Network Fundamentals: Models, Hardware, Addressing, and Protocols
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Network
a group of computers and other devices connected by some type of transmission device
Topology
How the parts of a whole work together
Physical Topology
How devices are connected physically through wiring
Logical Topology
How to access a network, use software, how users gain access, and how specific resources are shared
Peer to peer network model
No server; The OS of each computer on the network is responsible for controlling its own resources, security, and administration
Cons of Peer to Peer Network Model
Not scalable; Not very secure due to the lack of a central server
Client-server network model
Resources are accessed via a centralized directory database managed by the NOS (network operating systems)
Domain
the group of computers whose network access is controlled by a server
Client
a computer making a request to another
Networking Operating System (NOS)
control access to the entire network
Scalability
ability to increase the size and add/remove elements of a network
Active Directory
centralized directory database that contains user account information and security for the entire group of computers
Active Directory Domain Services
manages the process of how users sign on to the network and get access to resources of the AD
Server
any computer or program that provides a service
LAN
Local area network
Switch
Receives incoming data from one of its ports and redirects it to 1 or more ports that will send the data to its intended destination; Uses MAC address to identify devices; Works at layer 2 of the OSI model; Use ethernet to transmit data; Contains the MAC address of the sender and the receiver
Hub
Physical device that transmits data to all devices on a network; Works at layer 1 of the OSI model
Router
Manages traffic between multiple networks; Used in SOHO (small office-home office) networks to connect the LAN to the internet
WAN
A group of LANs spread over a wide geographical area
Metropolitan area network (MAN/CAN)
A group of connected LANS in the same geographical area
PAN
Network of personal devices; Smallest network
OSI Model (Open System Interconnect)
A conceptual framework used to understand network interactions in seven layers.
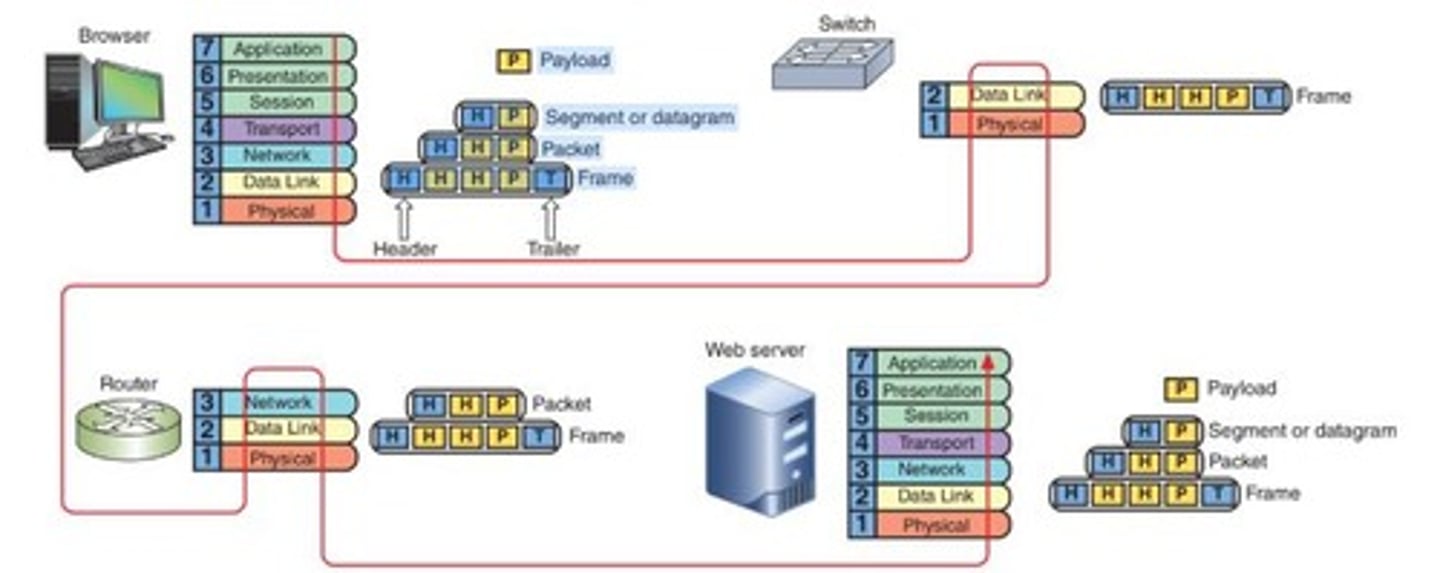
Transport Layer
Purpose is to guarantee that information is transmitted; Can also slow down or speed up a message
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
makes a connection with the end host, checks whether data is received, and resends if needed
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
used for broadcasting, where delivery is not as important as fast transmission.
