Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes & Chromatin Structure Module 10 Final
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
telomere
A series of repeated sequences found at the ends of a DNA molecule, forming a cap at each end of the chromosome.
nucleosomes
The lowest level of chromosome organization, consisting of DNA wrapped around a core complex of histone proteins.
histones
A group of highly conserved proteins that help package DNA into nucleosomes.
octamer
A complex formed by two copies each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
linker DNA
The part of DNA that connects one nucleosome core particle to the next.
30-nm fibers
Higher-order structures formed by the organization of nucleosomes.
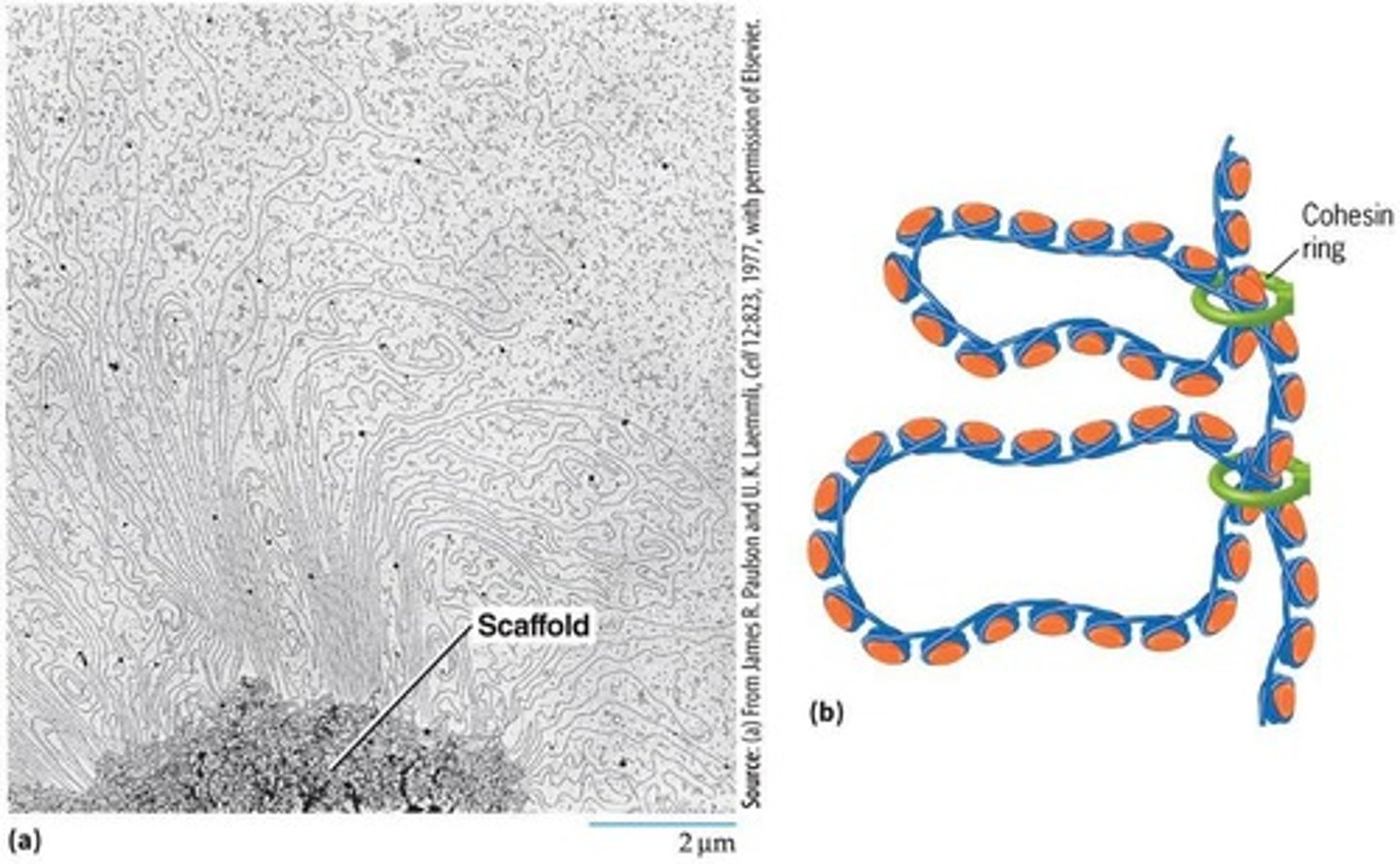
mitotic chromosomes
Highly compacted structures formed from chromatin when cells prepare for mitosis.
cohesin
A protein that holds replicated DNA molecules together during mitosis and maintains DNA loops.
euchromatin
The loosely packed form of chromatin that returns to a dispersed state after mitosis.
heterochromatin
The tightly compacted portion of chromatin that remains condensed during interphase.
constitutive heterochromatin
Heterochromatin that remains condensed all the time, found mostly around centromeres and telomeres.
facultative heterochromatin
Heterochromatin that is inactivated during certain phases of the organism's life or in certain types of differentiated cells.
chromatin fibers
Structures composed of DNA and associated proteins that make up chromosomes.
basic amino acids
Amino acids such as arginine and lysine that have a positive charge and are abundant in histones.
