Quiz on Bonds, Water, pH, carbon, molecular diversity
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Basic chem (esp. bonds), Water structure, bonds involved, Properties of water: what they are and why they are important to life, Acids and Bases, pH and pH scale, Carbon and molecular diversity, Isomers, Functional groups
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Hydroxyl
Polar
Found in SUGARS
Methyl
Nonpolar
Hydrophobic
“Turns genes off”
Includes fatty acids, oils, waxes (all lipids)
Carbonyl
Polar, Hydrophilic
Carboxyl
Charged, ionizes to release H+
Polar, Weak Acid, Hydrophilic
Ex) Amino acids and Fatty Acids
Amino
Charged, ionizes to accept H+ to form NH3+
Polar
Hydrophilic
Phosphate
Charged, ionizes to release H+
Polar, Acid, Hydrophilic, negative
Important in energy transfer
ex) Nucleotides, phospholipids, ATP
Sulfhydryl
Form disulfide bridges
Help stabilize tertiary structure of proteins
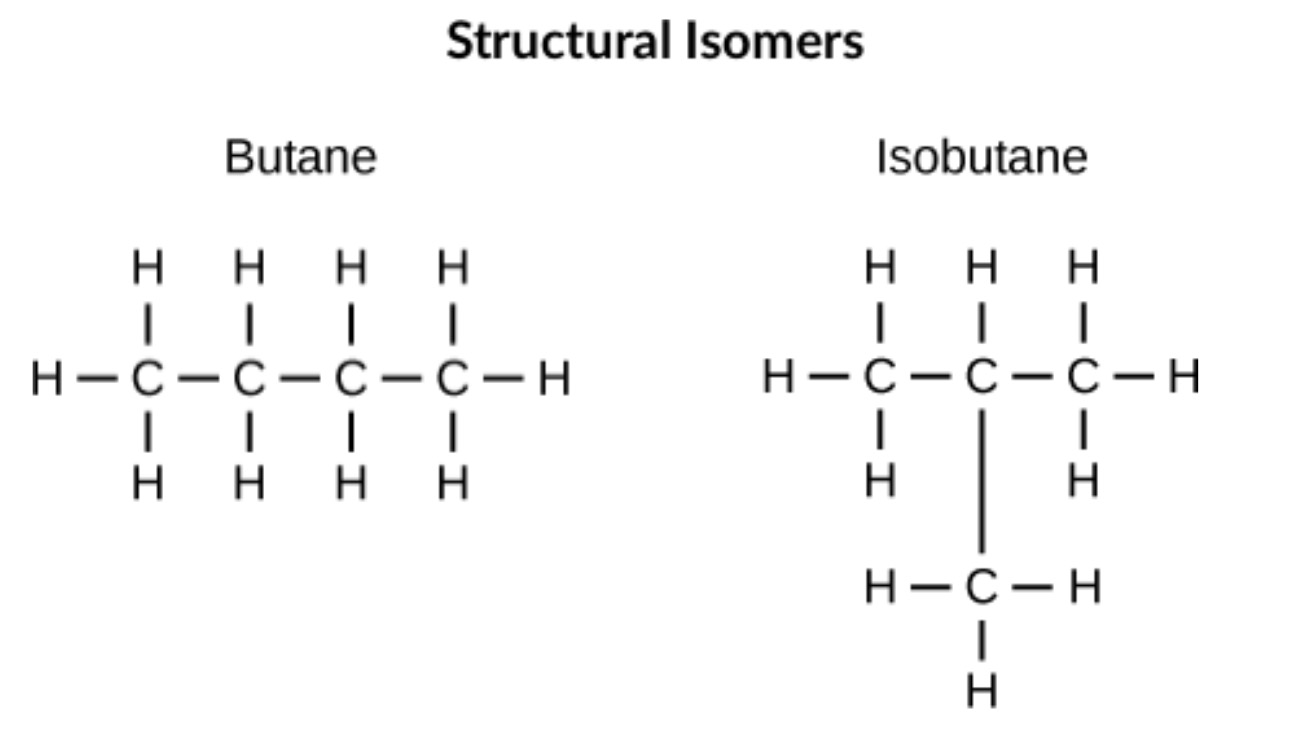
Structural Isomers
Differ in arrangement of atoms
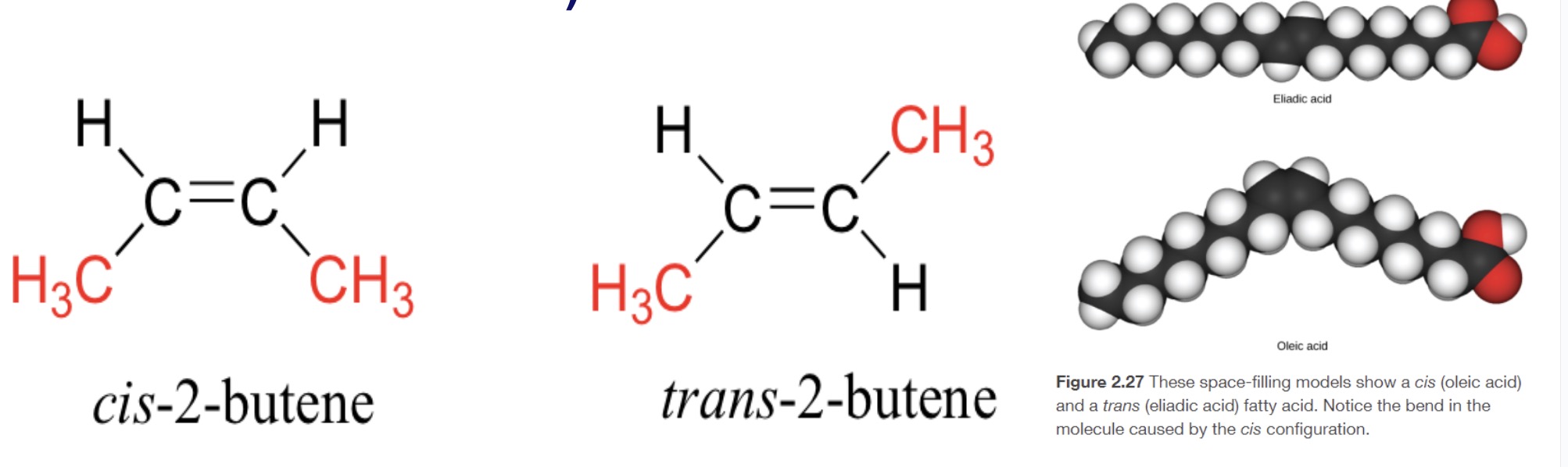
Geometric Isomers
Differing structurally only with the placement of groups around the double bond (esp. seen w/ C=C)
