Unit 5: Revolutions
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Scientific Revolution
a new vision of science developed during the renaissance in the 17th + 18th century
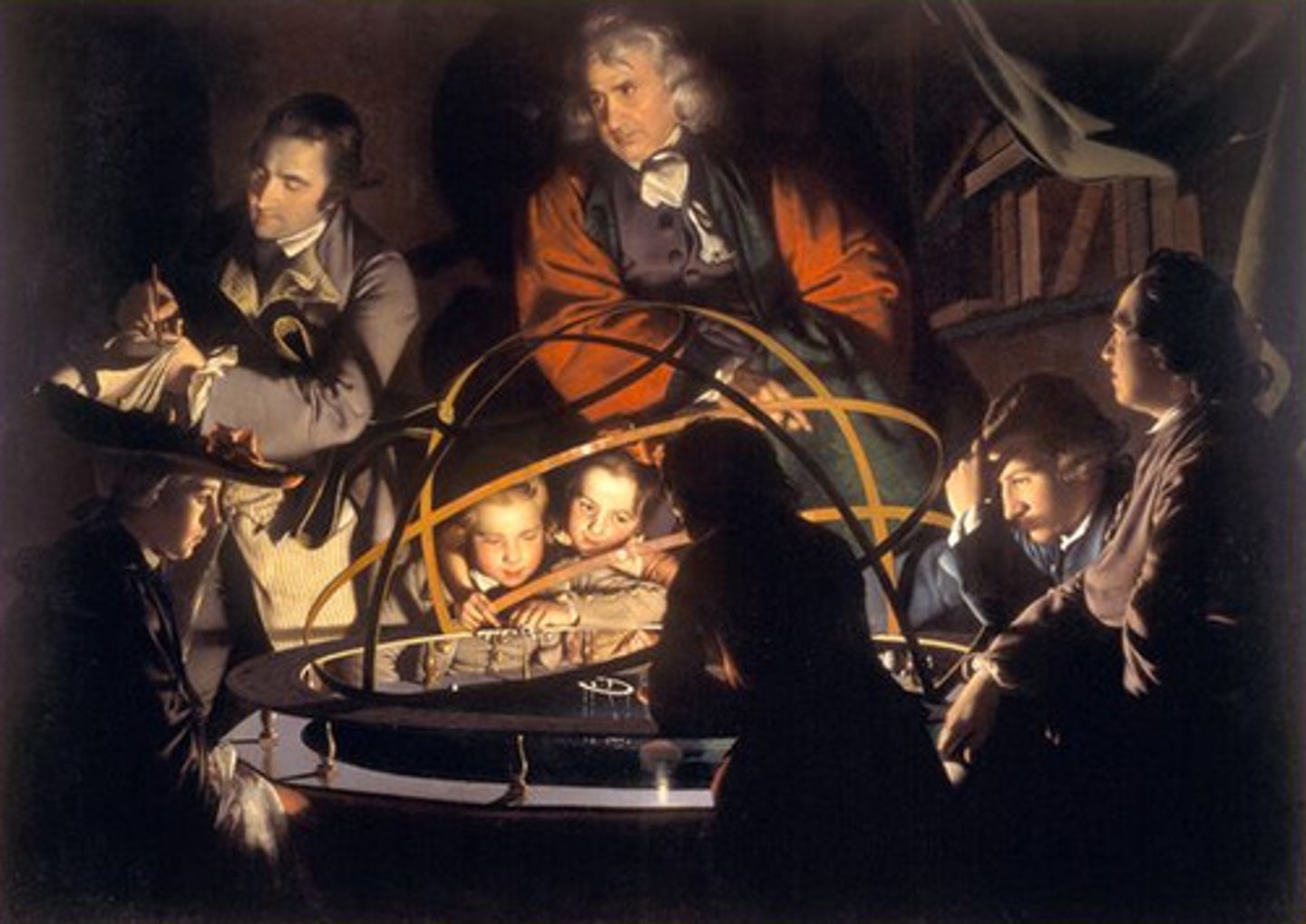
Galileo
used the first telescope during the Renaissance in 1609, where he made many large discoveries in the solar system, until he was put under house arrest for spreading conflicting ideas

Isaac Newton
discovered the basic principles of motion + gravity, where he captured the vision of a entire universe in simple laws

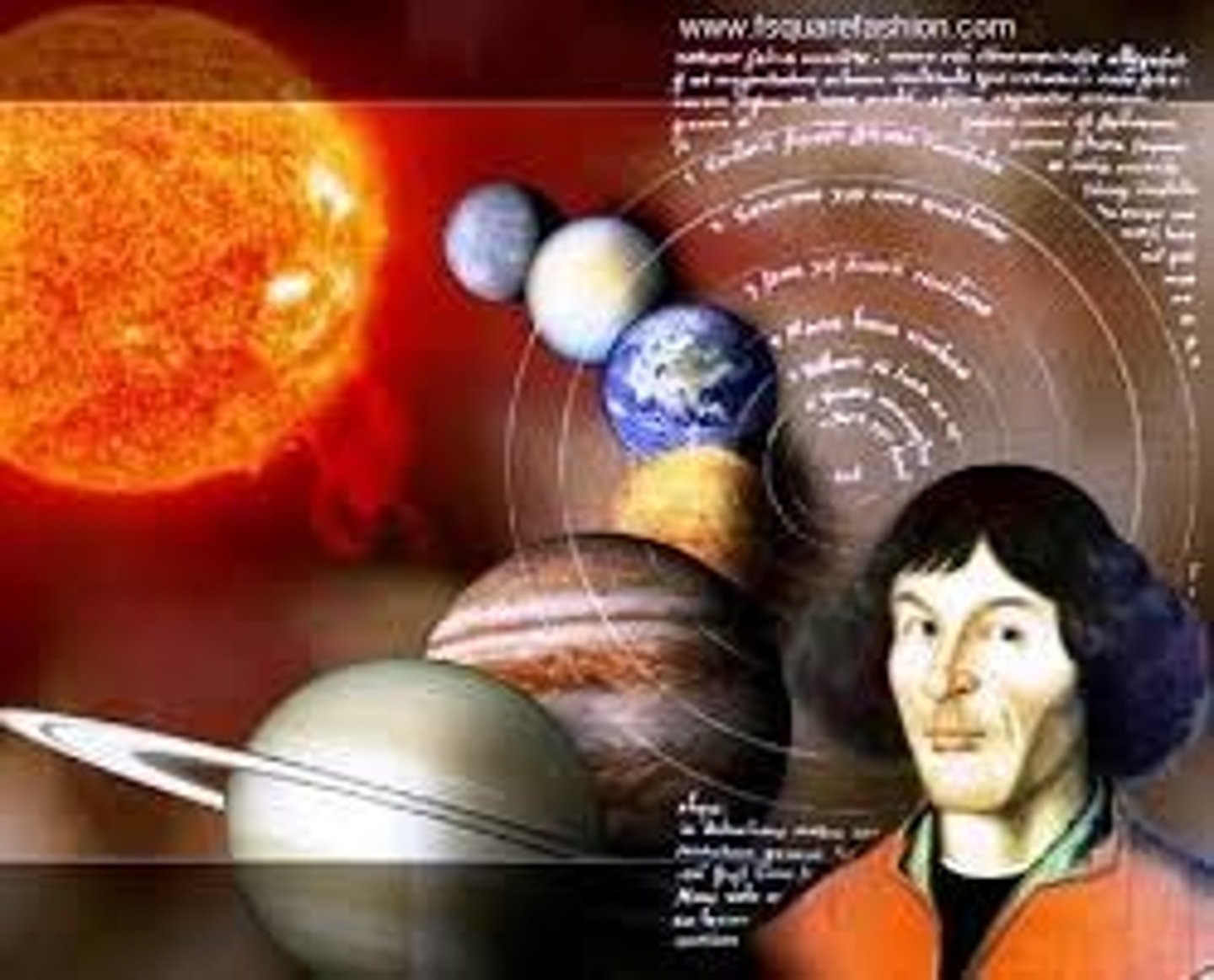
Nicholas Copernicus
a Polish monk who based tables on those by Nasir Al-Din, an Islamic scholar, to correct inaccurate calendars.
Deism
God built the universe and let it run. Clockmaker theory.

Adam Smith
He analyzed the natural law of supply and demand that governed economies in his classic book, "The Wealth of Nations"

Enlightenment
the emphasis on human abilities and accomplishments and the importance of independent and rational thought

John Locke
sought to understand the impact of the "laws of nature" on human liberties

Thomas Hobbes
English materialist and political philosopher who advocated absolute sovereignty as the only kind of government that could resolve problems caused by the selfishness of human beings (1588-1679)

Montesquieu
admired the British Parliament that had successfully gained power at the expense of the king, who also advocated a three-branch government with three branches that shared political power
Voltaire
wrote witty criticisms of the French monarchy and the Roman Catholic Church. He believed both institutions to be despotic and intolerant, limiting freedoms

Rosseau
the most radical of the common philosophers, he proclaimed in his social context that "Man is born free: and everywhere he is in chains". Since society had "Corrupted" human nature, he advocated a return to nature in a small, co-op community

Divine Right
with God's blessing of the king's authority, the legitimacy of royalty across Europe was enhanced, and occurred under the reign of Louis XIV during the 17th and 18th centuries

Absolute Monarchies vs. limited monarchies
absolute monarchies held complete control over their kingdom vs. the limited power.
Capitalism
an economic system based on private ownership of property and business that provide goods to be bough and sold in a free manner

Bourgeoise
middle class; factory owners who put long hours and much of their profits into their businesses
Balance of Power
states forming a temporary alliance to prevent the state form being too powerful. used at Congress of Vienna after Napoleon
abolitionist movement
An international movement that between approximately 1780 and 1890 succeeded in condemning slavery as morally repugnant and abolishing it in much of the world; the movement was especially prominent in Britain and the United States

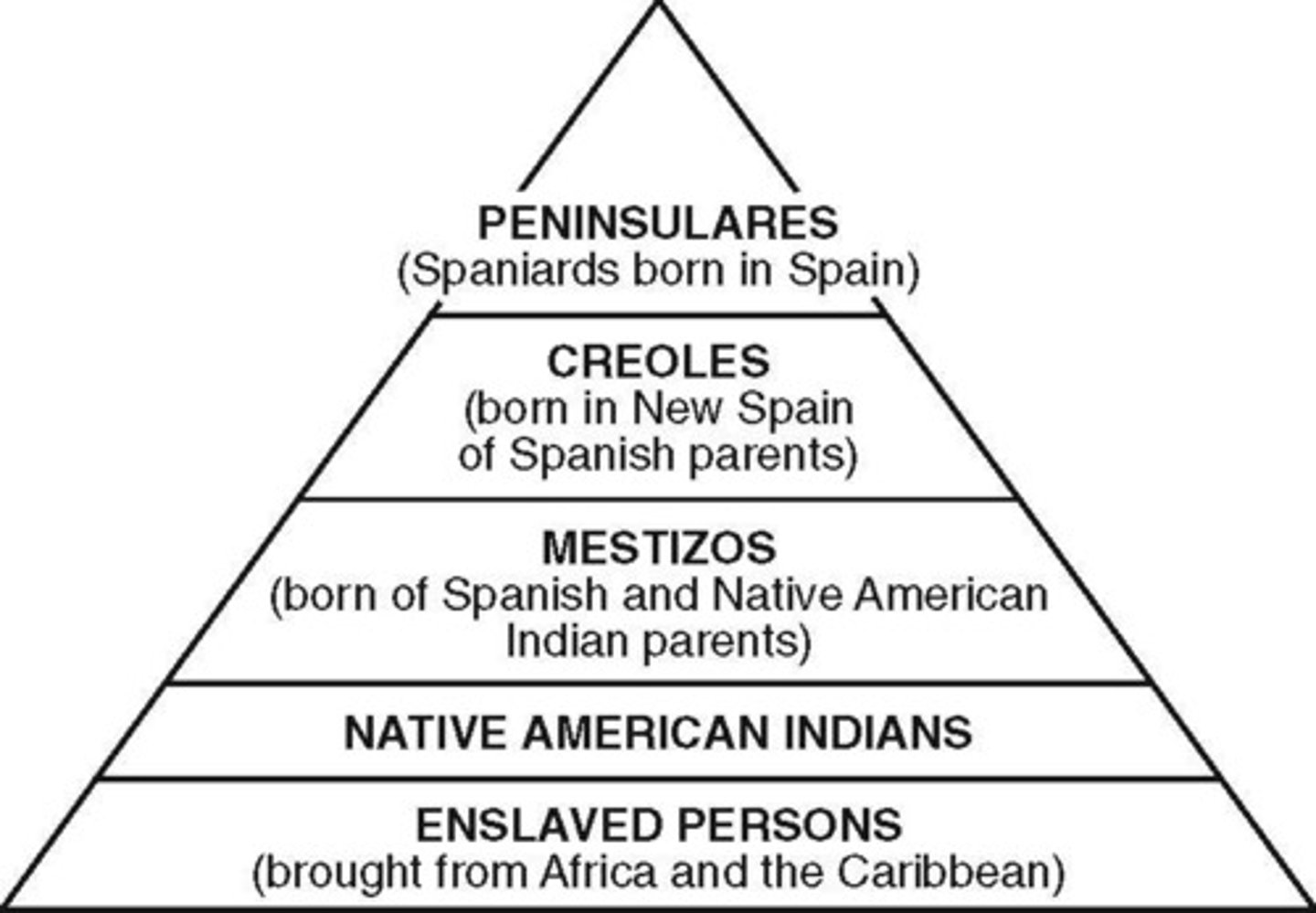
creoles
Native-born elites in the Spanish colonies. often led revolutions after embracing enlightenment ideas

Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
Document drawn up by the French National Assembly in 1789 that proclaimed the equal rights of all men; the declaration ideologically launched the French Revolution.

