exam 2 full review
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Which fatty acid has the highest melting point
steric acid (more solid at room temp., fewer double bonds = more hydrogen on a molecule)
what would decrease water requirement as a percent of body weight
the animal getting fatter
what vitamin is involved in blood clotting
vitamin K
What is the carbon notation for docosahexanoic acid (DHA)
22:6
What disease/conditions is most likely to be caused by an iodine deficiency
goiter
Which trace mineral is only required by ruminants
cobalt
The requirement for dietary intake of which vitamin increases in climates with shorter daylength
vitamin D
What macrominerals is not involved in bone formation
sodium
Which of the following minerals has a negative charge
chloride
Phytate decreases the bioavailability of which mineral
phosphorus
zinc
What fatty acid is essential
arachidonic acid
7 physiological roles of lipids
Provide long-term energy storage,
Cell signaling,
Formation of steroid hormones (Cortisol, Testosterone, Estrogen, Progesterone),
Formation of vitamin D,
Bile acid,
Inflammatory signals (eicosanoids/oxylipins),
Provide cellular structure,
Provides insulation for nerve cells
general structure of a triglyceride
glycerol back bone and 3 fatty acid tails
general structure of a diglyceride
glycerol backbone and two fatty acids
monoglyceride
glycerol backbone and 1 fatty acid tail
difference between a “free fatty acid” and an “esterified fatty acid”
free fatty acid: chain of carbon molecules with methyl and carboxyl end
esterified fatty acid: formed an ester bond with a glycerol molecule
name the 4 general roles that steroids have in metabolism
cholesterol: lipid transport
bile acids & salts: emulsification of fats in digestive tract
vitamin D: required hormone for calcium metabolism & immune system
steroid hormones: corticosteroids, estrogens, androgens, progesterone
what type of hormones are derivatives of cholesterol
steroids
hormones within that would be derived from cholesterol
corticosteroids (stress hormones)
estrogens (sex hormones)
androgens (sex hormones)
progesterone (pregnancy hormone)
which type of fatty acids are pro-inflammatory
omega-6
which type of fatty acids are anti-inflammatory
omega-3
which end of a fatty acid do you begin counting from using the delta counting scheme?
count from carboxyl end
which end of a fatty acid do you begin counting from using the omega counting scheme?
count from methyl end
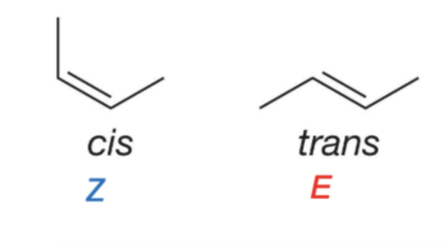
cis double bond and a trans double bond
cis is more of a hexagonal shape
trans is like a squiggle
C16:0
palmitic acid
C18:0
stearic acid
C18:1
oleic acid
C18:2
linoleic acid
C18:3
linolenic acid (essential, omega-3)
C20:4
arachidonic acid (conditionally essential, omega-6)
C20:5
EPA (conditionally essential, fish oil, omega-3)
C22:6
DHA (conditionally essential, fish oil, omega-3)
antidioxants prevent which type of rancidity of fats
oxidative rancidity
which type of fatty acid is responsible for causing milk-fat depression
CLA-Conjugated Linoleic Acids
specifically, trans-10 cis-12 CLA
rank the following animal species by their fat requirement: cats, pigs, horses, ruminants
highest: cats, pigs, horses, ruminants : lowest
saturated fats
no double bonds between carbon atoms in fatty acid chains
saturated with hydrogen atoms
unsaturated fats
1 or more double bonds (kinks) between carbon atoms
have fewer hydrogen atoms than saturated fats
how does the amount of saturation affect melting point of the fat, and oxidation of the fat
as saturation goes up, melting point goes up
as saturation goes down, oxidation goes up
what is iodine a measure of
unsaturation of fat
more unsaturated bonds = higher iodine number
symptoms of a dietary fat deficiency
reduced growth & feed deficiency
poor reproductive performance
skin lesions, hair loss, poor feathering
subcutaneous hemorrhage
what are the 3 essential fatty acids in all animals
linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic
how does age affect the relative amount of body water within an animal
At birth: water is 60-85% of total body weight
At maturity: water is 45-65% of total body weight
functions of water
Maintains shape of body cells
Lubricates and cushions joints
Insulates vital organs
Assists digestion
Removal of wastes
Transports nutrients and signals
Required for chemical reactions within the body
Regulates body temperature
Regulates osmotic and acid base balance
Where does metabolic water come from
nutrient metabolism
approximately how much of the total body water does metabolic water account for?
accounts for 5-10% of total body water
What factors affect water intake in animals?
