SNC 1W1 final exam - Tam
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Compound
A substance made up of two or more different elements that are chemically bonded
Density
the mass of the substance and how much space it takes up
proton
positively charged particle
Nucleus
Center of an atom (holds protons and neutrons)
isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same amount of protons but different numbers of neutrons
alpha particle
A cluster of 2 protons and 2 neutrons emitted from a nucleus in one type of radioactivity
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
mixture
a substance made by mixing other substances together.
solubility
The ability to dissolve in another substance
neutrons
neutral charge
atomic mass
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
beta particle
A fast-moving electron that is given off as nuclear radiation
percipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.
ion
an atom or group of atoms that has an electric charge
element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
electrons
Negatively charged particles
atomic number
the number of protons in an atom (# of protons = # of electrons)
family
a vertical column of elements in the periodic table whcih have similar properties.
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
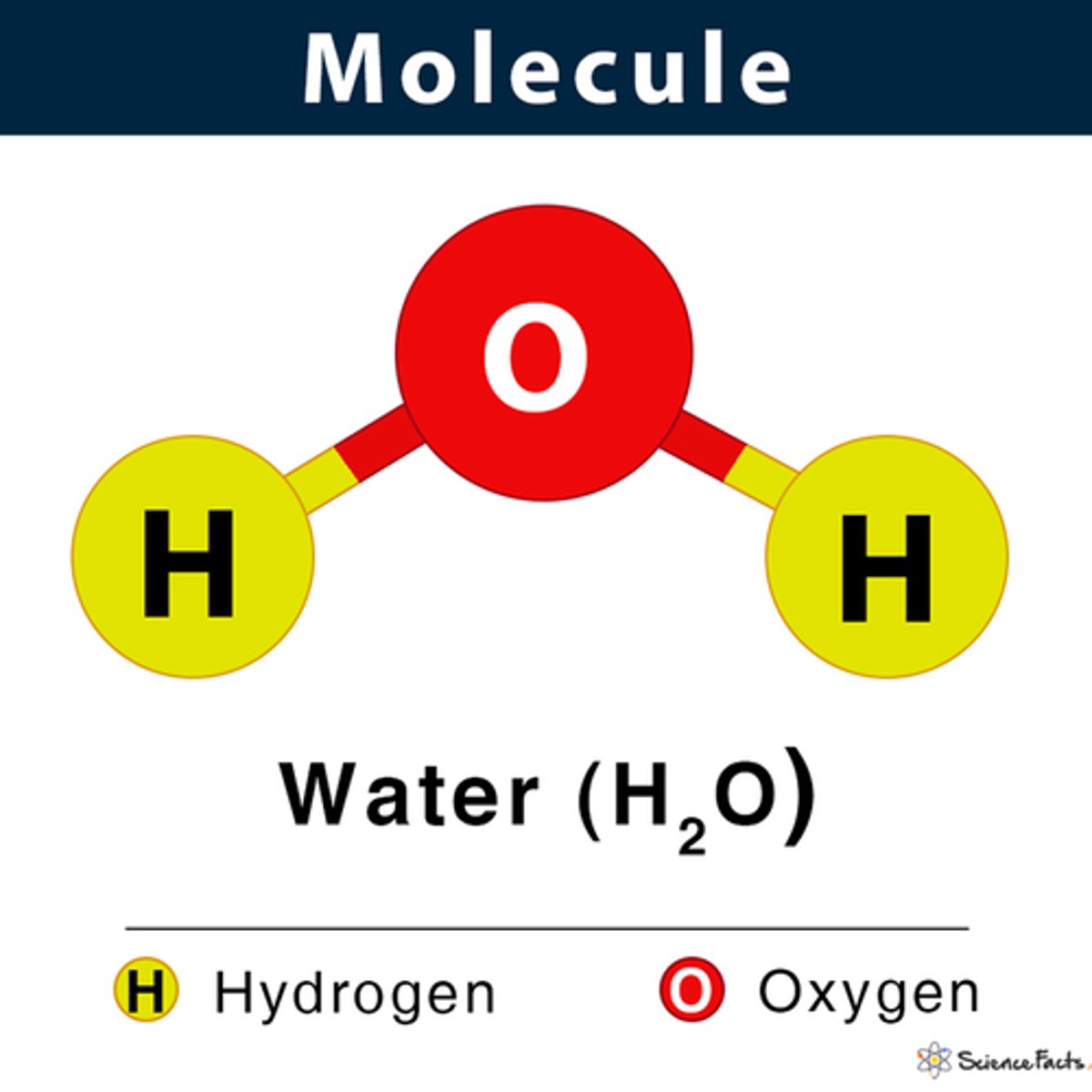
molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
Particle Theory of Matter
- always moving
- Pure substances are made up of their own kind of particles
- All matter is made up of particles
- attracted to each other
- have spaces between them
- Move faster when heated
Classification of matter
pure substances and mixtures
subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, electrons
What are the two main types of compounds?
Molecular and ionic compounds
What is the composition of ionic compounds?
Metal + non-metal
What is the composition of molecular compounds?
Non-metal + non-metal
changes of matter
physical change and chemical change
Changes of state
the change of a substance from one physical state to another
Bohr-Rutherford diagram
a simple drawing that shows the numbers and locations of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom
3 main classes of elements
metals, non metals, metalloids
Metals
metals are solid at room temp, shiny, good conductors, malleable and ductile.