Declaration of the Rights of Woman
Short work written by the French feminist Olympe de Gouges in 1791 that was modeled on the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen and that made the argument that the equality proclaimed by the French revolutionaries must also include women.
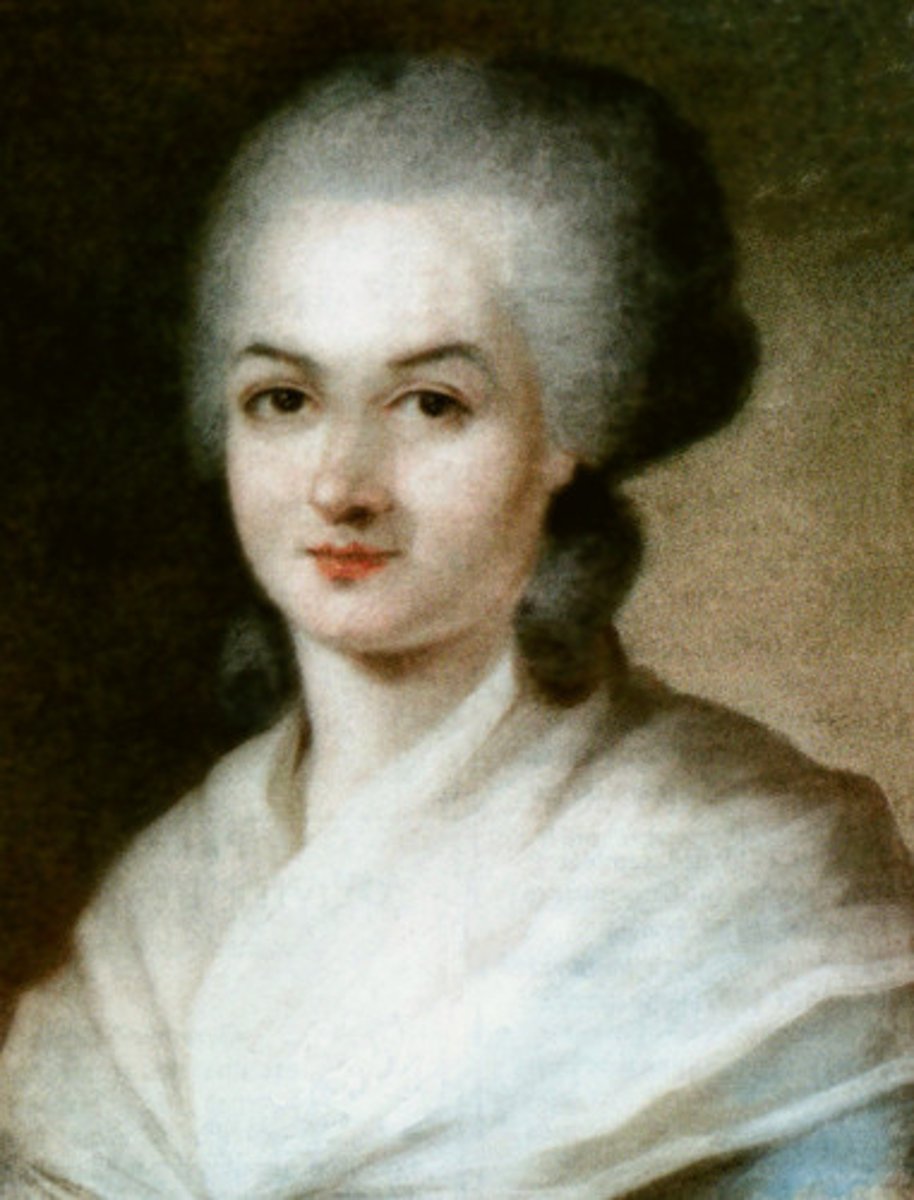

French Revolution
Massive dislocation of French society (1789-1815) that overthrew the monarchy, destroyed most of the French aristocracy, and launched radical reforms of society that were lost again, though only in part, under Napoleon's imperial rule and after the restoration of the monarchy.
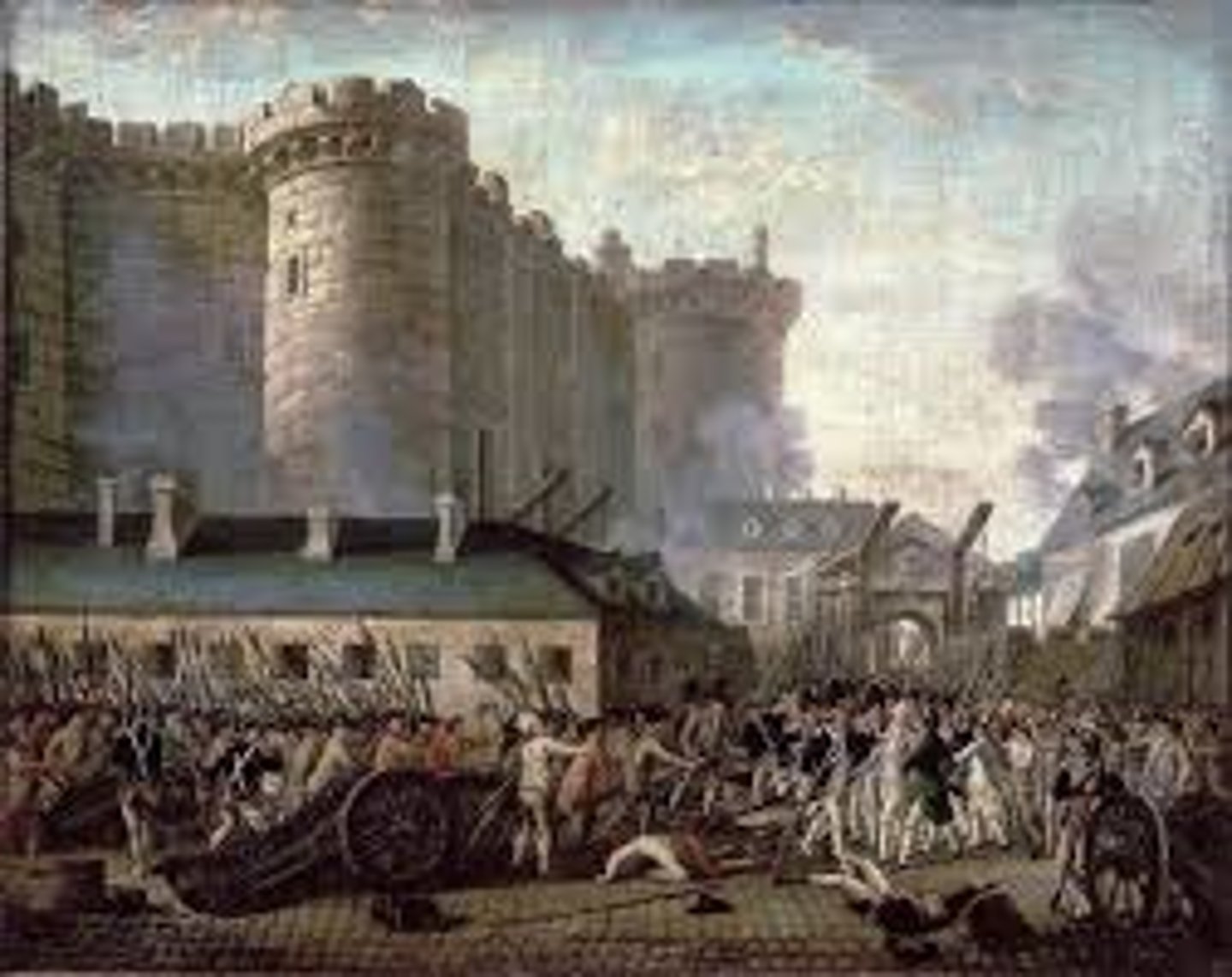

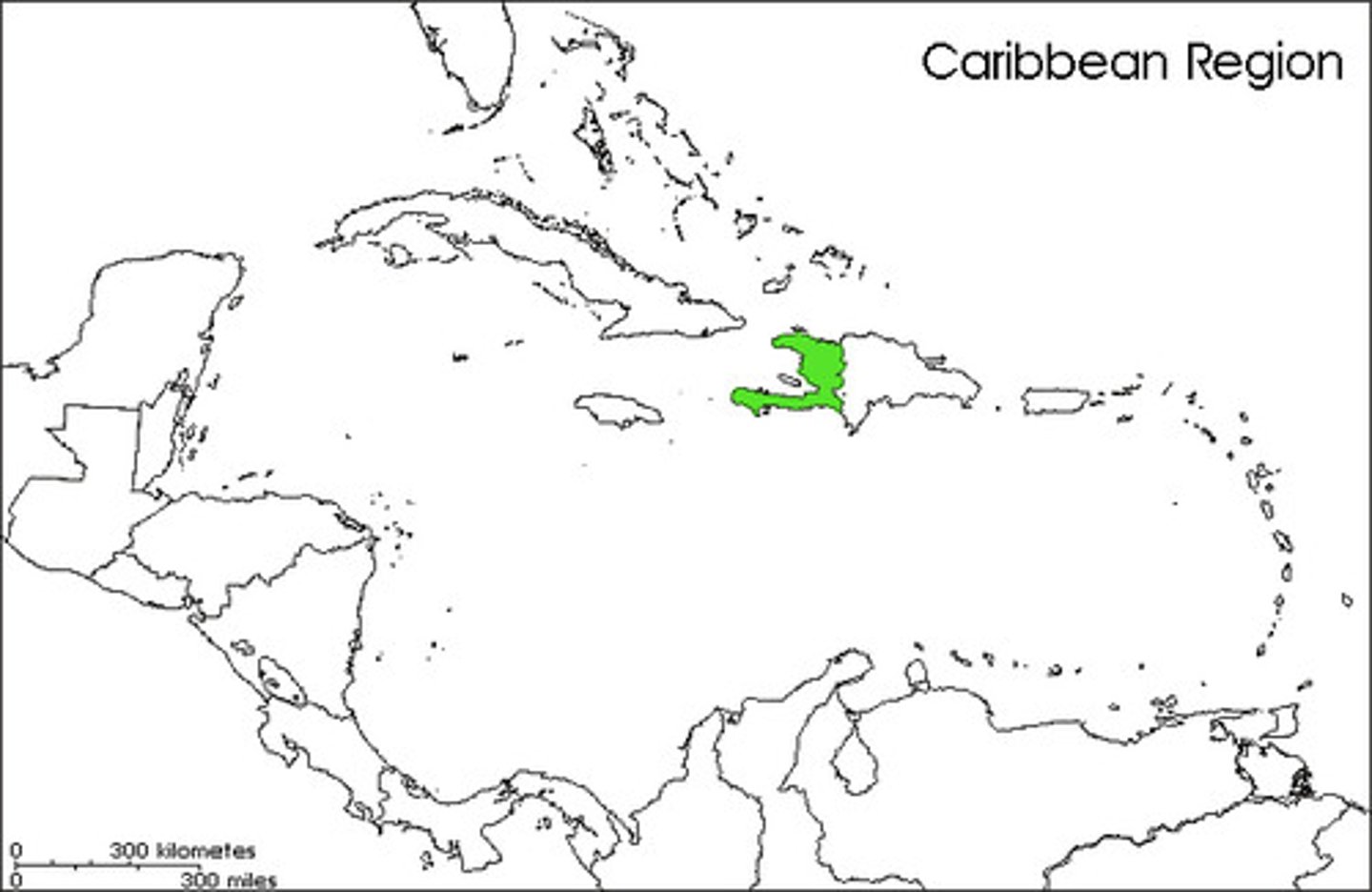
Haiti
Name that revolutionaries gave to the former French colony of Saint Domingue; the term means "mountainous" or "rugged" in the Taino language.
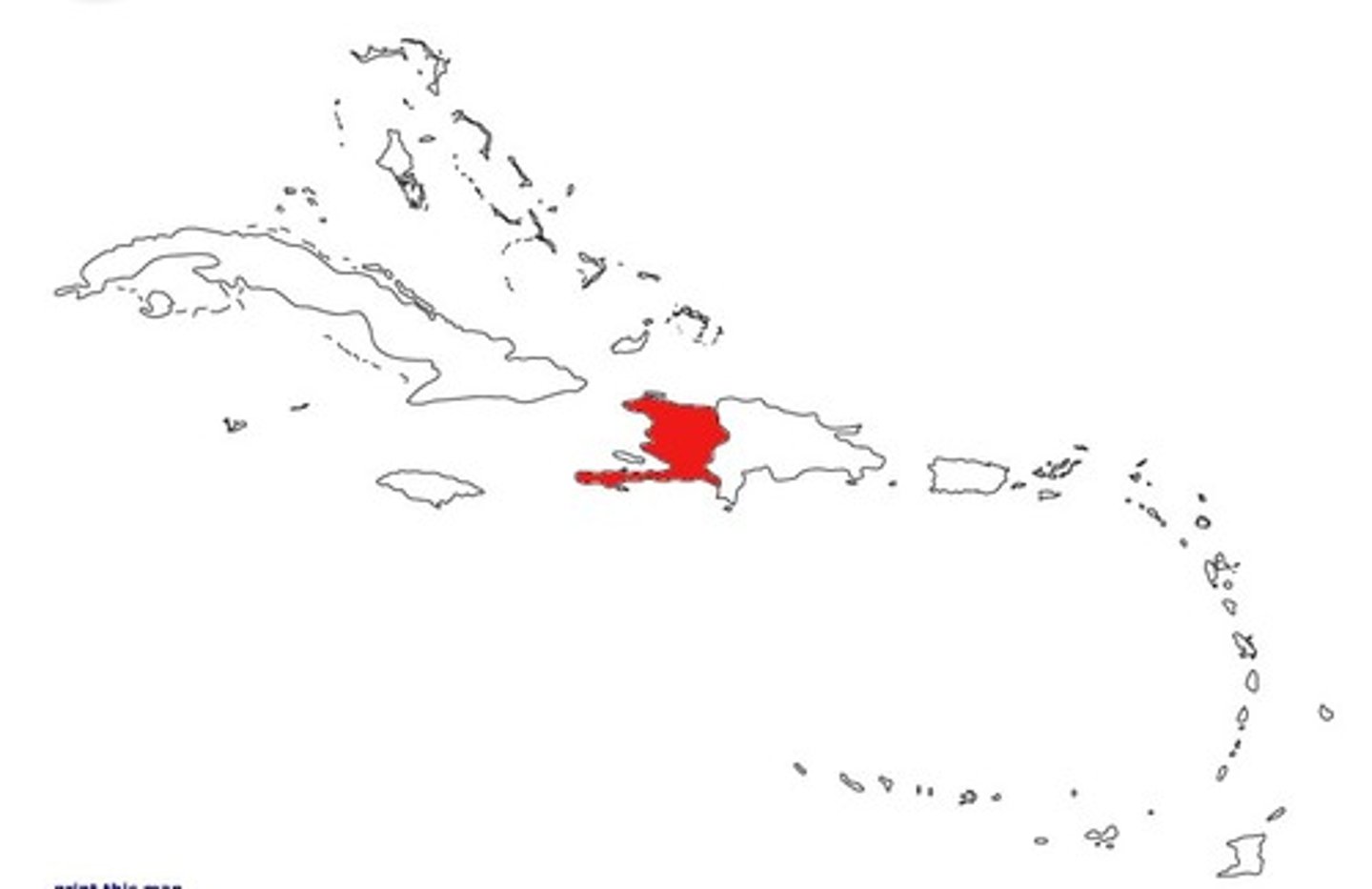
Haitian Revolution
The only fully successful slave rebellion in world history; the uprising in the French Caribbean colony of Saint Domingue (later renamed Haiti) was sparked by the French Revolution and led to the establishment of an independent state after a long and bloody war (1791-1804).

