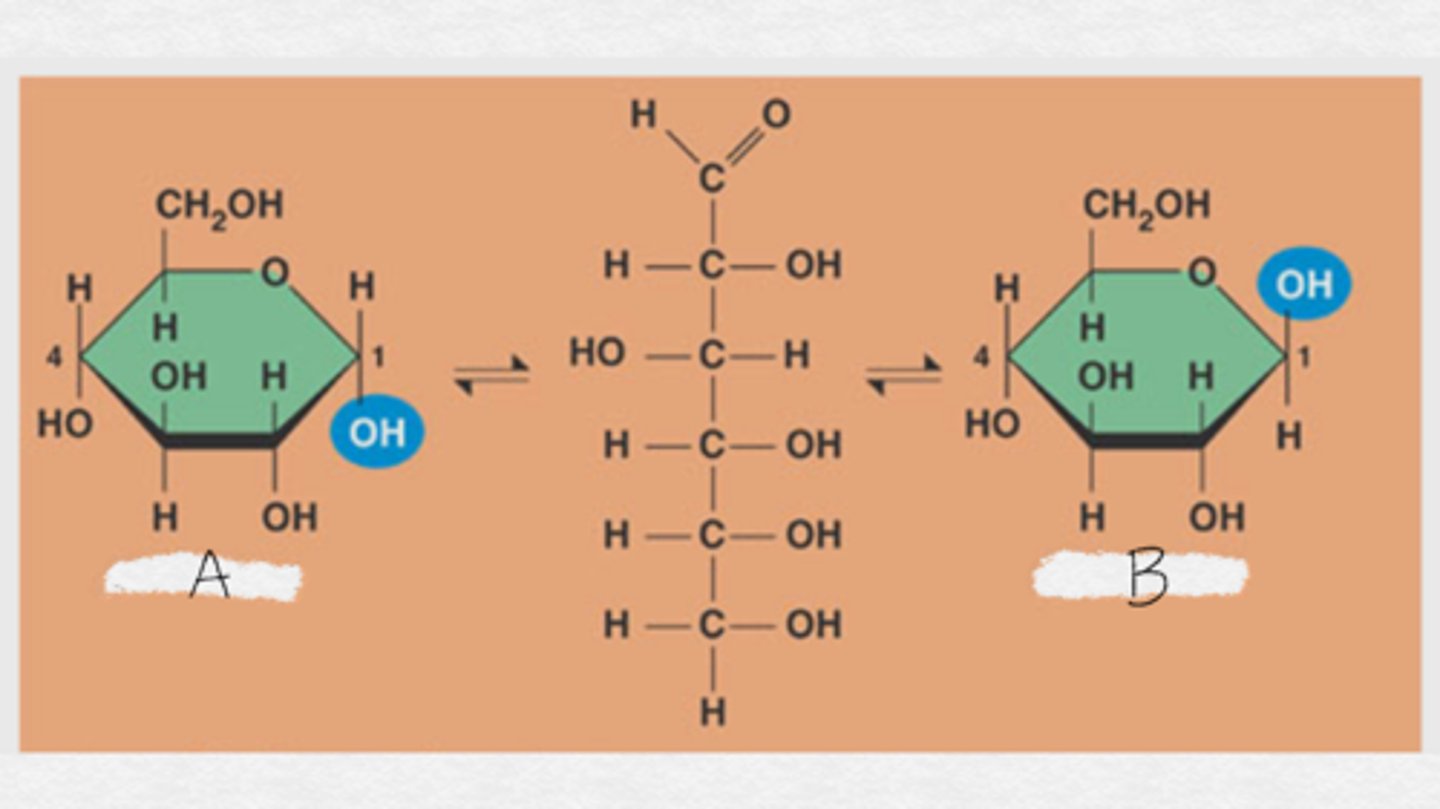
A. alpha glucose
B. beta glucose
Label these glucose molecules (which is alpha and which is beta)
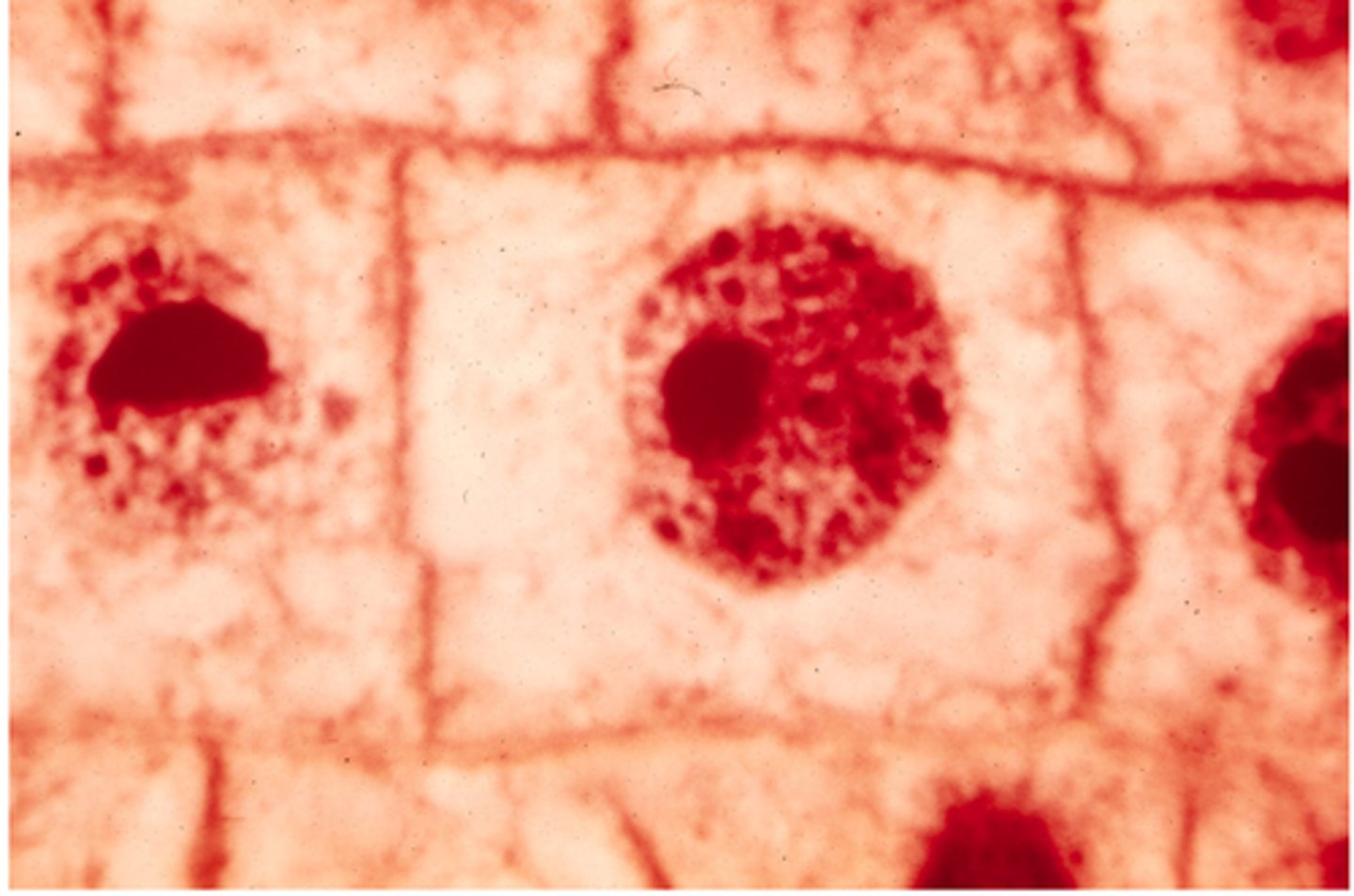
interphase
This shows _______ in onion cells.
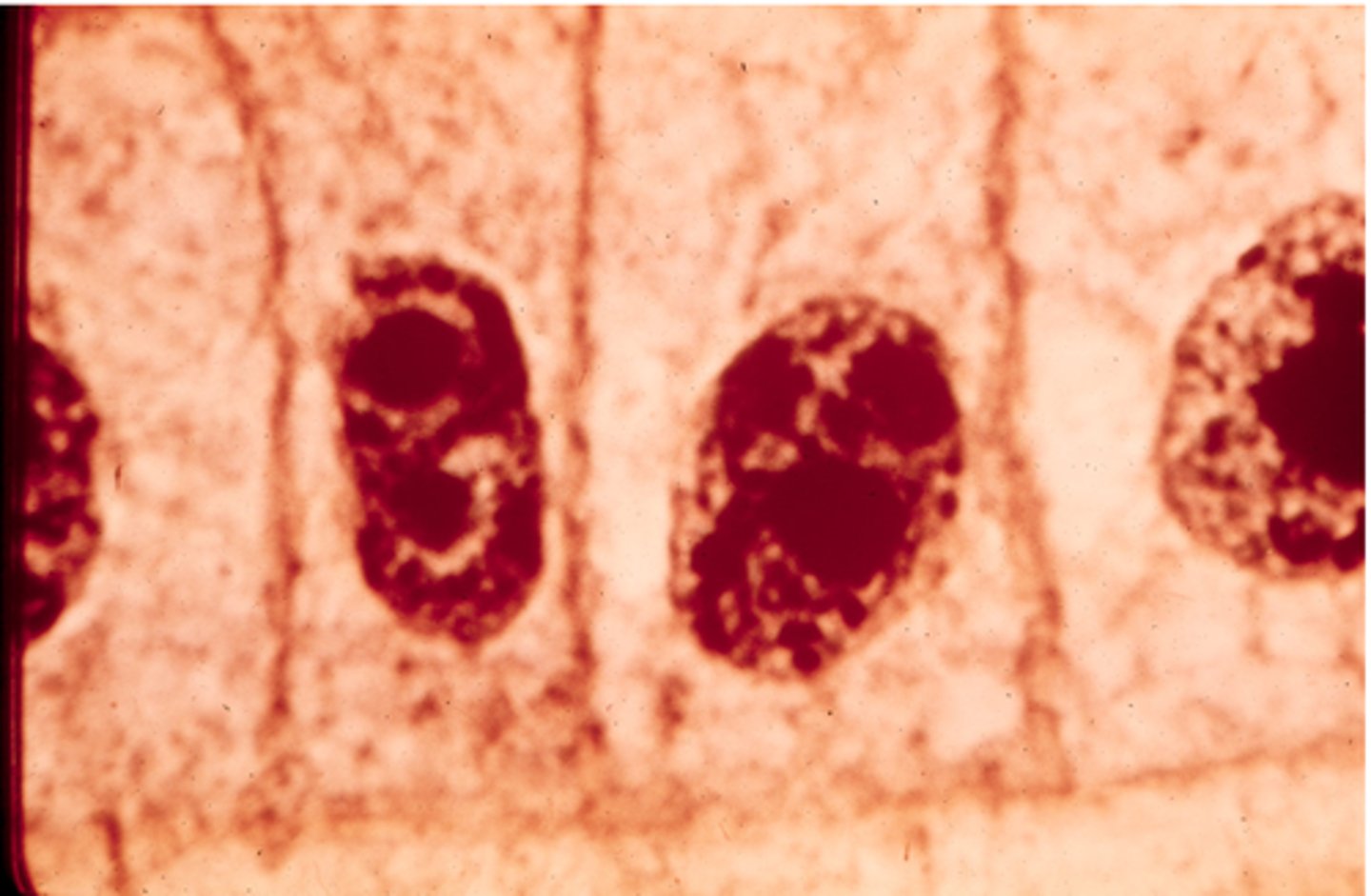
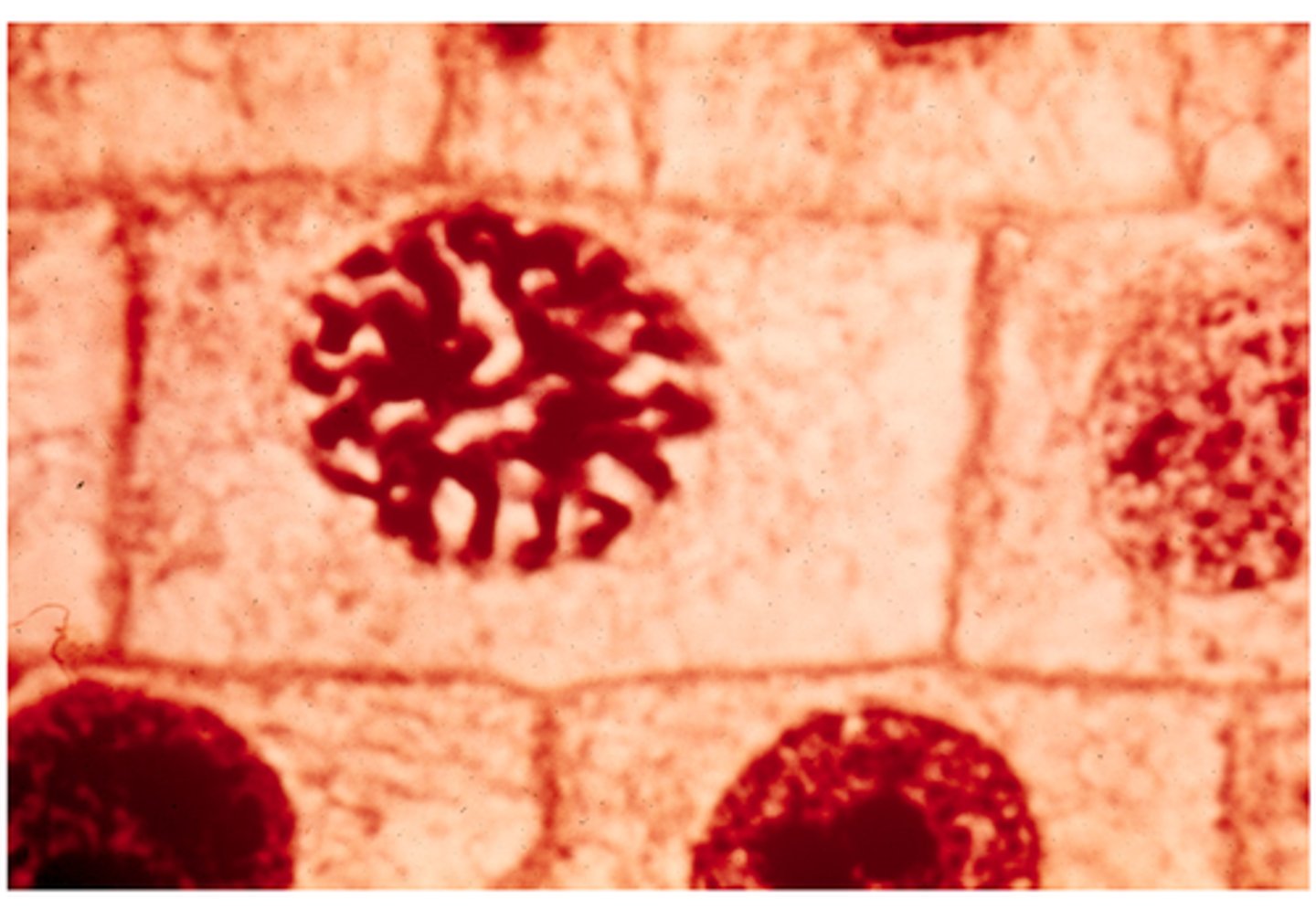
prophase
This shows ________ in onion cells.
