Surgery of the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
VSUR 152
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
drooling
dysphagia
anorexia
bleeding
foul smelling mouth
Clinical signs of unhealthy oral cavity/ oropharynx
pre operative assessment
endotracheal tube placement
proper patient positioning
preparation of specialized instrument
local anesthesia
disinfection with hexetidine rinse
General pre and peri operative and considerations
Rabies
CS: excessive salivation, biting indiscriminately, to look at the eyes of the dog for precautionary measures
halitosis
“bad breath”
gingivitis
foreign material stuck between cheek and teeth
Carnassial tooth Abscess
Clinical sign:
- halitosis
- +/- dysphagia
- abscess
Carnassial tooth Abscess
TX
- radiography to see extent of the damage
- address inflammation and infection (ATB/NSAID) before extraction
- toot extraction
Carnassial tooth Abscess
Extraction:
- section the tooth, elevate periosteum, extract the cadual and rostral section of the tooth
- check if complete extraction
- flush with antiseptic (chlorhexidine)
- suture with SISP/ horizontal mattress
- close/crush socket before suturing if needed
- continue antibiotics
ELEVATE —> EXTRACT —> FLUSH —> SUTURE
Flow of sectioning of the tooth
Glossectomy
amputation/ excision of the tongue
- done when dog cannot eat or swallow properly anymore
Glossectomy
CS:
- ptyalism
- halitosis
- dysphagia
- dyspnea (sometimes)
Glossectomy
Due to:
-Trauma (most common)
- blood
- chemical
- lung lesion
- dog fights
- neoplasia (Squamous cell carcinoma)
Partial
sub-total
near total
Total
Types of glossectomy
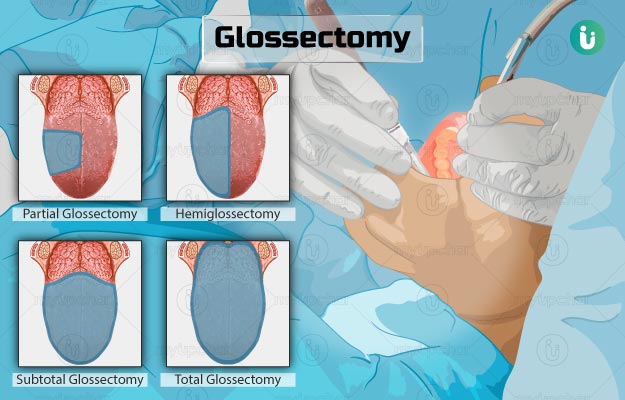
Partial
free tongue (not attached to the frenulum) will be removed
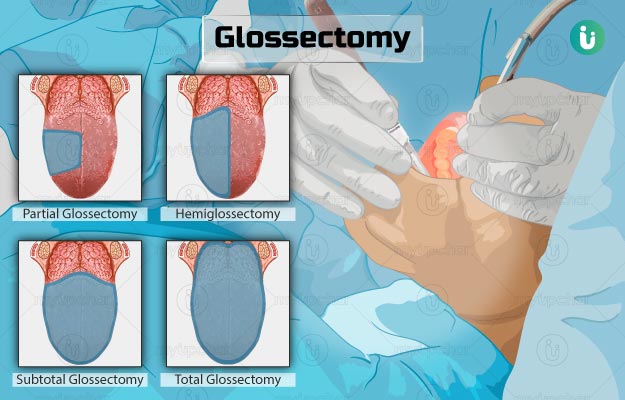
Sub-total
entire free tongue and part of genioglossus and genio-hyoid muscles
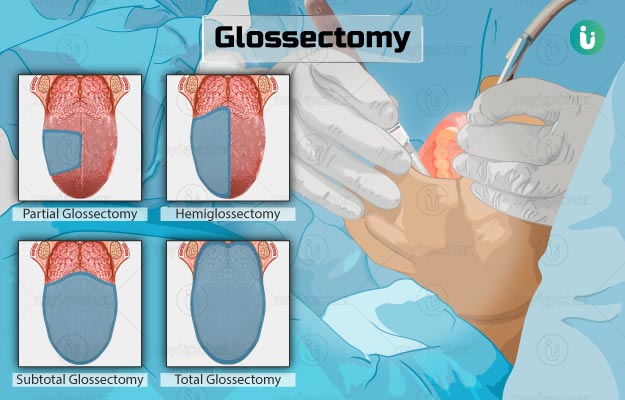
Near total
remove 75% of the tongue
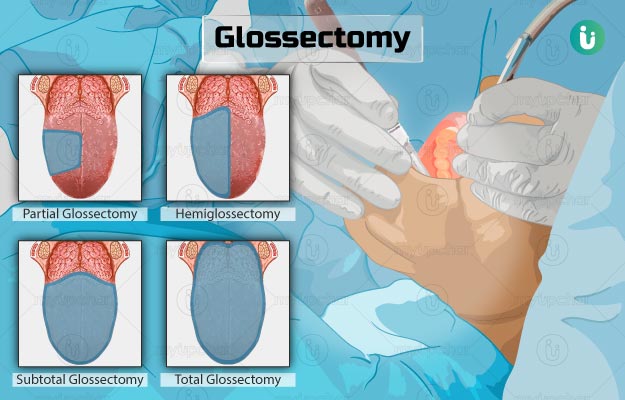
Total
100 % Amputation of the tongue
Doven clamp/ A mattress suture
Technique that uses lateral recumbency
- minimum of 2 cm of normal tissue + lesion
- non crushing clamp at base of tongue
- control of hemorrhage by ligation/ pressure cautery
closure
- HMS