Latin American revolutions
Series of risings in the Spanish colonies of Latin America (1810-1826) that established the independence of new states from Spanish rule but that for the most part retained the privileges of the elites despite efforts at more radical social rebellion by the lower classes
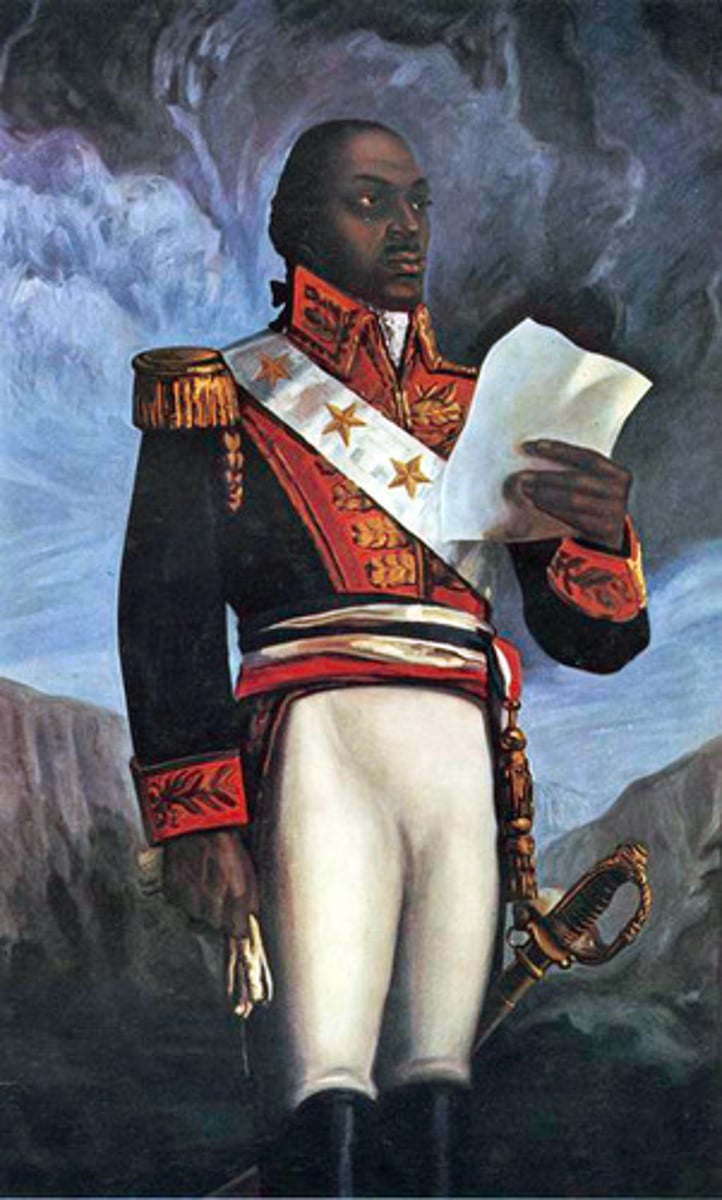
Louverture, Toussaint
First leader of the Haitian Revolution, a former slave (1743-1803) who wrote the first constitution of Haiti and served as the first governor of the newly independent state.

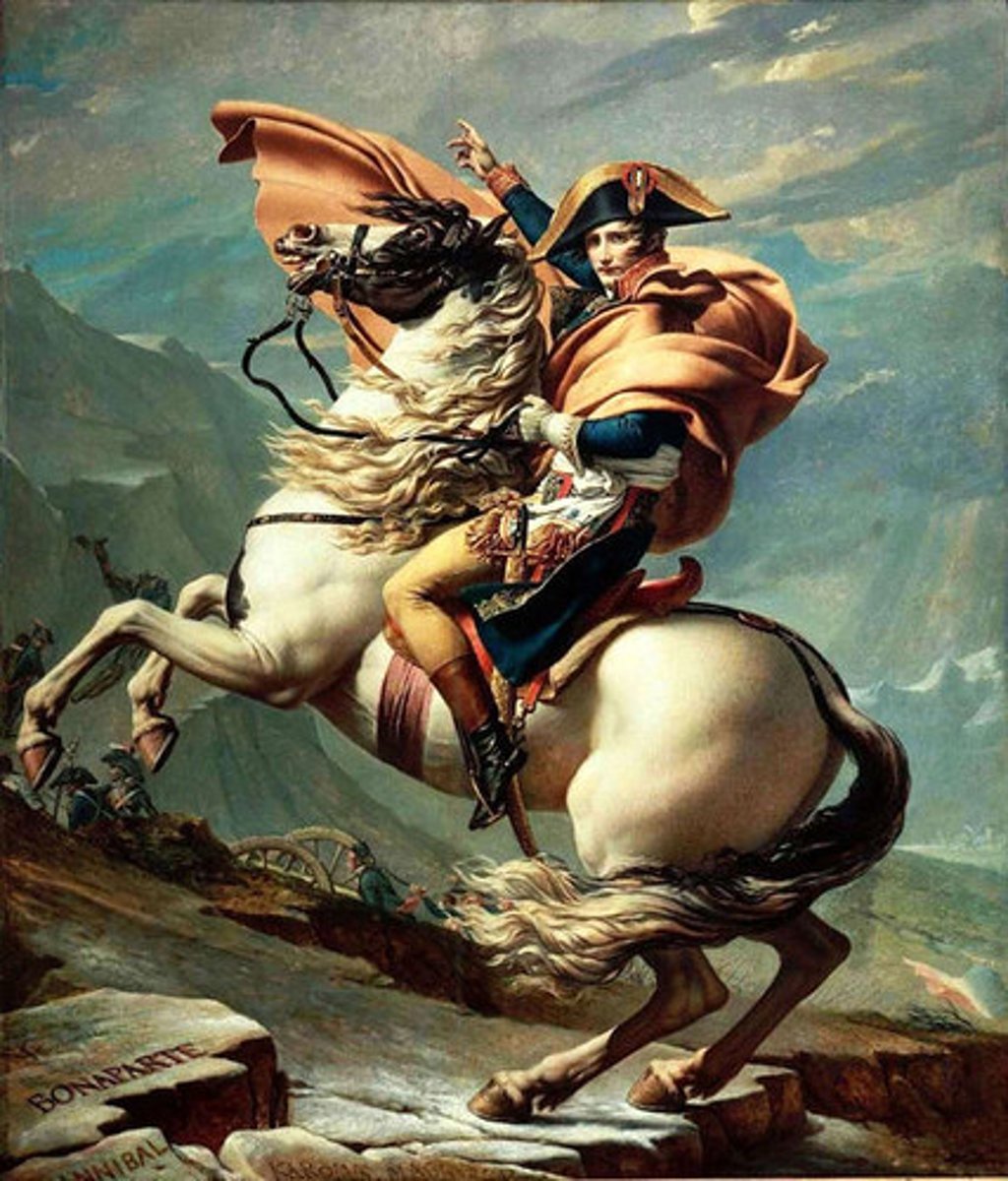
Napoleon Bonaparte
French head of state from 1799 until his abdication in 1814 (and again briefly in 1815); Napoleon preserved much of the French Revolution under an autocratic system and was responsible for the spread of revolutionary ideals through his conquest of much of Europe.

nationalism
The focusing of citizens' loyalty on the notion that they are part of a "nation" with a unique culture, territory, and destiny; first became a prominent element of political culture in the nineteenth century.
North American Revolution
Successful rebellion conducted by the colonists of parts of North America (not Canada) against British rule (1775-1787); a conservative revolution whose success assured property rights but established republican government in place of monarchy

petit blancs
The "little" (or poor) white population of Saint Domingue, which played a significant role in the Haitian Revolution.
Seneca Falls Conference
The first organized women's rights conference, which took place at Seneca Falls, New York, in 1848.
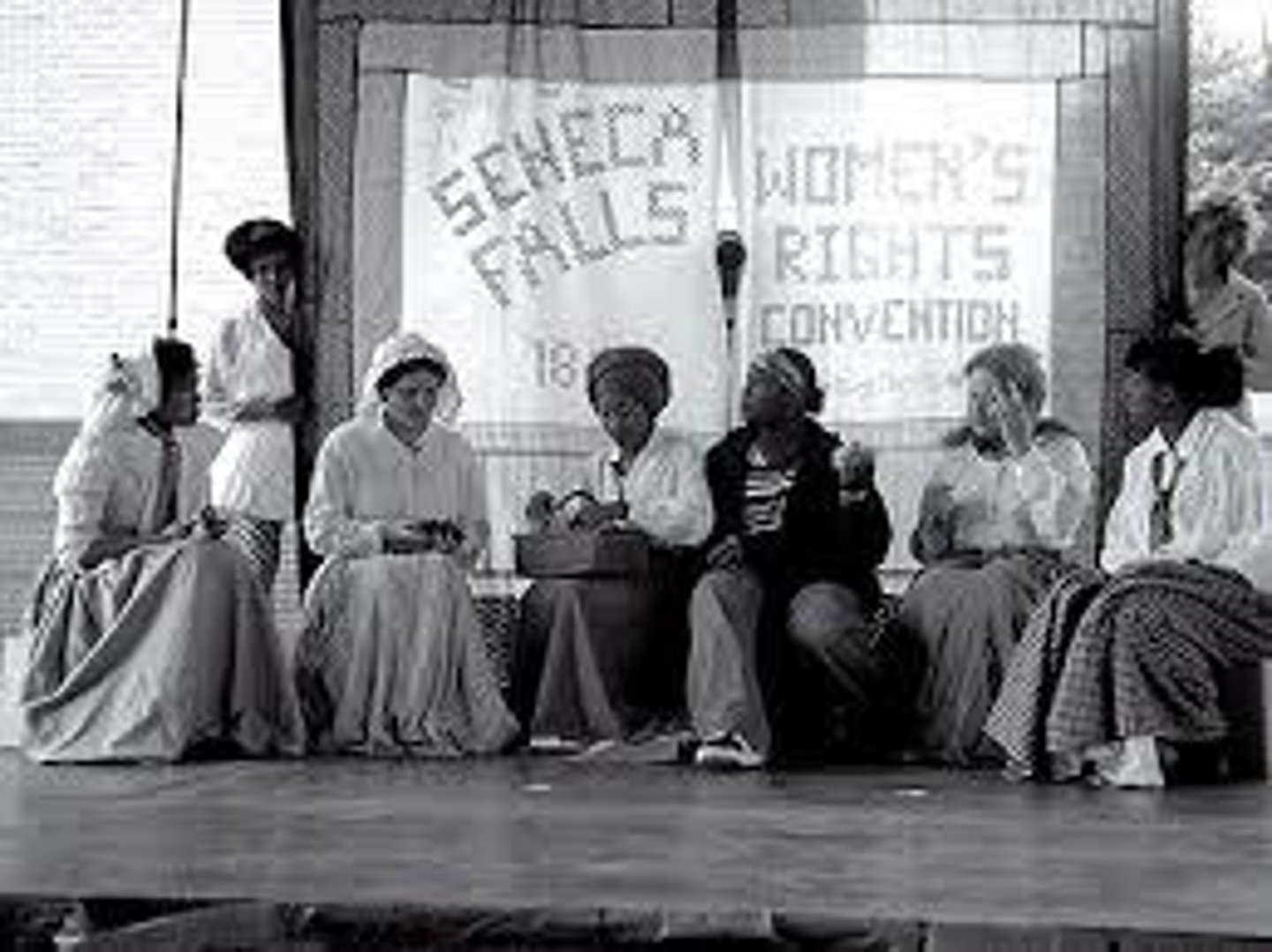

Stanton, Elizabeth Cady
Leading figure of the early women's rights movement in the US

Third Estate
In prerevolutionary France, the term used for the 98 percent of the population that was neither clerical nor noble, and for their representatives at the Estates General; in 1789, the Third Estate declared itself a National Assembly and launched the French Revolution

bourgeoisie
Term that Karl Marx used to describe the owners of industrial capital; originally meant "townspeople."
Indian cotton textiles
For much of the eighteenth century, well-made and inexpensive cotton textiles from India flooded Western markets; the competition stimulated the British textile industry to industrialize, which led to the eventual destruction of the Indian textile market both in Europe and in India.