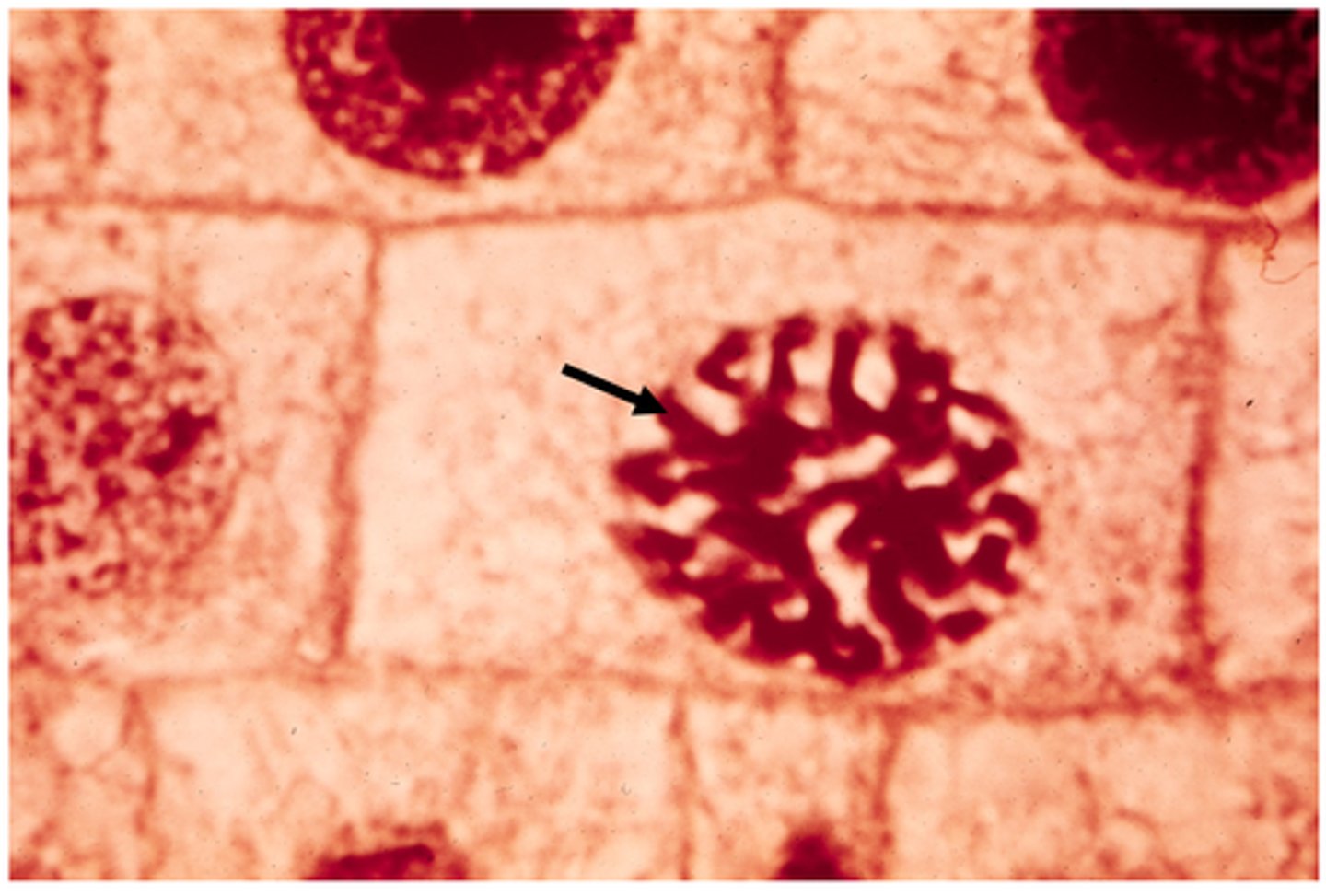
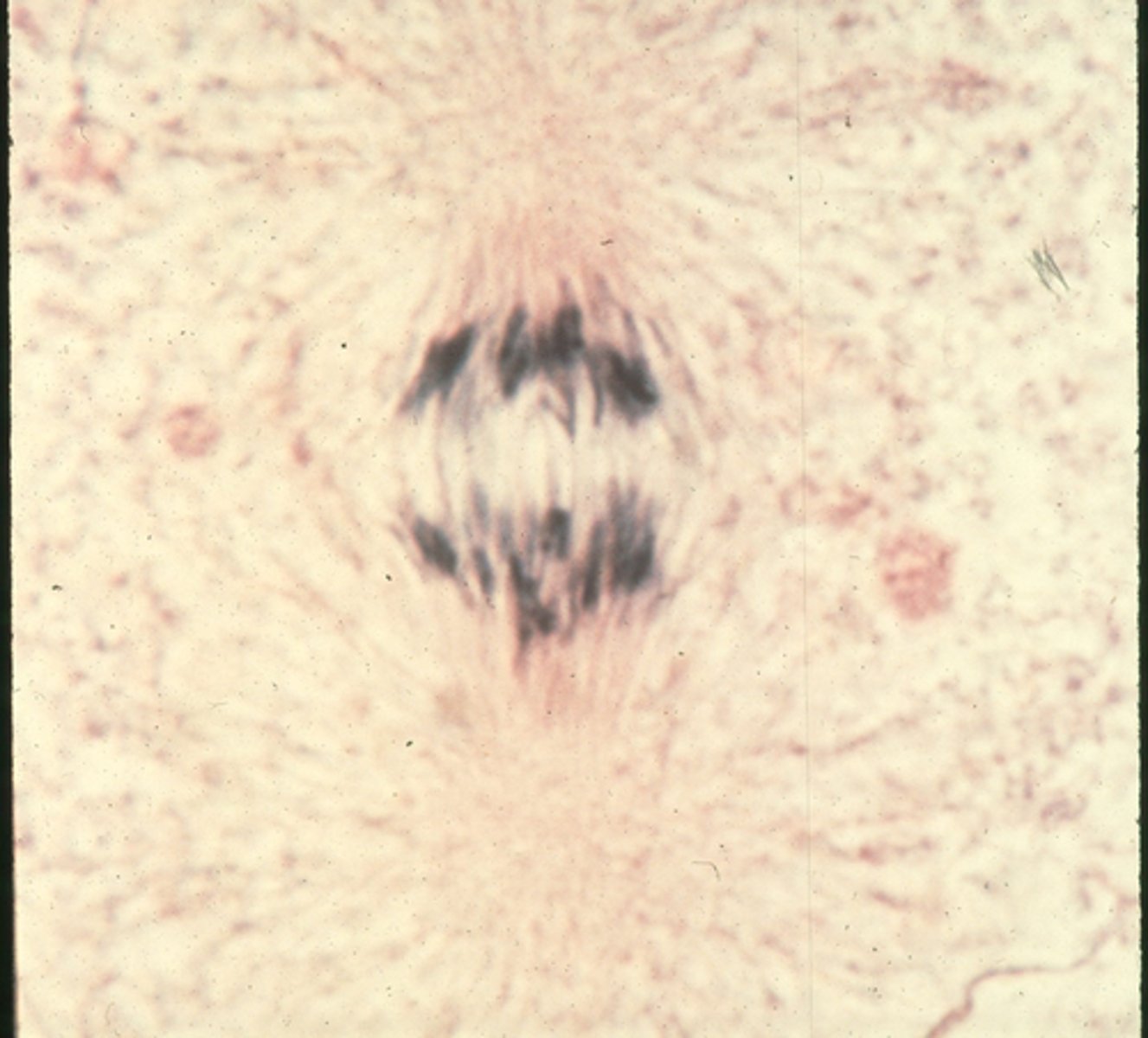
metaphase
This shows ________ in onion cells.
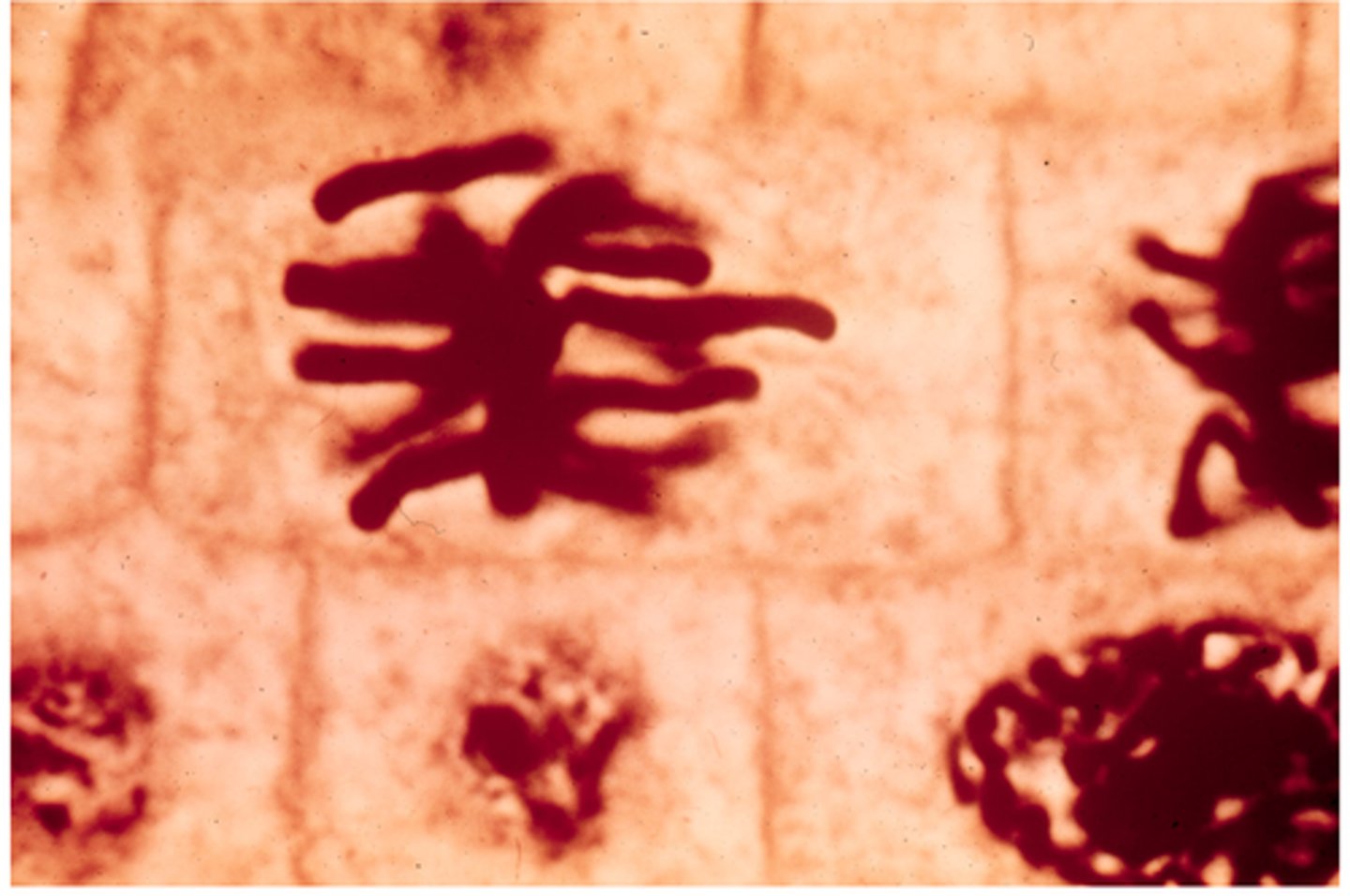
anaphase
This shows ________ in onion cells.
