Drugs affecting blood flow
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
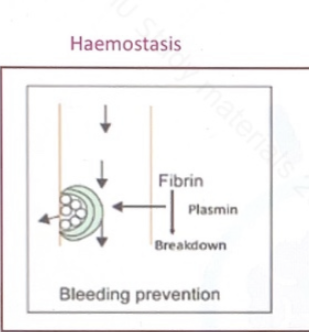
What is hemostasis?
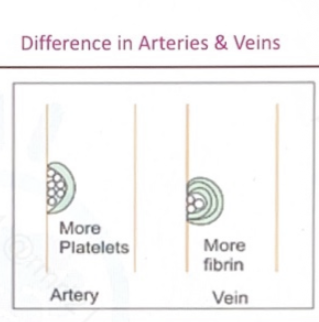
Drug categories that affect blood flow
Anti-platelet drugs
Oral anti-coagulants /anti-fibrin drugs
Injectable anti coagulants/ thrombin inhibitors
Thrombolytic drugs
What injured blood vessels release?
Thromboxane A2 - vasoconstrictor and platelet activator
ADP (adenosine diphosphate) - promote platelet aggregation
GP receptors ( GP lIb/IIIa ) - makes sticky ( Exteriorization)
Thrombin - convert fibrinogen to fibrin→platelet plug formation
Types of Antiplatelet drugs
Drugs acting on Thromboxane A2 - Aspirin
Drugs acting on ADP - Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine
Drugs acting on Gp IIb/IIIa - Abciximab, Tirofiban, Eptifibatide
Drugs acting on PAR-1 receptors of Thrombin - Atopaxar, Vorapaxar
TXA2
ADP
Thrombin
Clopidogrel
Ticlopidine
Abciximab
Tirofiban
Eptifibatide
Atopaxar
Vorapaxar
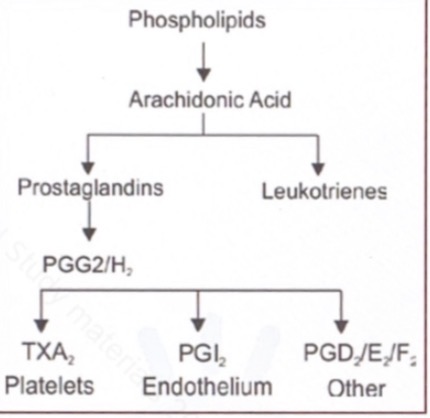
Prostaglandins / arachidonic acid pathway
Arachidonic acid pathway
Cell membrane phospholipids release arachidonic acid via phospholipase A₂ when cells are stimulated (injury, inflammation).
Arachidonic acid is metabolized mainly by two pathways: cyclo-oxygenase (COX) → prostaglandins/thromboxanes, and lipoxygenase (LOX) → leukotrienes.
In the COX pathway, arachidonic acid is first converted to unstable intermediates PGG₂ and PGH₂.
PGH₂ is the common precursor for several prostanoids, depending on the tissue-specific enzymes present.
In platelets, PGH₂ is converted to thromboxane A₂ (TXA₂) → promotes platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction.
In vascular endothelium, PGH₂ is converted to prostacyclin (PGI₂) → inhibits platelet aggregation and causes vasodilation.
In other tissues, PGH₂ forms PGE₂, PGD₂, and PGF₂α, which mediate inflammation, pain, fever, smooth muscle contraction, and other local effects.
