1.3 1.4 market failure and government intervention
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
market failure definition
when the price allocation leads to a misallocation of resources
negative externalities
cost or benefit third party receives outside the price mechanism.
negative externalities
marginal cost - the lowest price willing to sell a good for. supply curve
marginal benefit - the highest price consumer willing to pay. demand curve
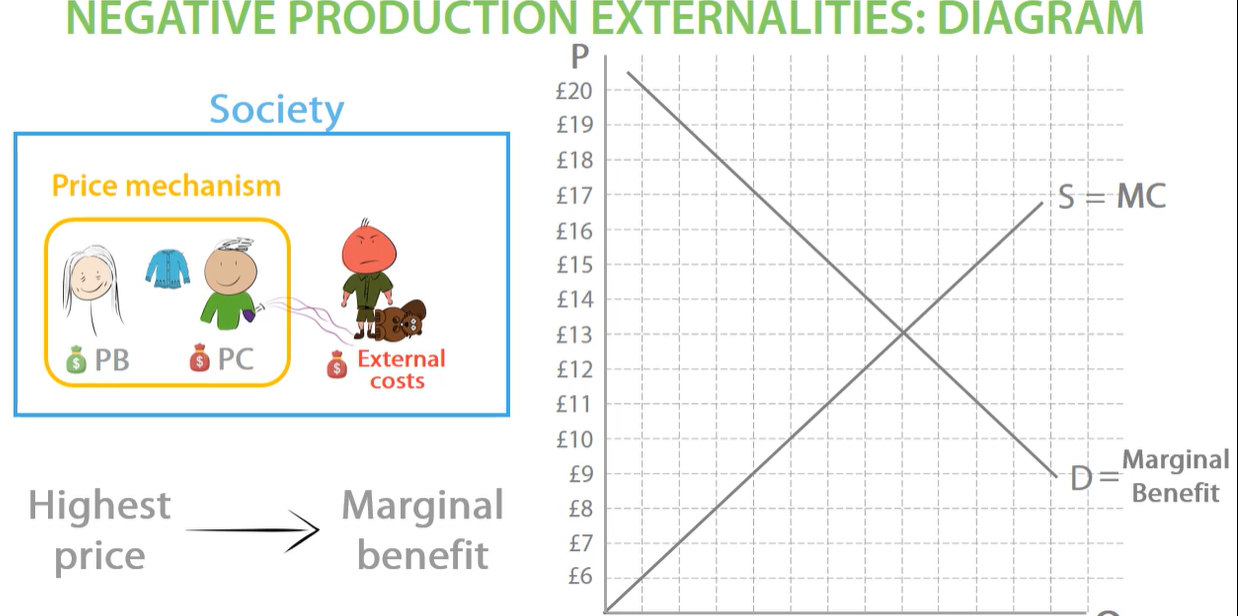
negative production externalities marginal private benefit and marginal private cost
negative production externalities social cost and social benefit

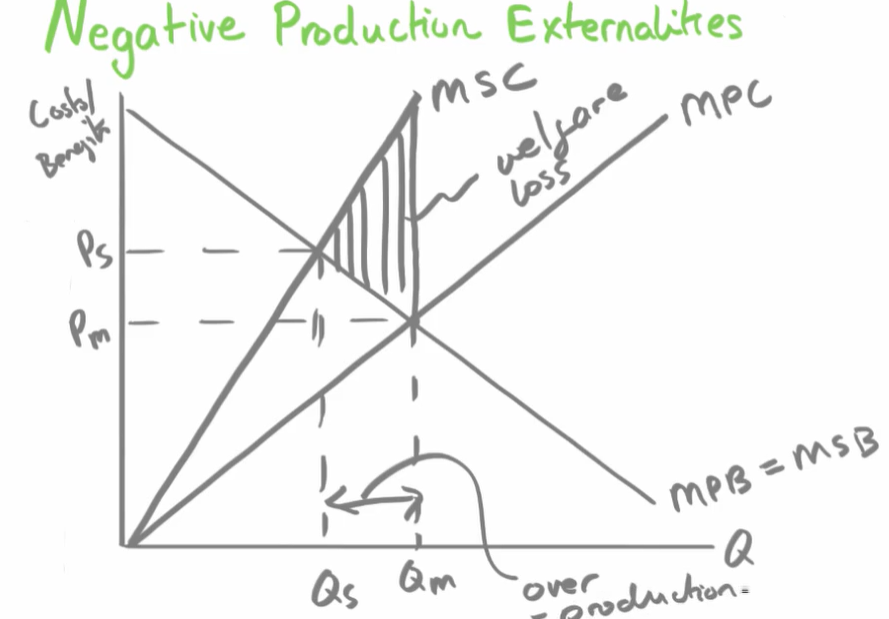
negative production externalities diagram
D= MSB = MPB because there is no social benefit
social cost on supply line= private cost plus external cost
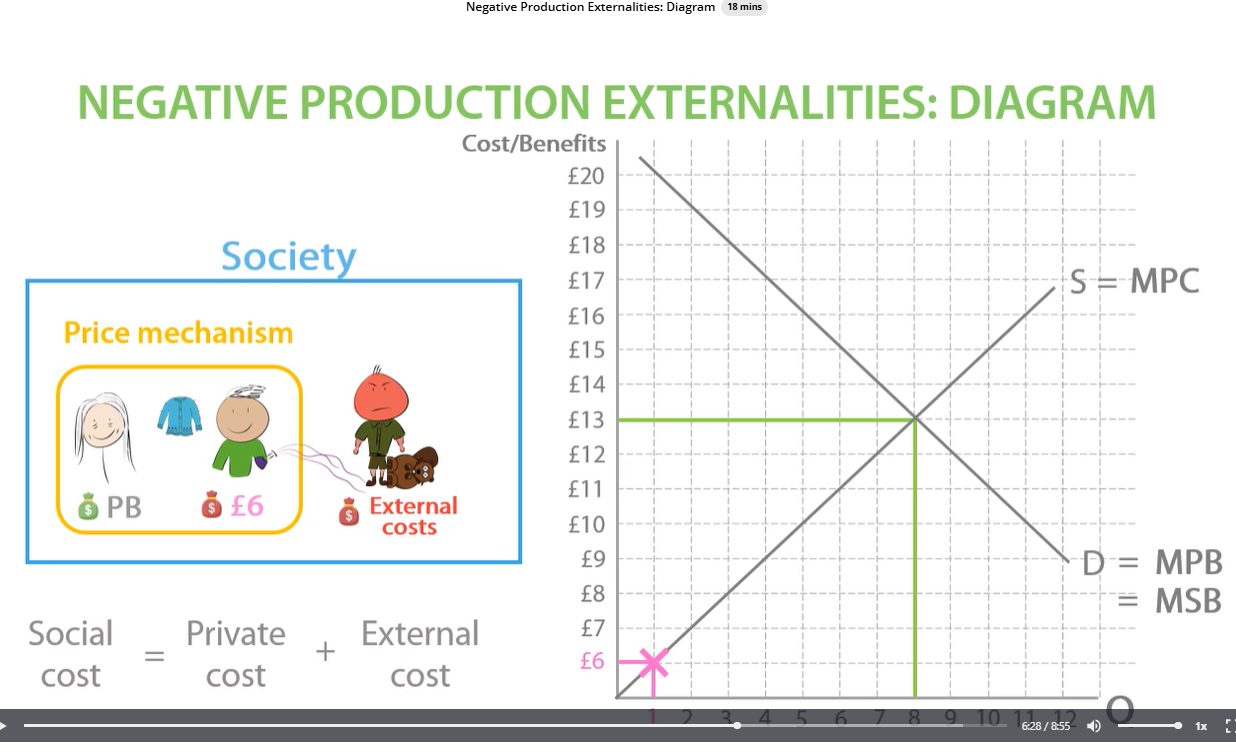
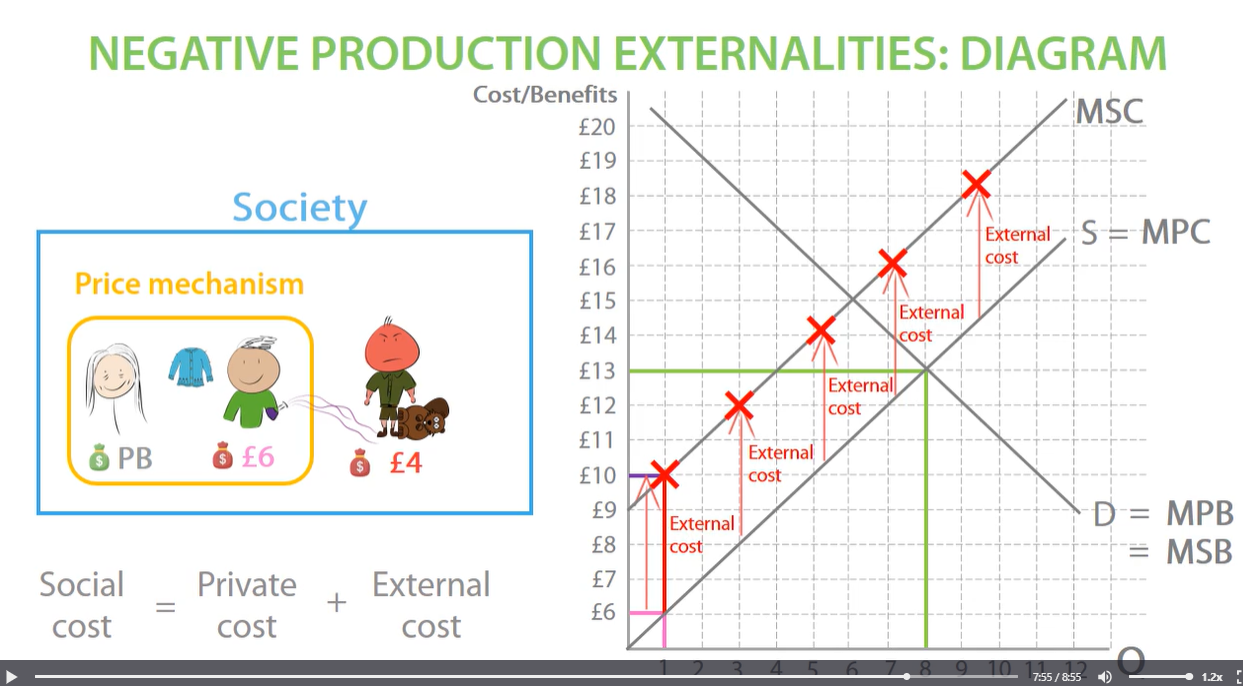
negative production externalities diagram
e.g. producing cloth and hurting animals MSC is higher than MPC
negative externalities definition
