AP Macro Unit 3 Definitions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
LRAS
Long Run Aggregate Supply
considers Aggregate Supply/productive capacity when @ FULL EMPLOYMENT no matter price level
goes vertical; called YFE
Caused by CIGNX
SRAS
Short-Run Aggregate Supply
considers productive capacity of aggregate supply based on temporary changes in price level
caused by two factors
Sticky Prices
Sticky Wages
Sticky Wages
When wages are not rising at the same rate as inflation
Will first have to wait for negotiation
In turn, companies can produce more product since wages are cut
ONLY CHANGES IN LRAS
Sticky Prices
When companies do not raise the price level in equilibrium to the rate of inflation
THEREFORE, there is an expectation that production is more rapid to meet demand, since ppl are more willing to buy with low prices
MPC
Marginal Propensity to Consume
This is how much people purchase from what they earn per dollar
*Both MPC and MPS have to add up to 1
MPS
Marginal Propensity to Save
This is how much people save in what they earn per dollar
*Both MPS and MPC have to add up to 1
Government Spending Multiplier
More effective in raising GDP over a reduction in taxes
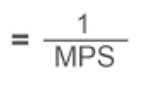
Tax Multiplier
Fraction of dollar spent on TAXES
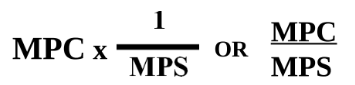
Lags in Fiscal Policy
They can lead to inflationary gaps withing the economy, hurting it even more
Aggregate Demand
The relationship between the Real GDP and price level of goods (indicator for a country’s economy)
IRE (in terms of Aggregate Demand)
Interest Rate Effect
Real Wealth Effect
Exchange Rate Effect
These are the outcomes when price levels increase/change, affecting GDP
Interest Rate Effect
When prices increase, money is worth less and people pull out cash, leading to banks raising interest rates to mitigate pull-outs
Real Wealth Effect
When prices increase, the money saved will be worth less, leading to less purchasing power
Exchange Rate Effect
When prices rise, a country’s goods become more expensive, so less foreigners purchase and therefore weakens the GDP
Automatic Stabilizers
Temporary action to mitigate inflation effects on the economy during a recession
Usually comes in the form of transfer payments and less taxes due to ppl getting laid off
Helps give govn’t time to implement better fiscal policies
Positive Demand Shock
A sudden demand shock in the demand for a product or service
Causes AD to move right & create new short-run equilibrium
Effects:
Higher prices
Inflationary Gap
Increased output
Causes AD to move to AD2 →SR Equilibrium
Inflationary Gap (Positive Output)
When there is a difference between how much we should be producing (YFE) and how much is actually being produced (Y1)
Recessionary Gap (Negative Output)
When the Short-Run Equilibrium is to the LEFT of LRAS
indicates a recssion
Shifters of Aggregate Demand
Consumer Spending
Investment
Government Spending
Net exports (export-import)
Shifters of Aggregate Supply (RAP)
Resource Prices
Price of Domestic + Imported Resources
Supply shocks
Inflationary Expectations
Actions of Government
Taxes
Subsidies
Regulations
Productivity
Technology
Labor Force & Capital Stock
Negative Supply Shock
Shifts in LRAS
Change in resource quantity or quality
Change in technology
SAME SHIFTERS AS PPC (RAP)