BSC2085L
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microscope, Body cavities, Cell structure and functions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
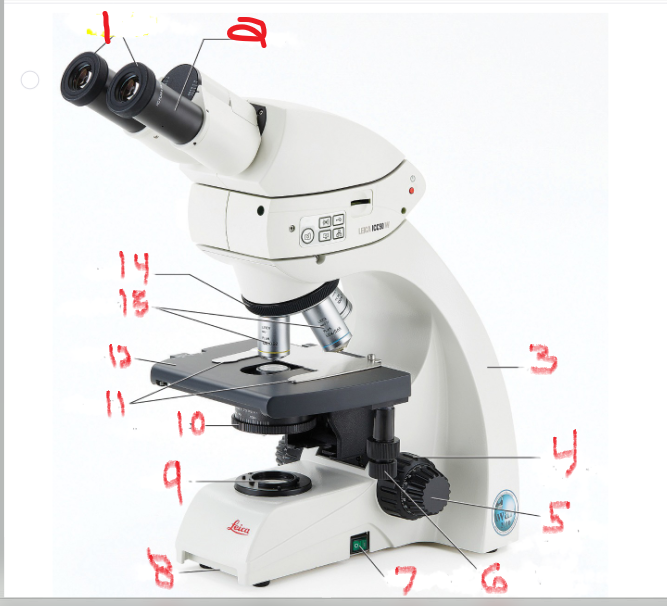
what is name and function of image 1
ocular lens
is the lens through which you look to examine the slide
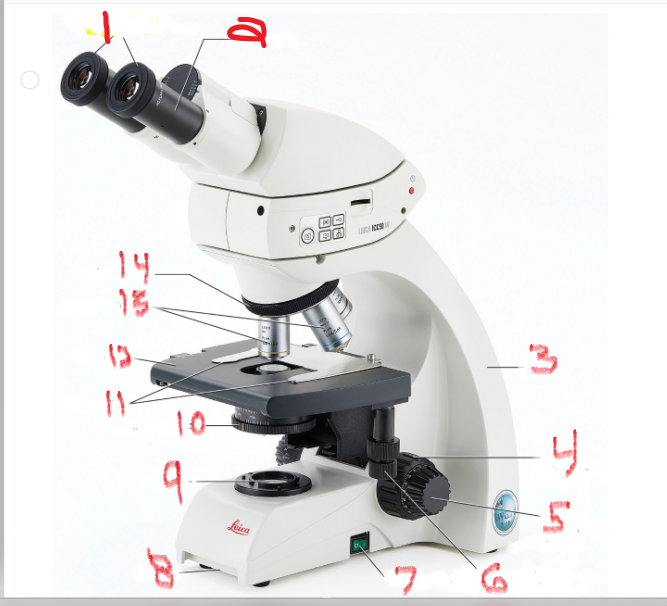
what is name and function of image 2
eyepiece
Many ocular lenses have pointers that can be moved by rotating the black piece
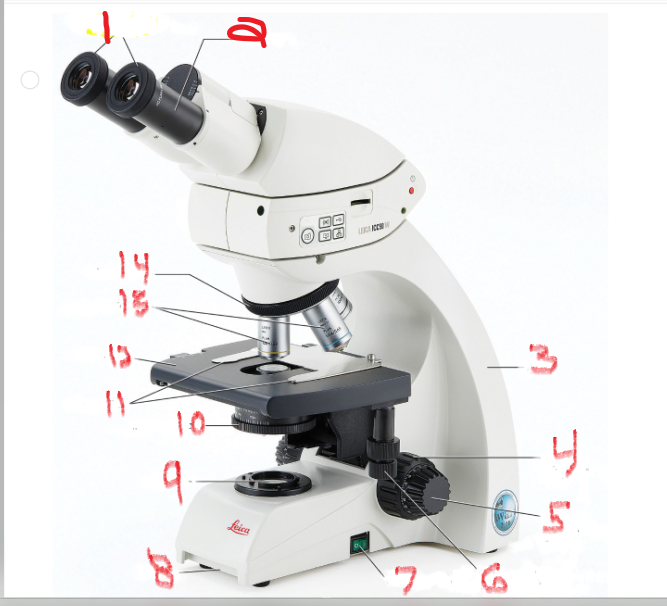
what is name and function of image 3
Arm
The arm supports the body of the microscope and typically houses the adjustment knobs
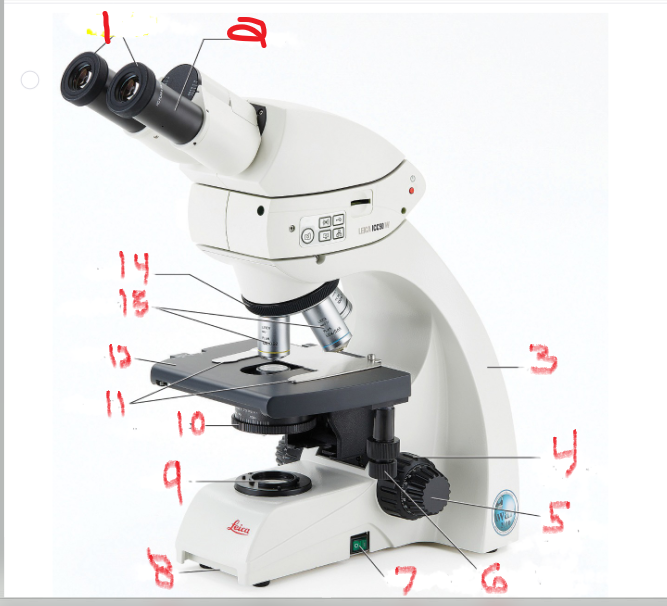
What is name and function of image 5
Fine adjustment knob
You turn it to fine-tune the image’s focus
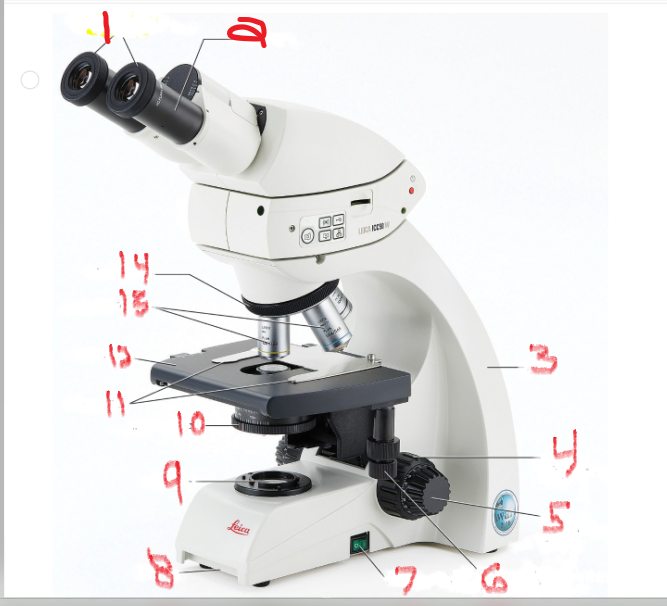
What is name and function of image 6