costs which affect 3rd parties outside the price mechanism
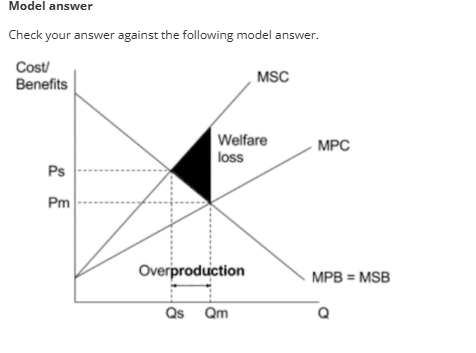
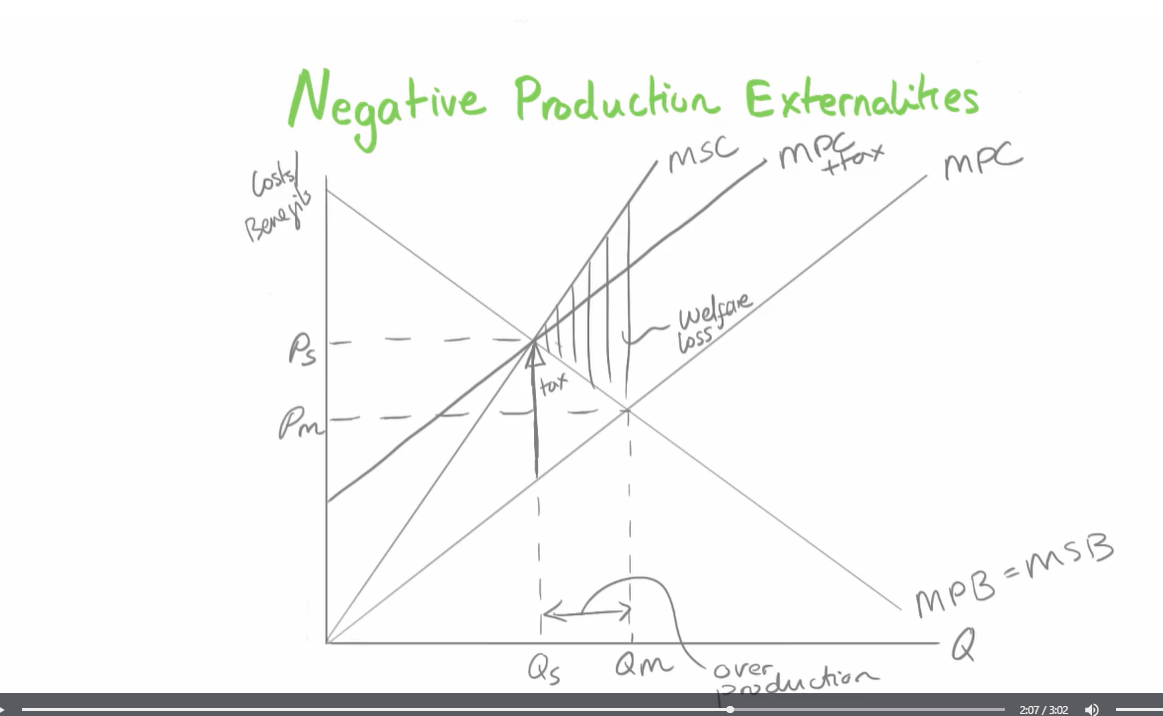
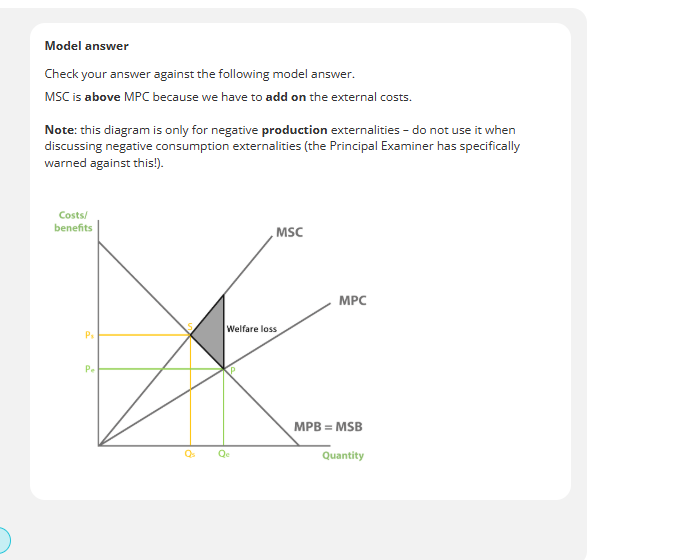
calculating welfare in negative externalities diagram
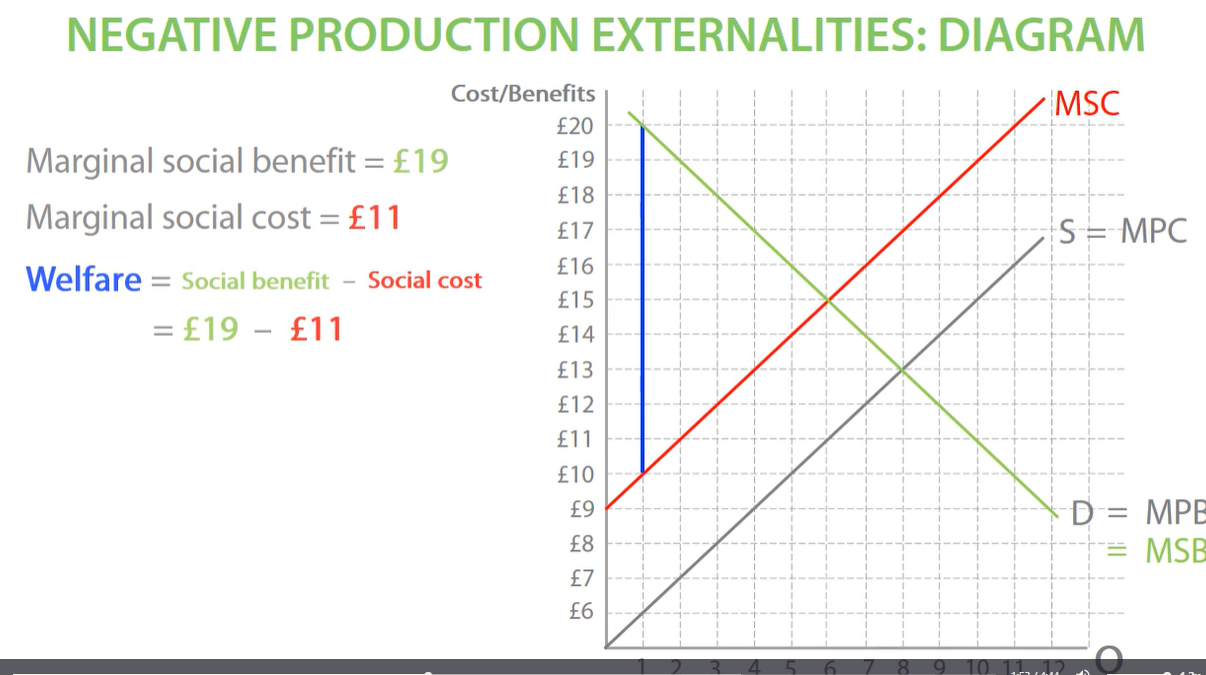
negative production externalities welfare
negative production socially efficient equilibrium
negative production externalities
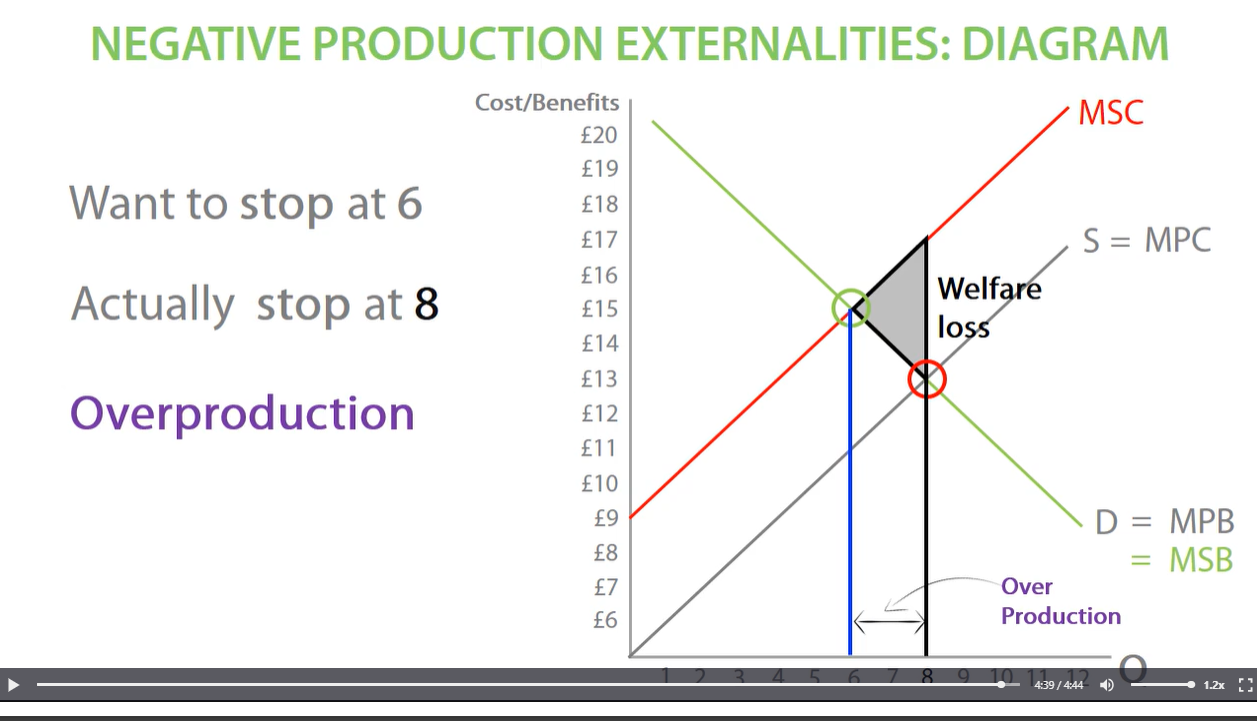
stop producing at equilibrium at MPC line, otherwise we overproduce, which means we suffer welfare loss
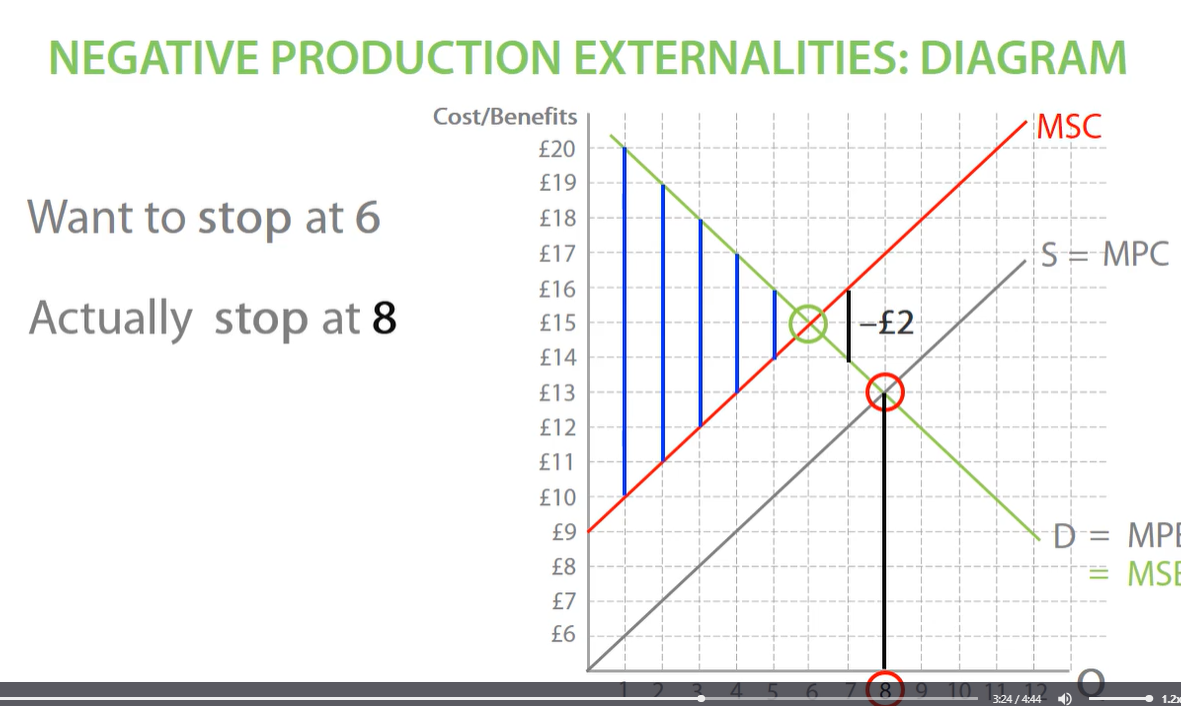
negative production externalities welfare loss
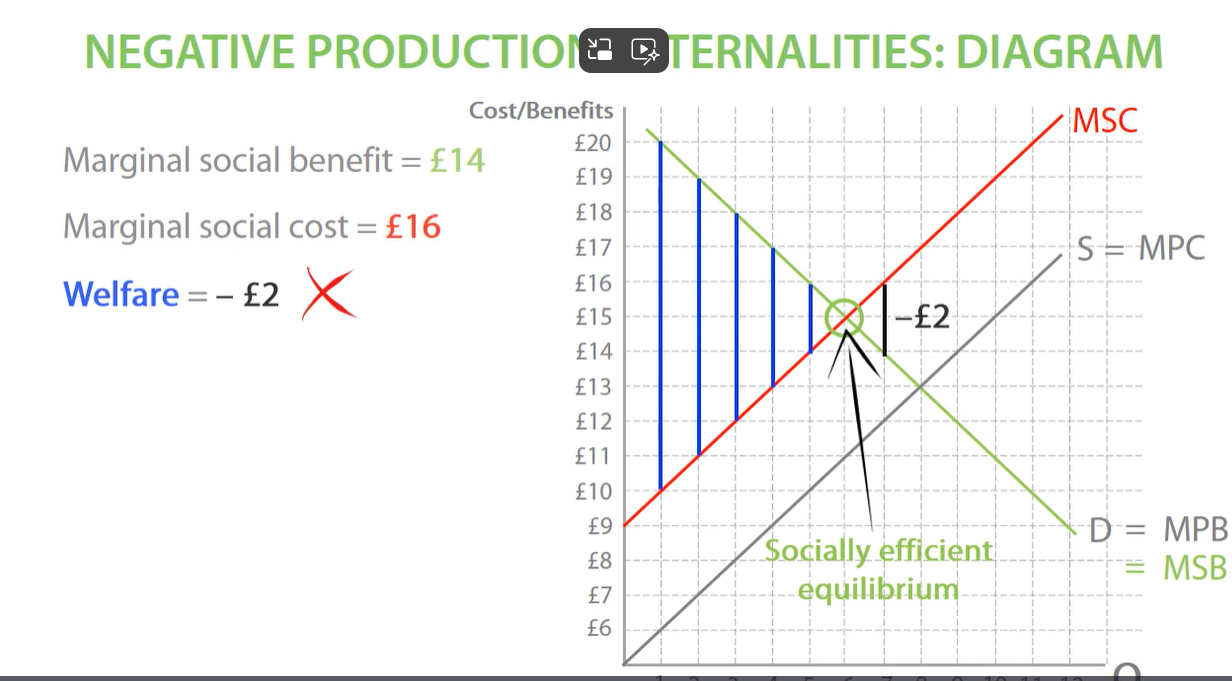
welfare loss is how much welfare society losses out on a result on the negative externalities
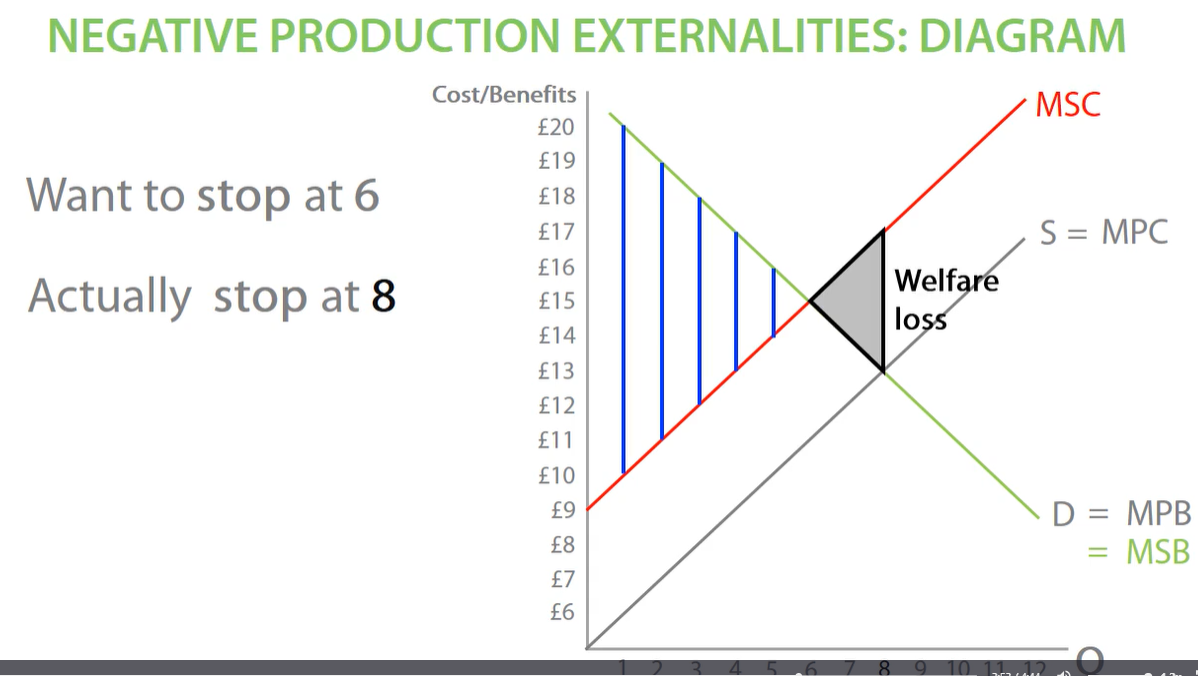
negative production externalities
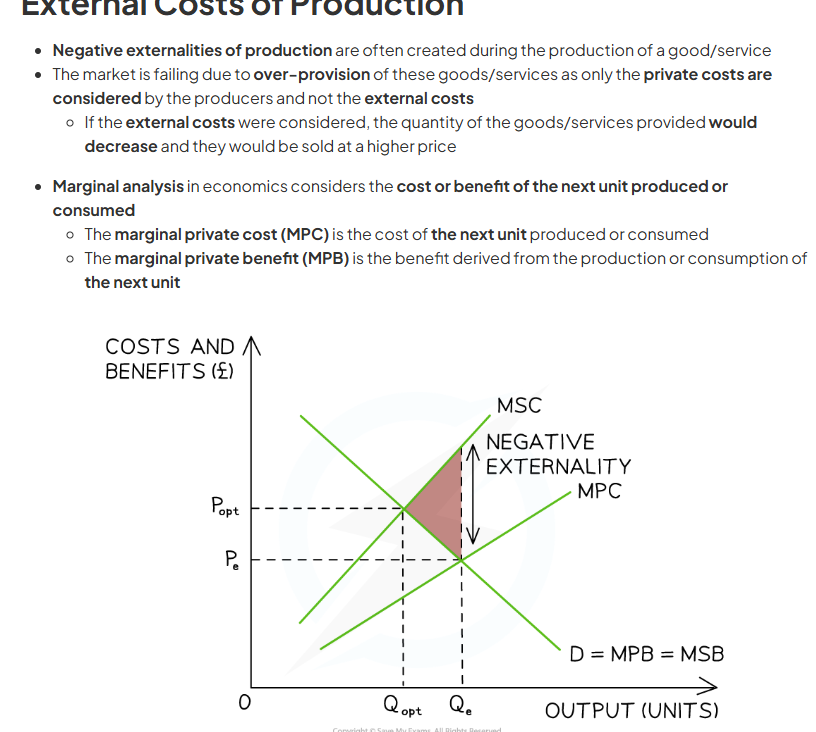
When producers do not think about external costs and only think about private costs, this leads to over production and negative externalities. also gap between MSB AND MSC represents external costs.
