Cartilage
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are the characteristics of Cartilage?
Firm, flexible tissues
Contains no blood vessels or nerves
Cell type - chondrocyte
What are the types of Cartilage?
Hyaline, Elastic, & Fibrocartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Chondrocytes are housed within lacunae in an amorphous but firm matrix
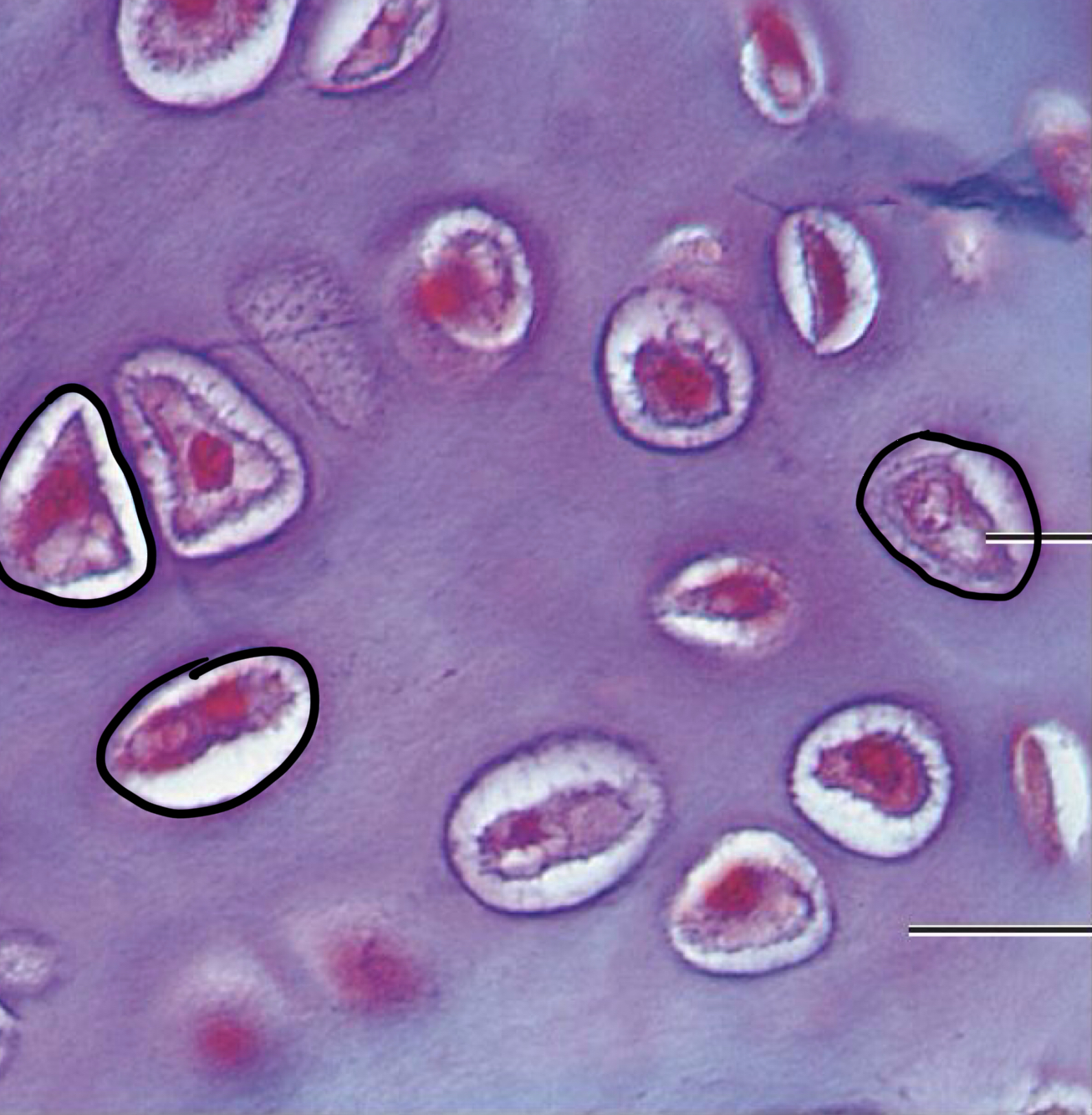
What is the function of Hyaline Cartilage?