mechanical stage adjustment
you can move the slide by turning this knob
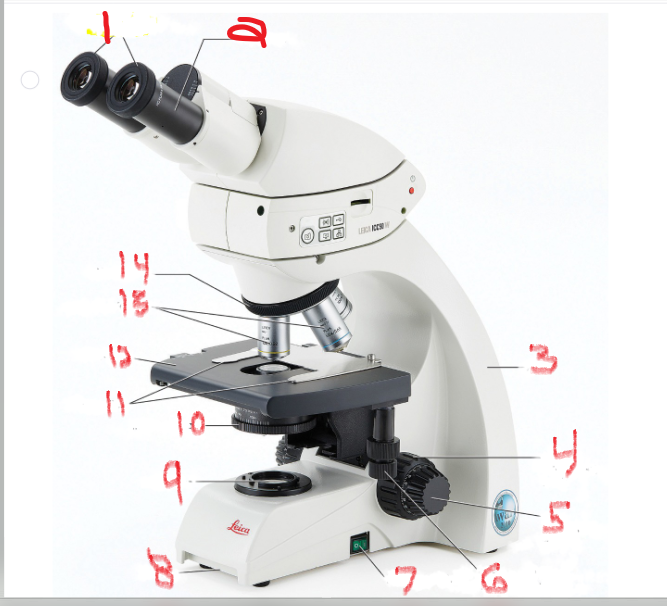
What is name and function of image 7
Power switch
provides power to microscope
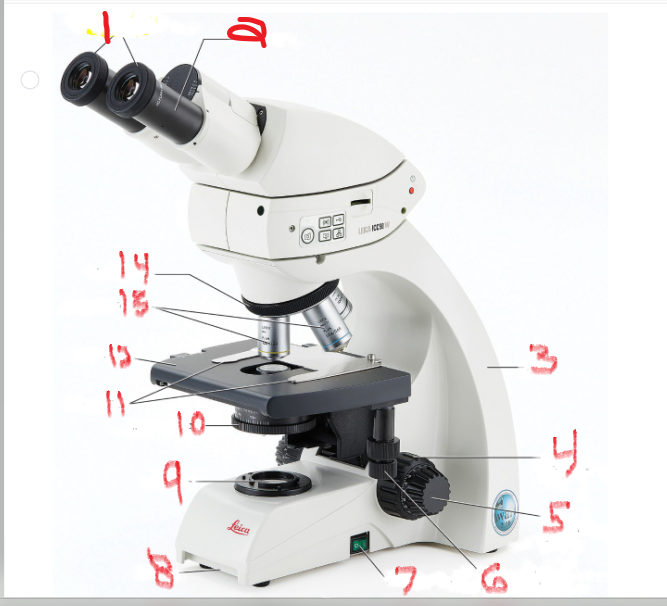
What is name and function of image 8
Base
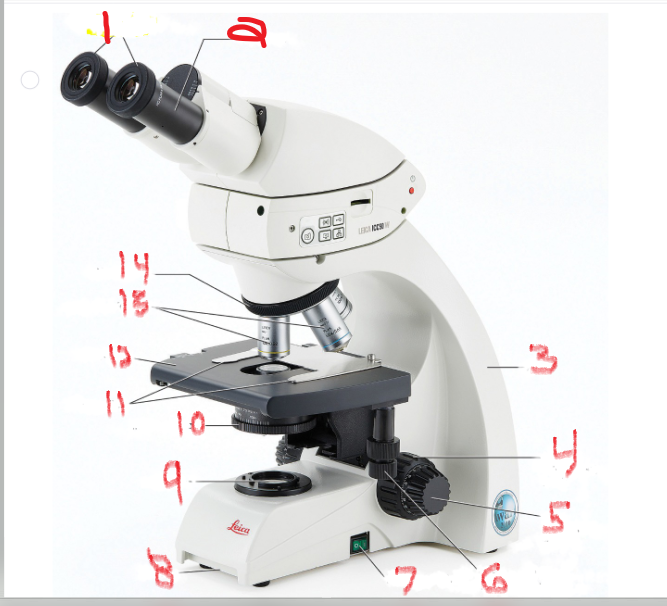
What is name and function of image 9
Lamb
also called the illuminator, provides the light source
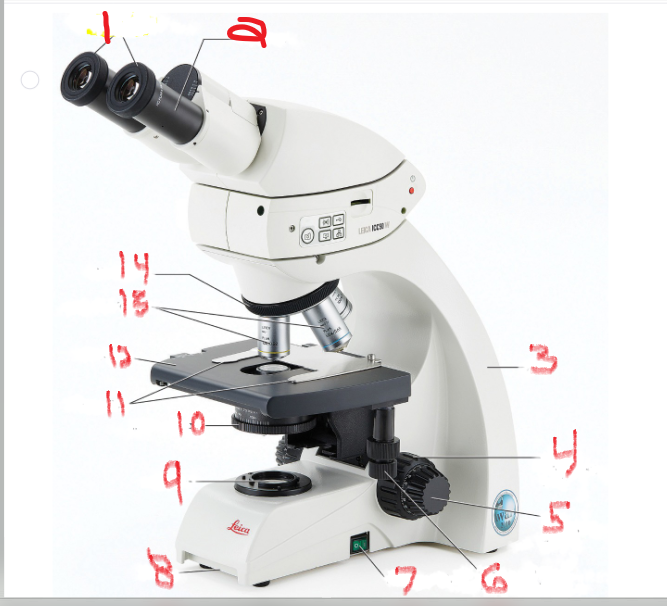
What is name and function of image 10
Iris diaphragm
that controls the amount of light allowed to pass through the slide
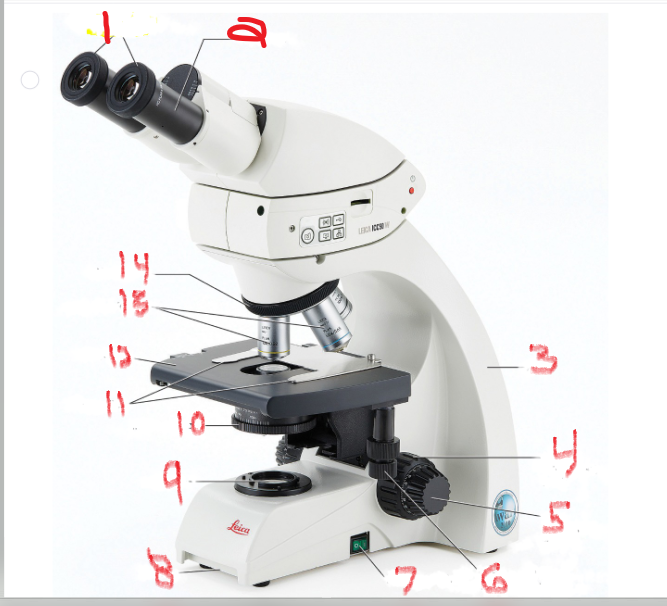
What is name and function of image 11
Stage clips
to hold the slide in place
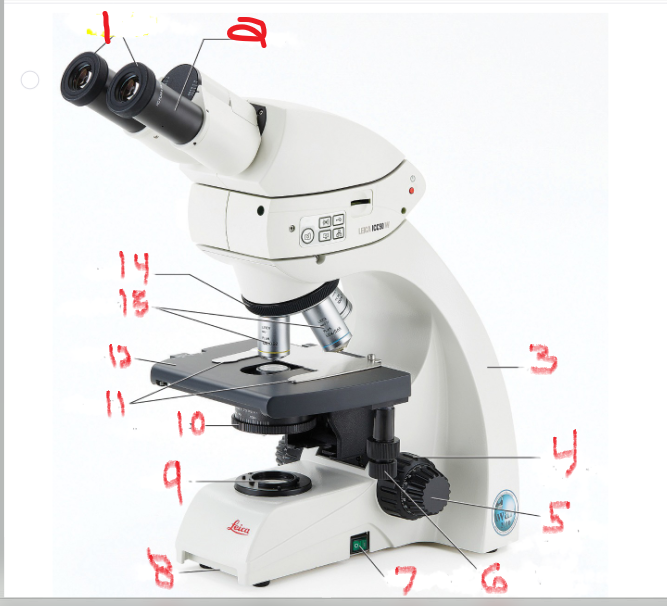
What is name and function of image 12
Stage
is the surface on which the slide sits
