Week 11 Anatomage: Kidney EPO to Sodium Balance
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
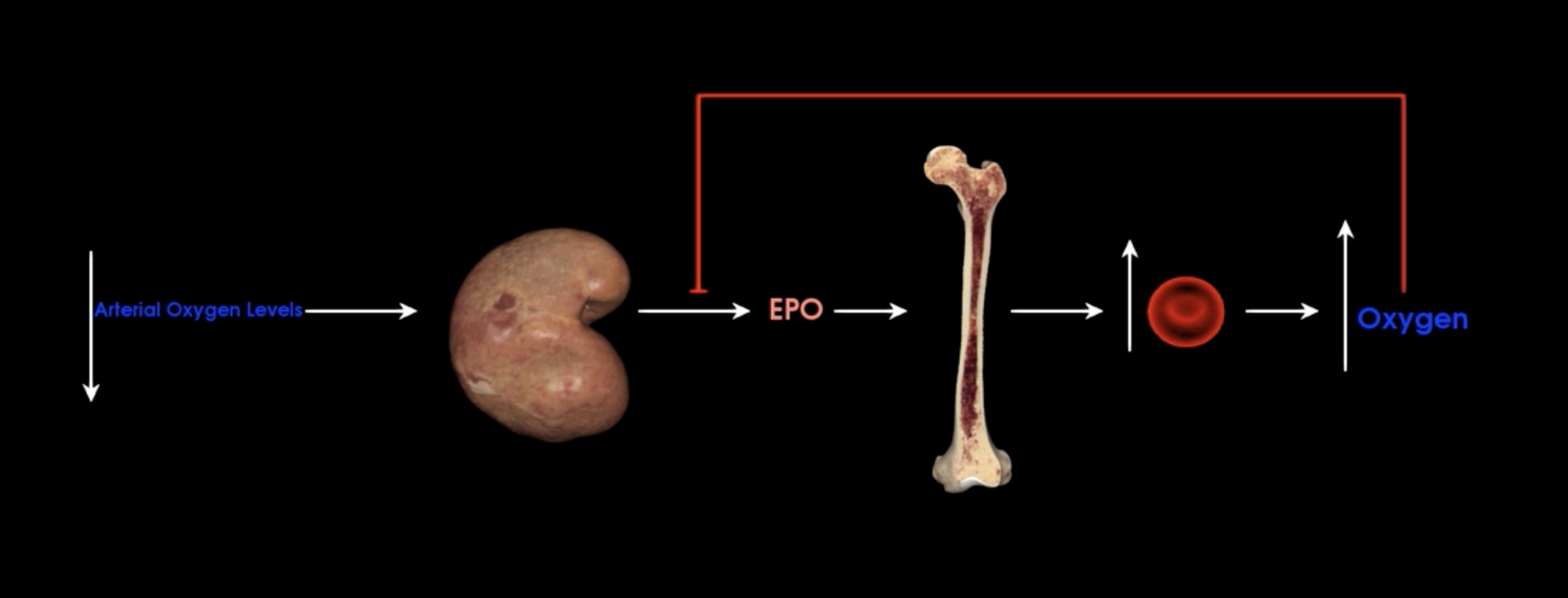
Kidneys release EPO
What happens when the kidneys detect a decrease in arterial oxygen levels?