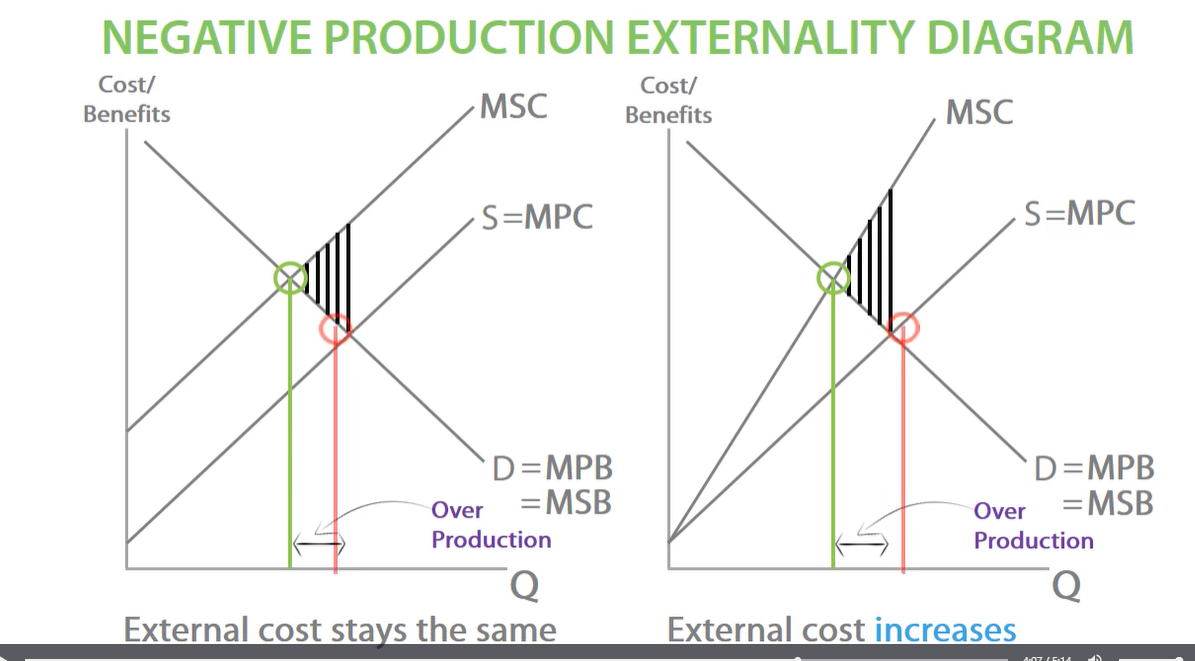
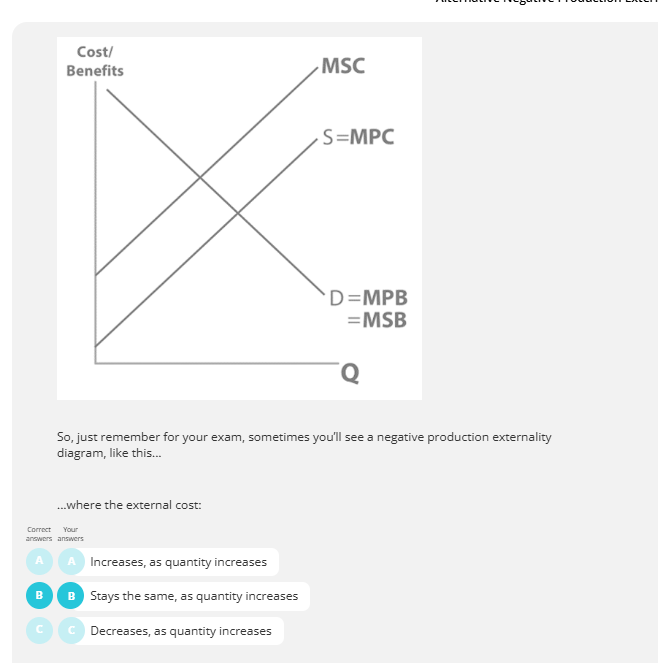
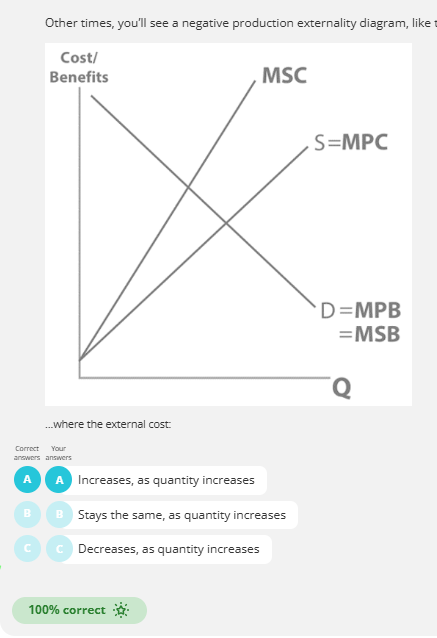
alternative negative production externalities
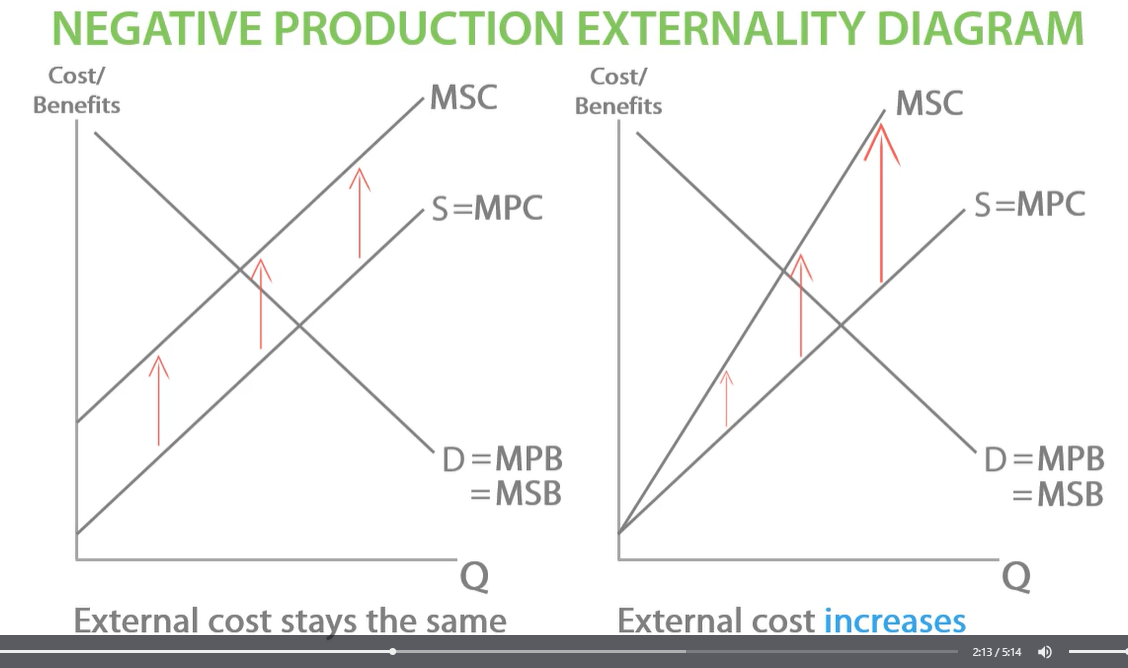
for second external cost increases for each unit produced.
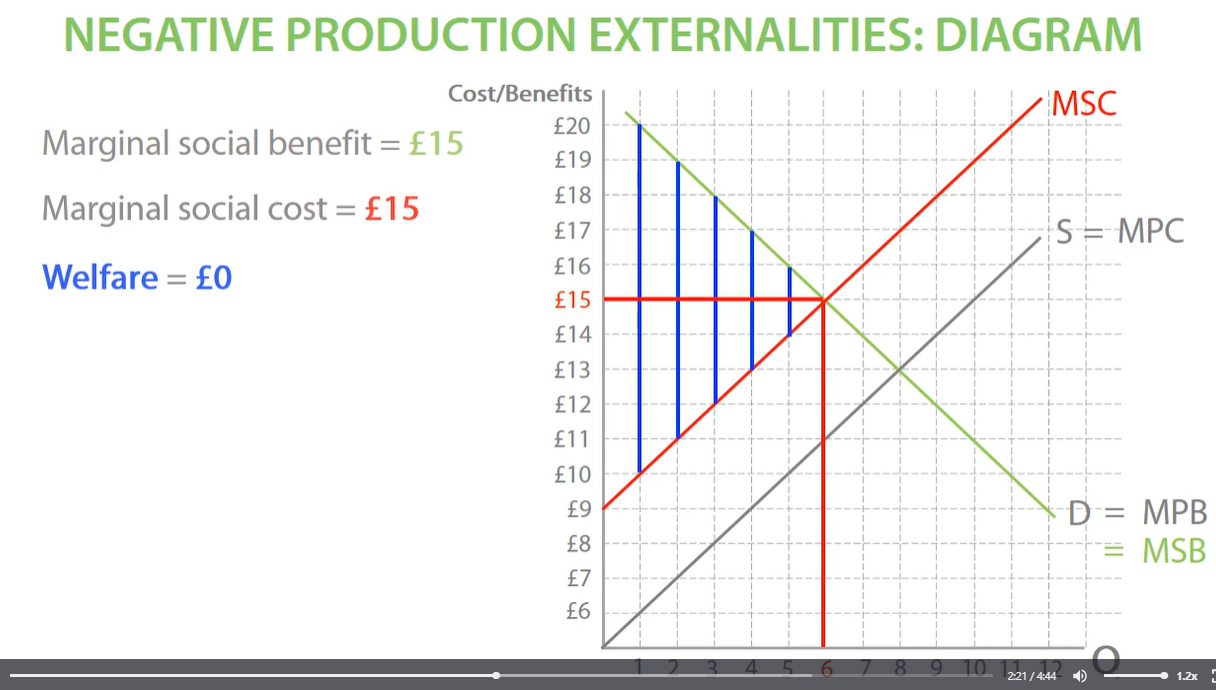
socially efficient equilibrium negative externalities
welfare loss negative externalities
after socially efficient welfare, society loses welfare on each unit, until producers stop producers stop producing at market equilibrium between MSC AND MPC. this leads to overproduction between socially efficient quantity and market quantity. this creates welfare loss as many units are overproduced.
negative production externalities diagram
negative production externalities diagram
FOR PRODUCTION NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES MSC IS HIGHER THAN MPC. external costs came from production of a good.