DNA
The molecule that contains the genetic instructions for the development and function of living things.
chromosomes
Structures that contain a single, continuous DNA molecule and are composed of chromatin.
cell division
The process by which a cell replicates its DNA and divides into two daughter cells.
mitotic spindle
A structure that separates chromosomes during cell division.
interphase
The phase of the cell cycle when the cell is not dividing and chromatin is loosely organized.
looped domains
Higher-order structures formed by the organization of 30-nm fibers.
chromosome packaging
The process of organizing DNA into a compact structure to fit within the nucleus.
Barr body
A condensed heterochromatic clump of one of the two X chromosomes in females that is not transcriptionally active.
Telomere
A cap at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes formed by repeated DNA sequences and specialized proteins, essential for complete replication.
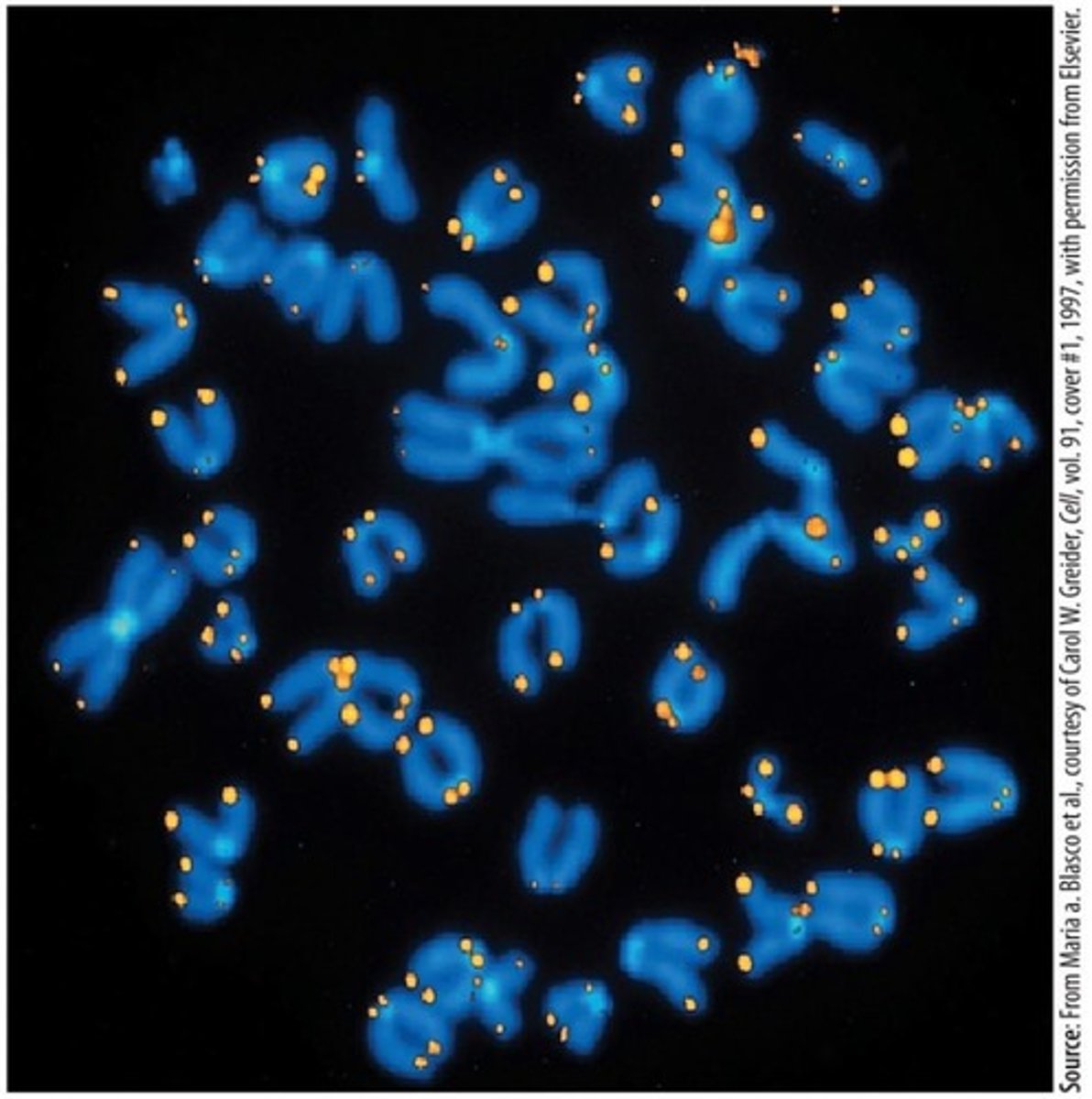
Telomere sequence
The repeated DNA sequence TTAGGG, which can be found 500 to 5000 times at the ends of chromosomes.
Significance of telomeres
They prevent the progressive loss of genetic material during cell division, protect chromosome ends from degradation, and maintain genome stability.