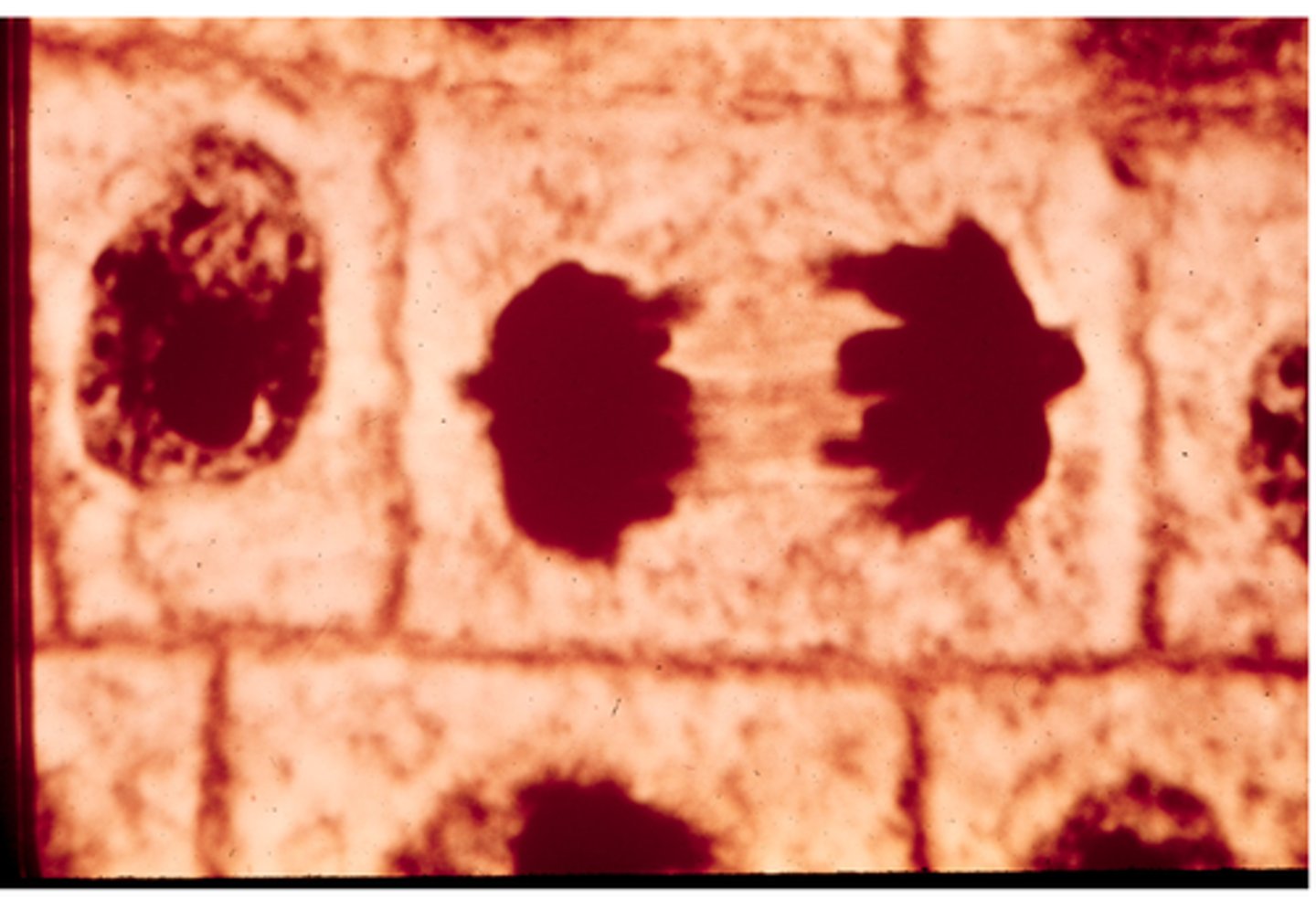
telophase
This shows ________ in onion cells.
interphase
This shows ________ in whitefish blastula.
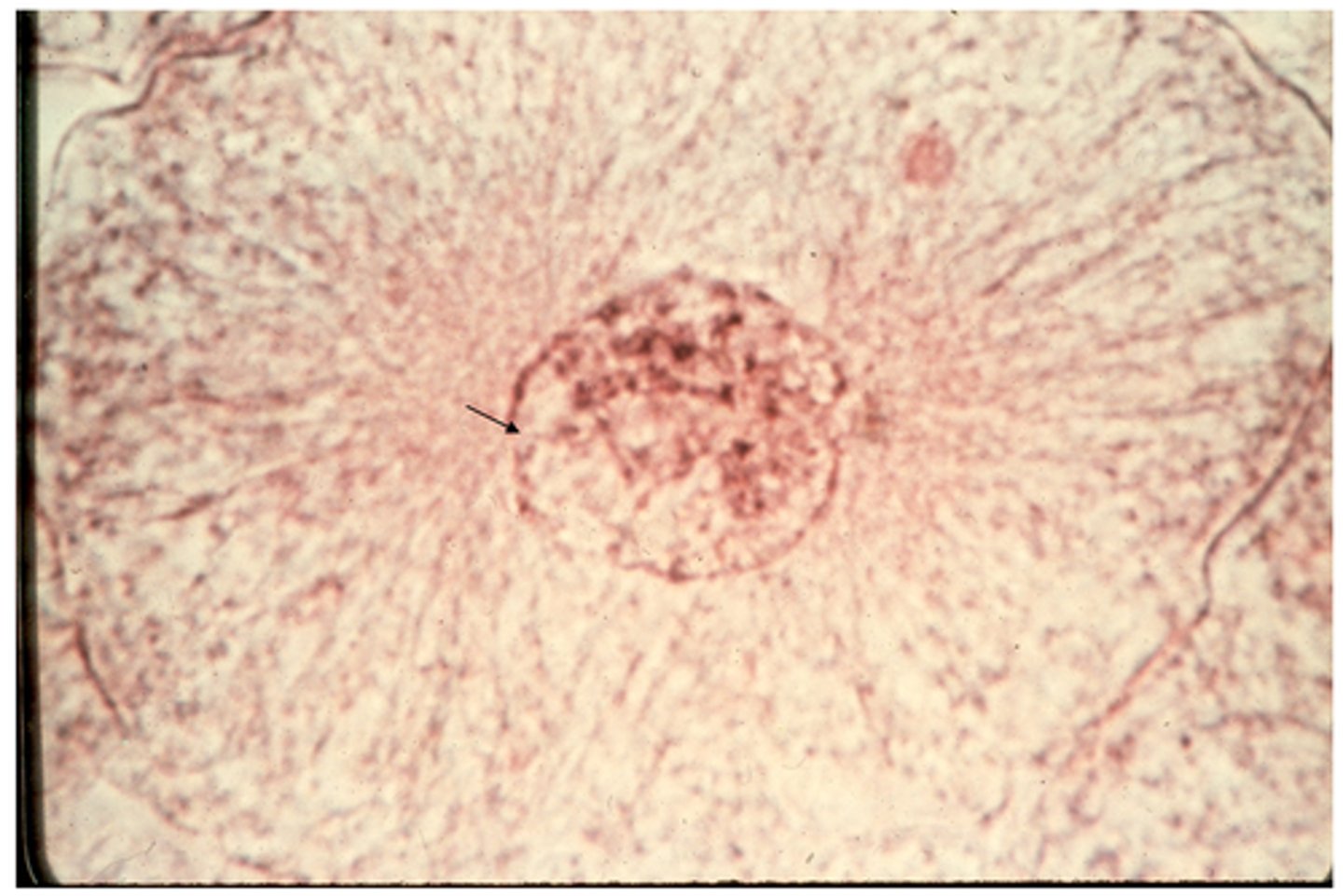
prophase
This shows ________ in whitefish blastula.
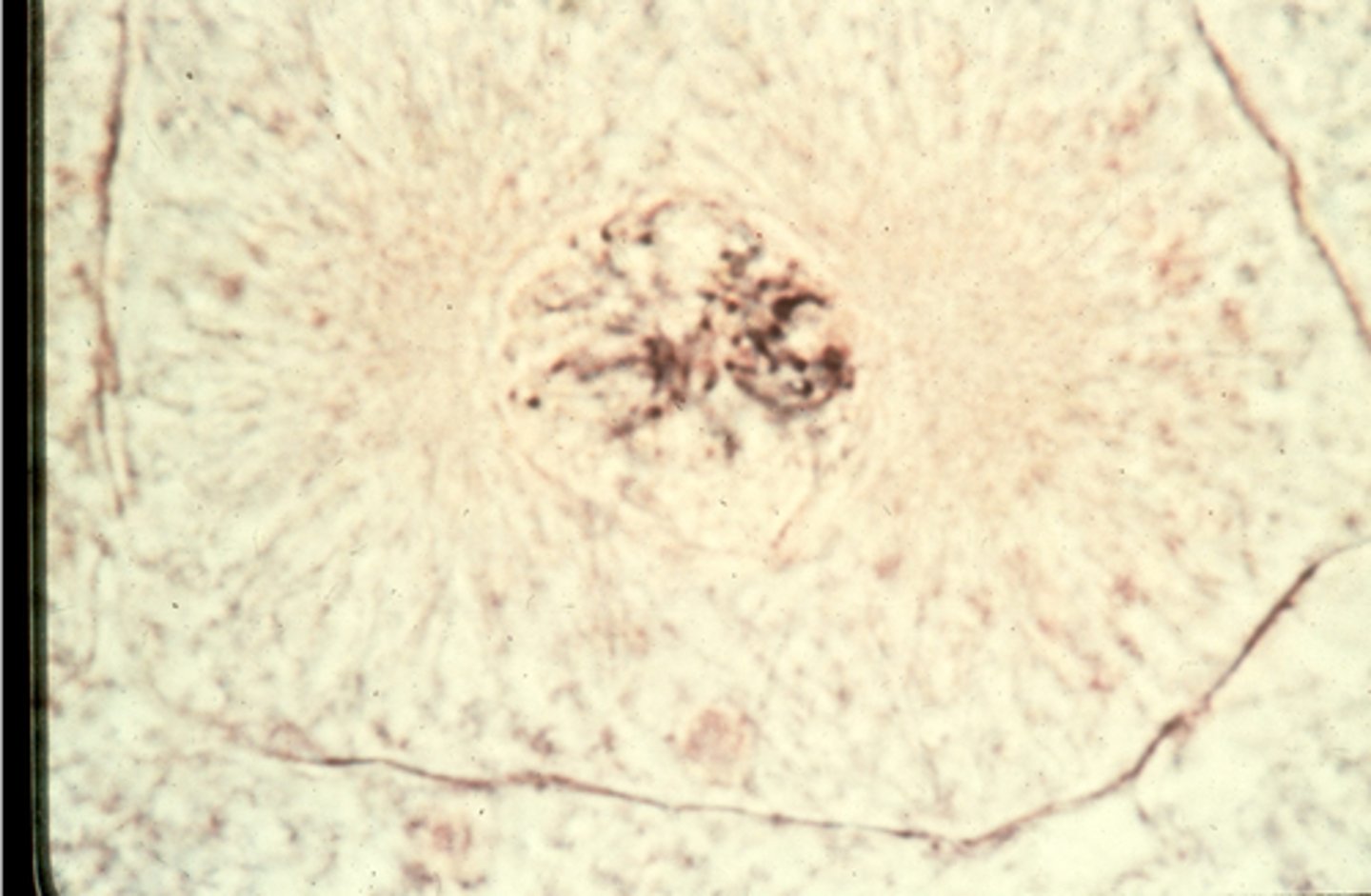
metaphase
This shows ________ in whitefish blastula.
