HESI A2 Chemistry
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Acid
a compound that is a hydrogen or proton donor. It is corrosive to metals, changes blue litmus paper red, and becomes less acidic when mixed with bases

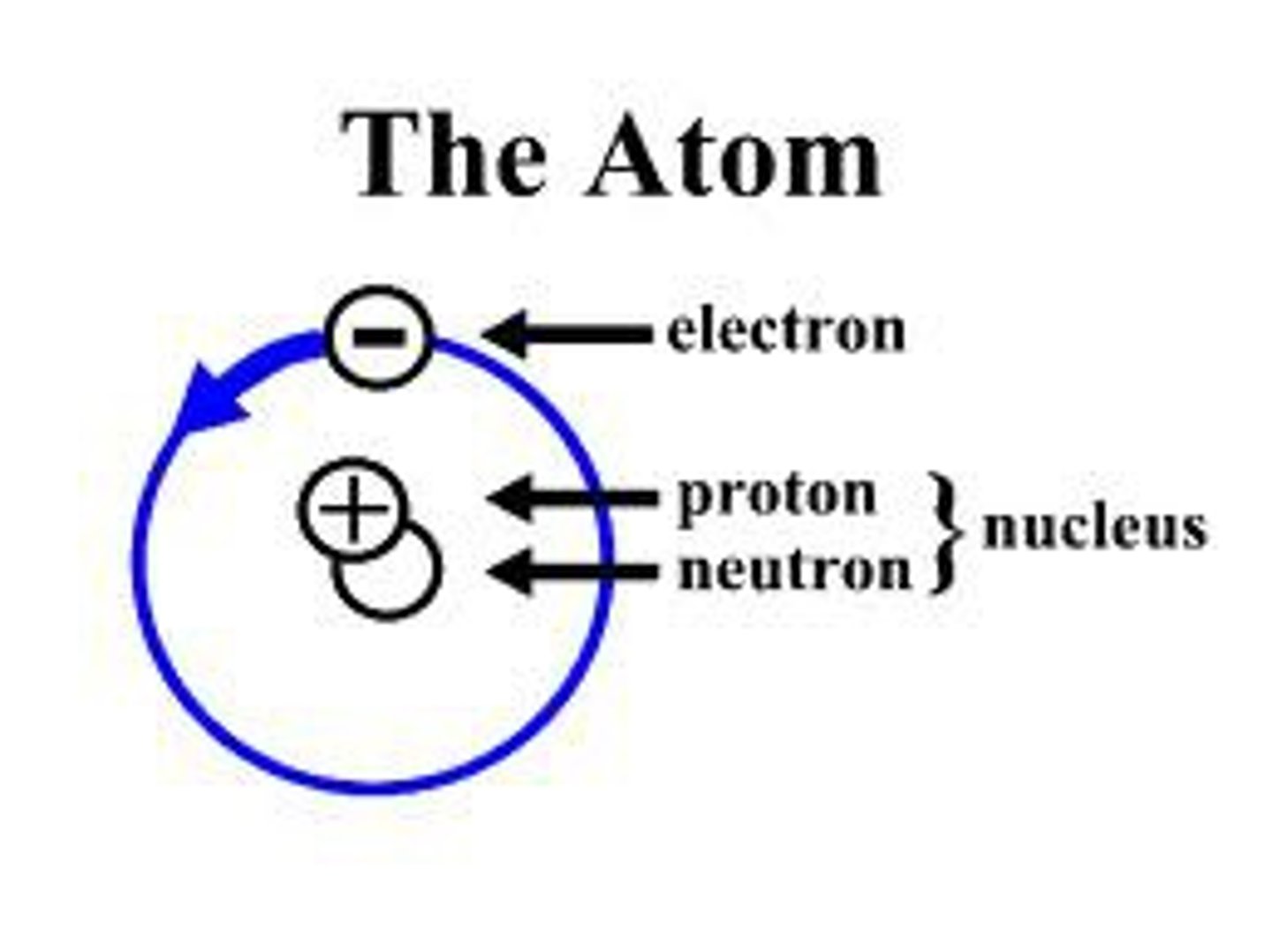
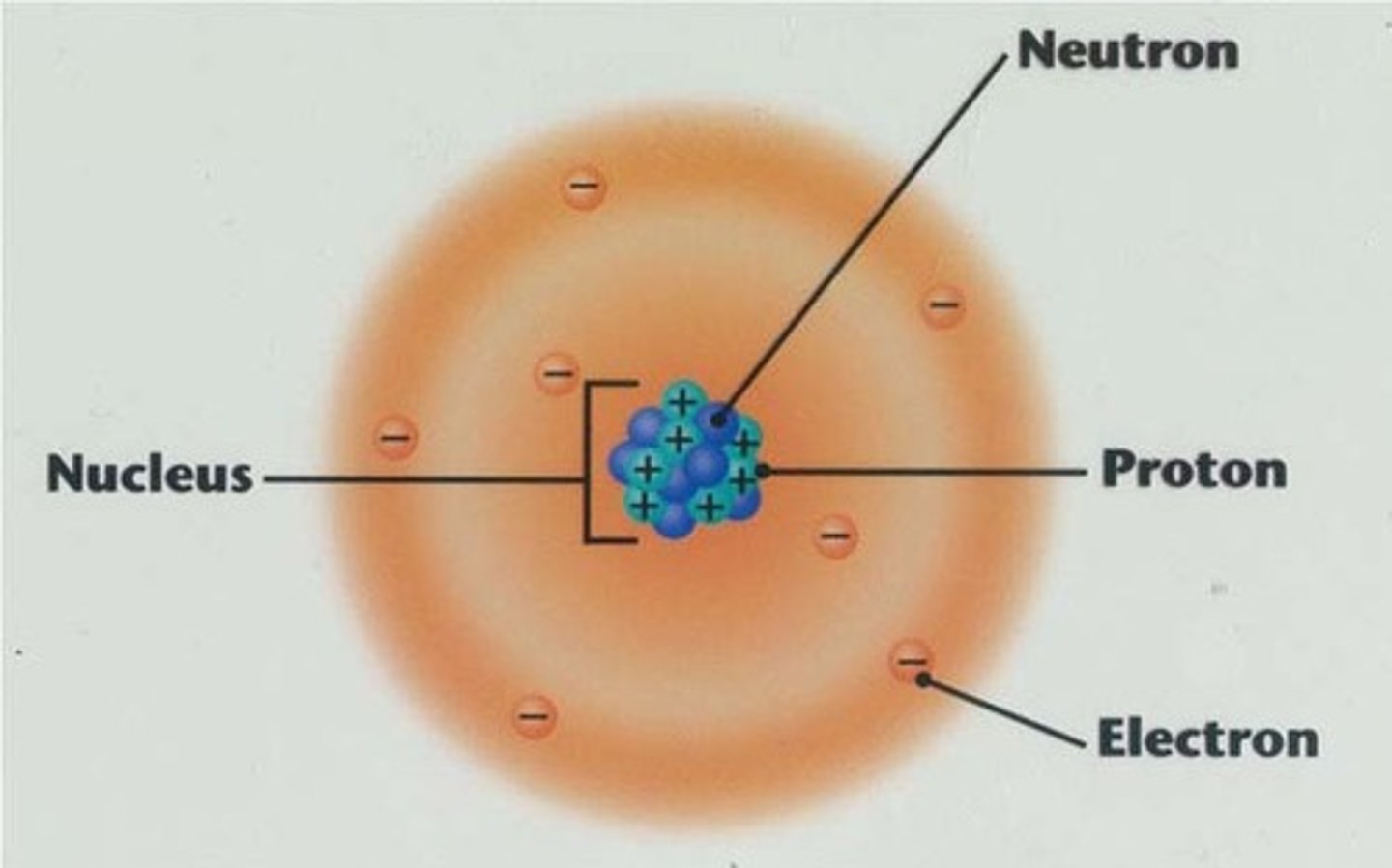
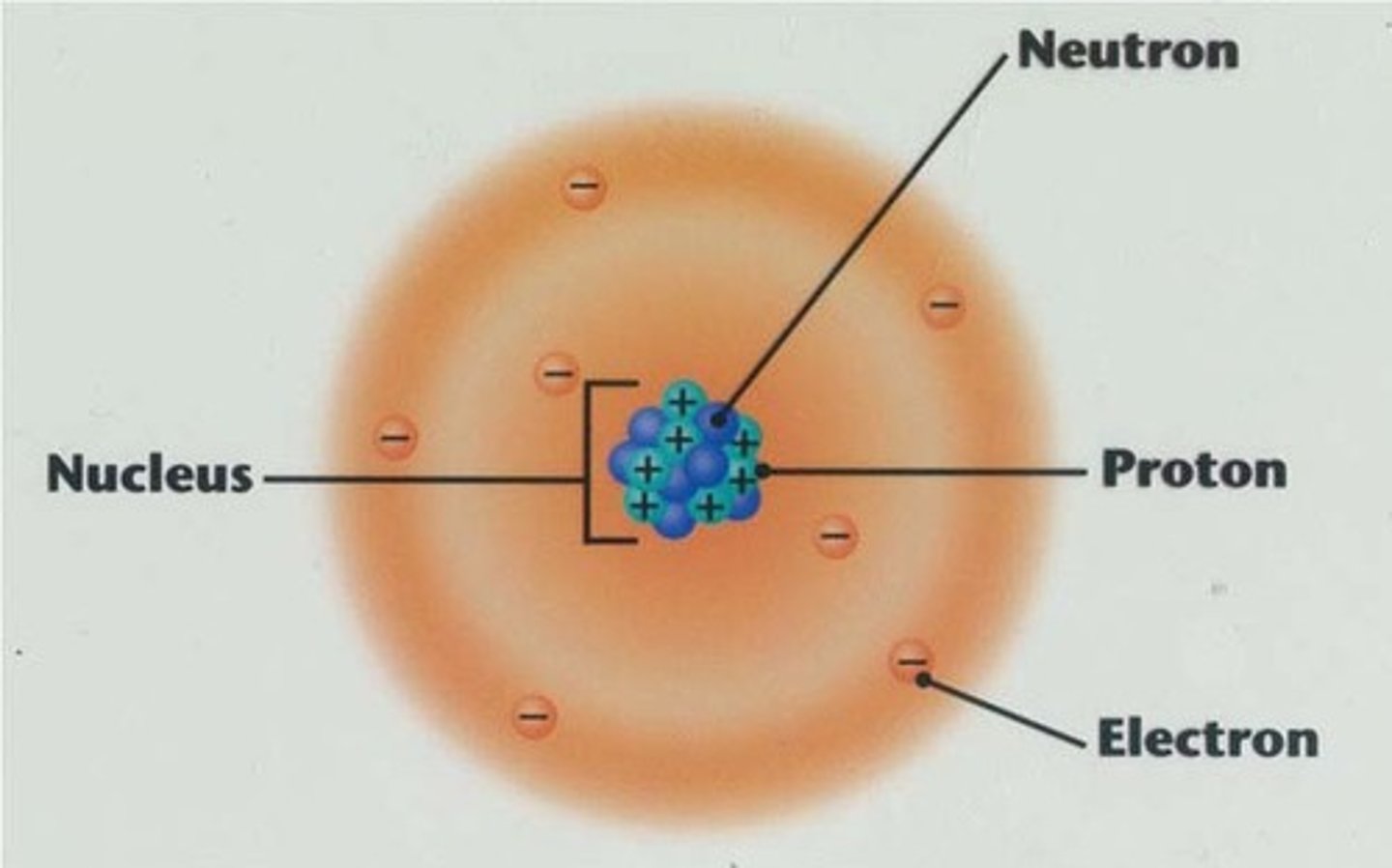
atom
the basic building block of a molecule that contains a nucleus and orbits
atomic mass
the average mass of each of that element's isotopes
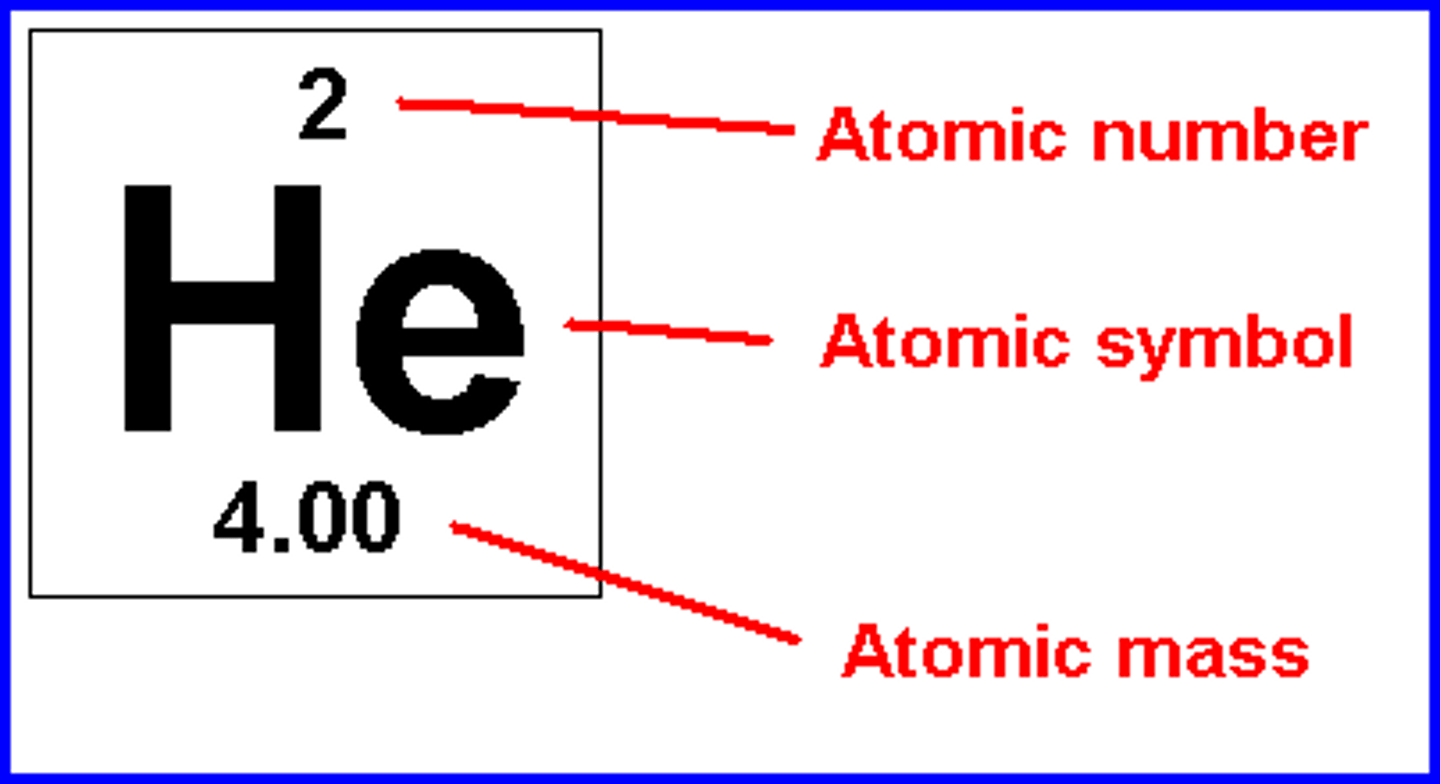
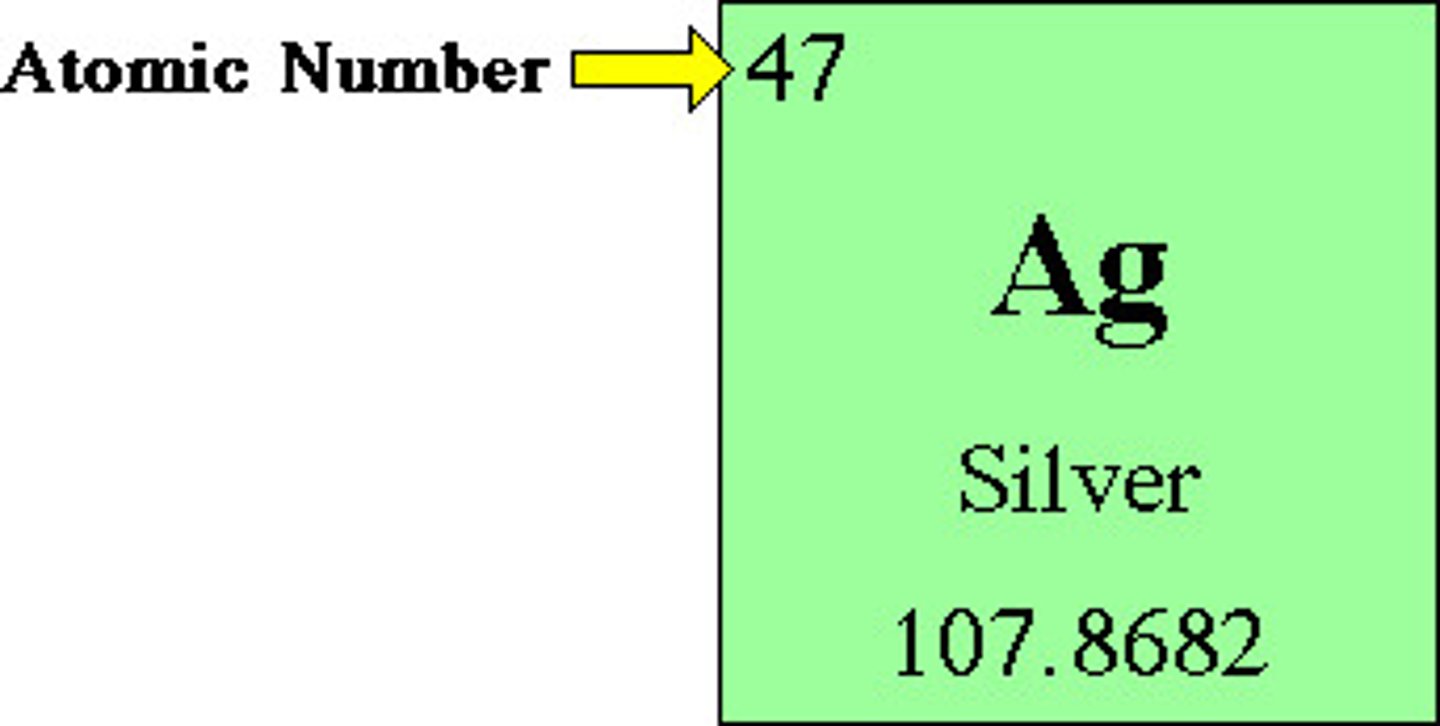
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus, and it defines an atom of a particular element
base
a hydrogen or proton acceptor and generally has a hydroxide (OH) group in the makeup of the molecule. Bases are also called alkaline compounds and are substances that denature proteins, making them feel very slick; they change red litmus paper blue and become less basic when mixed with acids.