negative consumption externalities
DO NOT DRAW NEGATIVE PRODUCTION EXTERNALITIES DIAGRAM
negative production externalities diagram (draw it out before ) external cost stays the same
negative production externalities diagram external cost increases
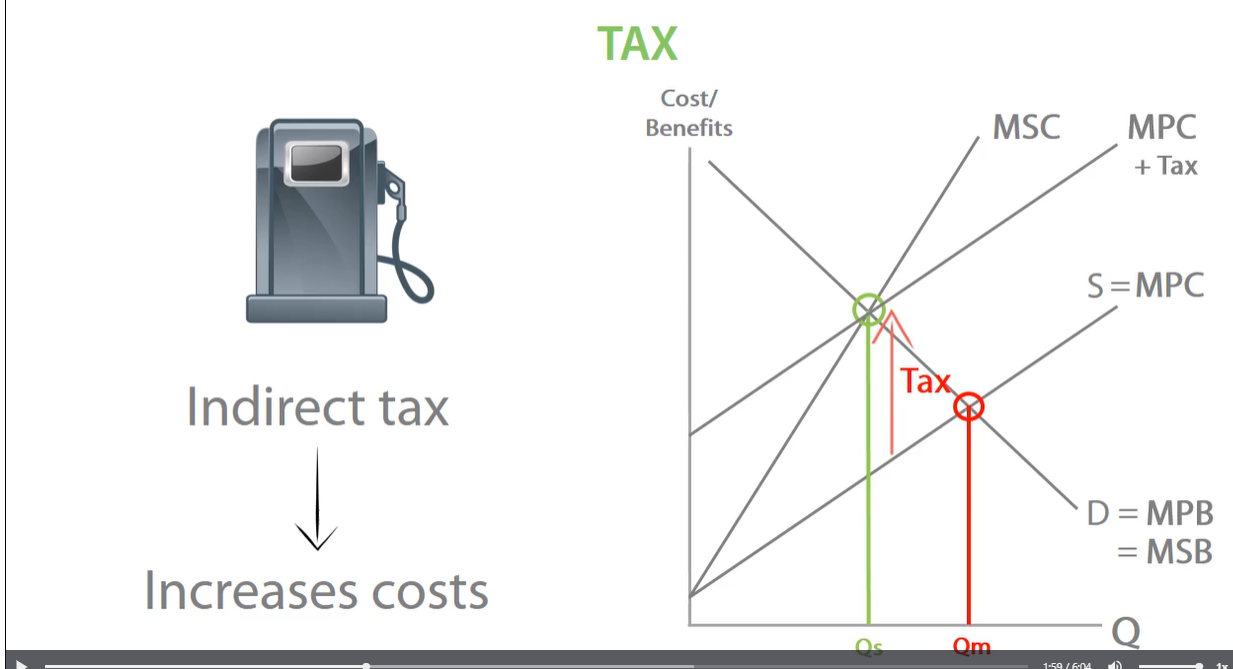
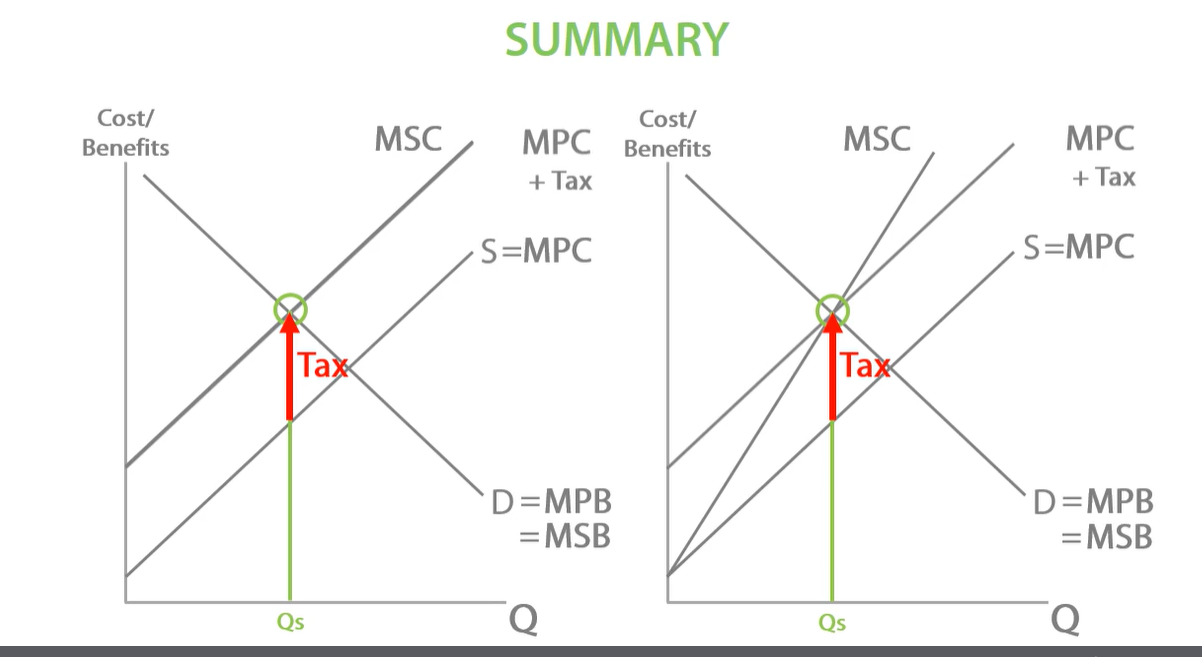
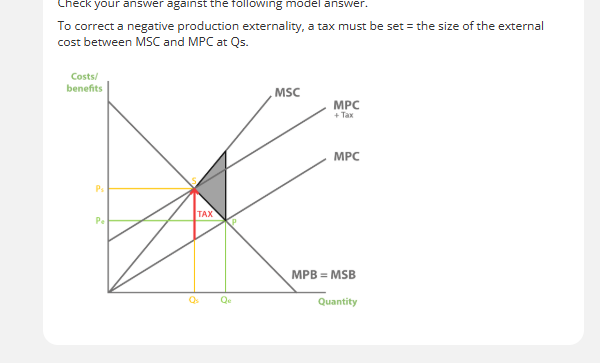
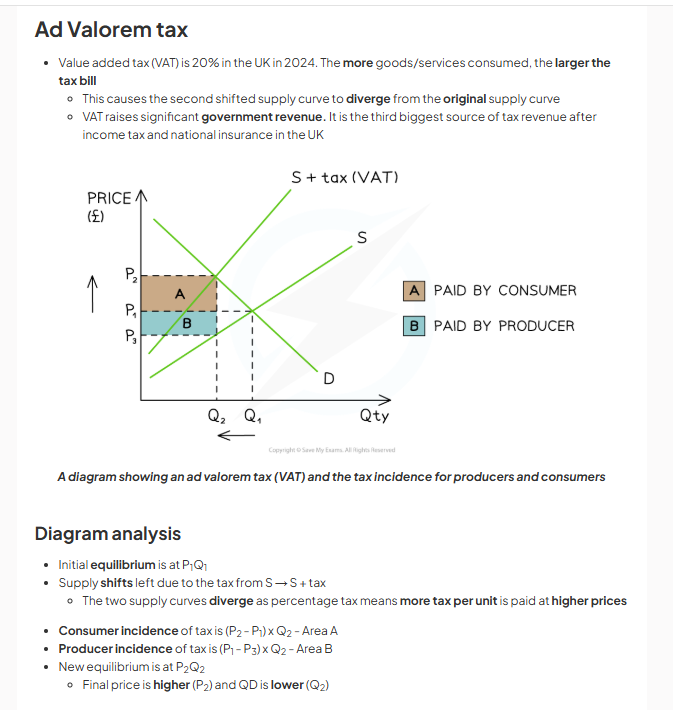
tax negative externalities, external costs say the same
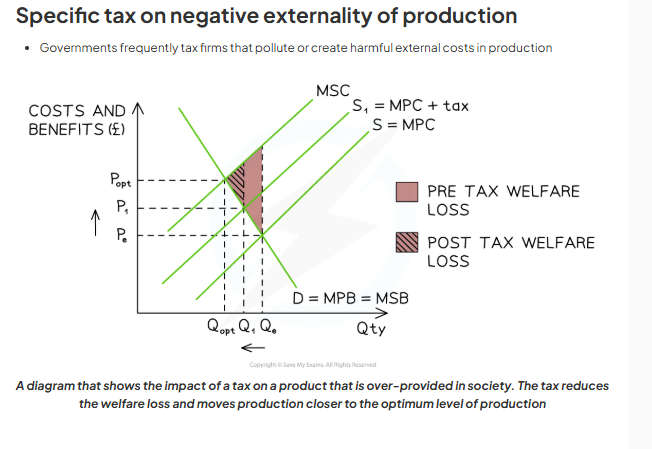
-tax makes production more costly for firms. tax increases marginal private cost of production, MPC shifts up from MPC to MPC + tax. government ensures producers no longer overproduce, only works with perfect tax. negative production externalities externalised.
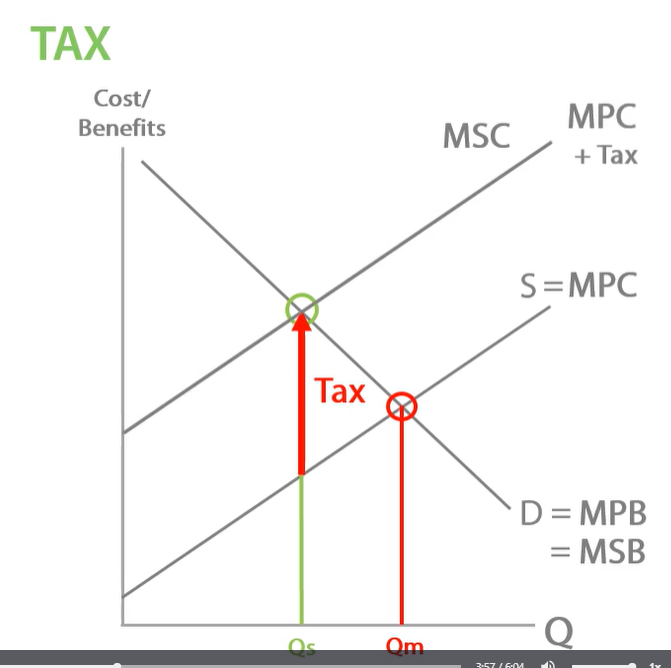
tax negative externalities, external costs increases as quantity increases
negative production externalities has been internalised. no overproduction and no welfare loss. move production to socially efficient equilibrium, eliminating any over production and internalising negative production externalities.
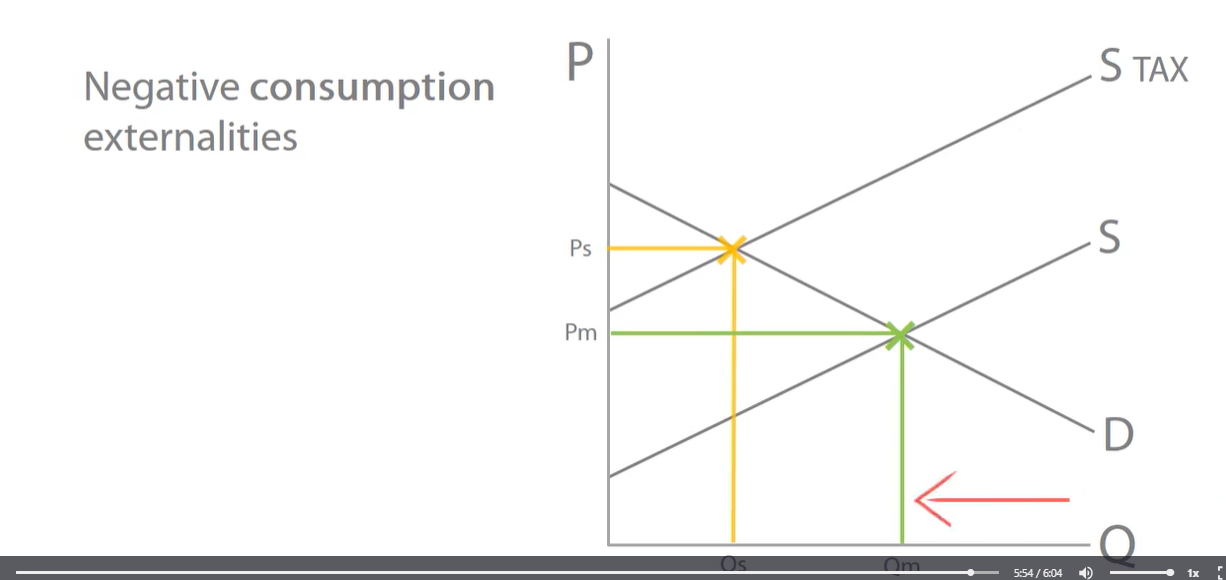
negative consumption externalities
supply shift vertically upwards, the quantity decreases reducing any overconsumption and internalise negative consumption externalities.
tax must be equal to
the external cost at he socially efficient quantity. shown by distance of MSC AND MPC
negative production externalities
tax is equal to social costs at the socially efficient quantity
How does the cap and trade system work?
-Firstly, the government sets a cap on how much pollution it will allow each year - this is the estimated socially efficient level of production. It then divides its permits between firms until cap is reached.
solve negative externalities: tradable pollution permits
government auctions remaining permits, raises tax revenue and uses it to subside econ friendly companies and fund renewable energy and pollution permits are tradable.
Firms finding it expensive to reduce their pollution can
Buy permits from firms finding it cheaper to reduce their pollution. firms can trade these permits which is efficient.