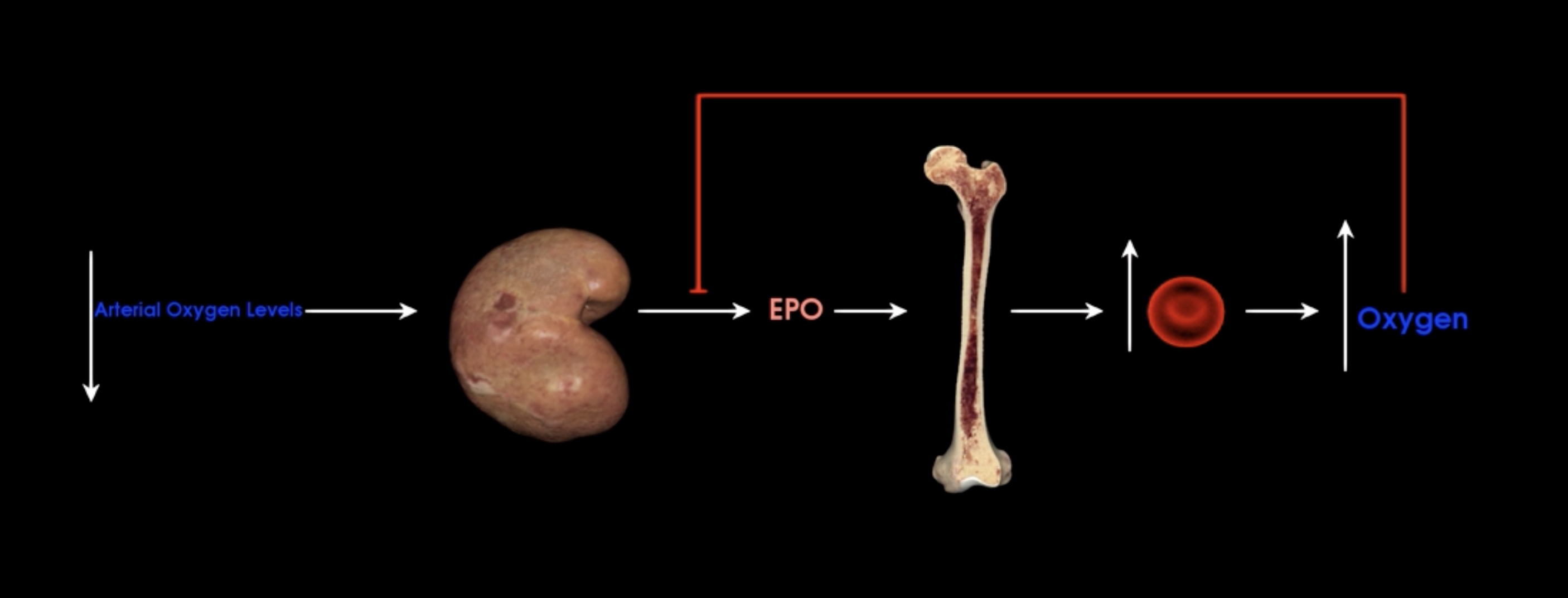
Erythrocyte progenitor cells in bone marrow promoting increased production of red blood cells
What does EPO stimulate?
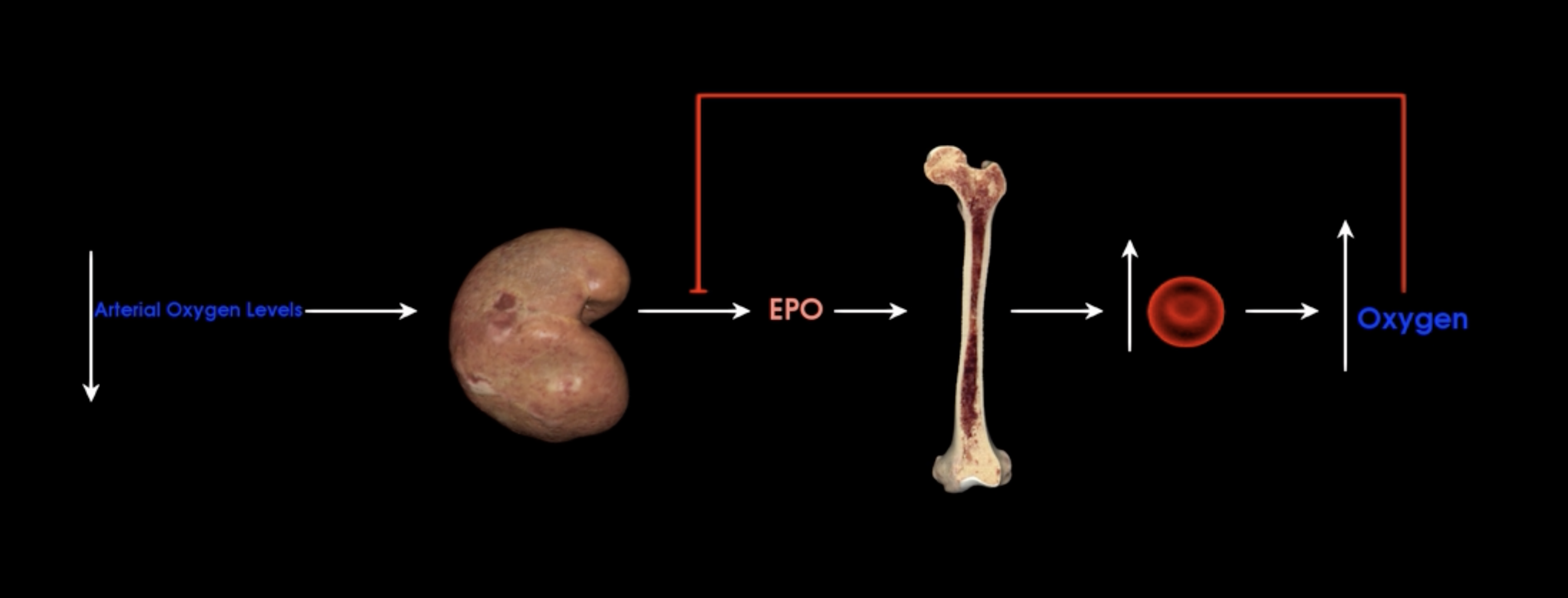
negative feedback to inhibit EPO
What does increased oxygen do to EPO?