Gene regulation
The process by which genes are turned on and off through interactions with regulatory proteins.
Levels of gene expression regulation
Four levels: transcriptional control, processing control, translational control, and posttranslational control.
Posttranslational control
Regulation of protein stability after translation, often influenced by the amino acids present.
Protein stability
Determined by factors such as the amino acids on the N-terminus and specific residues that signal for degradation.
Proteasome
A hollow, cylindrical structure that degrades proteins marked for destruction.
Ubiquitin
A small protein that is transferred to proteins being degraded, marking them for recognition by the proteasome.
Polyubiquitination
The process of attaching multiple ubiquitin molecules to a protein, signaling it for degradation by the proteasome.
N-terminus
The end of a polypeptide chain that has a free amino group, which can influence protein stability.
Short-lived polypeptides
Polypeptides that terminate in amino acids like arginine or lysine, which are typically marked for rapid degradation.
Cell cycle proteins
Proteins that are marked for destruction at specific times during the cell cycle when certain residues are phosphorylated.
Chromosome replication
The process by which chromosomes are duplicated before cell division.
Effect of telomere replication failure
If cells cannot replicate the ends of their DNA, the chromosomes should get shorter with each round of cell division.
Question: What is the term for a series of repeated sequences found at the ends of a DNA molecule?
a) telomere
Question: If cells cannot replicate the ends of their DNA, what should happen with each round of cell division?
d) The chromosomes should get shorter.
Repressible operon
An operon where the repressor cannot bind to the operator DNA unless it is complexed with a specific factor that functions as a corepressor.
Inducible operon
An operon that is turned on in the presence of an inducer, such as lactose.
Trp operon
A repressible operon that is regulated by the presence of tryptophan.
Lac operon
An inducible operon that regulates the production of enzymes needed to degrade lactose.
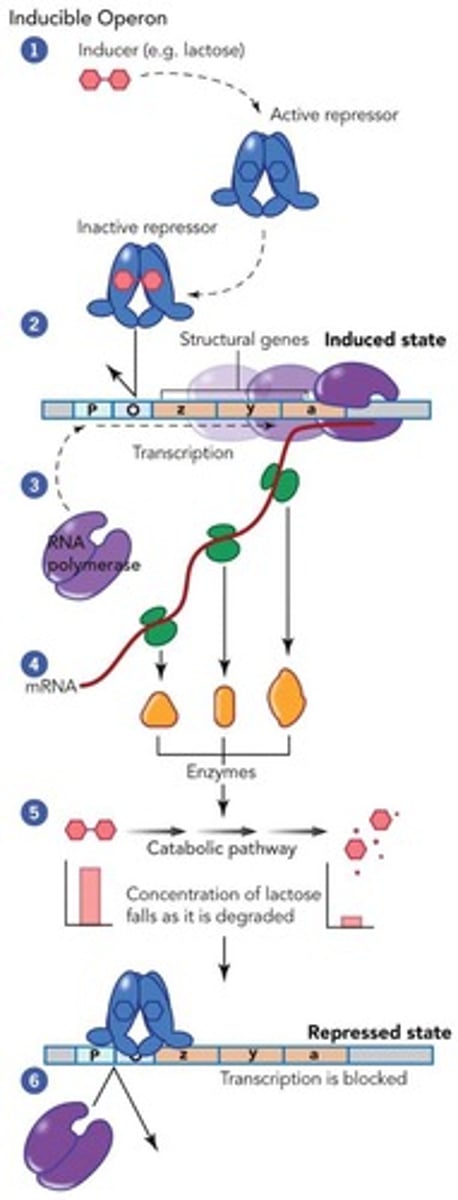
Corepressor
A specific factor that allows the repressor to bind to the operator in a repressible operon.
