Lab B: Synthesis of Aspirin
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab B
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Reaction Scheme for Synthesis of Aspirin
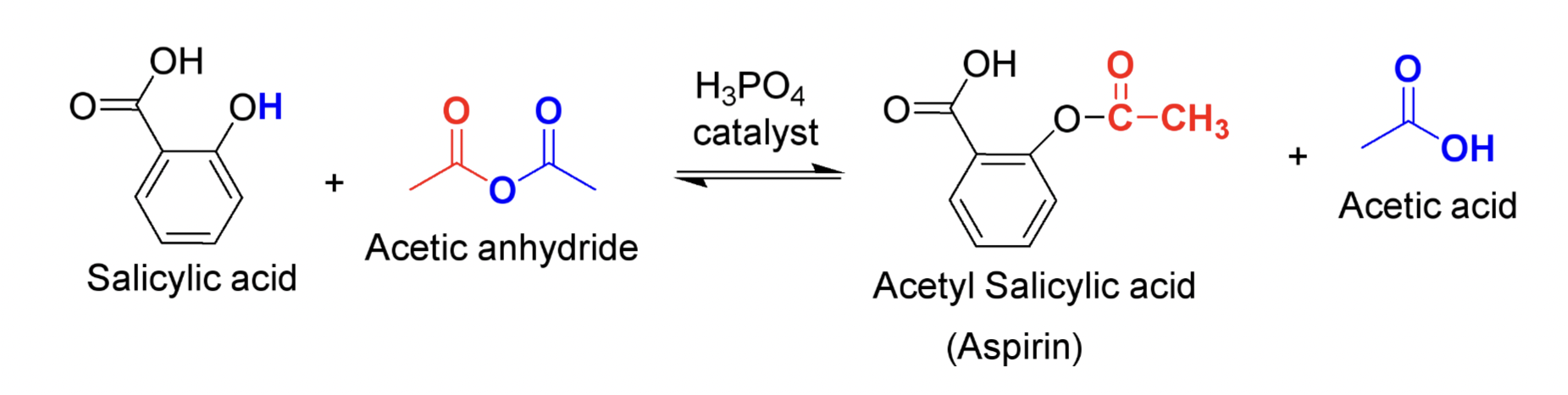
What type of reaction is the synthesis of Aspirin?
An Esterification reaction
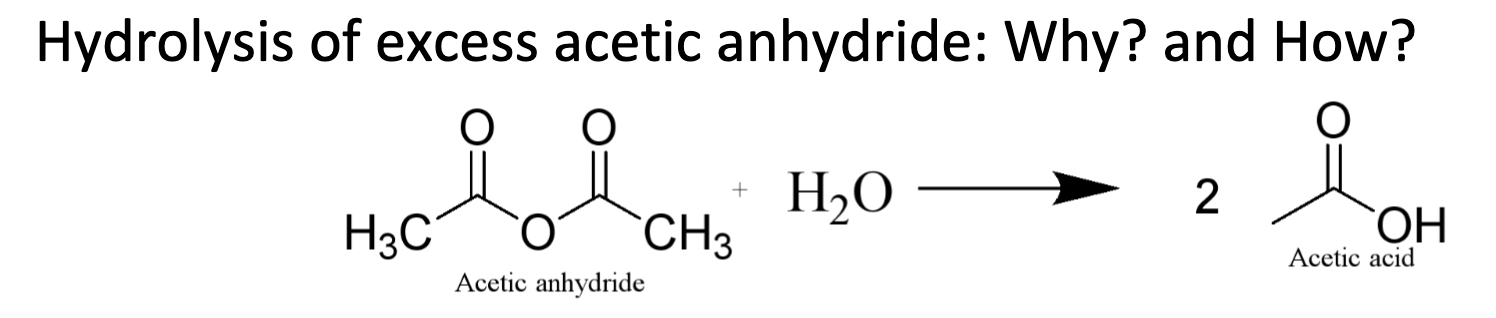
Why do we use excess acetic anhydride?