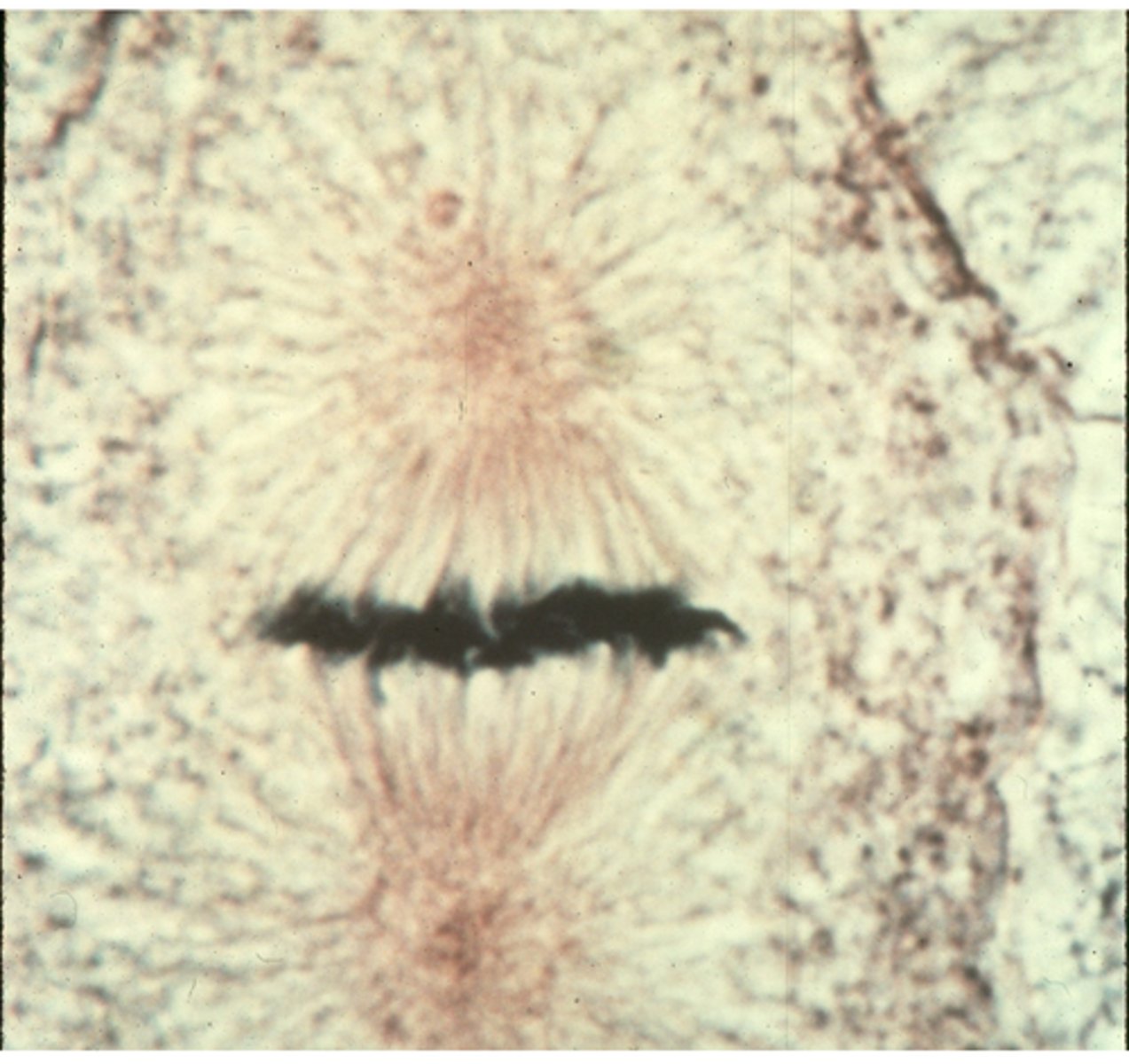
anaphase
This shows a cell entering ________ in whitefish blastula.
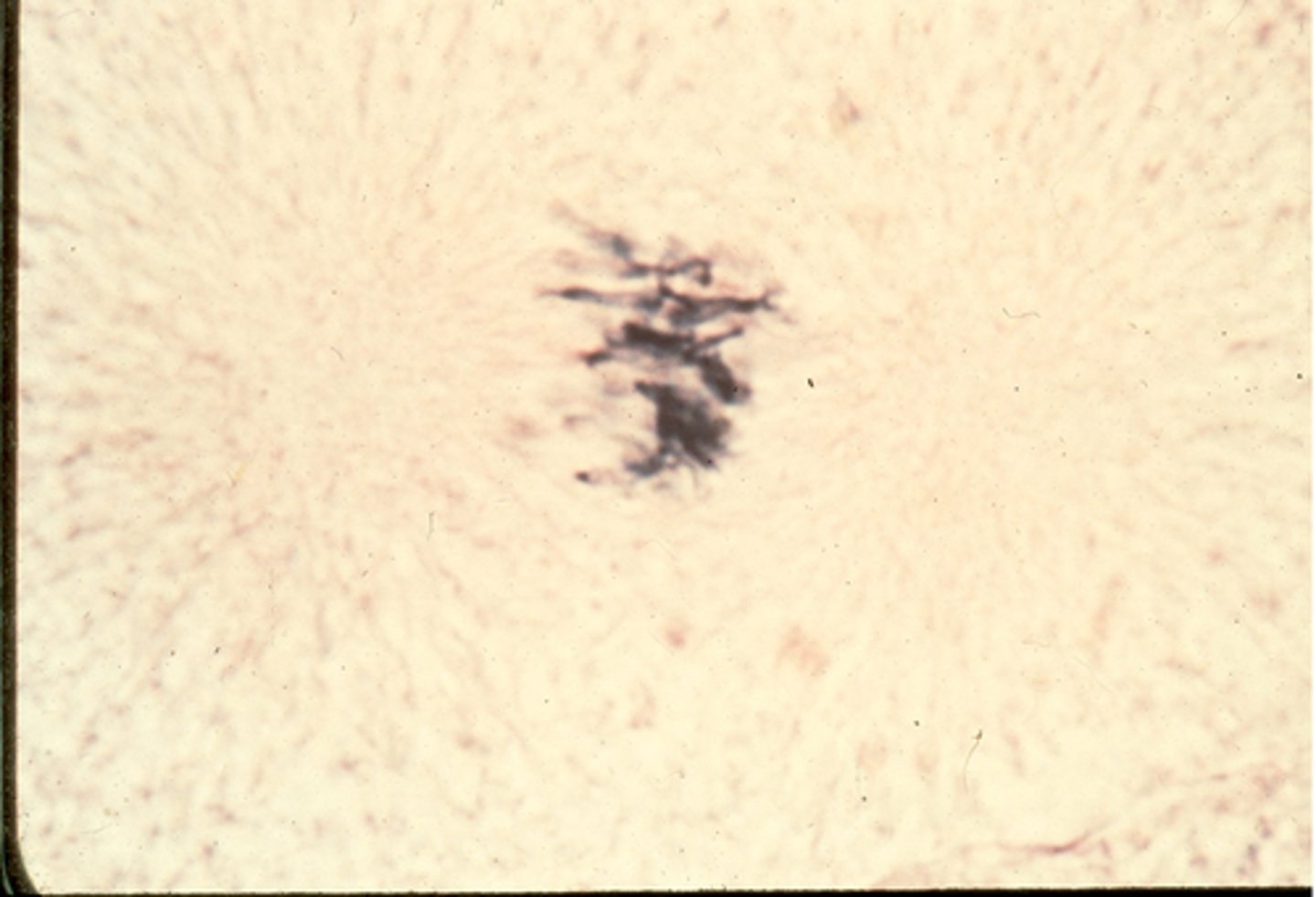
anaphase
This shows ________ in whitefish blastula.
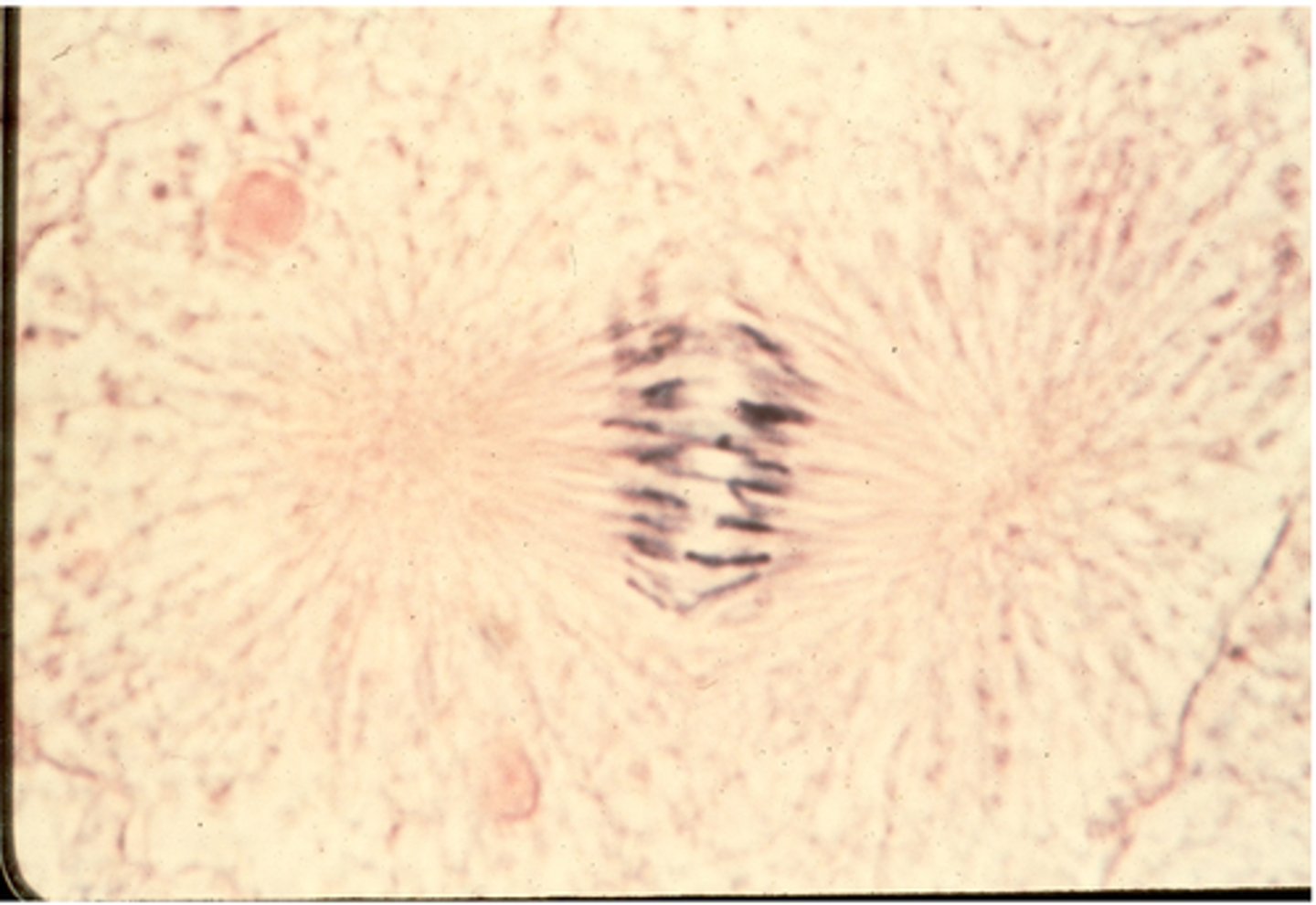
anaphase
This shows ________ in whitefish blastula.