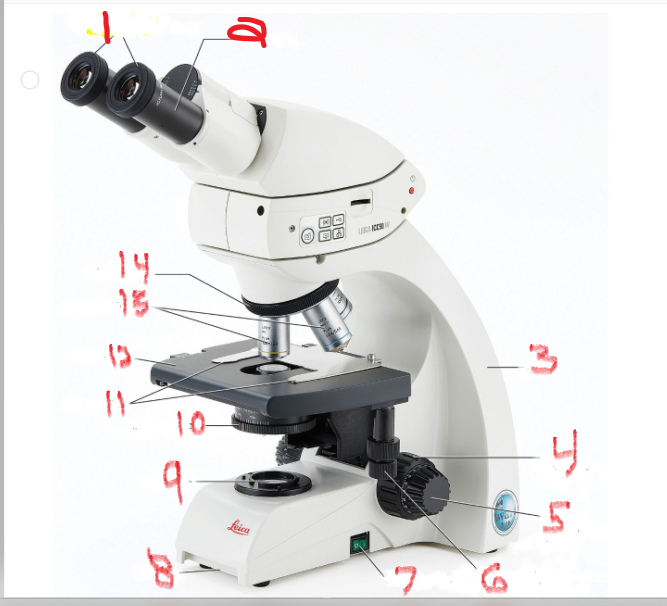
What is name and function of image 13
objective lenses
are lenses with various powers of magnification
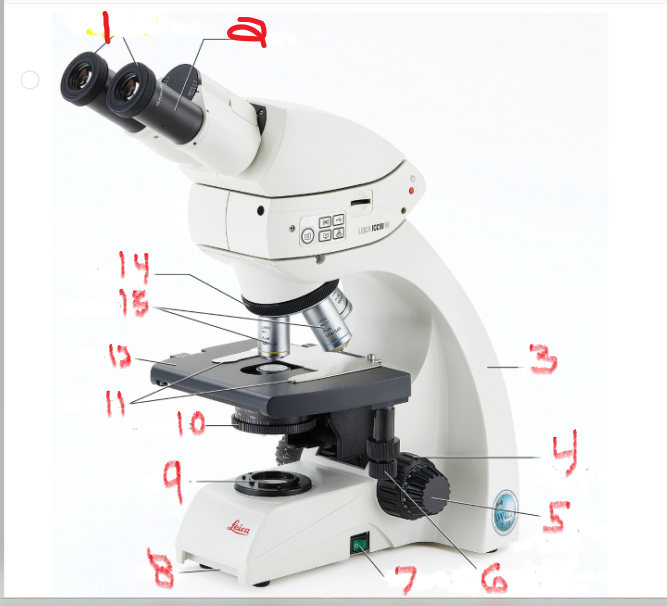
What is name and function of image 14
nosepiece
which allows the user to switch between objectives
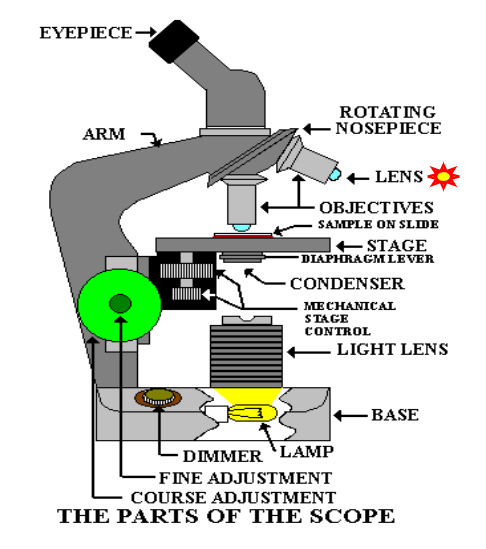
What are the objective lens and functions
Microscope has 3 to 4 objective lens (4x,10x, 40x, 100x with oil emersion lens)
Define Parfocal
stays in focus when switching lenses
Working distance
space between lens and specimen
Field of view
visible area under microscope
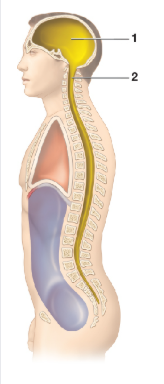
Which cavity is image 1
Cranial Cavity
Contains bain
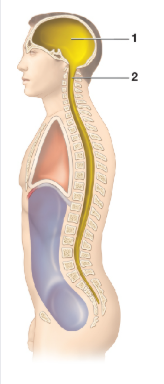
Which cavity is image 2
Vertebral cavity
contains the spinal cord
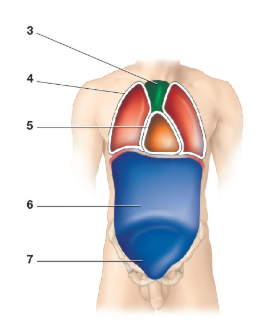
What cavity is image 4
Pleural cavity