influencing movement of fluid between different fluid compartments
Creating membrane potentials in electrically excitable cells
Controlling secretory activity of cells
Acting as chemical messengers
Roles of electrolytes
sweat, vomit, urine, feces
How are salts lost?
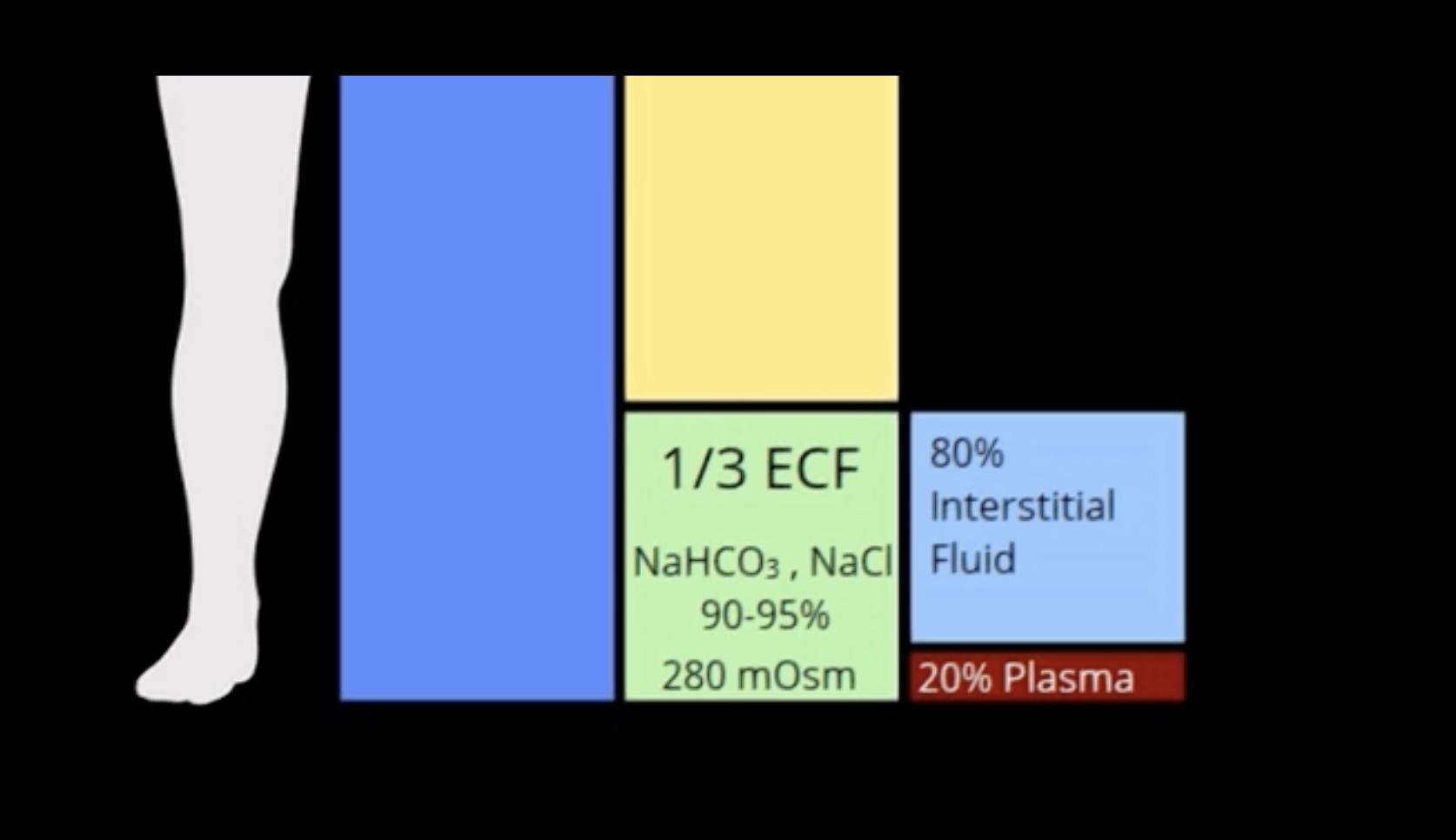
