patterns of inheritance and meiosis chap 9 and 10 BIO I
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
Genetics explains and predicts?
inheritance patterns
Most genes encode proteins that have nothing to do with outward
appearance. The enzymes essential to our lives are also the
products of?
genetics.
Studying genetics also allows scientists to breed superior crops
and doctors to track genetic illnesses.
Recall that a chromosome is a piece of DNA containing many different genes. Each gene’s ___ is its location on a chromosome
locus
When two haploid sex cells fuse during fertilization a __ zygote with two full sets of chromosomes is formed.
diploid
Each chromosome is a member
of a ___ of chromosomes
homologous pair
diploid cells hace —’ alleles for each gene
two
members of a homologous pair have the same genes but might have different versions or === of those genes
alleles
are alleles always identical
No, they may differ in form.
How do meiosis, fertilization, diploid cells, and haploid cells
interact in a sexual life cycle?
Meiosis produces haploid gametes from diploid cells, which then fuse during fertilization to form a new diploid organism, continuing the sexual life cycle.
Gregor Mendel uncovered basic laws of?
inheritance through pea plant experiments.
explain medels experiment, what were the results
Mendel's experiments involved cross-breeding pea plants with distinct traits to observe inheritance patterns across generations, leading to the formulation of his laws of segregation and independent assortment.
true breeding plants
self fertilization yields offspring with same seed color as parent plant
hybrid plants outwardly resemble true breeders but produce?
mixed offspring
__ alleles exert their effects whenever they are present crossing a yellow-seed plant with a green-seed plant always yields some yellow seeds
Dominant
A ___ allele, like green seed color, is one whose effect is
masked if a dominant allele is also present.
Recessive
Recessive alleles usually encode ___ proteins.
nonfunctional
Why do some plants produce both yellow and
green seeds?
The answer has to do with each plant having two alleles for each
gene (because of their homologous pairs of chromosomes). If one allele is dominant and the other recessive, the dominant trait may be expressed alongside the recessive trait, leading to mixed seed colors.
A genotype represents an individual’s ___ for ____
two alleles, for one gene
The genotype confers a ___ which is the physical
appearance—for example, an observable characteristic such as
seed color.
phenotype
homozygous dominant
individuals have two dominant alleles for a gene
heterozygous individuals
have one dominant and one recessive allele
homozygous recessive
individuals have two recessive alleles for a gene
can individuals with the same phenotype have different genotypes?
Yes, individuals can exhibit the same phenotype but have different genotypes, a condition known as phenotypic variance.
The seed color gene encodes a ____ enzyme
pigment-metabolizing
The seed color gene encodes a pigment-metabolizing enzyme.
The dominant allele, Y, is active and produces yellow color; the
recessive allele, y, is inactive.
In the absence of enzyme activity the seeds ?
will be green in color.
Distinguish between dominant and recessive, heterozygous and
homozygous, phenotype and genotype
Dominant alleles mask the effect of recessive alleles, heterozygous individuals have two different alleles for a trait while homozygous individuals have two identical alleles, phenotype is the observable trait and genotype is the genetic makeup.
Punnett squares represent?
gamete formation
and fertilization
a punnet square uses what?
the genotypes of the parents to reveal which alleles the offspring may inherit
in this example a female parent heterozygous Yy for seed color is crossed with a male parent also heterozygous Yy for seed color, this is a ____ since both parents are heterzygous
monohybrid cross
do punnet squares show how alleles sepeate or come together during meiosis?
seperate
When germ cells divide by meiosis, the gametes receive how many alleles per gene?
one allele per gene.
For the seed-color gene, there is an equal chance of receiving?
either the dominant or recessive allele.
© McGraw Hill 20
Punnett squares show how the alleles get back ___ at fertilization
together
This Punnett square is a prediction that shows the
relative proportion of the offspring phenotypes and genotypes.
Offspring can reveal parental genotypes
homozygous dominant
If a cross between a yellow seed pea plant (YY or Yy) and a green-seed pea plant (yy) yields all yellow seeds, the yellow- seed parent is homozygous dominant.
offspring can reveal parental genotypes: heterozygous
If a cross between a yellow-seed pea plant (YY or Yy) and a green- seed pea plant (yy) yields some green seeds, the yellow-seed parent is heterozygous
the two alleles for the seed color gene are packed into separate which are then combined at___
gametes; fertilization
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele. If a healthy carrier
and an affected individual have a child, what is the chance the
child will be affected?
