A&P chap 13 & 14 shorten
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
What is Respiration?
The entire process of gas exchange between the atmosphere.
Ventilation
Breathing.
External Respiration
Gas exchange between blood and air in the lungs.
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange between blood and the cells of the body.
Circulation
Gas transport in blood between the lungs and the body cells.
Cellular Respiration
Oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is produced by the cell.
List the Two Divisions of the Respiratory System
Upper- nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, and pharynx; Lower- trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs.
What composes the nose?
Cartilage and bone.
What is the function of the internal hairs in the nose?
To filter out large particles.
What is the nasal cavity?
A hollow space behind the nose, containing a mucus membrane.
List 3 things the nasal cavity does for air.
Warms air, moistens air, and traps dust and small particles with mucus.
What pushes mucus and particles to the pharynx?
Cilia.
The nasal septum divides the nose into...
Left and right halves.
Explain a deviated septum.
It is bent to one side.
What are paranasal sinuses?
Air-filled spaces that reduce the weight of the skull and affect the quality of the voice.
List 4 sinuses.
Maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid.
What are the 2 functions of the sinuses?
Reduce the weight of the skull and affect voice quality.
Another name for the pharynx is the...
Throat.
What passes through the pharynx?
Air and food.
The larynx conducts air in and out of the...
Trachea.
The larynx contains the...
Vocal cords.
What is the Adam's Apple?
Cartilage in the larynx.
How do the vocal cords produce sound?
Air is forced between the vocal cords causing them to vibrate.
How does a person control the pitch of their voice?
By contracting and relaxing muscles to alter tension on the vocal cords.
Define glottis.
The triangular slit between the vocal cords.
What is the epiglottis and its function?
A flap-like structure that covers the trachea when swallowing.
Another name for the windpipe is the...
Trachea.
What is the trachea made out of?
Made up of 20 C-shaped pieces of hyaline cartilage.
The first branch off of the trachea is the...
Primary bronchi.
Trace the air through the respiratory system.
Trachea, primary bronchi, bronchioles, ducts, sacs, alveoli.
How does carbon dioxide/oxygen exchange take place?
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood through the alveoli wall.
How many alveoli does the average person have?
Approximately 300 million.
What are the lungs and where are they located?
Soft, spongy, cone-shaped organs located in the thoracic cavity.
Visceral Pleura
Attaches to each lung's surface.
Parietal Pleura
Lines the inner wall of the thoracic cavity.
What is the Pleural Cavity?
Potential space between the visceral and parietal pleura.
Contrast the right lung to the left lung.
The right lung is larger with 3 lobes; the left lung has 2 lobes.
Inspiration
Inhalation; diaphragm flattens, external intercostals move the ribs up and out.
Expiration
Exhalation; diaphragm domes, internal intercostals move in and out.
What aids in inhaling and exhaling?
Abdominal muscles.
What is atmospheric pressure?
The weight of air, approximately 760 mm Hg.
What is the diaphragm?
A dome-shaped muscle that assists in breathing.
Define surfactant.
A lipoprotein that reduces the tendency of alveoli to collapse.
What is Infant Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
A condition affecting premature babies.
What is Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)?
Impairment or removal of surfactant due to accidents or inhalation of foreign substances.
What is a Pneumothorax?
Air gets into the pleural cavity.
What is emphysema and what causes it?
A progressive degenerative disease in which alveoli rupture.
What arises in the lungs?
Primary pulmonary issues.
What causes most lung cancers?
Smoking and second-hand smoke.
List and describe three treatments for lung cancer.
Surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
What is a spirometer?
A device used to measure the amount of air exchanged in breathing.
How much is the average amount of air exchanged in breathing?
About 1 pint.
What does a respiratory cycle include?
One inspiration and one expiration.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
The amount of air that can be inhaled during forced breathing in addition to tidal volume.
Expiratory Reserve Volume
The amount of air that can be exhaled during forced breathing in addition to tidal volume.
Residual Volume
Air that remains in the lungs after a forced exhale.
Vital Capacity
Inspiratory reserve volume plus tidal volume plus expiratory reserve volume.
Inspiratory Capacity
Tidal volume plus inspiratory reserve volume.
