Cartões: Buffer Solutions | Quizlet
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Buffer Solution
A buffer solution is a system that does not change significantly if small amounts off acid or base are added to it. pH only changes a small amount as the buffer works.
An Acidic Buffer Solution
Made from a weak acid and a salt of that weak acid (weak acid with strong base).
A Basic Buffer Solution
Made from a weak base and a salt of that weak base (weak base with strong acid).
Ways To Make A Buffer Solution
By partially neutralising a weak acid and base and therefore producing a mixture of salt and acid.
On Addition Of An Acid
1. [H+(aq)] increases
2. H+(aq) ions react with conjugate base A-(aq)
3. The equilibrium position shifts to the left removing most of the H+ ions
On Addition Of An Acid
1. [OH-(aq)] increases
2. The small concentration of H+(aq) ions reacts with the OH-(aq) ions
3. HA dissolves shifting the equilibrium position to the right to restore most of H+(aq) ions
pH And Buffer Solutions
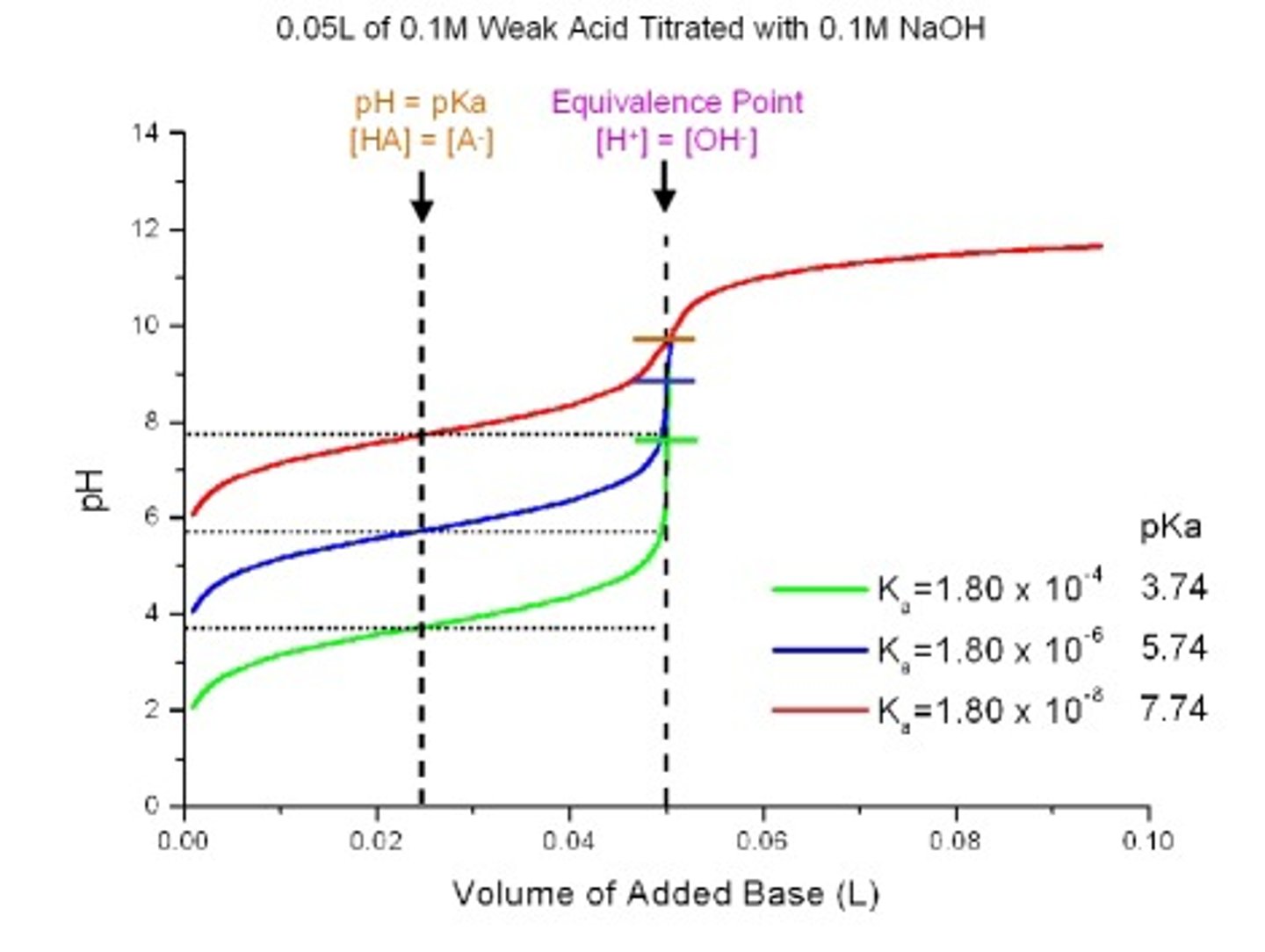
Different weak acids result in buffer solutions that operate over different pH ranges and a buffer is most effective at removing either added acid or alkali when there are equal concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base.