accounting of 90-95% of all extracellular solutes and 280 mOsm of 300 mOsm ECF concentration
Sodium is the most abundant cation in the ECF in the form of NaHCO3 and NaCl, accounting of ___% of all extracellular solutes and ___ of 300 mOsm ECF concentration
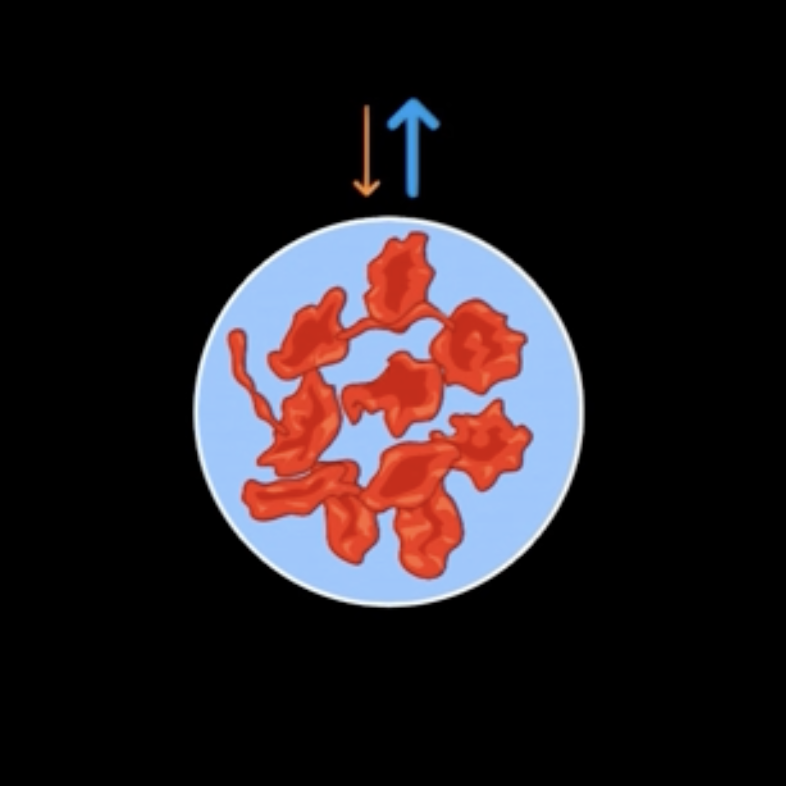
hypernatremia
elevated Na+ in the ECF, ____, can draw water out of the cells; leads