- SCSP
50-60%
____ % tolerated by dogs; may make eating and drinking difficult —> feed by tossing food or animal can suck food
bilateral sialoadenectomy
solution of hypertyalism that is seen in subtotal to total glossectomy
major glossectomy
may put in feeding tube
Salivary duct mucocele/ Ranula
acute and abrupt
mucocele found under the tongue
involves the duct and not the gland
Salivary duct mucocele/ Ranula
CS:
- tongue is always out
- ptyalism
Salivary duct mucocele/ Ranula
TX:
marsupialization
Marsupialization
incise mucocele
suture edge to mucosa
interior of mucocele suppurates
close by granulation
draining
creates surgical window on wall of cyst
maintain continuity between cyst and oral cavity/ maxillary sinus
can also used on other cyst of the body
Salivary duct mucocele/ Ranula
Post op:
histologic exam (to rule out neoplasia)
change bandage daily if penrose drain used (removed 24-72 hrs post op) when drainage is minimized
2nd intention healing for drainage site
apply warm compress
soft food (3-5 days)
Salivary duct mucocele/ Ranula
Complications
droopy face
dysphagia
seroma
infection
mucocele recurrence (drainage was done, inadequate gland excision, LN mistaken for gland)
Epulis
most common benign oral neoplasm (accounts for 30%)
rare in cats
firm tumors, gingival mass
arise from periodontal ligament
Fibromatous
Ossifying
Acanthomatous
Types of epulis
Fibromatous Epulis
pink, smooth, firm gingival mass arising from periodontal ligament
non-invasive
originates from gingival sulcus
may be single/multiple, pedunculated/sessile
primary cell type: periodontal ligament stroma
Ossifying
large amount of osteoid matrix in stroma
firm and difficult to cut
may transform into malignant tumor —> osteosarcoma
Acanthomatous
benign, aggressive, most common type
can infiltrate bone —> lysis
occur at rostral/mandibular canine teeth
Epulis
Tx:
excision (2mm from edge of neoplasm —> wide surgical excision to prevent recurrence, remove also the healthy parts
neoplasia
laceration
abscess drainage
glossitis
severe trauma
congenital ankyloglossia (tongue is connected on the floor of the mouth)
limited movement movement of tongue
difficulty in prehension and food acquisition
Indication for tongue surgeries