negative externalities solves
tax and tradable pollution permits
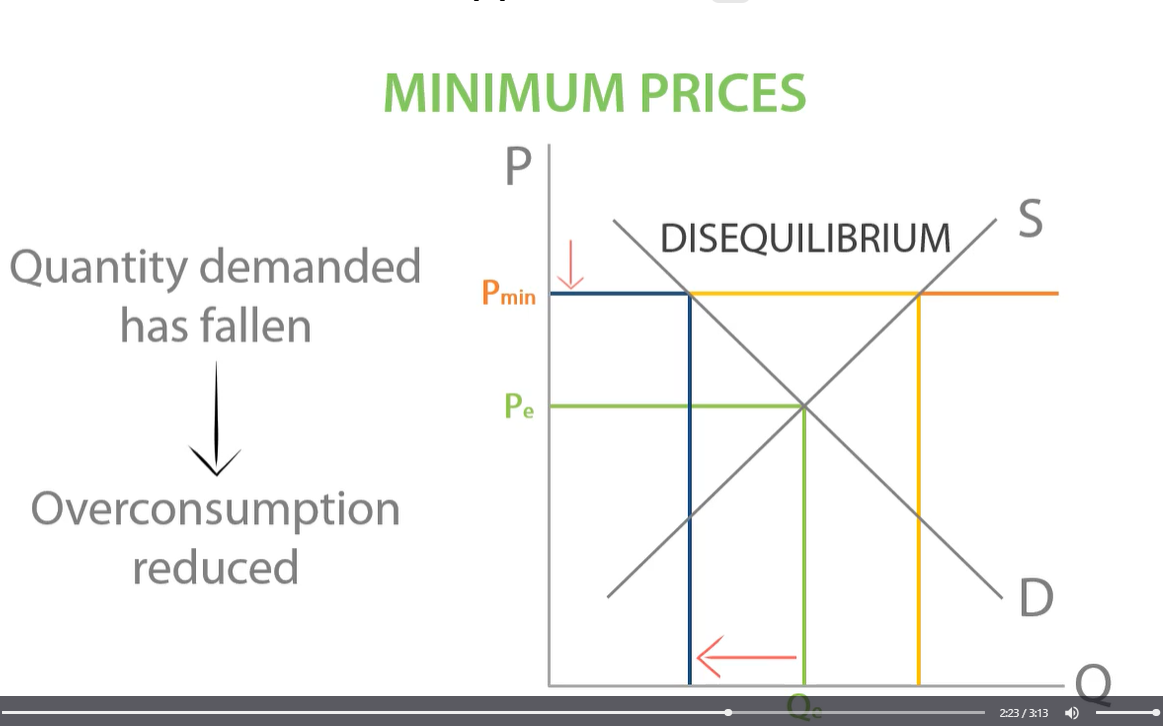
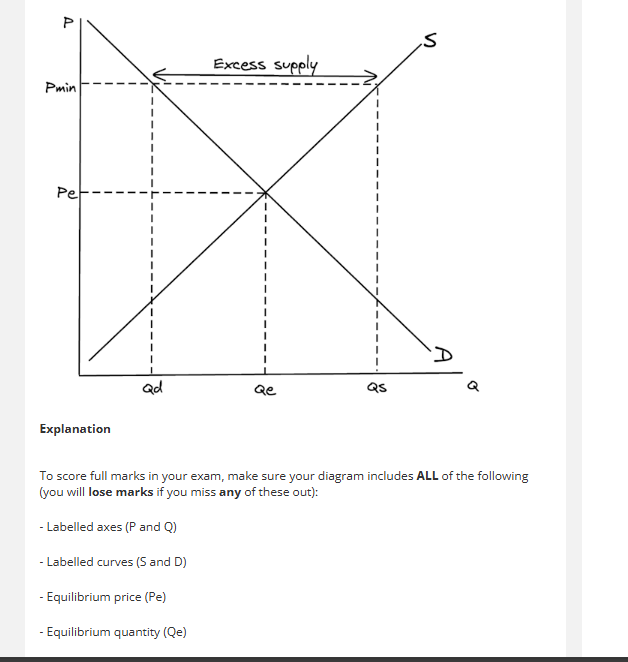
solving negative externalities: minimum price
the lowest price suppliers of a good can sell for
government can keep price with alcohol high with minimum price which will lead to
a reduction in demand
minimum prices
keep prices high, keep quantity demanded low and reduce overall consumption
To reduce consumption the government would want to set the price
above the equilibrium price. This creates excess supply and reduces quantity demanded through rationing but signals and incentives to increase the quantity supplied.
solve negative externalities through minimum price
e,.g minimum price of alcohol reduce the fights and internal affects such as increase NHS spending
solving negative externalities
tax, regulation, minimum costs and cap and trade system
solving negative externalities tax
-regulation to address market failure such as guns causing harm.
-regulation is less strict for smoking, government legally requires cigarette companies to label packets ‘smoking kills. regulation for alcohol such as you have to be over 18.
use regulation to reduce negative production externalities
-such as pollution, cars have to meet certain environmental requirements to be legally sold. and factories have to meet environmental standards to operate otherwise government regulators will shut them down.
private cost
cost to producer or consumer inside price mechanism
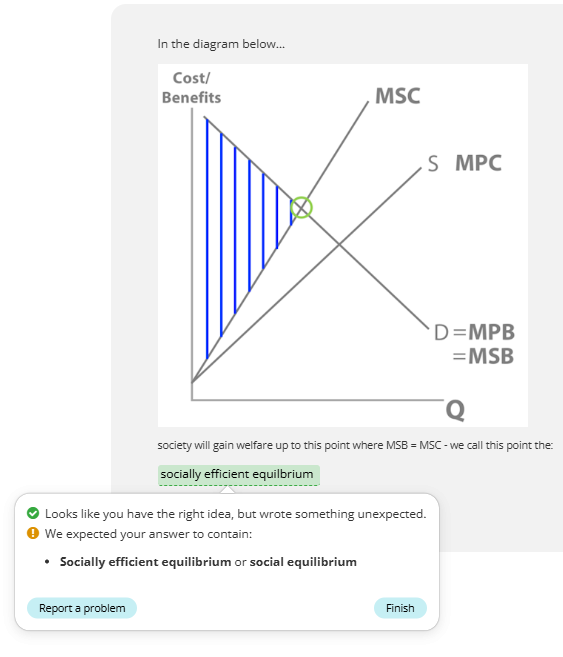
socially efficient equilibrium
where MSB equals MSC and society’s welfare is maximised
effects of minimum price
tradable pollution permits
permits which allow firms to pollute up to a certain limit. these permits can be traded between firms.
minimum price definition and graph
-lowest price a good can be legally sold for
regulation
when the government makes changes to the law to address market failure
negative production externality diagram
tax to internalise a negative production externality
PED NASBIT
necessities, addiction, substitutes, branding, income, time
PED TEASS
time, economy, state of economy, spare capacity, stockpiles and perishability.
how does subsidies and providing help