to shrinking of the brain > altered mental status, seizures, and even death
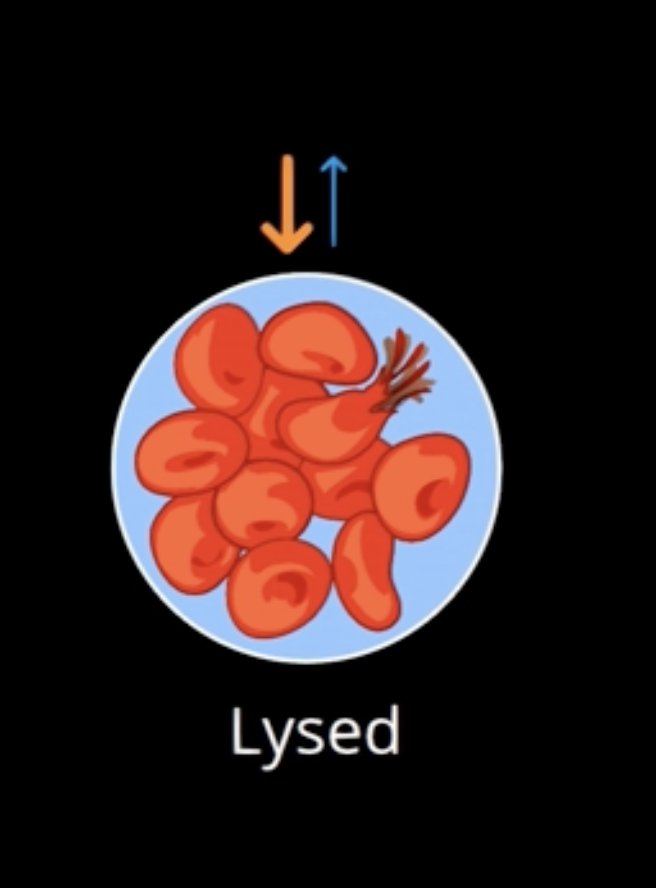
hyponatremia
low levels of Na+, ____, can cause swelling
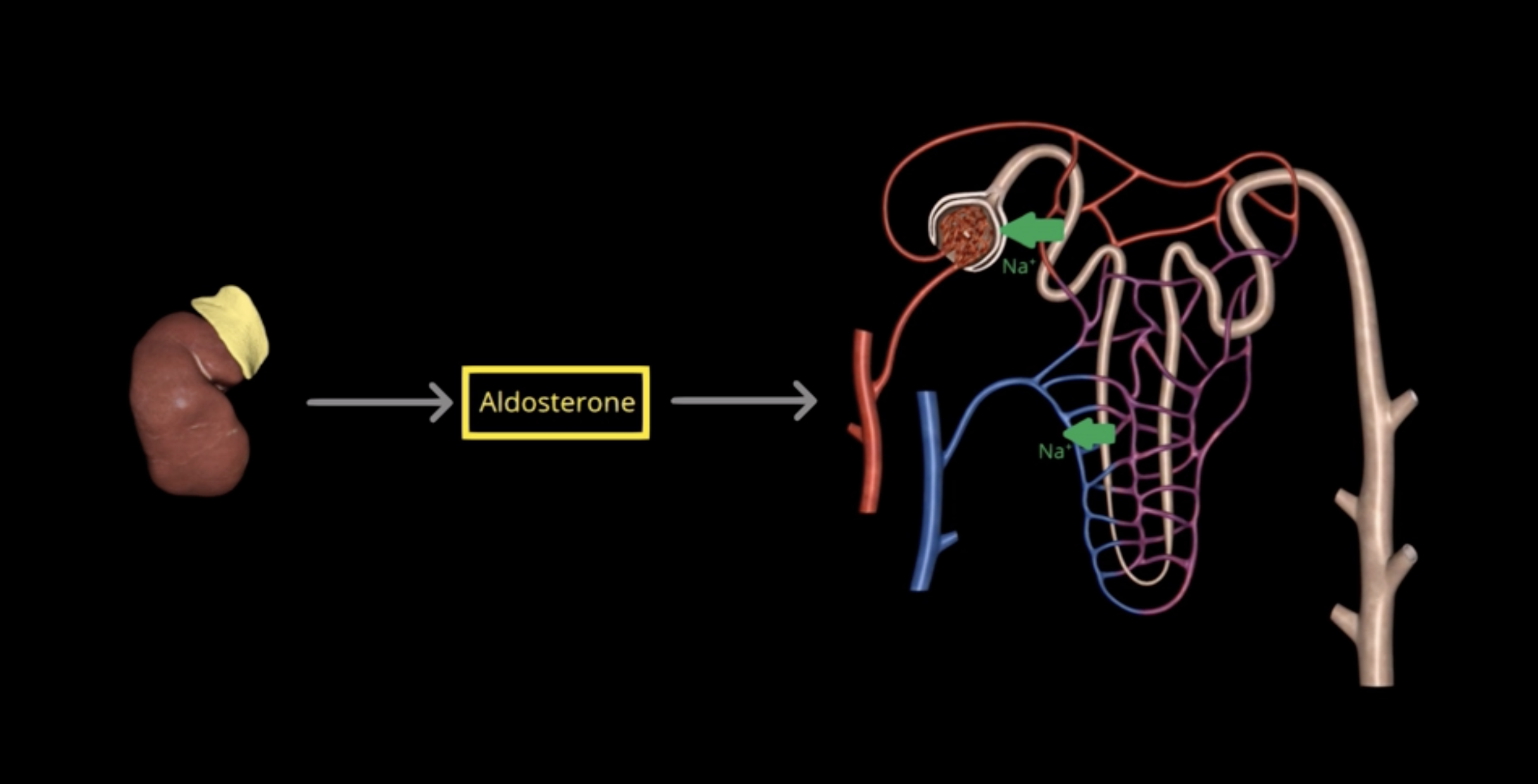
Aldosterone
90% of Na+ is reabsorbed within the PCT and loop of Henle
What is the primary regulator of Na+ concentration?
