ATI TEAS Cardiovascular System
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
cardiovascular system
-ALSO called the circulatory system
-made up of the heart, blood vessels, the blood, and lymphatic system.
-waste removal, nutrient distribution, communication, protection.
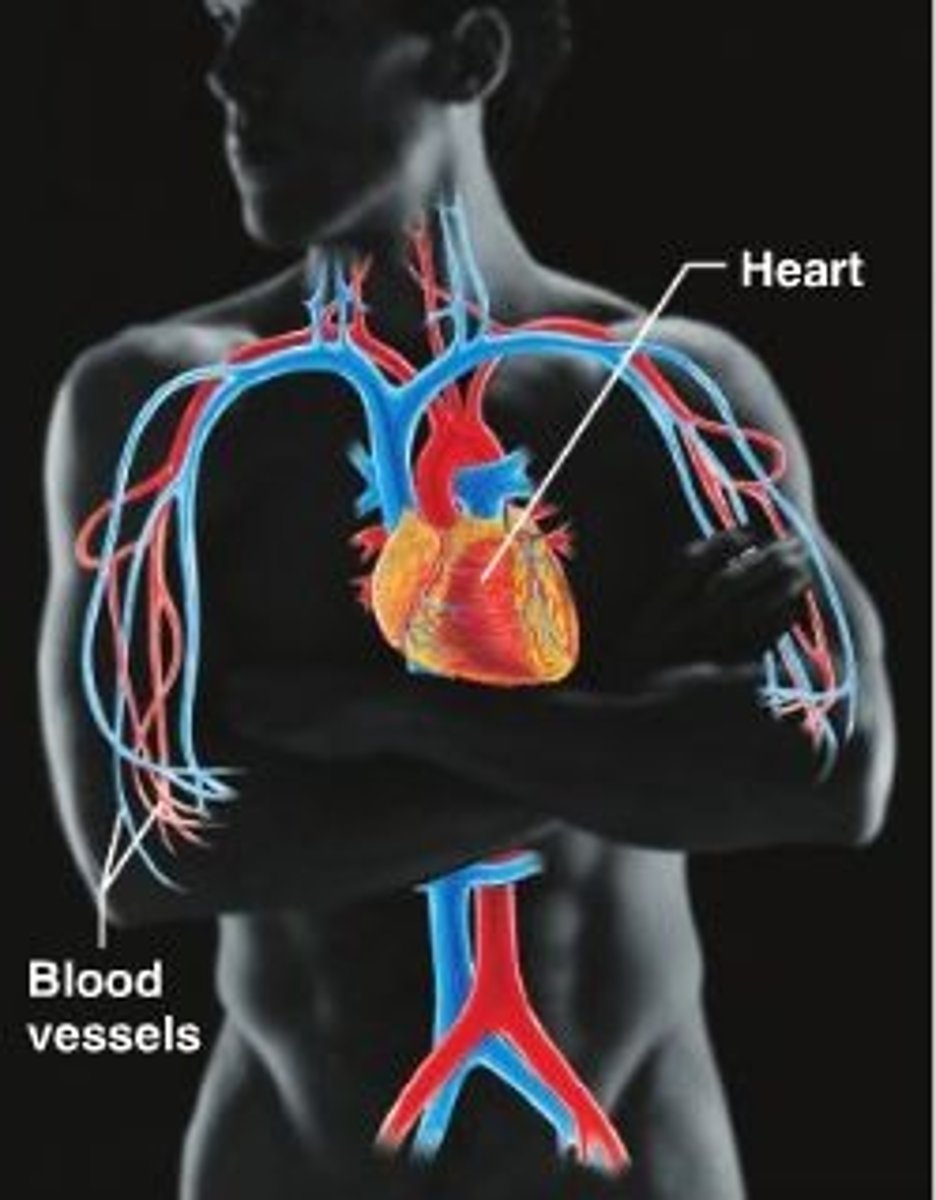
heart
-composed of cardiac muscle tissue
-4 muscular chambers of heart: right and left atria and the right and left ventricles
-regulates blood flow through a double-loop system, pumping oxygenated blood to body tissue and deoxygenated blood to the lungs
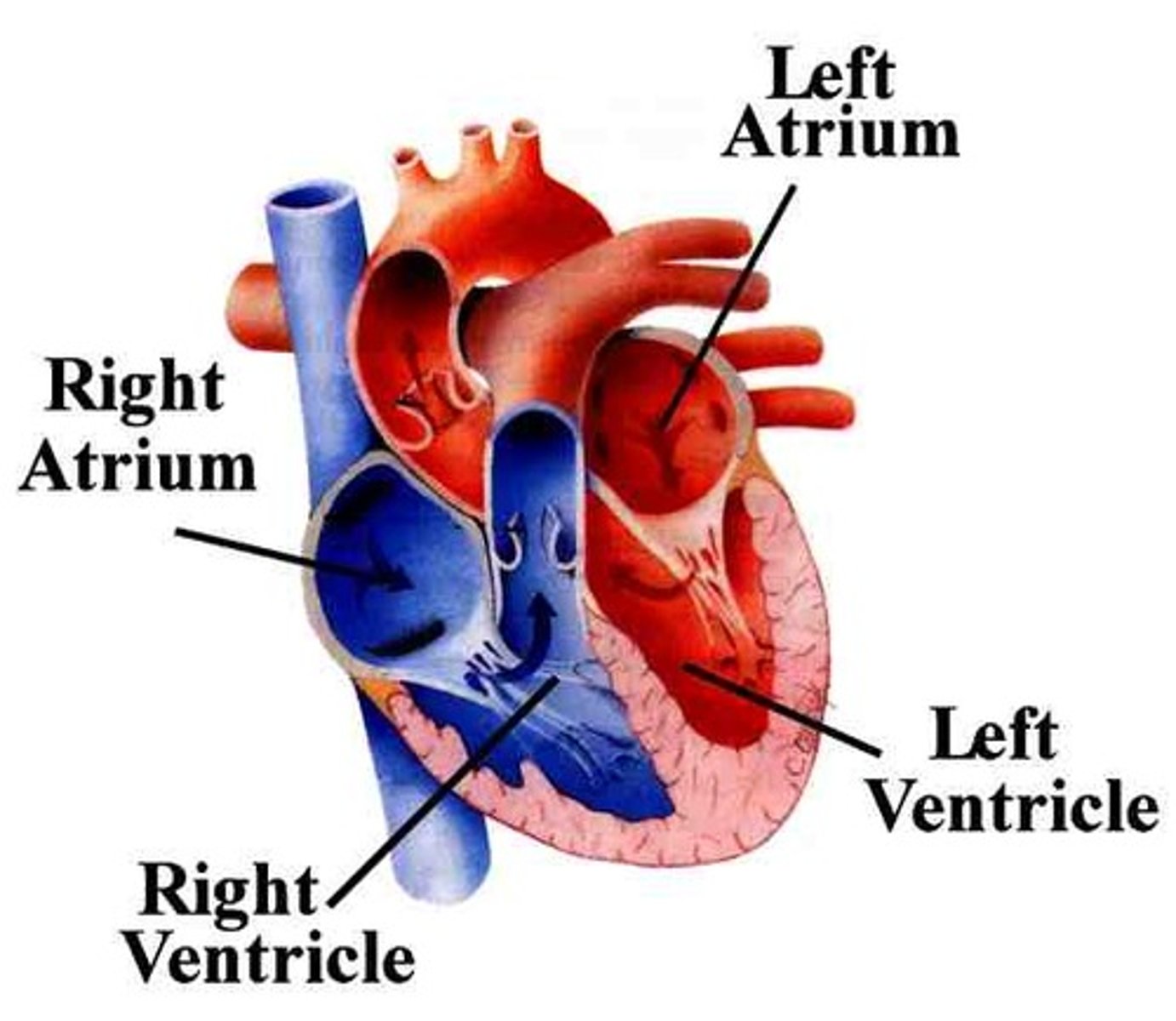
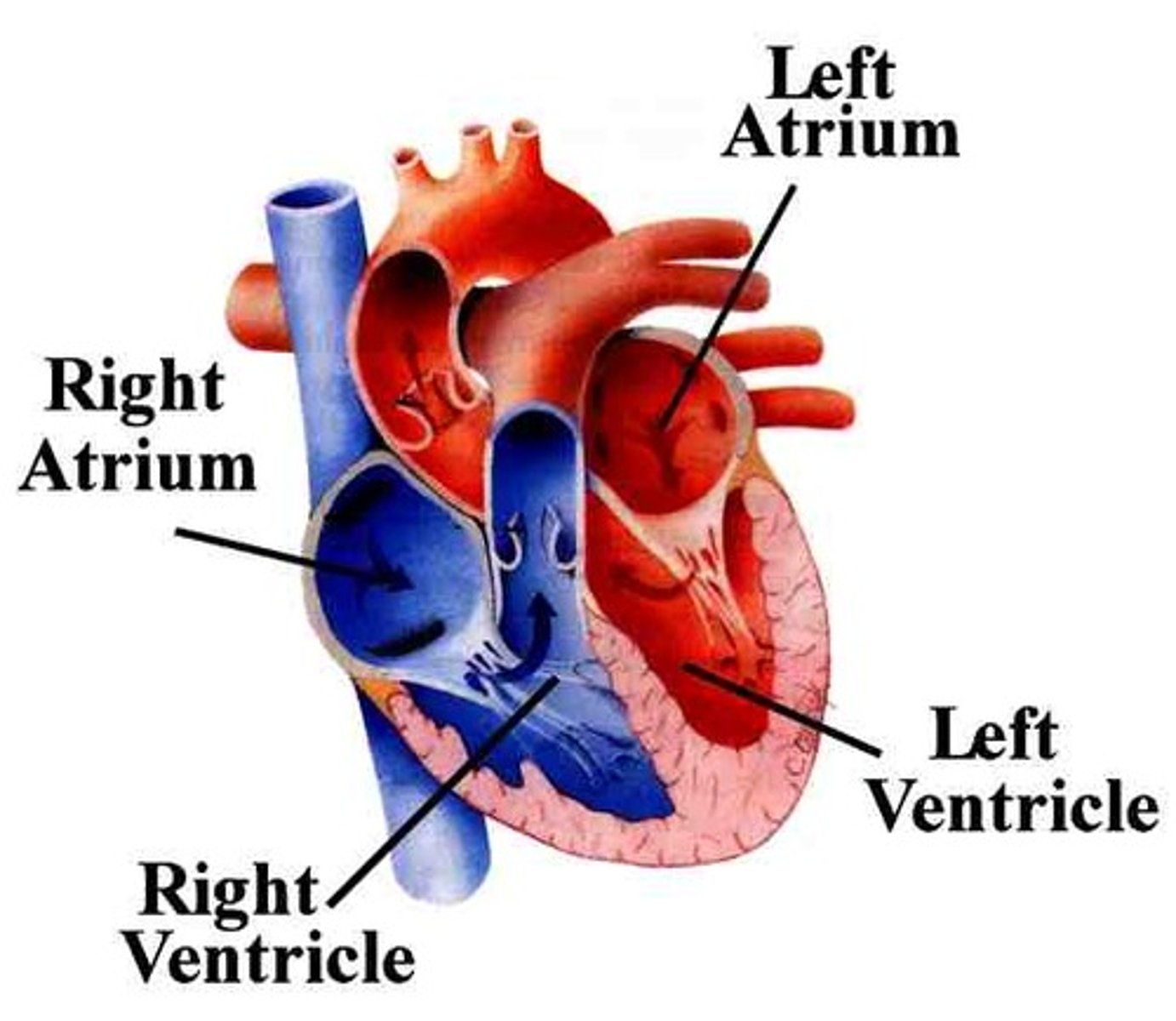