The people around you! If you’re healthier you can be more productive and helpful at work. If you’re better educated, you can pass on your knowledge to others. If you’re more eco-friendly, you’re saving the rest of the world from global warming!
positive externalities
benefits which affect third parties outside the price mechanism
positive consumption externalities
consuming healthy food , less likely to fall ill which reduces NHS spending and saves taxpayers money and you are more productive at work which maximise the firms profit and boost the economy
positive production externalities
efficient transport help workers get to work on time which benefits the company they are working for. renewable energy helps reduce global warming.
positive consumption externalities
if someone goes university they will get private benefits such as a degree and finding a job and making more friends and the benefit outside price mechanism, benefit local businesses which is positive externalities
social cost and social benefit positive consumption externalities
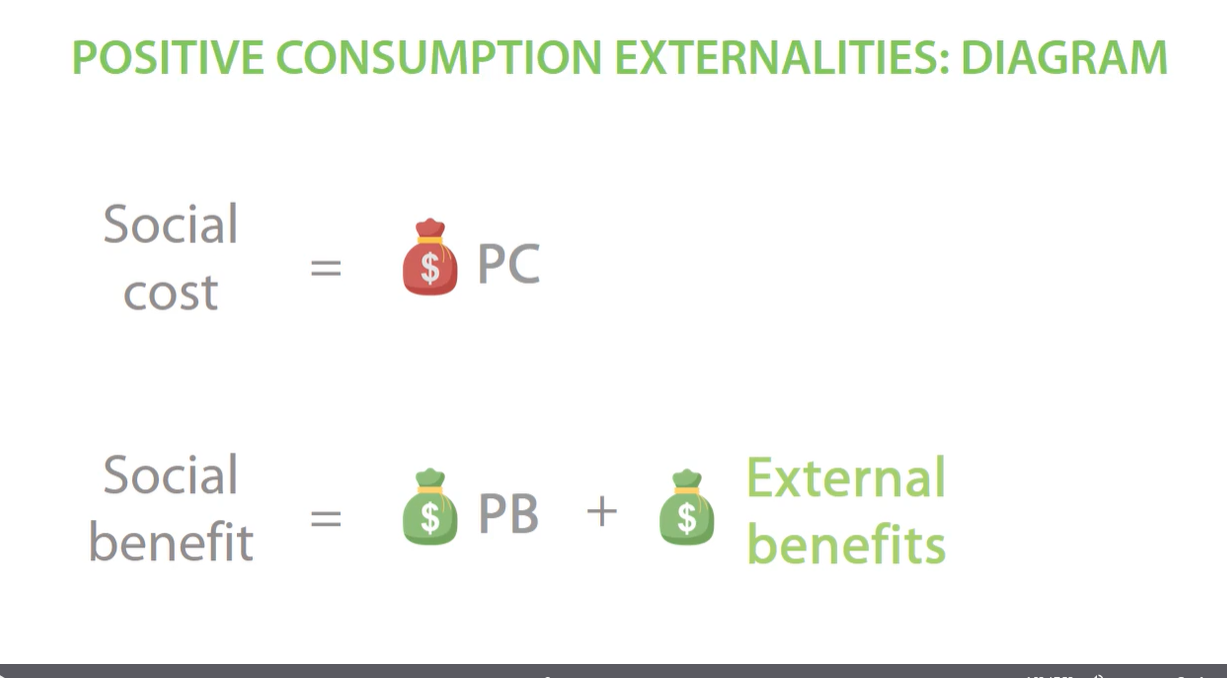
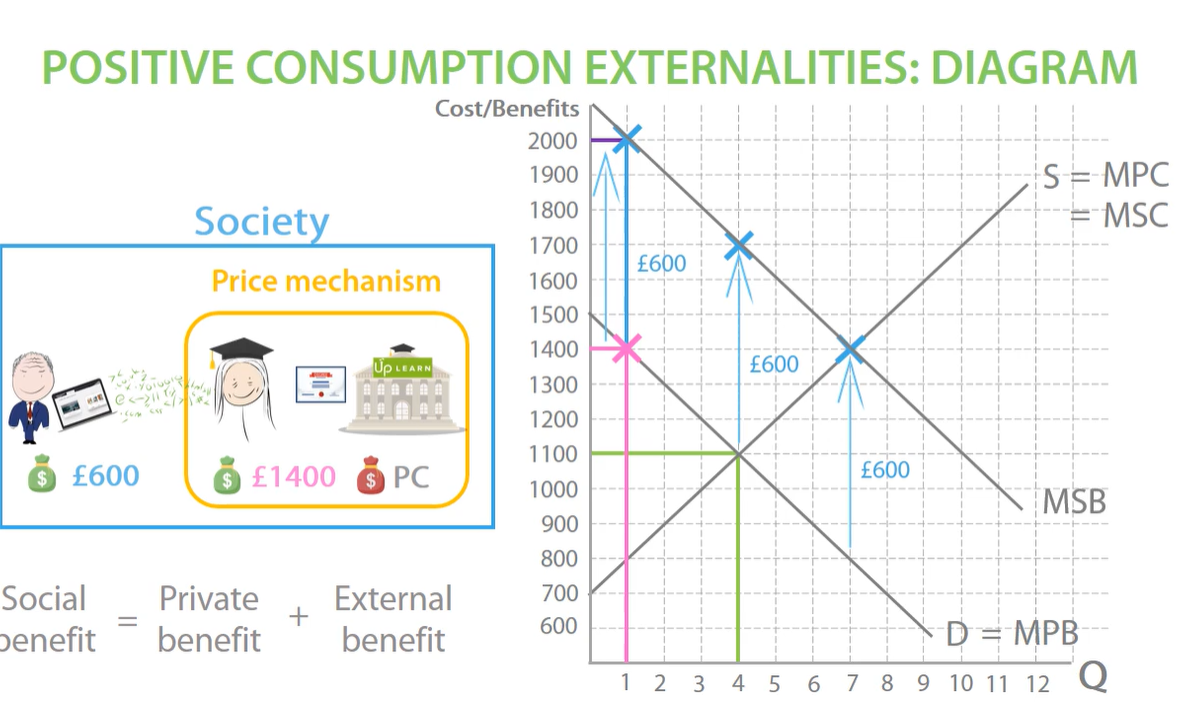
positive consumption externalities diagram
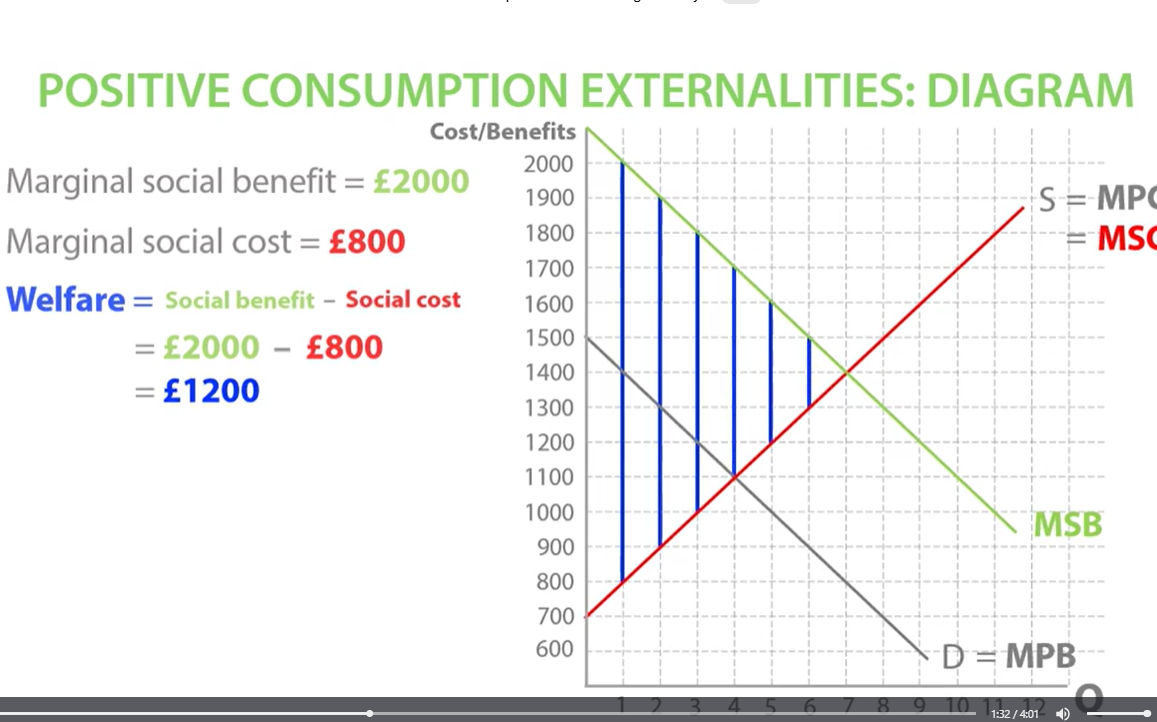
positive consumption externalities welfare
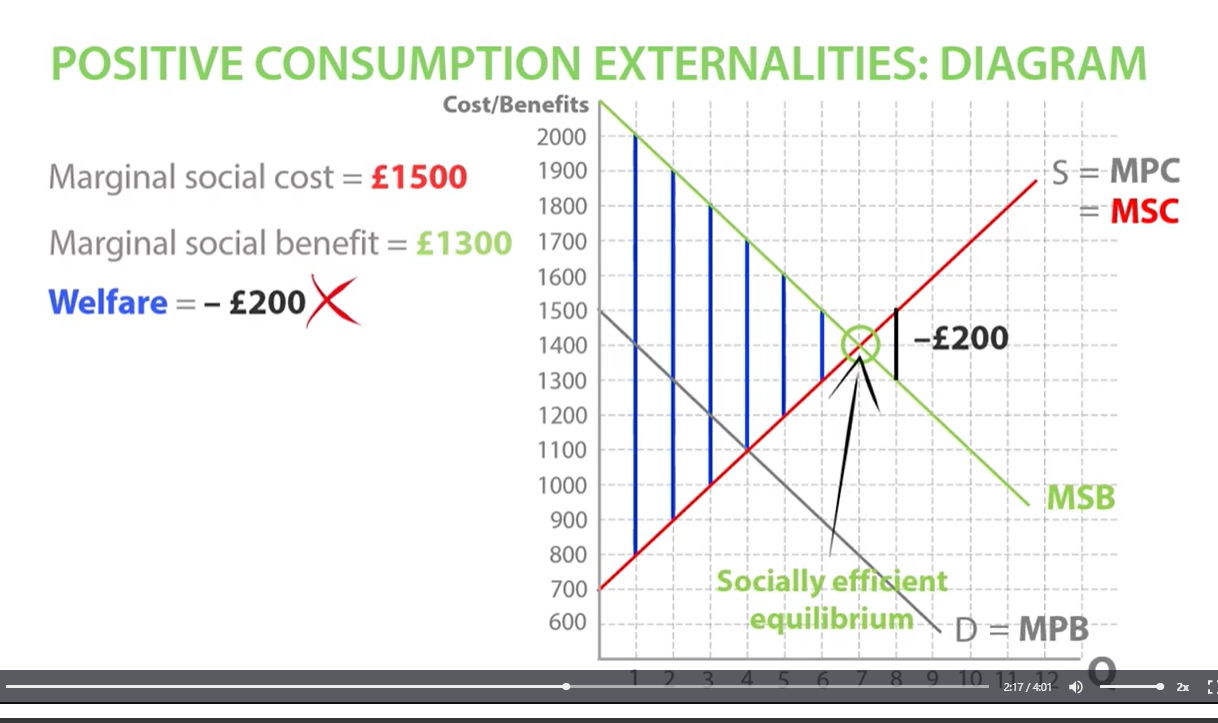
positive consumption externalities socially efficient equilibrium
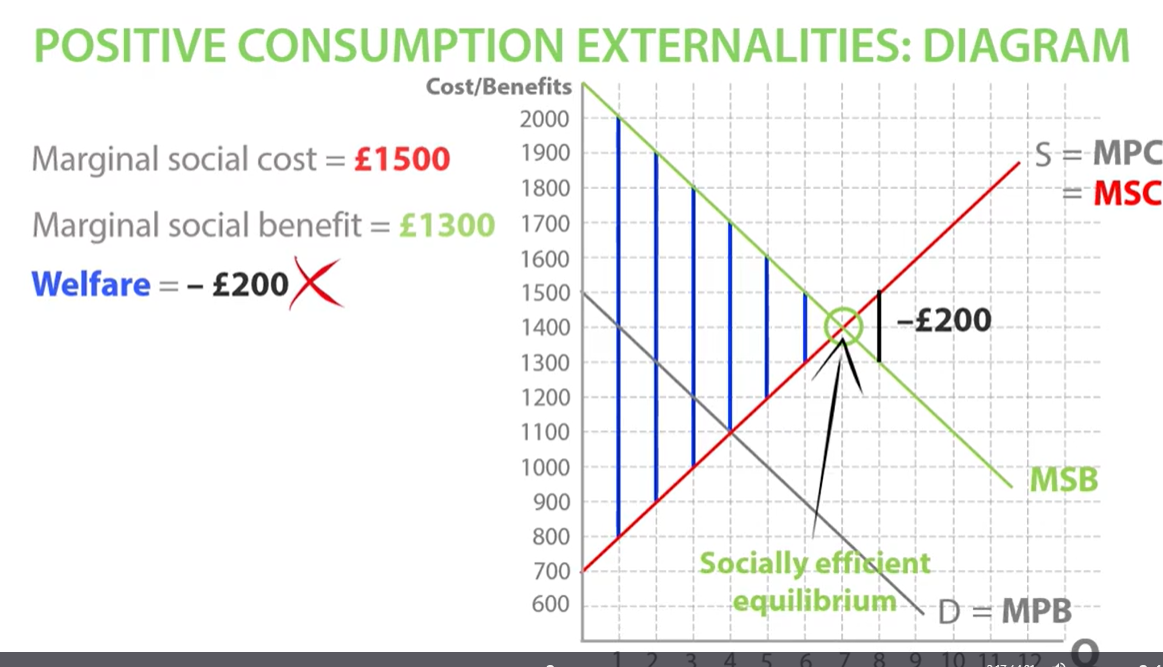
marginal social benefit - marginal social cost = welfare
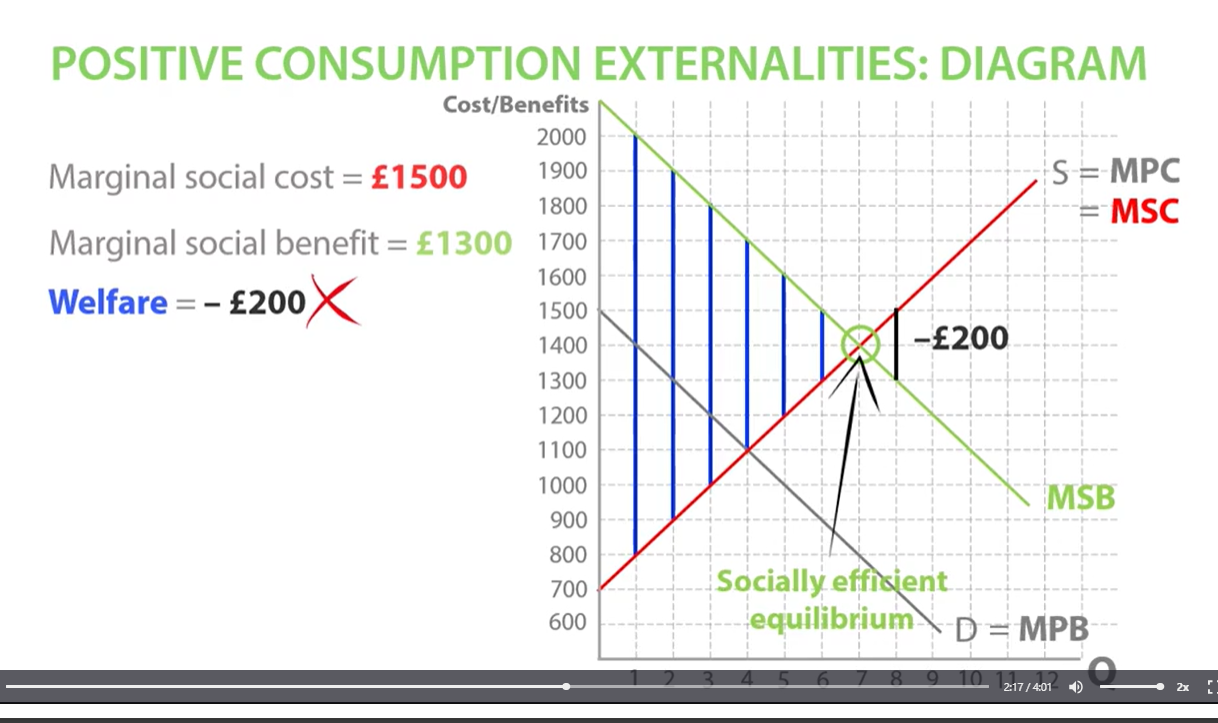
positive consumption externalities welfare loss
welfare loss if we consumed the quantity of 8 so we want to stop at socially efficient equilibrium
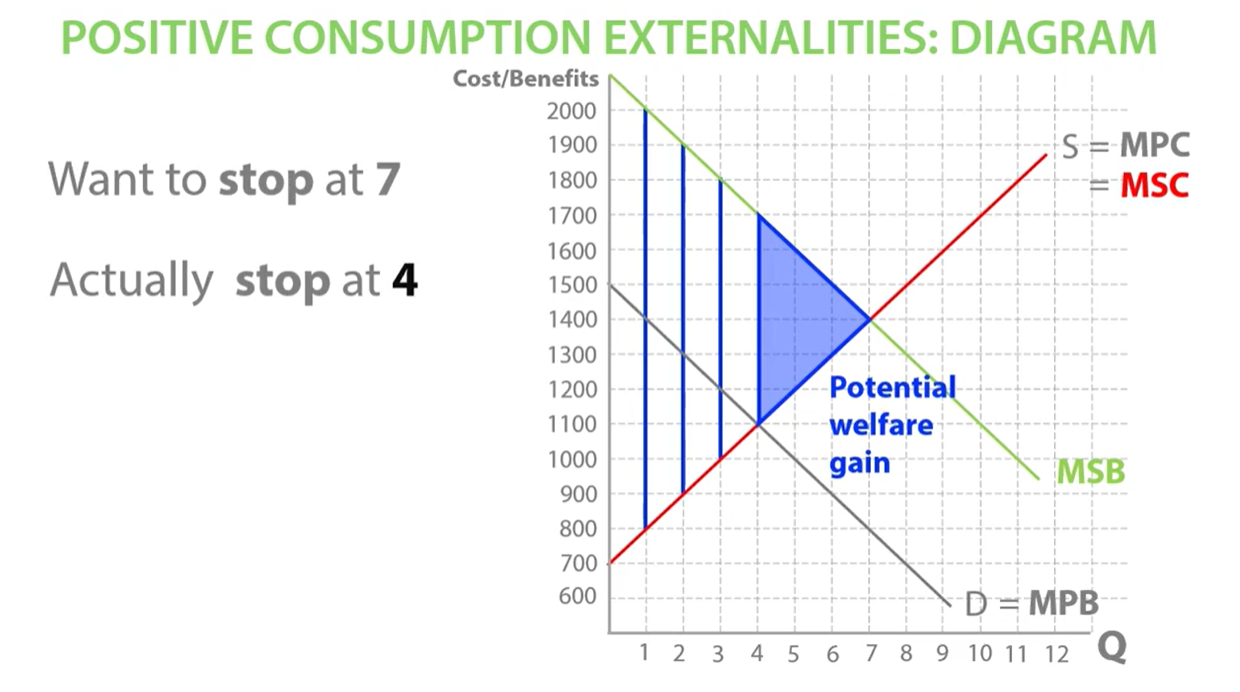
positive consumption externalities welfare gain
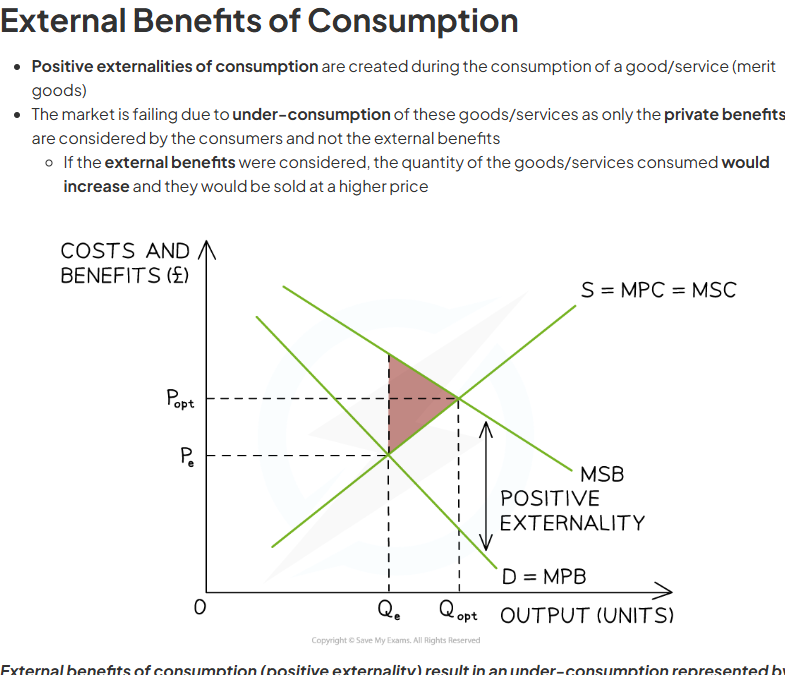
underconsumption. consumers do not think about external benefits which leads to underconsumption as they do not consider profits they’ll make for future employers
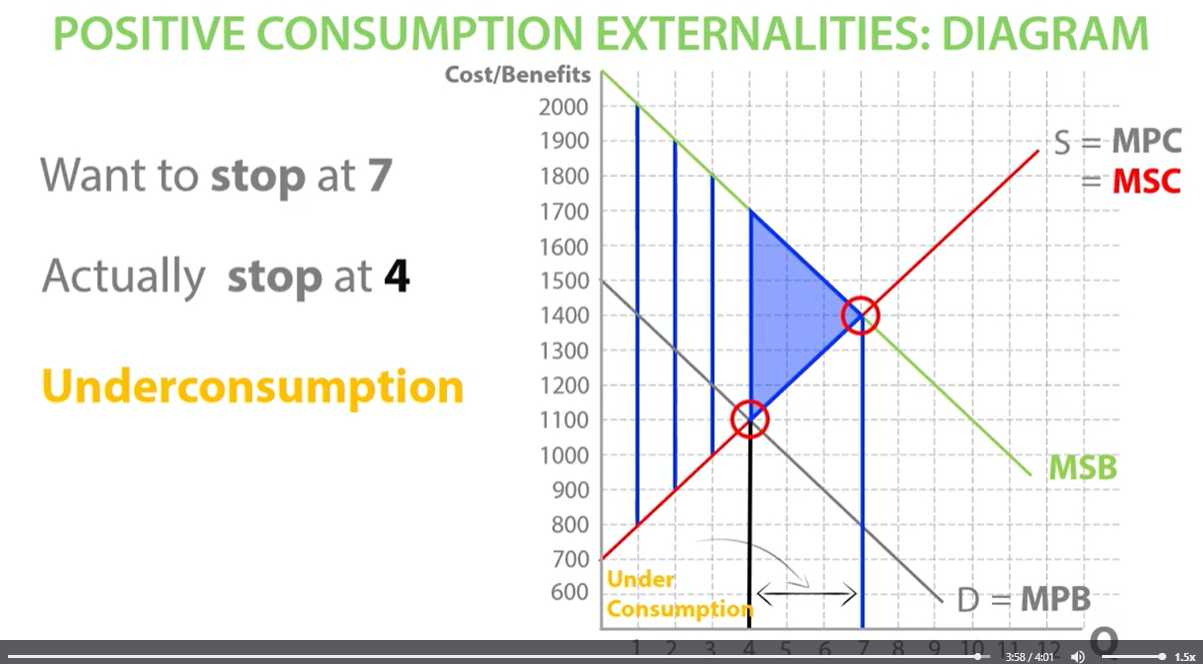
positive consumption externalities diagram
End up under- consuming if they do not think about marginal social benefits
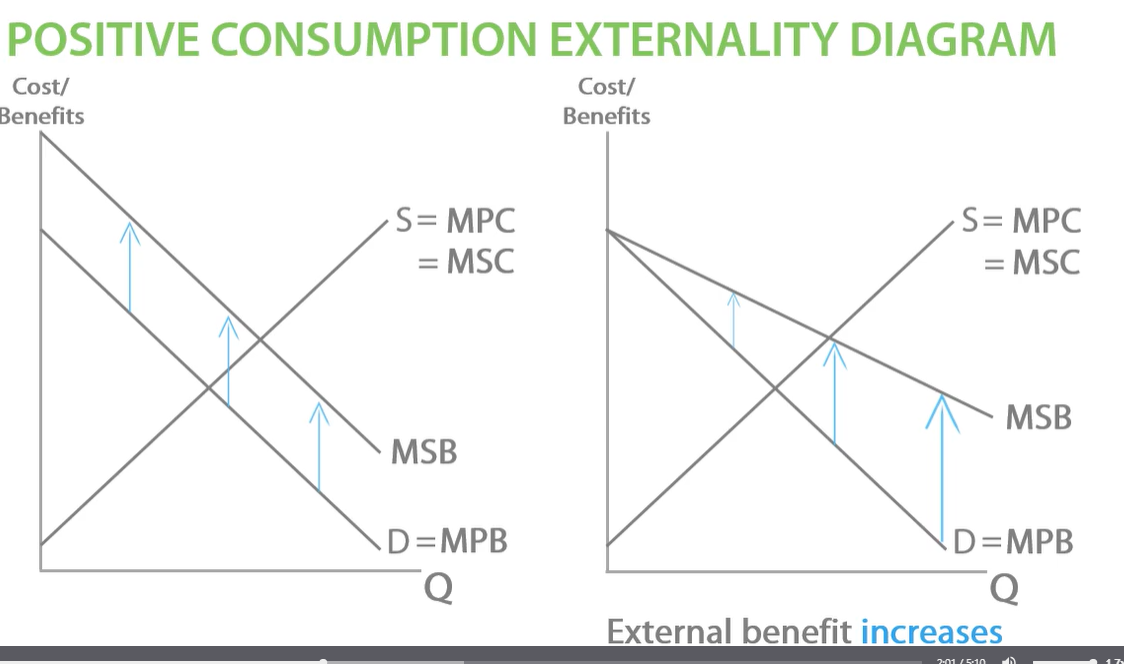
positive externalities diagram external benefit increases
e.g. external benefit increases as vaccinated protected from disease, others benefit as less risk of catching disease, more people vaccinated then much lower risk of catching diseases, representing a larger external benefit.
