Sound and Energy Transfer key terms CIE Checkpoint
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Oscillation
A repeated back-and-forth movement around a central point like a vibration.
Transverse wave
A wave where oscillations move at right angles to the direction of the wave.
Longitudinal wave
A wave where oscillations move in the same direction as the wave.
Compression
The region in a longitudinal wave where particles are close together.
Rarefaction
The region in a longitudinal wave where particles are spread apart.
Amplitude
The maximum distance a wave moves from its rest position.
Frequency
The number of waves passing a point each second (measured in hertz, Hz).
Wavelength
The distance between two identical points on a wave (e.g., peak to peak).
Peak/Crest
The highest point of a wave.
Trough
The lowest point of a wave.
Pitch
How high or low a sound is, related to frequency.
Loudness
How loud a sound is, related to amplitude.
Waveform
The shape of a wave when drawn on a graph.
Constructive interference
When two waves meet and combine to make a bigger wave.
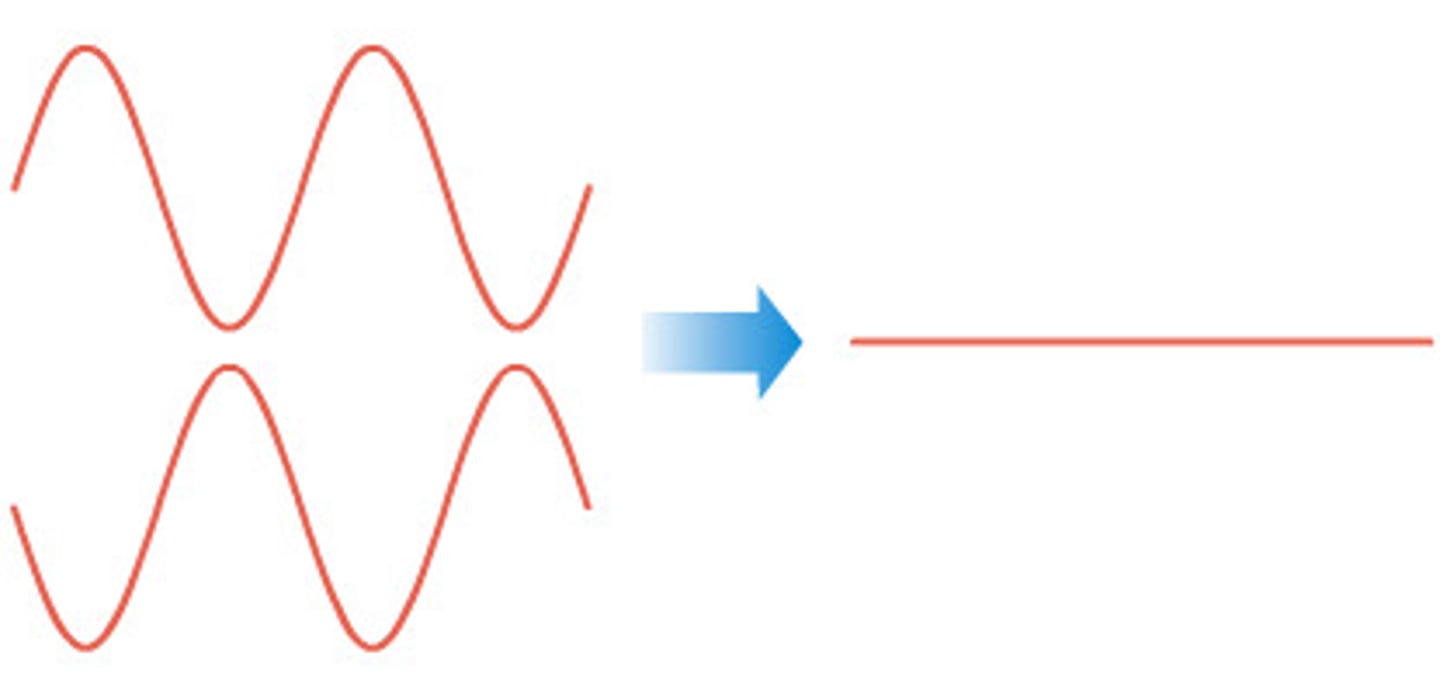
Destructive interference
When two waves meet and cancel each other out.
In phase
When two waves line up with peaks and troughs matching.
Out of phase
When two waves do not line up (peaks match troughs).
Superpose
When two waves overlap.