atria
-2 of them; left and right
-chambers of the heart that receive blood returning to the heart from other areas of the body
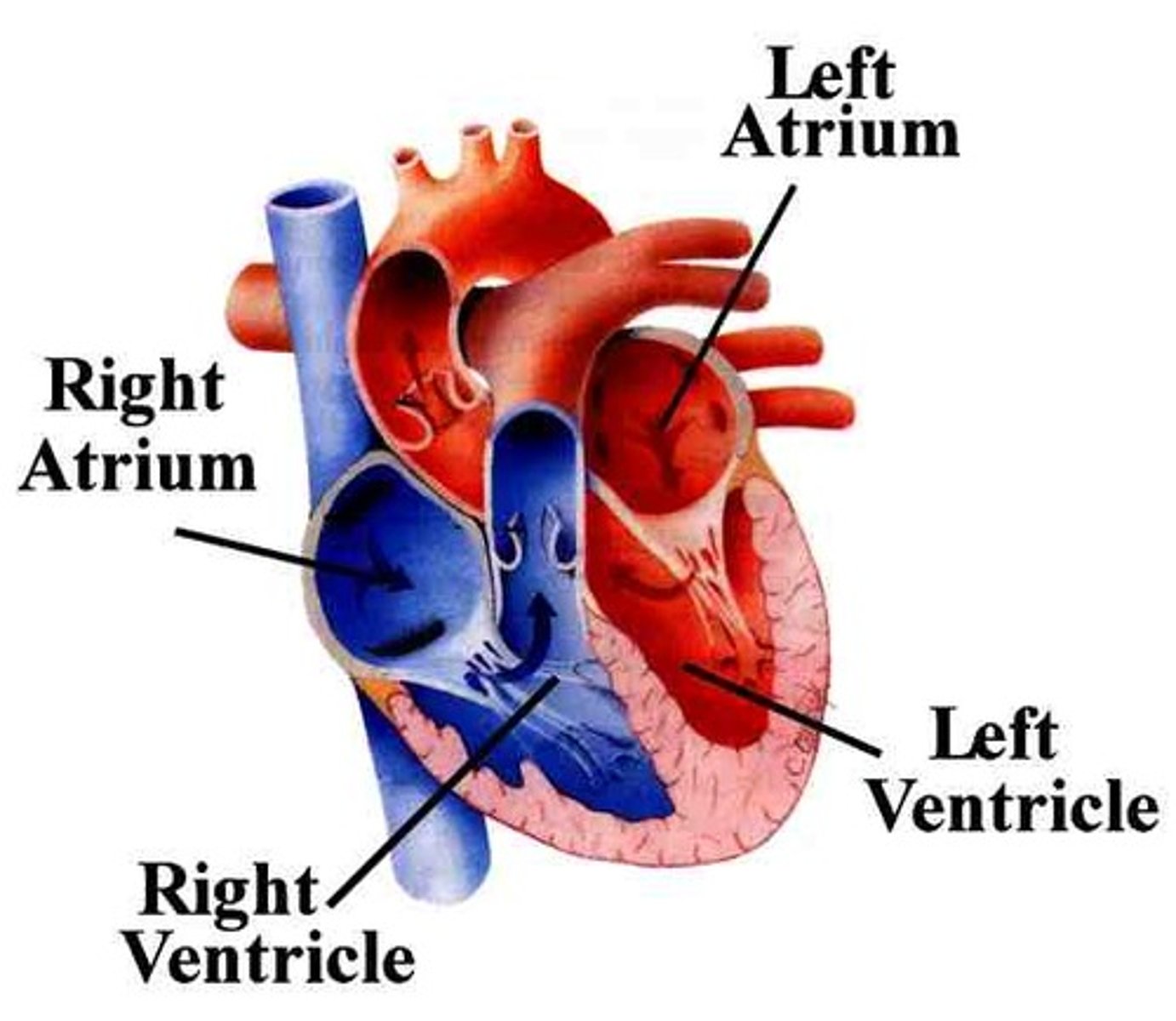
ventricles
-chambers of the heart that collect and expel blood from the heart
-2 of them; left and right
atrioventricular valves
valves that separate the atria and ventricles in the heart
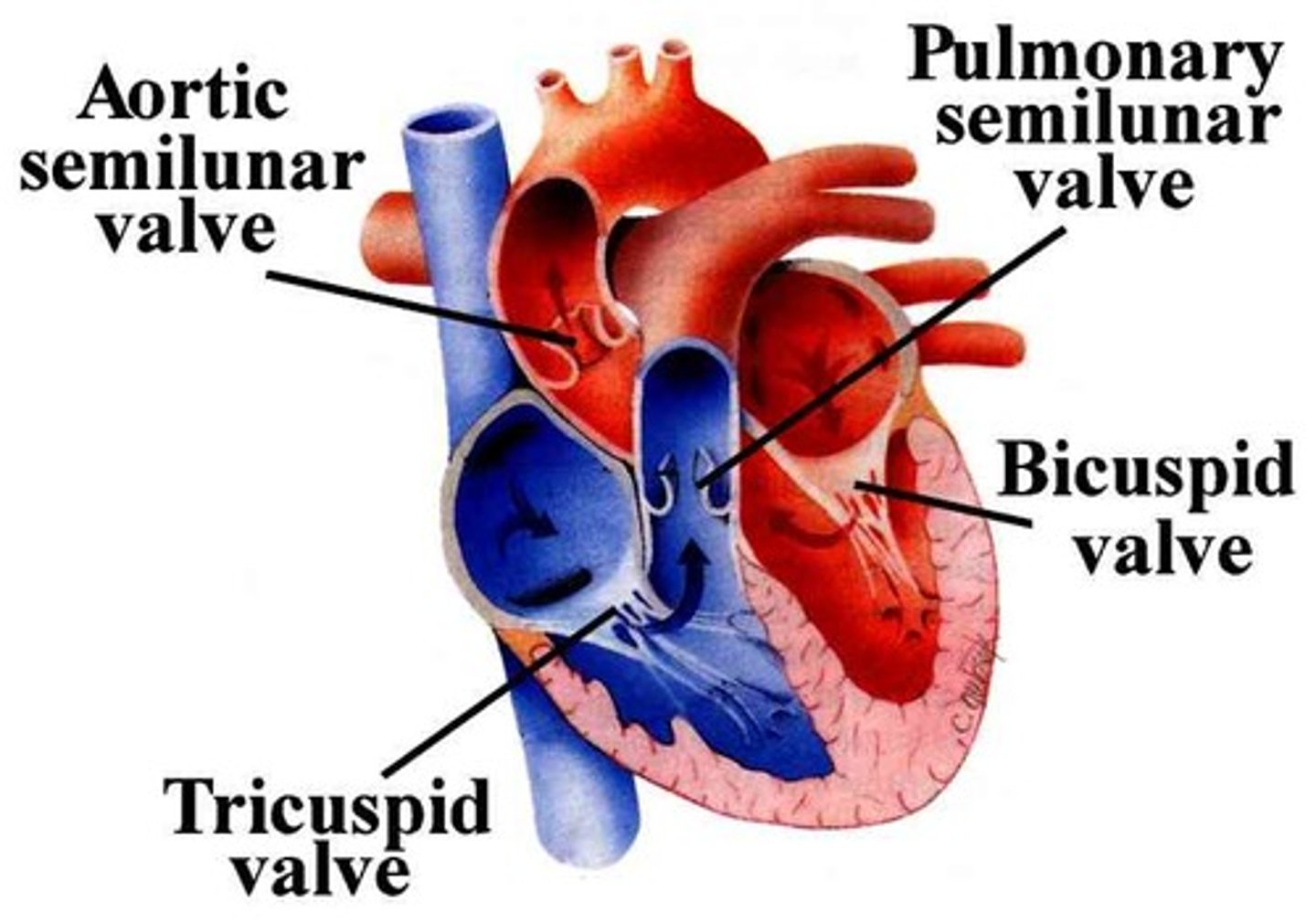
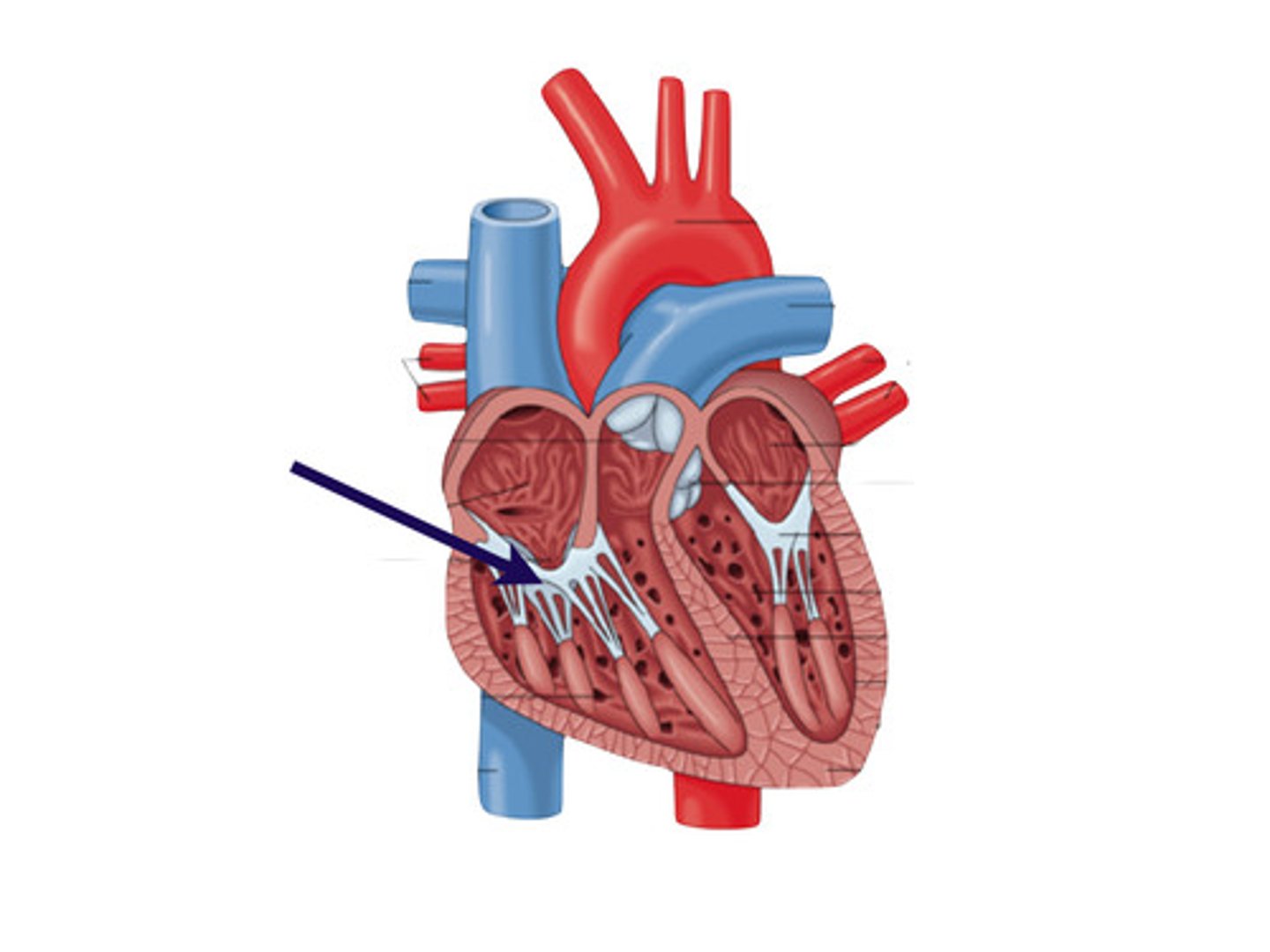
tricuspid valve
separates the right atrium and right ventricle
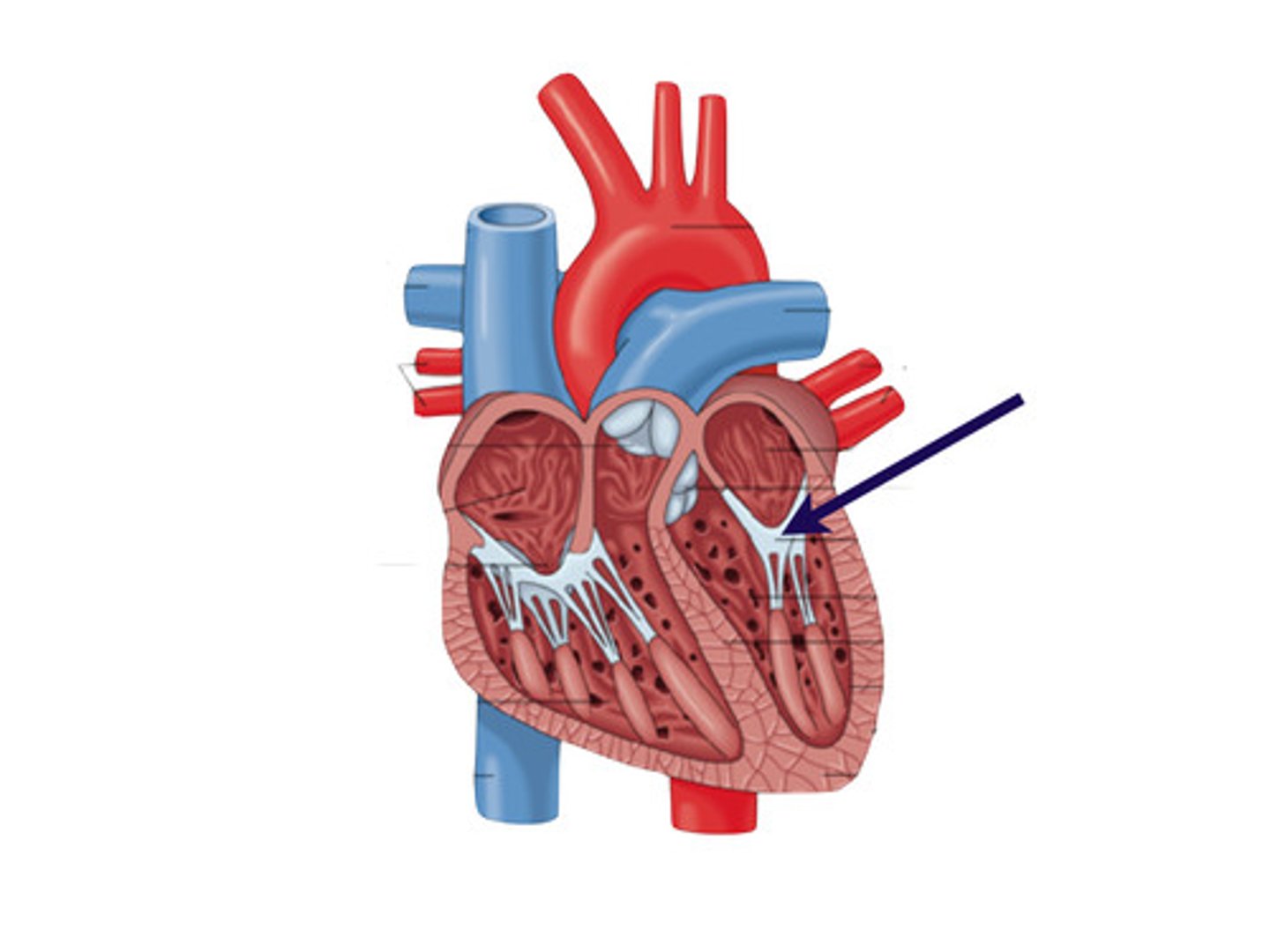
mitral valve (bicuspid)
-ALSO called bicuspid
-separates left atrium and left ventricle
types of blood vessels