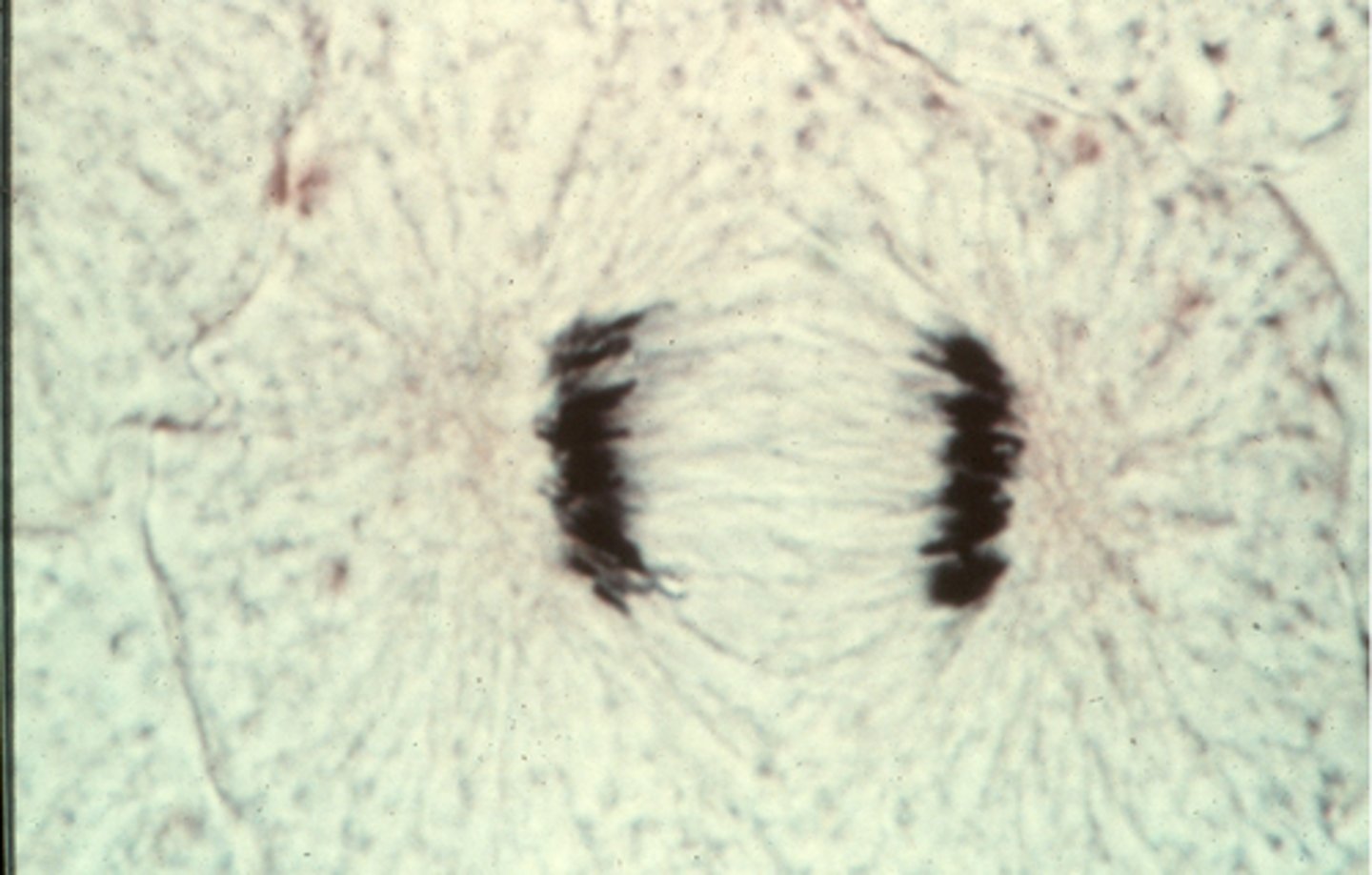
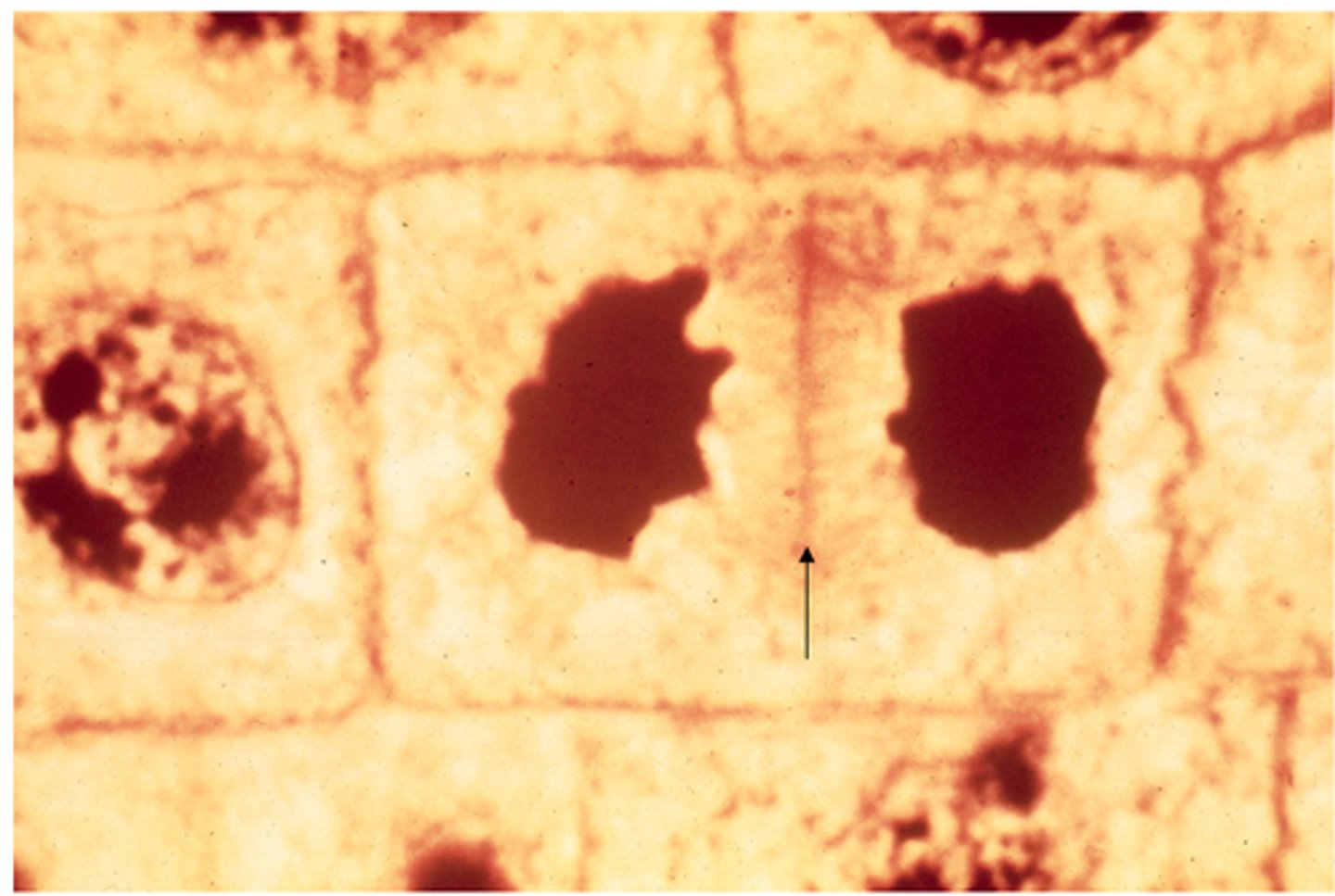
telophase, cleavage furrow
This shows ________ in whitefish blastula. The arrow indicates the _______ ________.
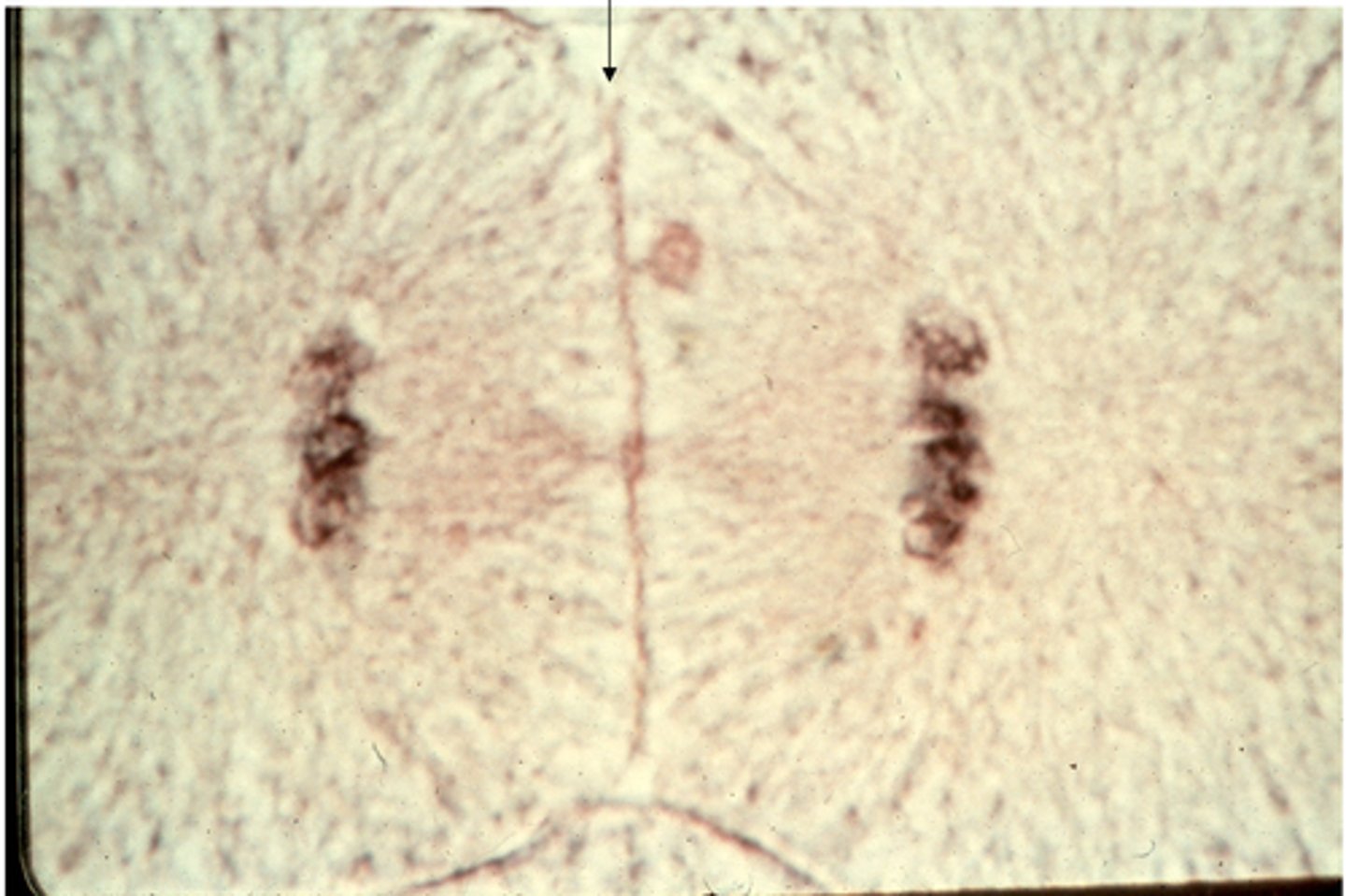
anaphase
This shows _______ in whitefish blastula.
interphase
This shows _______ in onion cells.
prophase
This shows _______ in onion cells.
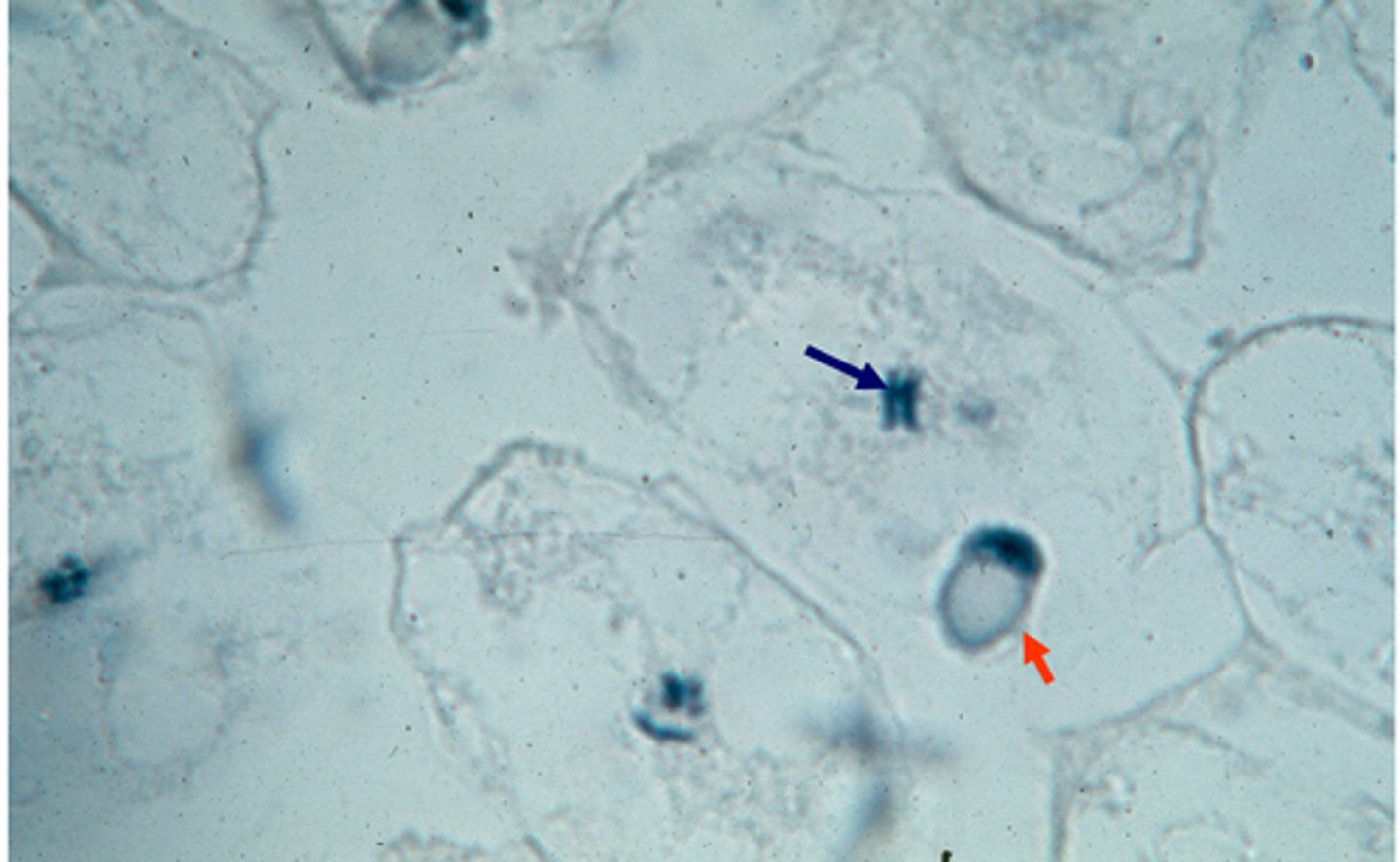
meiosis, sperm, egg, egg chromosomes
This shows _______ in the parasitic worm, Ascaris lumbricoides. The red arrow indicates the ______ entering the ____ (the large clear bubbles). The blue arrow indicates the ___ _________, which have already started dividing.