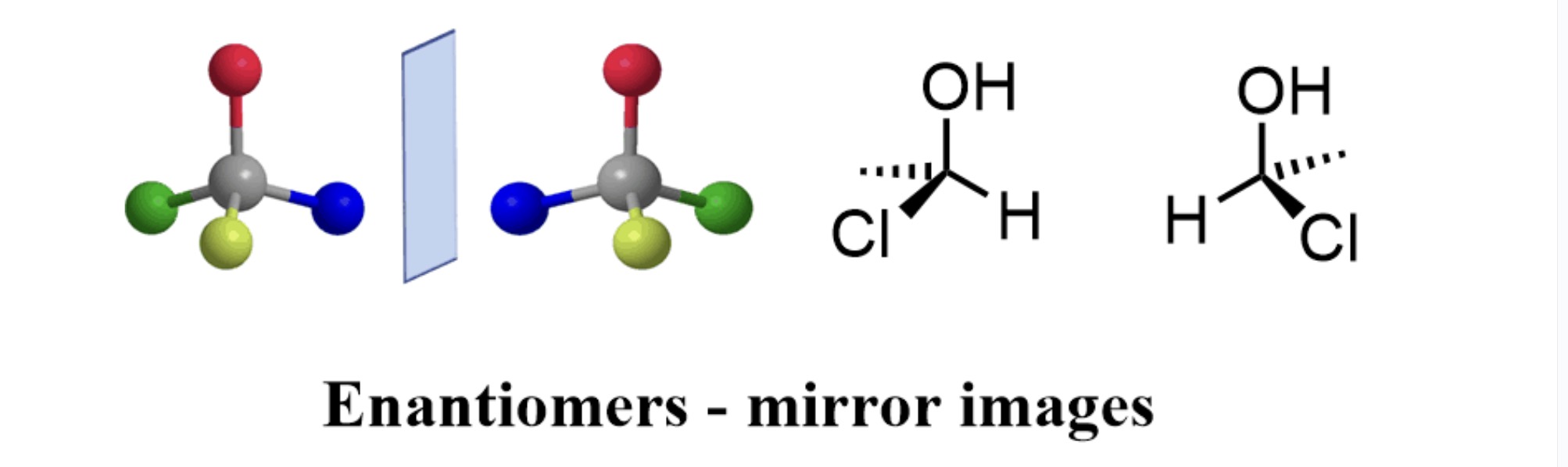
Enantiomers
Mirror images of one another, occurs w/ asymmetric carbon
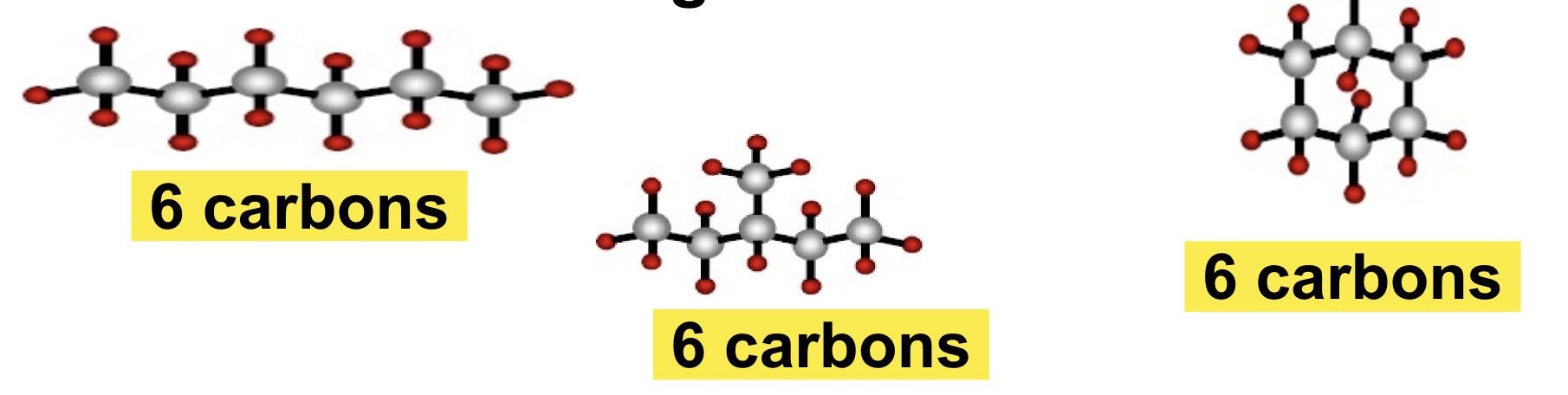
What is an Isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures/shapes.
These different shapes leads to different chemical and biological properties.
What does pH measure?
Concentration of H+ ions
What happens if you go up on the pH scale?
Concentration of H+ ions goes DOWN
Concentration of OH- goes UP
What is the concentration of both H+ and OH- at pH 5?
[H+] = 1.0 × 10^-5
[OH-] = 1.0 × 10^-9
What are solutions from 0-7?