When HA = A-...
1. pH of the buffer solution is the same as the pKa value of HA
2. the operating pH is typically over about two pH units, centred at the pH of the pKa value
Buffer Solutions In The Body
pH control in blood plasma which needs to be maintained at pH 7.35 - 7.45. Controlled by carbonic acid & hydrogrencarbonate (most important).
If pH goes below 7.35, people can develop acidosis (can cause fatigue, shortness of breath, shock/death - extreme).
If pH goes above 7.45, people can develop alkalosis (can cause muscle spasms, light headedness, nausea).
How Buffer Solution In Blood Plasma Works
There are more acidic materials than alkaline which HCO3- converts to H2CO3-. The body prevents H2CO3 building up by converting it to CO2 gas which is then exhaled by the lungs.
Strong Acid - Strong Base
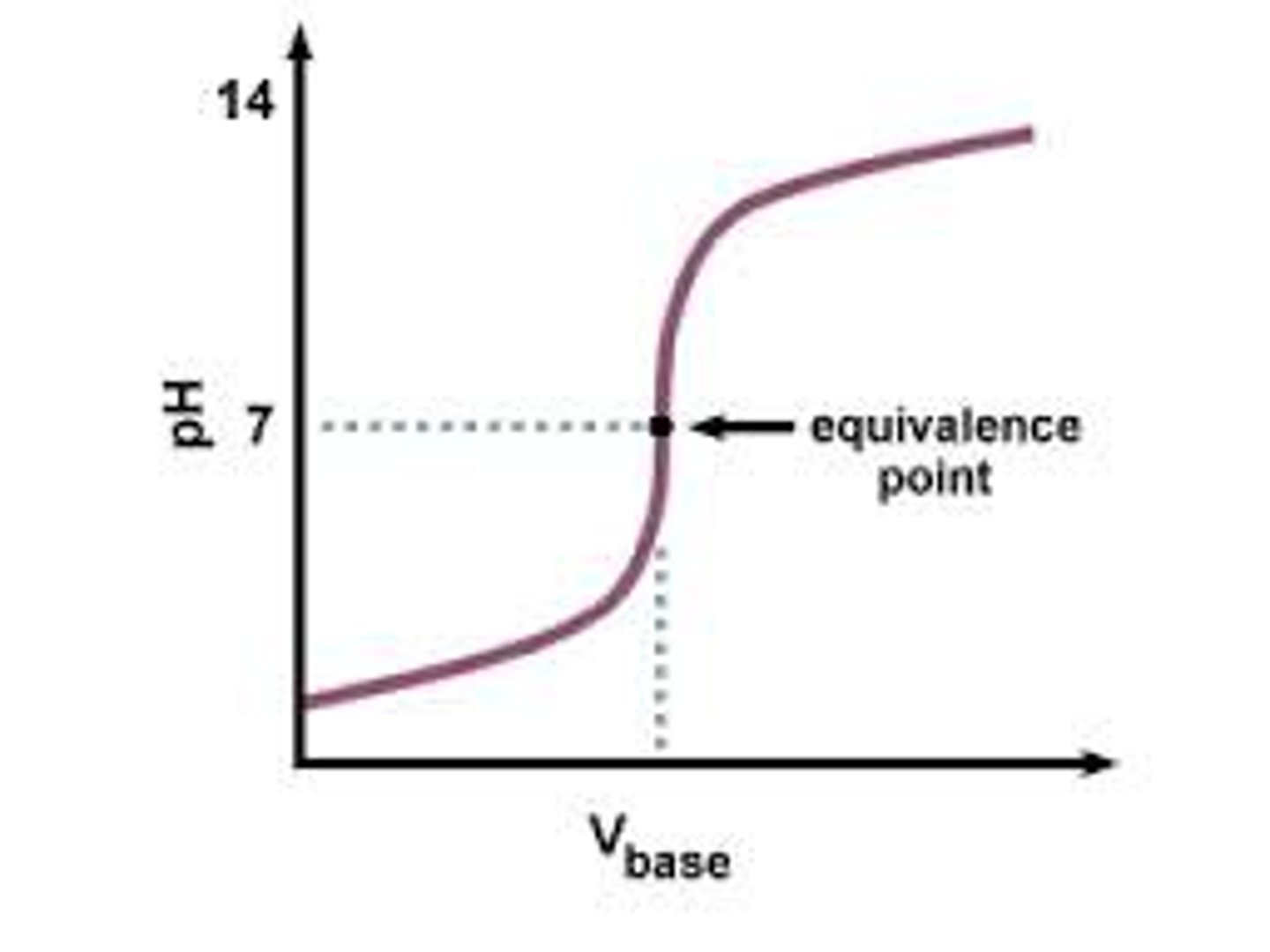
Weak Acid - Strong Base
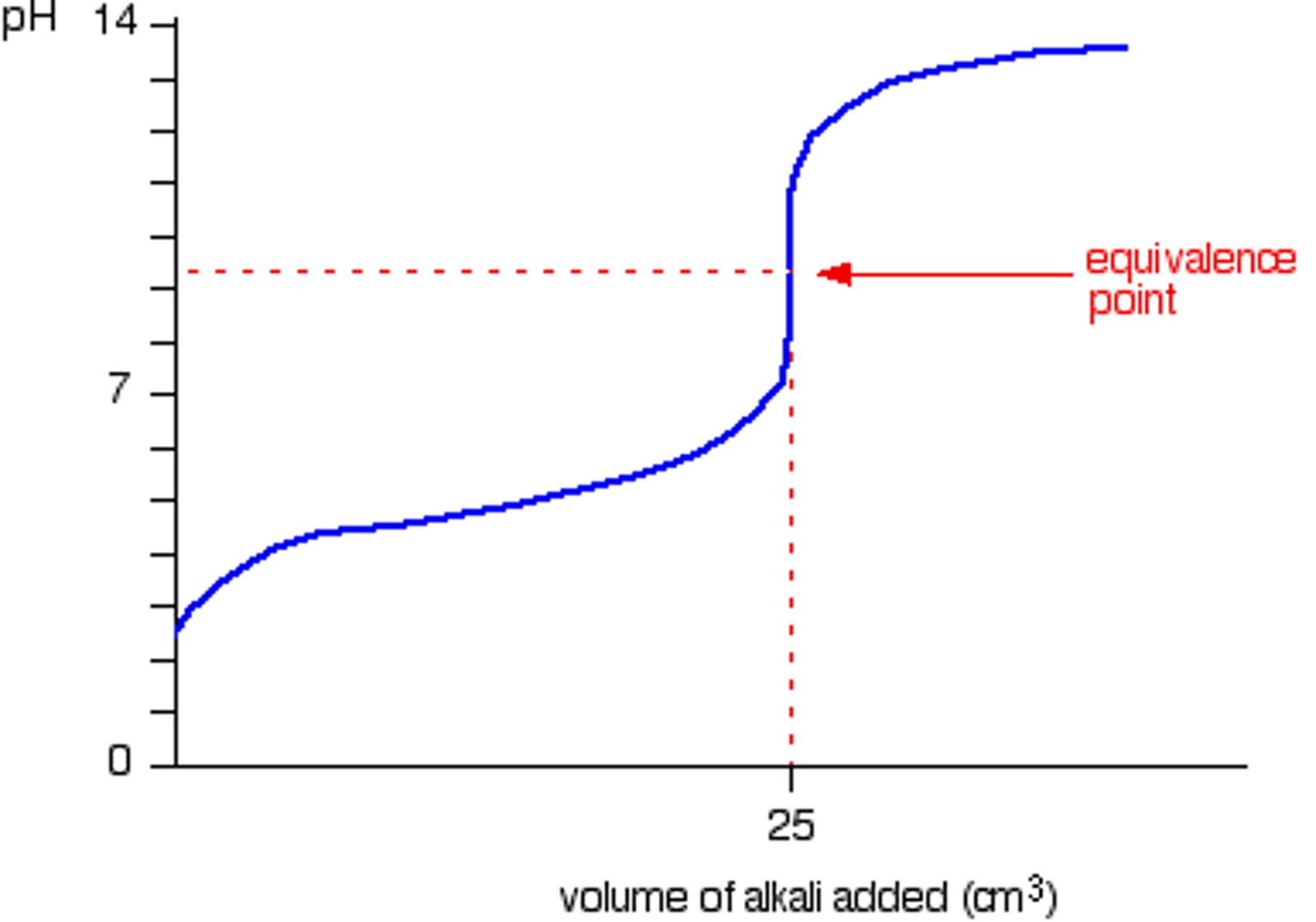
Strong Acid - Weak Base
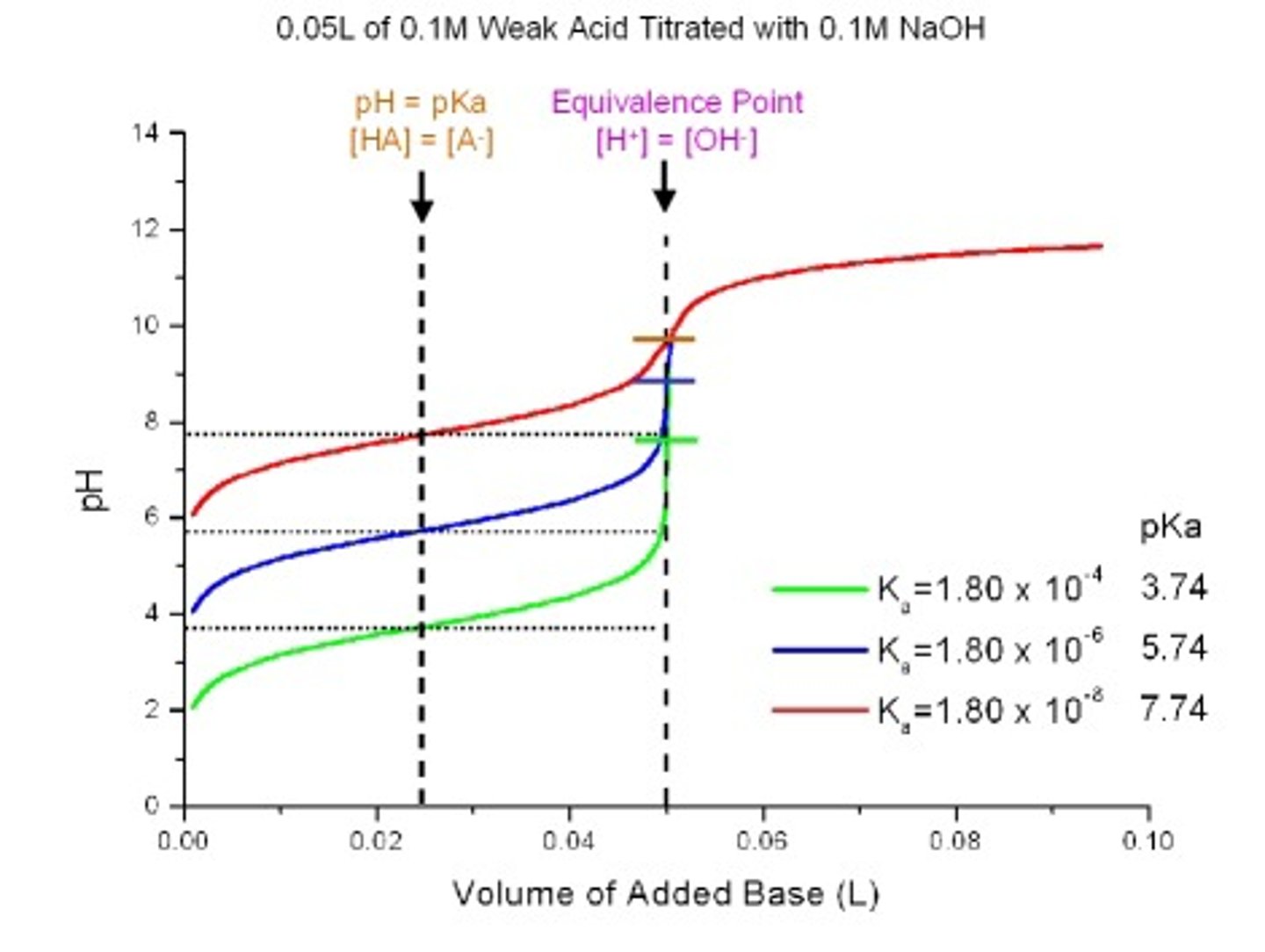
Weak Acid - Weak Base
Equivalence Point
This point of the titration is the volume of one solution that exactly reacts with the volume of the other solution. It is the centre region on the graph.
Acid-Base Indicators
An acid - base indicator is a weak acid HA that has a distinctly different colour from its conjugate base A-. A common indicator is methyl orange. At the end point the indicator contains equal concentrations of HA and A- and the colour will be in between the two extreme colours.
Why Dies The Indicator Colour Change
The indicator is a weak acid. The equilibrium position is shifted towards the weak acid in acidic conditions or towards the conjugate base in basic conditions changing colour as it does so.
Weak Acid - Weak Base Indicator
No indicator is suitable for a weak acid - weak base titration as there is no vertical section
Strong Acid - Strong Base
Methyl orange & Phenolphthalein
Strong Acid - Weak Base
Methyl Orange
Weak Acid - Strong Base
Phenolphthalein