basic unit of measure
standard unit of a system by which a quantity is accounted for and expressed (grams, liters, or meters)
catalysts
substances that accelerate a reaction by reducing the activation energy or the amount of energy necessary for a reaction to occur

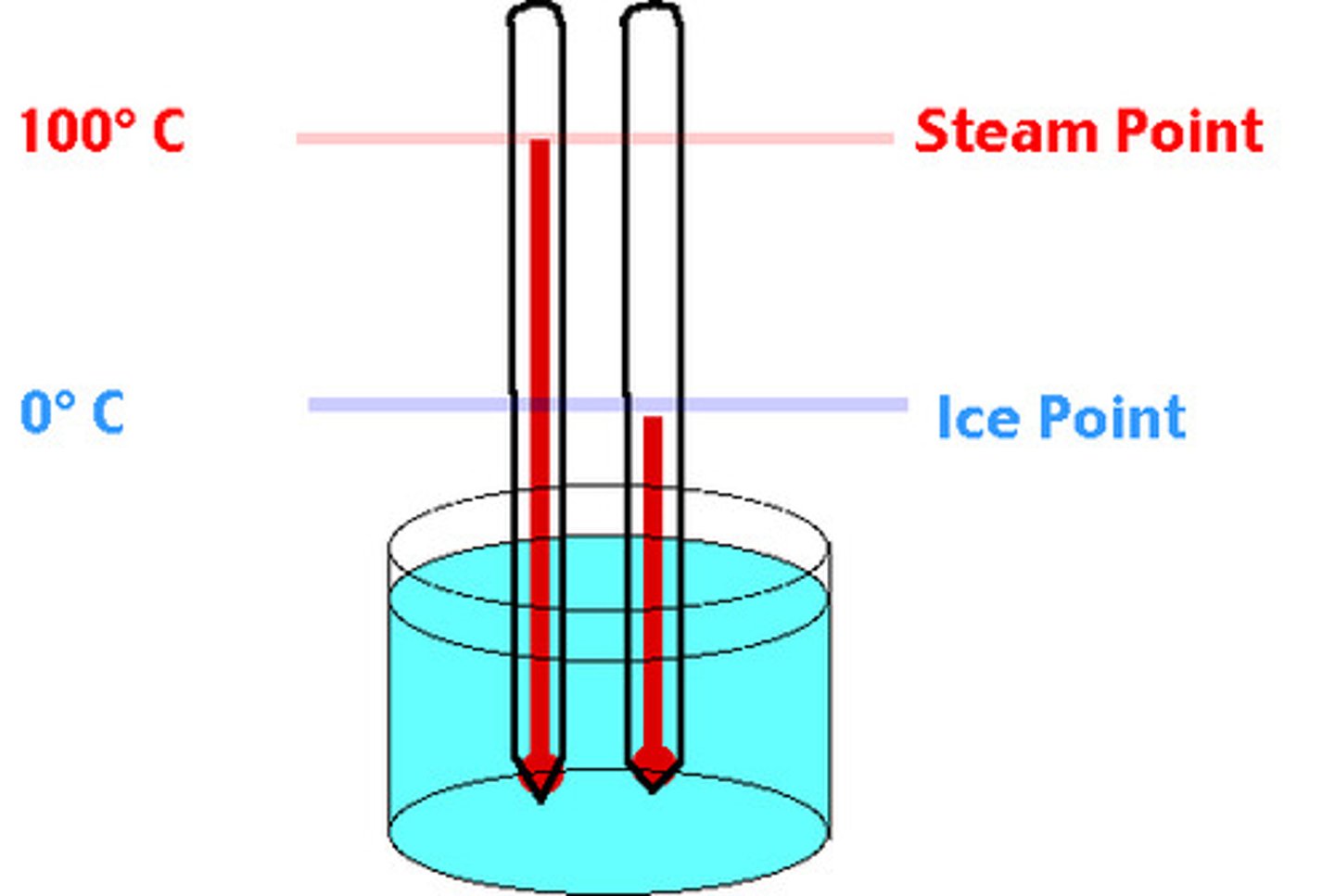
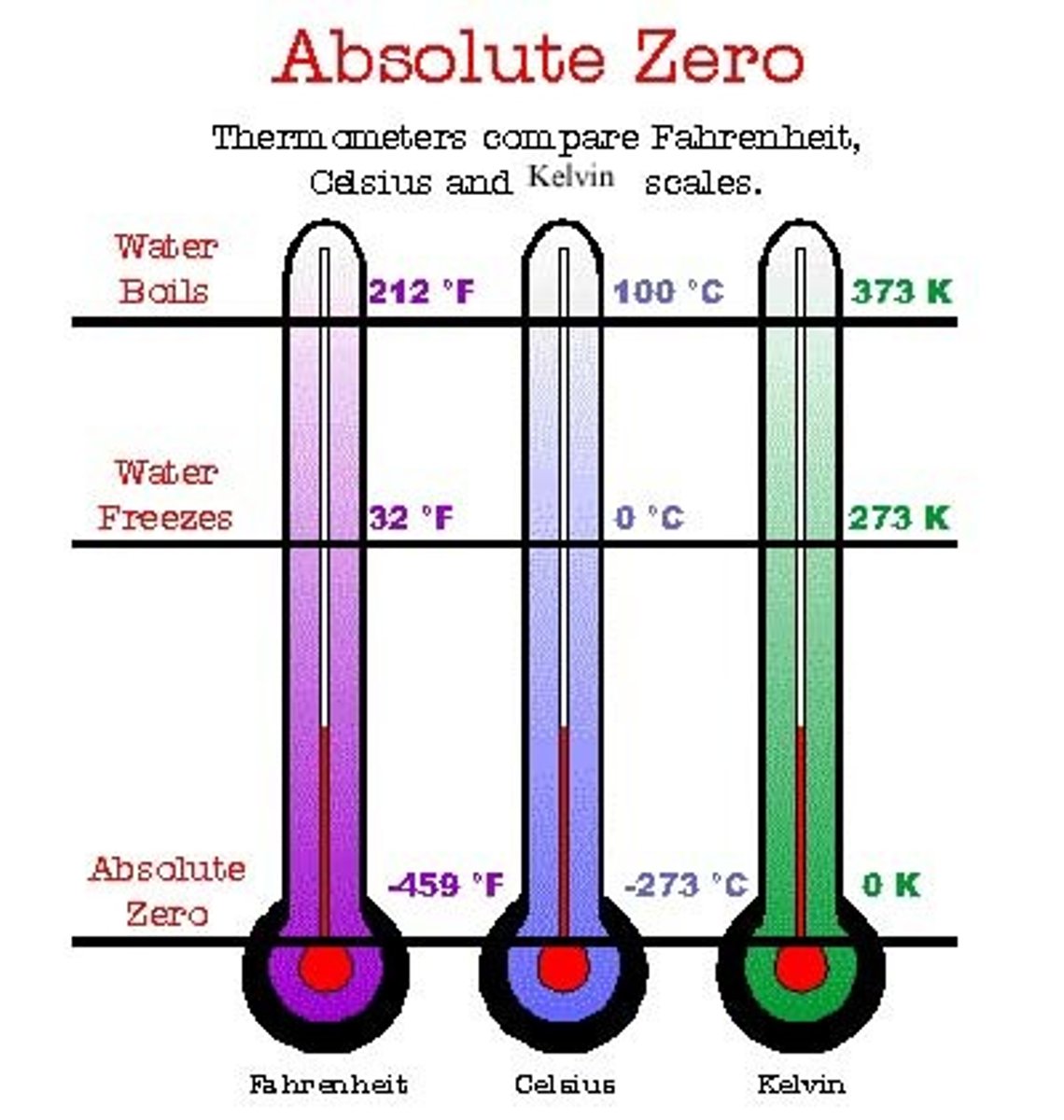
Celsius
a temperature system used in most of the world and by the scientific community; It has these characteristics:
zero degrees = freezing point of pure water at sea level
100 degrees = boiling point of pure water at sea level.
Most people have a body temperature of 37 degrees Celsius.
chemical equations
combination of elements or compounds called reactants responding to create a product or end result. Equations are written in the following manner: reactants ---> products. The arrow can go the other way or both ways
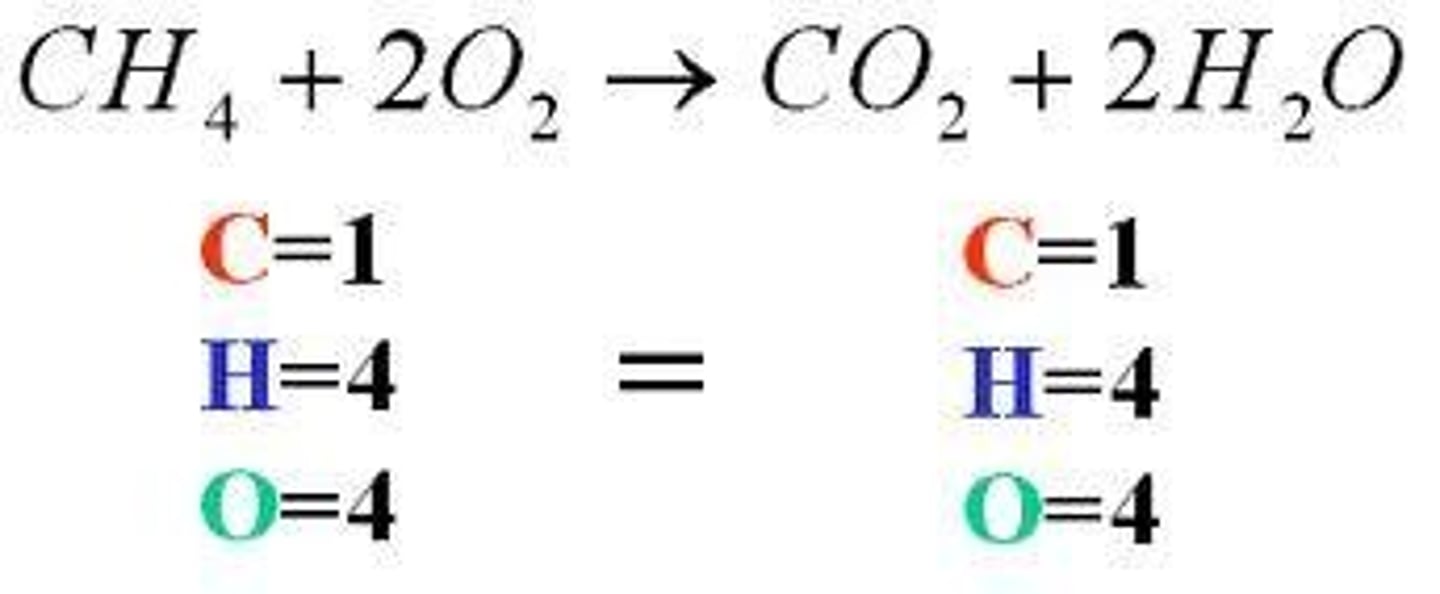
combustion
a self sustaining exothermic chemical reaction usually initiated by HEAT acting on OXYGEN and a fuel compound such as hydrocarbons
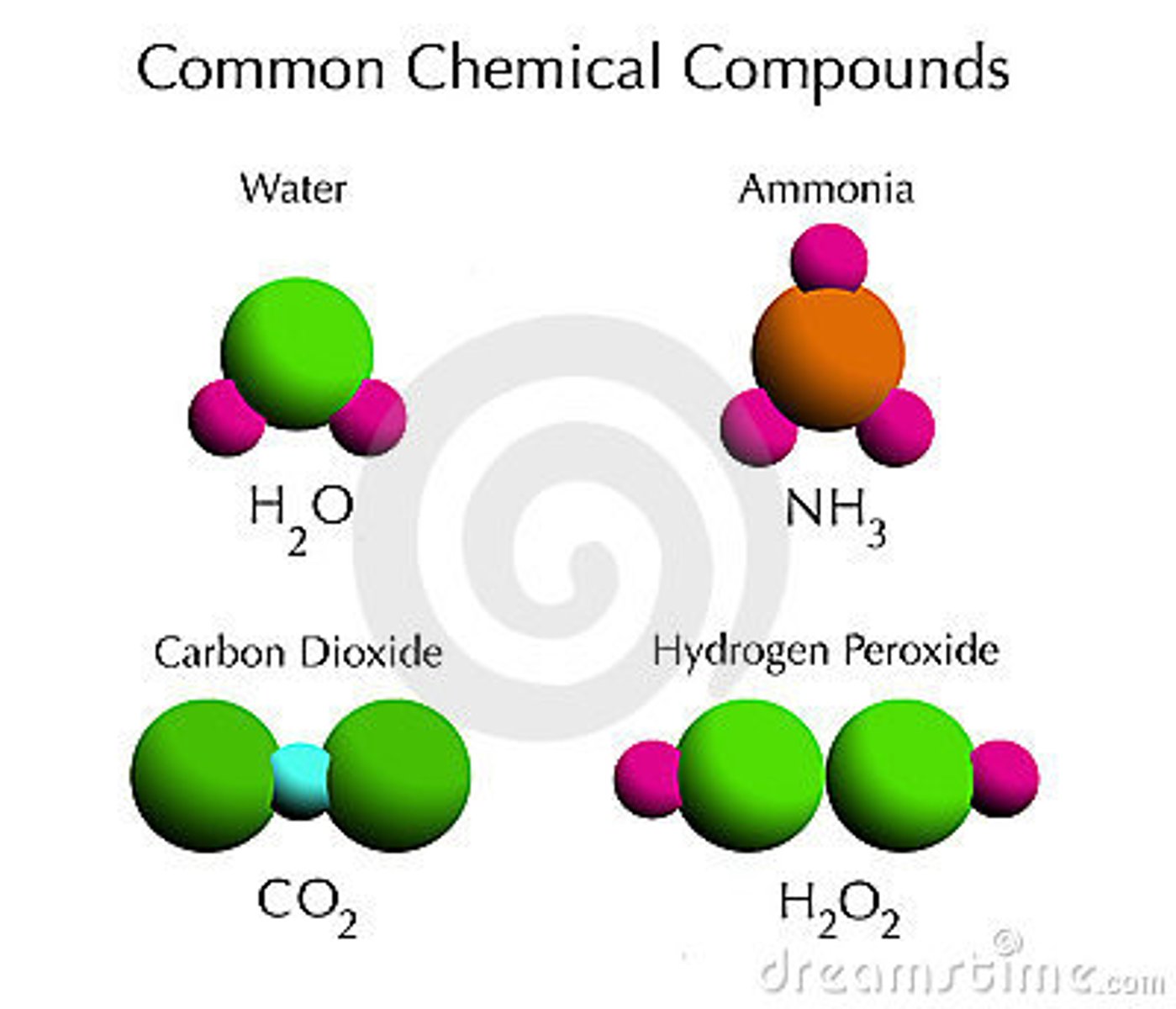
compound
the combination of two or more elements or atoms
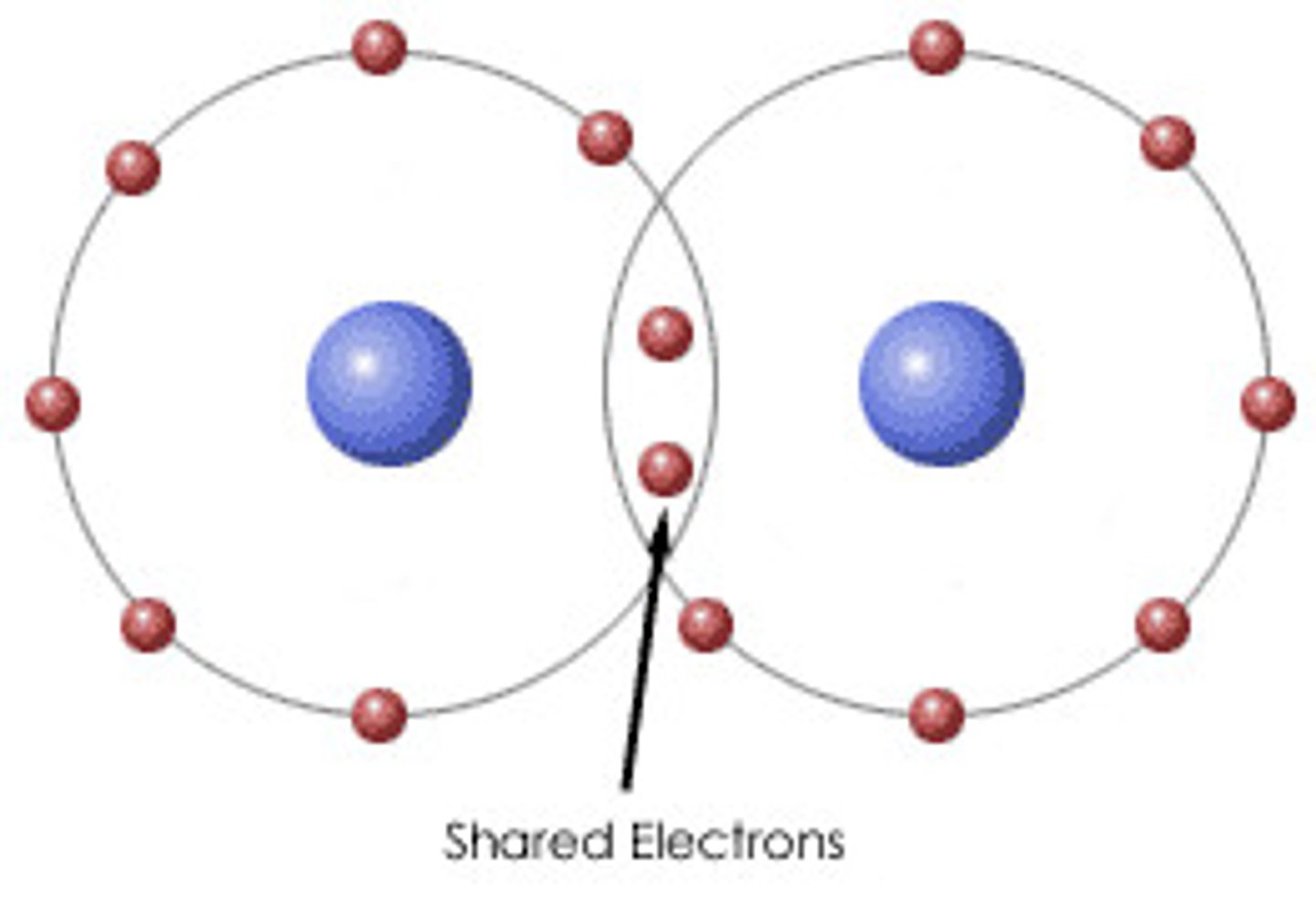
covalent bond
2 atoms share electrons, generally in pairs, one from each atom
decomposition
a chemical reaction often described as the opposite of synthesis because it is the breaking of a compound into its component parts

deoxyribose
a sugar used in the formation of DNA
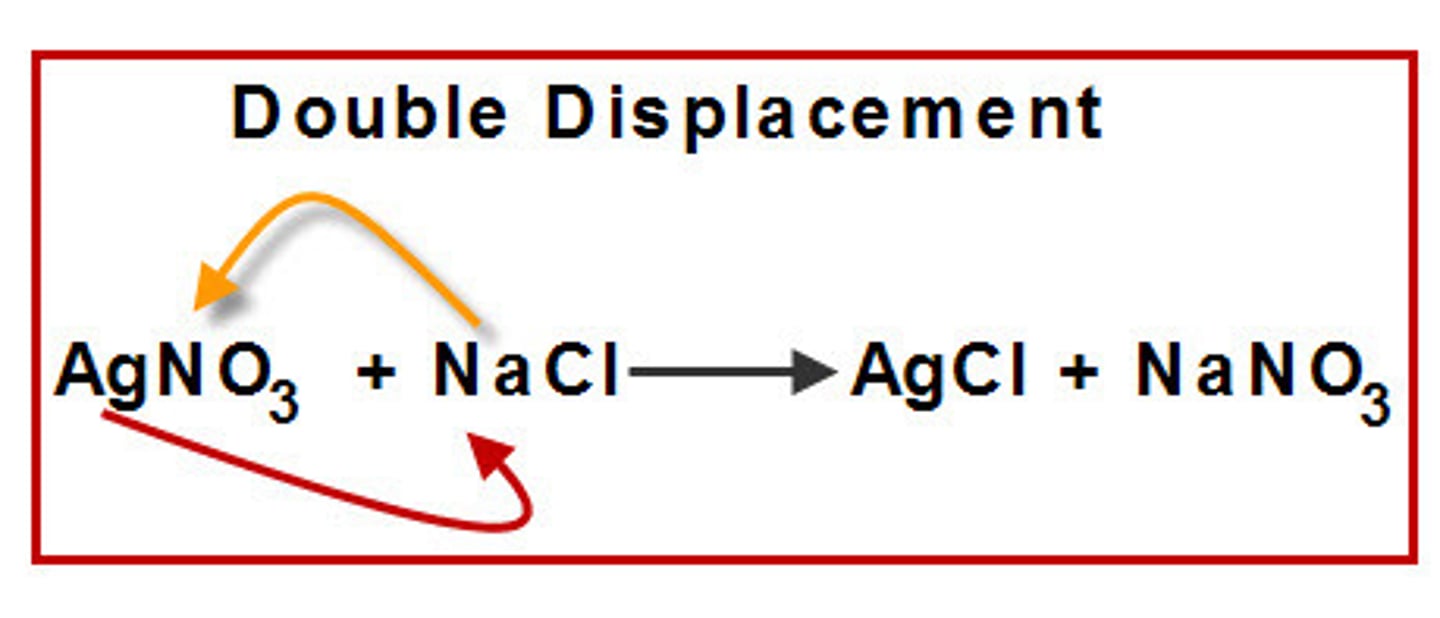
double replacement
a reaction that involves two ionic compounds. The positive ion from one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound. The result is the two new ionic compounds that have "switched partners"
electron clouds
the group of electrons revolving around the nucleus of an atom; a cloudlike group of electrons
equilibrium
a state in which reactants are forming products at the same rate that products are forming reactants
fahrenheit
a temperature measuring system used only in the US, its territories, Belize, and Jamaica. It is rarely used for any scientific measurements except for body temperature.