What are solutions from 0-14?
0-7 are acids
7-14 are bases
How much more concentrated is pH 7 compared to pH 10?
1 × 10³ = 1000
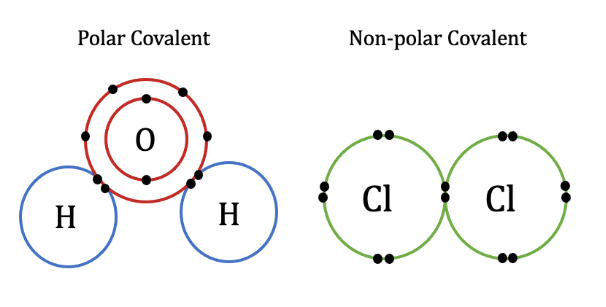
Covalent Bonds, polar vs nonpolar
Share electrons, Intramolecular, STRONG
Polar —> unequal sharing of electrons
non-polar —> equal sharing of electrons
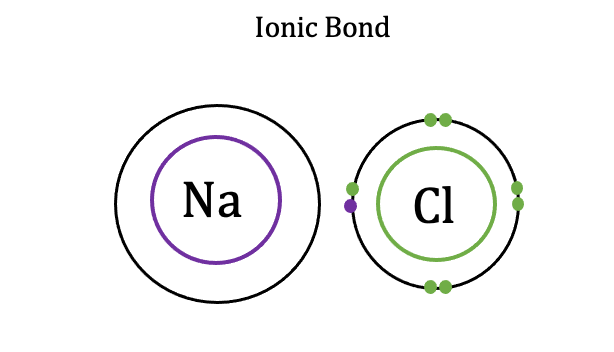
Ionic Bonds
Forms between ions of opposite charges, Intramolecular, STRONG
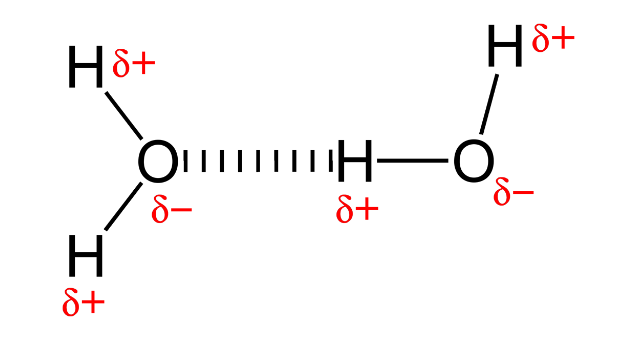
Hydrogen Bonds
Forms between Hydrogen of one molecule and F,O,N of another
Intermolecular, weak
Cohesion of water
water molecules stick to each other (w/ H-Bonds)
Adhesion of water
Water molecules sticks to surfaces
Why is cohesion/adhesion important in water?
Capillarity - Allows for water to move against gravity, good for transport of water in plants
Surface Tension in Water
H2O molecules at the surface are more strongly attracted to each other, allows for insects to walk on water

Water is a Good Solvent
H2O dissolves many polar/charged substances, they are called hydrophilic substances. Hydrophobic, non-polar won’t dissolve
Allows for chemical reactions to happen in cells/bodies
Ice floats (less dense than water)
Water expands when it freezes. Allows for bodies of water to freeze from the top down, acts as an insulator for aquatic ecosystems
High Heat Capacity of Water
Resists temperature changes
Heat absorb breaks H-Bonds without changing its temperature
Allows for stable temperature in our body and aquatic ecosystems.
High Heat needed to Vaporize
Water needs lots of energy/heat in order to vaporize. When water evaporates, energy is taken up by the process, cooling the place where it takes place. The Evap of sweat cools us.
As sweat evaporates, it absorbs heat/energy from the body, which cools it.
What are Buffers?
Buffers absorb excess H+ or OH–, keeping the pH of the body within its range.
ex) in blood - bicarbonate