Superposition
The effect of two or more waves overlapping.
Reinforce
When waves add together to make a bigger wave.
Cancel
When waves add together to make a smaller wave or zero.
Law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or stored.
Energy store
A way energy is kept, such as chemical, thermal, or kinetic.
Chemical store
Energy stored in fuels, food, or batteries.
Kinetic energy
Energy of a moving object.
Thermal energy
Energy stored in hot objects.
Gravitational potential energy
Energy stored in an object raised above the ground.
Elastic potential energy
Energy stored in a stretched or compressed object.
Energy dissipation
Energy spreading out, often as heat to the surroundings.
Thermal store
Energy stored in a warm object.
Heat (energy)
The amount of thermal energy stored. measured in Joules. Difficult to measure. depends on the temperature and mass.
Temperature
the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance. measured with a thermometer in degrees Celsius (°C).
Joules (J)
The unit of energy.
Kinetic theory
Explains matter as particles moving; faster movement = higher temperature.
Solid, liquid, gas
The three states of matter
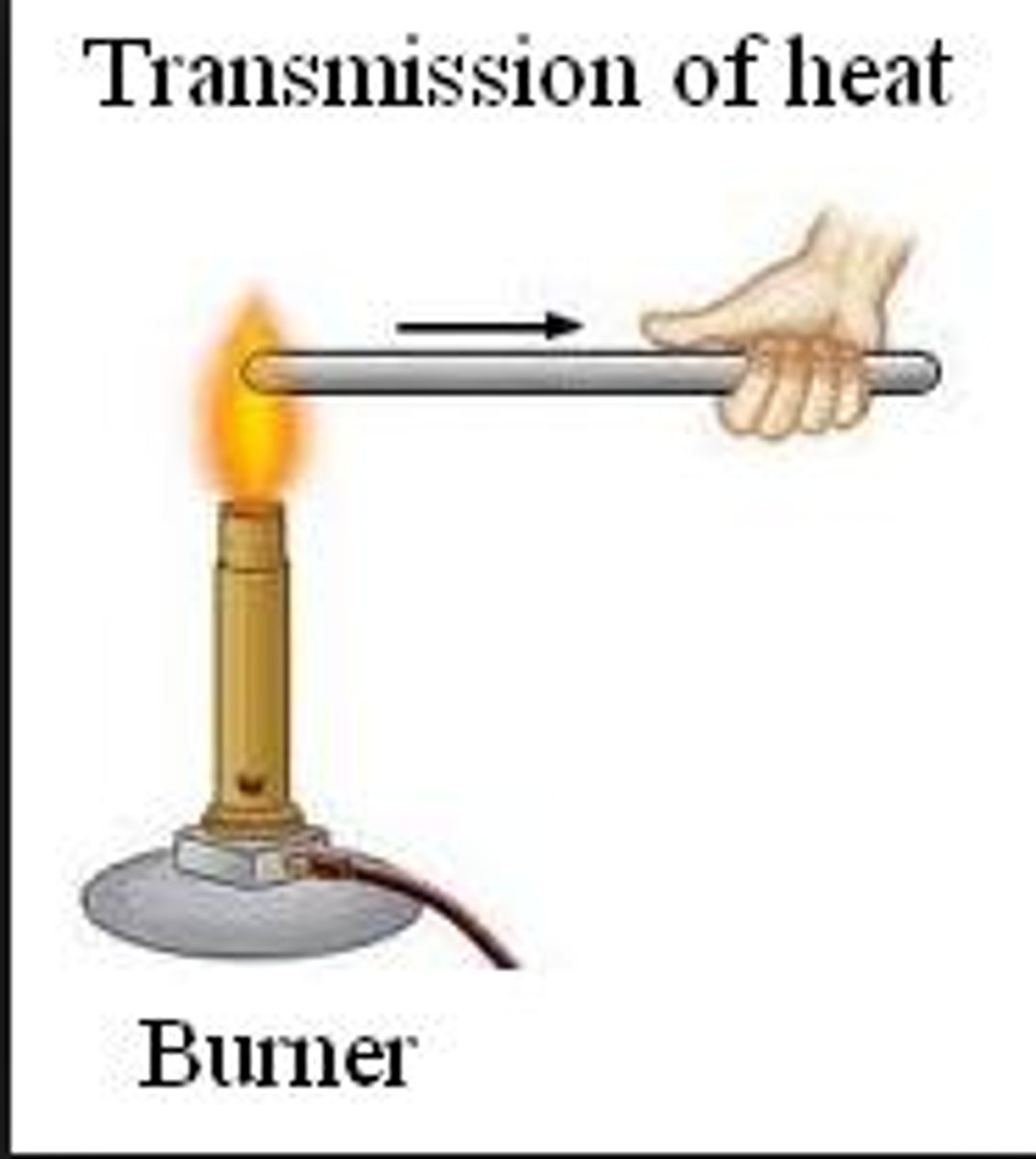
Conduction
Heat transfer through solids by particle vibration.