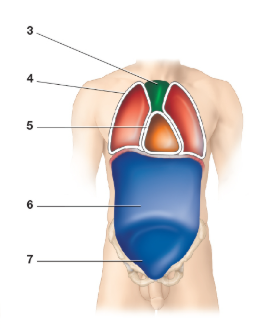
What cavity is image 5
Pericardial cavity
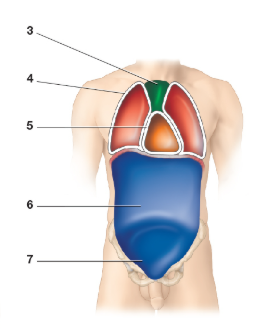
What cavity is image 6
Abdominal cavity
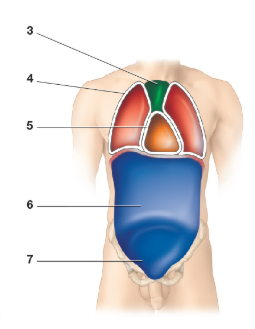
What cavity is image 7
Pelvic cavity
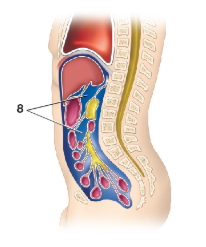
What cavity is image 8
Peritoneal cavity
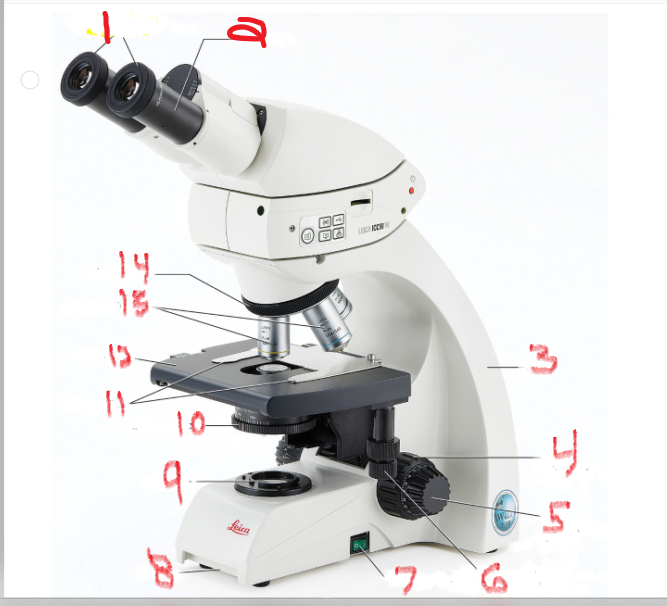
What is name and function of image 4
coarse adjustment knob
Turning it moves the stage up and down to change the distance of the stage from the objective lenses
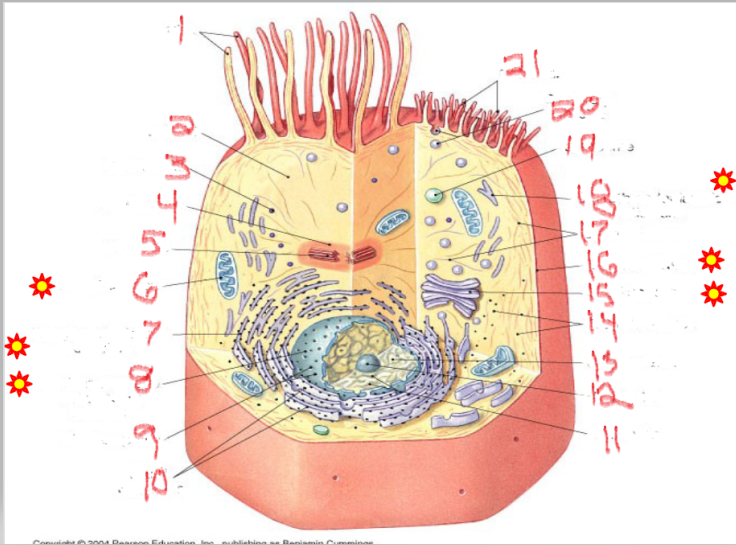
What is the structure and function of image 2
cytosol
Functions of cytosol include transport of molecules across the cell, provide structural support to the cell organelles, signal transduction to the target compartments, gives a platform for cellular metabolic processes and reactions.
