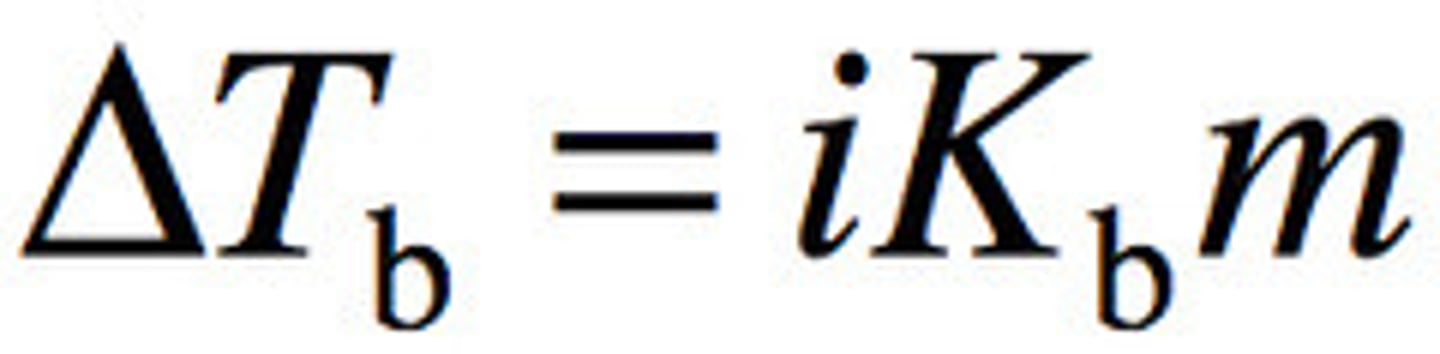Ch 13 | Ions in Aqueous Solutions and Colligative Properties
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
dissociation
separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves

net ionic equation
Includes only those compounds and ions that undergo a chemical change in a reaction in an aqueous solution

spectator ions
Ions that do not take part in a chemical reaction and are found in solution both before and after the reaction
ionization
process in which ions are formed from solute molecules by the action of solvent; molecular/nonpolar in polar
dissociation vs ionization
dissociation starts with an ionic compound and ionization starts with a molecular compound
