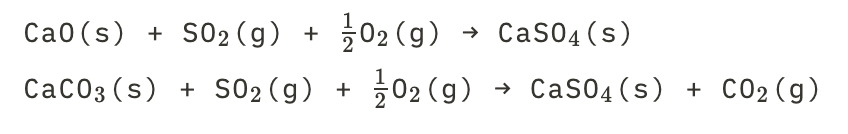IB Chemistry HL - CHAPTER 8
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
Brønsted-Lowry acid
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is a species that gives away a proton.
2
New cards
Brønsted-Lowry base
A Brønsted-Lowry base is a species that accepts a proton (H^+) using its lone pair of electrons.
3
New cards
Conjugate acid-base pair
A conjugate acid-base pair is two species that are different from each other by a H{^+}-ion.
4
New cards
Amphiprotic
Amphiprotic describes a substance that can both accept or donate a proton.
5
New cards
Amphoteric
Amphoteric describes a substance that have the ability to act as both an acid and base.
6
New cards
Acid + metal
→ salt + hydrogen
7
New cards
Acid + metal hydroxide
Acid + metal oxide
Acid + metal oxide
→ salt + water
8
New cards
Acid + metal carbonate
→ salt + water + carbon dioxide
9
New cards
Acid + metal hydrogencarbonate
→ salt + water + carbon dioxide
10
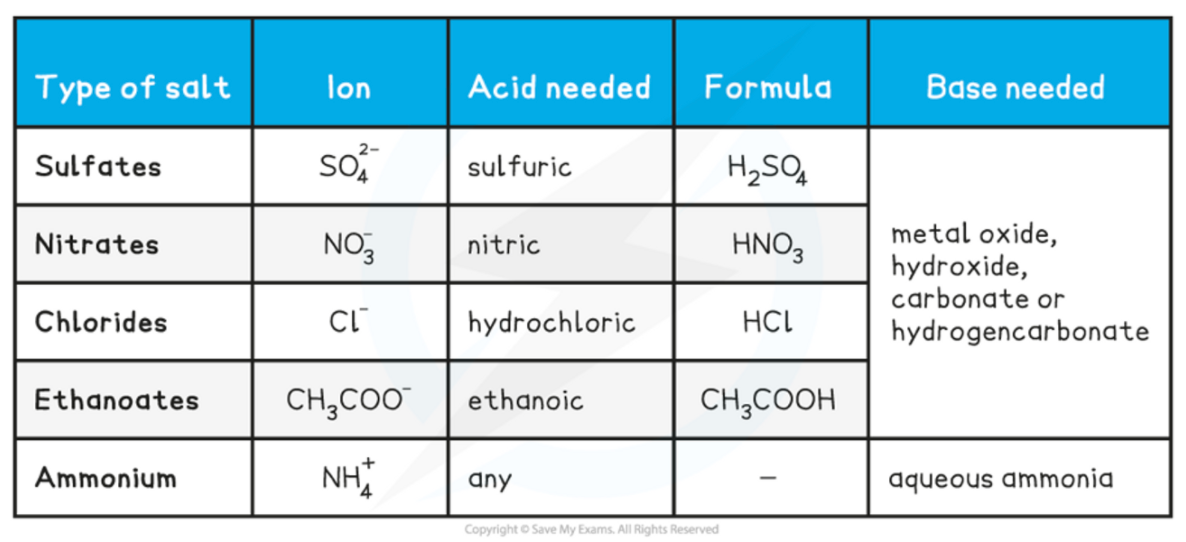
New cards
How to make different types of salt
This is how:
11
New cards
Neutralization reaction
A neutralization reaction is: Acid + base (alkali) → salt + water
12
New cards
Indicators
Indicators are weak acids and bases where the conjugate bases and acids have a different color.
* A good indicator gives a very sharp colour change at the equivalence point.
* A good indicator gives a very sharp colour change at the equivalence point.
13
New cards
pH equation
pH = -log\[H^+\]
14
New cards
Water at 298
See picture.