Because this acts as a catalyst to drive the reaction forward
Hydrolysis of excess acetic anhydride
What is an Equivalent?
The experimental ratio in which reactants are added to the reaction.
What ratio does acetic anhydride and salicylic acid react?
1:1, but to favor formation of aspirin it reacts 3:1 which means 3 times the number of moles of acetic anhydride compared to the moles of salicylic acid
Equation for theoretical yield of salicylic acid

Equation for volume of acetic anhydride needed to synthesize Aspirin
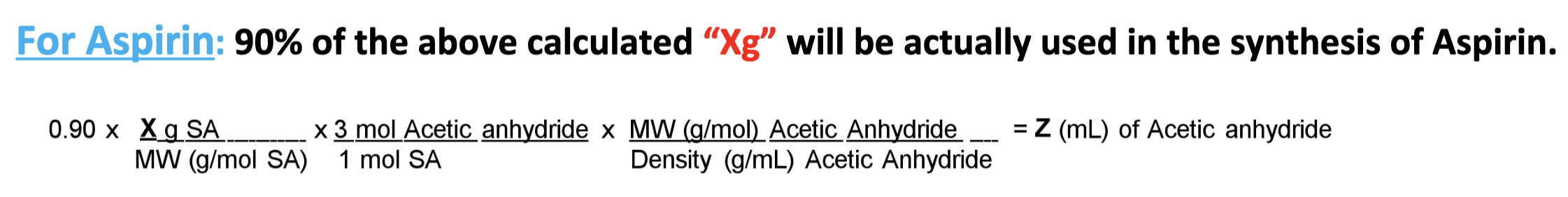
Equation for overall % yield of Aspirin Synthesis
% yield from lab A x % yield from lab B x 100
How to find the solvent of choice to recrystallize Aspirin?
-Put a small amount of Aspirin (spatulas worth) into two different test tubes
-Fill one test tube 1/3 of the way with water and the other test tube 1/3 of the way with ethanol
How to test for purity of Aspirin?
-Phenols will react with FeCl3 (aq) to produce a deep purple