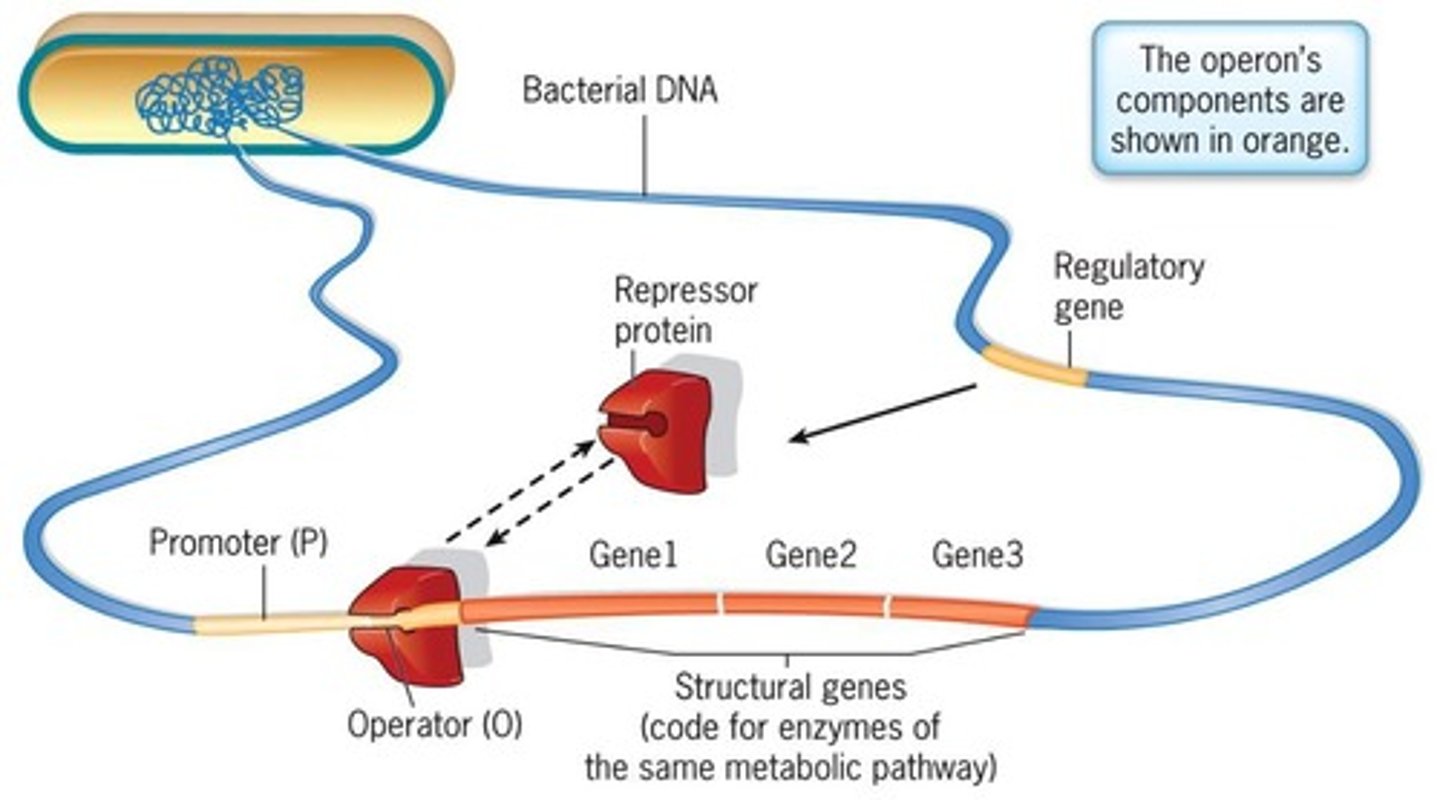
Operator
A site next to the promoter where the regulatory protein can bind.
Promoter
The region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
Structural genes
Genes that code for the enzymes involved in a metabolic pathway.
Regulatory gene
A gene that encodes the repressor protein which regulates transcription.
Repressor protein
A protein that binds to a specific DNA sequence to determine whether a particular gene is transcribed.
Polycistronic mRNA
A single mRNA molecule that is transcribed from an operon and translated into separate polypeptides.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Catabolite repression
A regulatory mechanism where the presence of glucose represses the production of various catabolic enzymes.
Positive control
A regulatory mechanism where the presence of a substance, like glucose, enhances the expression of genes.