activation of RAAS > release of aldosterone > Na+ is reabsorbed by DCT and collecting ducts
What happens when Na+ concentration is decreased?
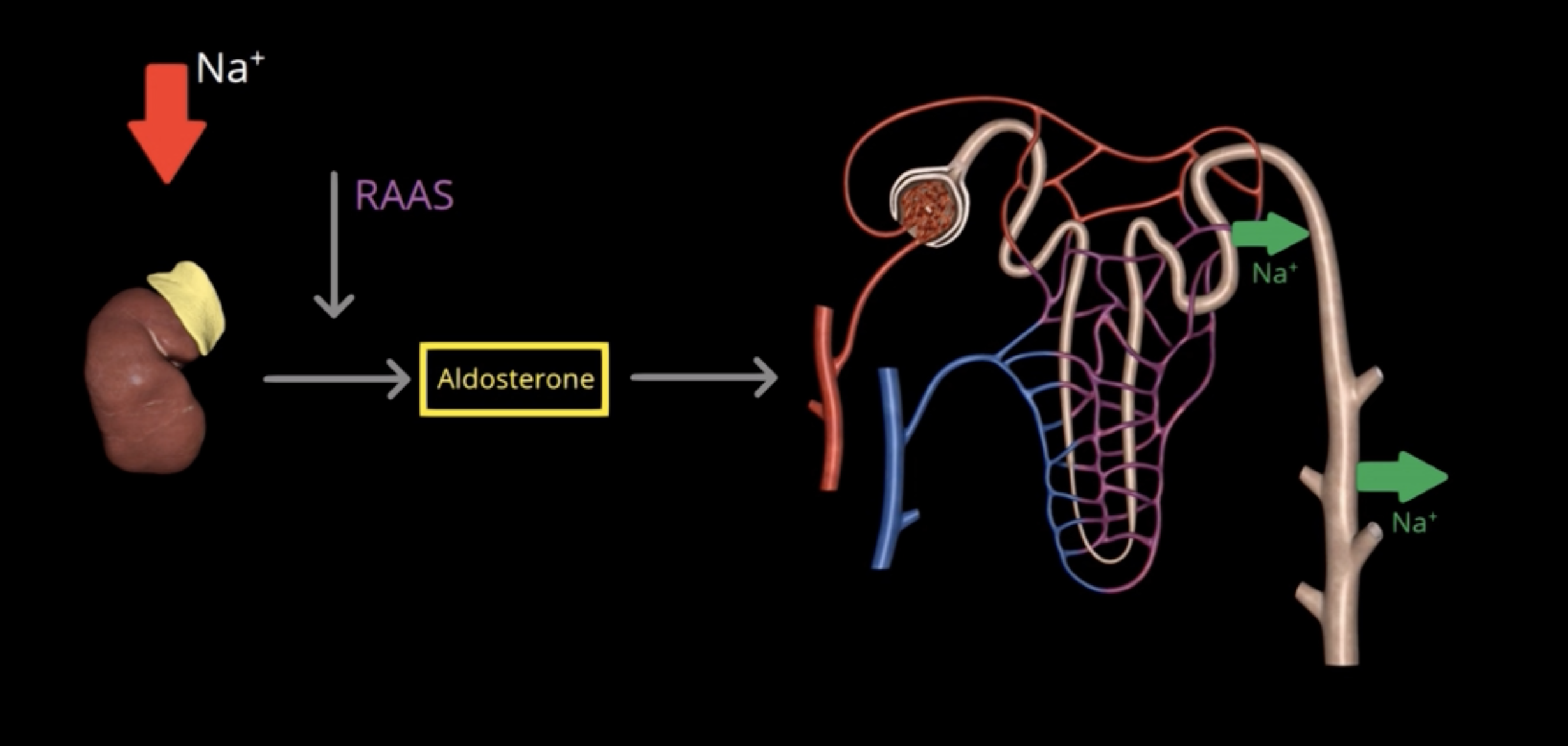