Clopidogrel
Ticlopidine
Prasugrel
Inhibits CYP2C19 and reduces effect ( because clopidogrel activated by CYP2C19)
Pantoprazole
Rabeprazole
Cangrelor
Ticagrelor
Example of Drugs acting on GP IIb/IIIa
Abciximab
Tirofiban
Eptifibatide
Oral
Parenteral / injectable
Oral anticoagulant group include
Vitamin K inhibitors
Direct thrombin inhibitors
Factor Xa inhibitors
Drugs in vitamin K inhibitors
Warfarin
Dicumarol
Clotting factors requiring vitamin K to become active
Factors II ,VII ,IX ,X
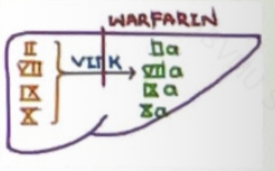
Gamma carboxylation of clotting factors II,VII,IX,X and activate them
Activation of anticoagulant proteins C,S
Protein C
Protein S
VKOR (vitamin K epoxide reductase)
Hypercoagulable state / Dermal vascularnecroosis / increased clotting
Occur for initial 1-2 days
Properties of Warfarin
Oral anticoagulant
Inhibit vitamin k
Need 4-5 days to produce action
Mainly for maintainence purpose
C/I in pregnancy →prevent osteocalcin action →Fetal warfarin syndrome → skeletal deformity (Microcephaly, Nasal hypoplasia, Microophthalmia)
Monitered by PT/INR
Microcephaly
nasal hypoplasia
microphthalmia
PT / INR
INR remains same across all labs but PT have different values in different labs

Four factor complex / Prothrombin factor complex contains which factors
IIa
VIIa
IXa
Xa
If both four factor complex and fresh frozen plasma unavailable then
Whole blood is given
Stop warfarin and give vitamin K
Stop warfarin and give four factor complex
Enzyme inhibitors
Drugs displacing warfarin from PPB sites
Antimicrobials
Liver disease
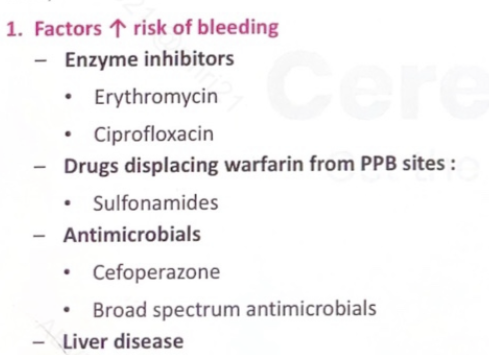
Erythromycin
Ciprofloxacin
Cefoperazone
Broad spectrum antimicrobial
Rifampicin
Carbamazepine
Idarucizumab (monoclonal antibody)
Direct factor Xa inhibitors drugs
Rivaroxaban
Apixaban
Edoxaban
Betrixaban
Riveroxaban
pneumonic - RiverOXABAN
River - Reversible
O - Oral
XA - Xa
B - Blocker
AN - Antagonist
Antidote for factor Xa inhibitors overdose
Types of injectable anti-coagulants
Indirect thrombin inhibitors
Direct thrombin inhibitors
unfractioned Heparin (UFH)
Low moleculer weight heparin (LMWH)
Fondaparinux
Immediate (in acute conditions)
Pneumonic - BOTHA
Bleeding
Osteoporosis
Thrombocytopenia ( HIT )
Hyperkalemia
Alopecia
HIT occurs how many days after starting heparin
Difference in Warfarin and HEparin
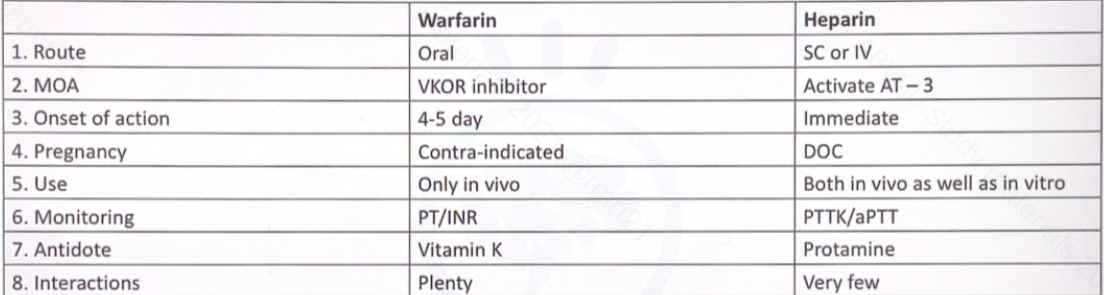
Warfarin - slow
Heparin - immediate
Direct thrombin inhibitor (injectable)drugs
Bivalirudin
Argatroban
Melagatran