MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
WHAT IS THE DEFINITION OF ECONOMICS ?
the study of how to use scarce resources to satisfy unlimited human wants
BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ECONOMIC SYSTEM
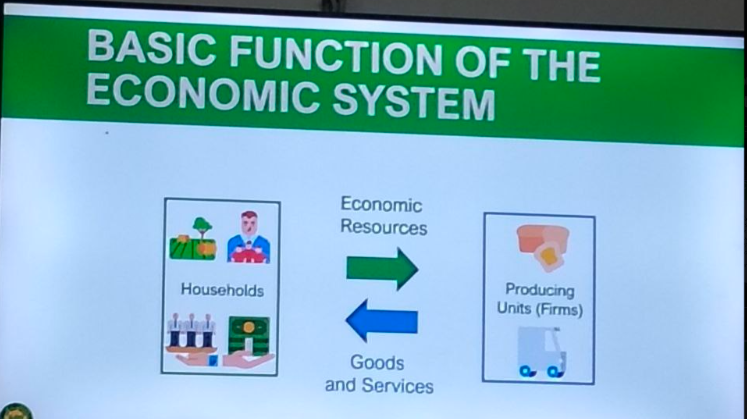
→ has the factors of production (Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship)
Households
→ supplied by the households (raw materials)
→ will supply the goods and services to the households,
Producing Units (Firms)
BASIC CONCEPT IN ECONOMIC

___ are tangible
goods
_____ are intangible
services
the act of making goods and services is called ___
production
the act of using goods and services to satisfy wants is called _____
consumption
_______ refers to the limited availability of resources relative unlimited human wants
Scarcity
because of scarcity, we must make _____
Choices
_____ represents the value of the best alternative forgone when making a choice
Opportunity Cost
The three fundamental questions every economy had to answer
✓ What should be produced?
✓ How should goods and services be produced?
✓ For Whom should goods and services be produced?
WHAT IS AN ECONOMIC INCENTIVES?
refers to rewards or penalties created to influence human behavior to produce desired results.
whar are the 4 economic incentives?
Positive Incentives
Negative Incentives
Market-Based Incentives
Non-Market Incentives
encourage desired behaviors by offering rewards or benefits
Positive Incentives
discourage undesirable behaviors by imposing costs or penalties
Negative Incentives
rely on market mechanisms to achieved desired outcome
Market-Based Incentives
operate outside traditional market forces, relying on social, moral, or psychological factors to influence behavior
Non-Market Incentives
MACROECONOMIC TOOL (PESTEL)
Political (P)
Economic (E)
Social (S)
Technological (T)
Environmental (E)
Legal (L)
ceteris paribus
all else equal
WHAT IS DEMAND?
the good or service consumers are willing and able to buy at various prices in a given time period
LAW OF DEMAND
When price goes up, quantity demanded falls and vice versa
DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND
Price of Good or Service
Buyer's Income
Price of related goods (substitutes/complements)
Consumer preferences
Future expectations
DOWN-SLOPING DEMAND CURVE
Is a graph that displays the change in demand resulting from a price change
It is a visual representation of the law of demand
WHAT IS SUPPLY?
The quantity of a good or service producers are willing and able to sell at various prices during a given time period
LAW OF SUPPLY
When price increases, quantity supplied increases, and vice versa
DETERMINANTS OF SUPPLY
Cost of production
Technology
Government policies (taxes, subsidies)
Expectations of future prices
Number of Sellers
UPWARD-SLOPING SUPPLY CURVE
Illustrates the law of supply or how price changes affect the quantity a seller provides
Usually depicted as an upward-sloping line — as prices increase, sellers are more willing to make more goods and services available