It has these characteristics:
0 degrees is the freezing point of sea water or heavy brine at sea level;
32 degrees F is the freezing point of pure water at sea level;
212 degrees F is the boiling point of pure water at sea level; most people have a body temperature of 98.6 F
groups
elements that are placed together in columns in the periodic table
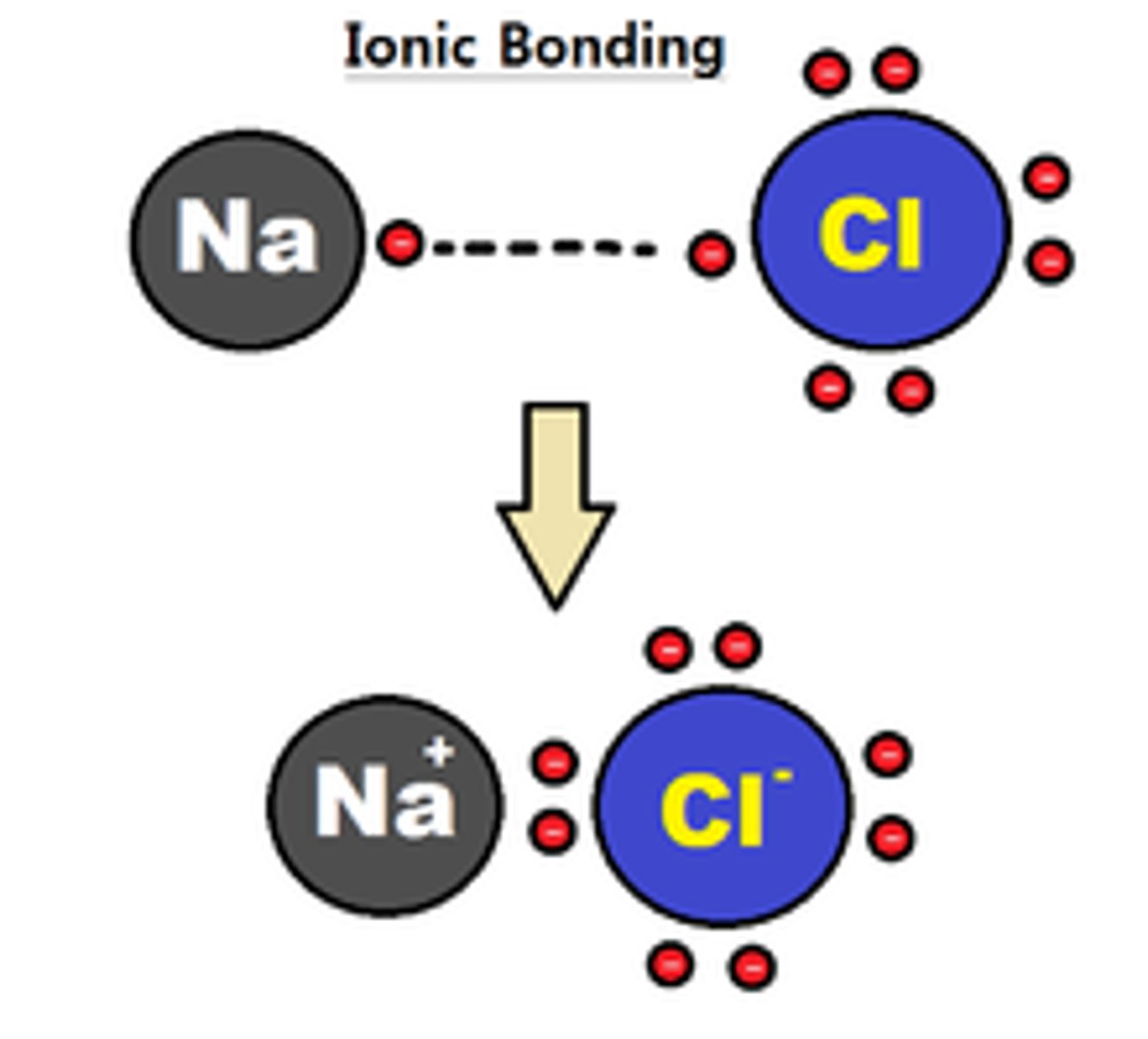
ionic bond
an electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions or a cation and an anion. This type of bond is generally formed between a METAL (cation) and a NON-METAL (anion)
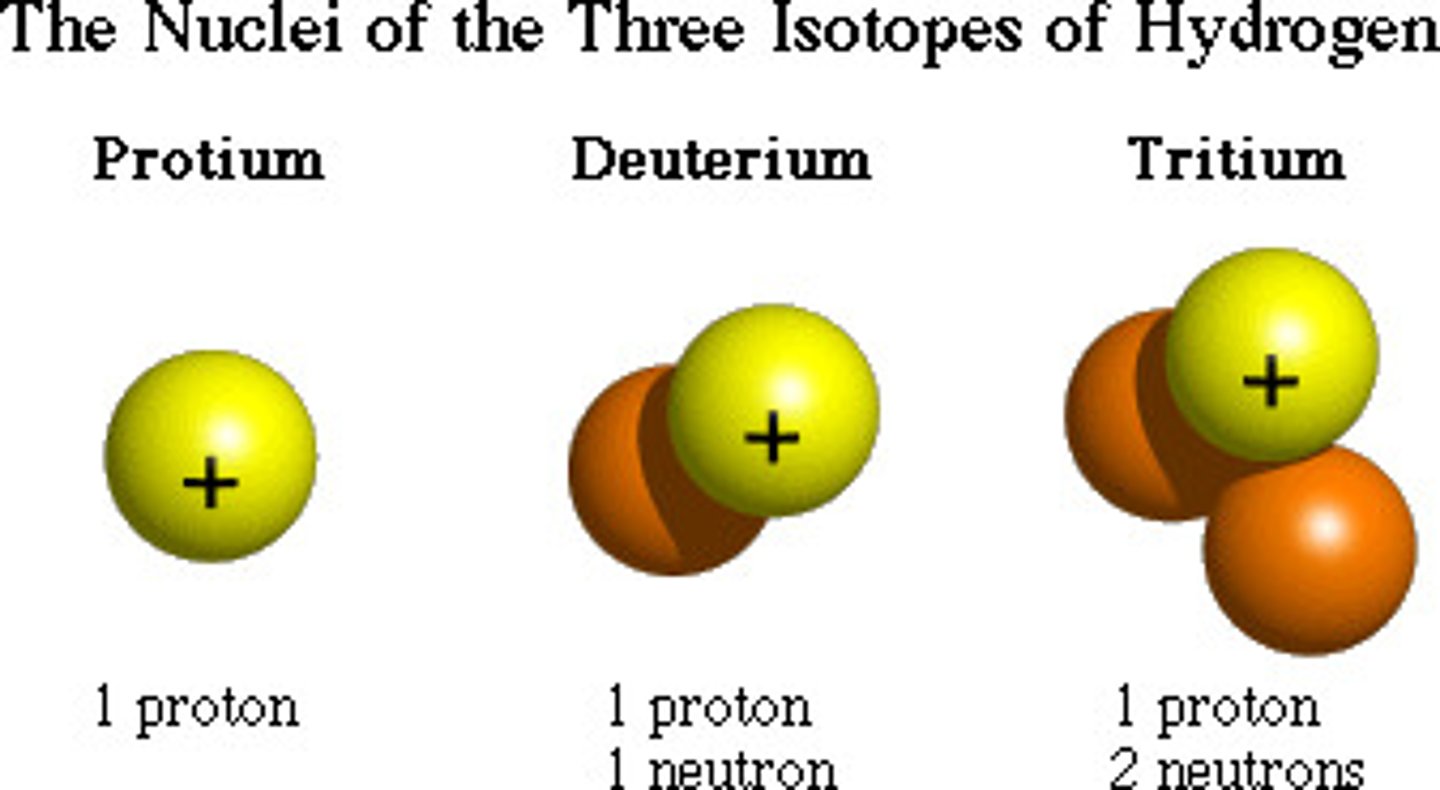
isotope
different kinds of the same atom that vary in weight; for a given element, the number of PROTONS=SAME, while the number of
neutrons = varies to make the different isotopes
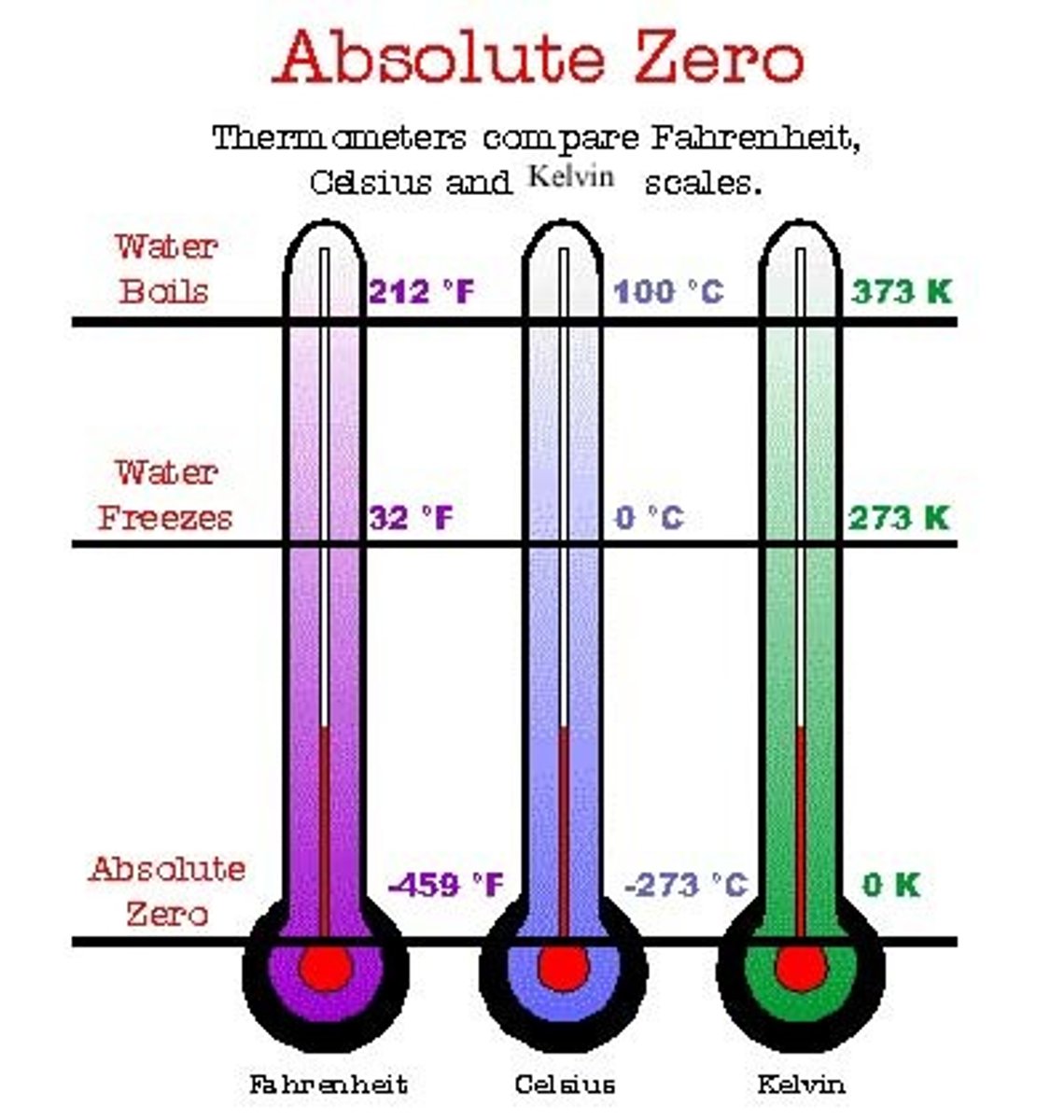
kelvin
a unit of measure that is used only in the scientific community. Kelvin has these characteristics:
0 degrees Kelvin = -273 degrees C and is thought to be the lowest temperature achievable or absolute zero (0);
the freezing point of waer is 273 degrees K;
the boiling point of water is 373 K; most people have a body temperature of 310 degrees K
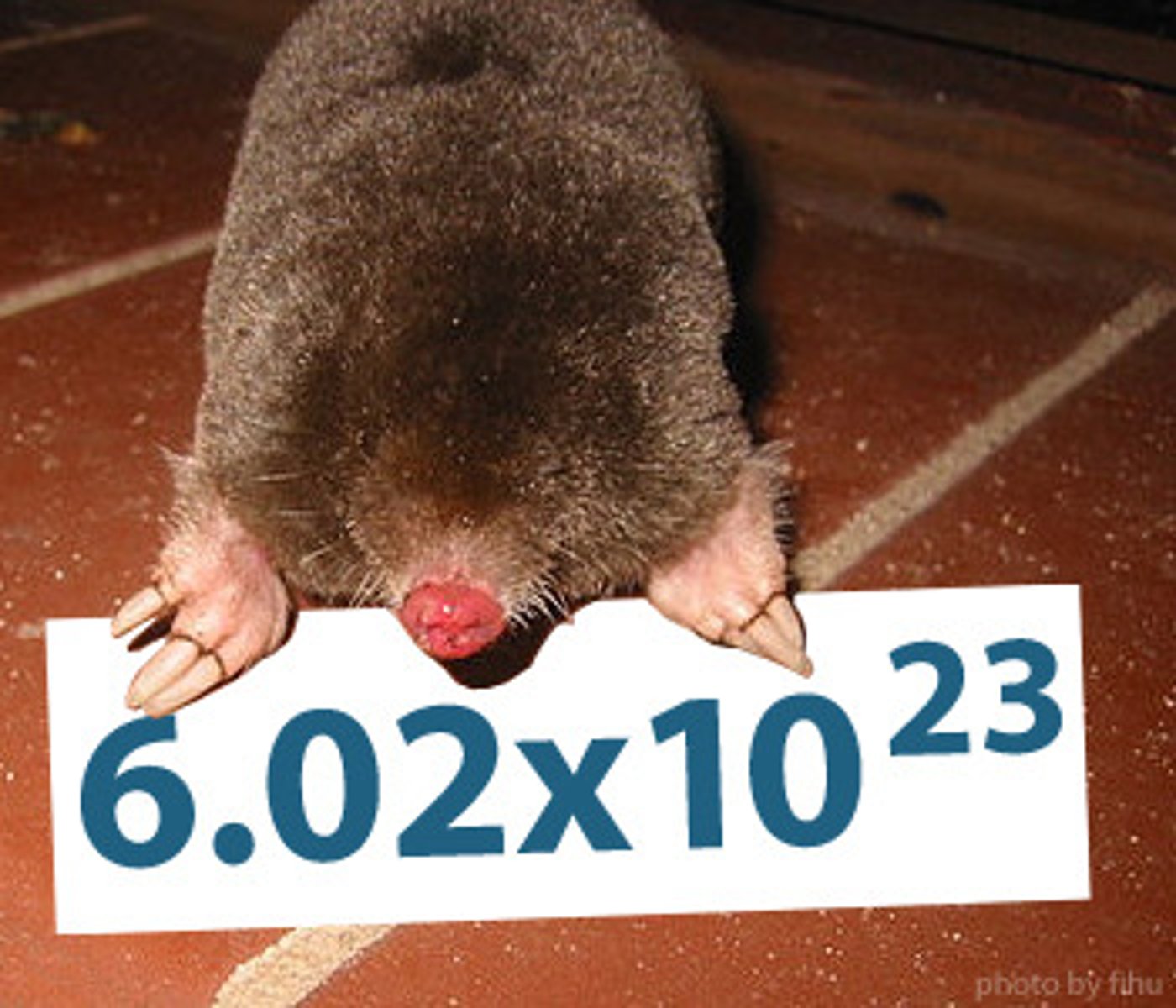
mole
a way to express concentrations of atoms. It is 6.02 x 10^23 of particles

nucleus
the positively charged mass within an atom, composed of PROTONS & NEUTRONS and possessing most of the mass but occupying only a small fraction of the volume of the atom
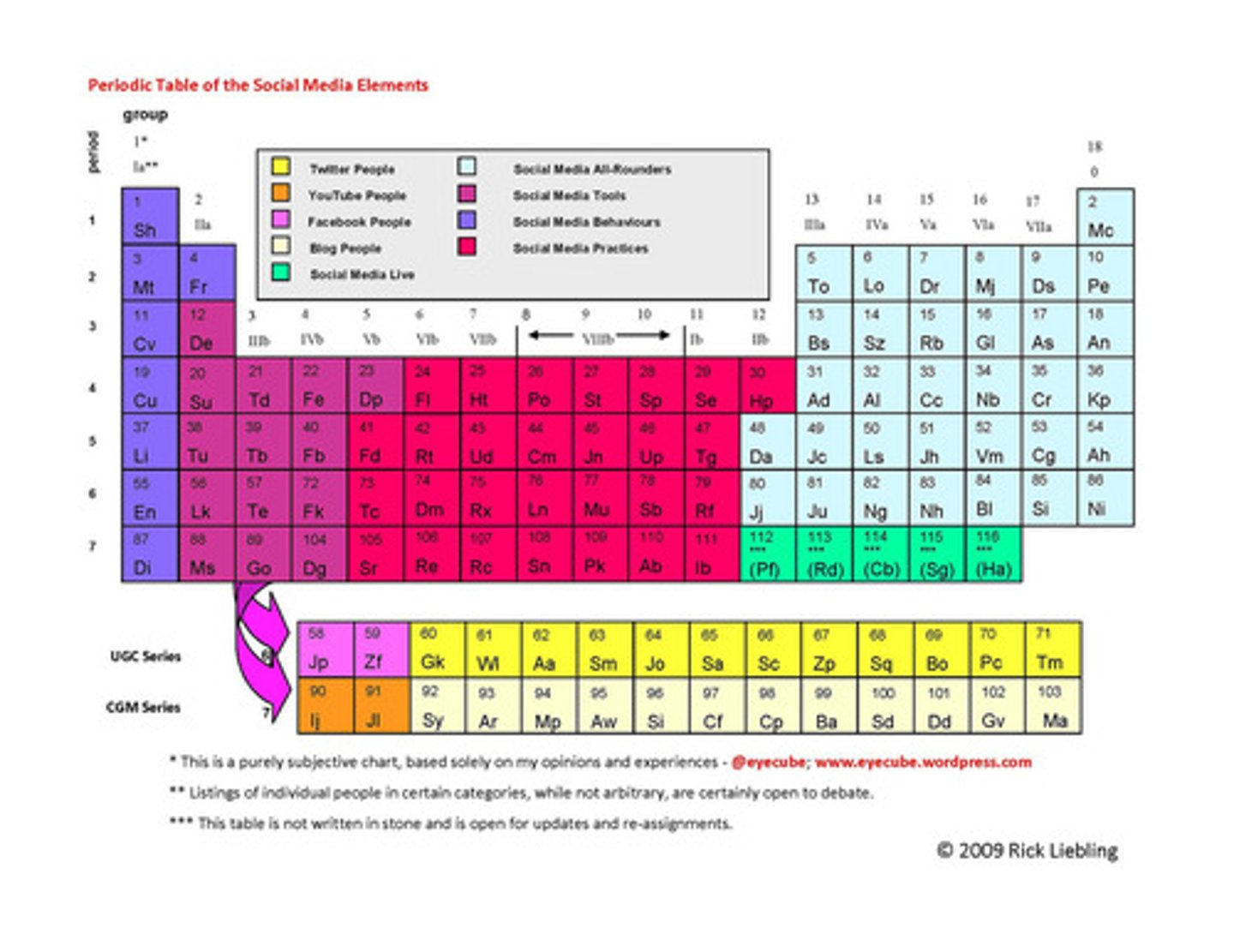
periodic table
a table that organizes the elements based on their structure and thus helps predict the properties of each of the elements. It is made up of a series of rows called periods and columns called groups
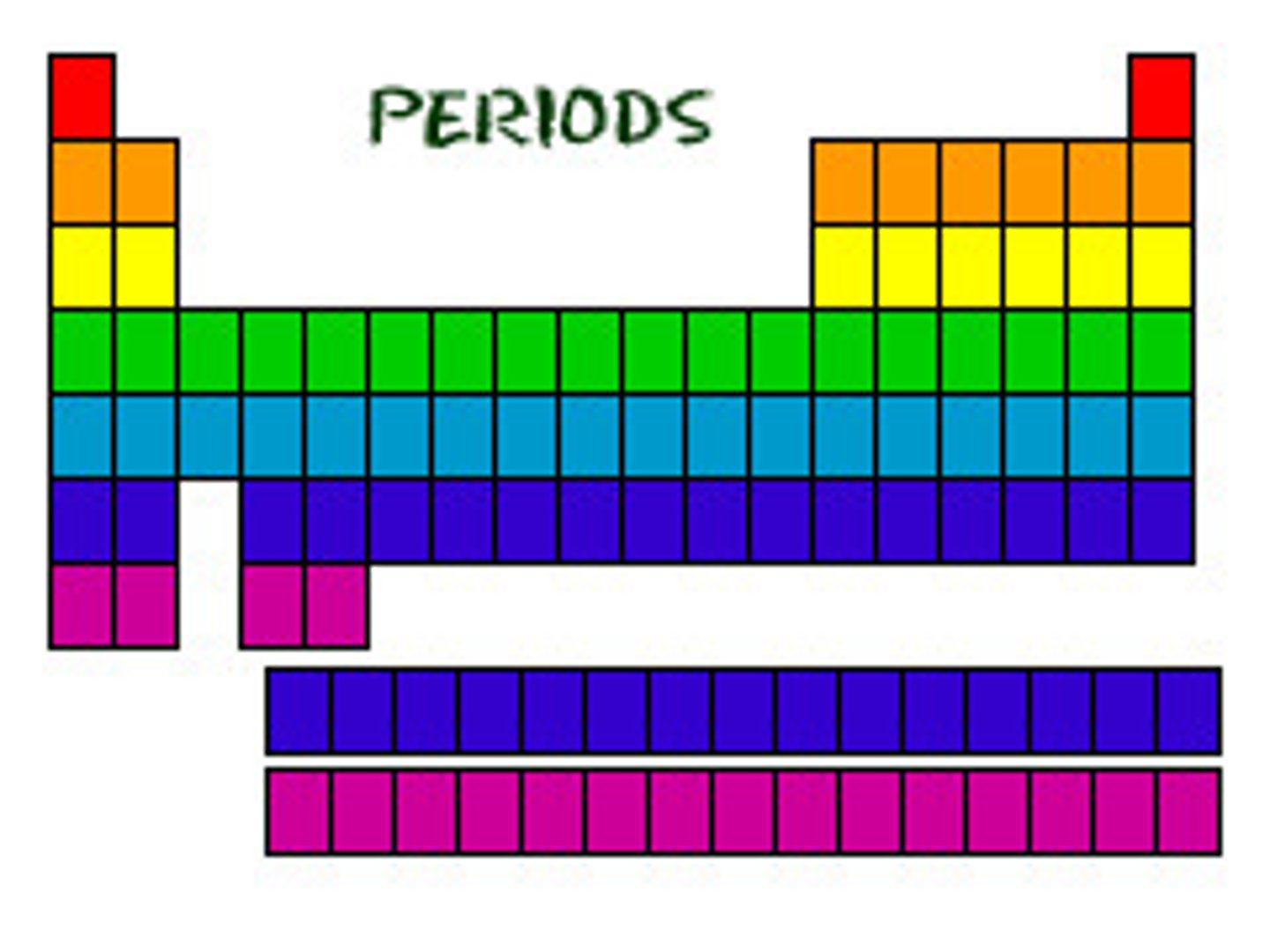
periods
a series of ROWS within the periodic table that classify the elements
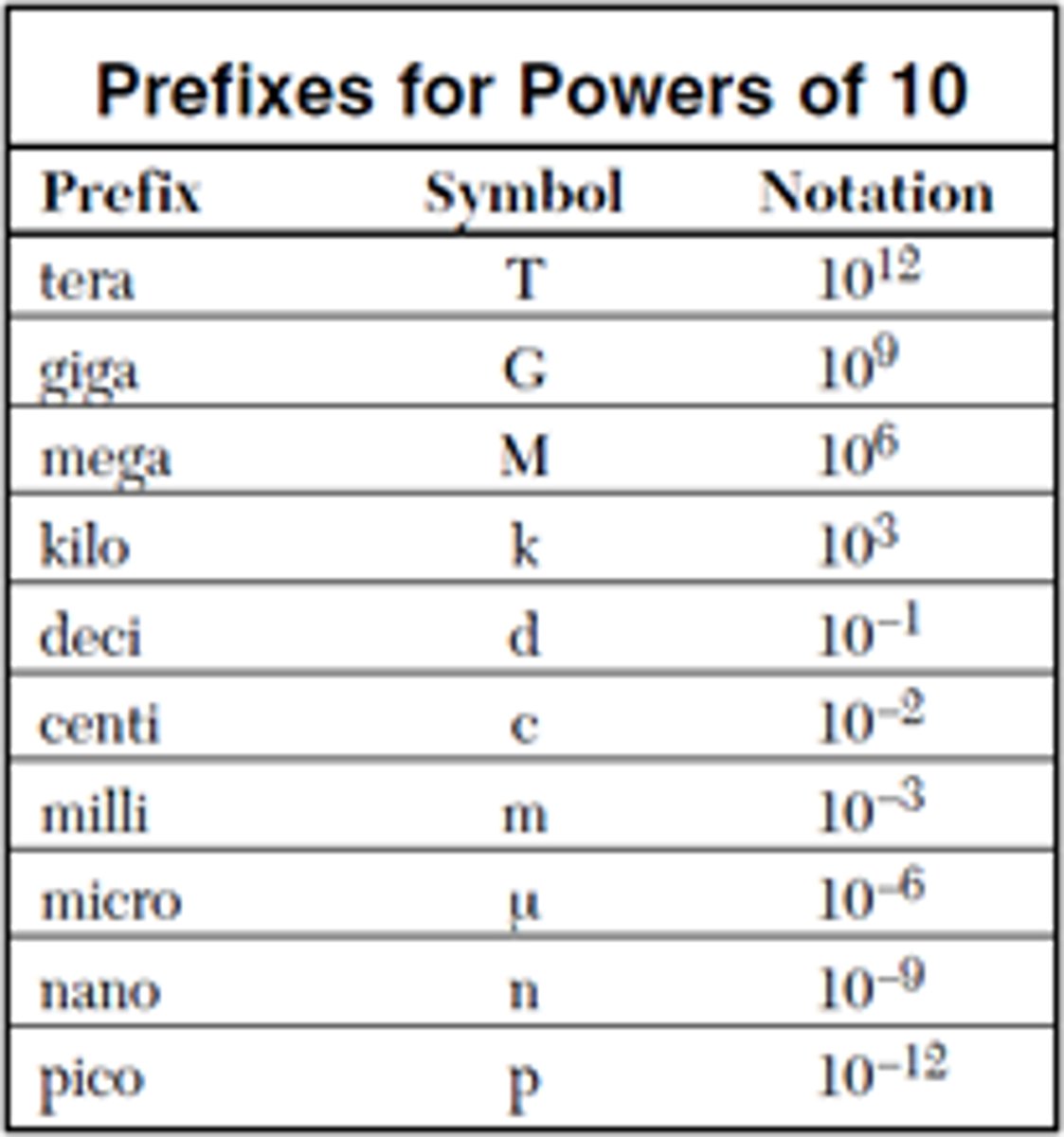
prefix
Prefixes are quantifiers of the measurement units. All prefixes are based on multiples of 10. Any of the prefixes can be comined with one of the basic units of measurement
products
a substance or compound created from a chemical reaction
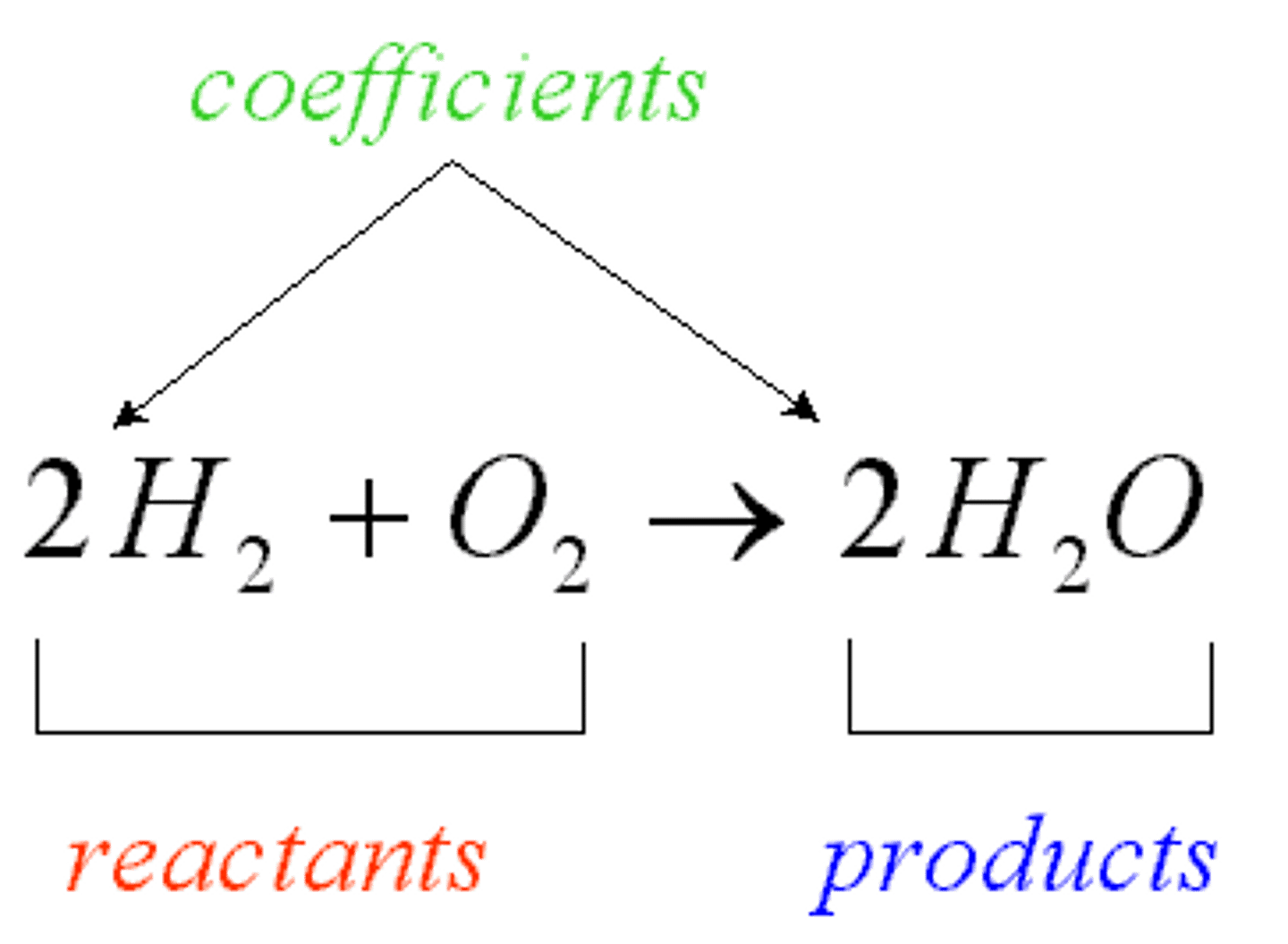
reactants