Non metals
Non metals are usually gases or solids at room temp, not shiny, poor conductors, brittle and not ductile
Metalloids
metailloids share both properities of both metals and non metals.
The four chemical families are...
alkai metals ( one electron beyond stability),
alkaine - earth metals (2 electrons beyond stability) ,
halogens (one electron short on stability),
noble gases (a stable outer shell)
How is the modern periodic table organized?
its organized to increasing atomic number, also grouped according to the amount of electron shells.
How many groups and periods are on the periodic table?
18 groups and 7 periods in the periodic table
Alkali metals
(group 1) hydrogen (H) , Lithium (Li) , Sodium (Na) Potassium (K)
Alkaline earth metals
Group 2 (Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, Radium)
Halogens
Group 17 (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine)
Noble gases
Group 18 (Hellium, neon , krypton, xenon, radon)
How are ionic compounds formed?
By the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
If an atom loses an electron, what kind of particle does it become?
If an atom loses one or more electron, it becomes positvely charged
If an atom gains an electron, what kind of particle does it become?
If an atom gains one or more electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion
what happens to electrons in a covalent bond?
electrons from each atom are attracted or "shared" by both atoms
What is the other term used for covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds are also called molecular compounds
Circuit
a path for an electrical current to flow around
static charge
Static charge is an electric charge that builds up on an object and stays there, usually because of friction, like when you rub a balloon on your hair.
voltmeter
a device used to measure voltage
resistor
A resistor is a device that limits or controls the flow of electric current in a circuit.
conductor
A material that allows heat and electricity to pass through it.
current electricity
the continuous flow of charge in a complete circuit
cells/battery
a single-unit device which converts chemical energy into electric energy.
Resistance
a measure of how much a material or object opposes the flow of electric current
potential difference
the difference of electrical potential between two points.
charging by friction
transfer of electrons between the two objects that are rubbed together
terminals
a point where a conductor from a component, device, or network comes to an end
static electricity
A buildup of charges on an object.
electroscope
An instrument used to detect electric charge
ammeter
A device used to measure current in a circuit
load
the force applied to a body or surface, or the weight of an object that needs to be moved
switch
a device that opens or closes a circuit
insulator
A material that does not allow heat or electrons to move through it easily.
Ohms law
V= I x R
current
A flow of electric charge.
series circuit
An electric circuit with a single path
charge
A measure of the extra positive or negative particles that an object has. (ex: positive or negative charge)
ground
an object that can supply large numbers of electrons, remove large amounts of electrons from a charged object, and can neutralize them.
parallel circuit
A circuit that contains more than one path for current flow.
Renewable resource (pros and cons)
Solar energy
- (+) clean and sustainable, doesnt cause any damage to the ecosystem
-(-) dependant on weather and light conditions. Making it less reliable in certain regions or times of day.
Non renewable resource (pros and cons)
Coal
- (+) Produces a large amount of energy and inexpensive
- (-) Creates significant enviromental damage like air pollution
Food web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
Food chain
a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next.
Trophic levels
A trophic level is a category of organisms that is defined by how the organisms gain their energy. Energy moves from one level to the next.
abiotic factors
Living and nonliving aspects of the environment
- river
-rocks
-sunlight
biotic factors
-animals
-trees
-plants
Effects of acid precipitation
It acidifies water, water storage, causes corrosion , can cause damage to trees, plants and soil (makes the soil less suitable for plant growth)
ecosystem services
Important environmental benefits, such as clean air to breathe, clean water to drink, and fertile soil in which to grow crops, that ecosystems provide
nitrogen cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere
Niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
Habitat
Place where an organism lives
Ecosystem
A community of organisms and their abiotic environment
Biodiversity
The number of different species in the same habitat / ecosystem
Limiting factors of populations
Limiting factors are environmental factors that keep a population's numbers from growing out of control. Some examples are food, water, living space, and disease.
what are the different trophic levels
primary producers, primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers, tertiary consumers (carnivores)
Denitrification
process by which bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas
Bioaccumulation
the build up of a substance (usually a toxin) as it passes through a food chain
Bioaugmentation
Bioaugmentation means adding helpful microbes (like bacteria, fungi, and viruses) to a place, like soil or water, to clean it or fix a problem.
biomass
Renewable organic material from plants and animals that can be used as energy. (ex: crops, manure/poop.., wood, leaves, etc.)
Excretion
Excretion is the process of getting rid of waste from the body, like sweat, urine, or carbon dioxide (exhaling).
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is when too many nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, build up in water, causing lots of algae to grow. This can harm fish and other animals by using up oxygen in the water.
nutrient
a substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life. (vitamins, minerals, food, etc.)
producer
An organism that makes its own food through photosynthesis.
consumer
An organism that obtains energy by eating other organisms
autotrophs
Organisms that are able to make their own food (same thing as a producer)
Hetrotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.
dominant species
a species that has the most influence or control in an ecosystem. It usually has the largest population or plays a key role in shaping the environment. (like how trees might dominate a forest.)
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
ecosystem engineers
species that dramatically alter their environment
endangered species
A species in danger of becoming extinct in the near future