Tryp operon repressor
In the presence of tryptophan, it changes its conformation, is activated, and binds to DNA at the operator.
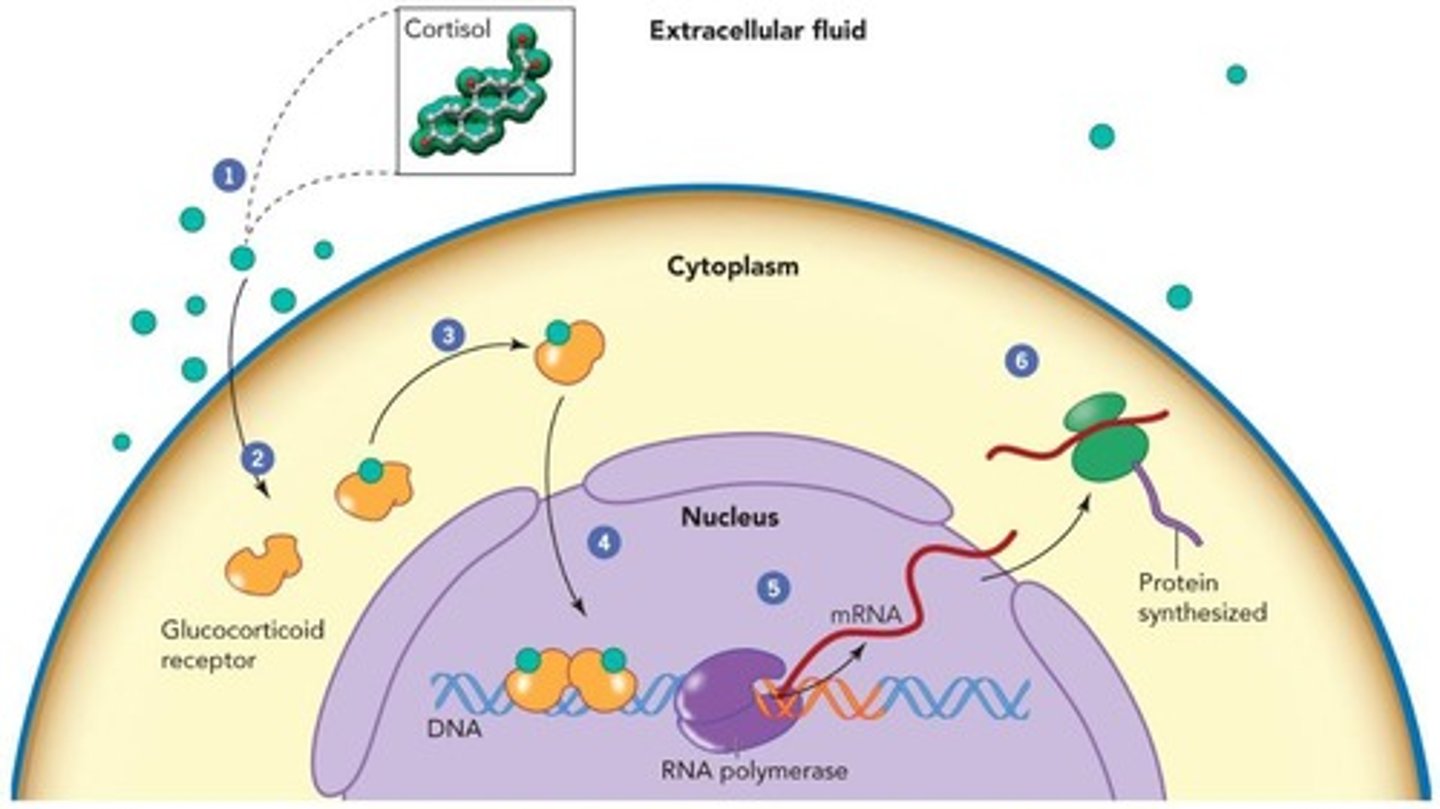
Transcription
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
Translation
The process of synthesizing polypeptides from mRNA.
Bacterial genome
The circular, double-stranded DNA that contains the genetic information of prokaryotic organisms.
Gene regulation
The mechanisms that control the expression of genes.
Nuclear pore complex
A structure that regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus.
Enzymes of a metabolic pathway
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions within a cell.
Glucose in the medium
Acts to repress the production of various catabolic enzymes.
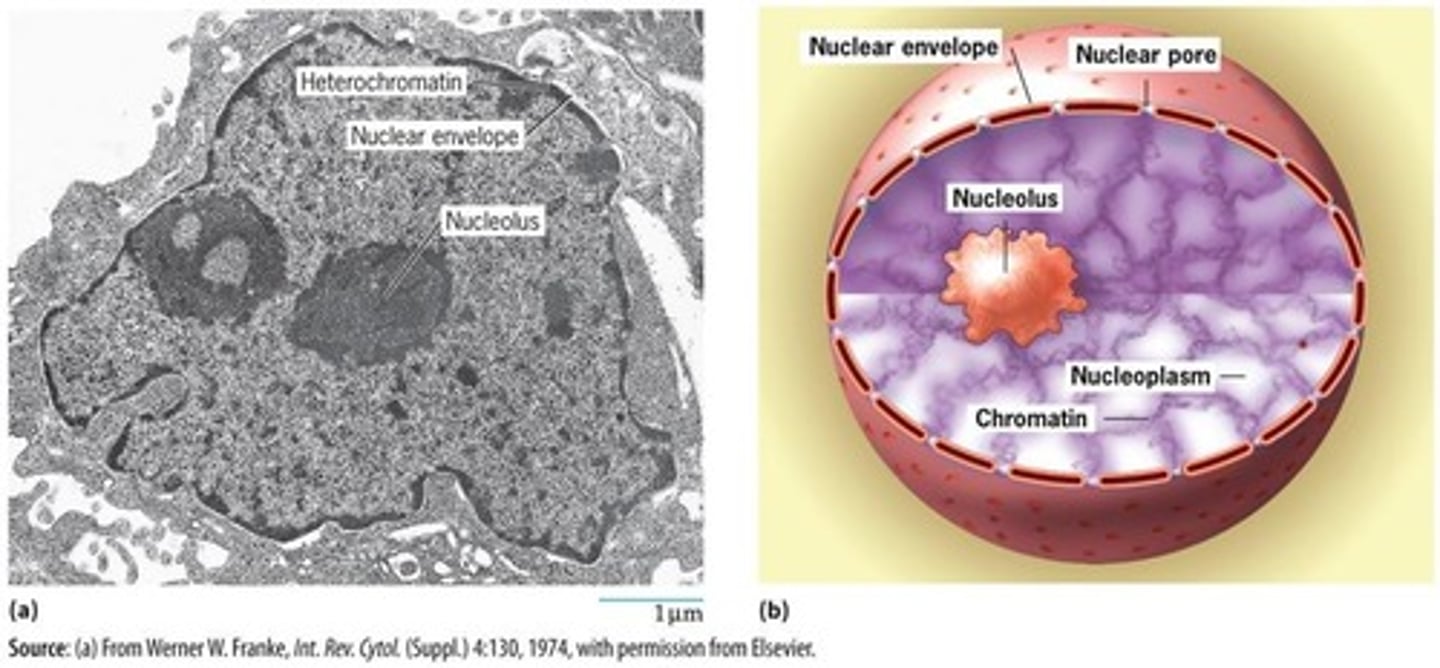
Nuclear Envelope
A barrier that houses a typical eukaryotic non-dividing nucleus.