1. arteries
2. capillaries
3. veins
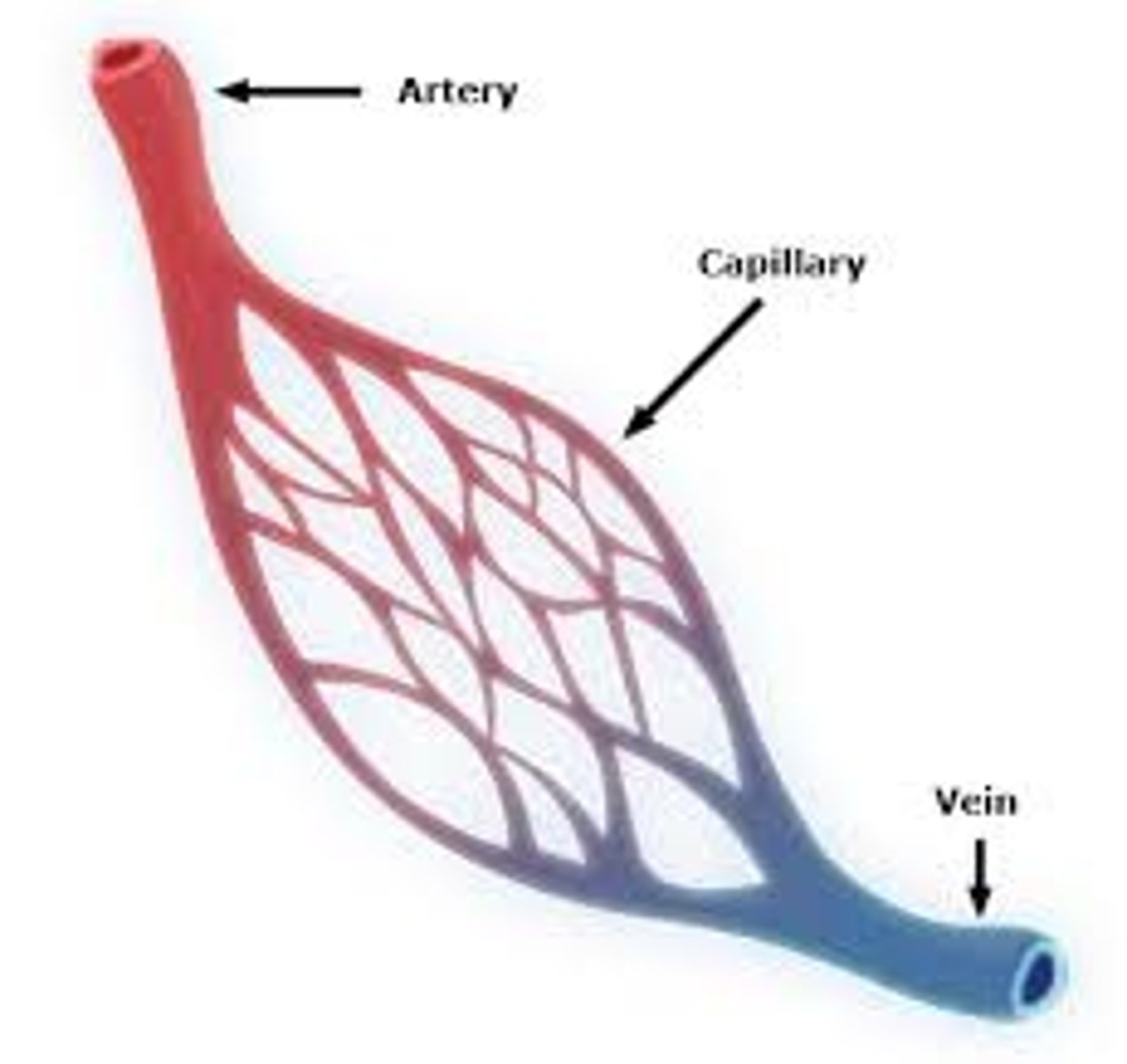
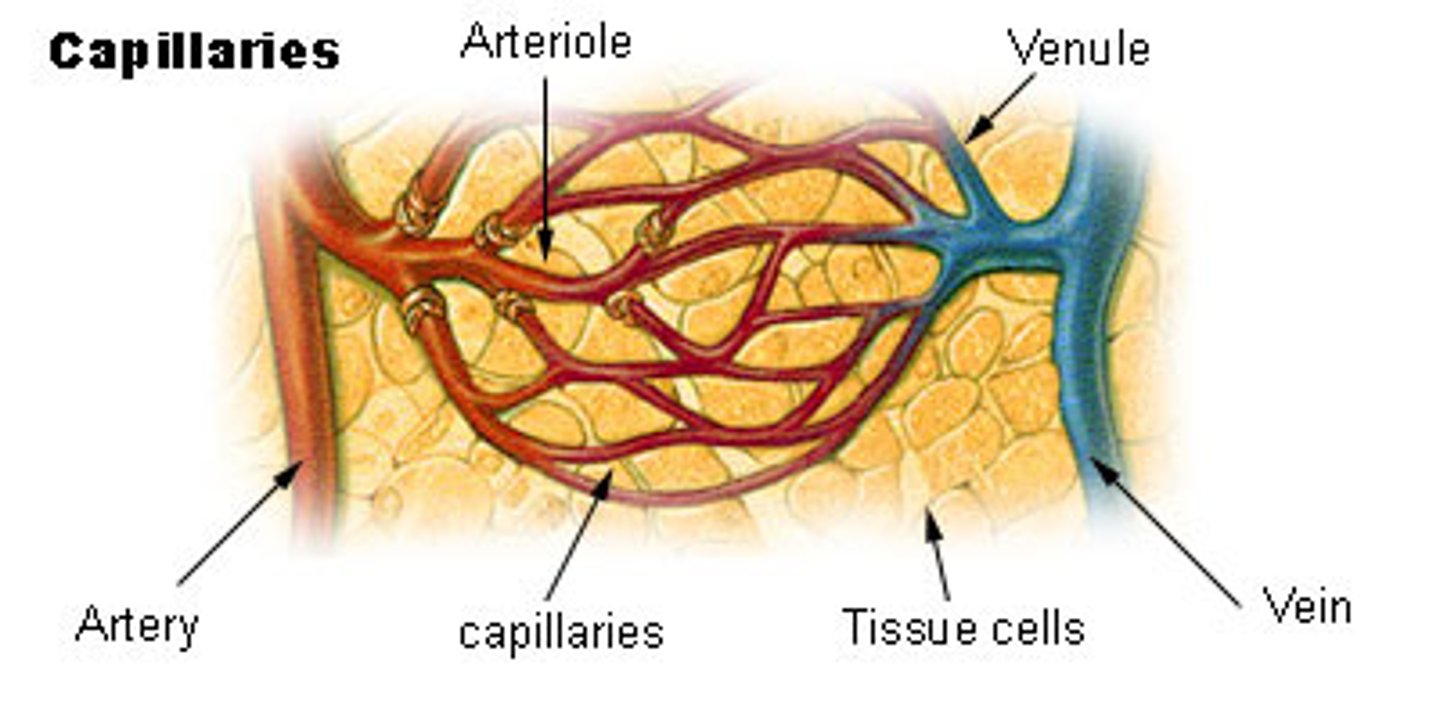
arteries
strong, elastic vessels adapted to the high pressure of blood as it leaves the heart
arterioles
-smaller branches of arteries
-supply blood to the capillaries
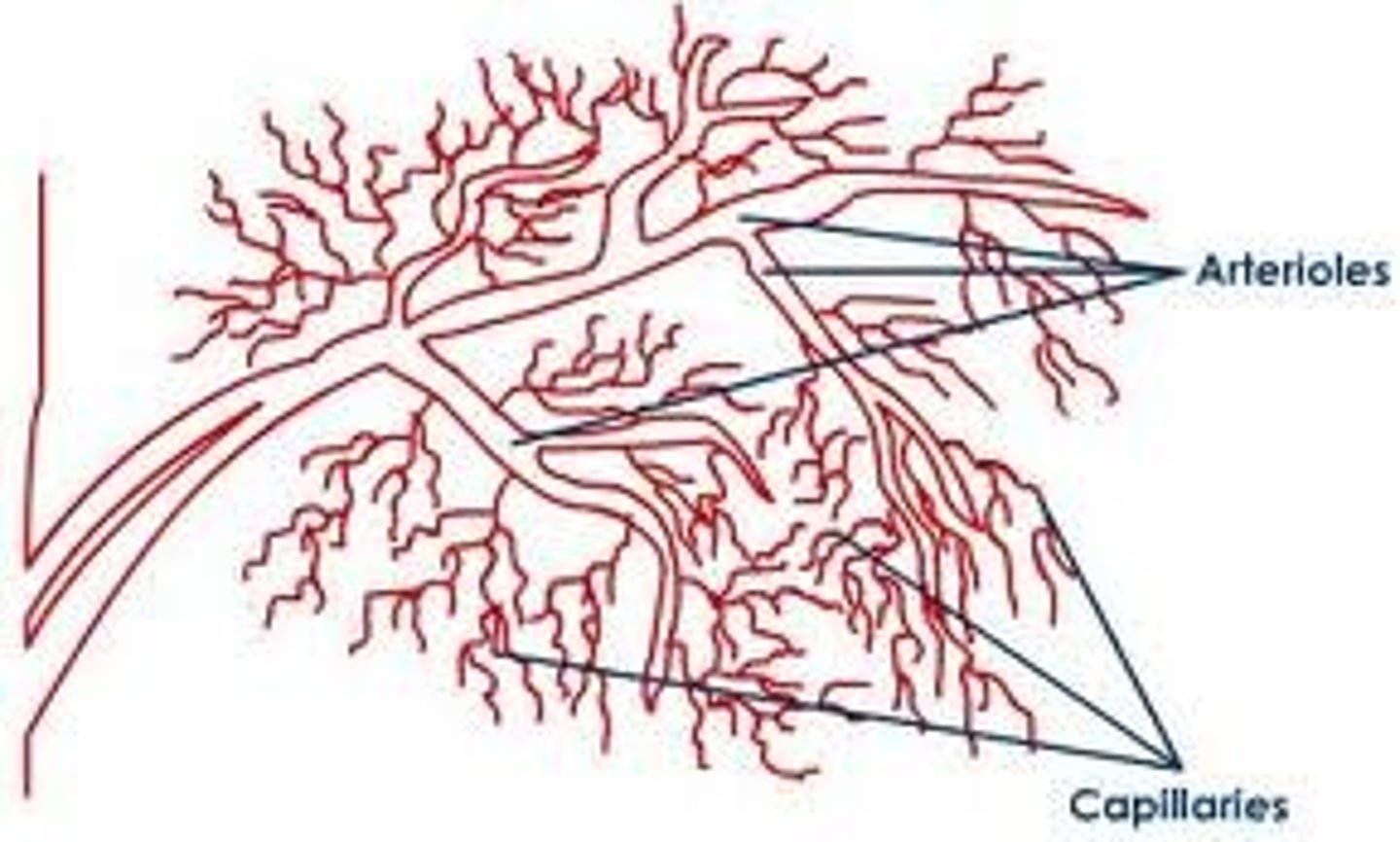
capillaries
-smallest blood vessels
-consist of only a single layer of epithelial tissue, which allows substances and gases to be exchanged b/t the blood and the cells of tissues via diffusion
-receive blood from the arterioles and return it to the venules
aorta
-largest artery in the body!
-the artery that carries blood pumped from the LEFT ventricle of the heart into systemic circulation
diffusion
-process by which substances and gases are exchanged across a membrane; in this case, blood and veins
-substances tend to diffuse from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
venules
-blood returns to the heart from the capillaries via venules, which merge to form veins
-vessels that receive blood from capillaries
veins
-walls of veins are thinner than those of arteries b/c veins do not have to carry blood under high pressure
-contain valves to prevent the back flow of blood
-vessels that return blood to the heart
inferior vena cava
-largest vein in the body!