the part of a chemical reaction that reacts to produce a desired end result or compound
ribose
sugar used in the formation of RNA
significand
the base value of the number or the value of the number when all the values of ten are removed. Used in scientific notation

single replacement
reactions that consist of a more active metal reacting with an ionic compound containing a less active metal to produce a new compound
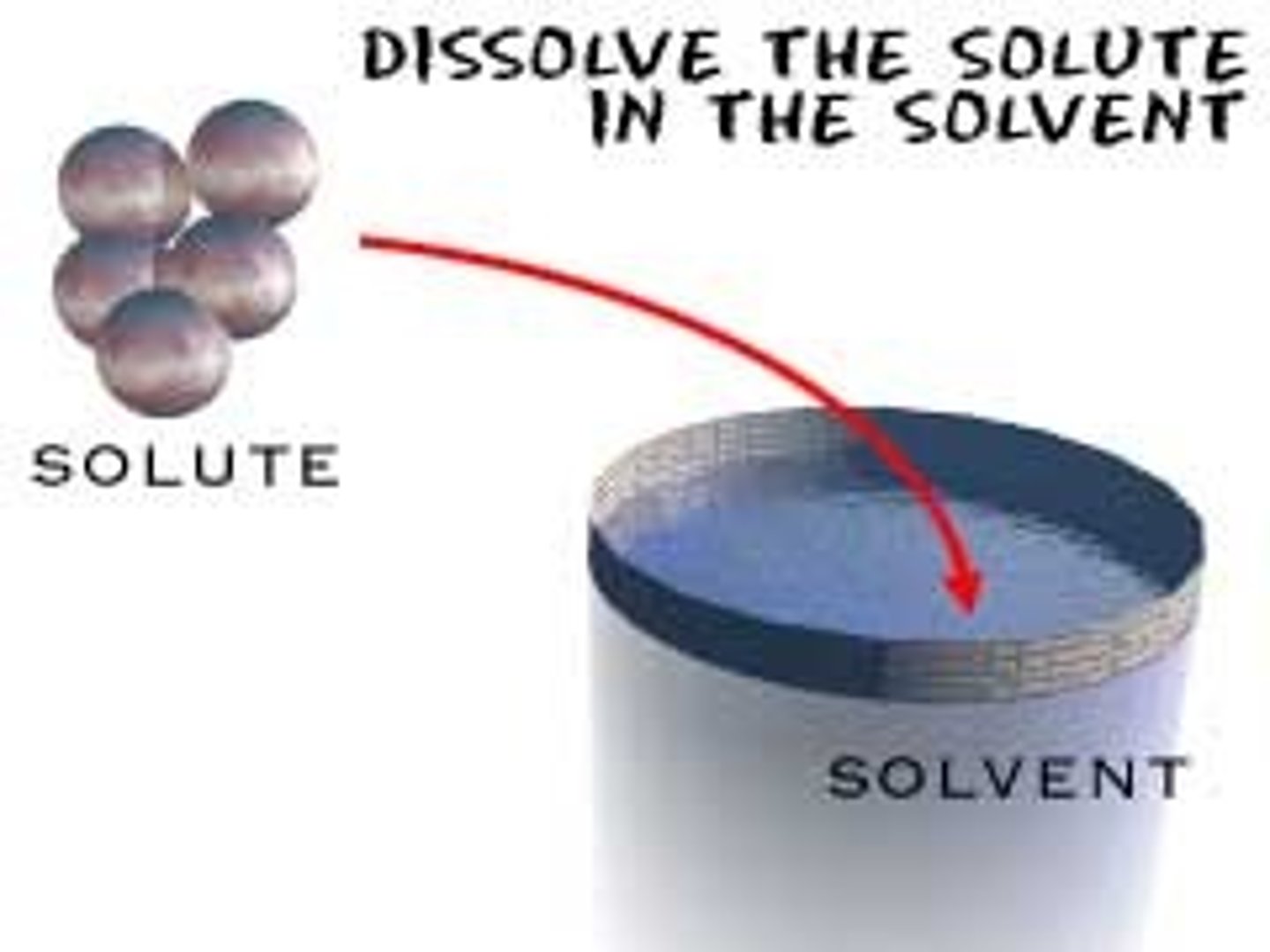
solute
the part of a solution that is being dissolved; the DRUG
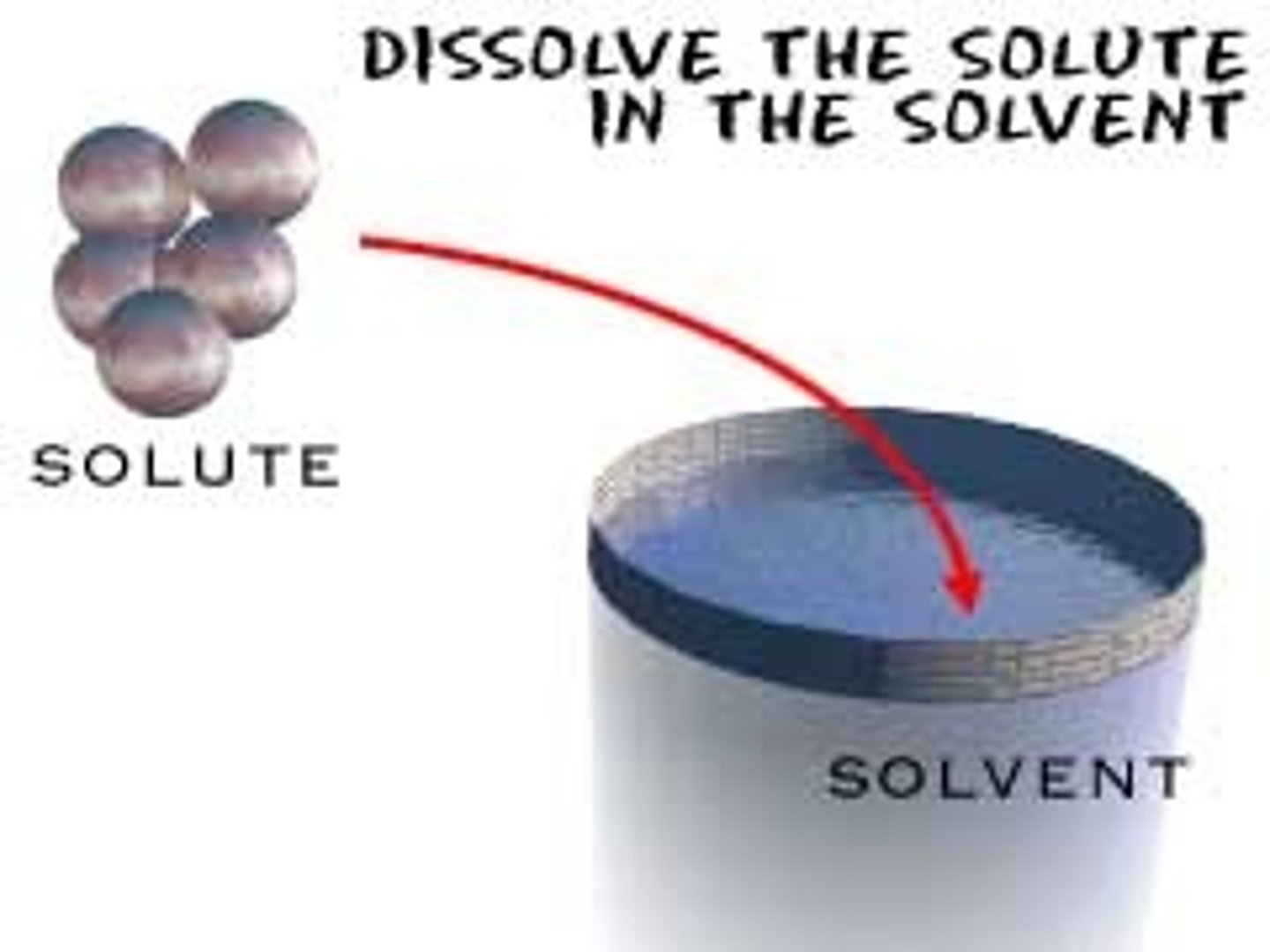
solvent
the SOLUTION that is doing the dissolving
synthesis
a type of chemical reaction in which two elements combine to form a product. An example is the formation of potassium chloride (KCl) salt when a solution of potassium combines with chloride
Melting Ice Temperature for C & F
21 C and 32 F
normal body temperature for Celsius and Fahrenheit
37 C and 98.6 F
boiling water temp for Celsius and Fahrenheit
100 C and 212 F
Tera (12)
T-
10^12
1 quadrillion times
Giga (9)
G-
10^9
1 billion times
Mega (6)
M-
10^6
1 million times
kilo (3)
k-
10^3
1 thousand times
hecto (2)
h-
10^2
10 times
deci (1/10)
d-
10^-1
1 tenth of
centi (1/100)
c-
10^-2
1 hundredth of
milli (1/1000)
m-
10^-3
1 thousandth of
micro (1/1,000,000)
µ-
10^-6
1 millionth of
nano
n-
10-9
1 billionth of
pico
p-
10^-12
1 trillionth of
femto
f-
10^-15
1 quadrillionth of
ELEMENT-- the number of protons remains...
the same, but the number of neutrons varies to make the different isotopes
the most common isotope of an atom
has the same number of protons and neutrons
the element carbon 12 has 6 protons and six neutrons
law of conservation
states that mass cannot be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction. Therefore, once the reactants have been written and products predicted, the equation must be balanced.
The same number of each element must be represented on each side.
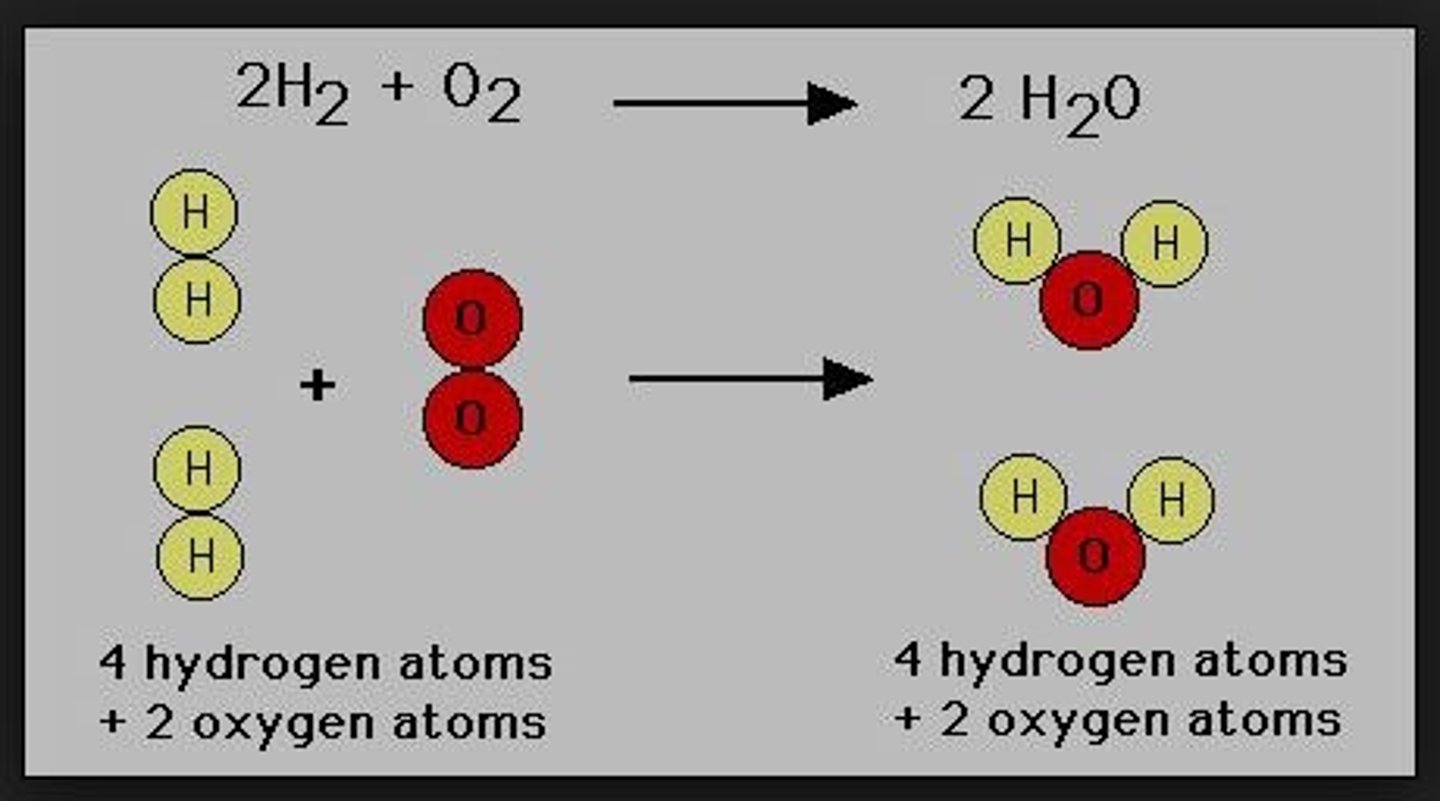
compounds
different ELEMENTS mixed to create a SINGLE matter
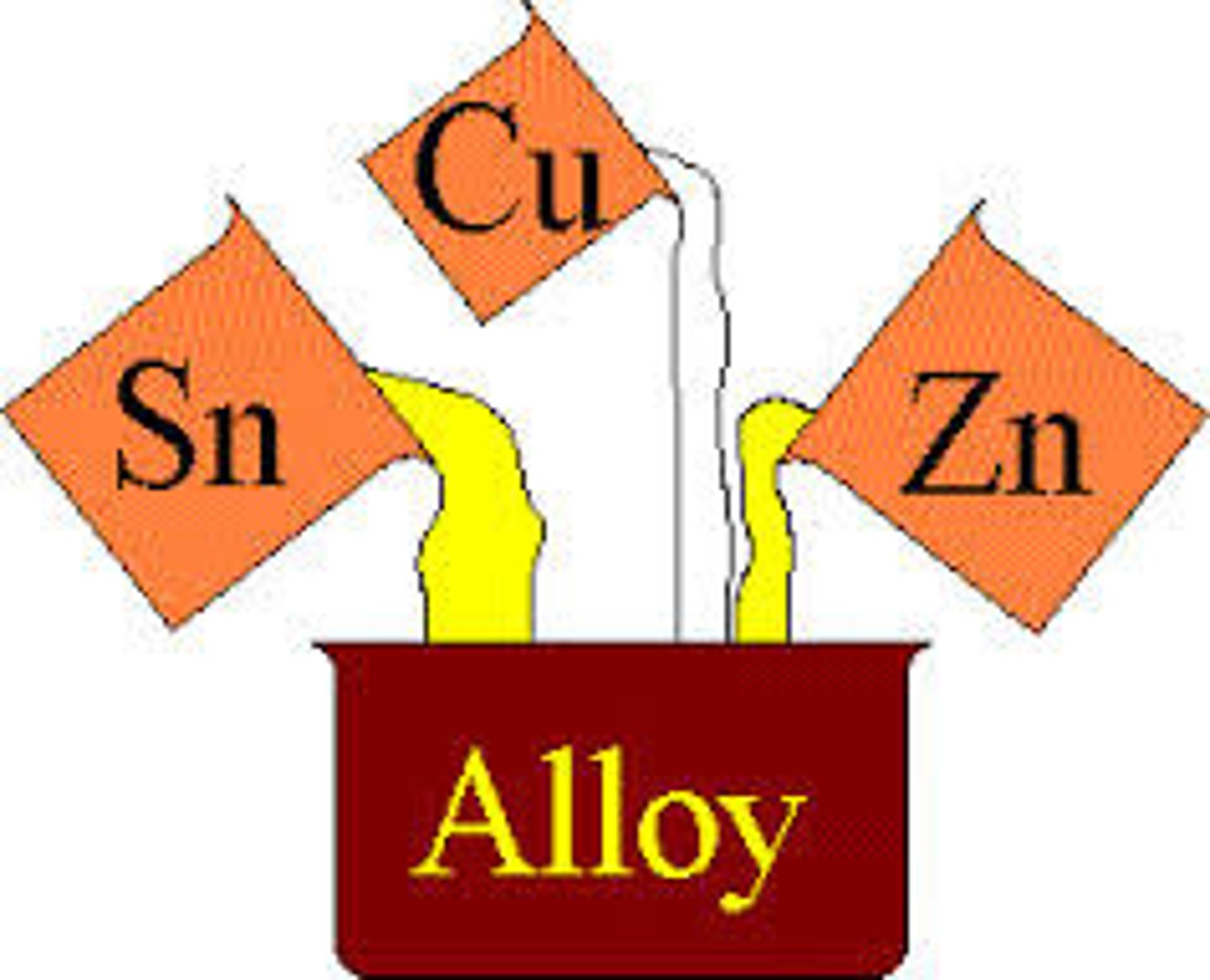
alloys
solid solutions of METALS to make a new one such as bronze, which is copper and tin, or steel, which is iron and carbon, tungsten, chromium, and manganese.