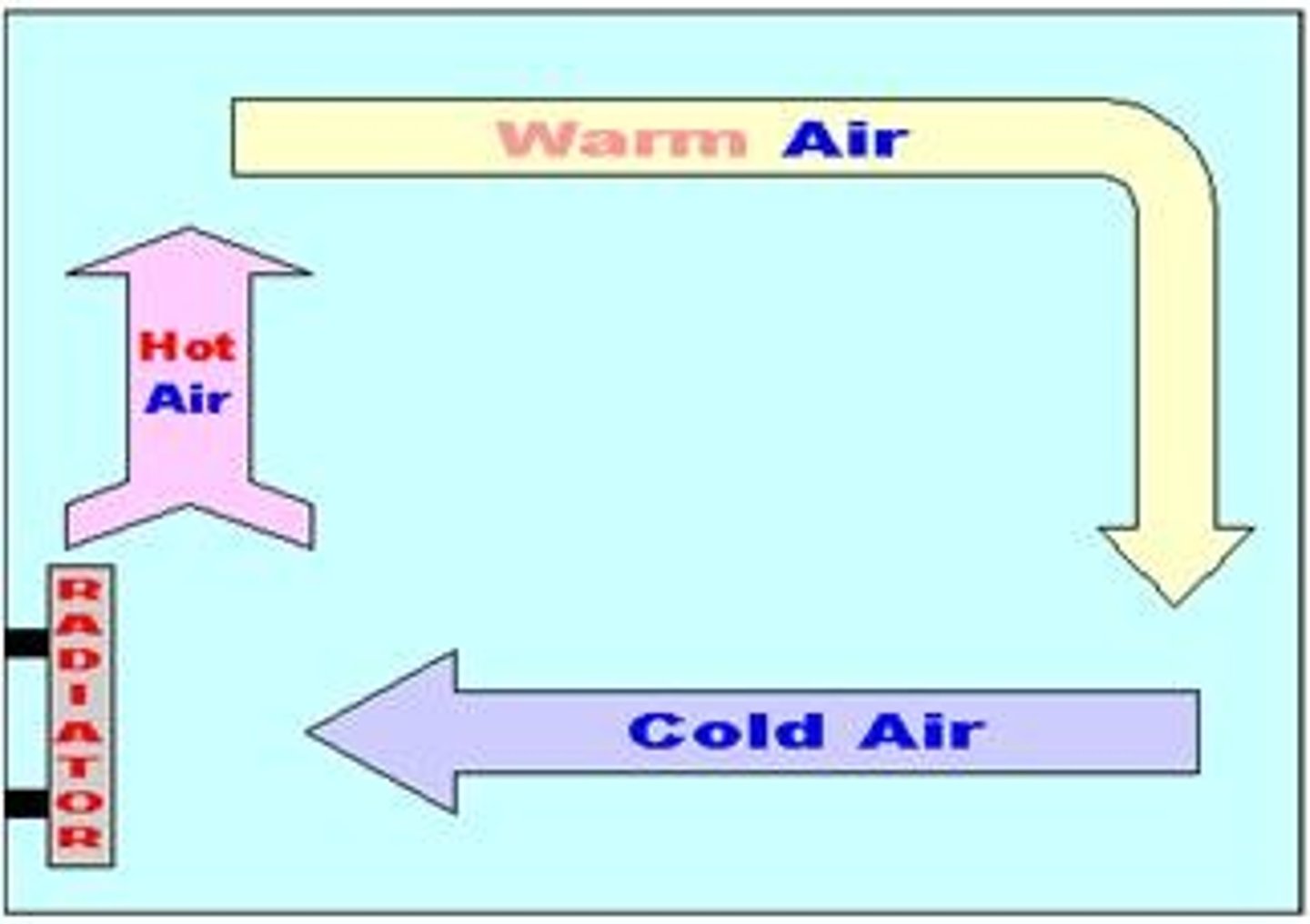
Convection
Heat transfer in fluids (liquids and gases) by moving particles.