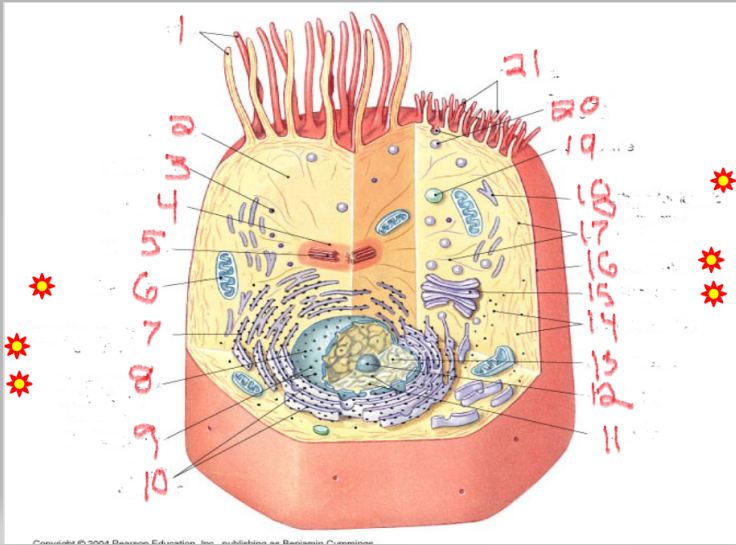
What is the structure and function of image 12
nucleolus
The nucleolus is the ribosome factory of the cell, critical for protein synthesis and overall cell function. Regulation of Cell Cycle and Stress Responses
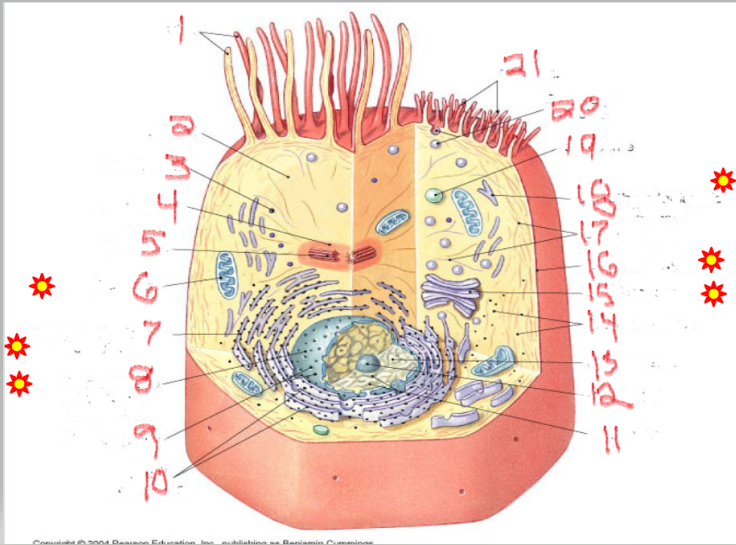
What is the structure and function of image 11
chromatin
Chromatin stores, organizes, protects DNA, and regulates gene activity.
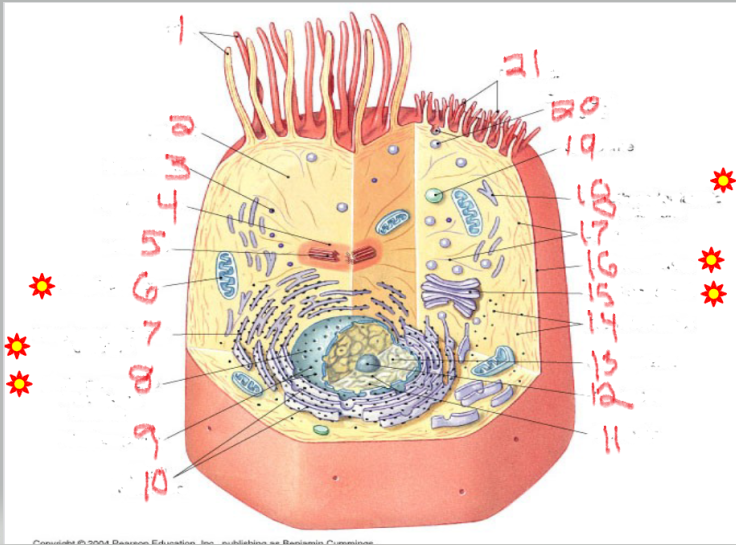
What is the structure and function of image 5
centrioles
cell division organization
Organize microtubules during cell division.
Form the mitotic spindle that separates chromosomes.
Help form cilia and flagella for cell movement.
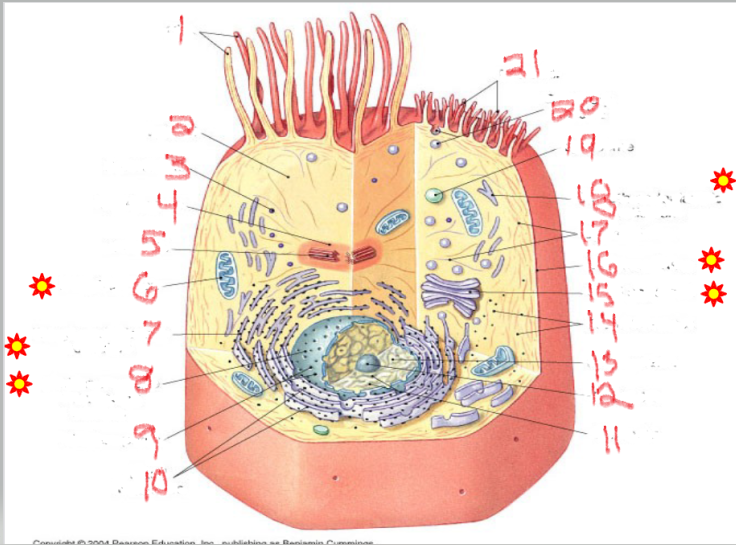
What is the structure and function of image 6
mitochondria
ATP energy - Adenosine Triphosphate
Produces ATP through cellular respiration.
Regulates cell metabolism.
Plays a role in apoptosis (programmed cell death).