-brings deoxygenated blood back to the heart
-runs from heart to down body
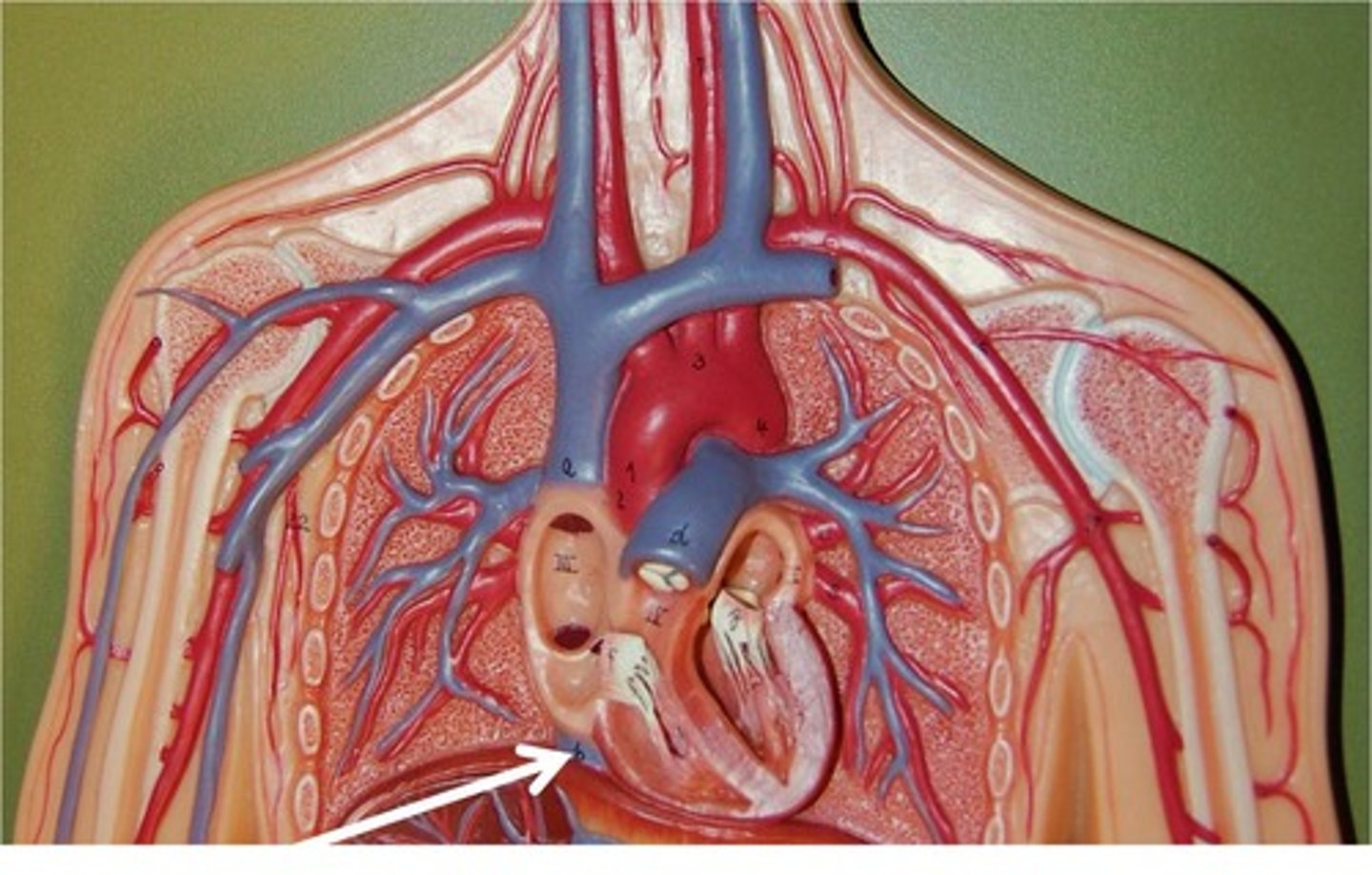
pulmonary veins
-bring blood from the lungs to the heart
-are among the few veins that carry oxygenated blood!
renal arteries
2 branches of abdominal aorta that supply the kidneys
blood
-essential bodily fluid that transports oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and removes waste products, including carbon dioxide and ammonia
-4 components of human blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma
Which layer of the heart contains striated muscle fibers for contraction of the heart?
myocardium: the layer of the heart that contains the muscle fibers responsible for contraction
endocardium/epicardium/pericardium
inner and outer layers of hear wall; pericardium - sac in which the heart sits inside the chest cavity
what is phagocytosis?
white blood cells eat aging red blood cells & release contents into the blood in this process called______.
What is erythropoiesis?
Production of red blood cells in red bone marrow is called what?
what is hematopoiesis?
process of developing various blood cells from pluripotent stem cells in bone marrow is called what?
what is thrombopoiesis?
The process by which platelets are produced w/in the bone marrow is called what?
components of human blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma
embolus
piece of plaque or clotted blood traveling thru vessels

s
plasma
-all blood components are suspended in a matrix of plasma!
-liquid component of blood that accounts for approximately half the blood volume
-in addition to blood cells, plasma contains proteins and electrolytes
erythrocytes
-red blood cells
-account for the second greatest component of blood by volume