Labour Party
British working-class political party established in the 1890s and dedicated to reforms and a peaceful transition to socialism, in time providing a viable alternative to the revolutionary emphasis of Marxism.
Latin American export boom
Large-scale increase in Latin American exports (mostly raw materials and foodstuffs) to industrializing countries in the second half of the nineteenth century, made possible by major improvements in shipping; the boom mostly benefited the upper and middle classes.
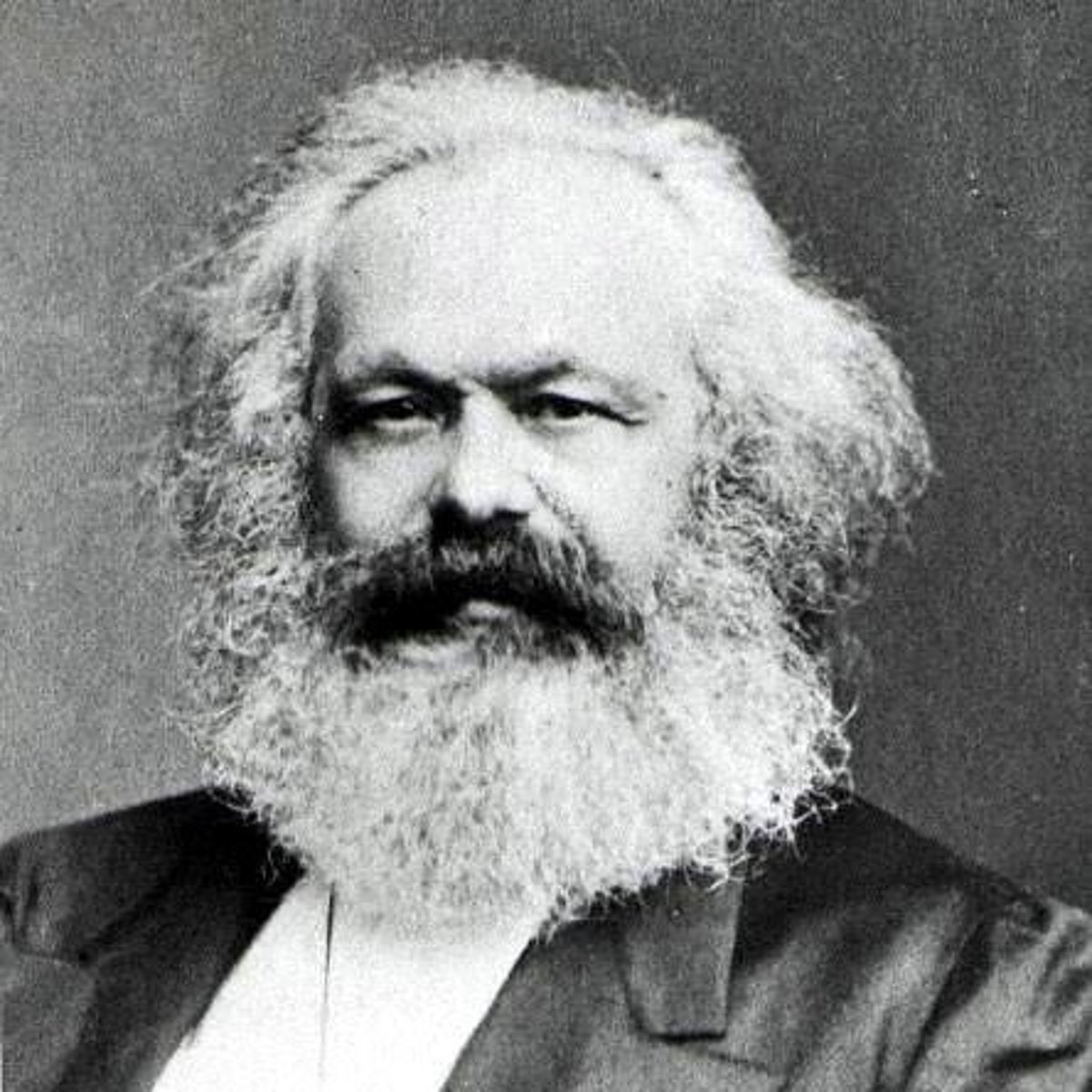
Marx, Karl
The most influential proponent of socialism, Marx (1818-1883) was a German expatriate in England who advocated working-class revolution as the key to creating an ideal communist future.

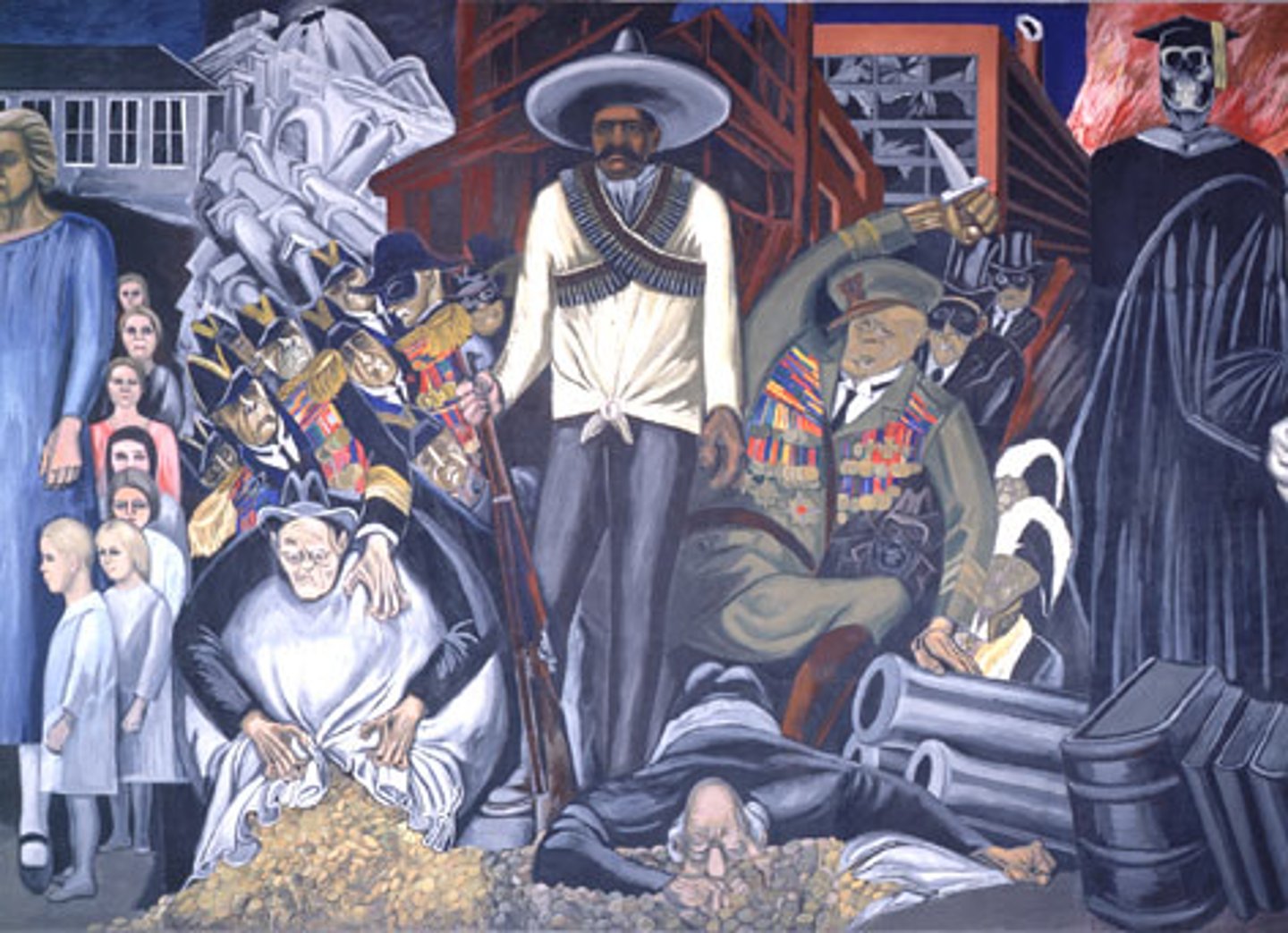
Mexican Revolution
Long and bloody war (1911-1920) in which Mexican reformers from the middle class joined with workers and peasants to overthrow the dictator Porfirio Díaz and create a new, much more democratic political order.

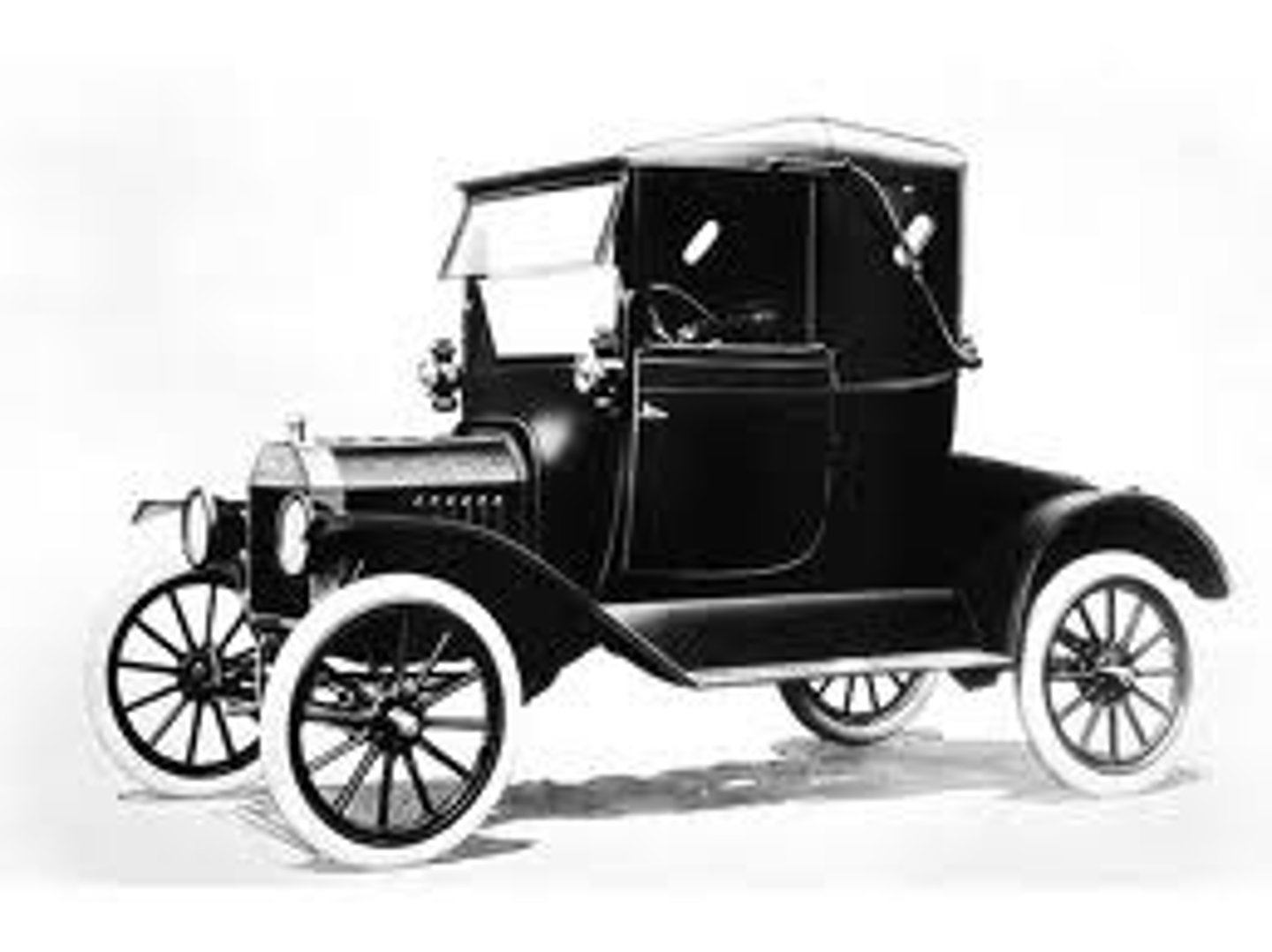
Model T
The first automobile affordable enough for a mass market; produced by American industrialist Henry Ford.

progressivism
American political movement in the period around 1900 that advocated reform measures to correct the ills of industrialization.
proletariat
Term that Karl Marx used to describe the industrial working class; originally used in ancient Rome to describe the poorest part of the urban population.