amalgams
a specific type of alloy in which another metal is dissolved in mercury
emulsions
mixtures of matter that readily separate such as water and oil

four ways to increase the reaction rate
-increasing the temperature
-increasing the surface area
-catalysts
-increasing the concentration
the atomic mass of any element in grams (g)
is one mole or 6.02X10^23 atoms of that element or compound
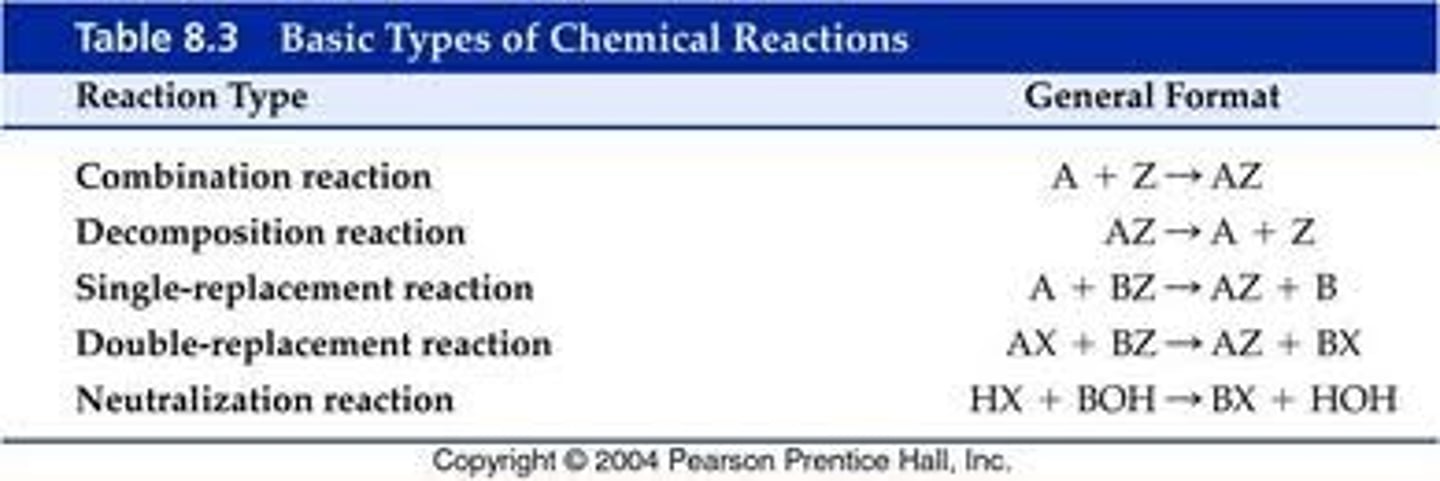
5 types of reactions
-synthesis
-decomposition
-combustion
-single replacement
-double replacement
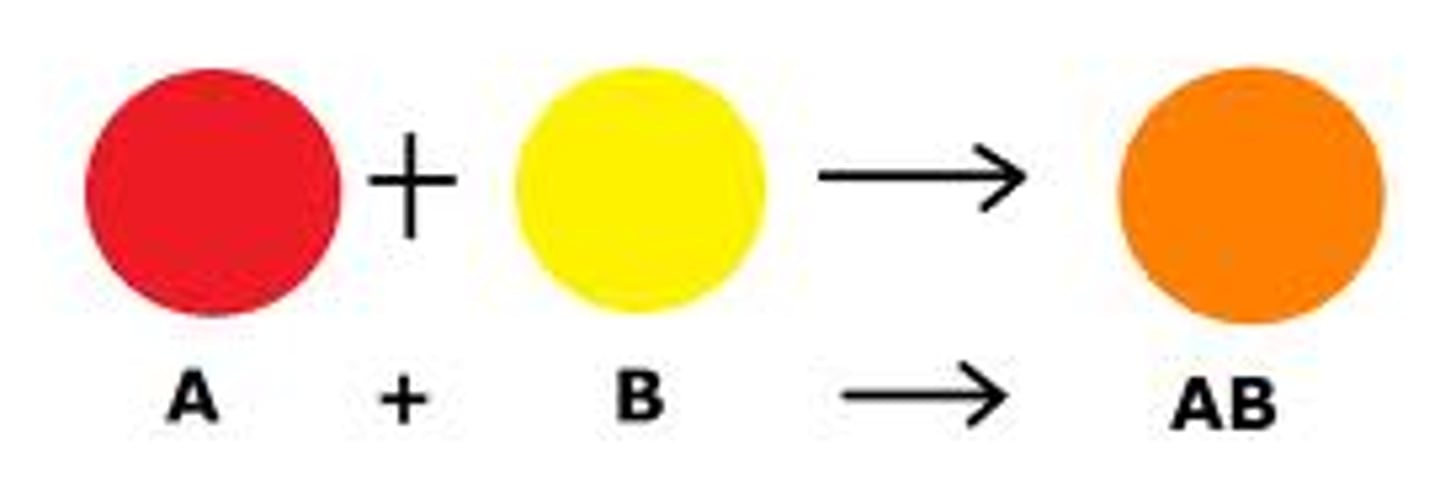
synthesis
1 ELEMENT + 1 ELEMENT = product
decomposition
breaking of a compound into its component parts

intermolecular forces
these are NOT BONDING interactions between atoms within a molecule but instead are WEAKER forces of attraction between whole molecules
the 3 forces of intermolecular forces
-hydrogen bonds
-Dipole-Dipole
-dispersion forces
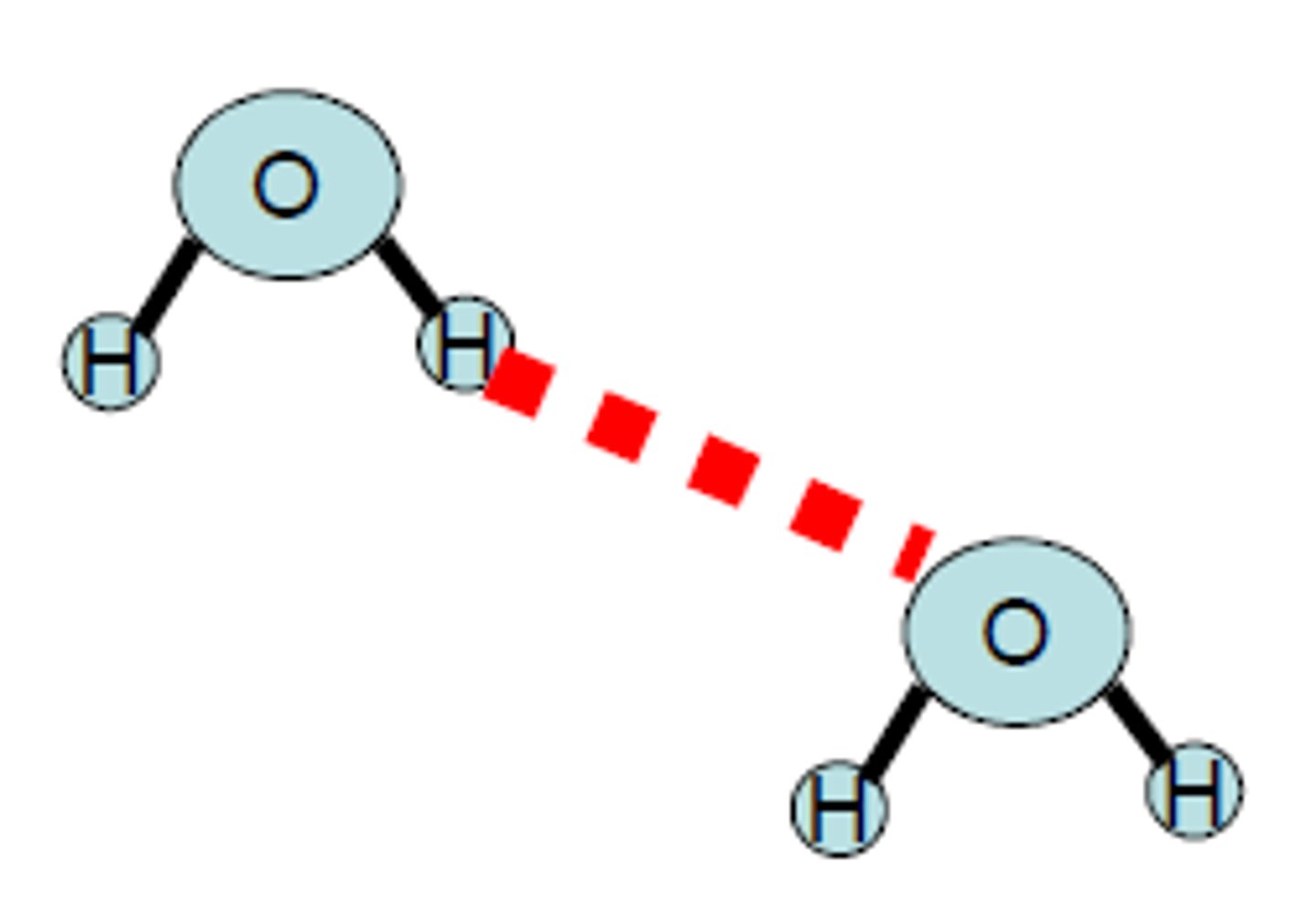
hydrogen bonds
An attraction for a hydrogen atom by a highly electronegative element.
The elements usually involved are flourine (F), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N).
-The STRONGEST of the intermolecular forces
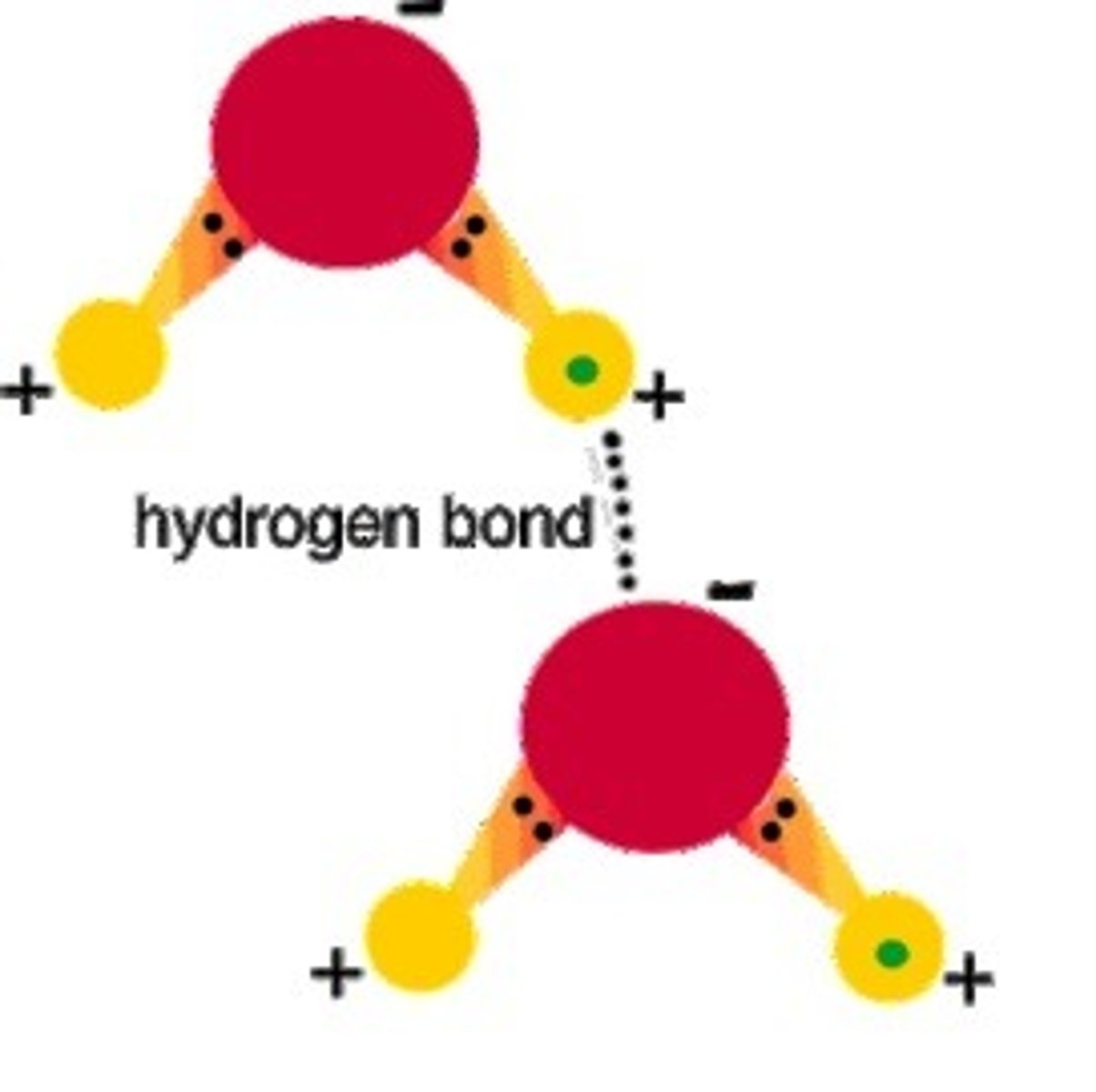
Dipole-Dipole interactions
The attraction of 1 dipole on one molecule for the dipole of another molecule. A dipole is created when an electron pair is shared unequally in a covalent bond between two atoms or elements.
Because the electrons are shared unequally, the molecule, not the covalent bond, will have a positive end and a negative end or side. The result is a WEAK bond between molecules.