age of animal
dry matter consumption
diet consumption
production status
activity work level
metabolic rate
weather
species differences
how does age affect water intake
Animals consume more total water as they get larger
water intake goes down with age because body fat is inversely correlated with body water
how does dry matter consumption affect water intake
Greater dry matter intake = greater water intake
Wetter feeds = less water intake
how does diet consumption affect water intake
Salt increases intake to balance osmotic pressure
Protein increases intake to flush out excess nitrogen via urine
Fiber increases intake due to excess salivation
how does production status affect water intake
Growing animals require more water for metabolism
Lactating animals require a ton of water for milk production
how does activity work level affect water intake
More activity = more water requirement
how does metabolic rate affect water intake
Faster metabolism = more water
Hibernating animals require nearly no water intake
High-strung animals require more water
how does weather affect water intake
Hot weather increases water consumption
Water intake decreases with decreasing temperature
how does species differences affect water intake
Mammals have greater requirements
Birds have a lower water requirement
Freshwater fish do not drink
Boney saltwater fish “drink”
4 contaminants that can affect water quality
minerals (especially salt, calcium, magnesium, & sulfur)
nitrates
blue-green algae
pesticides
where do minerals (especially salt, calcium, magnesium, & sulfur) come from
ground/soil
where do nitrates come from
Occurs in groundwater during over application of manure or nitrogen fertilizer
Contamination can occur from septic tanks or manure storage
where does blue-green algae come from
Occurs when high nitrogen is found in water supply
can occur in water troughs/stock tanks if not cleaned
where do pesticides come from
comes from agricultural runoff & accidental spills
which units are vitamins measured in
A, D, E : ug (international units)
K, B, C : ppm (mg/kg) or (mg/lb)
4 fat soluble vitamins
A-retinol
D-calciferol
E-tocopherol
K1-phylloquinone
all water soluble vitamins
vitamins B1,2,5,7,6,3,9,12, & C
vitamin A
retinol
vitamin D
calciferol
vitamin E
tocopherol
vitamin K1
phylloquinone
vitamin B1
thiamin
vitamin B2
riboflavin
vitamin B5
pantothenic acid
vitamin B7
biotin
vitamin B6
pyridoxine
vitamin B3
niacin
vitamin B9
folic acid
vitamin B12
cobalamin
vitamin C
ascorbic acid
on average what is the shelf life of vitamin mixes
3-4 months
what is the shelf life of vitamin trace-mineral premixes
30 days or less
role of vitamin A
visual pigments
2 precursors of vitamin A
B-carotene
retinoic acid
deficiency symptoms of vitamin A
night blindness
eye lesions
eye ulcers
pig bone deformities
abortions (sleep & cattle)
which mineral is most likely to be toxic within an animal
vitamin D
symptoms of vitamin D toxicity
anorexia
reduced growth rate
reduced liver rate
hypercalcemia
reduced weights of the radius & ulna
calcification of the aorta, heart, kidney, and lung
dehydration, vomiting, fatigue
roles of vitamin D
bone formation
increase intestinal Ca & P absorption
CHO metabolism
2 deficiencies of vitamin D
rickets
soft egg shells
3 major functions of vitamin E
antioxidant
muscle structure
reproduction
immune function
3 natural sources of vitamin D
cod liver oil
beef liver
alfalfa, sun cured
egg yolk
mushrooms, uv-irradiated
the active form of which vitamin is synthesized in the skin in the presence of UV light
vitamin D
which mineral is associated with vitamin E
selenium
deficiencies of vitamin E
Nutritional muscular dystrophy
Impaired sperm production
Hemorrhage in pig embryos
Retained placenta
Milberry heart disease (pigs & elephants)
White muscle disease in cows
Inability to resolve inflammation/oxidative stress
which vitamin is responsible for blood coagulation/clotting
vitamin K
Dicoumerol in moldy sweet clover is an antagonist for vitamin K, what does it cause?
Fatal Hemorrhaging/uncontrolled bleeding
Causes vitamin K deficiency
which B vitamin can only be synthesized by microbes
vitamin B12 (cobalamin)
how does basal metabolic rate affect the requirement for B vitamins
greater metabolic rate = greater B vitamin requirement
Pellagara, red tongue, and black tongue, are deficiency symptoms of which B vitamin?
vitamin B3 (niacin)
role of choline in fat metabolism
involved in the one-carbon metabolism pathway (methyl donor), liver lipid export
rank the vitamin C requirement of the following animals: horses, guinea pigs, cows, pigs
highest: guinea pigs, pigs, horses, cows : lowest
what is an “organic” trace mineral
mineral bound to organic molecule
what does it mean for a mineral to be “chelated”
trace minerals are minerals bound to an amino acid