Convection current
The circular movement of fluid caused by heating and cooling.
Radiation
Heat transfer by infrared waves, no particles needed.
Conductor
A material that allows heat to pass through easily (e.g., metals).
Insulator
A material that does not allow heat to pass through easily (e.g., wood).
Evaporation
When particles at the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to become gas.
Radiation example
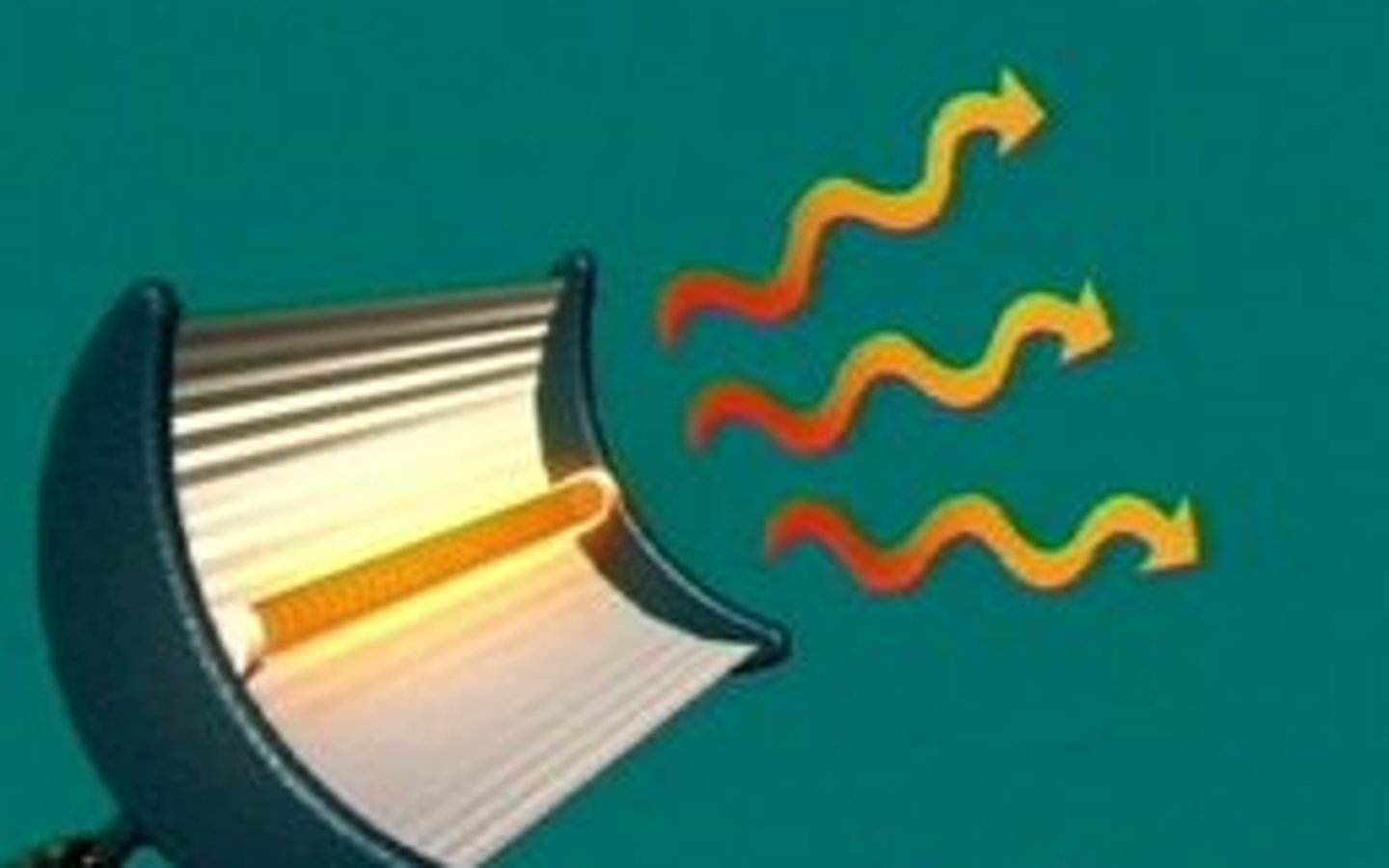

Convection example
Conduction example
A good absorber and emitter of radiation
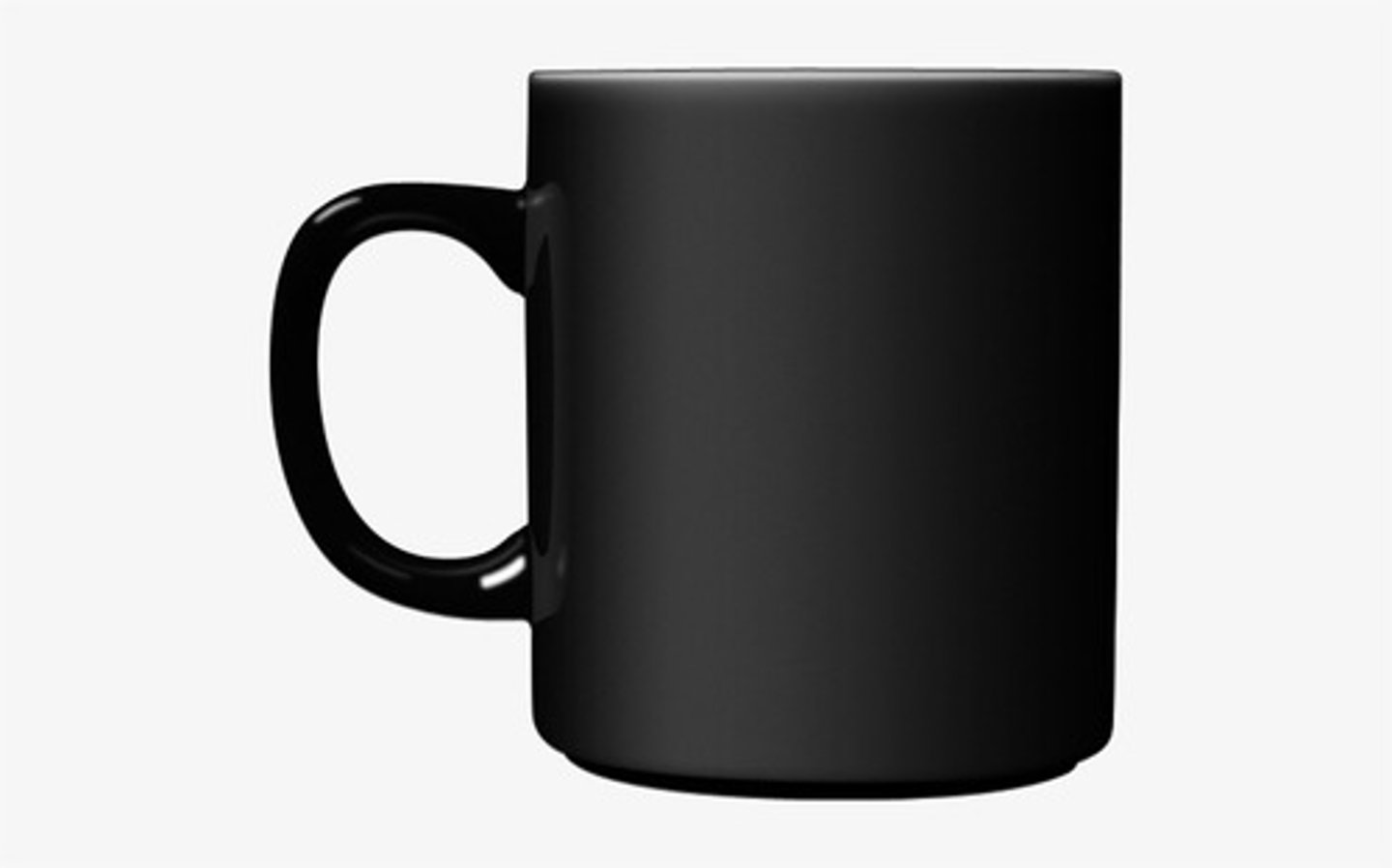

A bad absorber and good reflector of radiation