sperm, egg, chromosomes, egg, meiosis
The black arrow indicates the ______. The green arrow indicates the ______. The red arrow indicates the __________ of the ____ that are in ________.
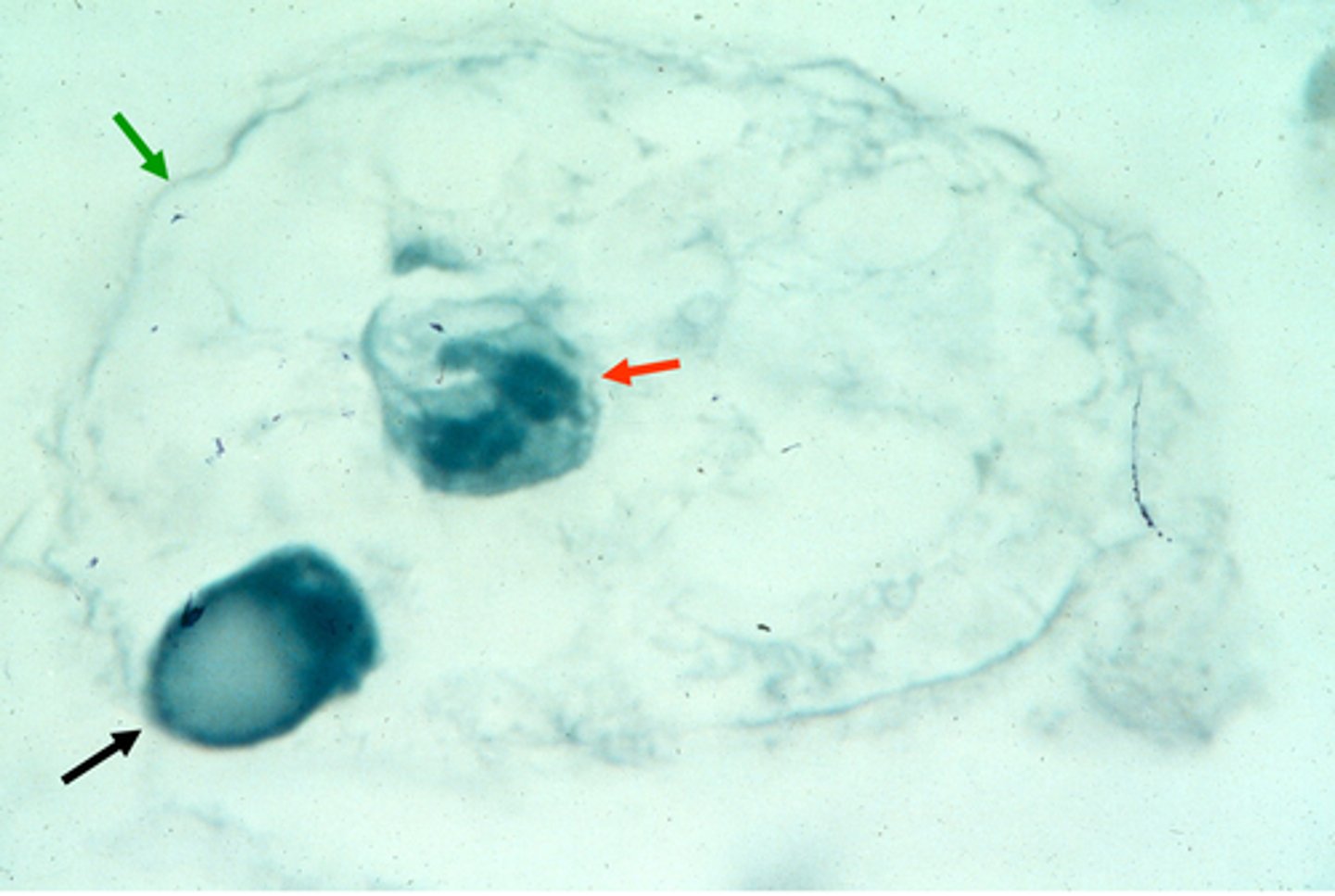
meiosis I, polar body, egg chromosomes, meiosis
This cell has completed ________ __. We know this because a _____ ____ (large black arrow) has been extruded. The ___ _________ (smaller, red arrow) are still undergoing _______.
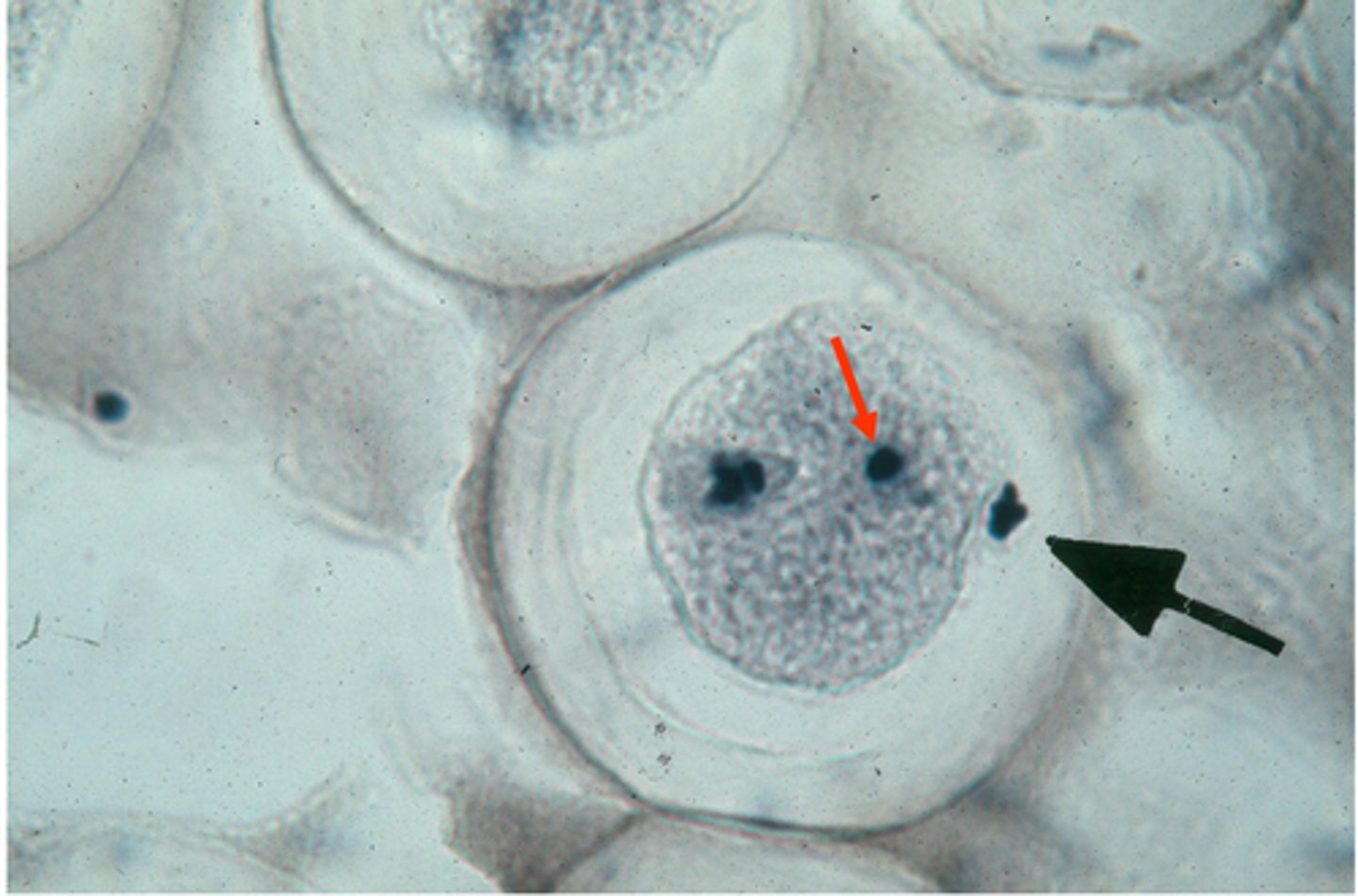
meiosis, haploid, haploid, pronucleus
The egg nucleus has completed _______ and is now ______. The sperm was already _____. Each nucleus indicated by a black arrow is now called a __________, and we cannot distinguish which nucleus is which.
