Organic tests
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is a test used to test for carbonyl groups?
2,4-DNP/ Brady’s reagent
What is a carbonyl group?
C=O
What is Brady’s reagent dissolved in?
Concentrated sulfuric acid and methanol
What is the change seen when there is a positive result?
Orange solution → orange precipitate formed
What are chemicals with carbonyl groups?
Aldehydes and ketones
What tests can be used to differentiate between an aldehyde and ketone?
Potassium dichromate test
Tollens’s reagent
Fehling’s solution/Benedict’s solution
What is the change seen in a positive potassium dichromate test?
Orange → Green
What type of agent is potassium dichromate and why?
It is an oxidising agent as it gets reduced and oxidises the unknown solution.
What are chemicals which would get positive results from the potassium dichromate tests?
Primary alcohols
Secondary alcohols
Aldehydes
Why do these chemicals give positive results?
They give positive results as they can be oxidised.
What do primary alcohols oxidise into?
Aldehydes
What do secondary alcohols oxidise into?
Ketones
What do aldehydes oxidise into?
Carboxylic acids
Why can ketones and tertiary alcohols not give a positive result when tested using the potassium dichromate test?
They cannot give a positive test as they can not be oxidised.
What are chemicals that give us positive results in a Tollens’s reagent test and Fehling’s/Benedict’s solution and why?
Aldehydes- as they can be oxidised whereas ketones cannot
What is the change seen in a positive Tollens’s reagent test?
Brown solution → Silver mirror (silver precipitate formed)
What is the change seen in a positive Fehling/Benedict’s solution test?
Blue solution → red precipitate
What test would you use to test for secondary alcohols and methyl carbonyl groups?
React unknown solution with heated iodine in the presence of an alkali (NaOH).
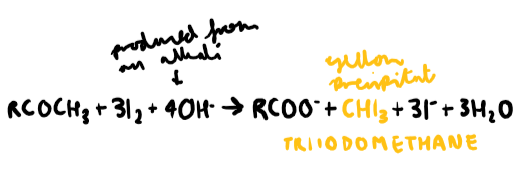
What do you see in a positive result when testing for methyl carbonyl groups and secondary alcohols?
Yellow precipitate
What compound is causing the yellow precipitate?
Triiodomethane
What tests can be used to test for carboxylic acids?
Adding carbonate
Adding PCl5
What do you see in a positive test when testing for a carboxylic acid with carbonate?
You will see bubbles (as carbon dioxide gas is produced)
If bubbled through limewater, you will see limewater turn cloudy
What do you see in a positive test with PCl5 when testing for a carboxylic acid?
Misty white fumes from HCl gas
How do you test for any alcohol (including tertiary alcohols)?
PCl5 test
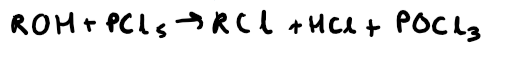
What do you see in a positive test for the PCl5 test which is testing for alcohols?
Misty white fumes
How do you test for alkenes?
Bromine water test
What do you see in a positive test with bromine water testing for alkenes? Also BONUS: what type of reaction occurs
Brown → colourless (type of reaction: electrophilic addition)
How do you test for haloalkanes?
Place haloalkanes in test tubes which are in water baths. Add aqueous silver nitrate solution and ethanol (acts as solvent).
What do you see in a positive test for haloalkanes?
Iodoalkane: yellow precipitate
Bromoalkane: cream precipitate
Chloroalkane: white precipitate

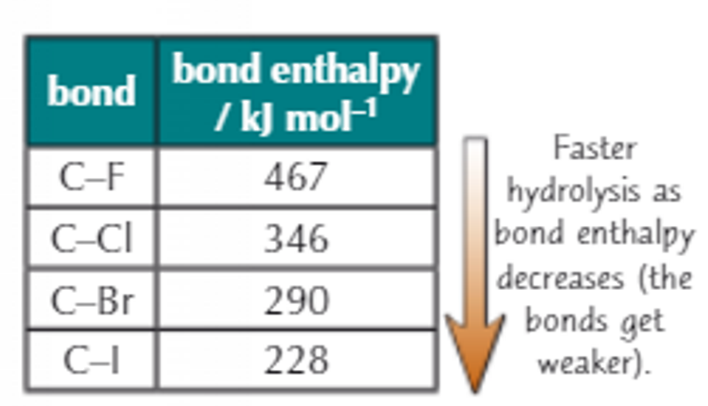
Which haloalkane reacts the fastest and which one reacts the slowest? Also include why!
Reactivity increases down group. (iodoalkane the fastest and chloroalkane the slowest)
Down the group, size of halogen increases → length of carbon-halogen bond increases → the lower the bond strength → the lower the bond enthalpy → the less energy needed to break the C-X (carbon-halogen) bond
Out of primary, secondary and tertiary haloalkanes, which reacts the slowest and fastest?
Tertiary reacts the fastest and primary reacts the slowest
How can you differentiate between aldehydes and ketones using DNP?
