Estimates of Breeding Values
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Which part of the phenotype equation is transmittable from parent —> offspring
P = A + D + I + E
A (additive genes) which is also breeding value (BV)
Why don’t parents transmit the same genes to all offspring?
Due to segregation during meiosis or Mendelian sampling
So estimated BV (EBV) = ½ BV sire + ½ BV dam
Actual BV of an individual is not known so how can we gain information?
From own performance
Performance of its relatives
Why use information of relatives?
Relatives have some genes in common
Relatives are related by descent
What is progeny?
Parent-offspring relationship
Confidence in the estimate of BV increases when?
By using the performance of its progeny and siblings
More relatives are used in the BV estimate
More relatives who are closely related to the individual are used in the BV estimate
Which type of relatives are appropriate in measuring BV in
Traits which can be measured only in one sex
Other traits
Carcass traits
Longevity or total lifetime productivity
Traits which can be measured only in one sex:
Progeny
Sibling
Other traits:
Progeny
Sibling
Carcass traits: Sibling
Longevity or total lifetime productivity:
Progeny
Sibling
What is the average effect of alleles (a)
How much an individual allele contributes to a trait on average in a population
What is the difference between genetic (phenotype) and breeding value (pass to offspring) and why?
Difference: Dominance deviation
Why: Offspring gain combination of alleles from both parents so it isn’t guaranteed that the same dominance interaction will occur
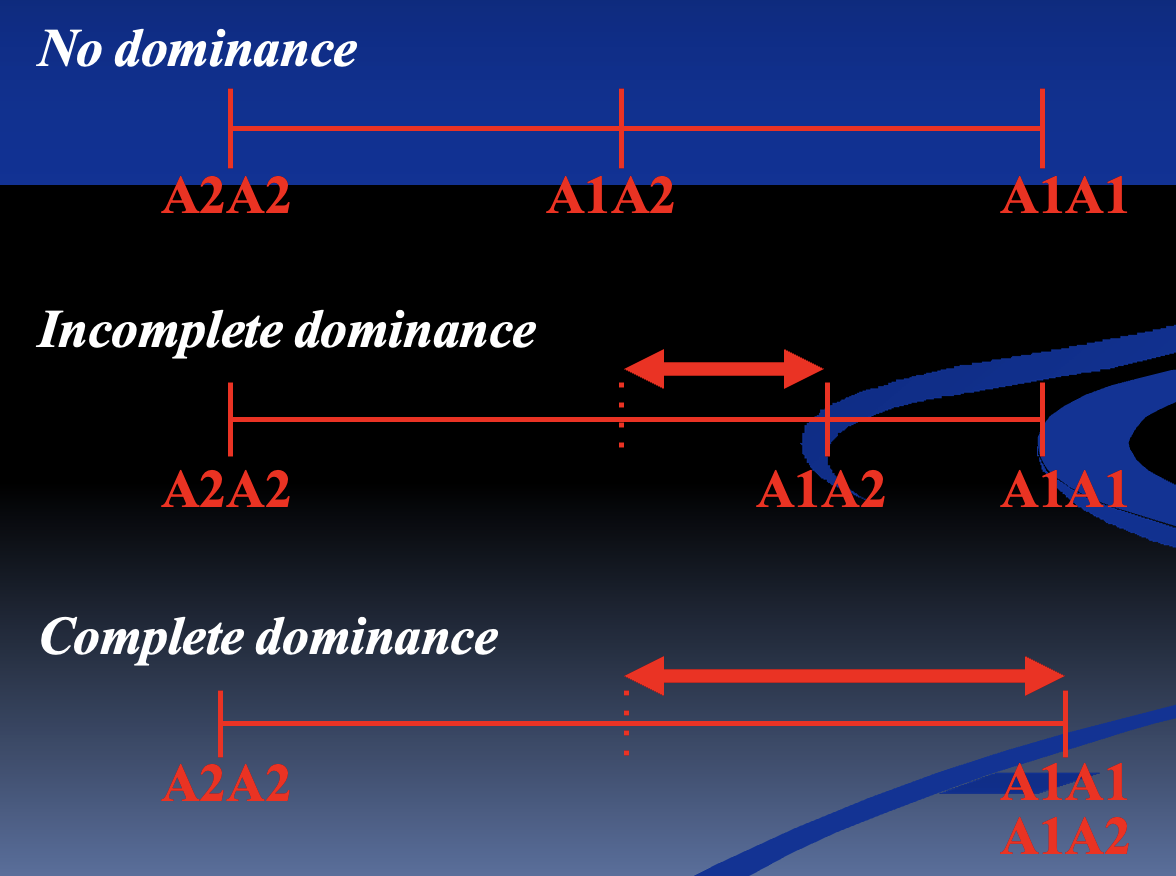
Dominance Deviation
What is dominance deviation
What does it mean where there’s no dominance
How does it affect breeding value predictions?
What happens in incomplete dominance?
How does it affect breeding value predictions?
What happens in complete dominance?
Why is it an issue for breeding value predictions?
What is dominance deviation: The difference between phenotype of a heterozygote and expected average of 2 homozygotes
What does it mean where there’s no dominance: Heterozygote lies exactly halfway between the 2 homozygotes, meaning there’s no dominance deviation
How does it affect breeding value predictions: Means that BV is highly accurate because all genetic effects are additive and passed on predictably
What happens in incomplete dominance: Heterozygote’s phenotype is closer to one homozygote (not exactly in middle) so there’s some dominance deviation
How does it affect breeding value predictions: Reduces accuracy of BV slightly as some of phenotype is due to non-additive effects (dominance)
What happens in complete dominance: Heterozygote has same phenotype as dominant homozygote, so large dominance deviation occurs
Why is it an issue for breeding value predictions: Because dominance is not consistently inherited like additive effects
What is breeding value?
Sum of all average effects of alleles on all relevant traits of an individual as a parent
What is estimated transmitting ability?
½ of BV
Why could there be a difference in phenotype among offspring of the same family?
Due to
Segregation and independent assortment of genes
Environmental effect
Estimating Breeding Value with Sibling Info
What happens to the accuracy of BV estimation as the number of sibs increases?
Why does each additional sibling contribute less accuracy to BV estimation?
For which traits is sibling information most useful?
Why
What happens to the accuracy of BV estimation as the number of sibs increases: Accuracy increases but each additional sibling contribute less than previous one
Why does each additional sibling contribute less accuracy to BV estimation: Because each new sibling adds less new data
For which traits is sibling info most useful: Traits with low heritability (fertility, disease resistance)
Why: Siblings average out environmental effects