Ainsworth's strange situation (1970)- types of attachment
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What types of experiment is this experiment?
a controlled observation
Episodes of strange situation: what happens before the episodes?
Caregiver and baby enter an unfamiliar playroom
Episodes of strange situation: episode one
Baby is encouraged to explore
tests: exploration and secure base
Episodes of strange situation: episode two
a stranger comes in, talks to the caregiver and approaches the baby
tests: stranger anxiety
Episodes of strange situation: episode three
caregiver leaves the stranger and baby together
tests: separation and stranger anxiety
Episodes of strange situation: episode four
caregiver returns and the stranger leaves
tests: reunion behaviour and exploration/ secure base
Episodes of strange situation: episode five
caregiver leaves baby alone
tests: separation anxiety
Episodes of strange situation: episode six
stranger returns
tests: stranger anxiety
Episodes of strange situation: episode seven
caregiver returns reuniting with the baby
tests: reunion behaviour
What behaviours are looked for to judge attachment?
Proximity seeking
Exploration and secure base behaviour
Stranger anxiety
Separation anxiety
Response to reunion
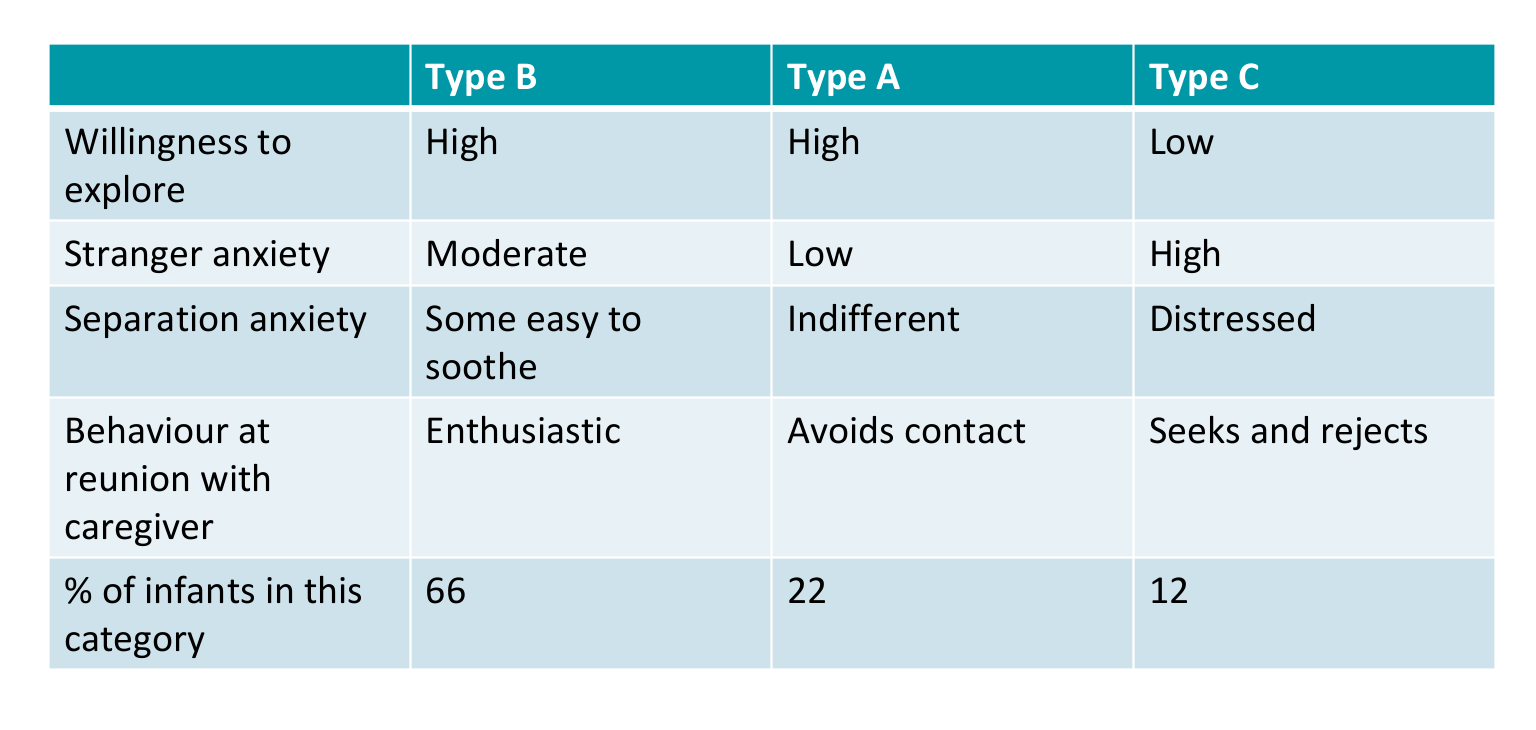
Findings: What are the types of attachment?
insecure- avoidant (type A)
Secure attachment (type B
Insecure- resistant (Type C)
What is Insecure- avoidant (Type A)?
willing to explore, had low stranger anxiety, were indifferent to anxiety and avoided contact when parent returned.
What is secure attachment (Type B)?
willing to explore, had high stranger anxiety, were easy to soothe and were enthusiastic at the return of their mother.
What is Insecure resistant (Type C)?
unwilling to explore, had high stranger anxiety, were distressed at separation but sought and rejected contact when parent returned.
What are the characteristics of the main attachment types with respect to the stranger situation findings?
What did Ainsworth conclude about the sensitivity of the mother?
attachment differences depended upon the sensitivity of the mother (i.e. how well the mother could read her infant’s feelings and moods)
sensitive mothers generally had infants who were securely attached
less sensitive and less responsive mothers (i.e. those who ignored their infant or were impatient with them) had babies who were more likely to be insecurely attached a baby’s attachment does seem to be affected to some extent by the quality and sensitivity of the caregiver
Evaluation: good predictive validity
P – A strength is there is a predictive validity of attachment types in the Strange Situation.
E – Attachment type predicts later development. For example, secure babies typically have greater success at school and more lasting romantic relationships.
E – In contrast, insecure-resistant attachment is associated with the worst outcomes eg bullying (Kokkino) and adult mental health problems (Ward et al).
L – This means that there is evidence for the validity of the concept because it can explain future outcomes.
Evaluation: culture bound
P – A limitation is that the Strange Situation may be a culture-bound test.
E – The test might not have the same meaning in countries outside Western Europe and the USA.
E – Cultural differences in children’s experiences mean they respond differently. Also, caregivers from different cultures behave differently.
L – Takahashi notes that Japanese mothers are rarely separated from infants thus the infants show high levels of anxiety. This means that the Strange Situation may not be a valid test of attachment across a variety of cultures.
Evaluation: socially sensitive
E – Evidence:
The Strange Situation places infants in mildly stressful situations, such as separation from their caregiver and interaction with a stranger, and uses their responses to categorise attachment types (secure, insecure-avoidant, insecure-resistant).
E – Explain:
These classifications may lead to labelling, where children or caregivers—particularly mothers—are judged as inadequate or blamed for insecure attachment. Additionally, the procedure is ethnocentric, as it was developed in a Western culture and may misinterpret culturally normal behaviours in other societies, raising ethical concerns.
L – Link:
Therefore, Ainsworth’s Strange Situation is socially sensitive because it can affect how children and caregivers are perceived and treated, highlighting the need for caution when applying attachment research across cultures.