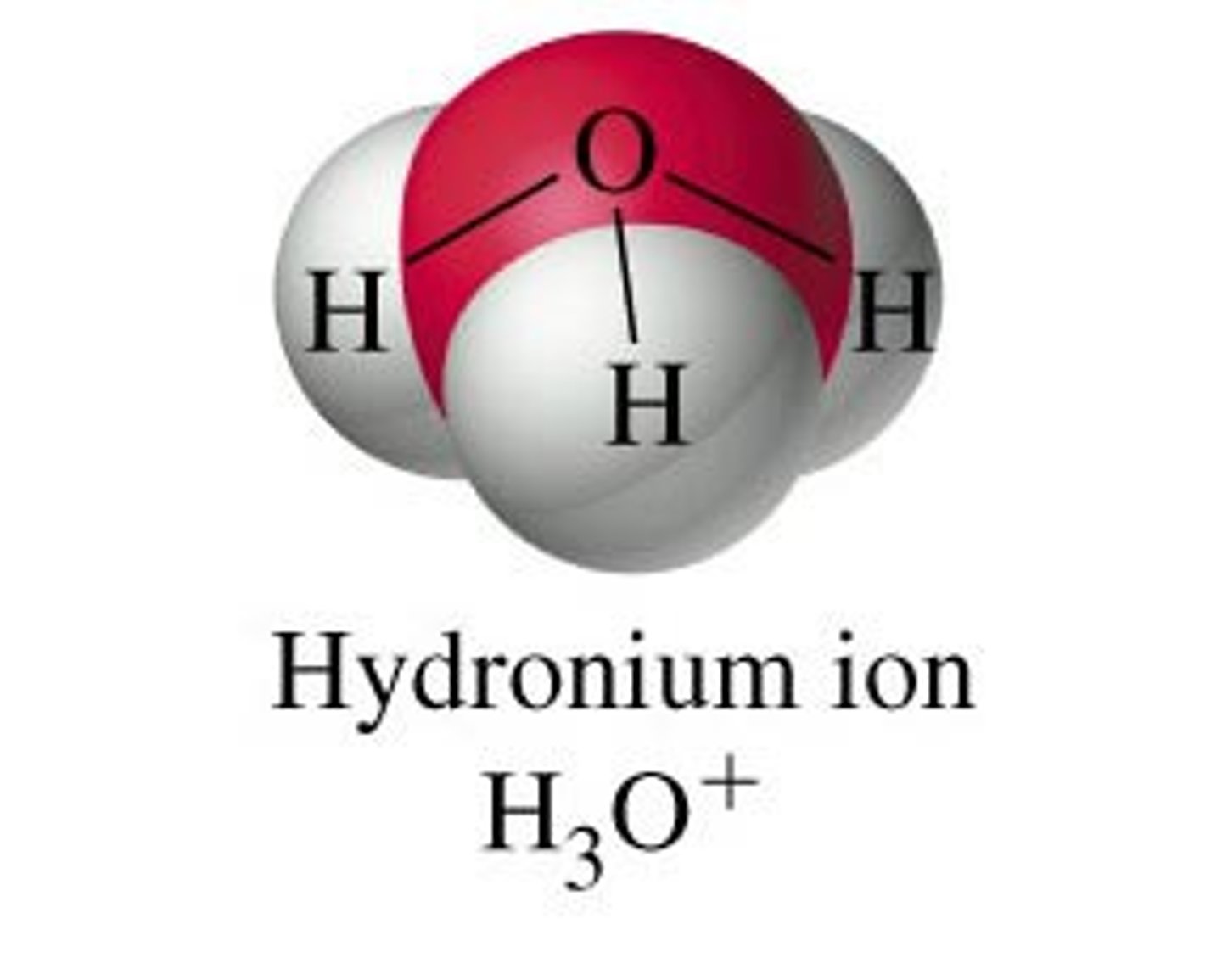
hydronium ion
hydrogen ion attracts other ions/molecule so strongly that is doesn't normally exist alone > bonds with a water molecule to form
electrolyte's strength depends on
how many dissolved ions it contains; related to their ability to form ions in solutions
strong electrolyte
any compound whose dilute aqueous solutions conduct electricity well; this is due to the presence of all or almost all of the dissolved compound in the form of ions
strong electrolyte examples
all soluble ionic compounds and HCl, HBr, HI, H2SO4, HNO3, HClO4, HClO3
weak electrolyte
any compound whose dilute aqueous solutions conduct electricity poorly; this is due to the presence of a small amount of the dissolved compound in the form of ions