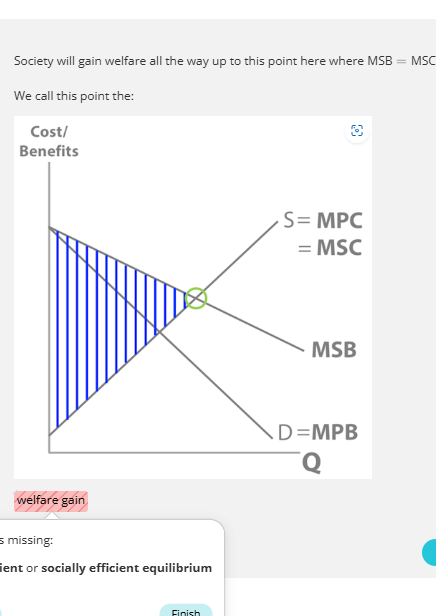
society gain welfare positive consumption externalities
society will gain welfare all the way up to the socially efficient equilibrium. MSB AND MSC intersect at the socially efficient equilibrium. in the free market, consumers stop consuming at the market equilibrium between marginal private benefit and marginal private cost leading to underconsumption between the socially efficient quantity and the market quantity which means society misses out on a potential welfare gain.
positive production externalities
external benefit come from production of good. e.g. renewable energy, solar panels.
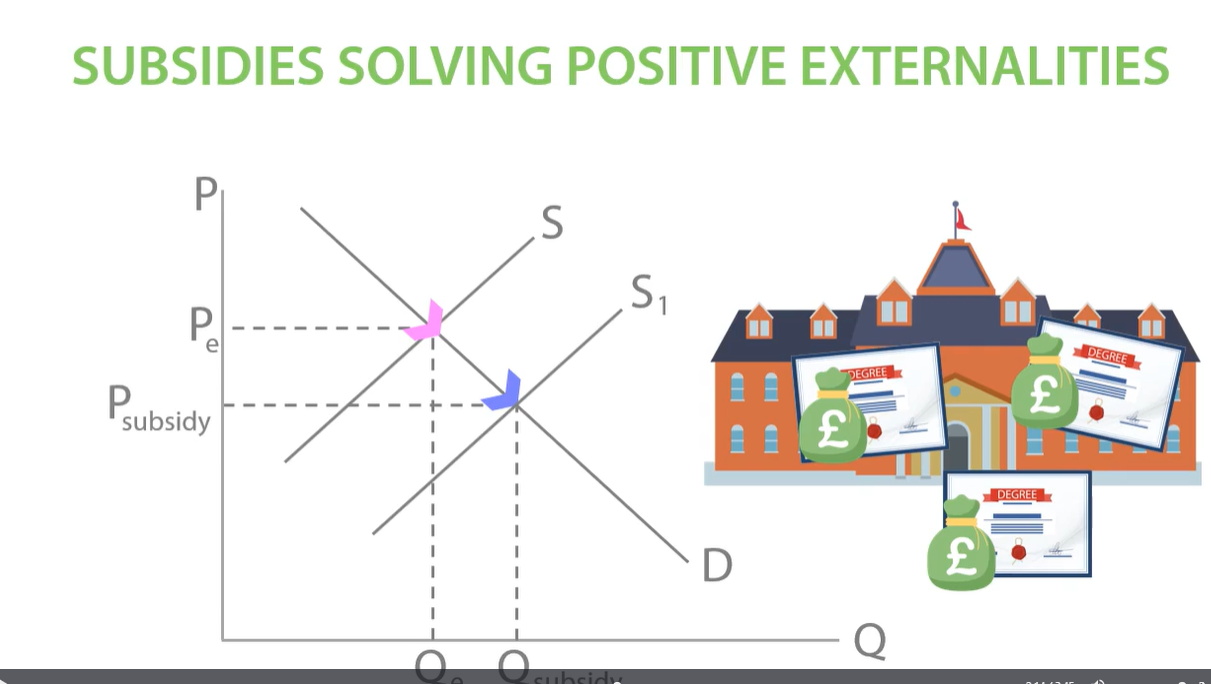
positive production externalities: subsidy
subsidy affects supply as it reduces the cost of production. it will shift supply to the right as producers are willing to supply more. increased the quantity of education consumed successfully improving the underconsumption of education.
e.g. new homes creates more jobs so housing has positive production externalities
positive production externalities before taking external benefits into account
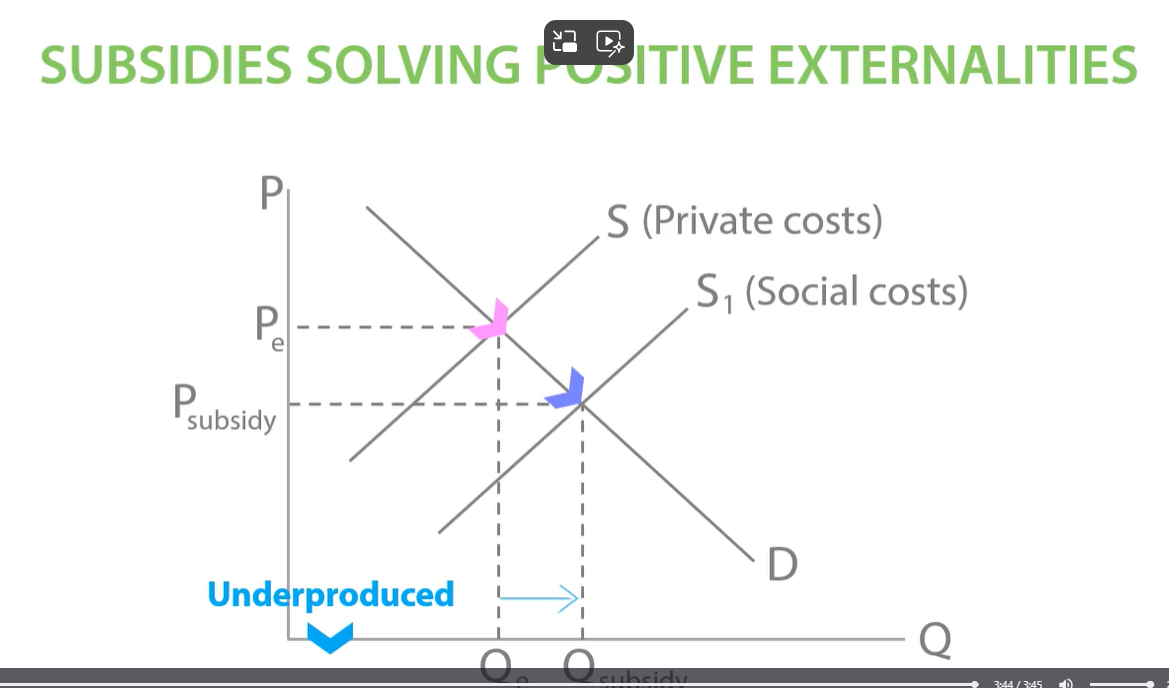
The market equilibrium is QePe where private costs meet the demand curve. At this level, producers don’t take into account the external benefits of house building and so they underproduce compared to the social equilibrium (QsPs).
positive production externalities subsidies diagram
at Qe the market equilibrium is underproduced because when producers produce houses they only consider private costs, so government subsidies housing which gives them the incentive to produce more houses shifting supply to the right. new equilibrium at q subsidy and p subsidy.
-increase quantity of house produced, successfully improving underproduction of houses.
subsidies benefits production externalities
unis- encourage them to offer new courses and take on more students.
eco technology companies- incentivise to innovate energy advanced saving gadgets
subsidies problem in positive externalities
housing market ineffective. housing is a necessity so demand is inelastic subsidies increasing homelessness as prices were too high so government set maximum price. highest price suppliers of a good can sell for.
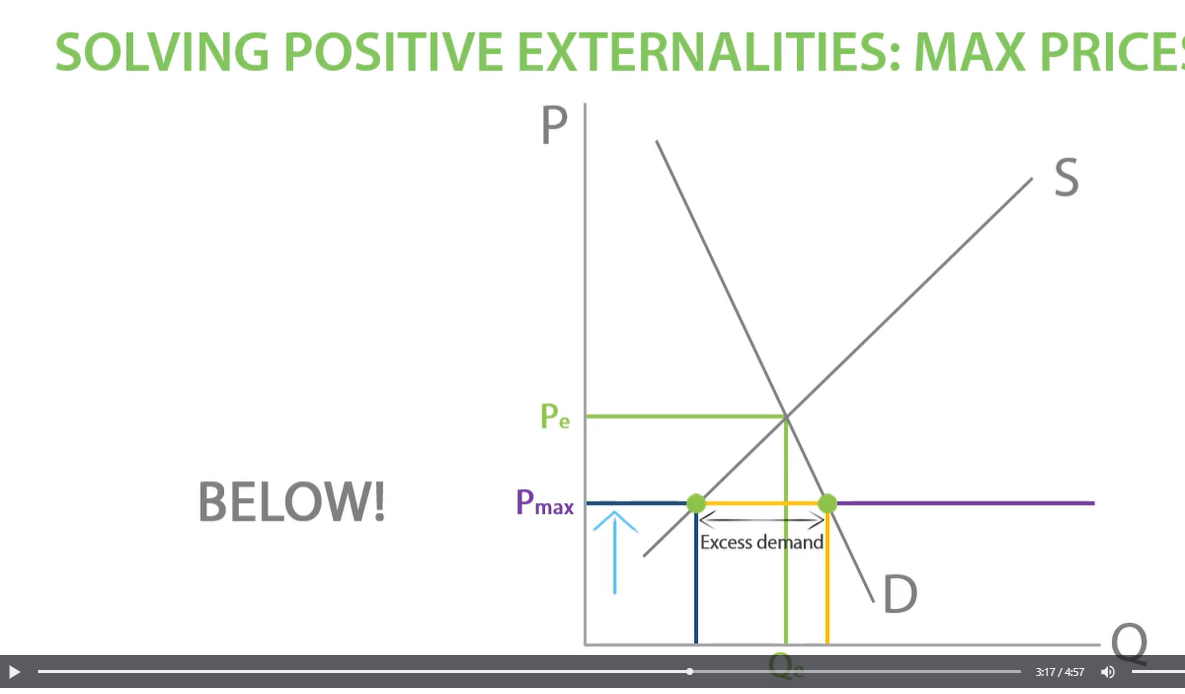
maximum price set solving positive externalities
the highest price suppliers can sell a good for. maximum price so landlords do not exploit tenants and less wealthy consumers can find a place to stay.
minimum price set solving positive externalities
-set maximum price below equilibrium which creates excess demand. price cannot go above max price so market is stuck in a disequilibrium. more people can afford prices. decreases prices in the market and set below price. however, this can lead to landlords not taking care of the houses properly as they are not maximising profit.