Support & reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties, resists compressive forces
Where is Hyaline Cartilage founded?
forms the embryonic skeleton, covers the ends of long bones & in joints; forms costal cartilage of the ribs, is the cartilage in the nose, trachea, & larynx
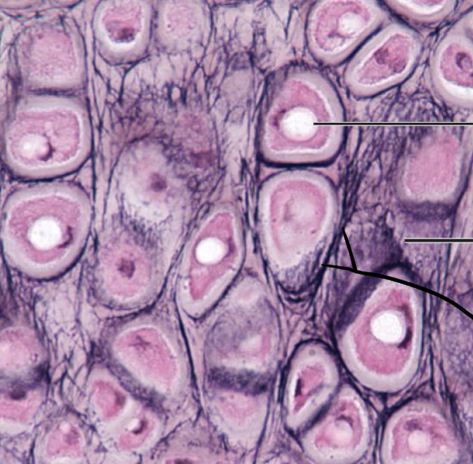
Elastic Cartilage
Similar to Hyaline, but with more elastic fibers in the matrix
What is the function of Elastic Cartilage?
Maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
Where is Elastic Cartilage founded?
supports the external ear
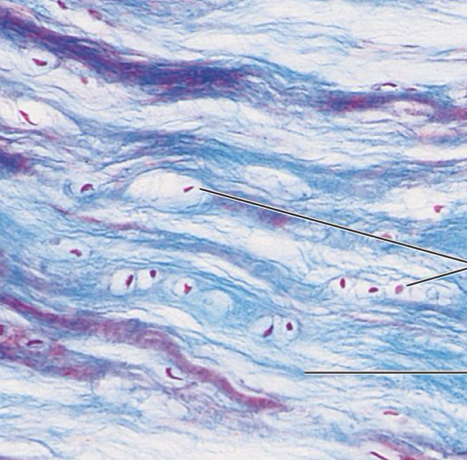
Fibrocartilage
similar to hyaline cartilage but less firm, has many thick collagen fibers
What does Fibro mean?
Tough
What is the function of Fibrocartilage?
has strength against tension (pulling) forces; also has the ability to absorb compressive forces
Where is Fibrocartilage founded?
Intervertebral discs between vertebrae, pubic symphysis & discs of the knee joint
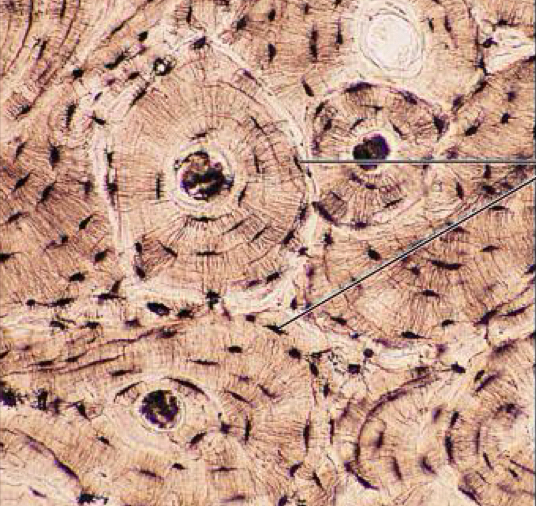
Bone
has osteocytes in lacunae, is ring-like in appearance
What is the function of the bone?
support & protects organ; provides an attachment site for muscles; stores calcium & other materials
Where is the bone found?
skeletal system
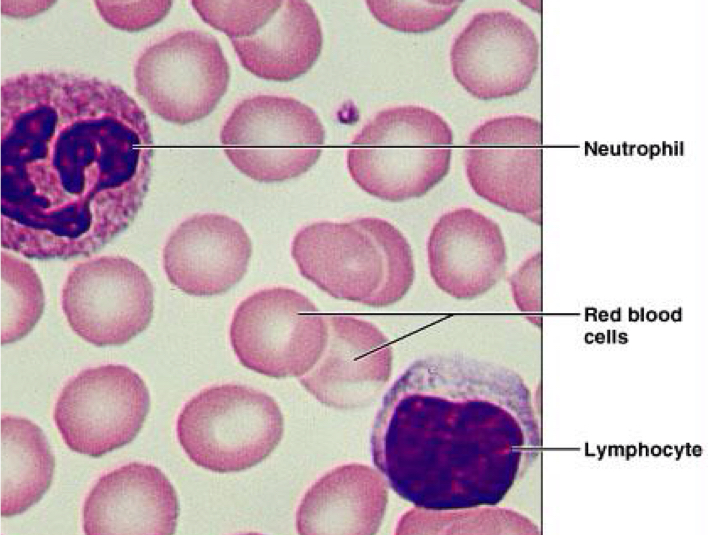
Blood tissue
Consists of cells surrounded by fluid matrix; contains RBC, WBC, platelets, & plasma
What is the function of blood tissue?
Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, & wastes (hormones)
Where is blood found?
Circulatory system