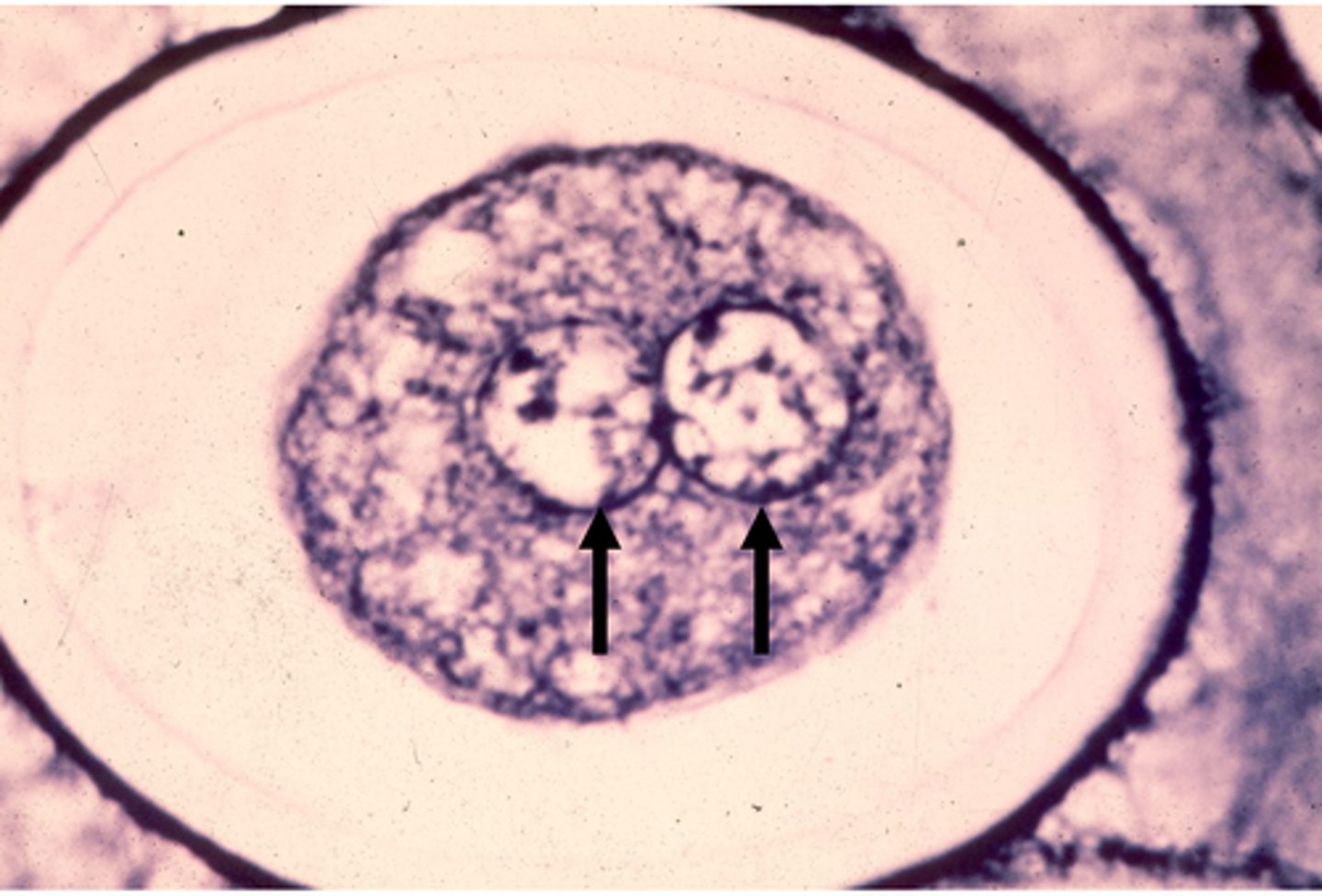
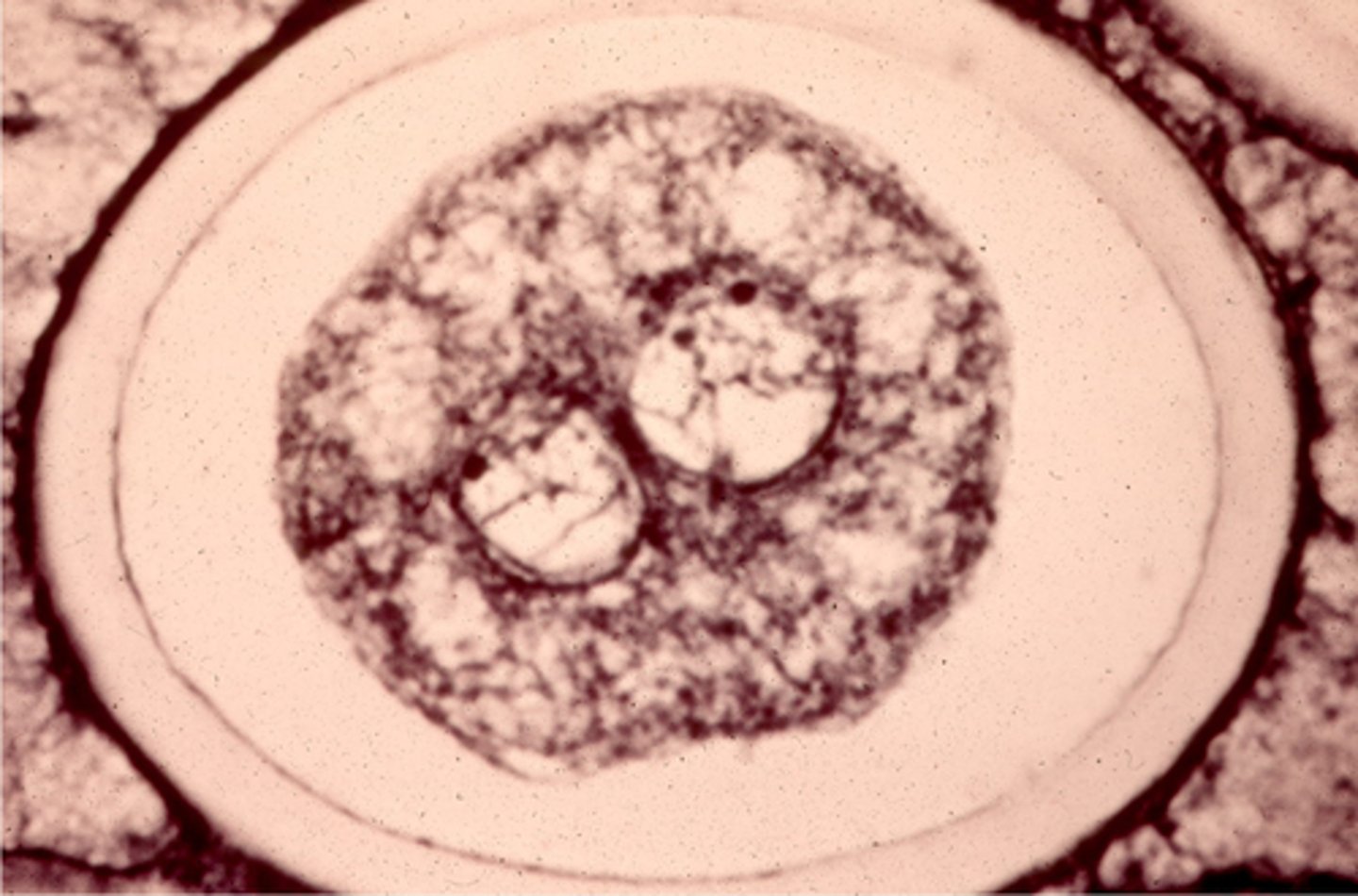
pronucleus, diploid nucleus, zygote
In this image, the 2 _________ are fusing to form a ________ ________, or a ______.
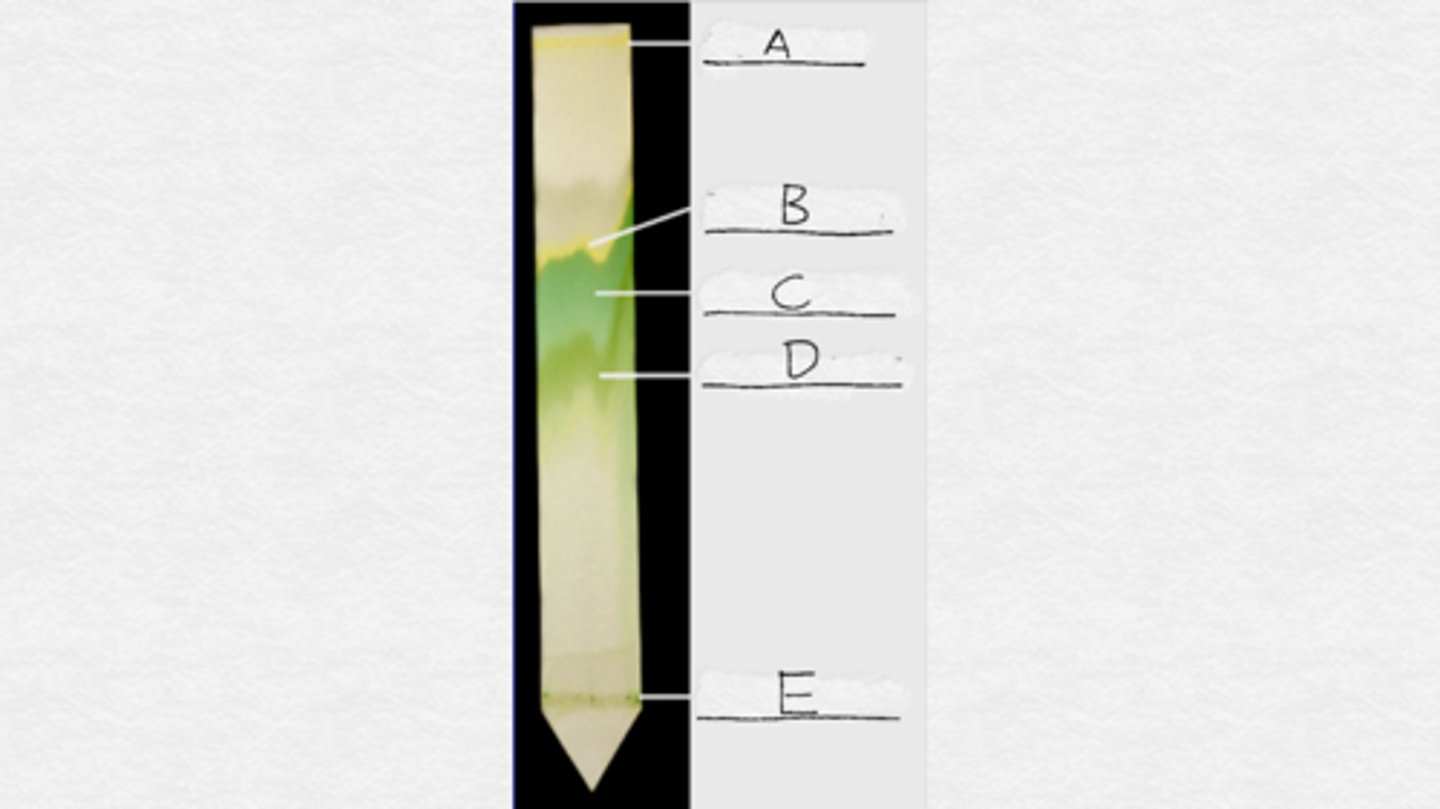
A. carotene
B. xanthophyll
C. chlorophyll a
D. chlorophyll b
E. loading line
Label the plant pigments in order from A to E.
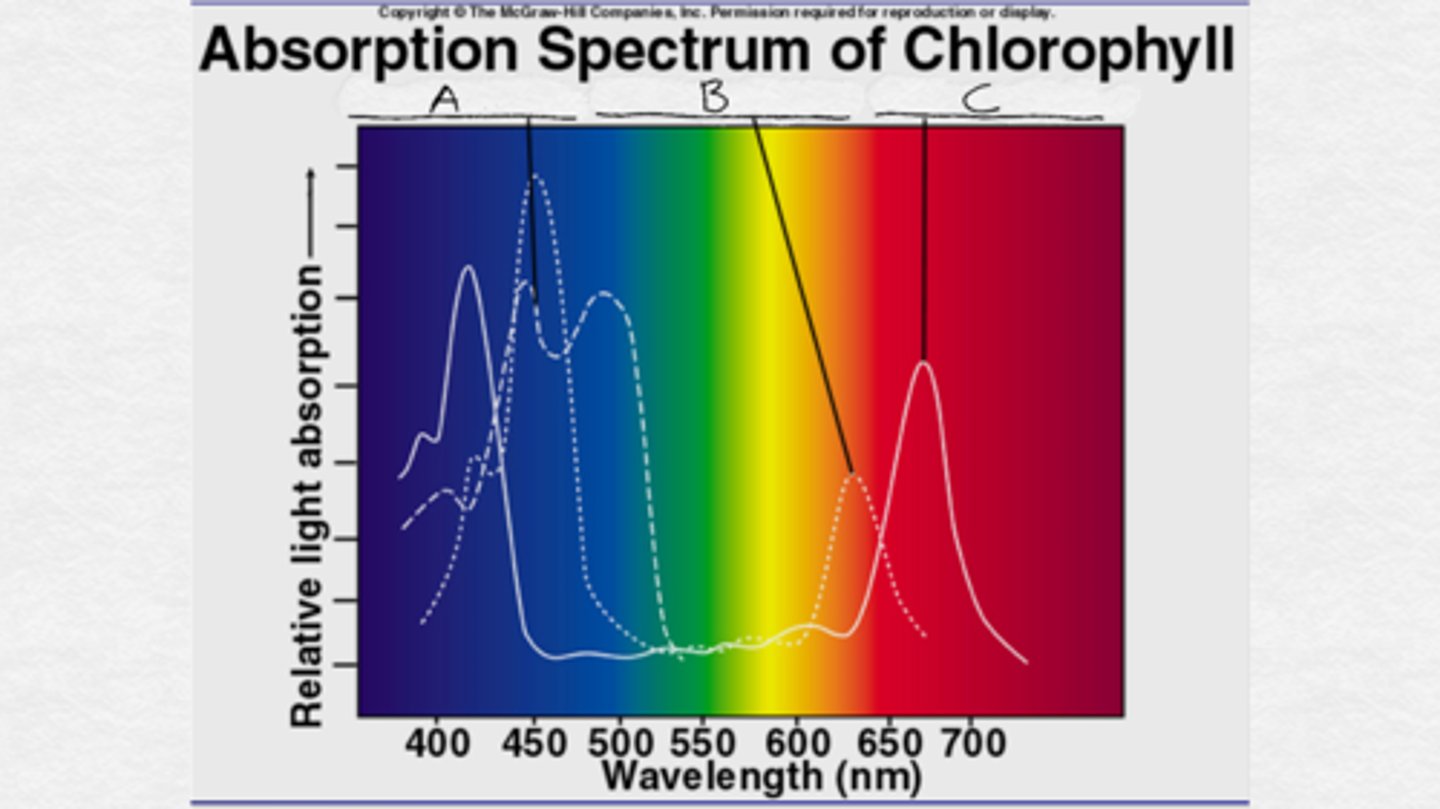
A. carotenoids
B. chlorophyll b
C. chlorophyll a
Label the pigments A through C.
quantitative
Data in the form of numbers is _________.
qualitative
Observations that do not involve numerical analyses give us ___________ data.
independent variable
One or more factors that the scientist varies during the experiment.
dependent variable
A feature that the scientist measures in order to determine if it changes in response to the independent variable.
decrease
If a daphnia is subjected to increased concentrations of ethanol, it's heart rate will _______.
increases
If a daphnia is subjected to increased concentrations of caffeine, it's heart rate will ________.
carbohydrates
monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are all _____________.
lipids
fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids are all _________.
proteins
Amino acids, dipeptides, and polypeptides are all ________.
nucleic acids
Mononucleotide and dinucleotide monomer, and polynucleotides (DNA and RNA) and all ___________.
mean
also known as average
median
the middle value in a set of data
mode
the most common value in a set of data
range
the distance between the lowest and the highest value in a set of data.
hydroxyl group
polar, found in alcohols
carbonyl group
polar, found in aldehydes and ketones
carboxyl group
weakly acidic, found in organic acids such as amino acids.
amino group
weakly basic, found in such things as amino acids.
sulfhydryl group
essentially nonpolar, found in some amino acids.
phosphate group
weakly acidic, found in such things as phospholipids and nucleic acids.
methyl group
nonpolar (thus hydrophobic), found in such things as lipids, and other membrane components.
orange-red
When testing for simple reducing sugars, if the sugars are present in high concentration, Benedict's reagent should turn _____.
iodine
______ is used to test for starch, a polysaccharide.
dark purple
When testing for the presence of starch, the iodine should turn __________ if starch is present.