A. 1/4
B. 1/3
C. 1/2
D. 3/4
E. 1
1/2
Use the following terms to explain how parents can be disease
carriers:
• Allele
• Genotype
• Phenotype
• Dominant
• Recessive
Parents can be carriers of diseases when they possess a recessive allele in their genotype that does not manifest in their phenotype due to the presence of a dominant allele. This means one parent may express a dominant trait while carrying a recessive allele for a genetic disorder, thereby passing it to offspring.
This Punnett square
is a prediction that
shows the relative
proportion of?
phenotypes and
genotypes.
Figure 10.6Access the text alternative for slide images.
Dihybrid crosses track the inheritance of __ genes at once
two different
__ on different chromosomes can be combined into one
large Punnett square.
two genes
during what process do alleles seperate
during meiosis
Based on dihybrid crosses, Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment which is?
the segregation of alleles for one gene
does not influence the segregation of alleles for another gene
Why doesn't the Punnett square below include a female gamete
with genotype rr?
A. Each germ cell only has one r allele.
B. The y allele is dominant to the r.
C. The r alleles separate during meiosis.
C. The r alleles separate during meiosis.
what is the prdouct rule what proble is it solving?
The product rule states that the probability of two or more independent events occurring together is the product of their individual probabilities. It is used to calculate the likelihood of specific combinations of alleles in offspring.
the product rule ___ individual probablities together
multiplies the
The probability that an offspring inherits genotype Rr Gg Tt =
probability of Rr x the probability of Yy x probability of Tt
A male with genotype Qq Bb Dd is crossed with a female with
genotype qq bb dd. What proportion of the offspring will be
homozygous recessive for all three genes?
A. 1/2
B. 1/3
C. 1/4
D. 1/6
E. 1/8
1/8
How does the law of independent assortment reflect the events of meiosis?
It states that alleles for different traits segregate independently during gamete formation, reflecting the random assortment of chromosomes during meiosis.
Genes close together on the same chromosome
are ___
linked
Punnett squares and the product
rule assume:
two genes are sorting independently.
• When genes are linked, they are physically near each other.
• Therefore, they do not sort independently.
• The linked genes are not inherited independently of each other.
Punnett squares and the product
rule cannot be used if genes are?
linked, because inheriting one allele influences the likelihood of inheriting a linked allele
Genes can become ___ during cross over
unlinked
crossing over physically seperates the two gene loci onto how many different chromosomes?
two different chromosomes
Very close genes are ___ by crossing over
less affected
The probability of a crossover event occurring between two linked alleles is ___ to the distance between the genes
directly proportional
Crossover events are counted by
tallying
offspring in which the genes are inherited
separately.
Crossover frequencies are used to find the relative
position of genes The letters below the linkage map of this chromosome represent
different gene loci. The numbers above represent crossover
frequencies relative to gene y
Explain how to use crossover frequencies to make a linkage map.
Crossover frequencies can be utilized to estimate the relative distances between genes on a chromosome by measuring the frequency of recombination between them. By calculating these frequencies, researchers can create a linkage map that visually represents the arrangement of genes.
what are alternative patterns of inheritance
Alternative patterns of inheritance refer to non-Mendelian inheritance patterns that include phenomena such as incomplete dominance, codominance, epistasis, and polygenic inheritance, which can affect how traits are transmitted from parents to offspring.
Dominant alleles masked recessive alleles in the genes
Mendel studied, creating patterns of
phenotypic and
genotypic ratios.
In other genes, alleles interact differently. This changes the nature of the
phenotypes, but not the genotypes.
In incomplete dominance:
the heterozygote has an intermediate
phenotype. Here, the red allele does not mask the white allele—if it did, heterozygotes would appear red.
Incompletely dominant alleles create a
blended
heterozygote phenotype When the red allele (r1) and white allele (r2) are both present, the heterozygote (r1r2) phenotype is an intermediate pink. The white allele encodes a nonfunctional pigment protein
what is codominant alleles?
Alleles that express both traits fully in a heterozygote. For instance, in a flower with red and white alleles, both colors may be present in the petals. they do not mask each other, and have more than one allele that encodes a functional protien
Codominant alleles create
double phenotype
Codominant alleles create a double phenotype
If two dominant alleles are present, both proteins encoded by
those alleles will be represented in the phenotype.
Human blood type alleles A and B are
codominant
In human blood
types, both IA and
IB are
dominant alleles
Genotype IA IB
Confers red blood
cells with
both A
and B molecules
Human blood type alleles A and B are both dominant
over the O allele true or false
True
The I gene also has
a recessive allele,
i, which encodes a
non-functional
protein.
But the two
dominate alleles IA
and IB, make
the
I gene codominant
pleiotropy
one gene has multiple effects on the phenotype. For
example, a gene might affect more than one biochemical pathway.