oxidation
the loss of elections, making it more POSITIVE
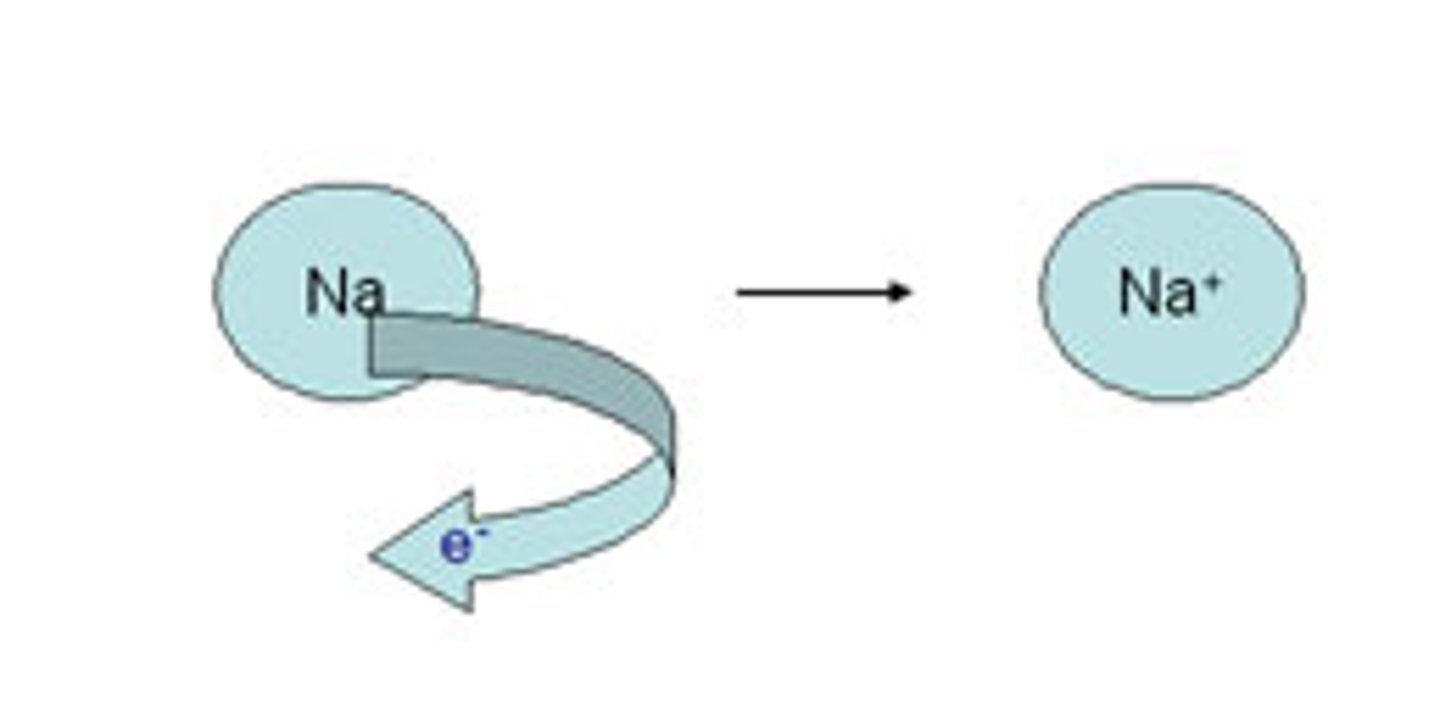
reduction
the gain of electrons, making it more NEGATIVE
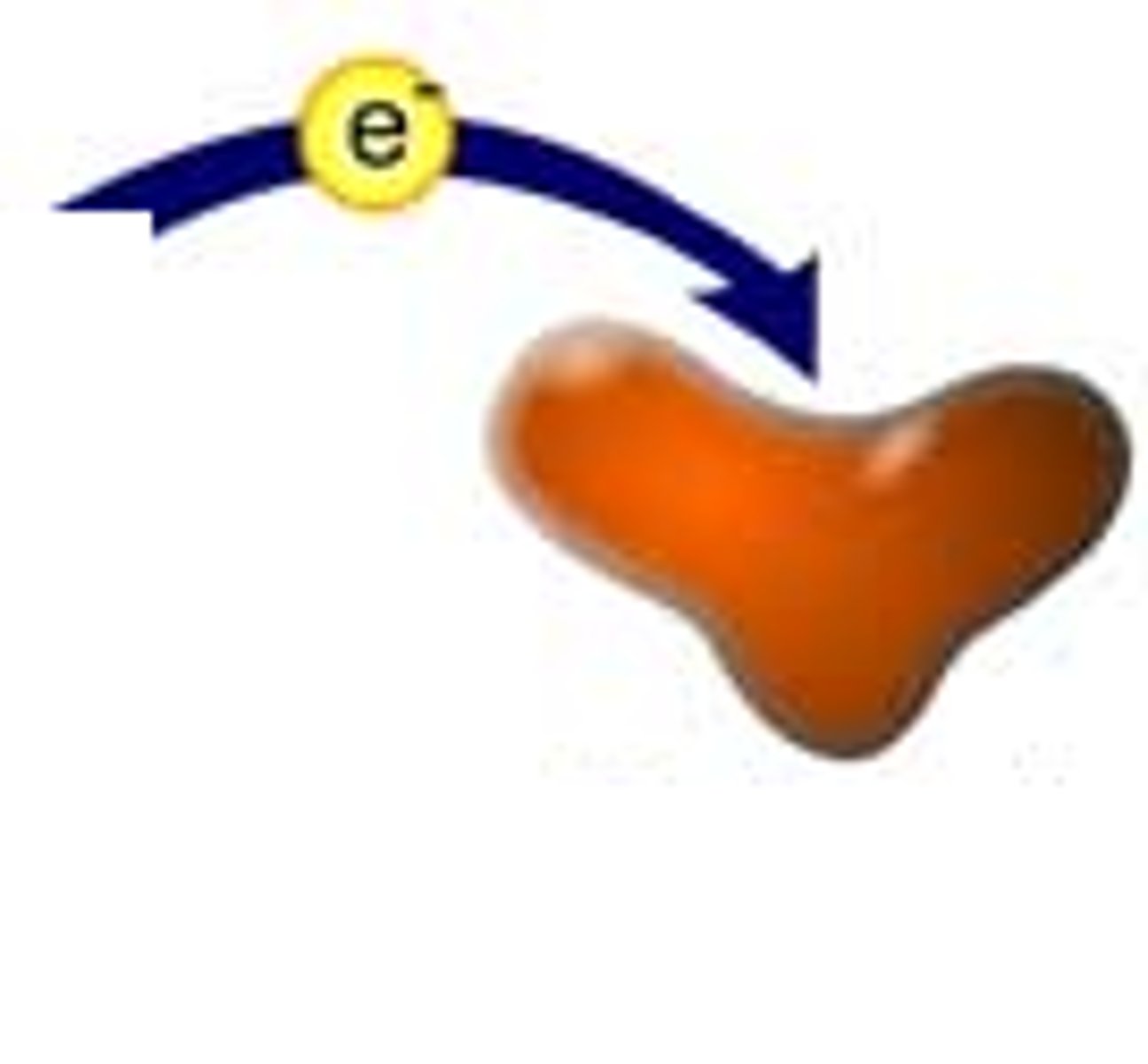
OIL-RIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
all acids produce _______ when placed in H2O
hydronium
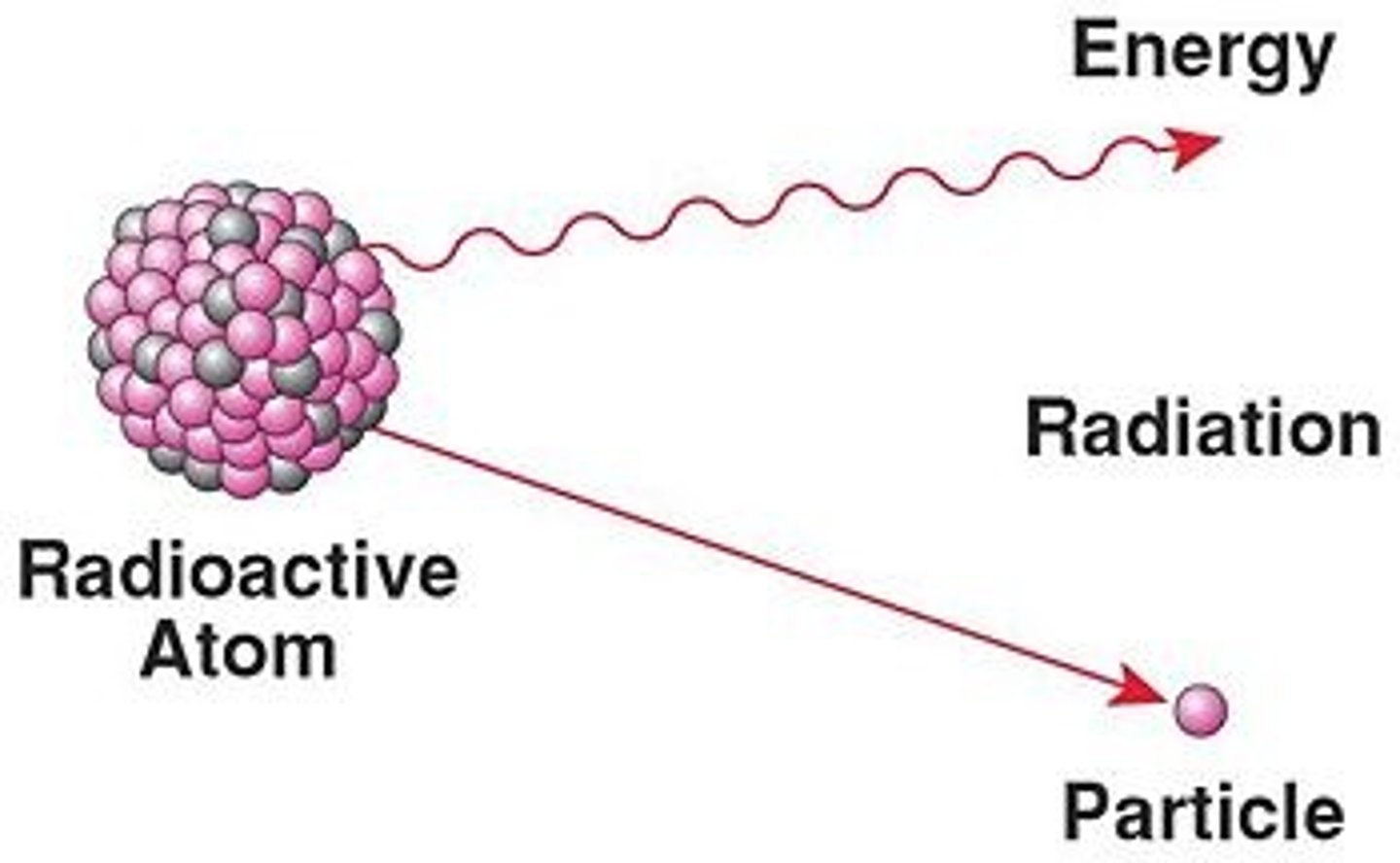
radioactivity
describes the emission of particles and/or energy from an unstable nucleus. The particles and/or energy that are emitted are referred to as radiation
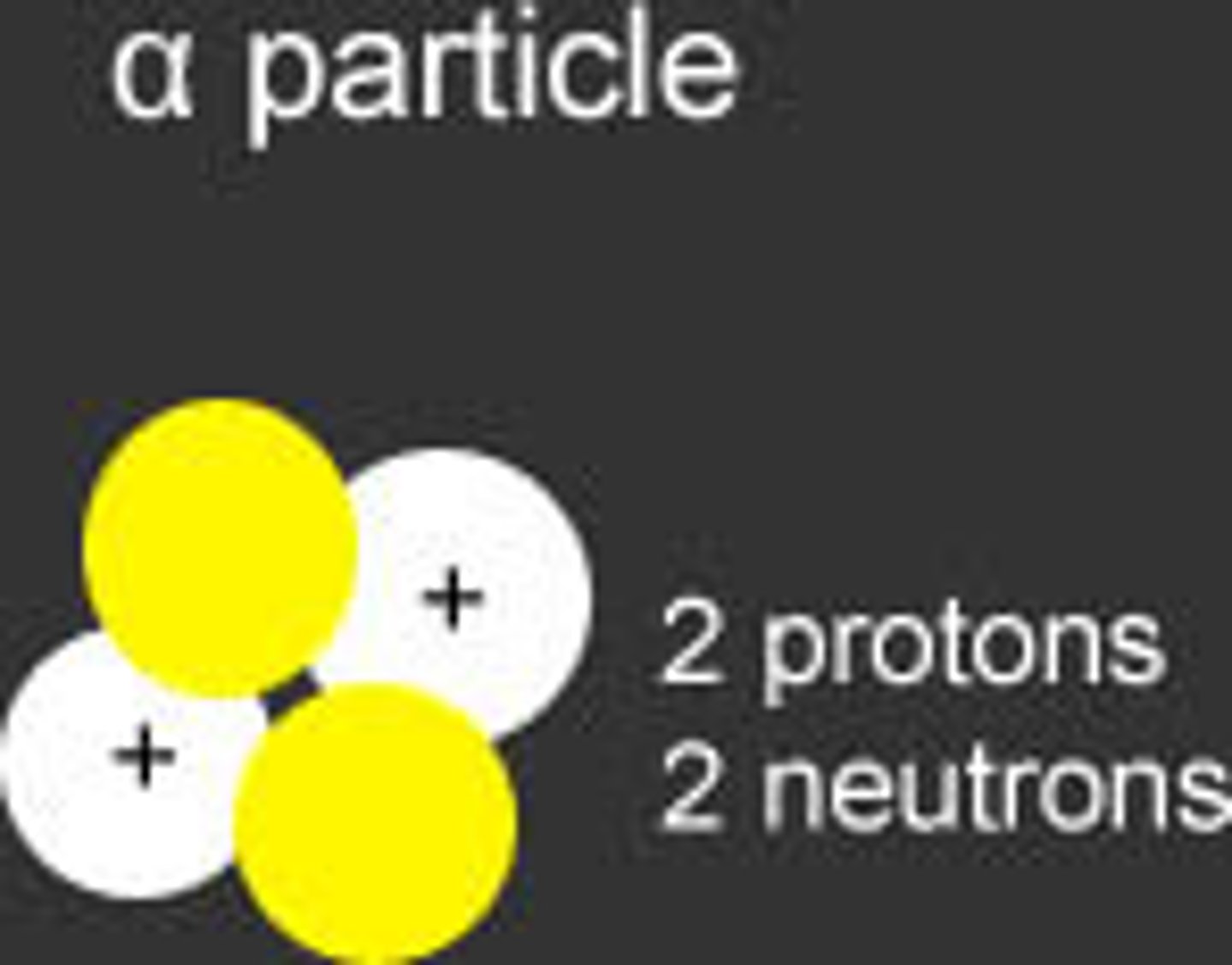
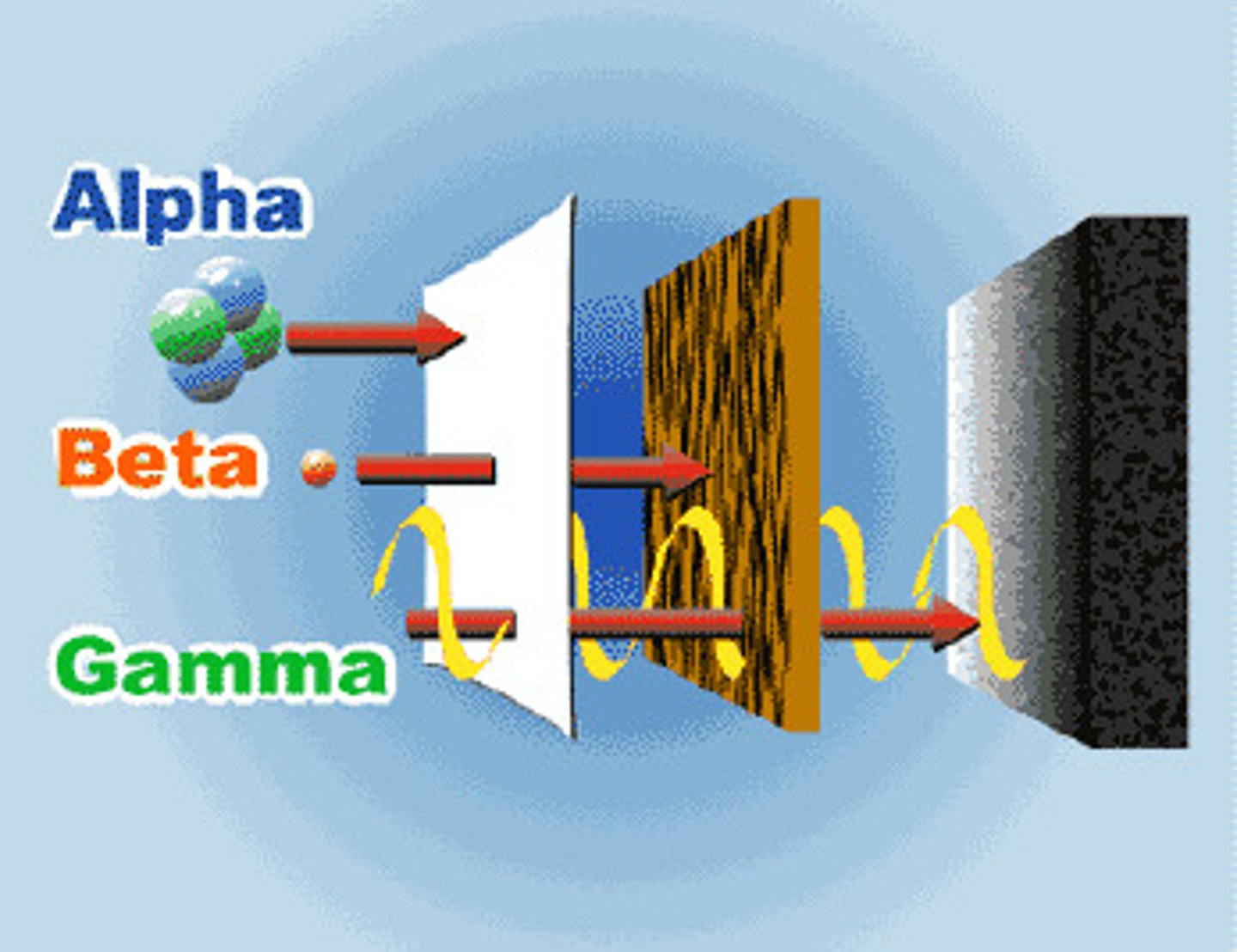
alpha radiation
the emission of helium nuclei.
These particles contain 2 PROTONS and 2 NEUTRONS, causing them to have a charge of PLUS TWO (+2). Alpha particles are the LARGEST of the radioactive emissions, and penetration from alpha particles can generally be stopped by a piece of PAPER
beta radiation
is a product of decomposition of a neutron and proton. It is actually composed of high-energy, high-speed electrons that began as neutrons or protons and have "decayed" to electrons. They have NO MASS and can be stopped by a thin sheet of aluminum FOIL, Lucite, or plastic.
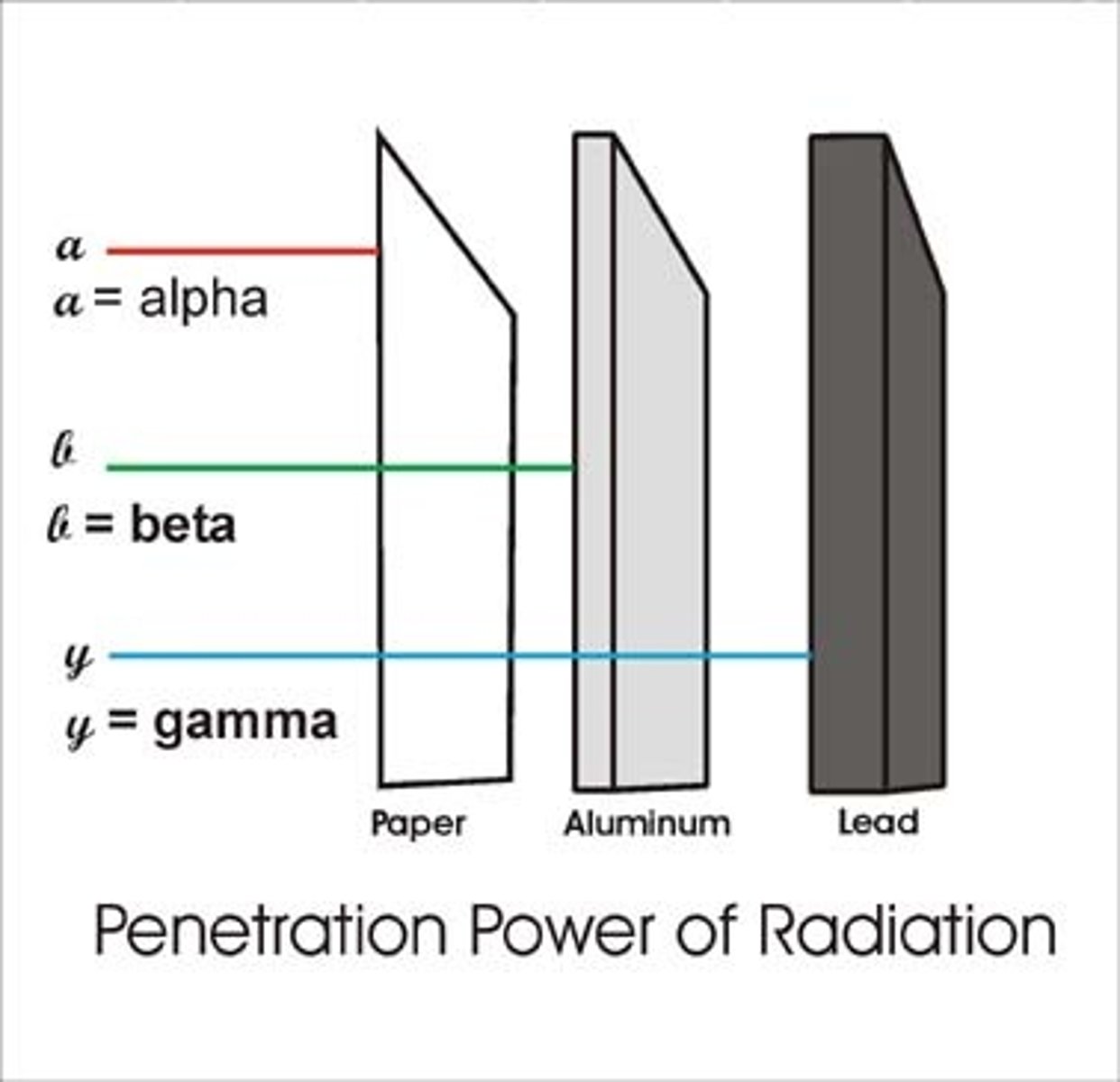
gamma radiation
HIGH-ENERGY electromagnetic radiation, similar to x-rays but with MORE ENERGY. It is very penetrating and can go through several feet of concrete or several inches of lead.
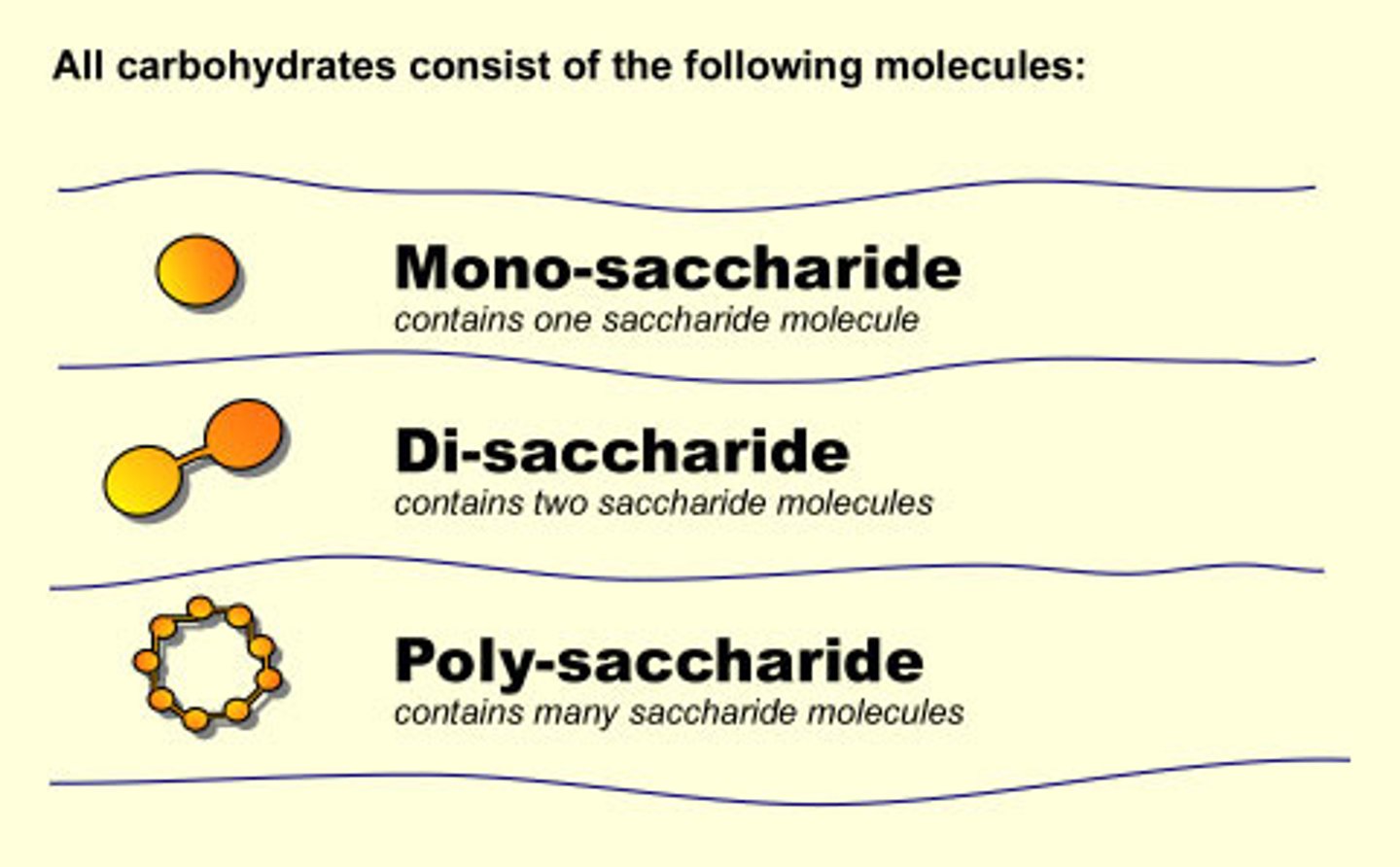
monosaccharides
the simplest type of carbohydrates.