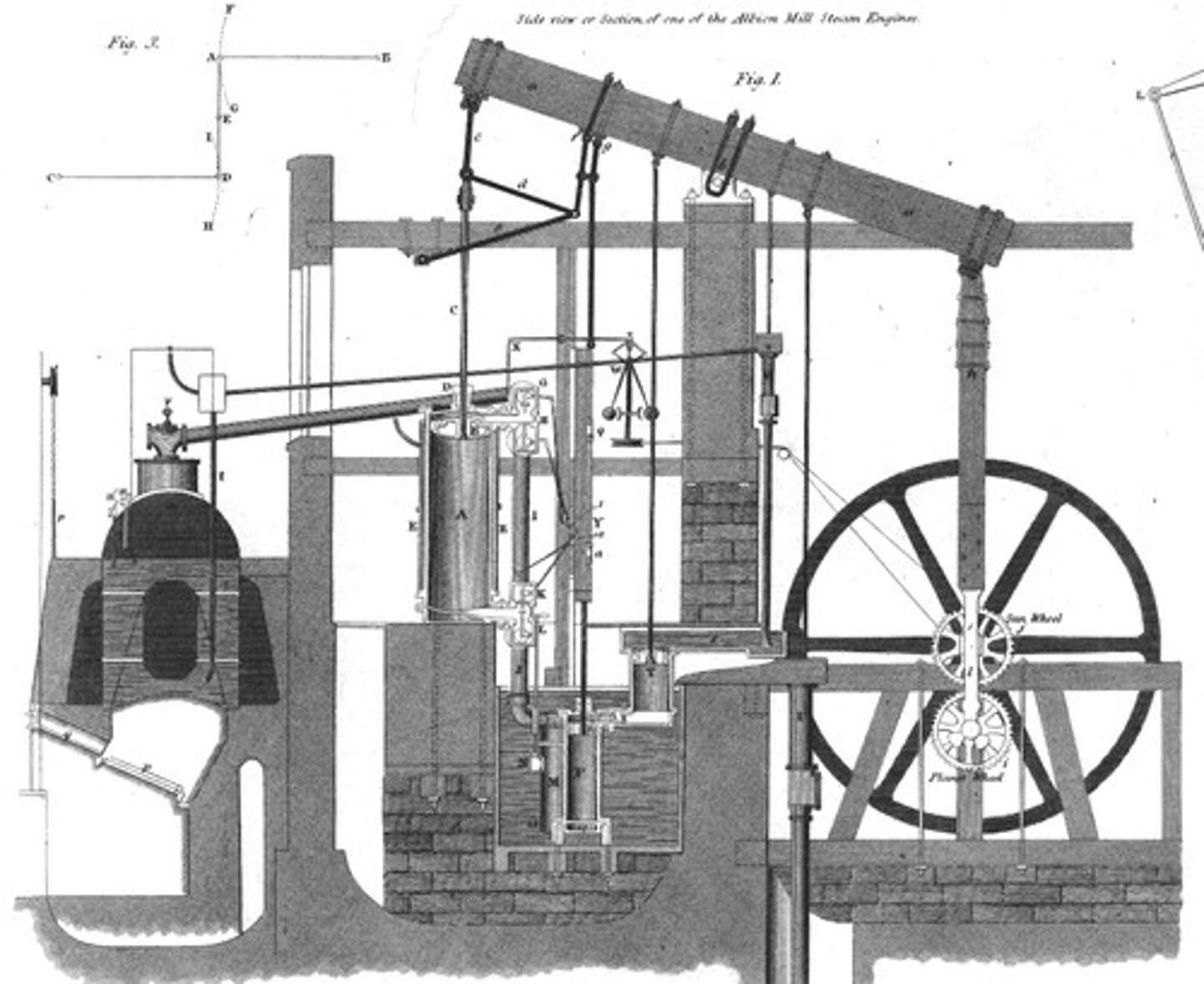
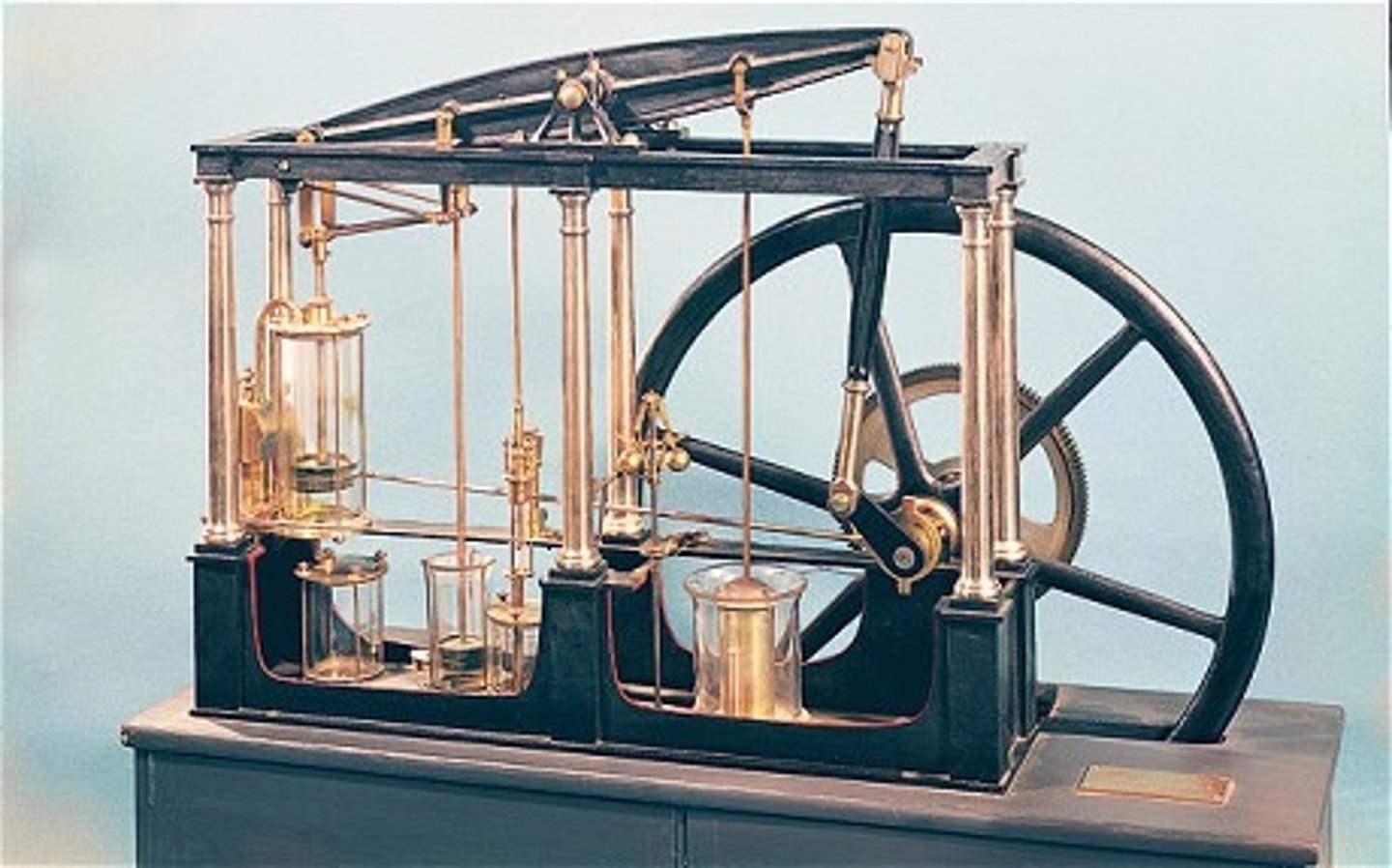
steam engine
Mechanical device in which the steam from heated water builds up pressure to drive a piston, rather than relying on human or animal muscle power; the introduction of the steam engine allowed a hitherto unimagined increase in productivity and made the Industrial Revolution possible.
Abd al-Hamid II
Ottoman sultan (r. 1876-1909) who accepted a reform constitution but then quickly suppressed it, ruling as a reactionary autocrat for the rest of his long reign.

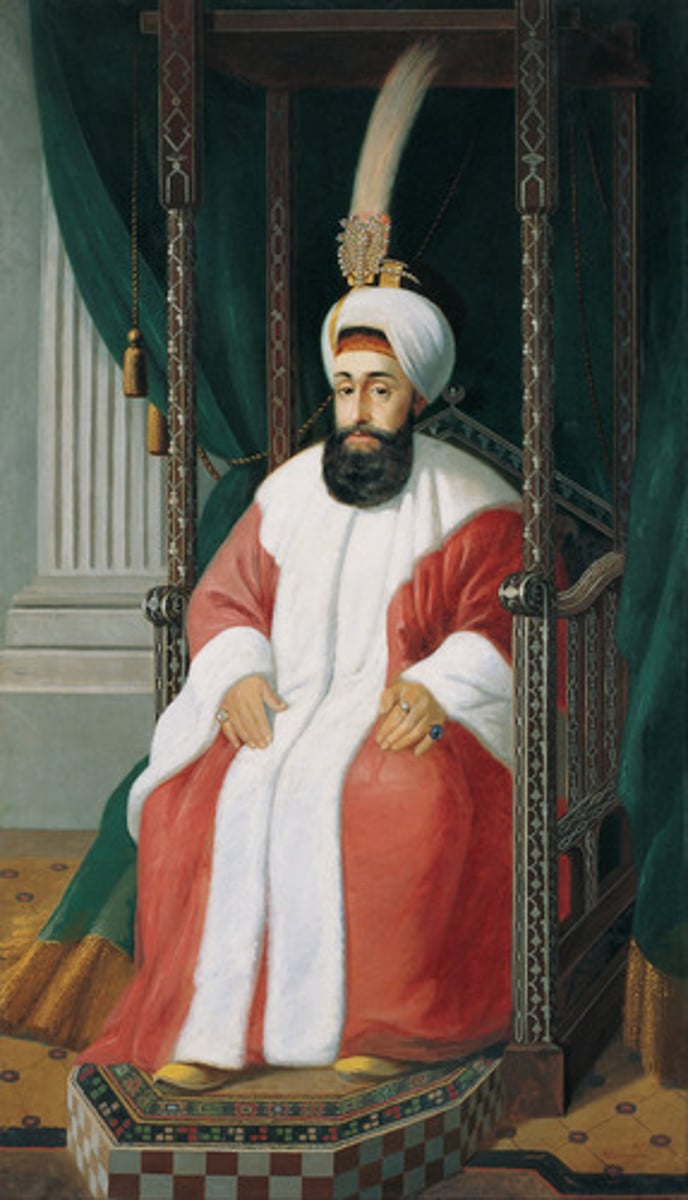
Selim III
Ottoman sultan (r. 1789-1807) who attempted significant reforms of his empire, including the implementation of new military and administrative structures.

"sick man of Europe, the"
Western Europe's unkind nickname for the Ottoman Empire in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, a name based on the sultans' inability to prevent Western takeover of many regions and to deal with internal problems; it fails to recognize serious reform efforts in the Ottoman state during this period.
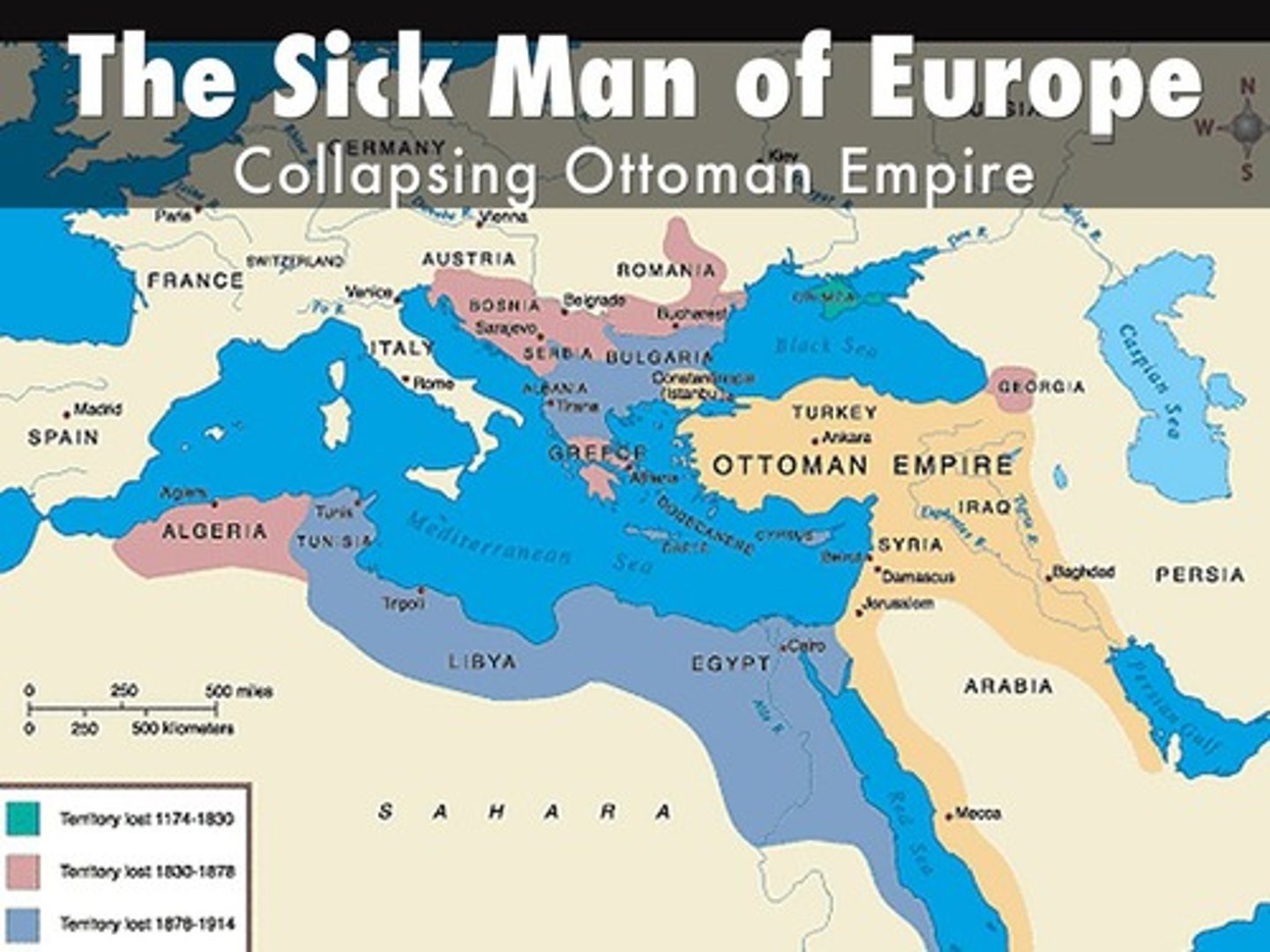
Young Ottomans
Group of would-be reformers in the mid-nineteenth-century Ottoman Empire that included lower-level officials, military officers, and writers; they urged the extension of Westernizing reforms to the political system.