Chromosomes
Present as highly extended nucleoprotein fibers of chromatin (DNA-protein complexes).
Nucleoli
Site for synthesis of ribosomal RNA and the assembly of ribosomes.
Nucleoplasm
The fluid where solutes are dissolved within the nucleus.
Nuclear Pores
Gateways in the nuclear envelope that regulate transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Nuclear Lamina
Provides mechanical support to the nuclear envelope and serves as a site of attachment for chromatin fibers.
Filaments of the nuclear lamina
Made of lamins, members of the same superfamily of polypeptides that assemble into intermediate filaments of cytoplasm.
Phosphorylation/Dephosphorylation
Regulates the integrity of the nuclear lamina.
Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC)
A doughnut-shaped structure composed of ~30 proteins called nucleoporins.
Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS)
Targets cytoplasmic proteins for transport into the nucleus.
Importins
Transport receptors that move molecules from the cytoplasm into the nucleus and recognize NLS in proteins.
Exportins
Transport receptors that move molecules from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and recognize Nuclear export signals (NES).
Ran proteins
GTPases that assist with the movements of proteins through the nuclear pore complex.
Ribonucleoproteins (RNPs)
The form in which mRNAs, rRNAs, snoRNAs, miRNAs, and tRNAs move through the nuclear pore complex.
Mature mRNAs
Only fully processed mRNAs are capable of nuclear export; unspliced introns retain mRNA in the nucleus.
trp operon repressor
In the presence of tryptophan, it changes its conformation, is activated, and binds to DNA at the operator.
Nucleus
Organized organelle containing genetic material.
Chromatin
DNA-protein complex that forms chromosomes.
Transcription Factors
Proteins regulating gene expression by binding DNA.
Transcriptional Control
Regulation of gene expression at transcription stage.
Differential Gene Expression
Variation in gene expression across different cell types.
Topologically Associated Domains (TADs)
Regions of DNA that interact more strongly internally.
Speckles
Irregular nuclear domains for splicing factor storage.
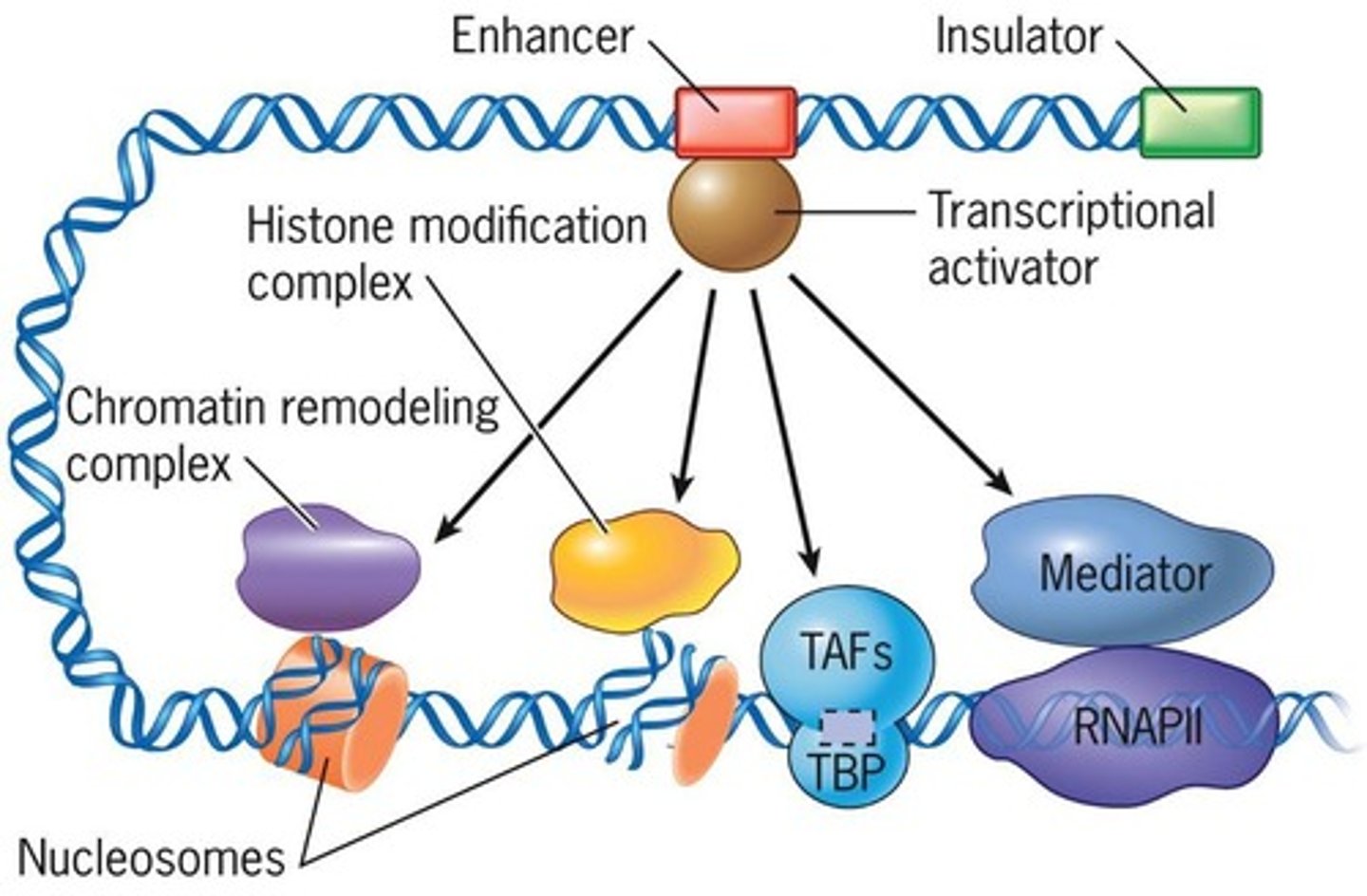
Enhancers
DNA elements that increase transcription levels.