-in two different test tubes put 1 mL of ethanol and 3 drops of FeCl3
-put a small amount of salicylic acid in one tube and a small amount of aspirin in another tube
-a purple colored solution will show that there’s unreacted salicylic acid present in the aspirin product
Waste Disposal Procedures for Lab B
-Put chemicals with C, H, and O in the Non-halogenated Container (ethanol from solvent test)
-Put chemicals with C, H, O, and halogens in the Halogenated Container
-Any waste acidic filtrates must be neutralized with NaCHO3 and rinsed down the sink
-Any waste from the FeCl3 test should be put in container labeled “Aq. FeCl3 waste”
Classifications based on Chemical Hazards
Flammable, Corrosives, Lachrymator, Carcinogen, Teratogen, Reactive
Flammable definition and example
-Flash point is the lowest temperature at which a liquid can form an ignitable mixture in air near the surface of the liquid
-Example: Acetone, diethyl ether, t-butyl methyl ether
Corrosives definition and example
-Materials that can attack and chemically destroy exposed body tissues, causing chemical burns, these are strong oxidizers that are either strong acids or bases
-Example: H2SO4, NaOH, HNO3, Ca(OH)2, Br2
Lachrymator definition and example
-An irritant that causes tearing (watering of the eyes)
-Example: Thionyl chloride, Acrolein, Methycryloyl chloride
Carcinogen definition and example
-A substance capable of causing cancer
-Example: Benzene, Arsenic, Methylene chloride/dichloromethane
Teratogen definition and example
-a drug or substance capable of interfering with the development of the embryo fetus which may lead to birth defects or malformations
-Example: Phenol, Benzene, Dinitrotoulene, Dioxane
Reactive definition and example
-things that go boom
-Example: Na metal, sodium hydride, calcium carbide
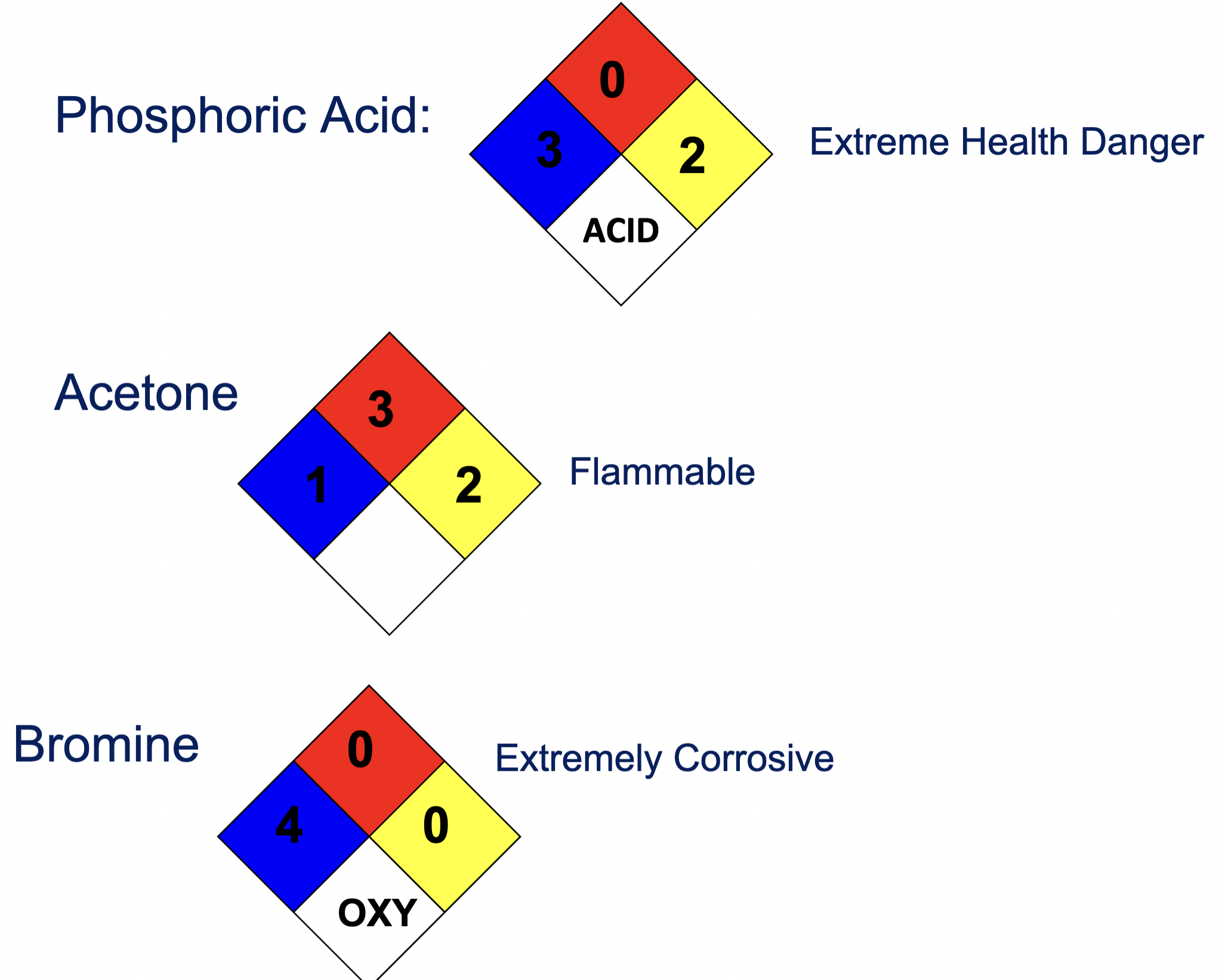
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Ratings
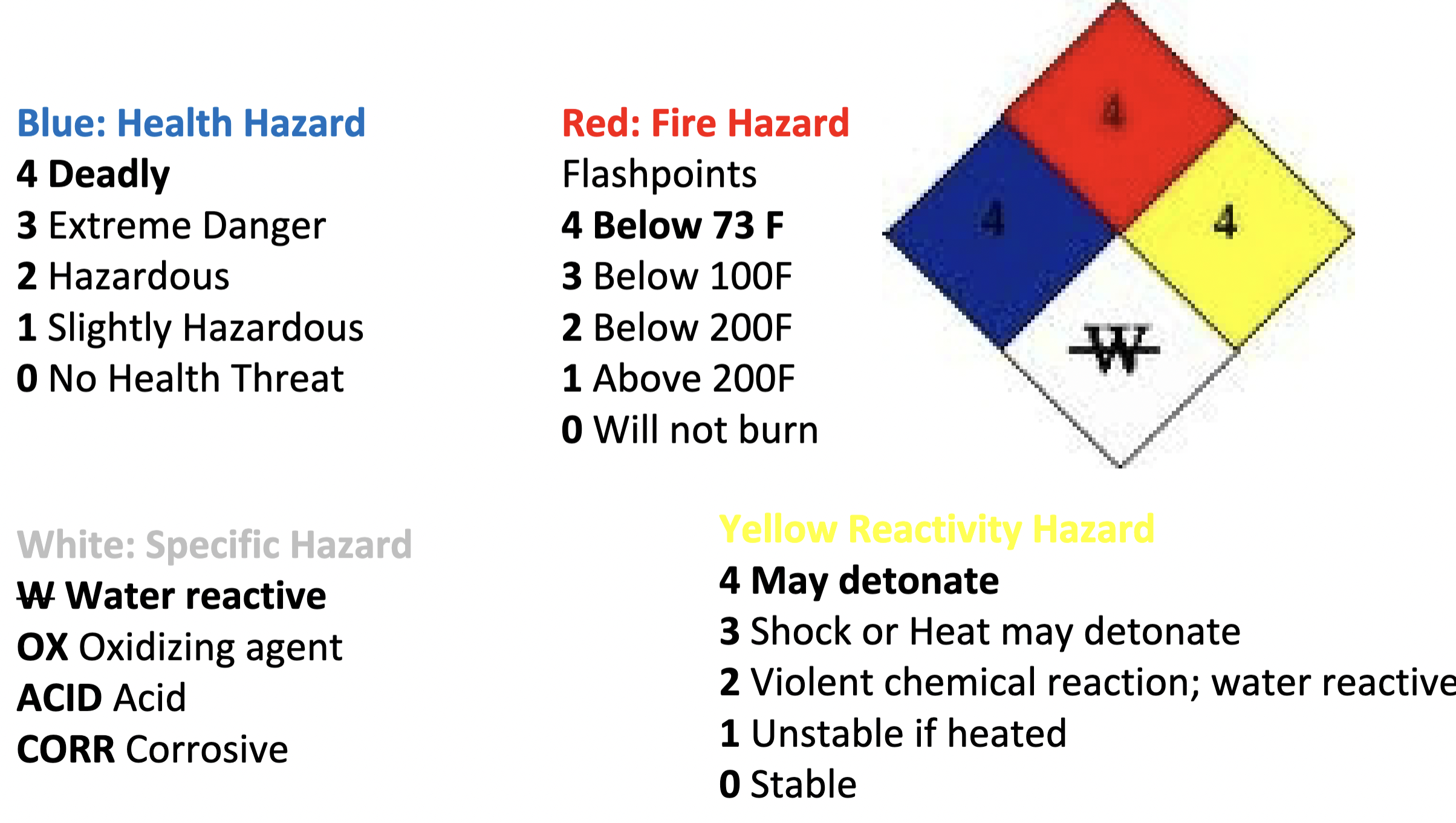
NFPA Triangles for Phosphoric, Acetone, and Bromine
What’s the boiling point range for acetic anhydride?
138-140 degrees celsius