Young Turks
Movement of Turkish military and civilian elites that developed ca. 1900, eventually bringing down the Ottoman Empire.

A Vindication of the Rights of Women (1792)
written by Mary Wollstonecraft argued that women must obey men that is was a direct contridiction to the beliefs of the same individual in that no ruler had the rights over their subjects, the ideal of the enlightment was based on innate reason in all human beings not just men

Women's Suffrage
Women's right to vote; many countries around the world gave women the right to vote after WWI due to their work to support the war effort

German Unification
In the 19th-century, various independent German-speaking states, led by the chancellor of Prussia Otto von Bismarck, unified to create a Germanic state. The state expanded with von Bismarck's military exploits against Austria, France and Denmark. Unification was complete by 1871 with the Prussian king, Wilhelm, named the first leader of Germany.

Italian Unification
During 1848, Italy was separated into many states. Cavour worked to unify the North then helped Giuseppe Garibaldi unify the South staring with Sicily. Garibaldi eventually stepped aside and handed over all of Southern Italy to Victor Emmanuel II (King of Sardinia) rule all of the now unified Italy

Balkan Nationalism
Movements to create independent nations within the Balkan possessions of the Ottoman Empire; provoked a series of crises within the European alliance system; eventually led to World War I.
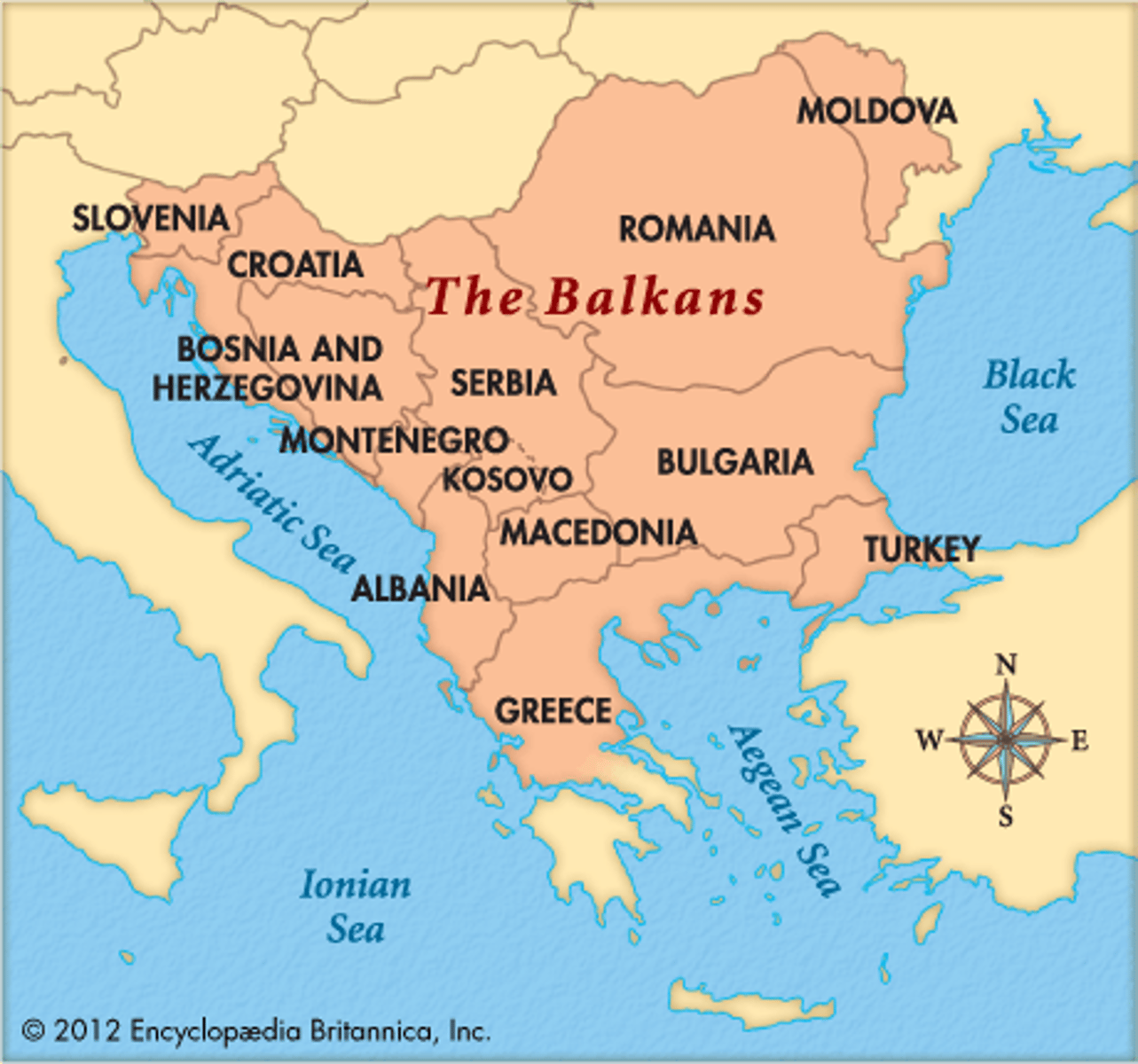
Ottomanism
An ideology developed by the Ottoman govt in order to strengthen their subjects' loyalty and solidarity. Focused on the idea the all subjects are equal (despite religious/ethinic/linguistic differences) and deserved equal rights (reinforced by Imperial decree of 1856).
American Revolution
This political revolution began with the Declaration of Independence in 1776 where American colonists sought to balance the power between government and the people and protect the rights of citizens in a democracy.
Letter from Jamaica
document written by Simon Bolivar, 1815 Bolívar explained his thoughts about the social and political situation of the Spanish America at the time, the power of the Spanish Empire and the possible future of the new nations that would be created after its collapse.

Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements. Began in England and led to an increase in industrial production
Factory System
This new system gradually replaced localized cottage industry. Workers were paid by the hour instead of for what they produce. On one hand it decreased the need for skilled labor, but in other ways it increased the amount of specialization due to labor being concentrated in factories.
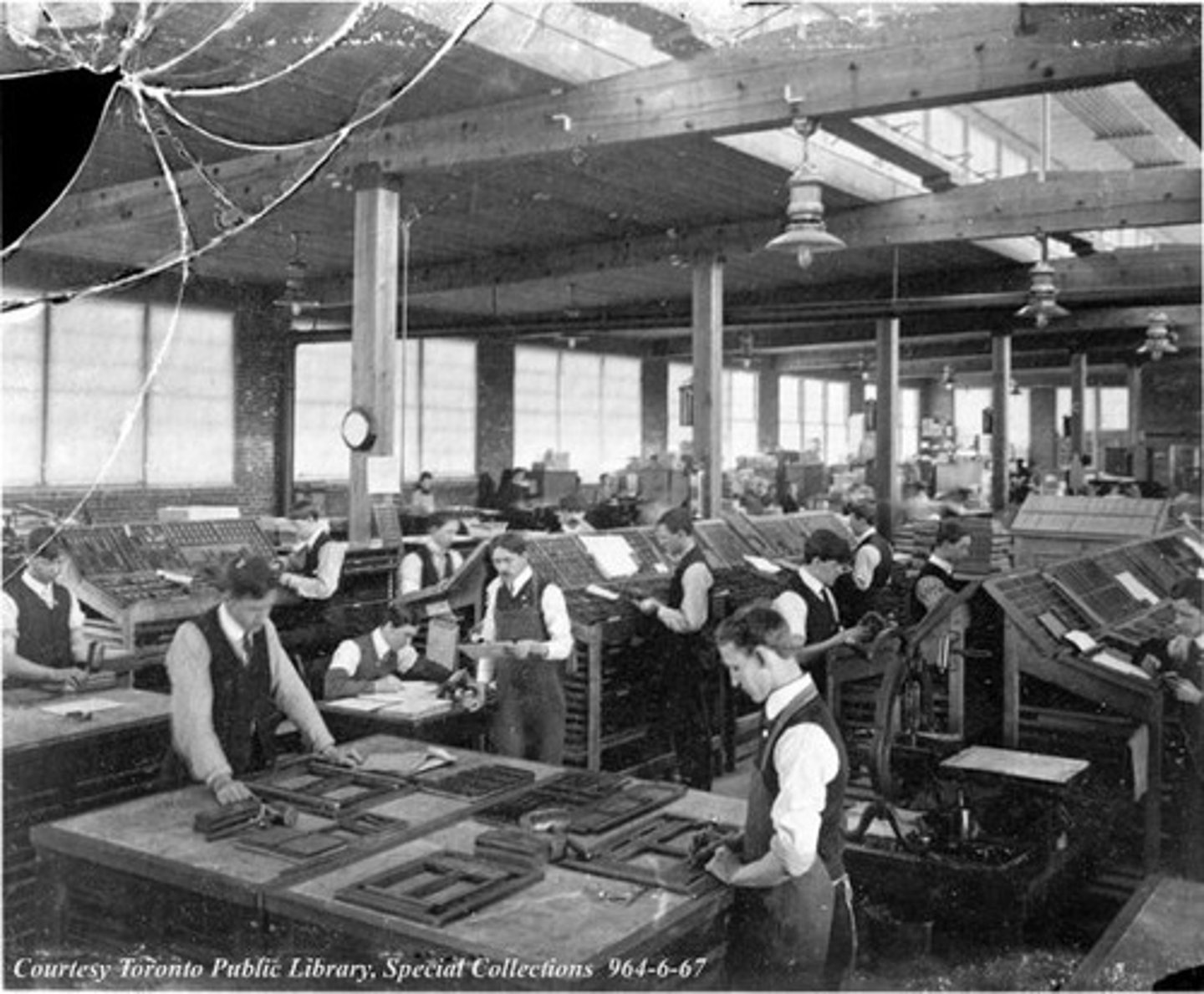

Second Industrial Revolution
Steel, chemicals, electricity. This is the name for the new wave of more heavy industrialization starting around the 1860s.
Fossil Fuels
Coal, oil, natural gas, and other fuels that are ancient remains of plants and animals. increased in use for energy during the Industrial Revolution
Technology in Industrial Age
railroads, steamships, and the telegraph made exploration, development, and communication possible. This led to an increase in migration and trade
Muhammad Ali (Egypt)
Commander in the Ottoman army in early 1800s and whose loyal followers executed the Mamluk leaders.
In the power vacuum created, he orchestrated the establishment of the modern state of Egypt through adoption of a western model of government [bureaucracy, streamline economics, and develop a modern military]
![<p>Commander in the Ottoman army in early 1800s and whose loyal followers executed the Mamluk leaders.</p><p>In the power vacuum created, he orchestrated the establishment of the modern state of Egypt through adoption of a western model of government [bureaucracy, streamline economics, and develop a modern military]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a99bb9f7-01c2-4086-be0b-1ee8cbaf1252.jpg)
Meiji Restoration
The political program that followed the destruction of the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1868, in which a collection of young leaders set Japan on the path of centralization, industrialization, and imperialism.

HSBC (Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation)
HSBC was established in 1865 to finance trade between Europe and Asia. Initially founded in the British colony of Hong Kong it benefitted from the opening of China to trade, including the opium trade.