15
New cards
K_w
See picture.
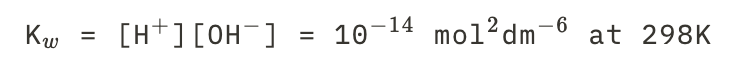
16
New cards
Strong acid
A strong acid is an acid that dissociates almost completely in aqueous solutions.
17
New cards
Weak acid
A weak acid is an acid that partially dissociates in aqueous solutions.
18
New cards
Strong base
A strong base is a base that dissociates almost completely in aqueous solutions.
19
New cards
Weak base
A weak base is a base that parially dissociates in aqueous solutions.
20
New cards
What does strong acids produce?
In general strong acids produce weak conjugate bases and weak acids produce strong conjugate bases.
21
New cards
What does strong bases produce?
In general strong bases produce weak conjugate acids and weak bases produce strong conjugate bases.
22
New cards
How can strong and weak acids be distinguished
* pH value
* Electrical conductivity
* Reactivity
* Electrical conductivity
* Reactivity
23
New cards
Acid rain
Acid rain is defined is rain with a pH lower than 5.6.
24
New cards
Acid deposition
Acid deposition includes all processes by which acidic components leave the atmosphere
25
New cards
Wet acid deposition
Wet acid deposition refers to rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog, mist and dew.
26
New cards
Dry acid deposition
Dry acid deposition refers to acidic particles and gases that fall to the ground as dust and smoke.
27
New cards
Acidrain droplets of sulfurous acid
See picture.
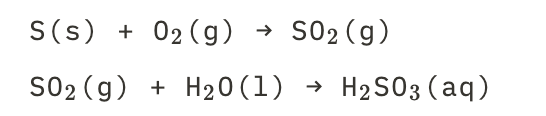
28
New cards
Acidrain droplets of sulfuric acid
See picture.
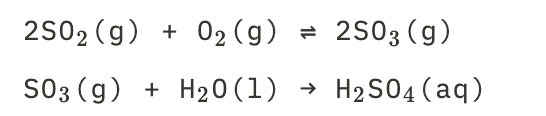
29
New cards
Acidrain droplets of nitrous and nitric acids
See picture.
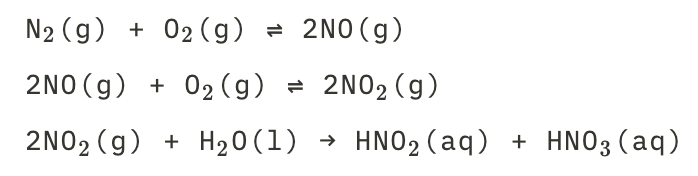
30
New cards
Acidrain droplets of nitic acid
See picture.
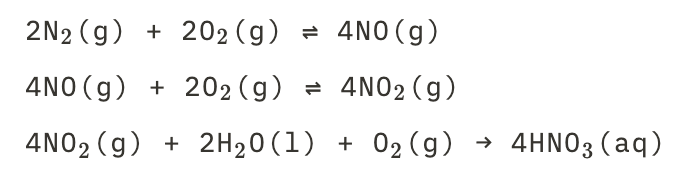
31
New cards
Effects of acid deposition on materials
See picture.
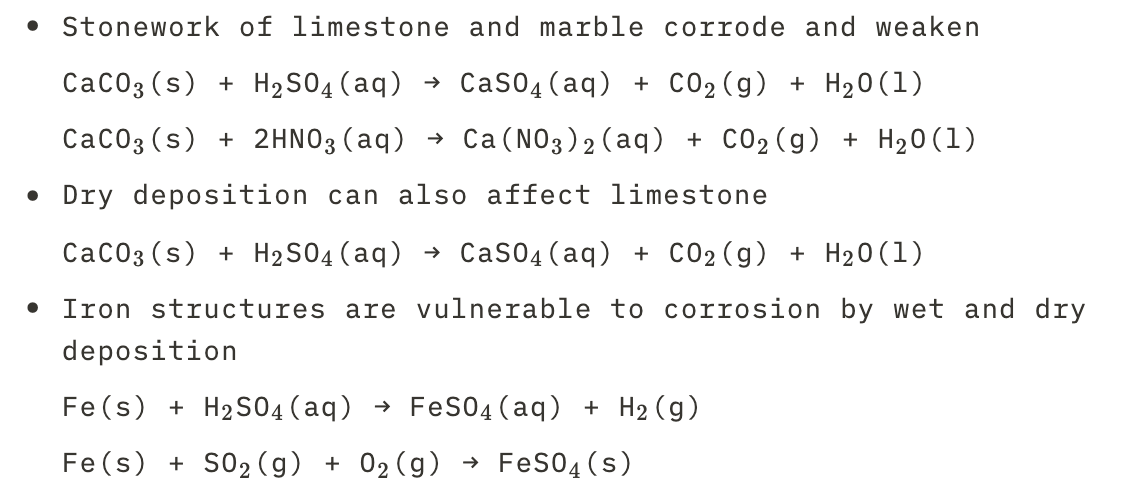
32
New cards
Effects of acid deposition on plants
* Acid particles can block stomata and prevent gaseous exchange
* Acid rain can fall on soils and wach away important minerals leaving them unavailable to plants
* Aluminium ions are released from rocks are toxic to many plants
* Acid rain can fall on soils and wach away important minerals leaving them unavailable to plants
* Aluminium ions are released from rocks are toxic to many plants
33
New cards
Effects of acid deposition on water
See picture.

34
New cards
Effects of acid deposition on human health
See picture.

35
New cards
Pre-combustion removal of sulfur
Pre-combustion removal of sulfur is a method of removing sulfur and takes place for coal and petroleum, although it is expensive to remove all the sulfur, so a small percentage often remains.
36
New cards
Hydrodesulfurization
Hydrodesulfurization is the process of removing sulfur by reacting it with hydrogen.
37
New cards
Post-combustion removal of sulfur
Post-combustion removal of sulfur is a method of removing sulfur from coal and is carried out on in coal-fired power stations.
38
New cards
How is post-combustion removal of sulfur done?
Post-combustion removal of sulfur is conducted by passing waste gases through a wet slurry of calcium oxide and calcium carbonate