Biuret Test
The __________ is a common test for proteins.
blue, violet, pink
In the biuret test, the biuret reagent (which is originally _____) should turn ______ if protein or long peptides are present, and it should turn ______ if short peptides are present.
Vegetable oil test, soluble
The ___________ is used to test for lipids, and is based on the fact that lipids are not _______ in water.
brown paper test
The __________ is used to test for lipids, and is based on the fact that lipids should spread and evaporate slowly.
slowly, evenly, wet
In the brown paper test, a lipid should spread ______ and ______ across the paper, and after 10 minutes, the paper should still be ____.
dissolve, 1
In the vegetable oil test, a lipid should ______ into the vegetable oil, forming __ layer(s)
10, 4, 10, 45
A compound microscope magnifies using 2 lenses: one eyepiece (ocular) lens that is constant provides __X magnification, and 3 objective lenses that can be switched out provide __X, __X, or __X magnification.
eyepiece, objective
In order to get the final magnification of a compound microscope, you multiply the _______ lenses magnification by the ________ lenses magnification.
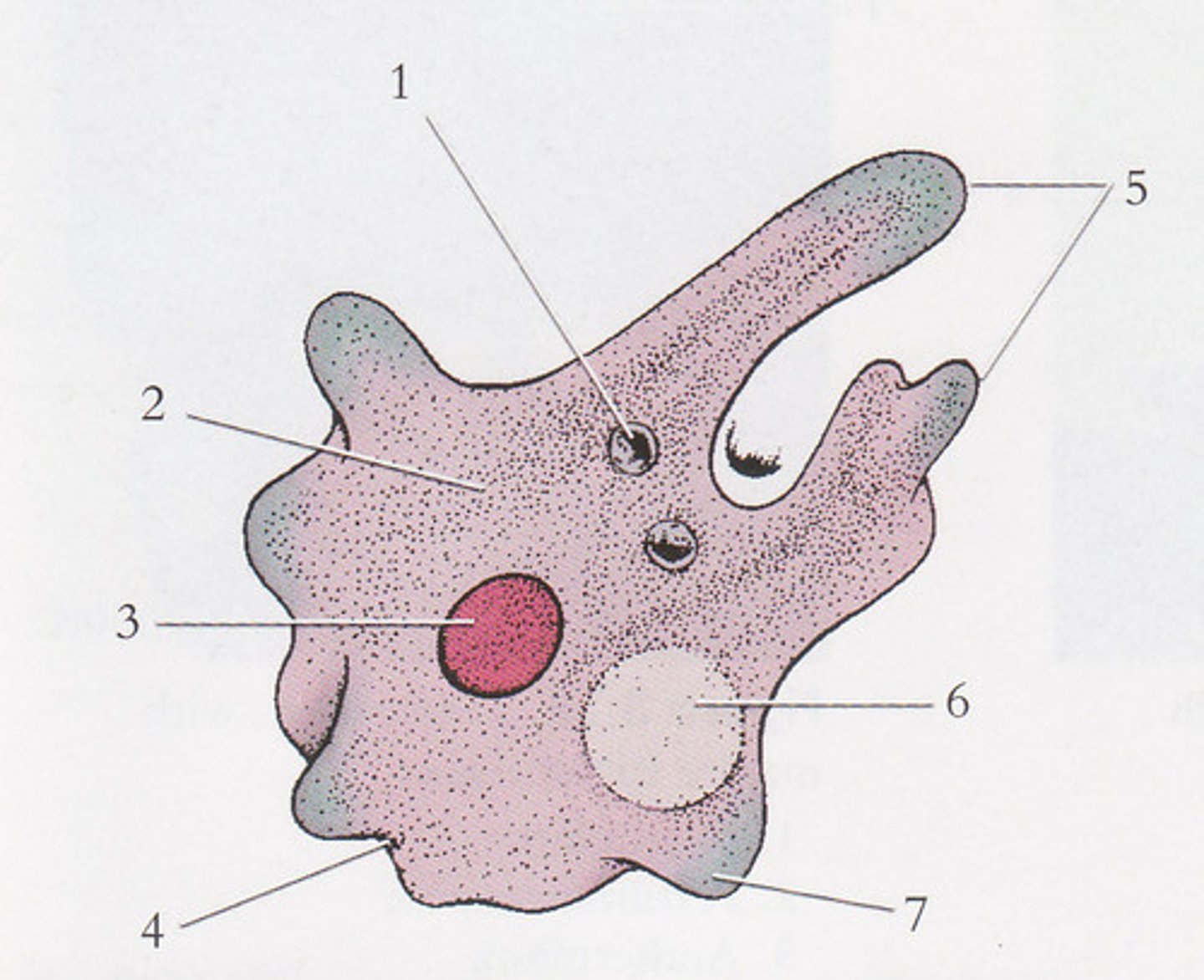
amoeba, food vacuole, nucleus, pseudopods
Label 1, 3, and 5 in order.
9+2
Flagella have a ____ arrangement of microtubules.
simple diffusion
the net movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
down
in simple diffusion, molecules move _____ a gradient.
Brownian motion
The colliding particles and molecules in a liquid or gas have a "jiggling" motion due to their random movement and collisions. This is called:
faster
higher temperatures led to ______ diffusion.
faster
smaller, lighter particles diffuse ______ than larger, heavier particles.
osmosis
the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of its higher molecular activity to a region of lower molecular activity.
active transport
the net movement of a substance, often against a gradient, that requires an input of energy and a carrier protein.
dynamic equilibrium
the point where 2 solutions are such that no net movement of molecules will occur.
hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, it is the solution that has the high concentration of the solute particles.
hypotonic
when comparing tow solutions, it is the solution that has the lower concentration of the solute particles.
isotonic
when two solutions have the same concentration of solutes.
molarity
the solute concentration of a solution (e.g. 0.2M glucose is one liter of solution that contains 0.2 moles of glucose dissolved in 1 liter of solution)
molecular activity
the random motion of molecules and atoms resulting from their own kinetic energy.
osmotic potential
the net tendency of water to move across a selectively permeable membrane into a solution.
greater
The greater the solute concentration gradient, the _________ the osmotic potential.
pressure
Osmotic potential is measured by measuring the _______ needed to stop water from flowing into that solution.
plasmolysis
shrinkage of a cell due to water loss (crenate)
water potential
The "potential energy" of water molecules.
high, low
water moves from a region of _____ water potential to a region of _____ water potential.
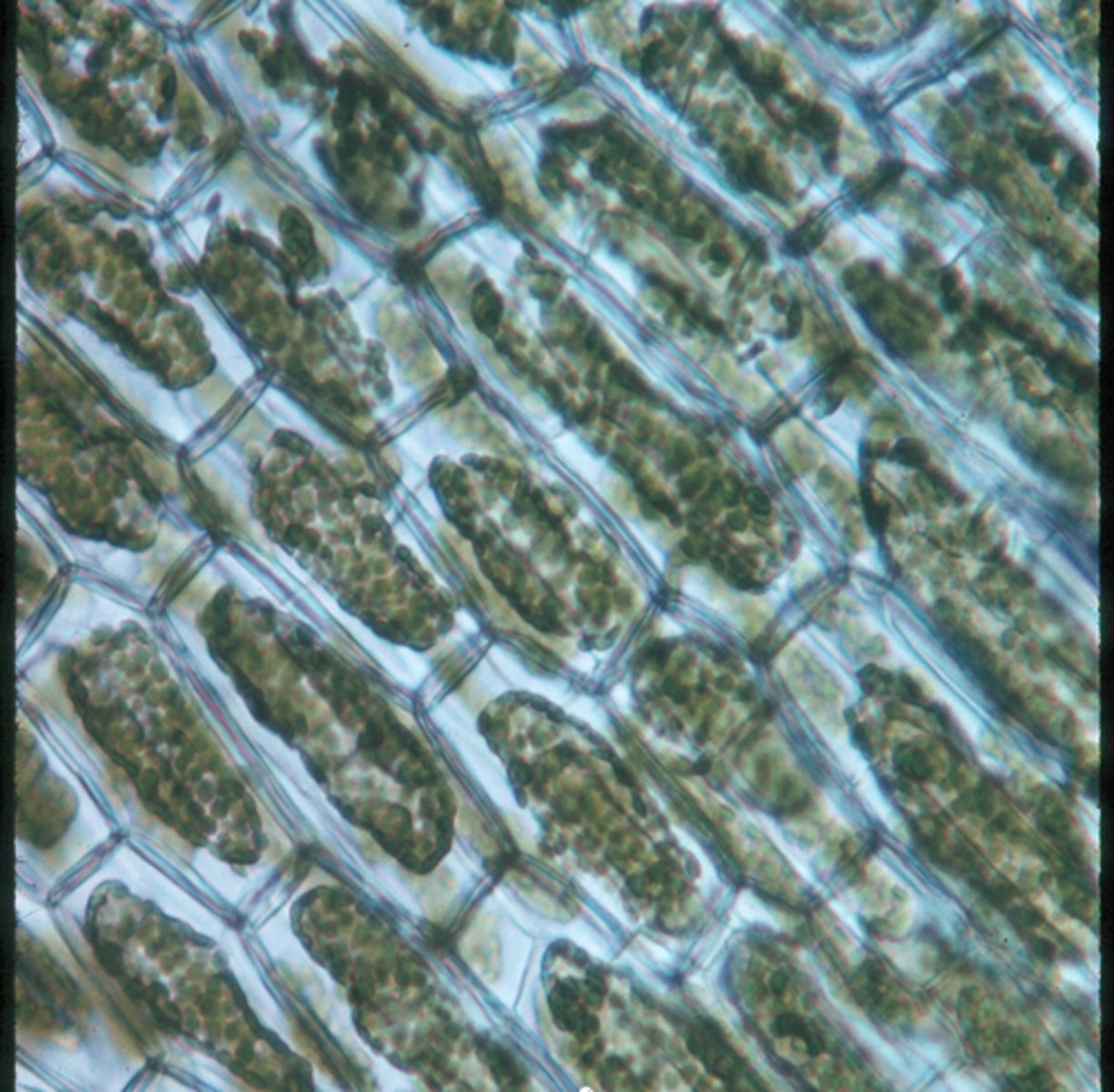
plasmolysed
This elodea is _________ because it was exposed to a salt solution
lose
Dialysis bags will ____ weight because the water in the bag will to diffuse out of the bag to balance out the hypertonic solution outside of the bag.
gain
Dialysis bags will ____ weight because the water outside of the bag is going to diffuse into the bag to balance out hypertonic solution inside the bag.
solvent
a liquid into which a substance is dissolved
solute
the dissolved substance
enzyme
an organic molecule (typically a protein) that acts as a catalyst.
activation energy
enzymes work by lowering the the __________ ________ of a reaction.
active site
the enzyme-substrate complex is formed at the enzyme's ______ ____.
benzoquinone, oxidation
When an apple turns brown shortly after you bite into it, the brown substance is _____________ in an ________ reaction
catechol, 1/2 O2, benzoquinone, H2O, catechol oxidase
In the reaction we studied, the substrates were _________ and _____, and the products were _______________ and _______. the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is called _________ ________
potato extract
The enzyme catechol oxidase can be found in ______ _______.
40, median
The optimal temperature for the enzyme catechol oxidase is __ degrees celcius, which is the ______ temperature of the range tested.
6
The optimal pH for catechol oxidase is __.
substrates, catechol
catechol, hydroquinone, and para-hydroxybenzaldehyde are all ________ that we tested for substrate specificity. Of these, the oxidation reaction only appears to occur with _______.
cellular respiration
Processes that cells use to get energy (stored in ATP) from their food molecules)