A wave form representing a loud high pitch sound
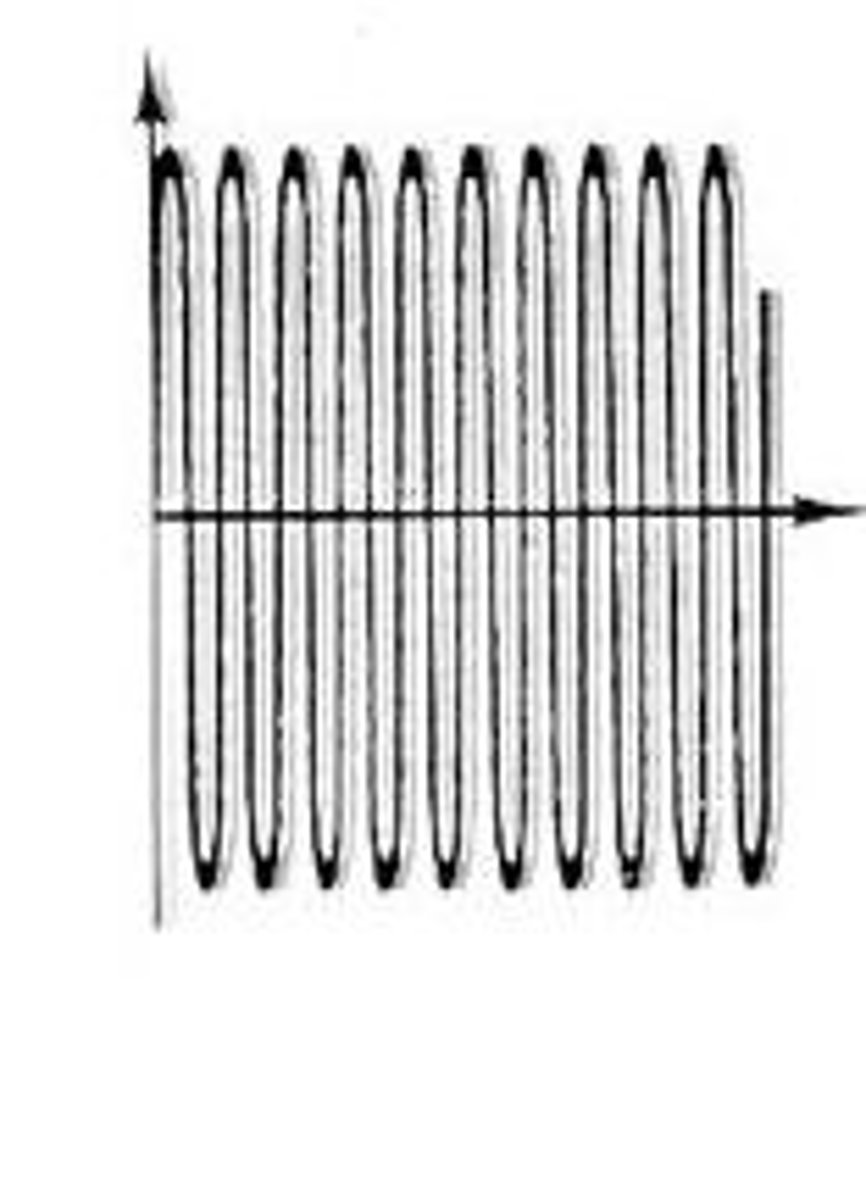
A wave form representing a low pitch sound
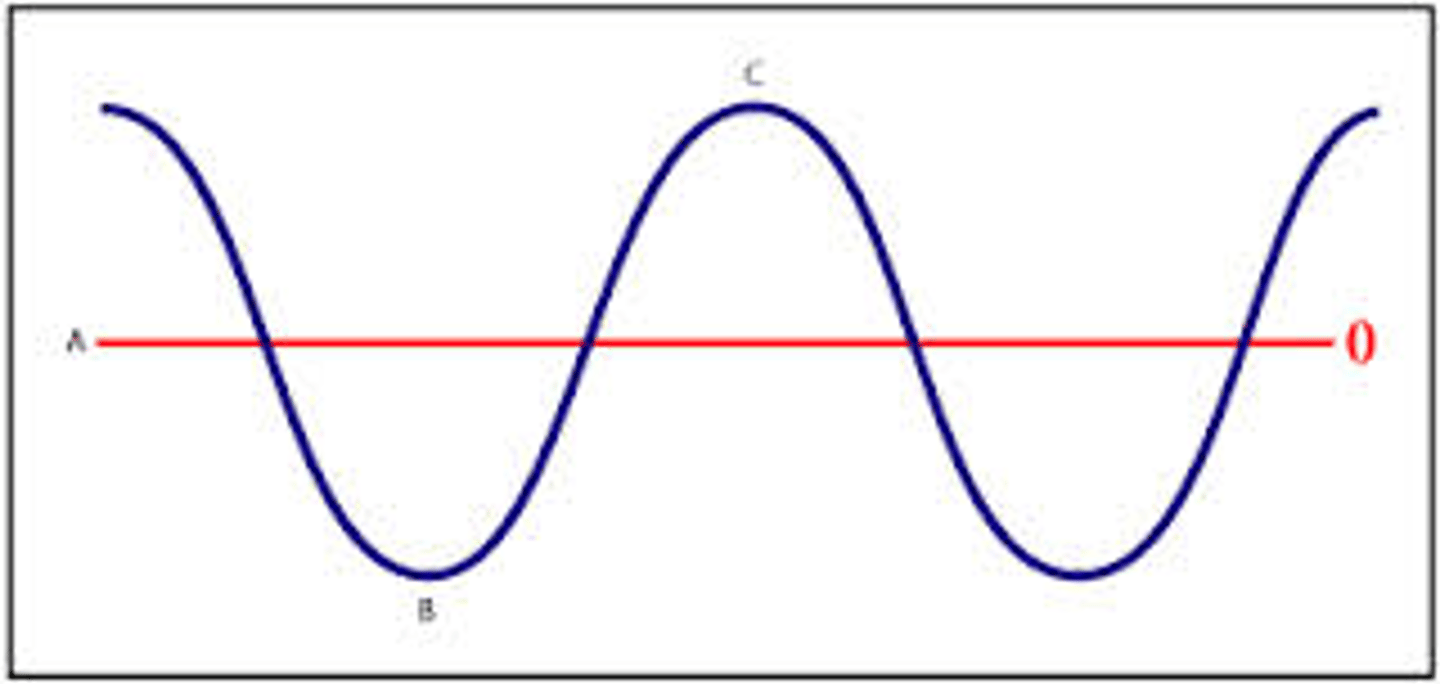