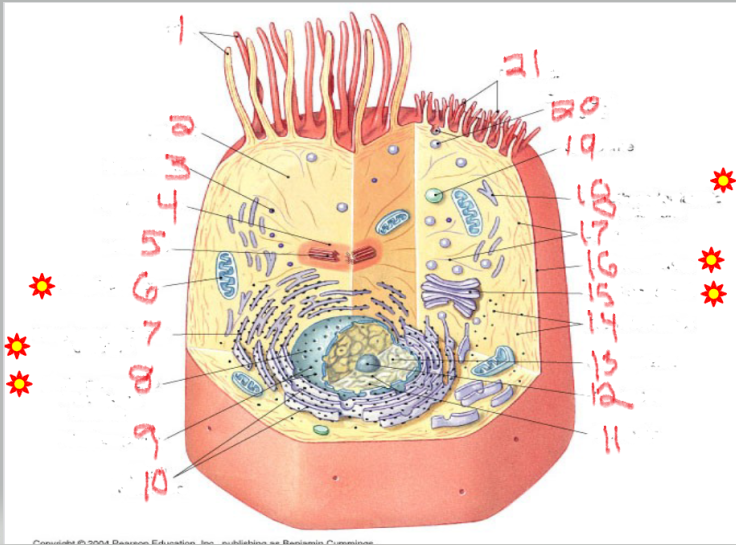
What is the structure and function of image 18
Smooth endoplasmic Reticulum
lipids + detox
Network of membranes without ribosomes.
Synthesizes lipids (fats, phospholipids, steroids).
Detoxifies drugs and harmful substances.
Stores calcium ions in muscle cells for contraction.
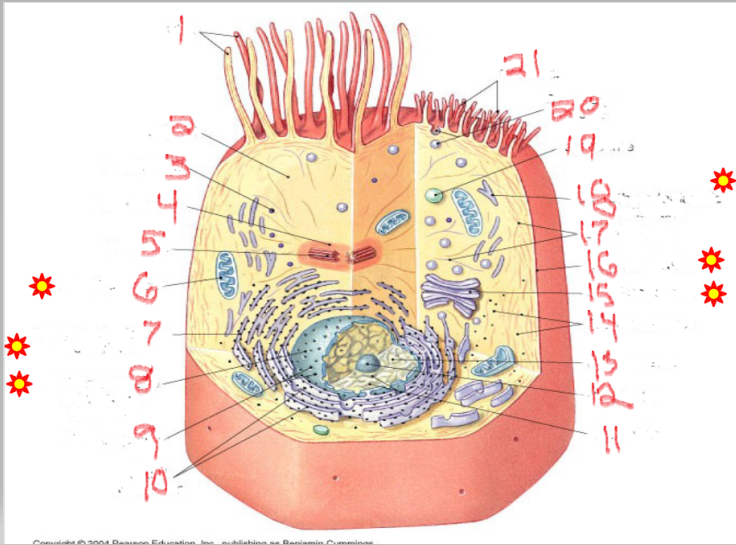
What is the structure and function of image 7
Rough endoplasmic Reticulum
proteins (with ribosomes)
Network of membranes studded with ribosomes.
Synthesizes proteins for export or for membranes.
Packages proteins into vesicles to send to the Golgi complex.
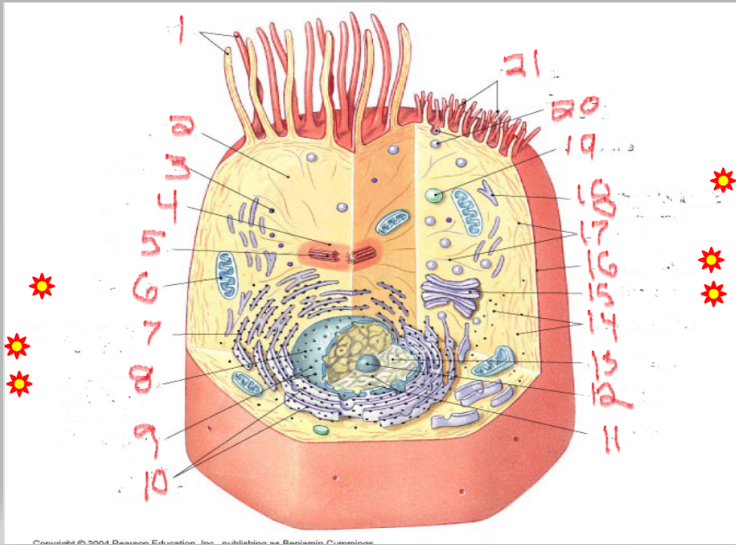
What is the structure and function of image 14
ribosomes
protein factories
Small particles made of rRNA and proteins.
Found free in cytoplasm or attached to RER.
Site of protein synthesis.
Free ribosomes → make proteins for use inside the cell.
Attached ribosomes → make proteins for secretion or membranes.
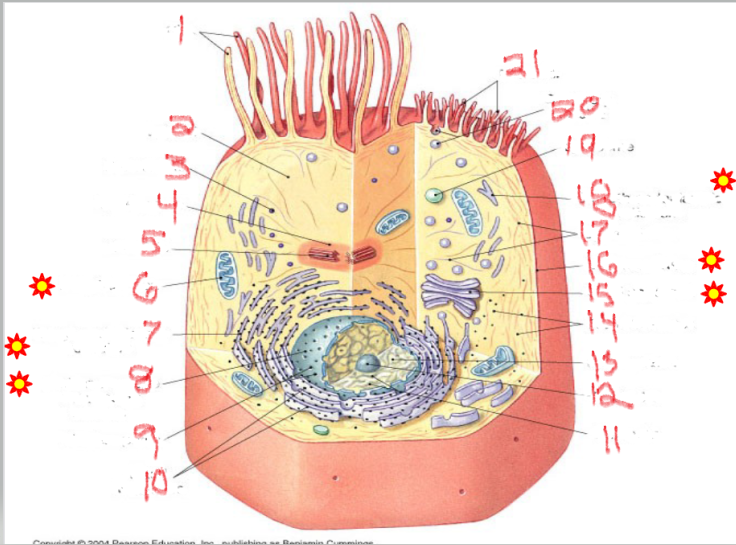
What is the structure and function of image 15
Golgi complex/apparatus
modify, sort, package proteins/lipids
Stack of flattened sacs.
Forms lysosomes.
Produces vesicles for transport within or out of the cell.