Unilever
Transnational business based in England and the Netherlands operating in British West Africa and the Belgian Congo
Stock Markets
New financial instruments--especially ways for businesses to raise money--were developed in this period. This includes insurance, corporations, and ____ ____, exchanges where corporate shares could be sold.
laissez-faire capitalism
an economic system written about by Adam Smith in which the means of production and distribution are privately owned and operated for profit with minimal or no government interference
Labor Unions
An organization formed by workers to strive for better wages and working conditions
Beseemer Process
method developed in the late 1850s to produce stronger steel at a lower cost.
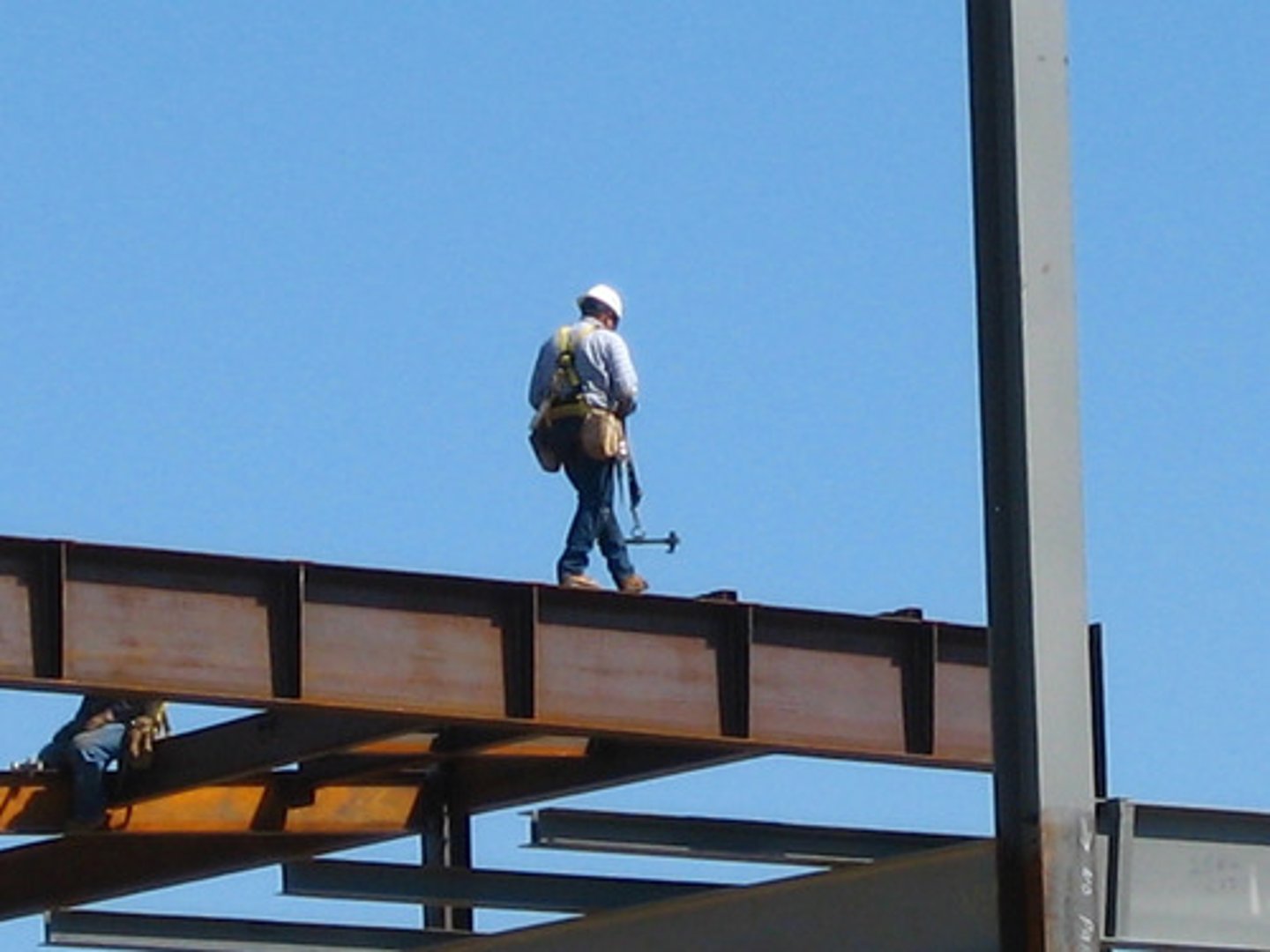

James Watt
Scottish engineer and inventor whose improvements in the steam engine led to its wide use in industry (1736-1819).
James Hargreaves
invented the spinning jenny
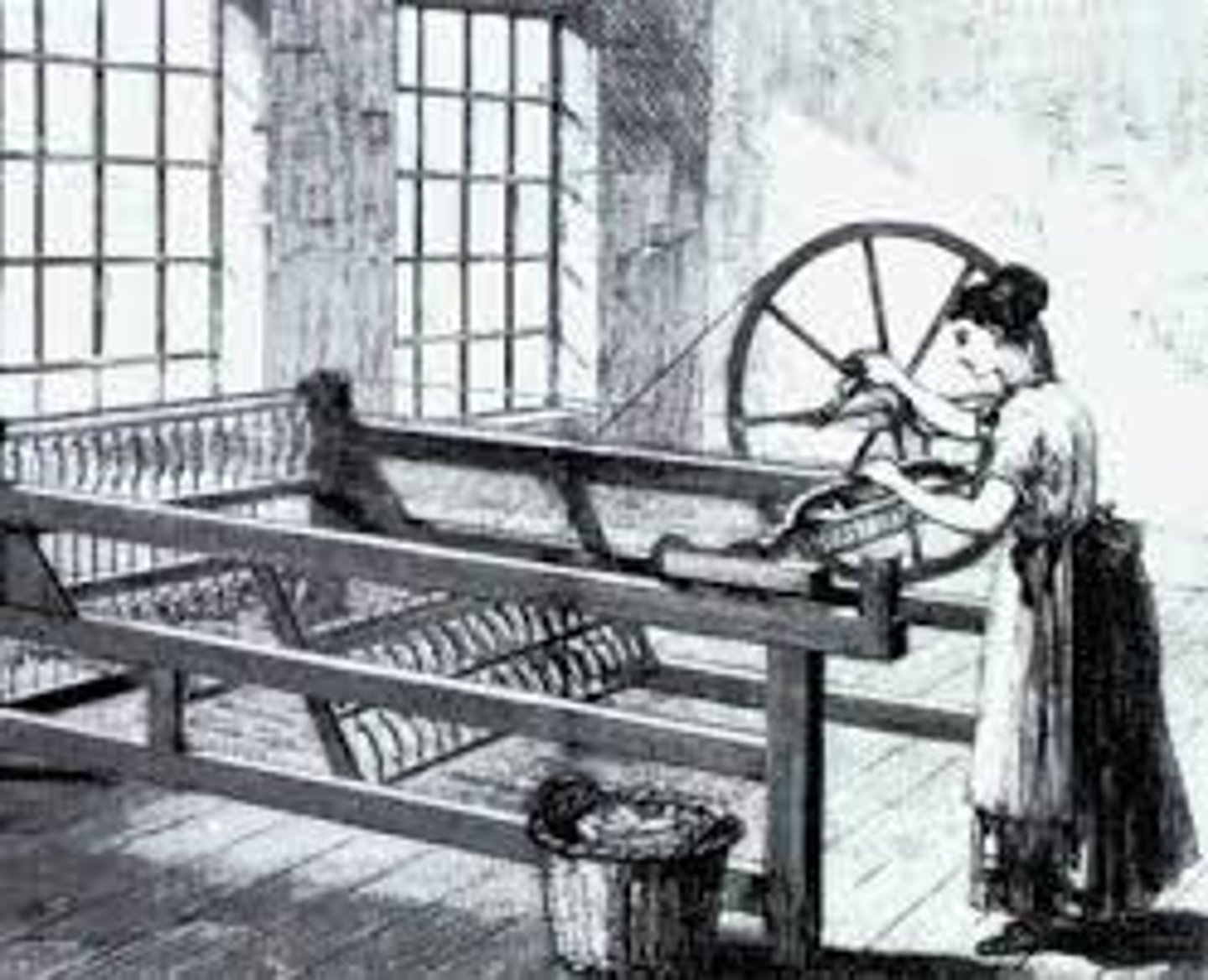

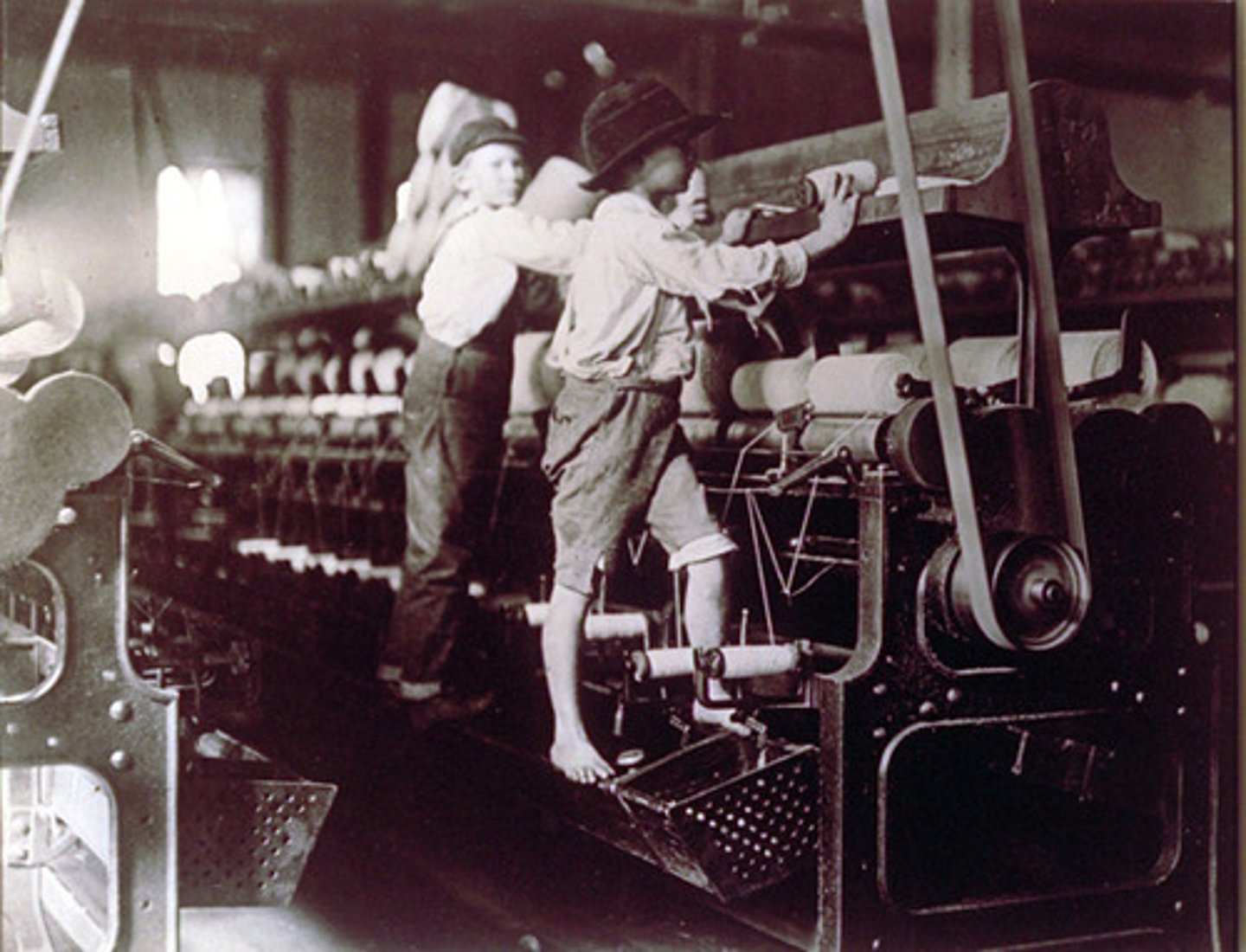
Women and Child Labor
By 1900 more than 1,000,000 women had joined industrial workforce
There were no laws that regulated worker salaries, so women earned about half of what men did for the same work
Child labor
Hundreds of thousands of children worked in factories
Many states passed laws saying no child under 12 could work in factories
These laws were mostly ignored by employers
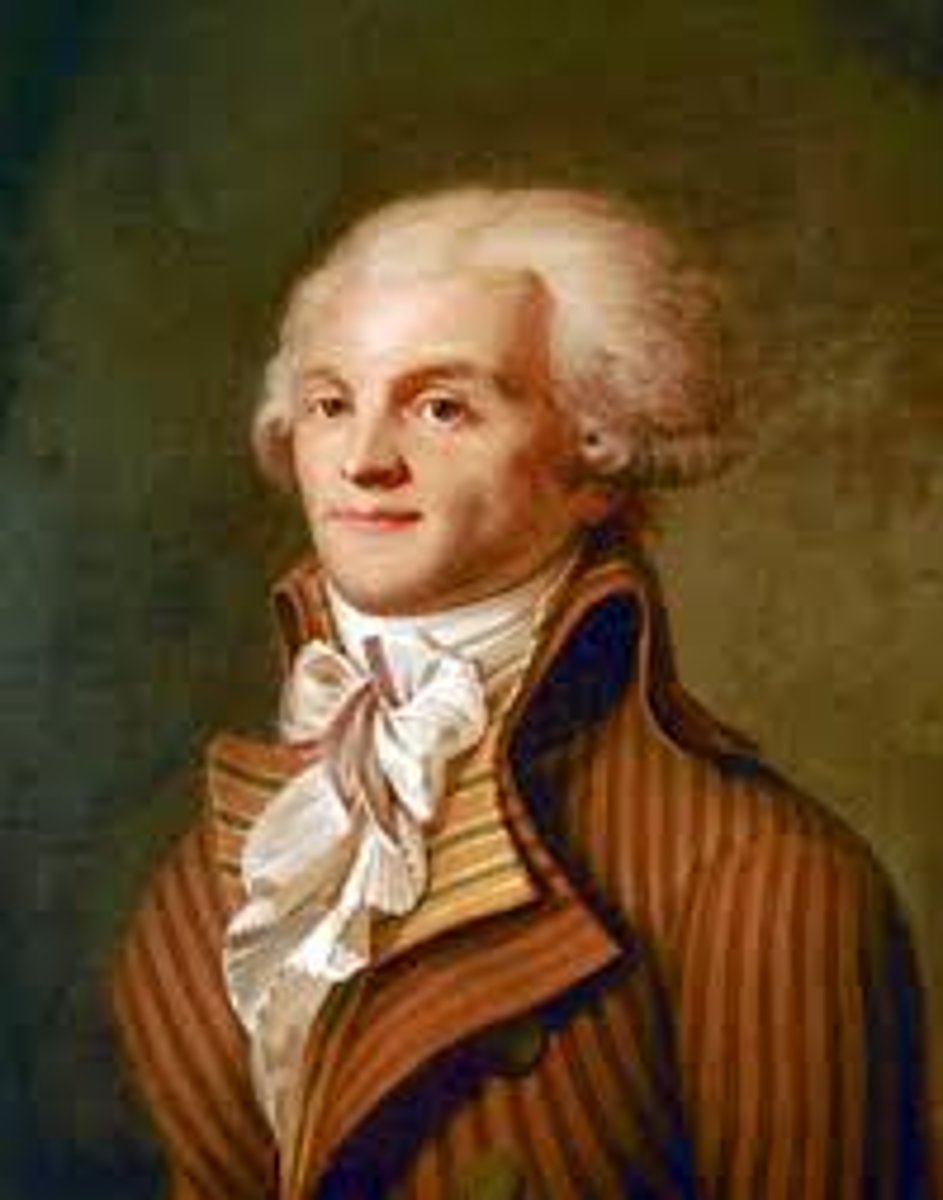
Maximilien Robespierre
Young provincial lawyer who led the most radical phases of the French Revolution; his execution ended the Reign of Terror.