Datagram
A message
Segments
A split message
Port addresses
2 port addresses are added to the message (new header).
HTTP port
port #80.
Session layer
Responsible for how data between applications are synced and recovered if messages don't arrive intact at the receiving application.
API call
Method an application uses when it makes a request of the OS.
Presentation layer
Responsible for reformatting, compressing, and/or encrypting data.
Application layer
The interface between two applications on separate computers.
HTTP application layer protocol
Applications that provide services to a user use HTTP application layer protocol.
Utility programs
Utility programs that provide services to the system.
Payload
Data
Structured cabling
Standard is known as structured cabling.
Entrance facility
The location where an incoming network, such as the Internet, connects with the school or corporate network.
Demarc
The device that marks where a telecommunications service provider's network ends and the organization's network begins.
MDF
The centralized point of interconnection for an organization's LAN or WAN.
Data room
the enclosed space that holds network equipment.
Patch panel
A panel of data receptors that provide a central termination point when many patch cables converge.
IDF
Provides an intermediate connection between the MDF and end-user equipment on each floor and in each building.
Patch cable
Short cabling used with connectors.
Backbone cables
Backbone consists of cables or wireless links that provide interconnection between the entrance facility and MDF, and between the MDF and IDFs.
Straight through
Same wiring order and connects two different devices.
Cross-over cables
Different order of wires and used to connect the same device.
Bend radius
The max radius a cable can bend before damaging the wires.
Network diagrams
Graphical representations of a network's devices and connections.
Nmap
An open-source network scanning tool used for network exploration and security auditing.
MAC address
Embedded on every NIC and are six hex numbers separated by colons.
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
addresses 32 bits and are 4 decimal numbers called octets.
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
128 bits and written as eight blocks of hex numbers.
Ports
A number used to find an application.
FQDNs
Fully qualified domain names are assigned to every host on a network and are unique.
Domain name
The last two parts of a host's name.
Host name
The first part of a host's name.
Static IP Addresses
Permanently assigned to a device.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Requested and received by a device from a DHCP server.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
manages the dynamic distribution of IP addresses to devices on a network.
Gateways
Computer routers or a device that a host uses to access another network.
Subnet masks
a 32-bit number that separates an IP address into a network portion and a host portion
Ipconfig
Used to find the current TCP/IP settings.
Classful addressing
5 classes: A-E, where Class A-C are available for internet use and are public.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
a technique designed to conserve the number of public IP addresses needed by a network.
Static Network Address Translation (SNAT)
the gateway assigns the same public IP to a host each time it makes a request.
Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT)
process where a host outside the network addresses a computer inside using a predetermined IP address.
Address translation
The process where a gateway device substitutes the private IP address with its own public address.
Port address translation (PAT)
process of assigning a TCP port number to each ongoing session between a local host and internet host.
Unicast addresses
Specifies a single node.
Global addresses
Can be routed on the internet
Link local addresses
Used for communications with nodes in the same link.
Multicast address
Delivery packets to all nodes in the targeted multicast group.
Anycast address
Identifies multiple destinations and delivers packets to the closest one.
Socket
Both a host's IP address and a process's TCP or UDP port separated by two values.
Standard port for Telnet
port 23.
Socket address for Telnet
10.43.3.87:23
Port range
#'s from 0 to 65535.
Well-known ports
ports from 0 to 1023.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
Assigns port numbers
Registered ports
ports from 1024 to 49151.
Dynamic and private ports
range from 49152 to 65535
Dynamic ports
assigned by a client or server as the need arises.
Private ports
assigned by network admin.
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
Most commonly used by computers (without user intervention) as they are booting up to request configuration files from another computer on the local network.
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
A simple protocol used to synchronize clocks on computers throughout a network.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
A standard protocol for accessing network-based directories.
Server Message Block (SMB)
First used by earlier Windows OSes for file sharing on a network.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
A signaling protocol that is used to make an initial connection between hosts but that does not participate in data transfer during the session.
H.323
Another signaling protocol used to make a connection between hosts prior to communicating multimedia data.
Top Level Domain (TLD)
The last part of an FDQN
DNS
An application layer client-server system of computers and databases.
Namespace
The entire collection of computer names and their associated IP addresses stored in databases on DNS servers around the globe.
Name servers
Computers that hold databases, organized in a hierarchical structure.
Resolvers
A DNS client that requests information from DNS name servers.
Primary DNS server
The authoritative name server for the organization and holds the authoritative DNS database.
Secondary DNS server
Backup ANS for the organization.
Caching DNS server
A server that accesses public DNS data and caches the DNS information it collects.
Forwarding DNS server
An optional server that receives queries from local clients but doesn't resolve the queries.
Recursive query
Demands a resolution or the answer 'It cant be found'.