glucose (C6H12o6)
Fructose (C6H12O6)
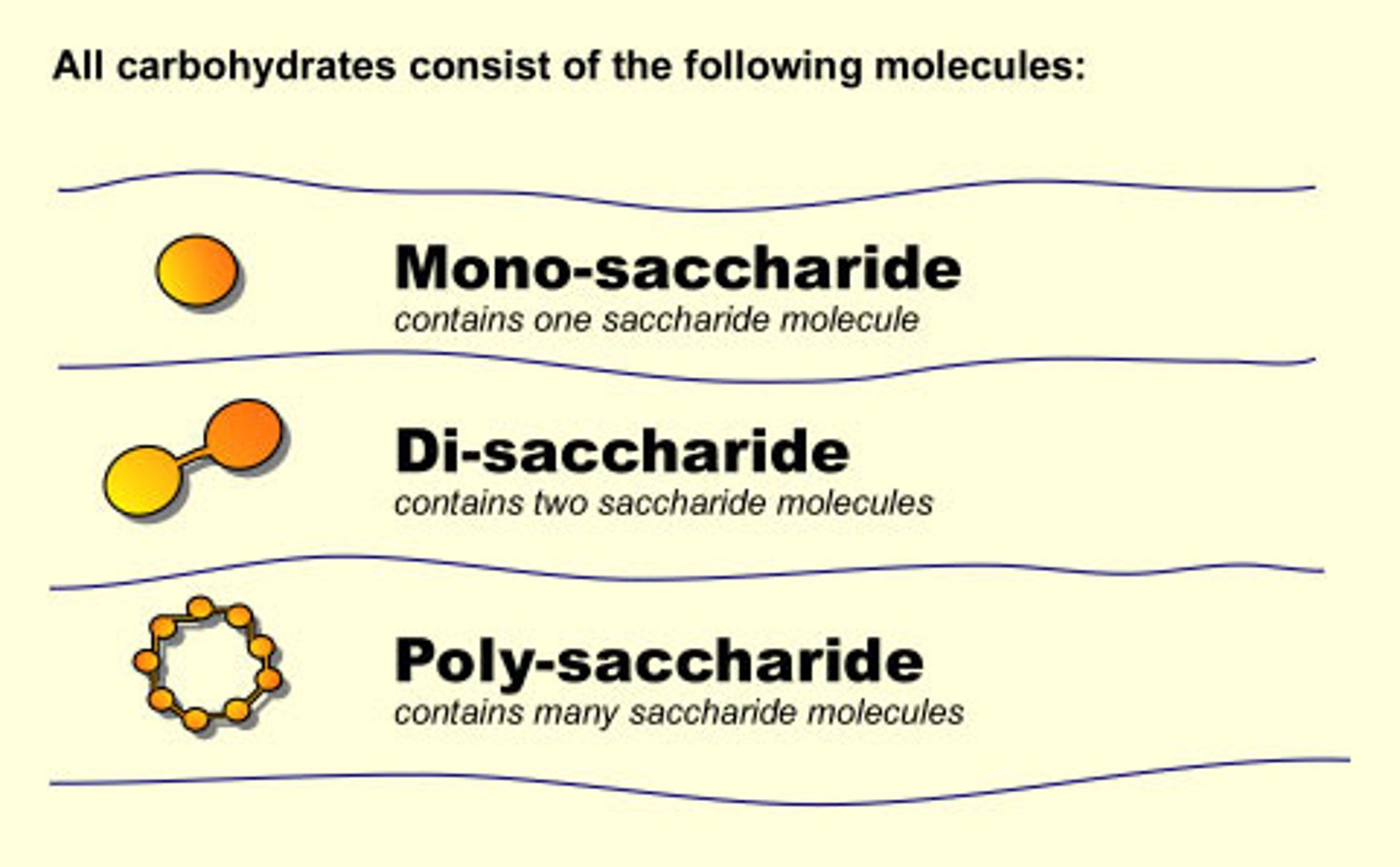
oligosaccharides
when 3 to 6 monosaccharides are joined together
polysaccharides
MORE THAN 6 and up to thousands of monosaccharides joined together make a polysaccharide, which can be called a starch
cellulose and glycogen
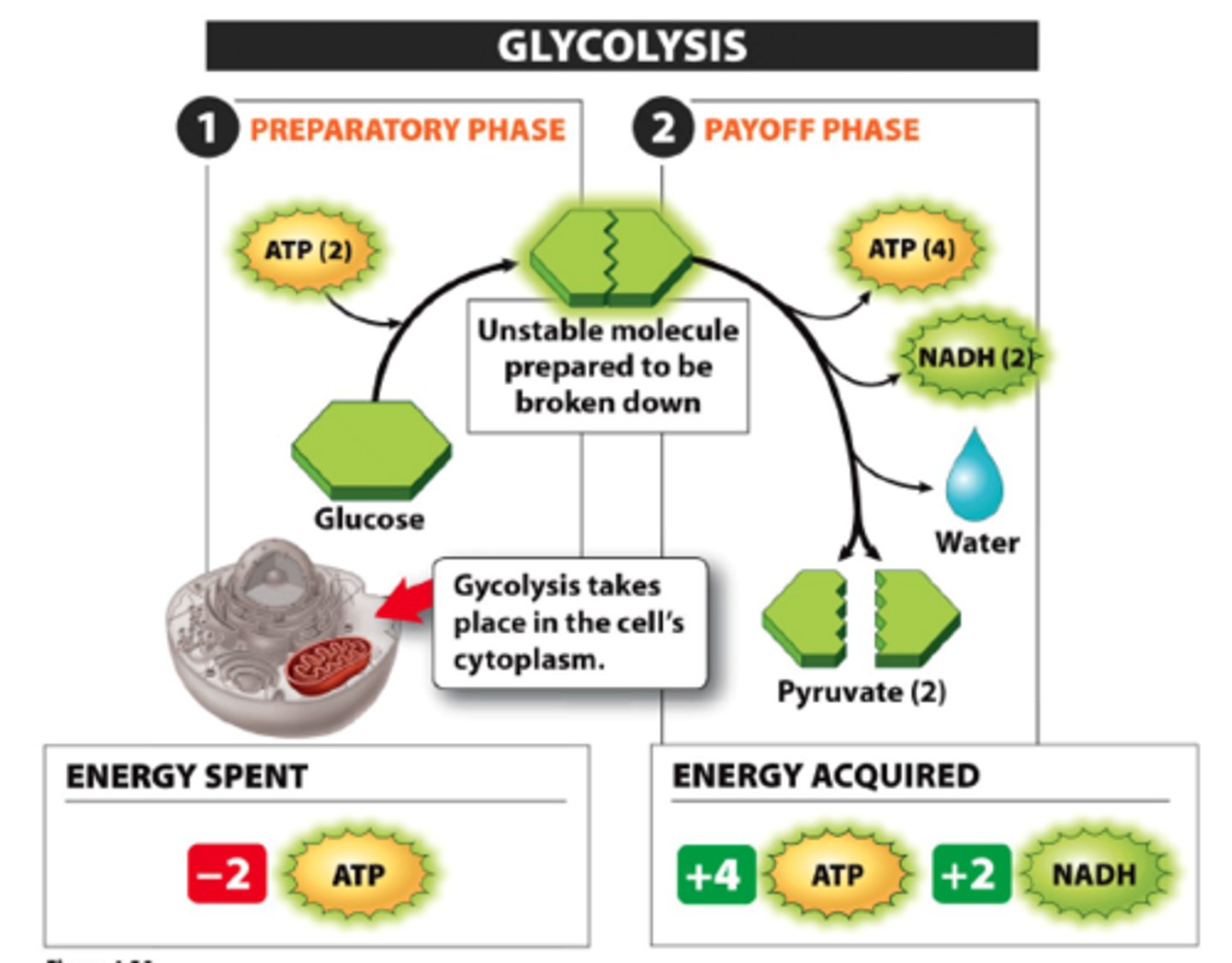
Glycolysis
-glucose is mainly metabolized by this
-breaks down one glucose to create 2 pyruvate and 2 ATP
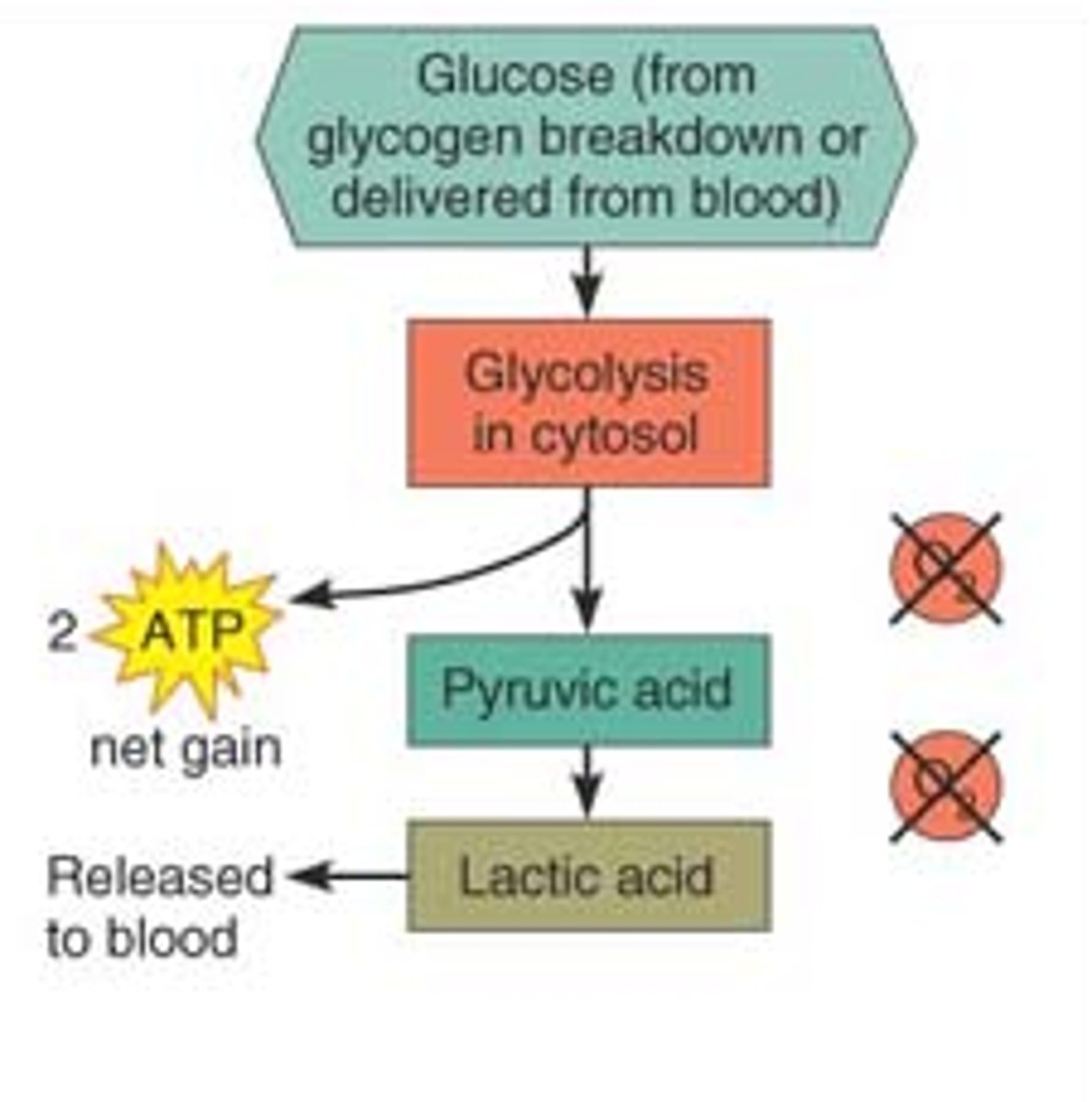
Anaerobic glycolysis
-during vigorous exercise skeletal muscles use anaerobic glycolysis to CONVERT GLUCOSE to LACTATE instead of pyruvate (as in aerobic glycolysis)
-Lactate produces CRAMPS
gluconeogenesis
the liver makes glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as proteins and parts of fats
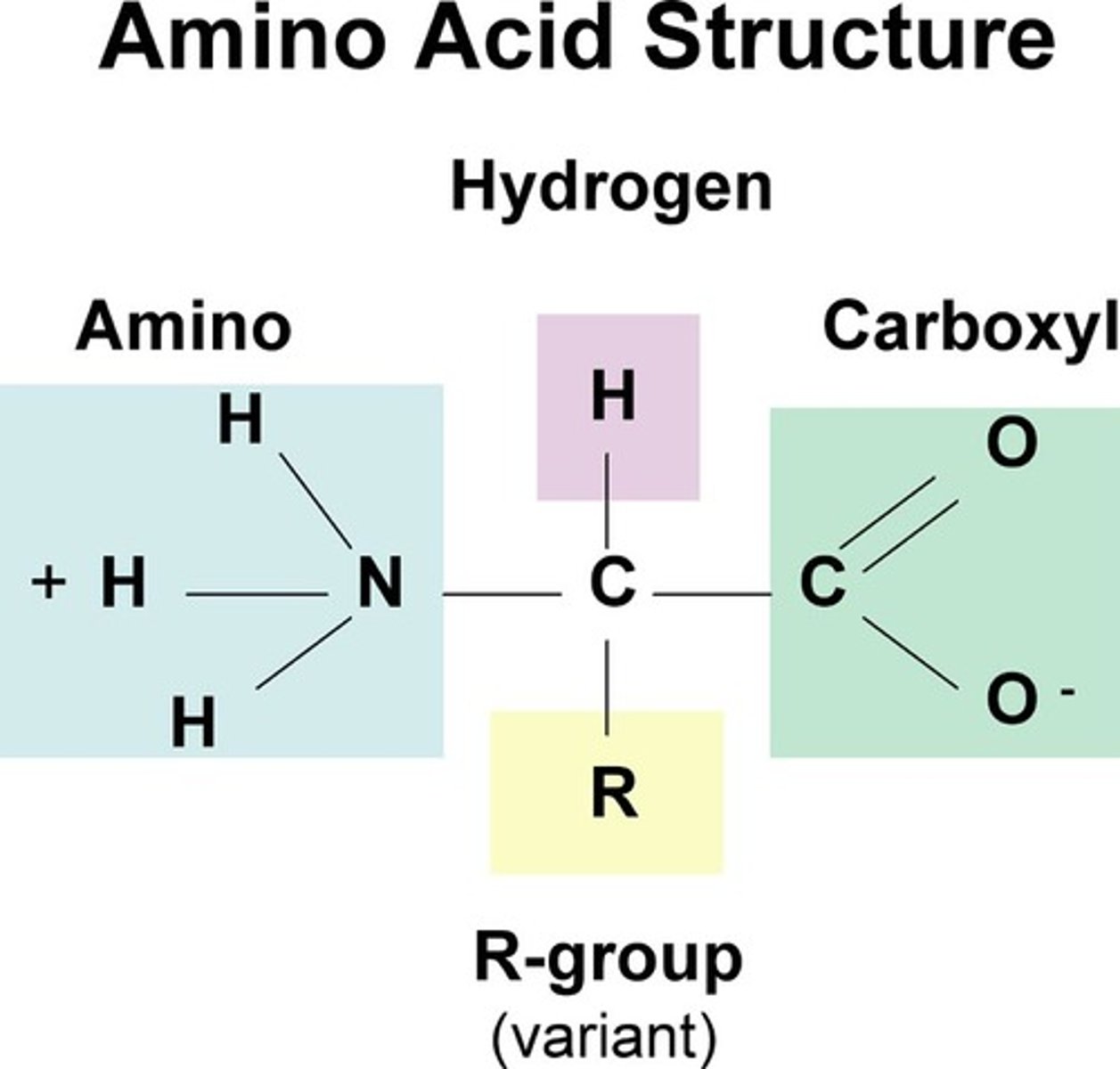
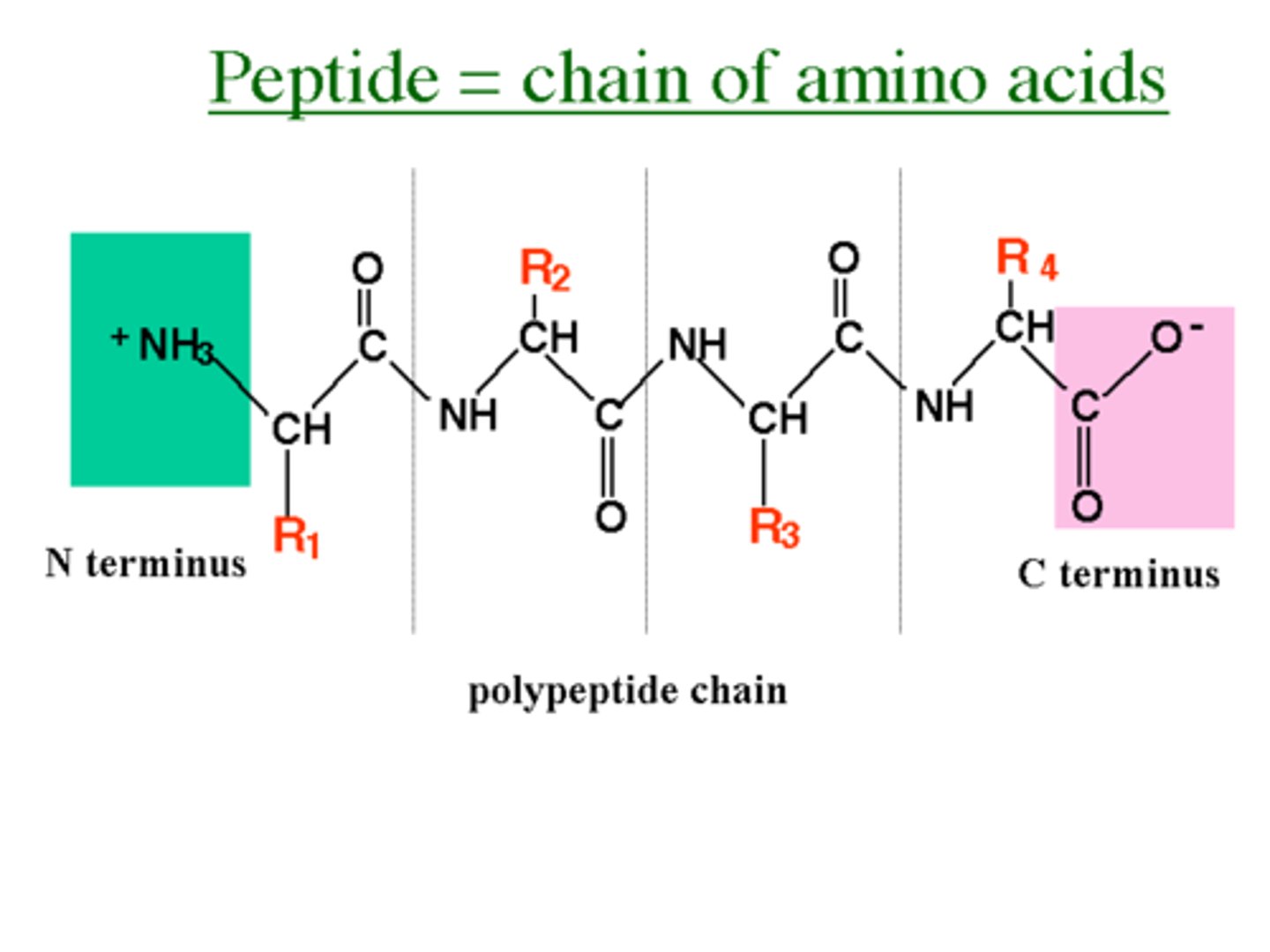
proteins are made up of amino acids. An amino acid is composed of a carbon atom bonded with four groups:
-an amine group (NH2)
-a carboxyl group (COOH)
-a hydrogen
-and an R group which is different for each amino acid
dipeptide
2 amino acids
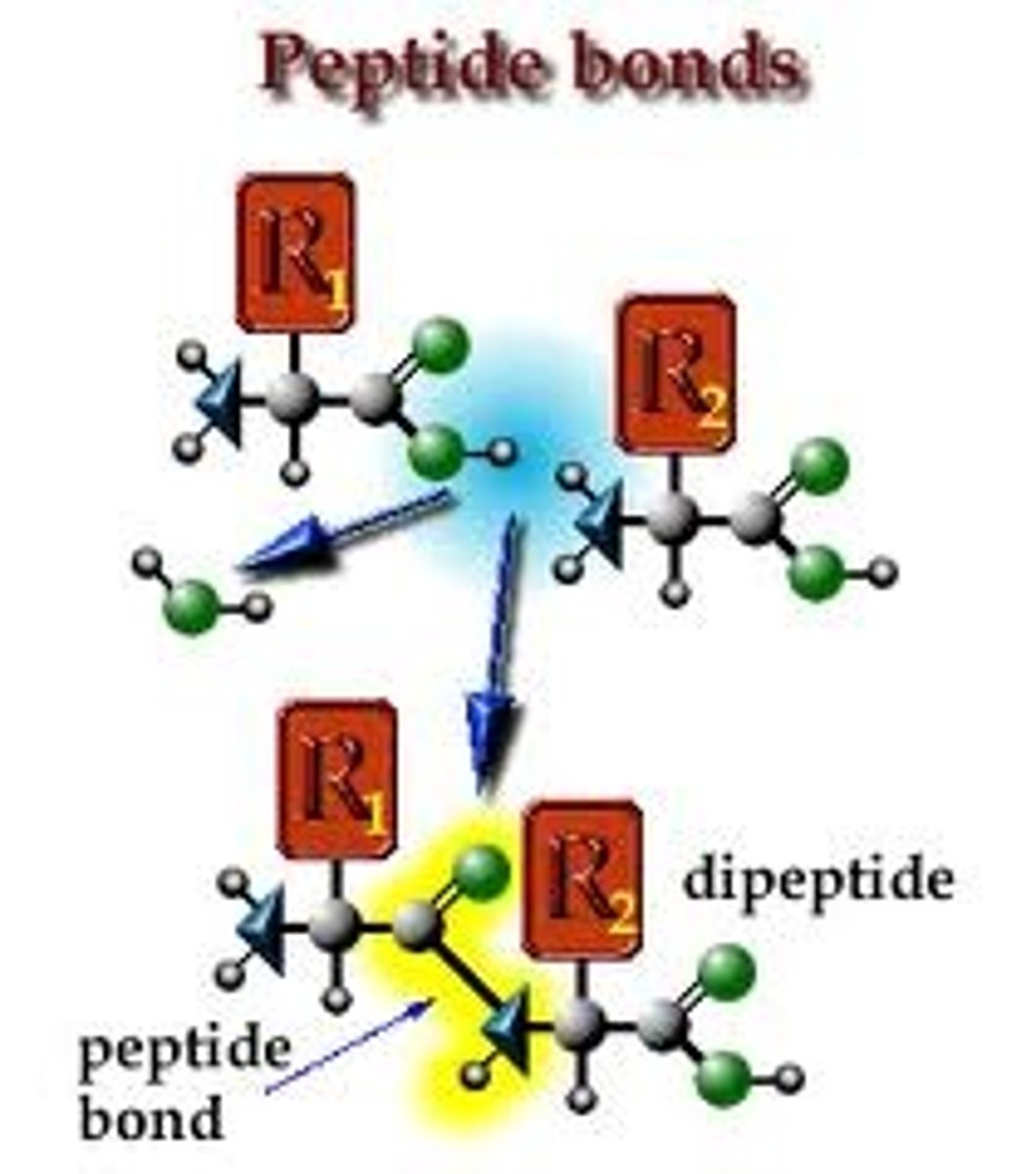
polypeptide or peptides
a group of LESS than 30 amino acids
albumin
contains 585 amino acid residues
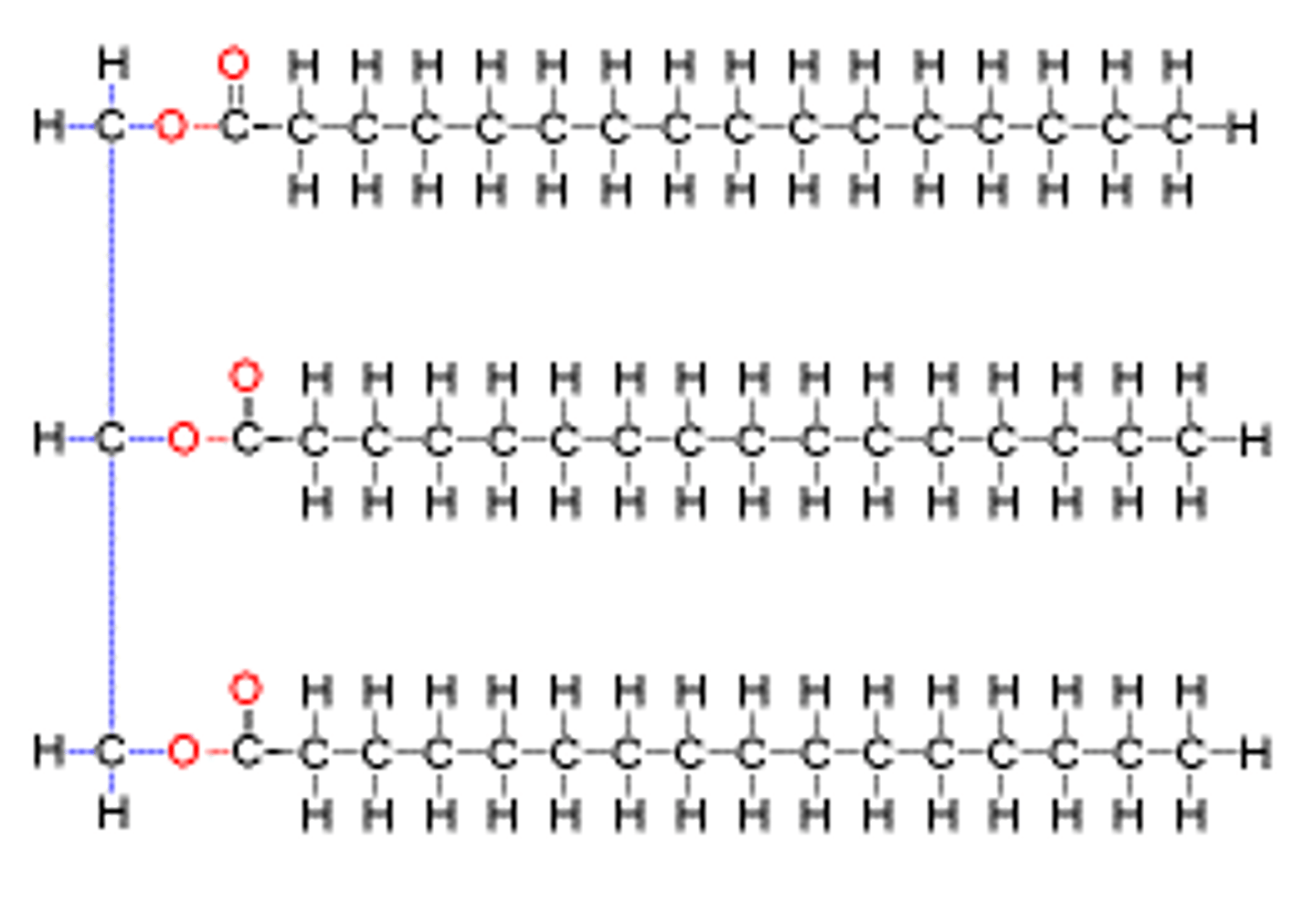
triglyceride