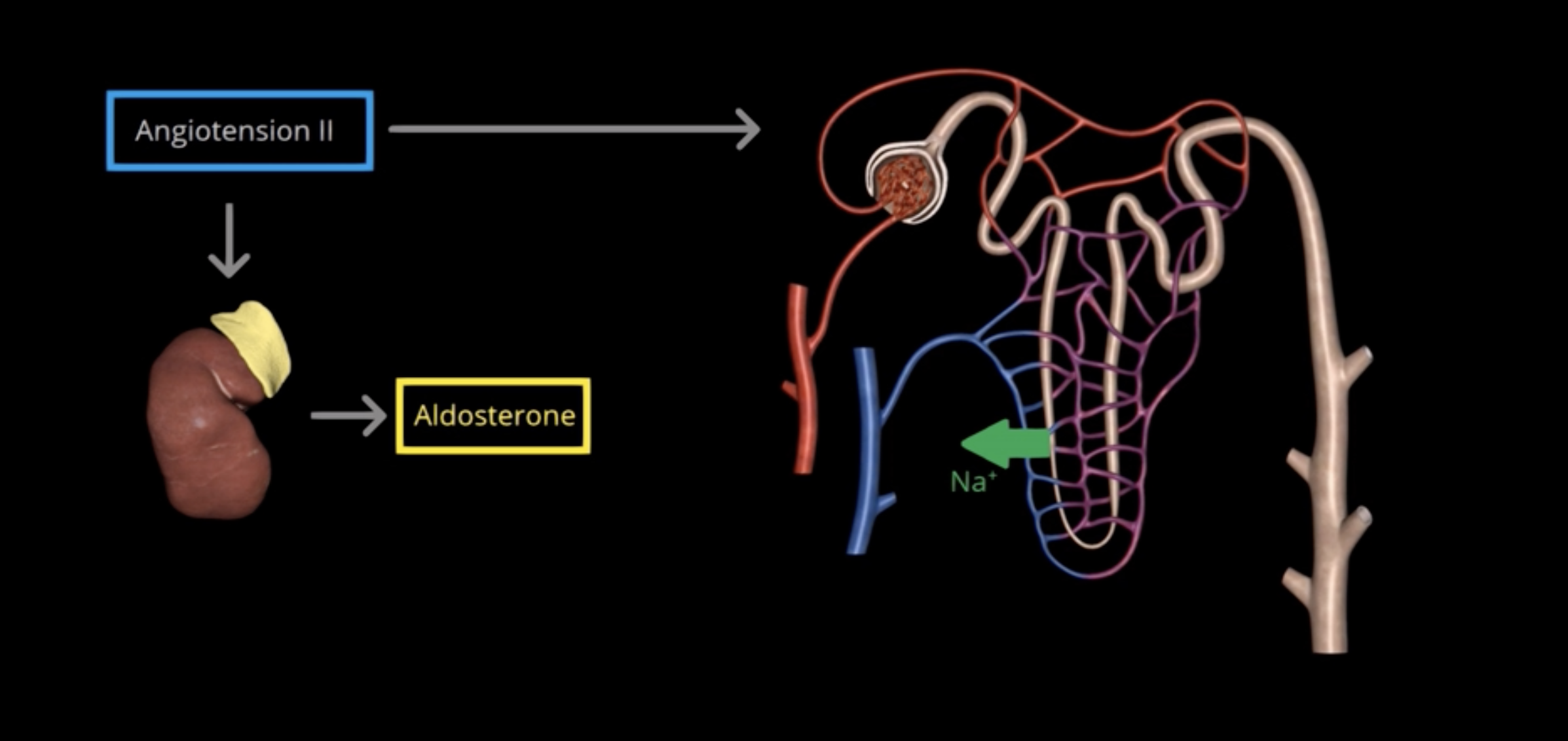
Angiotension II, also acts directly on the renal tubules to increase Na+ reabsorption
What stimulates aldosterone production?