colligative property
depends on the concentration of solute particles but not on the identity
freezing point depression
the difference in temperature between the freezing point of a solution and the freezing point of the pure solvent
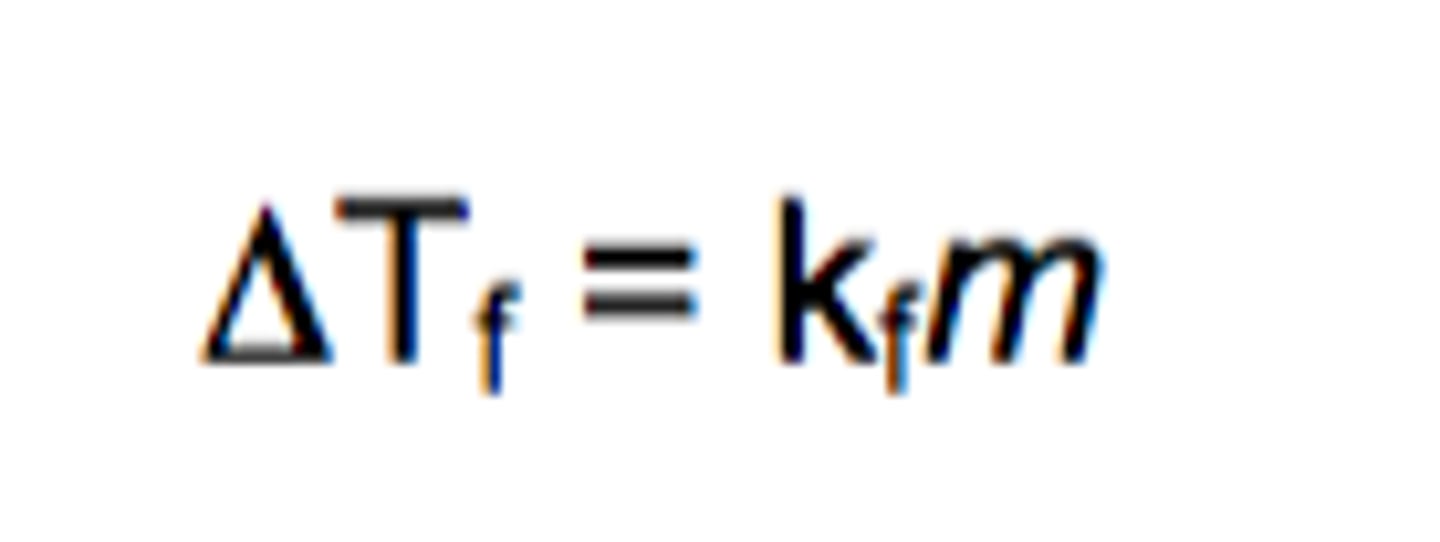
determining actual freezing point (solvent is water)
negative of ΔTf
determining actual freezing point (solvent is not water)
Tf (solvent) - ΔTf
boiling-point elevation
the difference in temperature between the boiling point of a solution and the boiling point of the pure solvent
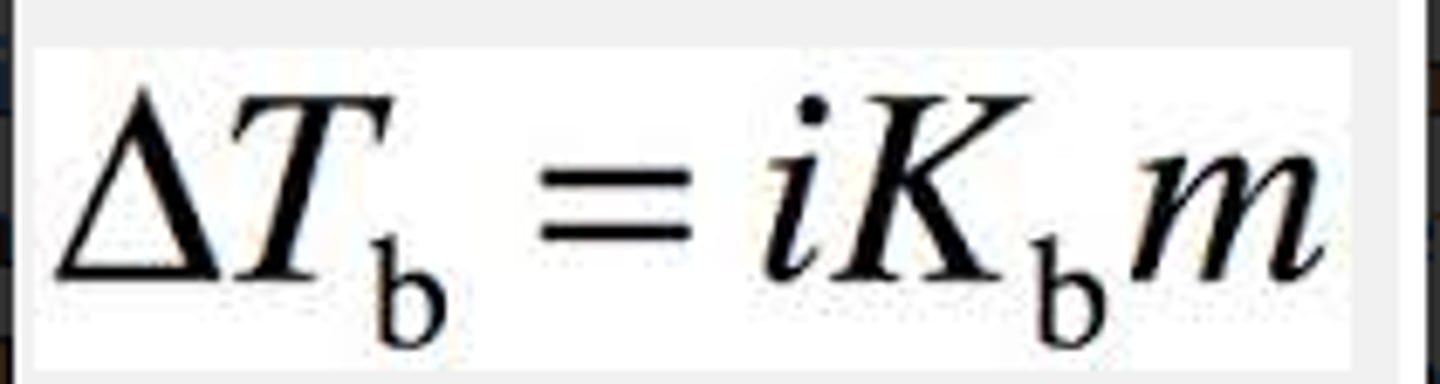
determining actual boiling point
Tb (solvent) + ΔTb
when solute is ionic/polar
multiply ΔT by # of solute ions