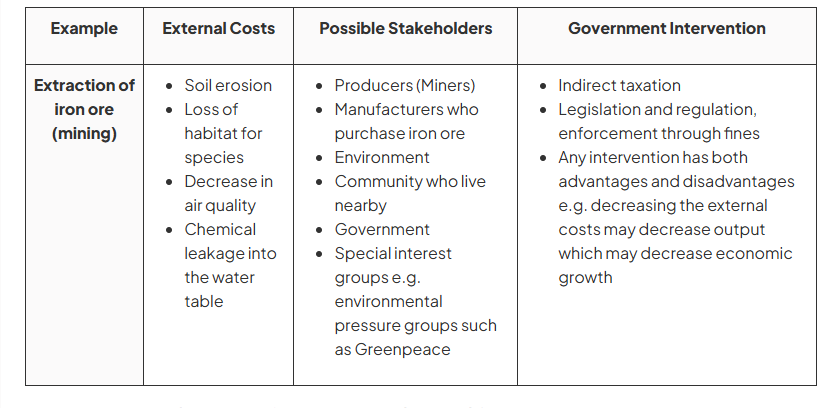
impact of negative externalities and government intervention
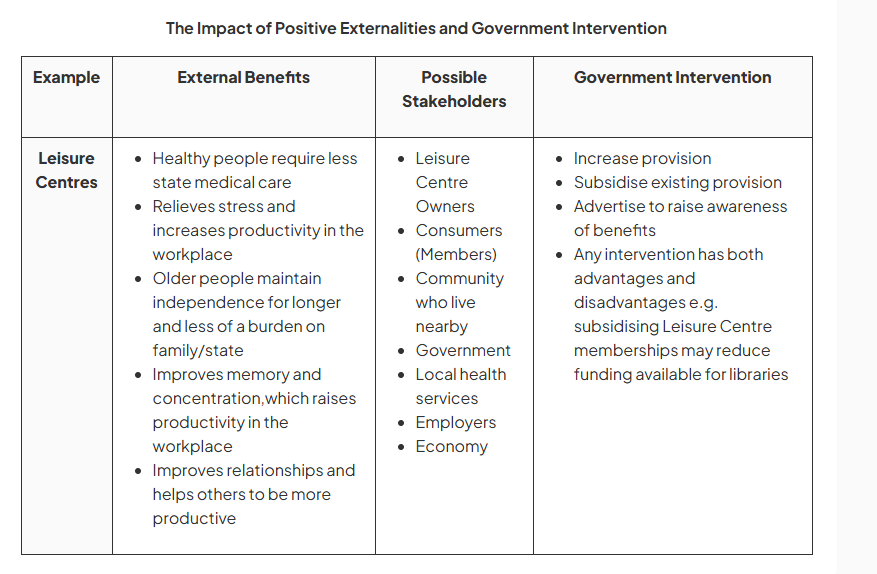
impact of positive externalities and government intervention.
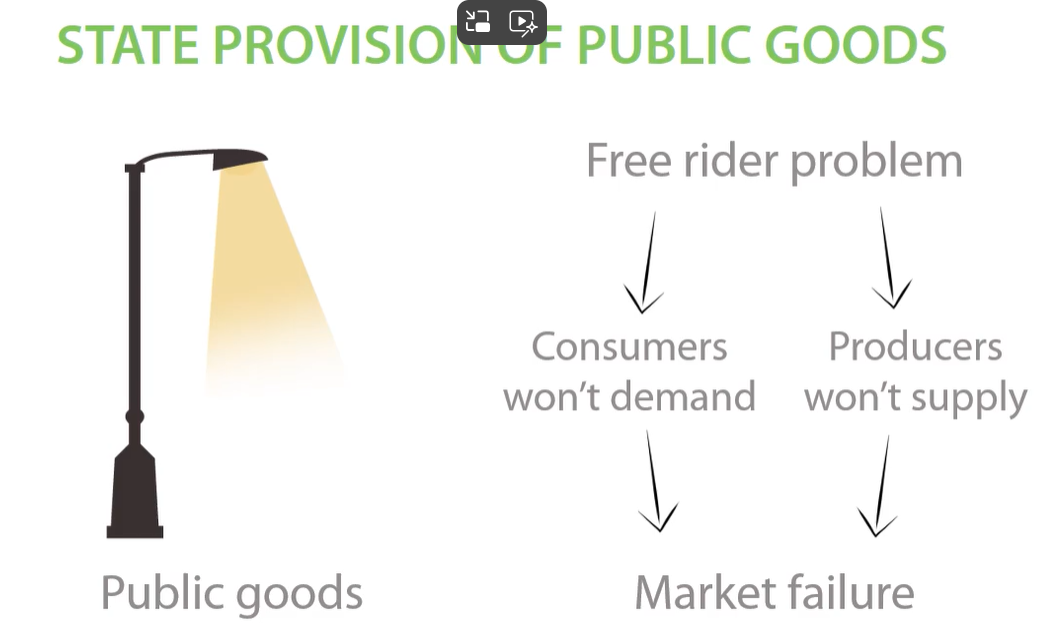
public goods
non excludable and non rival

public goods free rider problem
-consumers wait for others to buy and free-ride. No one demands the public good. producers wont supply public goods because cant make a profit.
-therefore public goods can lead to market failure to government must intervene.
free rider problem leads to
an inefficient allocation of resources .
however government intervenes through using direct and indirect tax and through tax revenue create street lights solving the free rider problem. this is called state provision.
public goods the government provides:
roads, bridges, parks, police, defences. healthcare and education are not public goods. government provide hospitals and schools because they create positive externalities.
public and private goods.
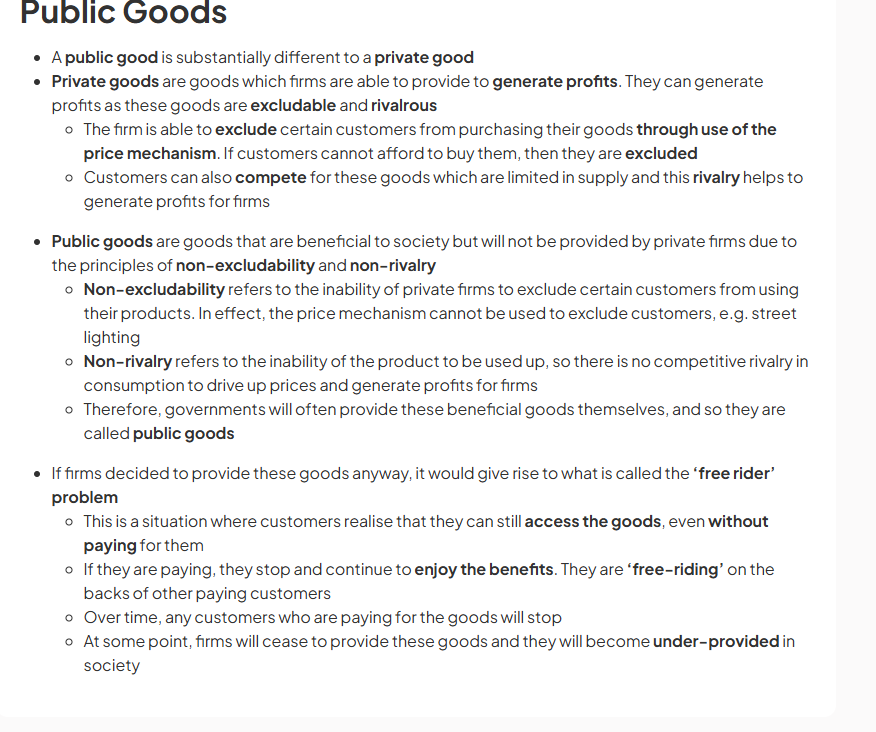
examiner tips and tricks public and private goods.
however not all public goods are pure public goods. e.g. fire brigade if there is a big scene then there will be many over there and limit amount of fire brigade for others or if all the benches in the park is used up then it is rival or if you block your road it is rival.

public goods
Public goods are non-excludable (you cannot stop others from using a public good) and non-rival (you can use the good at the same time as someone else).
E.g. A streetlight. You can't stop someone using the light from your streetlight so it's non-excludable. And several people can use the light from the street light at the same time so it's non-rival.
free rider problem
Public goods (e.g. streetlights) are non-excludable so others can use your public good for free, without paying.
Therefore, consumers won’t demand a public good, because they can just wait for someone else to buy and will use it for free.
Producers will not supply a public good because consumers will just use it for free, so producers cannot make a profit.
So, public goods will be underprovided by the market
incomplete information: underconsumption
-doesn’t have enough information about the benefits or costs about their decisions. This leads to underconsumption and misallocation of resources when then leads to market failure. Government intervene to prevent market failure.
incomplete information
government intervene to prevent market failure due to incomplete allocation through regulation and subsidies. e.g. students do not know benefit of education so they are legally required to stay in education till 18 and subsidies tuition fees.
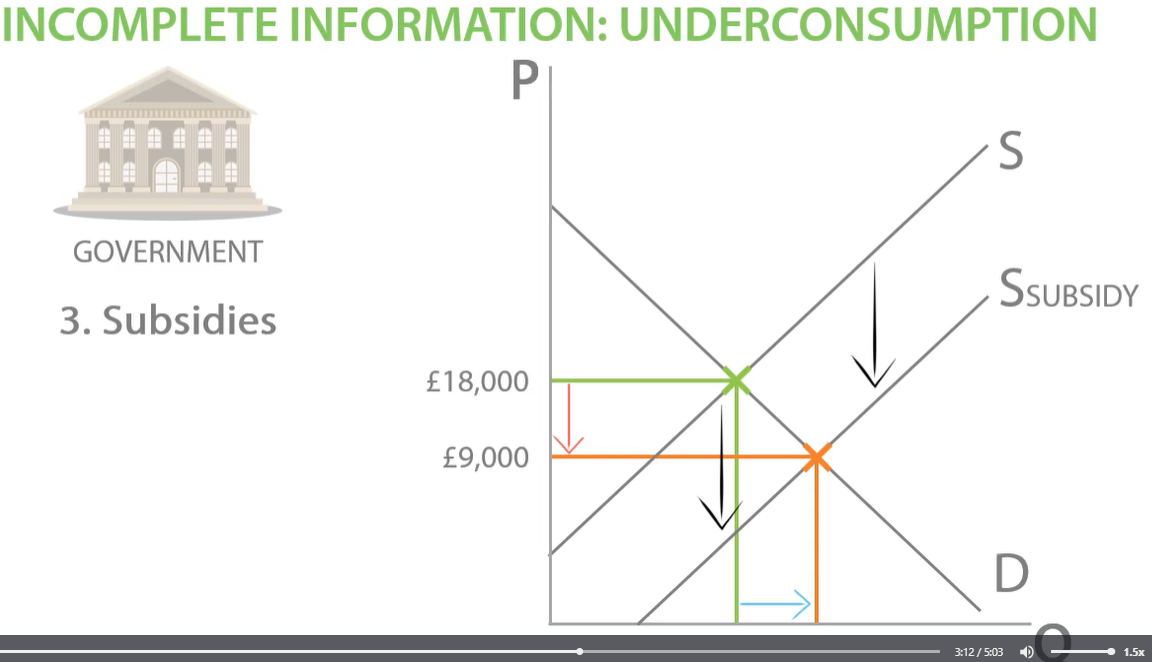
subsidies in incomplete information
subsidies encourages people to allocate more of their resources consuming education, help to fix the market failure.
-subsidy will reduce the price and increase the quantity.
government intervene to prevent market failure due to incomplete information
subsidies, regulation, advertising and providing information.
incomplete information
someone doesn’t have full information about the benefits or costs about their decisions.
incomplete information: overconsumption
market failure can occur due to incomplete information and overconsumption such as cigarettes.
incomplete information about cigarettes and lead to overconsumption. government intervention:
-regulation, companies stick labels on their packages. illegal for people to smoke in public places and ban cigarette advertising.
-advertising- what cigarettes do to your lungs
-specific taxes - increase price and reduce quantity
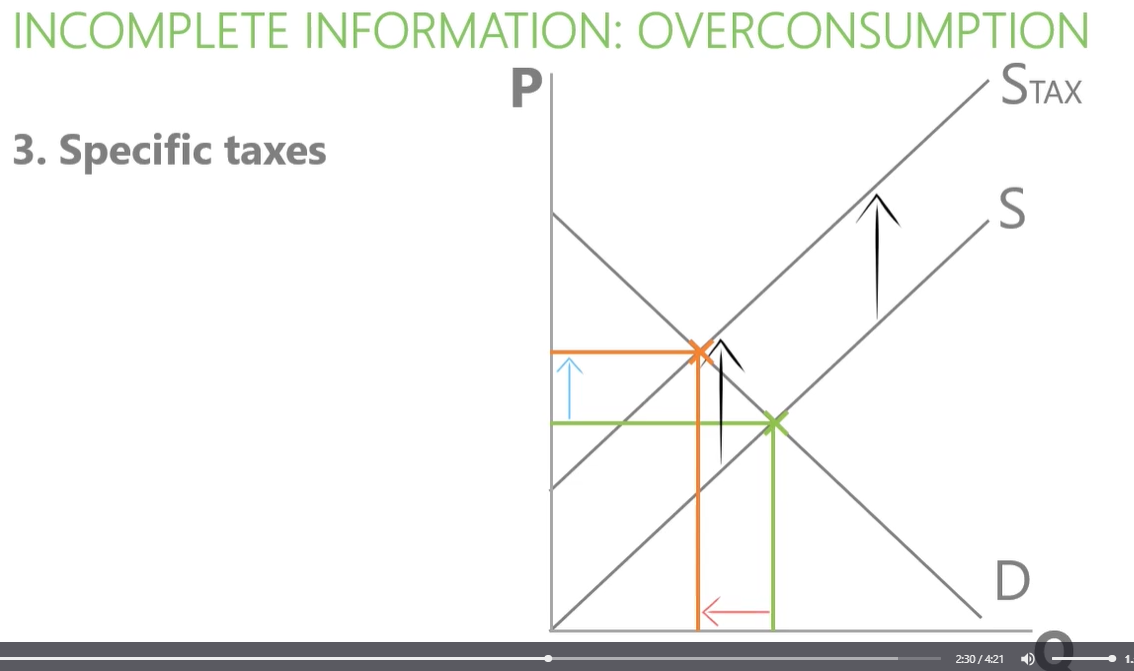
government intervene incomplete information: overconsumption
asymmetric information
-when one party knows more than another party in a transaction
symmetric information
all parties know as much as each other
asymmetric information can…
lead to a misallocation of resources and market failure
government intervention in asymmetric information
e.g. six month after buying a car you can get a refund, replacement or repair. asymmetric information when selling second hand cars or private healthcare which results in a misallocation of resources. government has regulators. or when you are in university and landlord sell you a dodgy department to maximise their profit.
purpose of intervention to government failure

government intervention in markets ad valorem
government intervention specific tax on negative externalities of production