A wave form representing a quiet low pitch sound
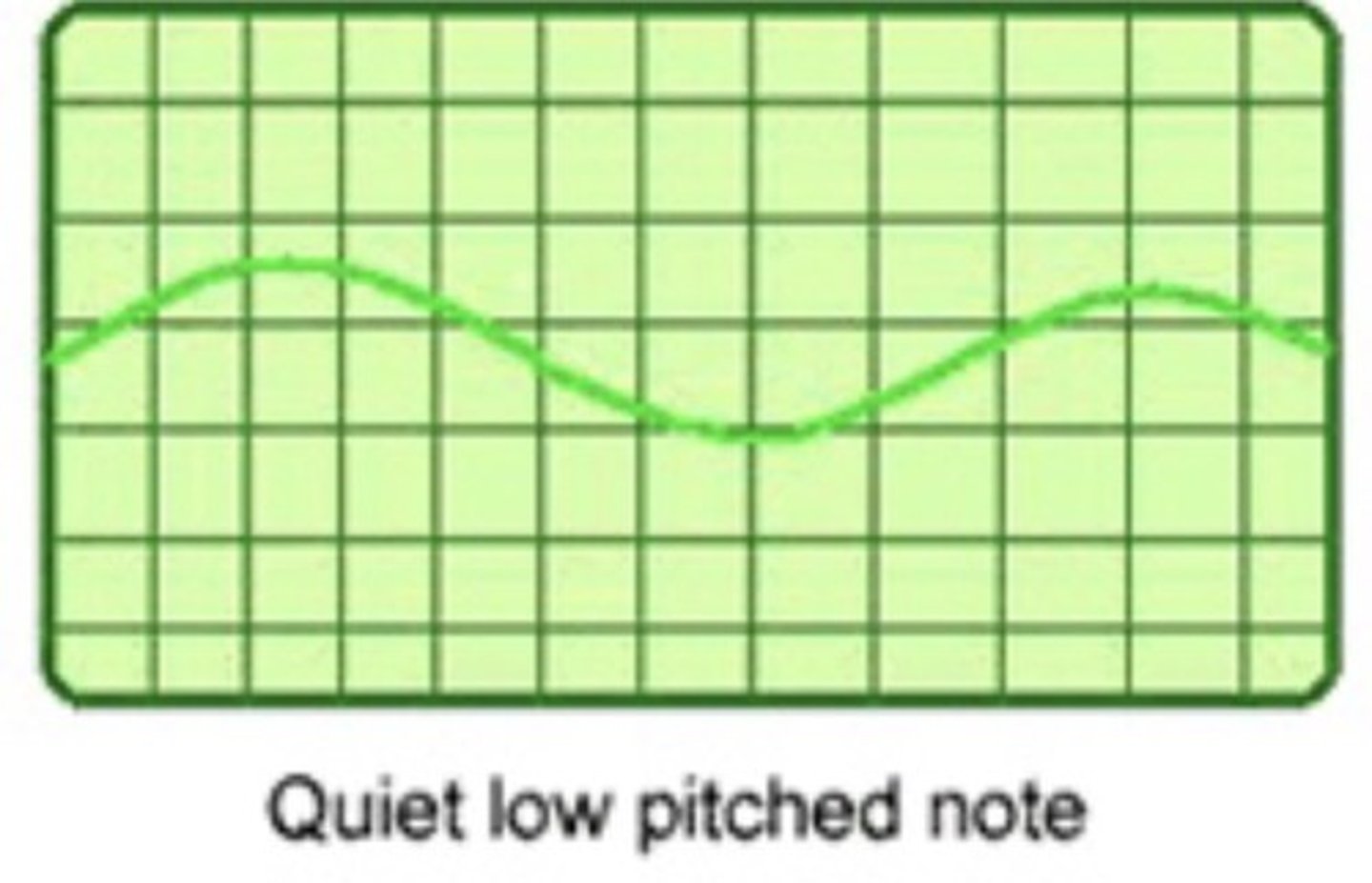
Diagram showing constructive interference
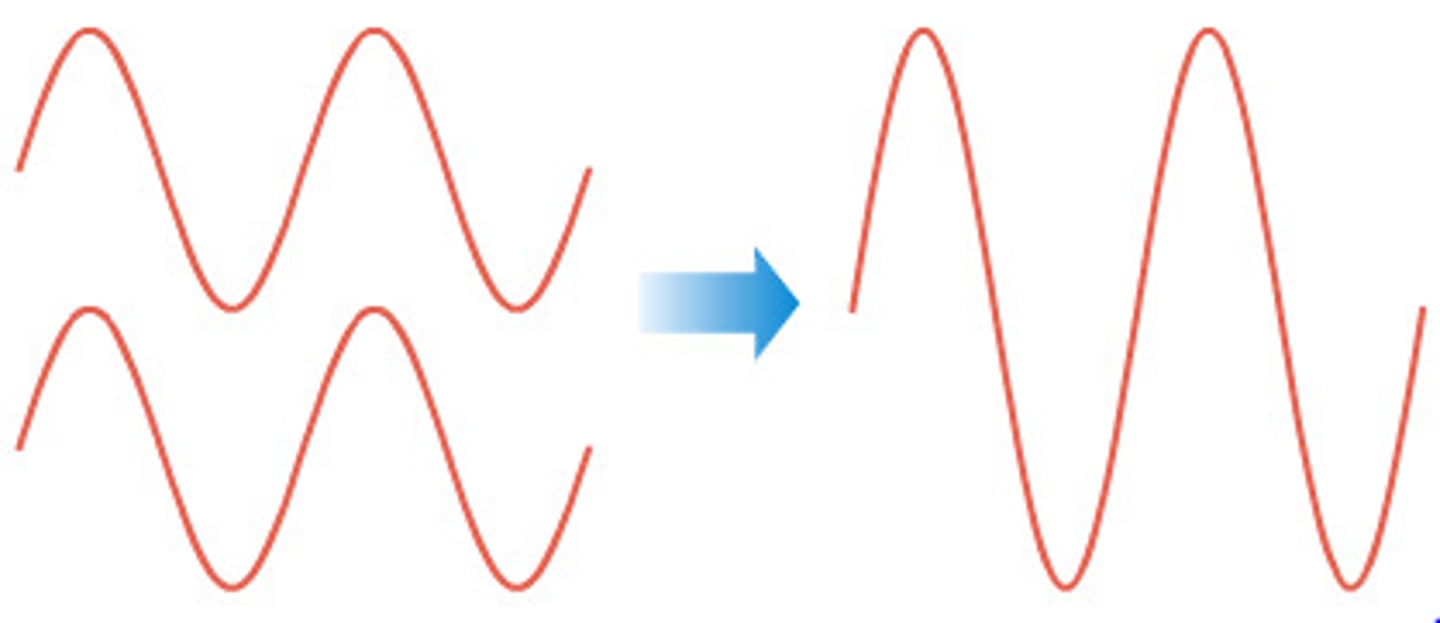
Diagram showing destructive interference