Products of different genes can interact with each other
Section Epistasis
occurs when one gene’s product affects the expression of another gene. Expression of the h allele (gene 1) affects the expression of A and B alleles (gene 2).
How do pleiotropy, epistasis, incomplete dominance, and
codominance increase the number of phenotypes
by altering the effects of genes on traits, allowing for a greater variety of expressed characteristics in offspring.
Sex-linked genes have unique inheritance patterns. In humans, females have two X chromosomes (XX). Males have one X chromosome and
one Y chromosome (XY). This can lead to traits on the X chromosome being expressed differently in males and females.
This Punnett square shows
that each fertilization event
has a
50% chance of producing
a female and a 50% chance of
producing a male.
Which gamete determines the sex of the offspring?
The egg will always carry an
X
chromosome.
The sex chromosome in the
sperm therefore determines if
the offspring is female or male.
males only have one allele for genes on the?
X chromosome
whichever allele males have on their single X chromosome is the one that expresses as their..?
phenotype.
females have two x chromosomes the interation of the two alleles determines the?
phenotype for traits linked to the X chromosome. `
recessive disorders effect more males or females?
males due to their single X chromosome. Males only need to inherit one X-linked recessive allele to express the recessive disorder. Females must receive a recessive allele on both X chromosomes to express the recessive disorder, which is less likely to occur.
Hemophilia is an X-linked recessive disorder. If an affected female
(has the disease) and an unaffected male (does not have the
disease) have a boy, what is the chance he will have hemophilia?
1
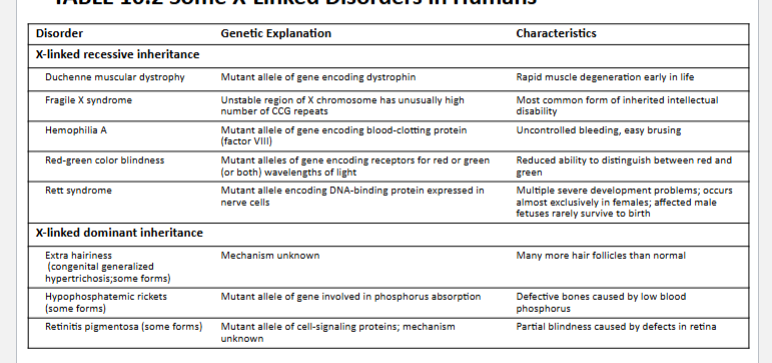
x linked disordersq
look at image
X-inactivation prevents double dosing of gene products
Each cell in an XX
individual, such as
these female cats,
randomly
inactivates one X
chromosome
X-inactivation produces unique inheritance patterns
f one X chromosome has an allele for orange fur, and the other has an allele for black fur, color patterns emerge when X chromosomes are randomly inactivated.
X-linked dominant disorders are less severe in female
In humans, an X-linked
disorder called Rett
syndrome is lethal to
boys and has varying
effects on girls,
depending on how
many cells inactivate
the X chromosome
carrying the Rett allele.
Why do males and females express recessive X-linked alleles
differently?
Males express recessive X-linked alleles more frequently because they have only one X chromosome, while females have two, which can result in one dominant allele masking the recessive allele.
A pedigree depicts
family relationships and phenotypes
© McGraw Hill 72
Pedigrees show modes of?
inheritance and can reveal patterns of genetic conditions within families.
This pedigree tracks an autosomal dominant disorder. What is
the genotype of I-2?
It is most likely heterozygous (Aa) if the phenotype is expressed.
How are pedigrees helpful in determining a disorder’s mode of
inheritance?
They provide a visual representation of family relationships and phenotypes, showing how traits are passed through generations.
can the enviroment alter phenotype?
Yes, environmental factors can influence an organism's phenotype by affecting gene expression and interactions.
Epigenetics is a
field of research that explores how cells adjust gene expression without altering underlying DNA sequence. Differences in lifestyle and experience can epigenetically influence gene expression and alter the chances of cancer, depression,alcoholism, and type 2 diabetes for some people.
Some traits depend on multiple genes Skin color is a
polygenic trait; it is
affected by more than one gene
How can the environment affect a phenotype?
The environment can alter a phenotype by influencing gene expression through factors such as diet, temperature, and exposure to toxins.
homozygous vs heterozygous
Homozygous refers to having two identical alleles for a particular gene, while heterozygous refers to having two different alleles for that gene.
genotype vs phenotype
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype refers to the observable traits and characteristics resulting from the interaction between the genotype and the environment.
Dominant vs recessive
Dominant alleles mask the effects of recessive alleles in determining an organism's phenotype. A dominant trait will be expressed if at least one dominant allele is present, whereas a recessive trait only appears if both alleles are recessive.