Coactivators
Proteins that assist transcriptional activators in gene expression.
Histone Acetyltransferases (HATs)
Enzymes adding acetyl groups to histones.
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)
Enzymes removing acetyl groups, repressing transcription.
DNA Methylation
Addition of methyl groups to DNA, silencing genes.
Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR)
Nuclear receptor that activates gene expression via GRE.
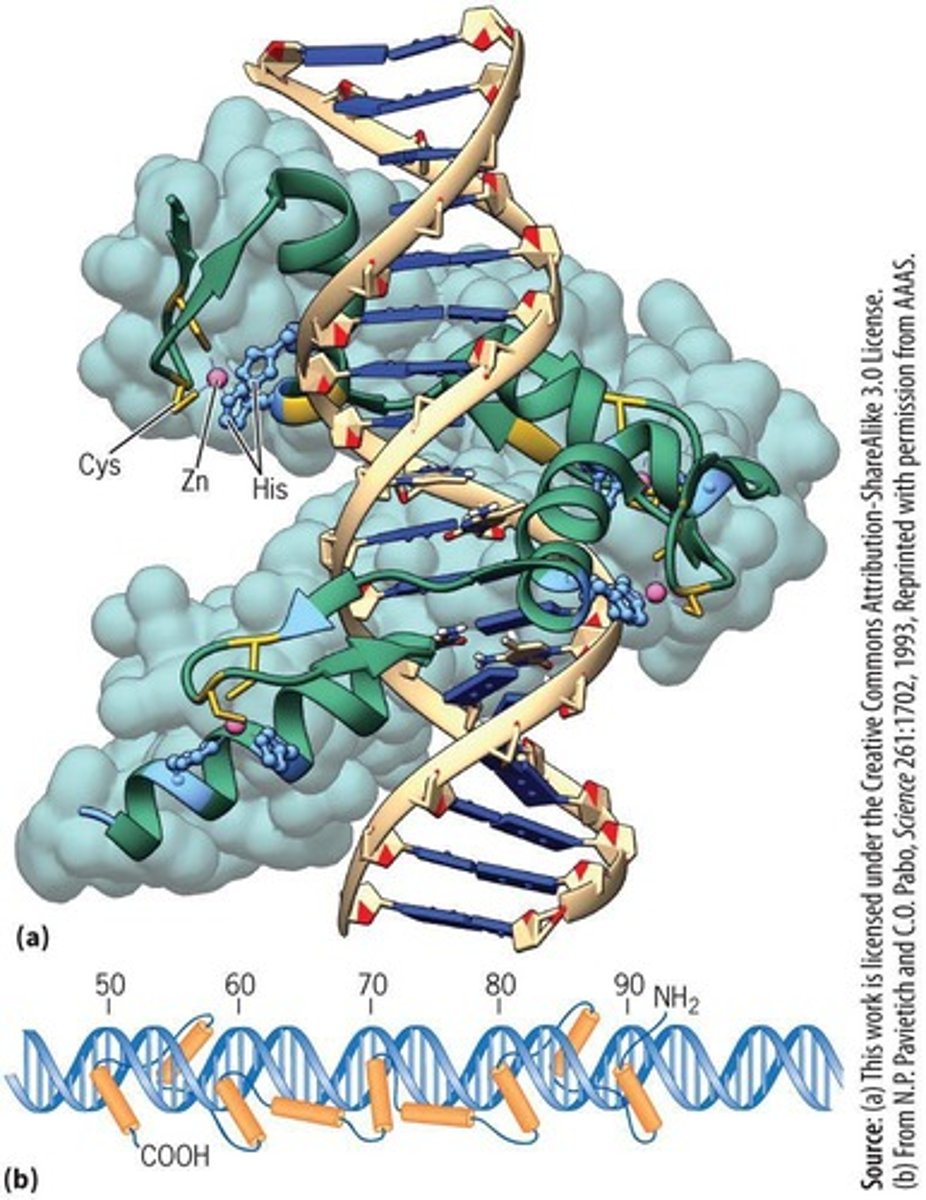
Zinc-Finger Motif
Transcription factor structure coordinating zinc ions.