Functional Residual Capacity
Expiratory reserve volume plus residual volume.
Total Lung Capacity
Vital capacity plus residual volume.
What is the average breaths per minute in an adult?
12 to 18 breaths per minute.
A normal respiratory rate is known as...
Eupnea.
Hyperventilation
Rapid deep breathing.
Hypoventilation
Slow shallow breathing.
Dyspnea
Labored or difficult breathing, often associated with hypoventilation.
Orthopnea
Dyspnea relieved by moving into an upright or sitting position.
Apnea
When breathing stops completely for a brief period.
Cheyne-Stokes Respiration
Cycles of alternating apnea and hyperventilation.
Respiratory Arrest
Failure to resume breathing after a brief period.
Sinusitis
An inflammation of the sinus cavity lining.
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the pleural membrane.
Acute bronchitis
An acute inflammation of the bronchi, typically due to infection.
What is pneumonia?
An acute inflammation of the lungs in which the alveoli and bronchi become plugged with thick fluid mucus.
What are tubercles?
Protective capsules the body forms around colonies of tuberculosis (TB).
List and describe three types of COPD.
Chronic Bronchitis - chronic inflammation of the bronchi with excessive mucus production blocking air passages; Asthma - an obstructive disorder characterized by recurring spasms in the air passages causing difficulty in breathing.
Nasal Cavity
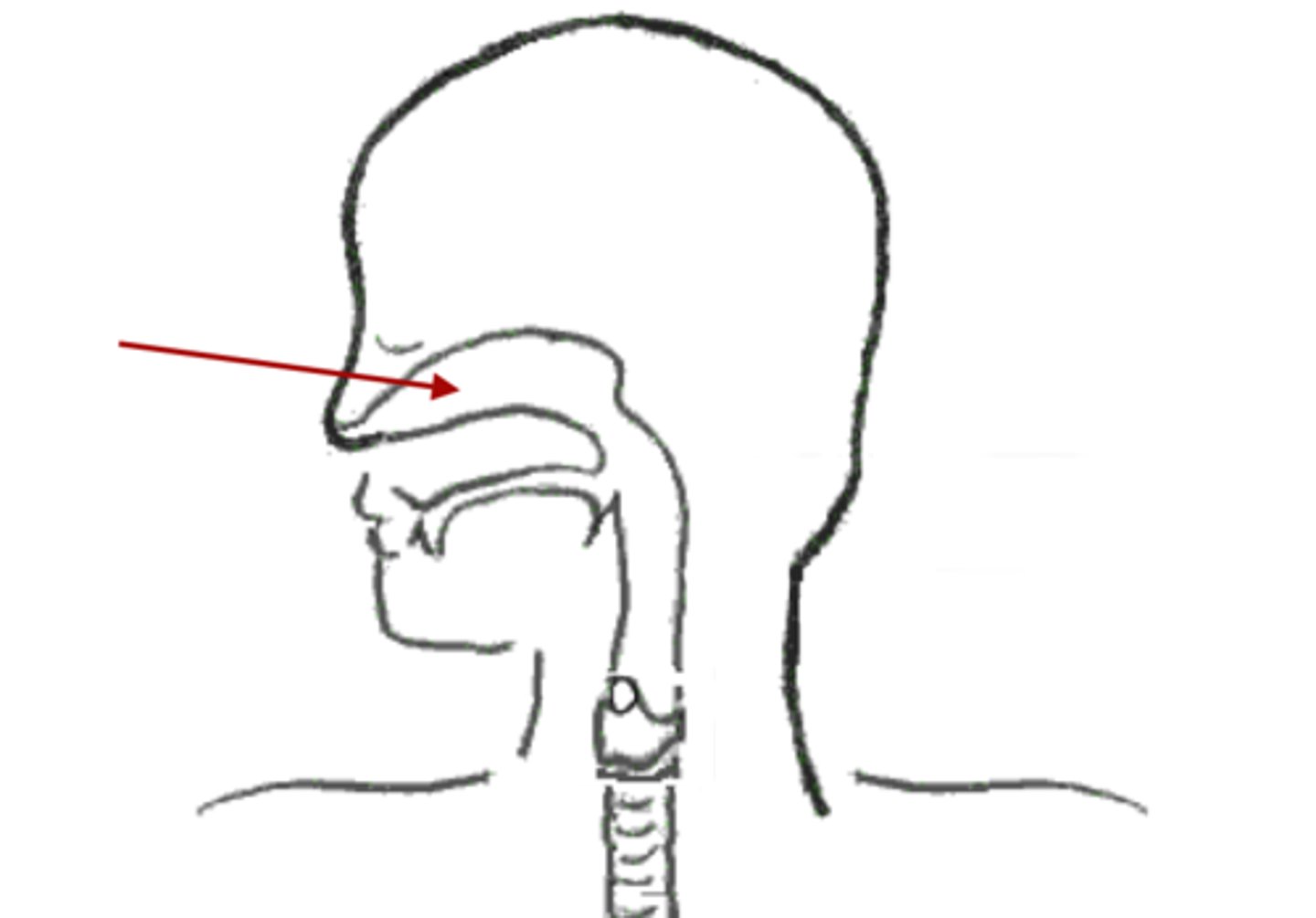
Mouth
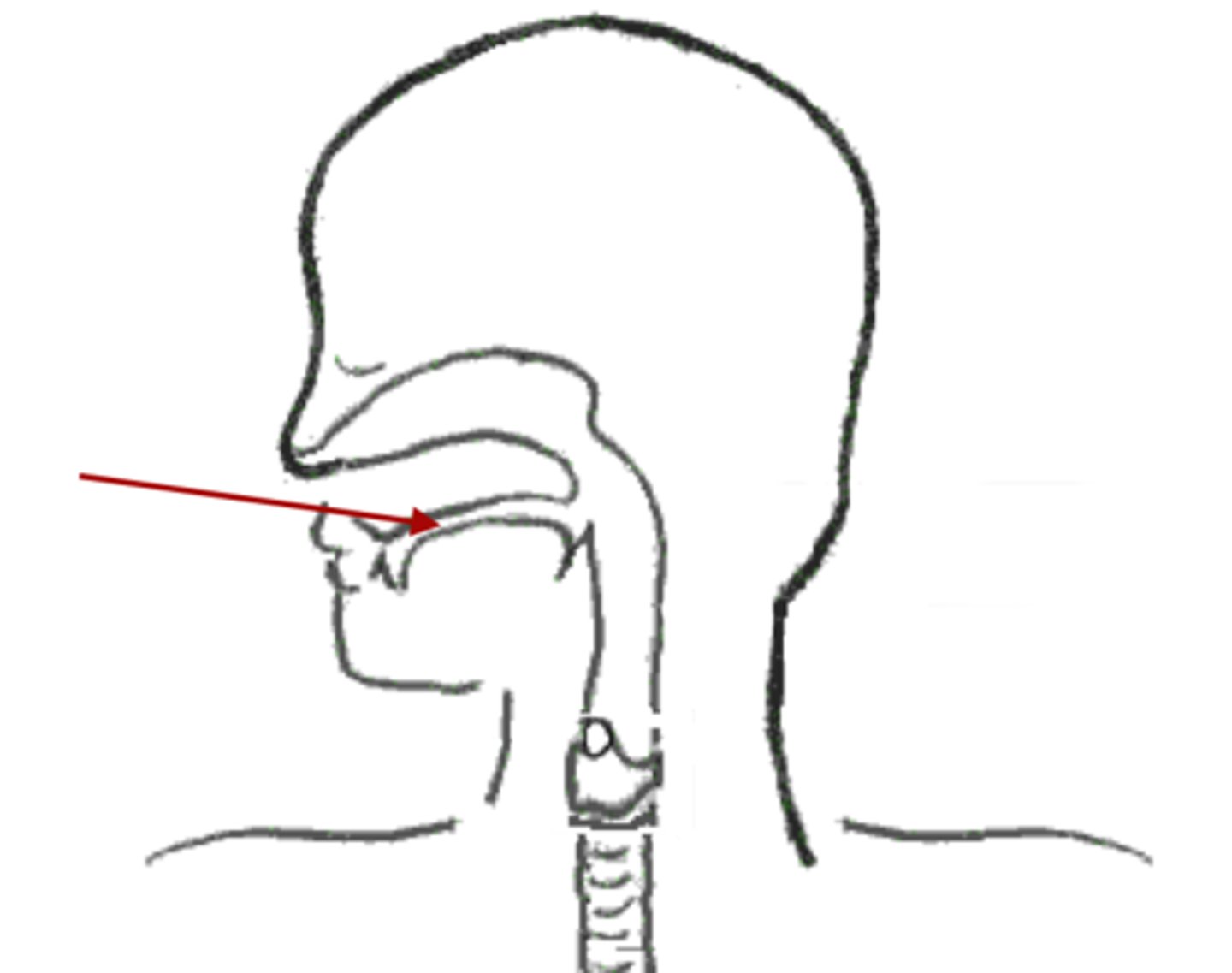
Pharynx
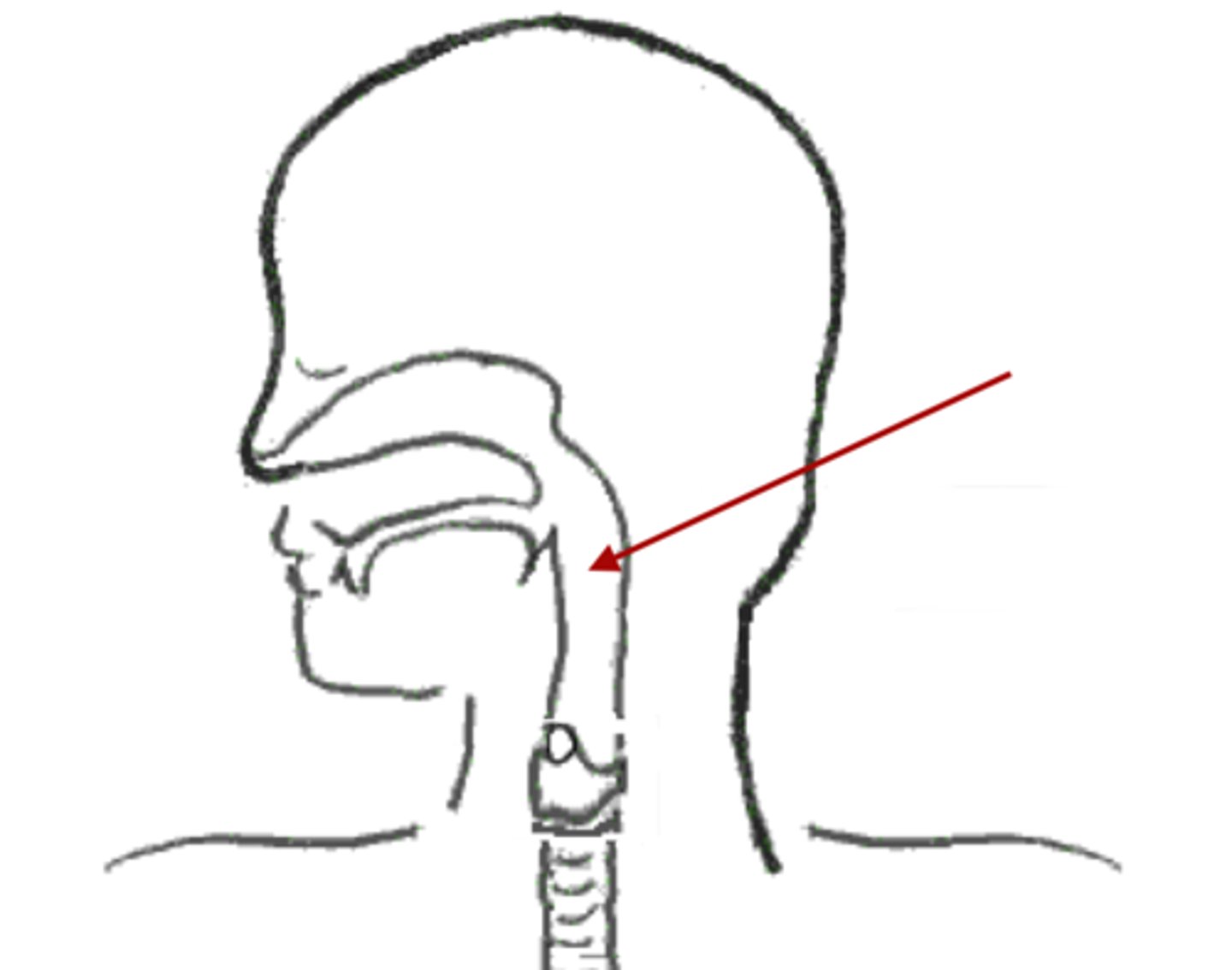
Larynx
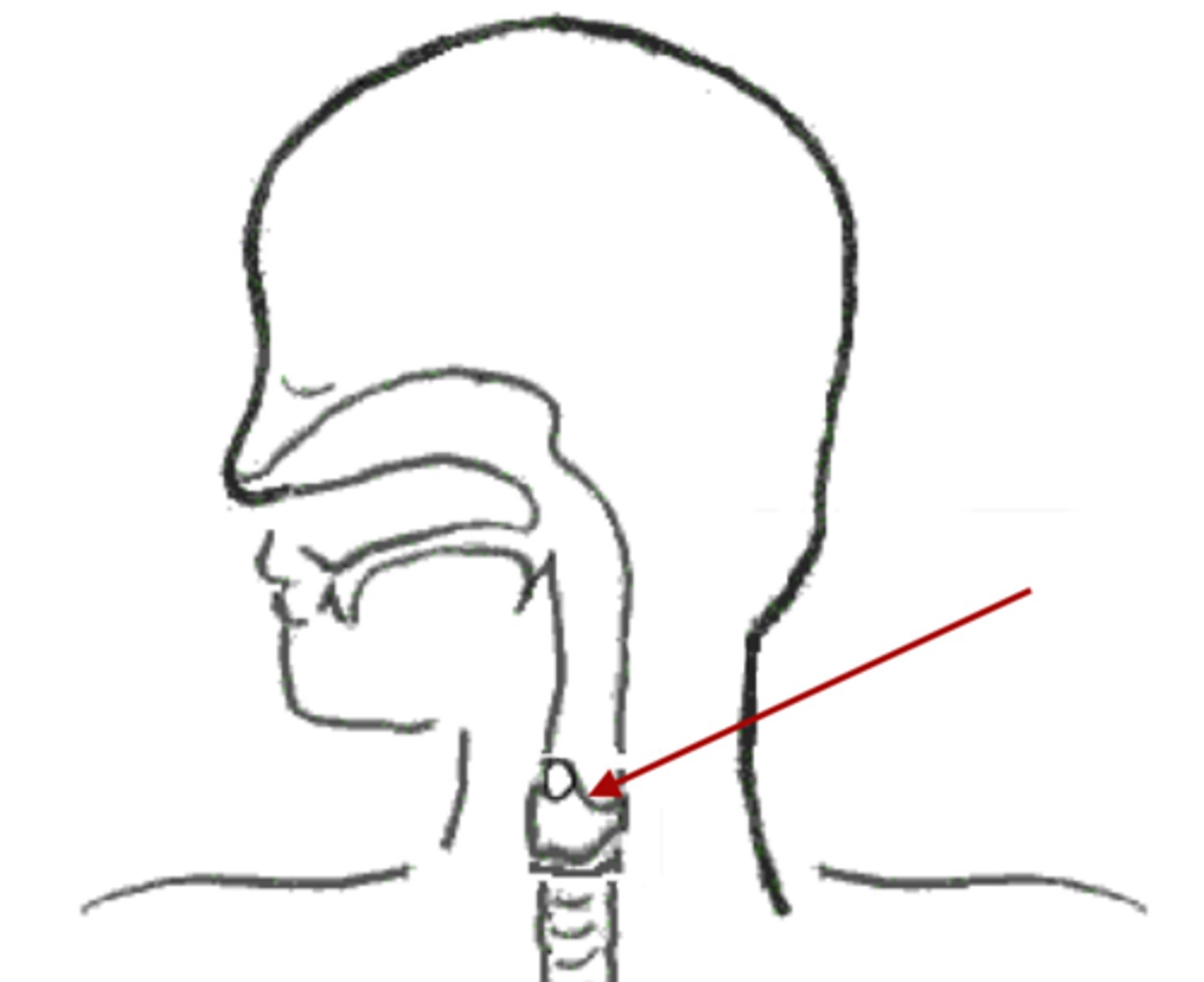
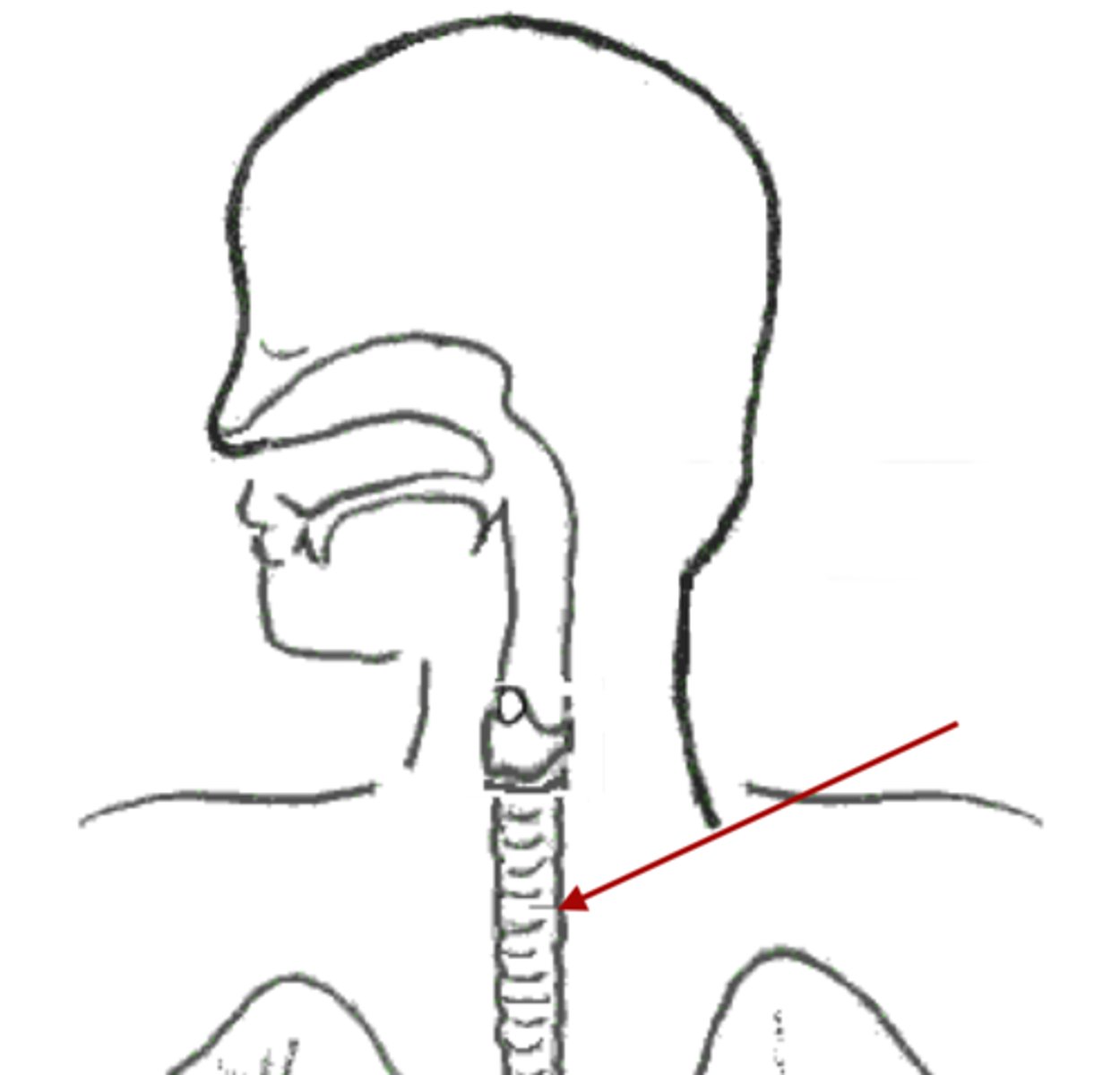
Trachea