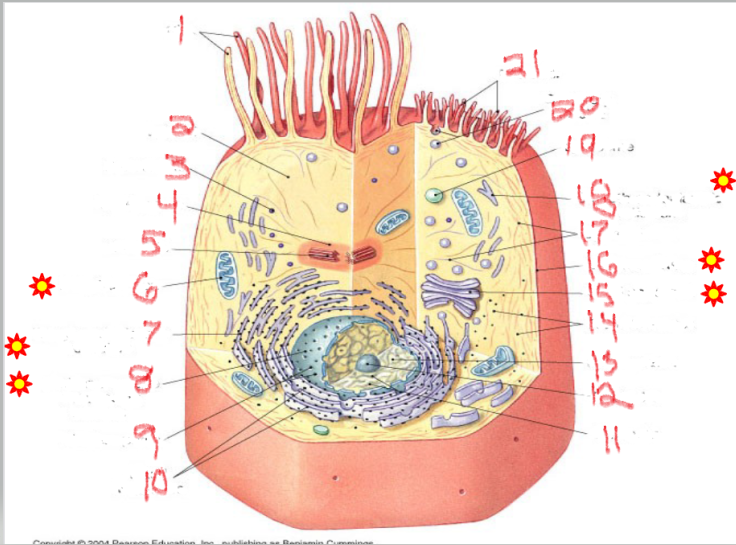
What is the structure and function of image 19
lysosome
digestion + recycling
Membrane-bound vesicles containing digestive enzymes.
Digest worn-out organelles and cellular debris ("cellular recycling center").
Break down bacteria, viruses, and large molecules.
Play a role in apoptosis (cell self-destruction when needed)
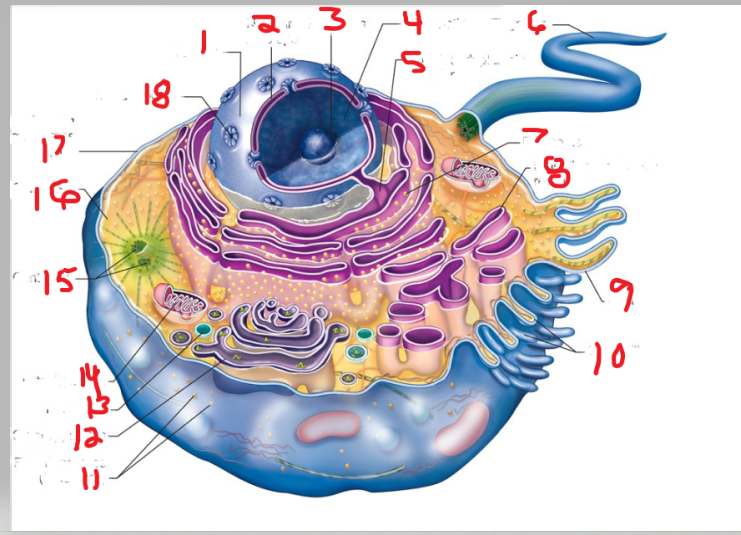
What is the structure and function of image 17
Plasma membrane
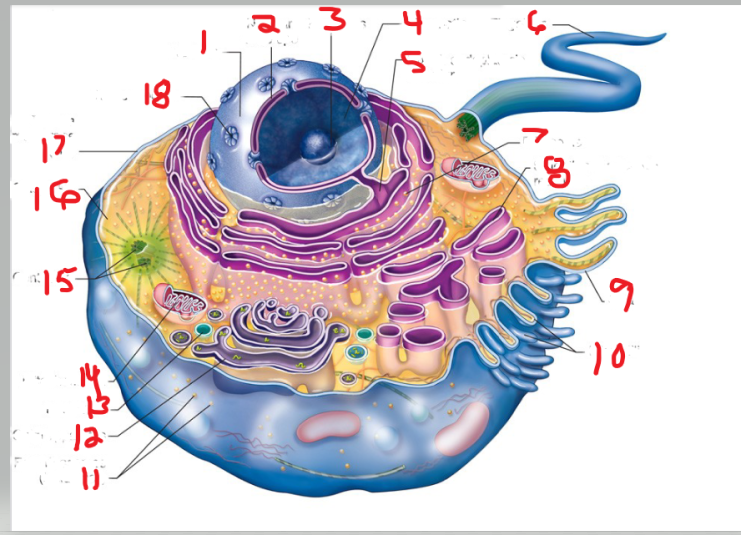
What is the structure and function of image 1
Nulceus
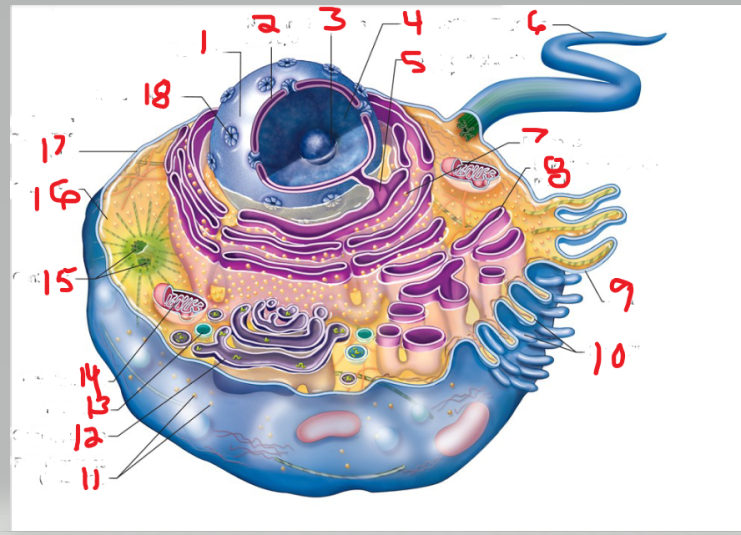
What is the structure and function of image 16
Cytoplasm
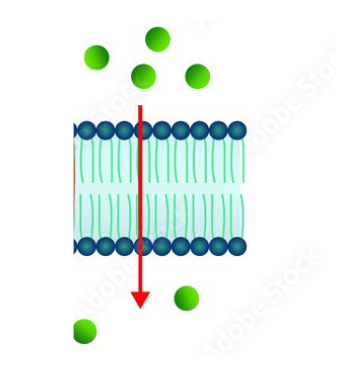
What membrane processes is occurring
Diffusion
Movement of solutes/ions
from high concentration to
low concentration
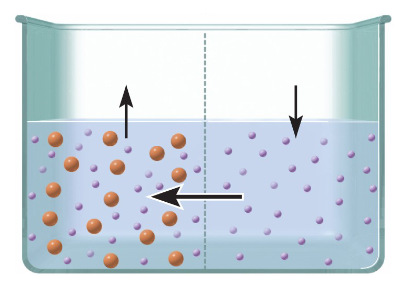
What membrane processes is occurring
Osmosis
Movement of WATER from
area of lots of water to
areas of little water
H2Oent of
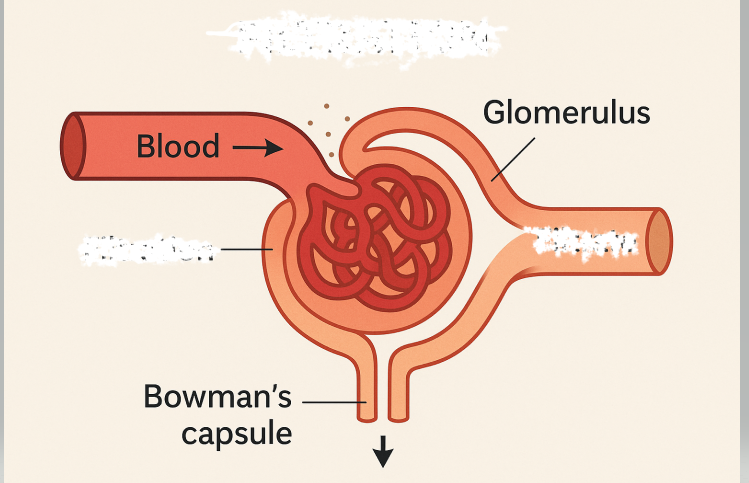
What membrane processes is occurring
Filtration
separation by pressure across membrane
Filter
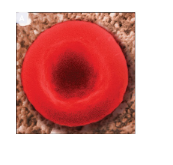
During osmosis what is the cell experiencing
Isotonic
there is no net movement of water into or out of a cell in an isotonic solution
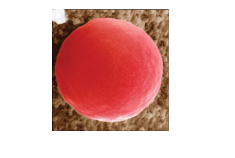
During osmosis what is the cell experiencing
Hypotonic
water will move into the cell by osmosis. This may cause the cell to swell and burst

During osmosis what is the cell experiencing