Helix-Loop-Helix (HLH) Motif
Transcription factor structure with two α-helices.
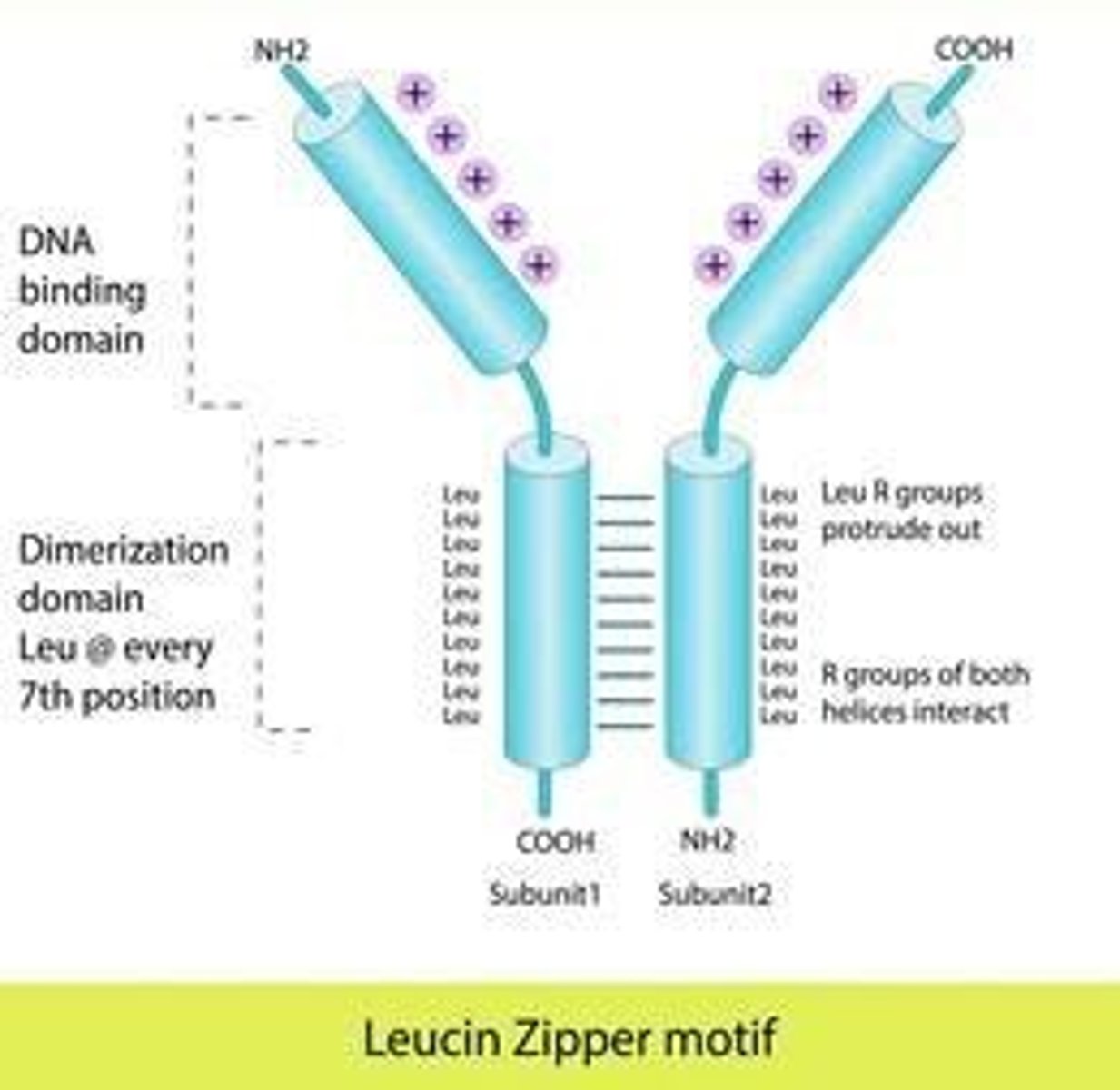
Leucine Zipper Motif
Transcription factor structure forming coiled-coil dimers.
Translational Control
Regulation of gene expression at translation stage.
Untranslated Regions (UTRs)
mRNA regions mediating translational control.
Transcriptional Repression
Inhibition of gene expression during transcription.
Methyl-Transferases
Enzymes adding methyl groups to DNA.
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme synthesizing RNA from DNA template.
Cajal Bodies
Nuclear structures involved in RNA processing.
PML Bodies
Nuclear bodies associated with gene regulation.