a neutral fat that is three fatty acids generally joined to a glycerol or some other backbone structure
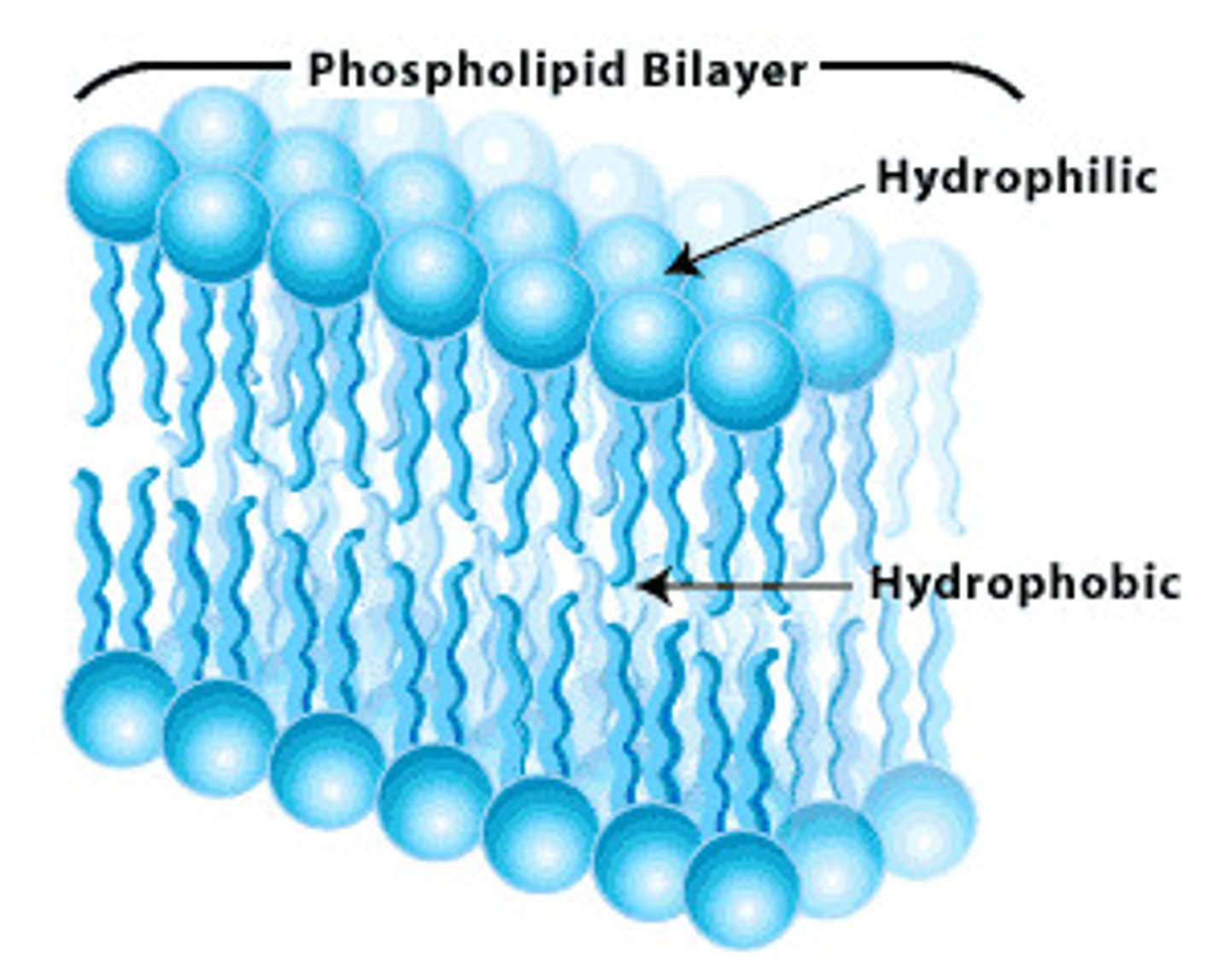
phospholipids
similar to triglycerides but one of the three fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group
fats are used by the body to:
-insulate body organs against shock
-to maintain body temperature
-to keep skin and hair healthy
-to promote healthy cell function
natural lipids can be classified by:
-unsaturated fats
-polyunsaturated fats
-saturated
saturated fats
have NO DOUBLE BOND between carbon atoms of the fatty acid chains
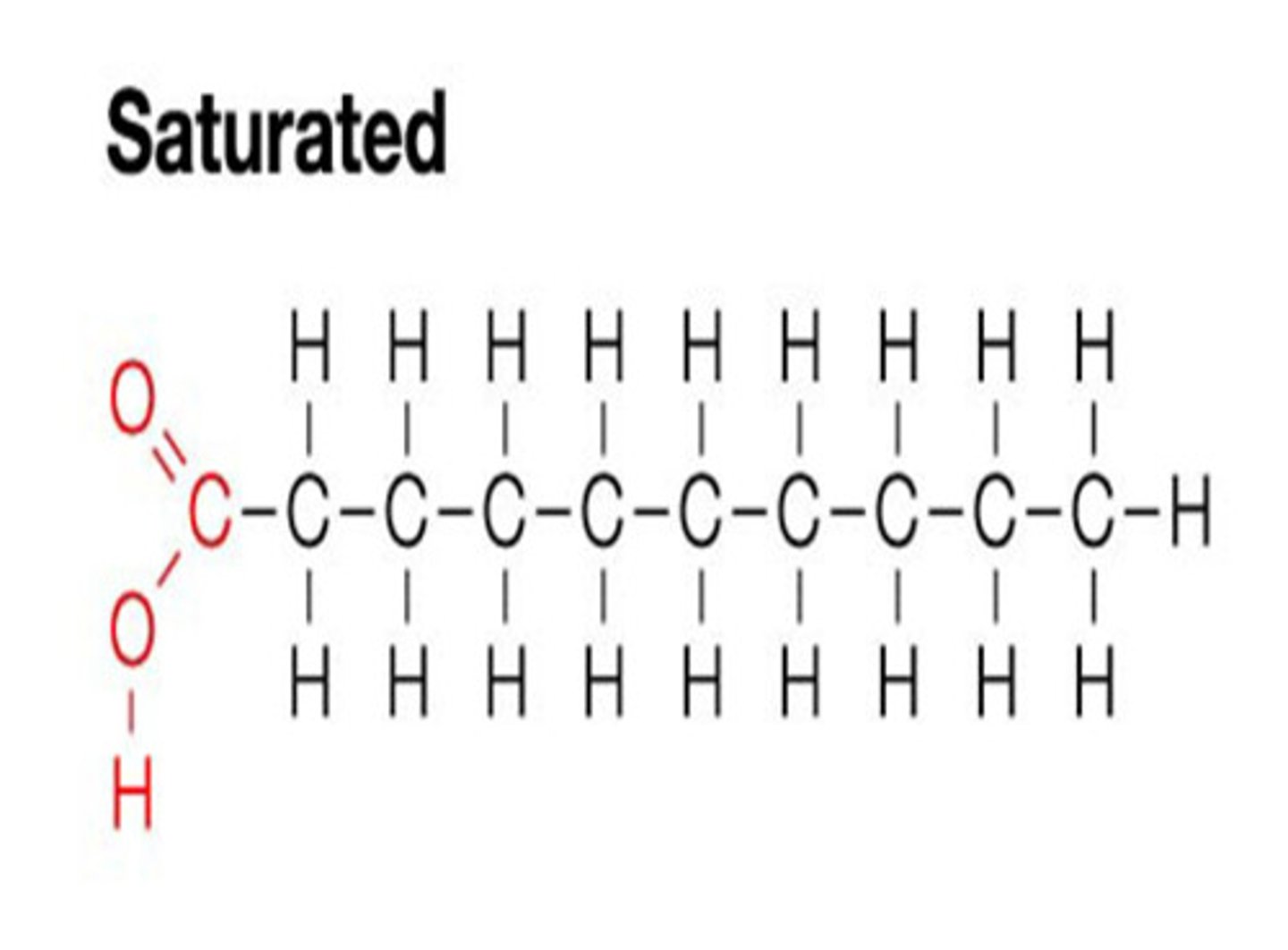
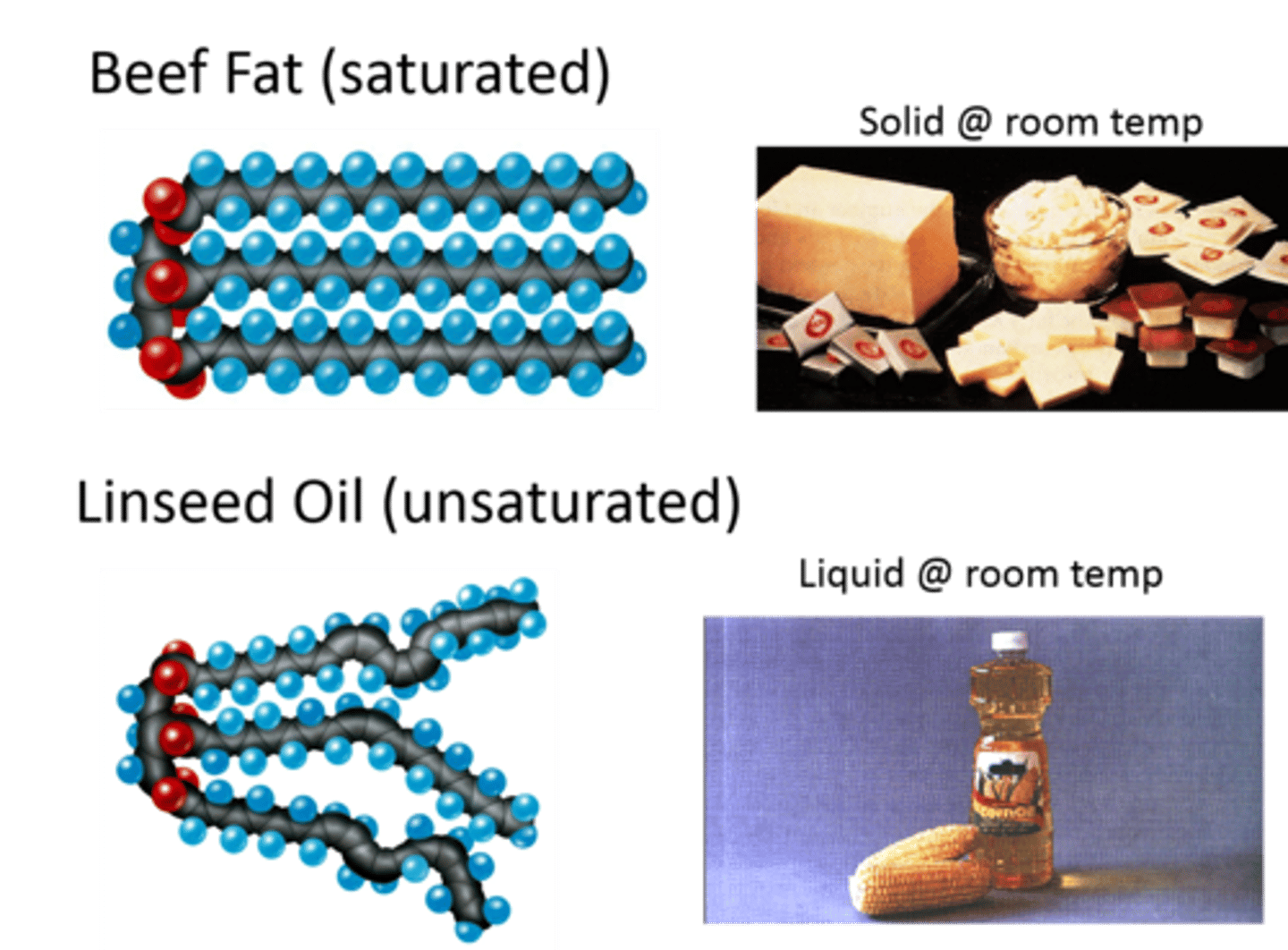
unsaturated fats
have one or more double bonds between some of the carbon atoms of the fatty acid chains and are more desirable in our diet than saturated fats
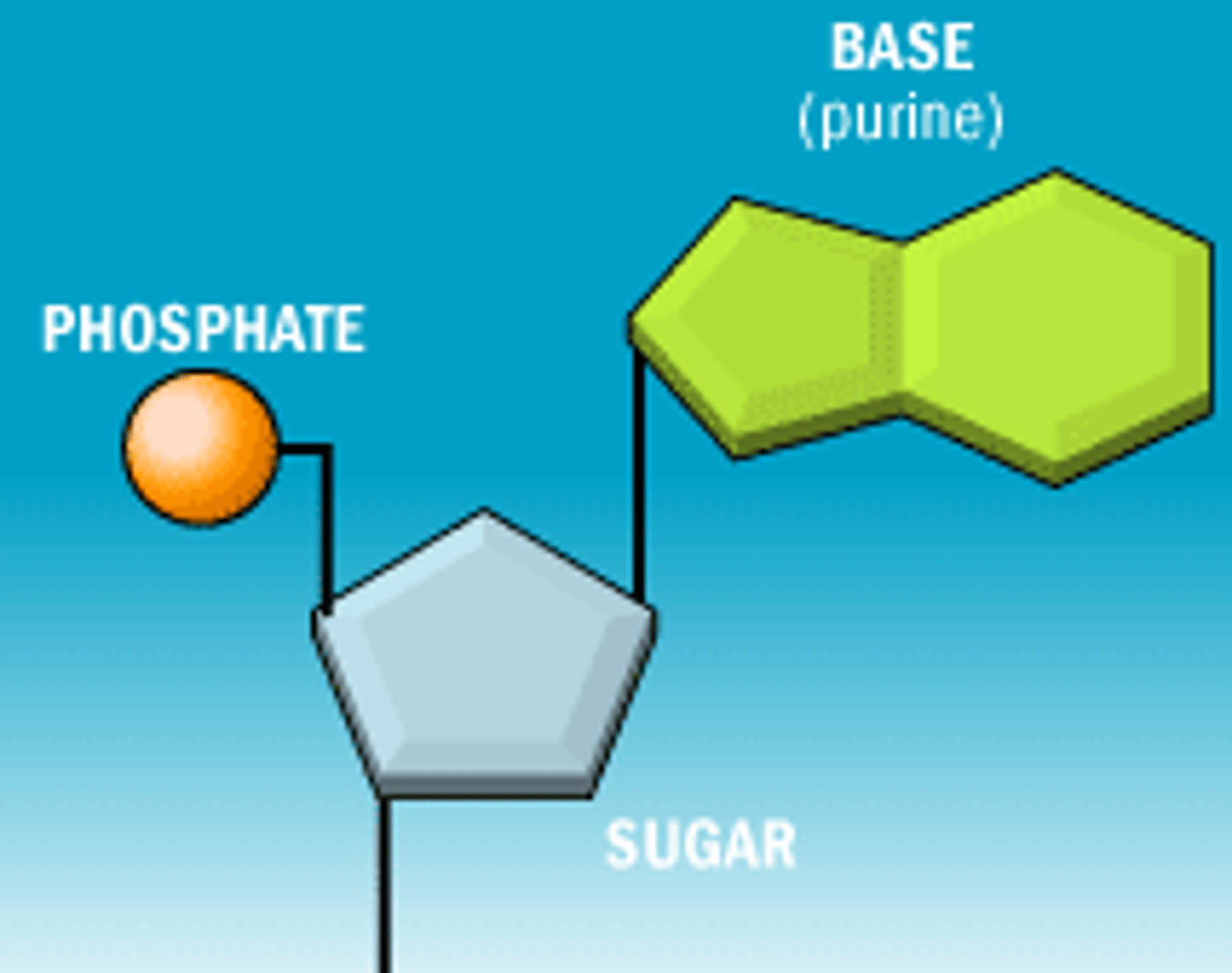
deoxyribose
a 5 carbon sugar that is also called a PENTOSE, and a PHOSPHATE, which alternate in the chain "sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate"
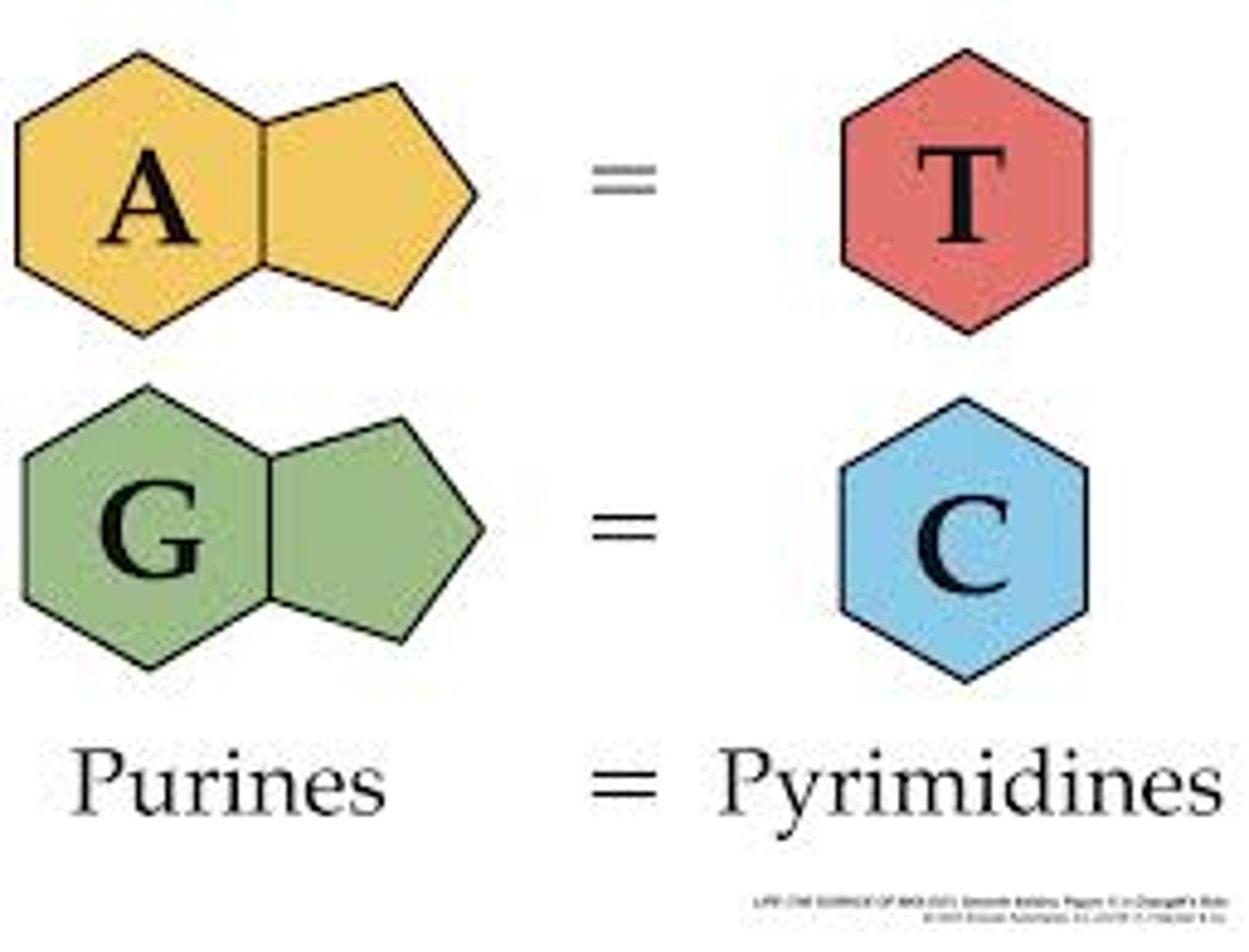
in DNA adenine pairs with
thymine
AT - CG
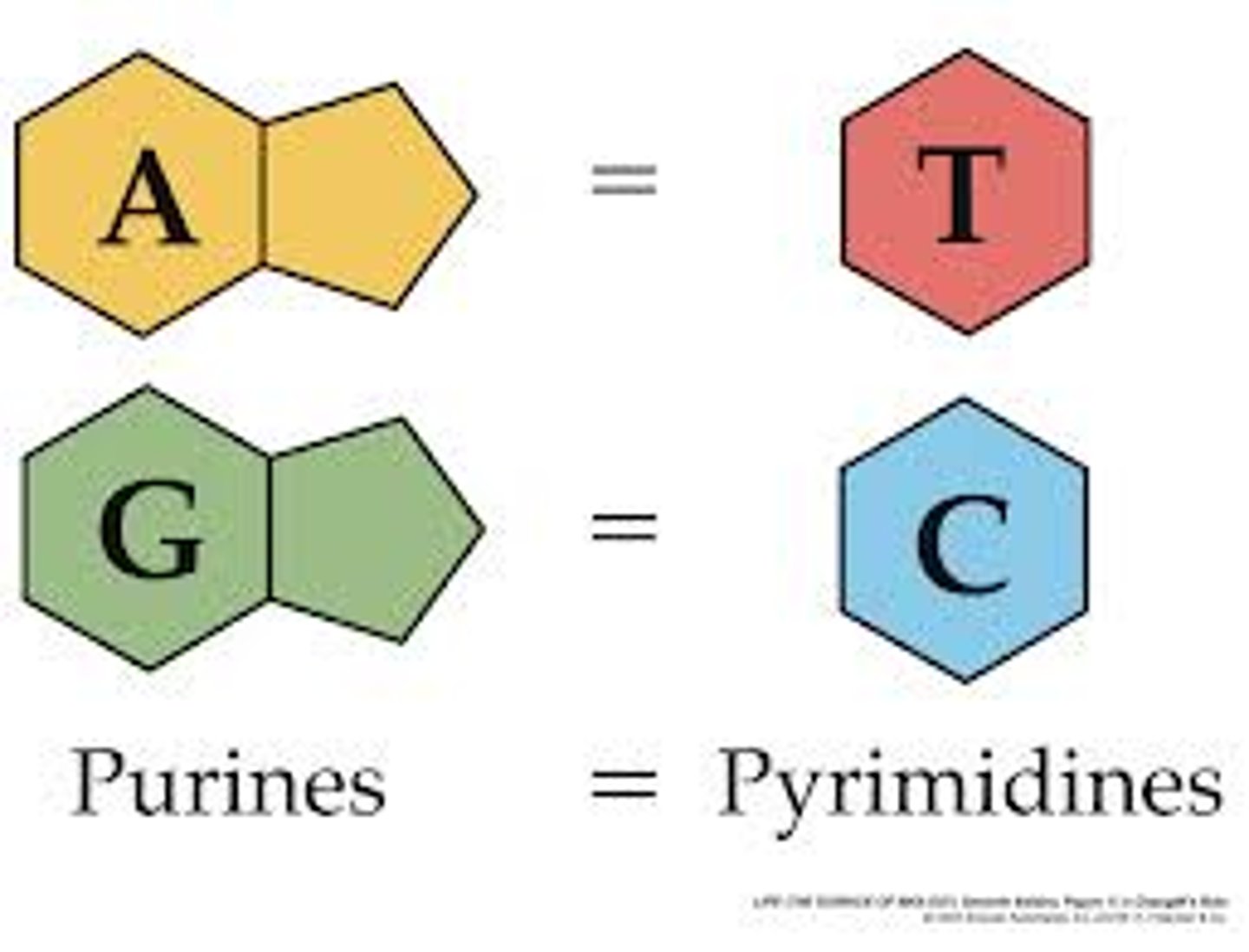
in DNA cytosine pairs with
guanine
RNA
-a single strand of ribose
-a five carbon carbohydrate, in a sugar phosphate chain
in RNA adenine binds with
uracil
Periodic Table