Hypertonic
This causes the ECF to pull water molecules out of the cytosol by osmosis. The cell may shrivel or crenate as it loses water to the ECF
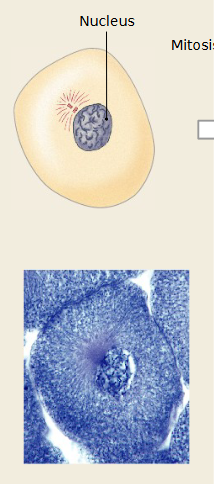
Which mitosis stage is occurring
Interphase
Cell is not dividing yet, but preparing.
DNA is replicated into sister chromatids.
Nucleus is visible, and chromosomes are not yet condensed.
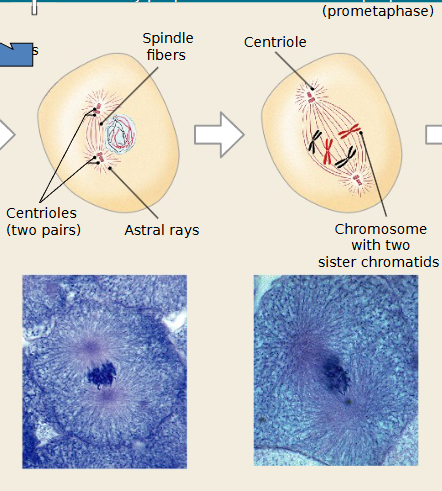
Which mitosis stage is occurring
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible.
Nuclear envelope begins to break down.
Spindle fibers form from centrioles.
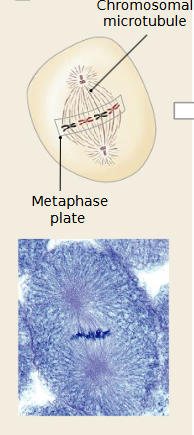
Which mitosis stage is occurring
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up at the equatorial plate (middle of the cell).
Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each chromosome.
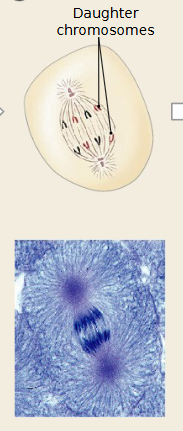
Which mitosis stage is occurring
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate at the centromere.
Spindle fibers pull chromatids to opposite poles of the cell.
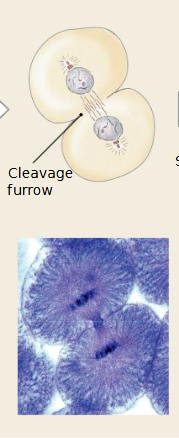
Which mitosis stage is occurring
telophase
Chromosomes reach poles and begin to de-condense.
Nuclear envelopes reform around each set of chromosomes.
Cell looks like it has two nuclei.
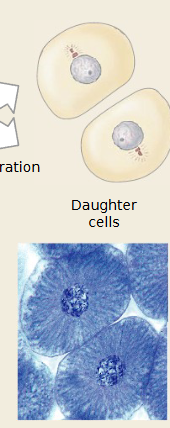
Which mitosis stage is occurring
cytokensis
Cytoplasm divides.
In animal cells → cleavage furrow forms.
In plant cells → cell plate forms.
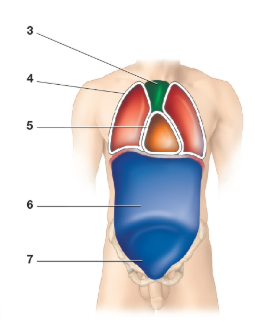
What cavity is image 3
Mediastinum