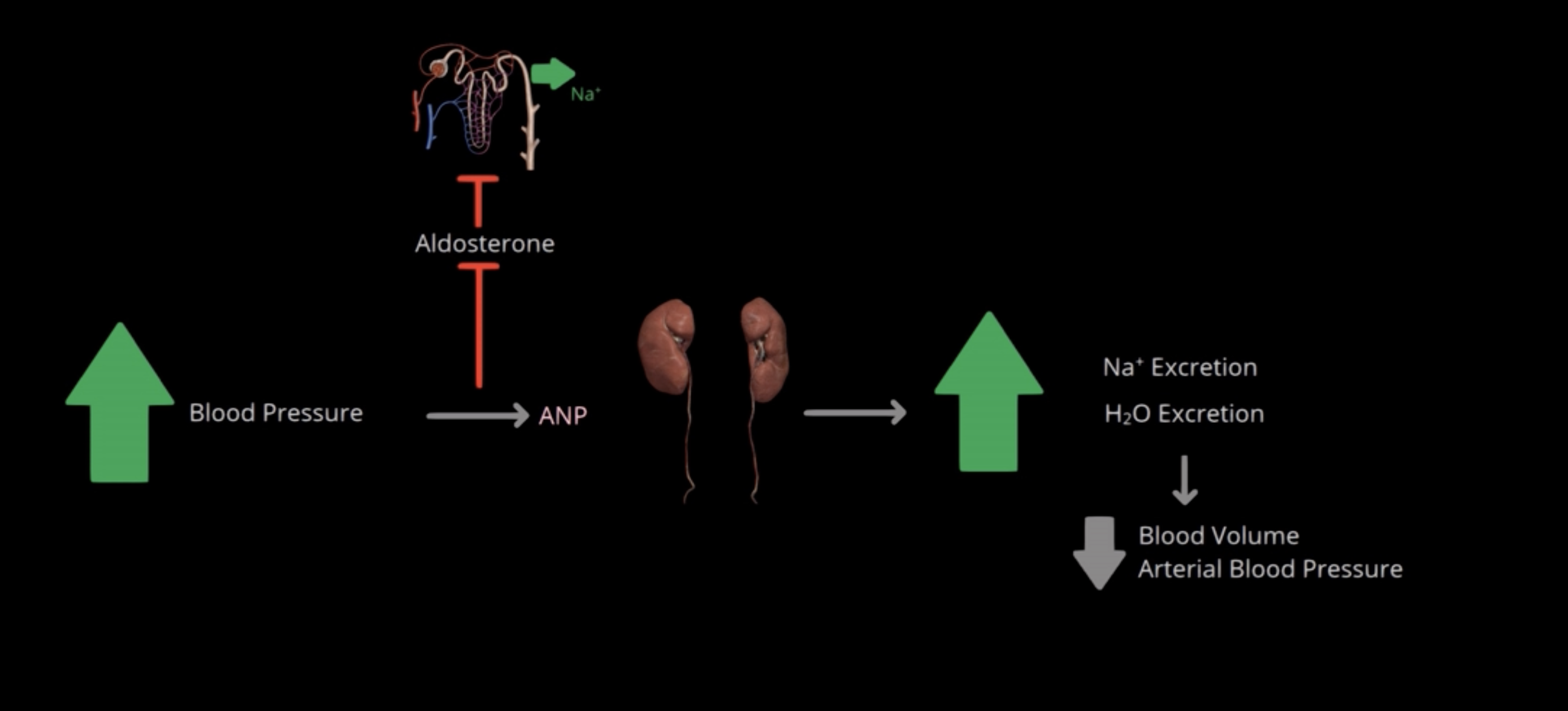
Response to elevated BP, inhibits release of aldosterone which inhibits reabsorption of Na+ by DCT and collecting ducts > increases both Na+ and water excretion by the kidneys > lowers blood volume and BP
What is the role of ANP?