-the functional unit of a erythrocyte is hemoglobin
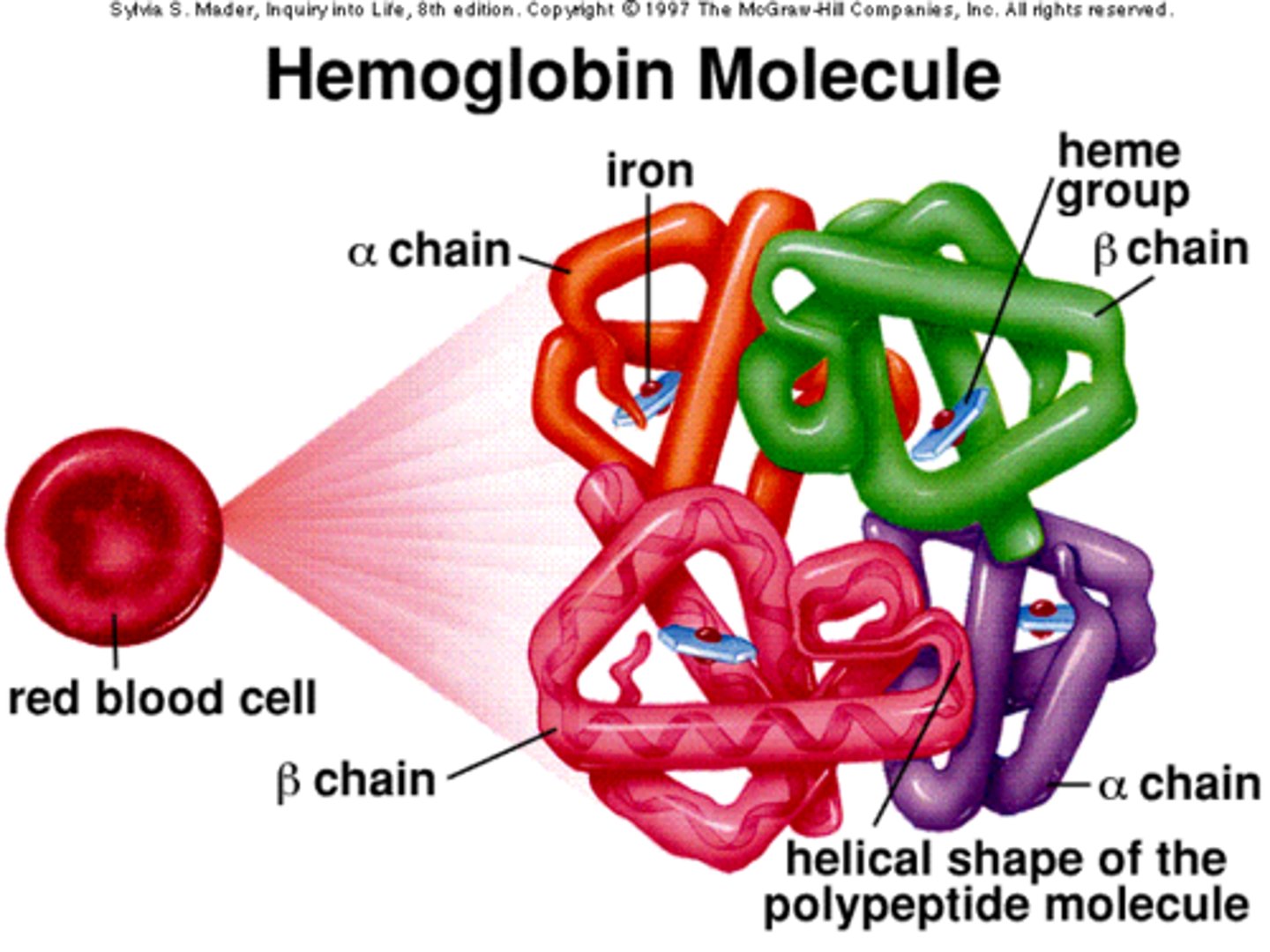
hemoglobin
-functional unit of a erythrocyte
-iron containing protein that facilitates gas exchange by binding to oxygen or carbon dioxide
anemia
condition that occurs when hemoglobin levels are low, either b/c the body isn't producing enough red blood cells, such as when someone has iron deficiency, or b/c of another underlying condition that causes the red blood cells to be irregularly shaped, such as the sickle-cell trait
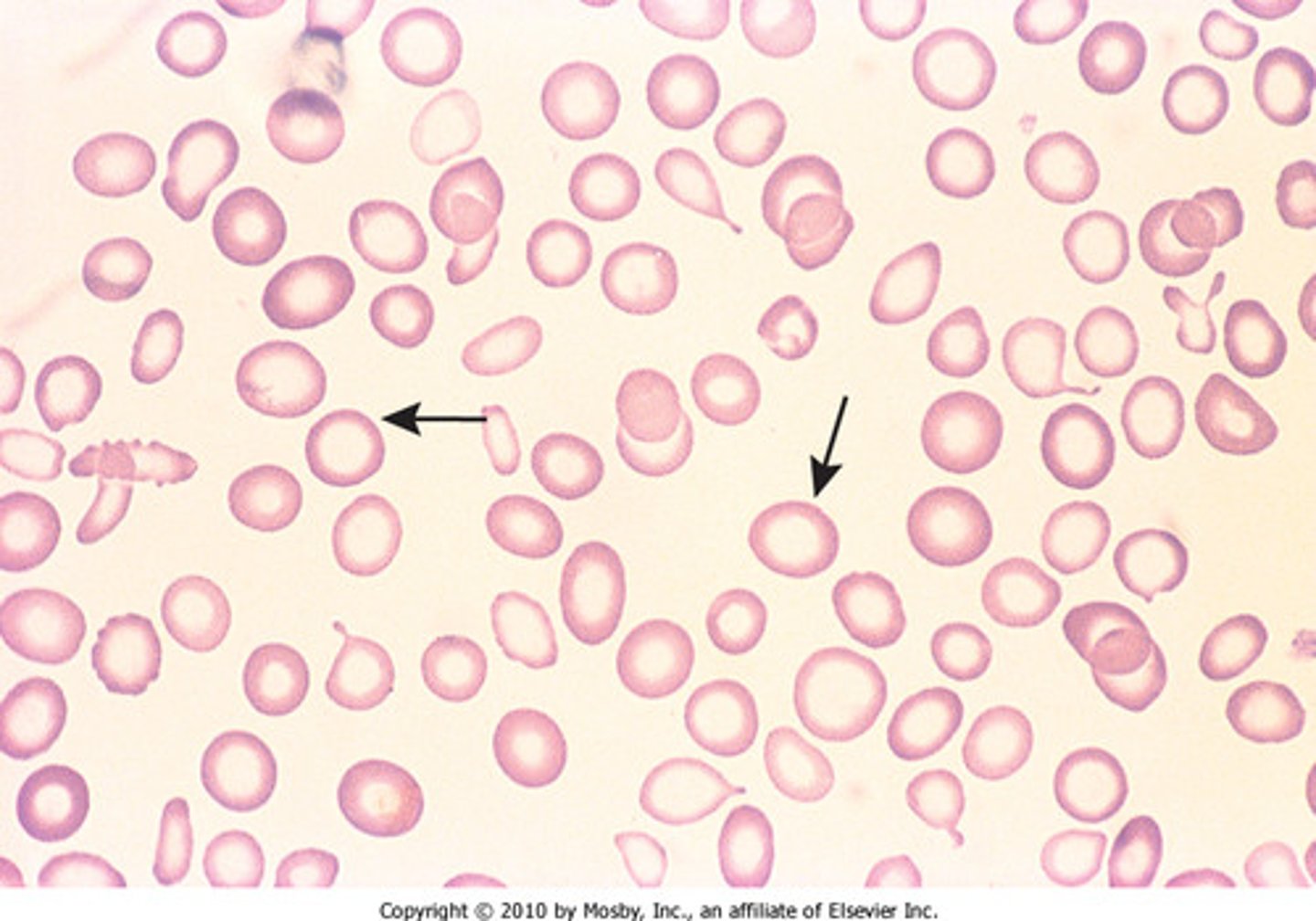
sickle-cell trait
genetic blood condition that causes irregularly shaped red blood cells
leukocytes
-white blood cells
-part of the body's immune response
-remove pathogens and foreign material from the blood
-there are several different types, each with their own function!
lymphocytes
type of white blood cell that releases antibodies in response to disease and harness other immune system responses
platelets
-cell fragments that prevent/mitigate bleeding by developing blood clots
-work w/ coagulating proteins to stick to vessel walls and to each other
thrombocytopenia
-condition of having too little platelets that can cause excessive bleeding
-can result in excessive external bleeding, such as nosebleeds, or bruising caused by uncontrolled bleeding under the skin
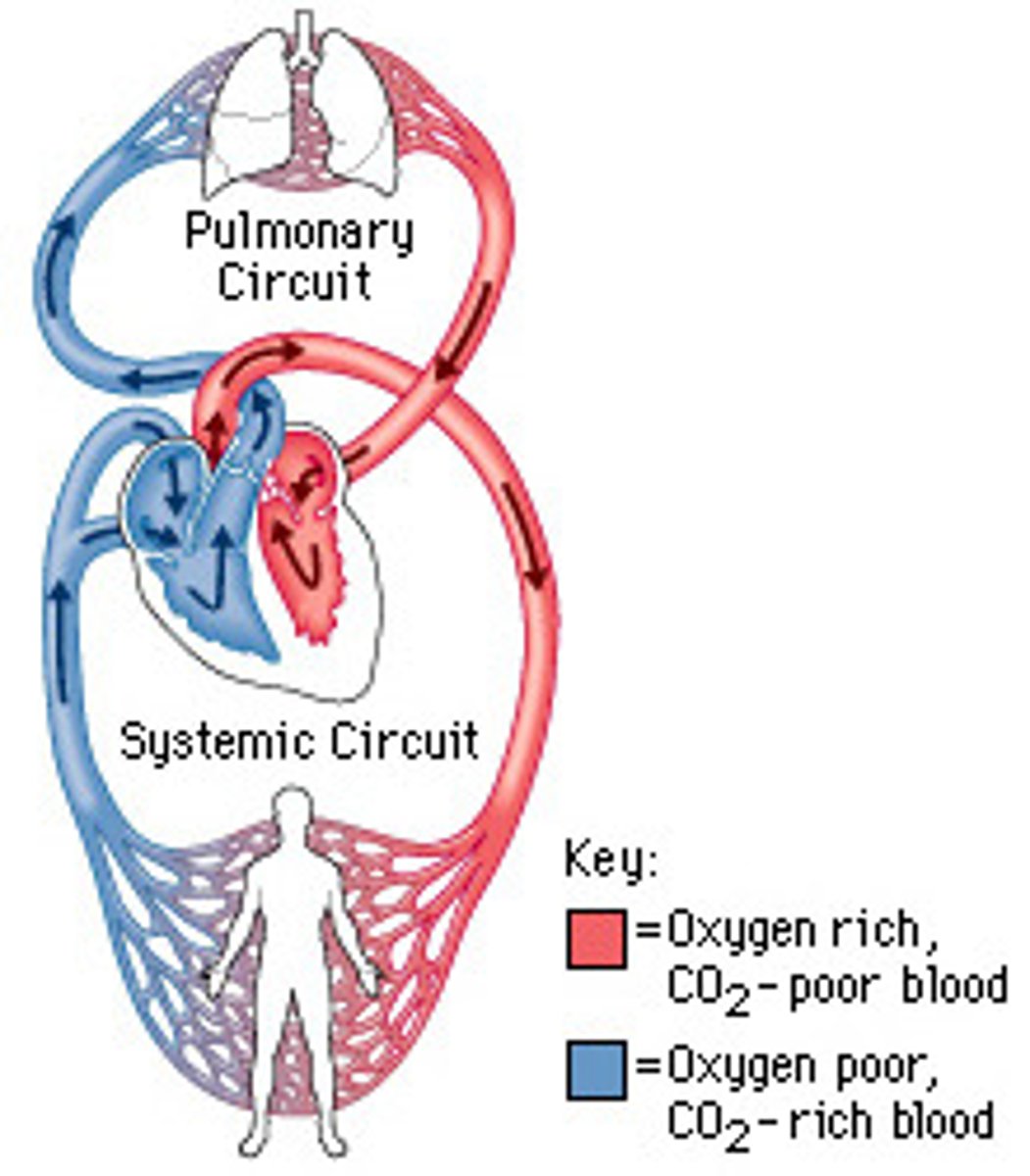
closed circulatory system
-often described as a double loop b/c blood flows through the heart twice:
1. once in its oxygenated state on its way to the body (systemic circuit)
2. once more when it is deoxygenated and on its way to the lungs (pulmonary circuit)
-these 2 pathways are called the systemic circuit and the pulmonary circuit!