19th Century Liberalism
Politically they emphasized popular sovereignty, individual rights, but shifted from laissez-faire (classical liberalism) to some interventionist economic and social policies on behalf of the less privileged; based on a rational approach to reform that addressed the impact of the Industrial Revolution on the individual
Calls for national unification or liberation
--Propaganda movement in phillippines
--maori nationalism in New Zealand
--Puerto Rico
--German and Italian Unification
--Balkan Nationalism
--Ottomanism
Lola Rodriguez de Tio
Puerto Rican who wrote patriotic poems that supported Cuban independence.

James Hargreaves
invented the spinning jenny which revolutionized the early spinning industry for Great Britain
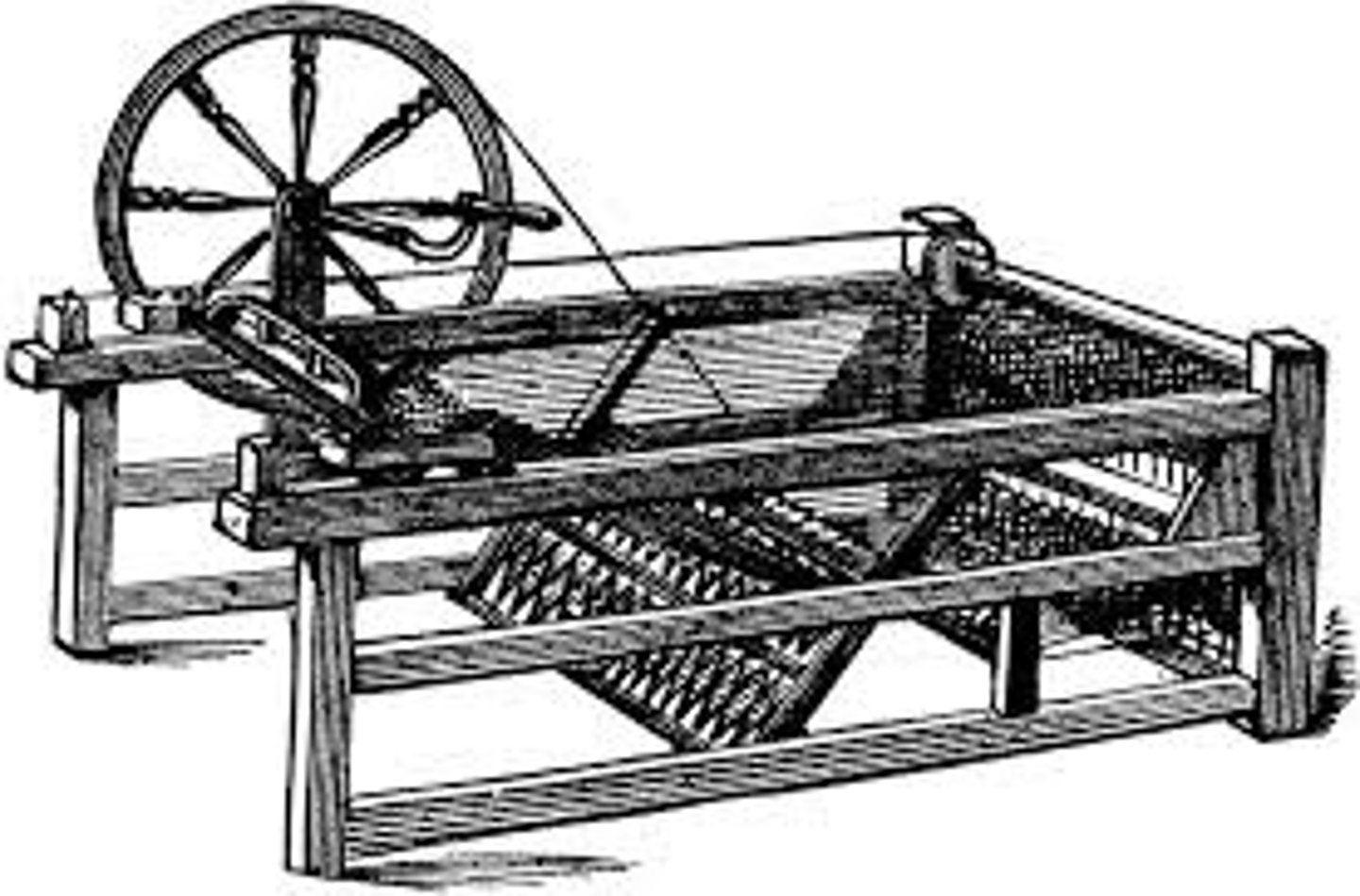
Advantages of England
Started Industrial Revolution in parts because of its abundance of colonies, natural resources, stable government, and new technologies
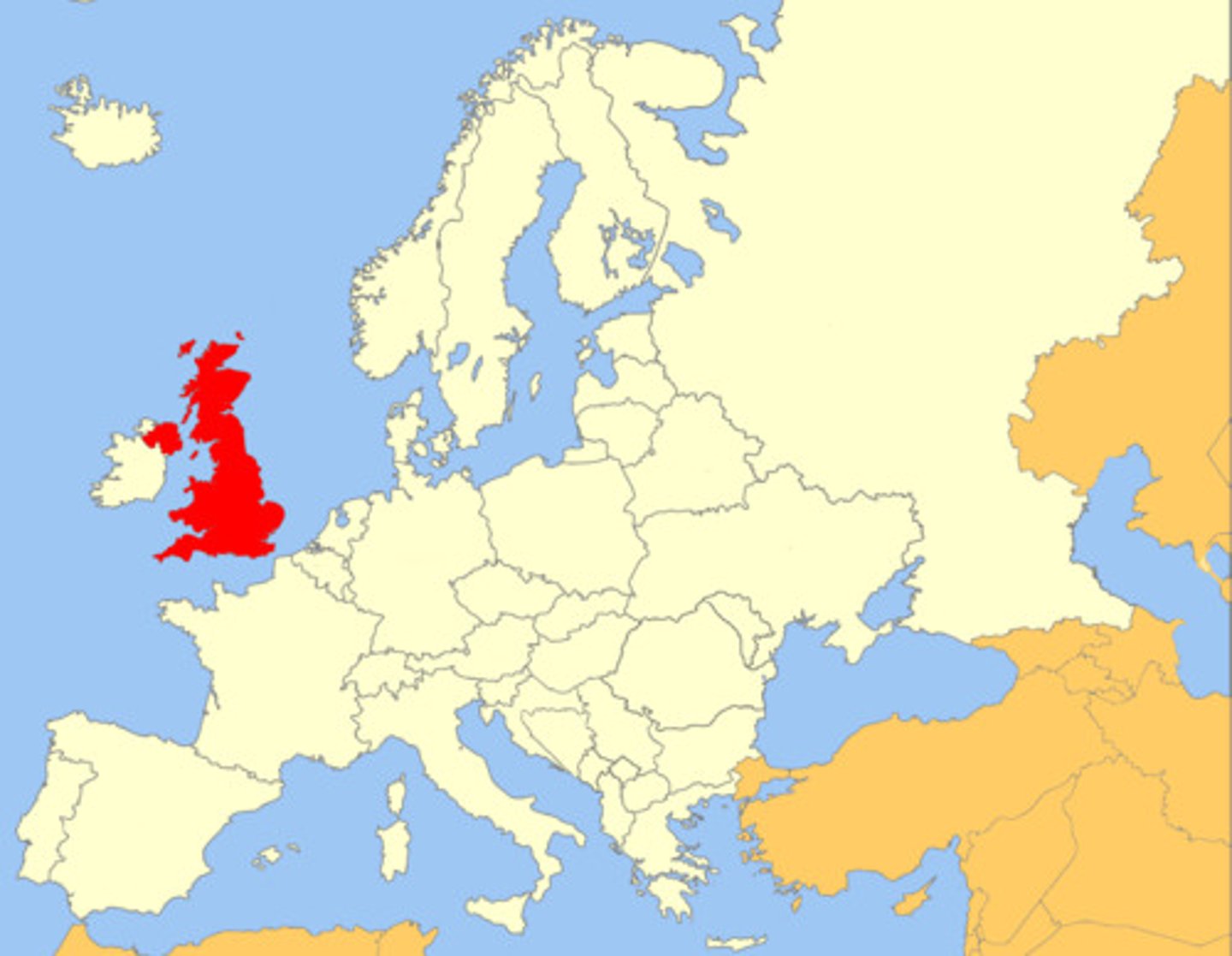
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities

Crop Rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil. allowed for population growth and caused the early Industrial Revolution

Enclosure Movement
The 18th century privatization of common lands in England, which contributed to the increase in population and the rise of industrialization.

Simon Bolivar
1783-1830, Venezuelan statesman: leader of revolt of South American colonies against Spanish rule.

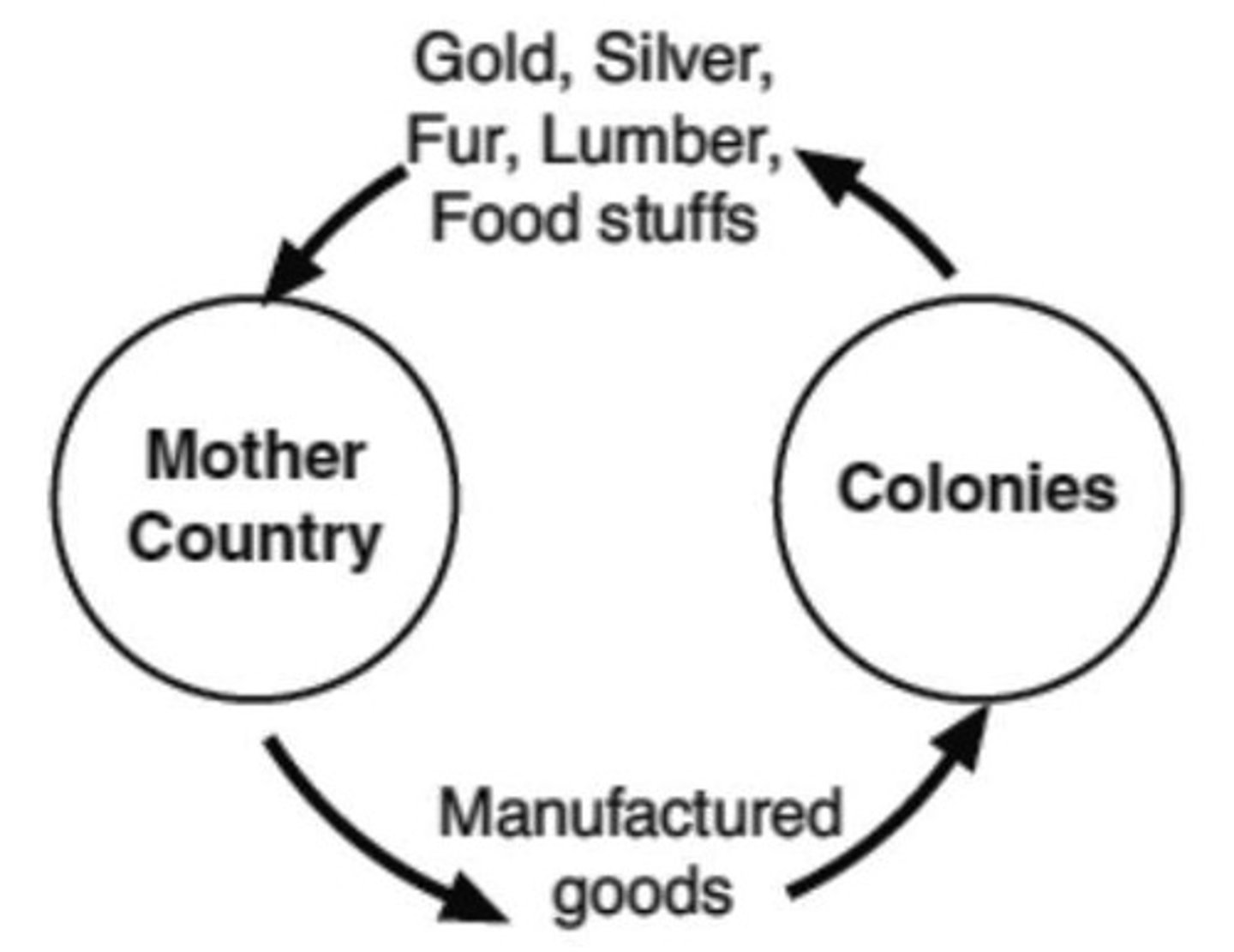
Mercantilism
major cause of revolutions in Latin America and the US as colonist felt exploited by European countries
Declaration of Independence (1776)
Written by Thomas Jefferson; influenced by the Enlightenment philosophers of his day.
Provisions:
Explains the necessity of independence for the preservation of basic laws and rights.