systemic circuit
-blood flows in its oxygenated state on its way to the body
-carries oxygenated blood away from the left ventricle of the heart and returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium
-includes the aorta and blood vessels leading to the body tissues, as well as the veins and venue cavae

pulmonary circuit
-blood flows once more when it is deoxygenated and on its way to the lungs
-contains the blood vessels that carry blood to and from the lungs
-deoxygenated blod flows from the right ventricle through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs, where blood picks up oxygen, then returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary valve
sinoatrial node (SA)
located in right atrium & starts cardiac cycle
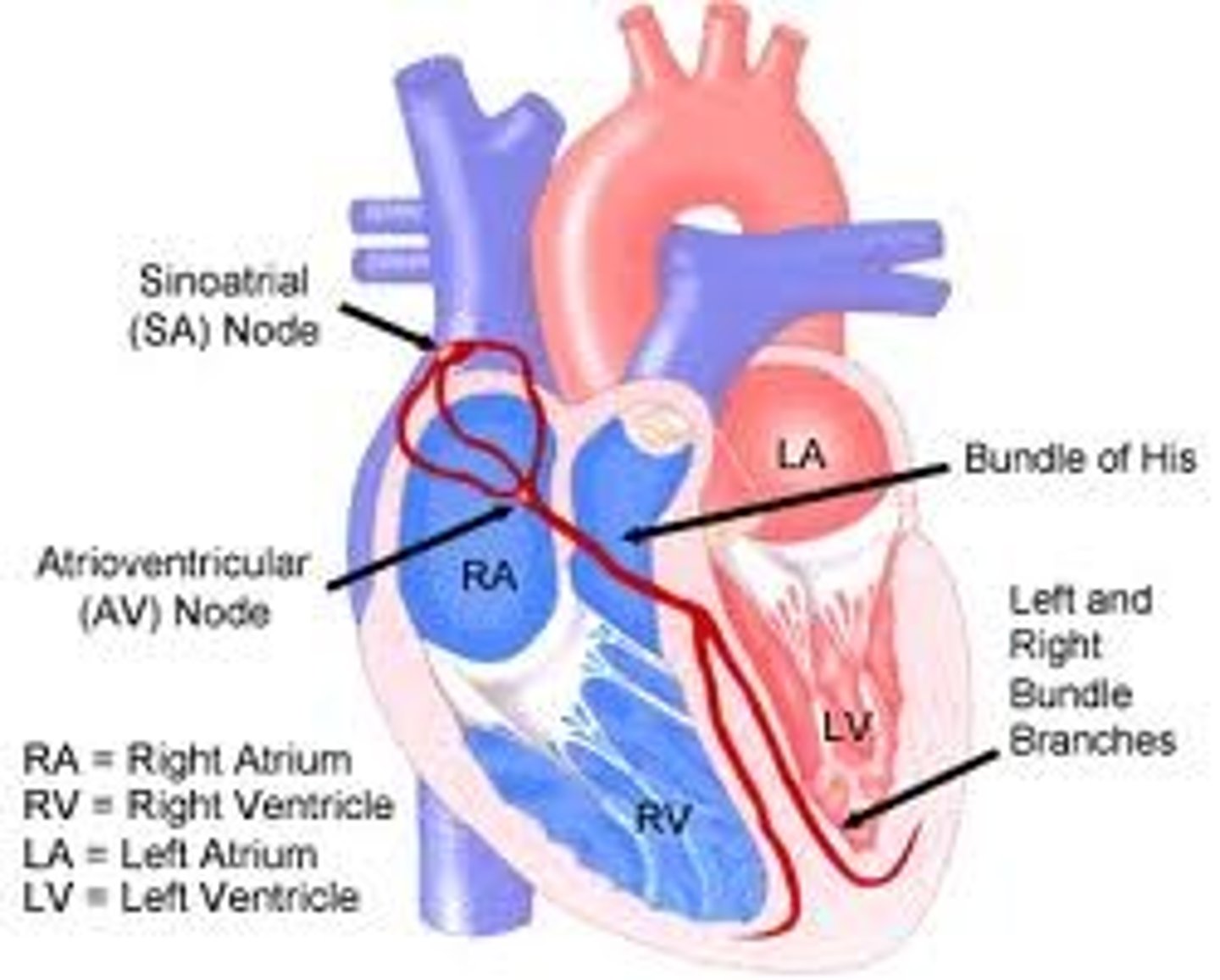
atrioventricular node (AV)
impulse after SA triggers contraction of right atrium; triggers contraction of ventricles.
lymphatic system (open circulatory system)
-also known as open circulatory system!
-network of capillaries that drain toxins and wastes away from the body tissues into the blood
-plays a vital role in monitoring and removing foreign entities in the body
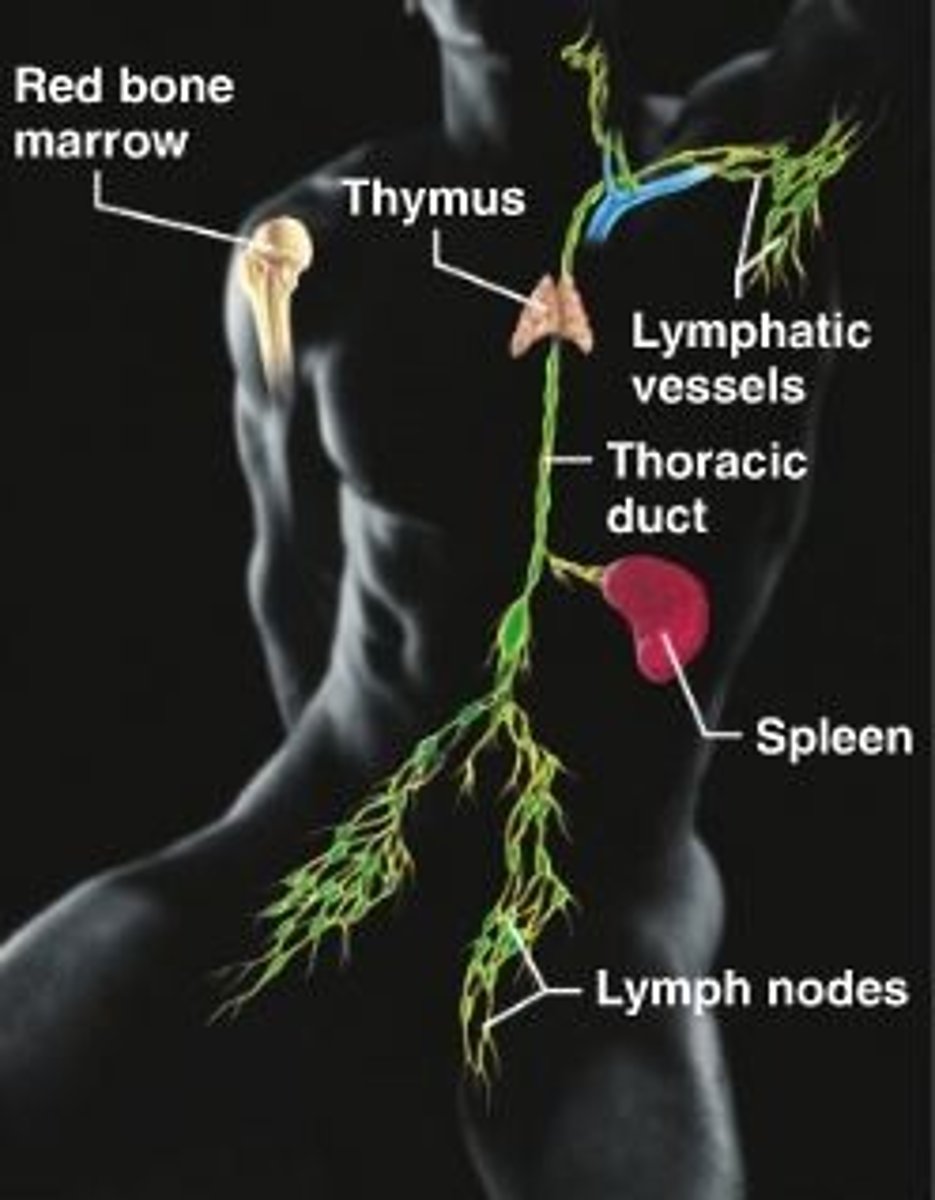
lymph
-bathes interstitial spaces b/n cells & circulates through lymph vessels.
-clear plasma-like fluid high in white blood cells that absorbs waste products
-filtered through one of several lymph nodes
-eventually drained into the subclavian veins
neutrophil is also known as_______
pus is also known as this type of cell
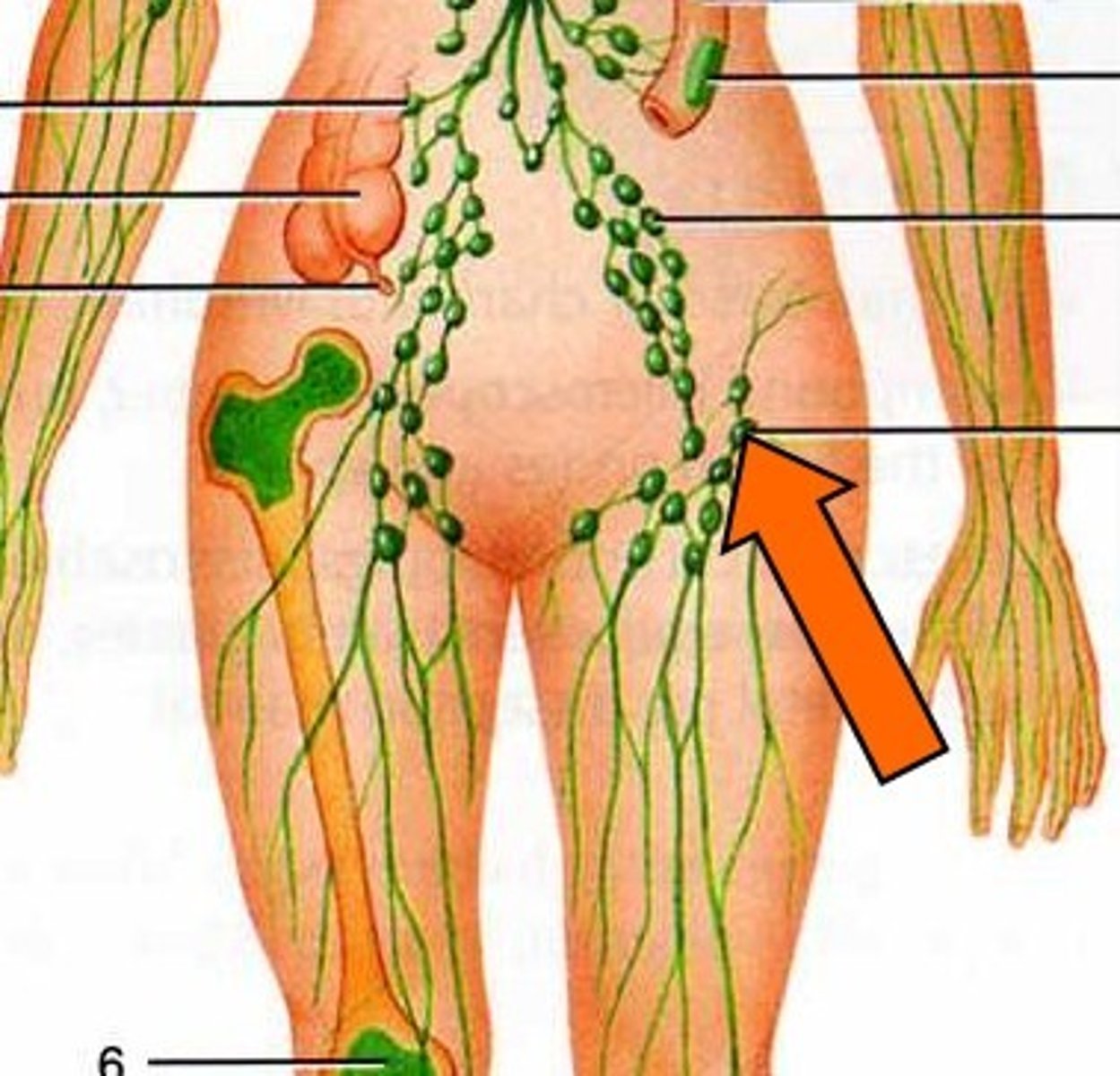
lymph vessels
thin walled and contain one way valves.
lymph nodes
-contain high concentrations of lymphocytes (make antibodies & target pathogens).
-small glands that filter lymph
-concentrated in neck, armpit & groin
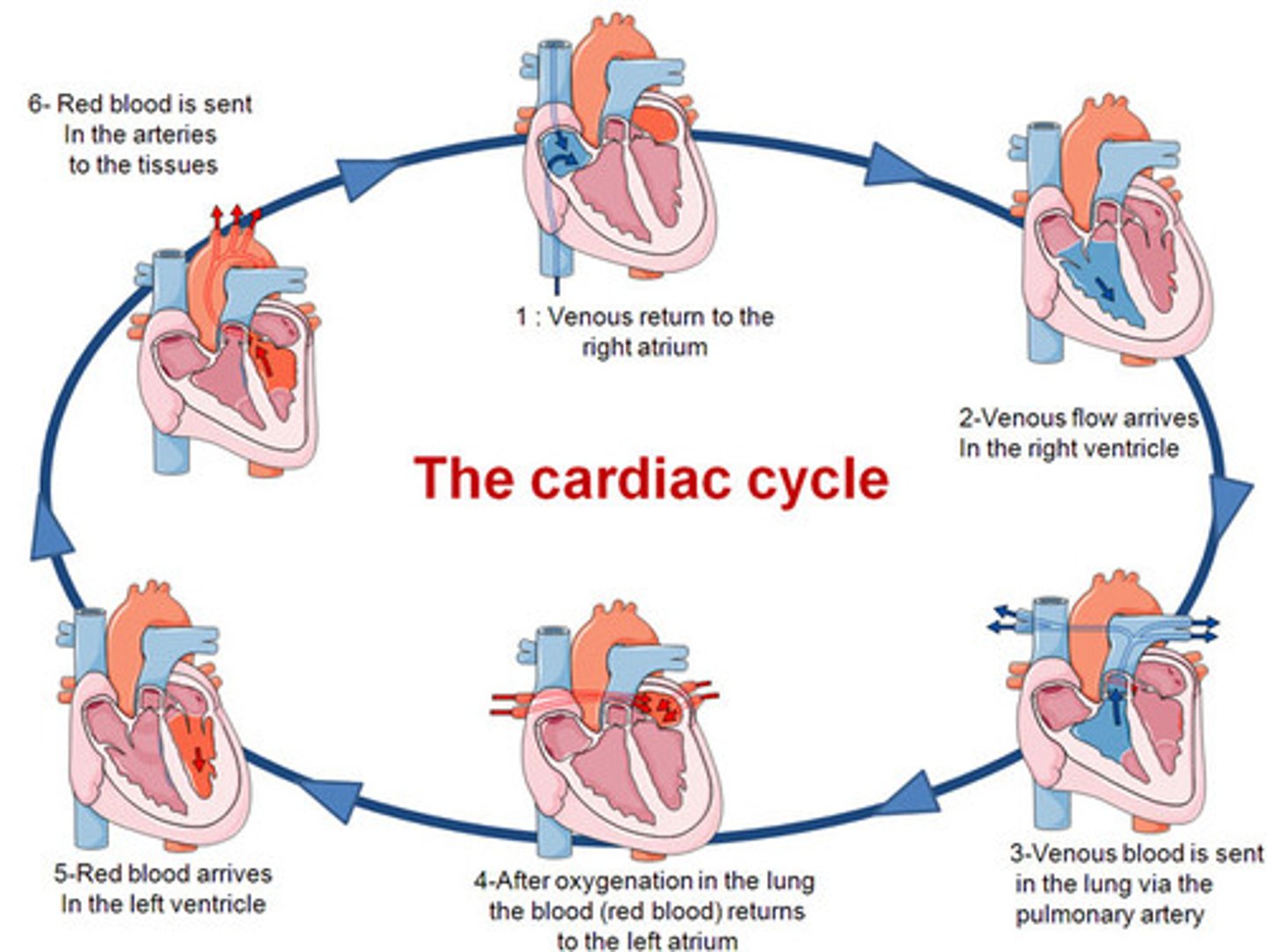
cardiac cycle
-describes the period b/t the start of one heartbeat and the beginning of the next
-2 phases: systole (SA triggers - contraction of atria - AV node triggers - impulse through Purkinje fibers - contraction of ventricles) and diastole (relaxation)
cardiac muscle
-unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle does NOT rely upon neural stimulation to initiate a contraction
-cardiac muscle can generate and conduct its own electrical impulses and can contract on its OWN
pulmonary system
--inferior & superior vena cava (venae cavae) delivers deoxygenated blood to right atrium (chamber)
-contraction of right atrium pumps blood through tricuspid valve (AV valve) into right ventricle (chamber)
- contraction of right ventricle pumps blood into pulmonary artery thru pulmonary semilunar valve and into lungs
from lungs oxygenated blood travels via the pulmonary vein into the left atrium

systemic system
Left atrium contracts, forcing blood through the left AV (bicuspid, mitral) valve and into the left ventricle.
Contraction of the left ventricule pumps blood through the aortic semilunar valve, through the aorta and towards rest of the body.
systole
portion of cardiac cycle in which heart expels blood.
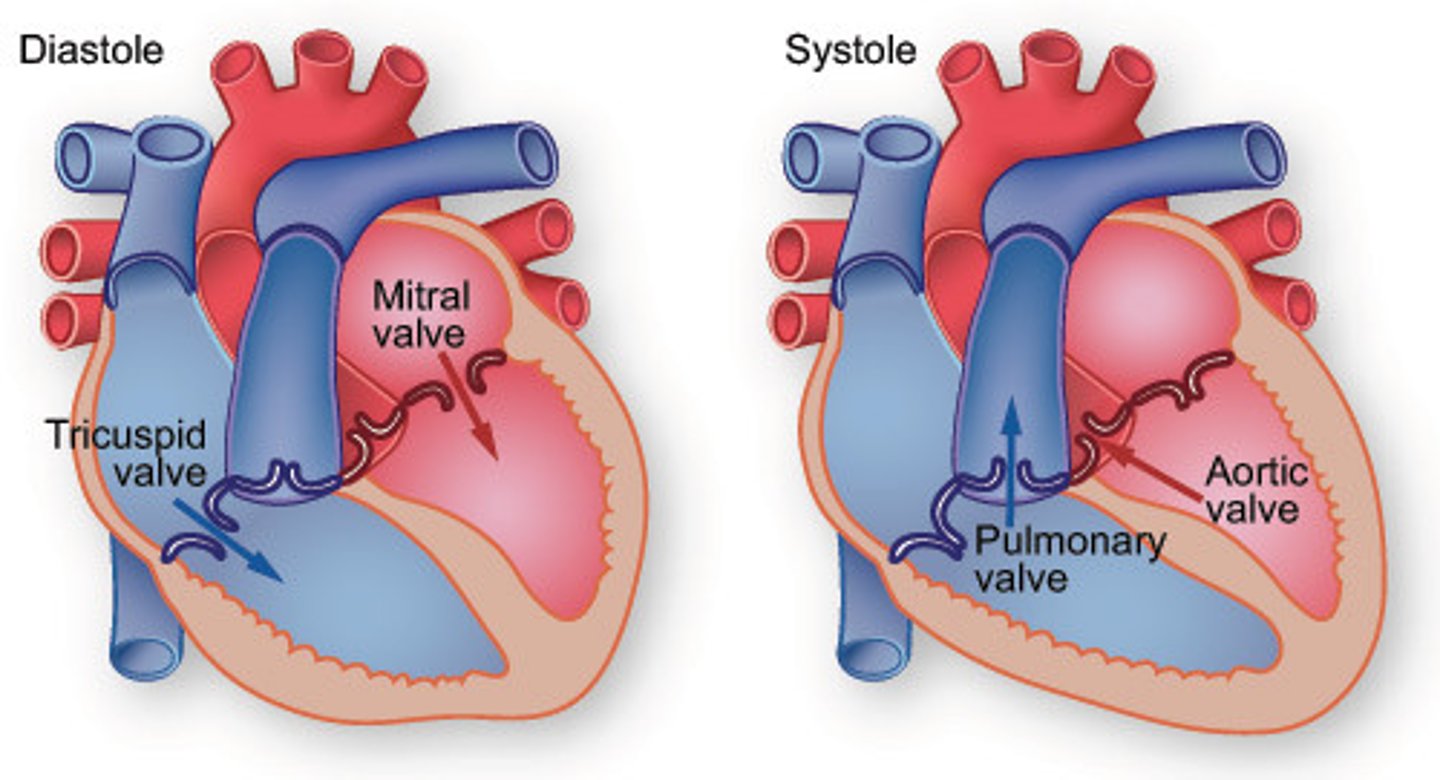
diastole
-the heart muscle relaxes, and the chambers are passively filled w/ blood
-during this, the alternating closures of the atrioventricular and semilunar valves are responsible for the distinct "lub-dub" of the heartbeat
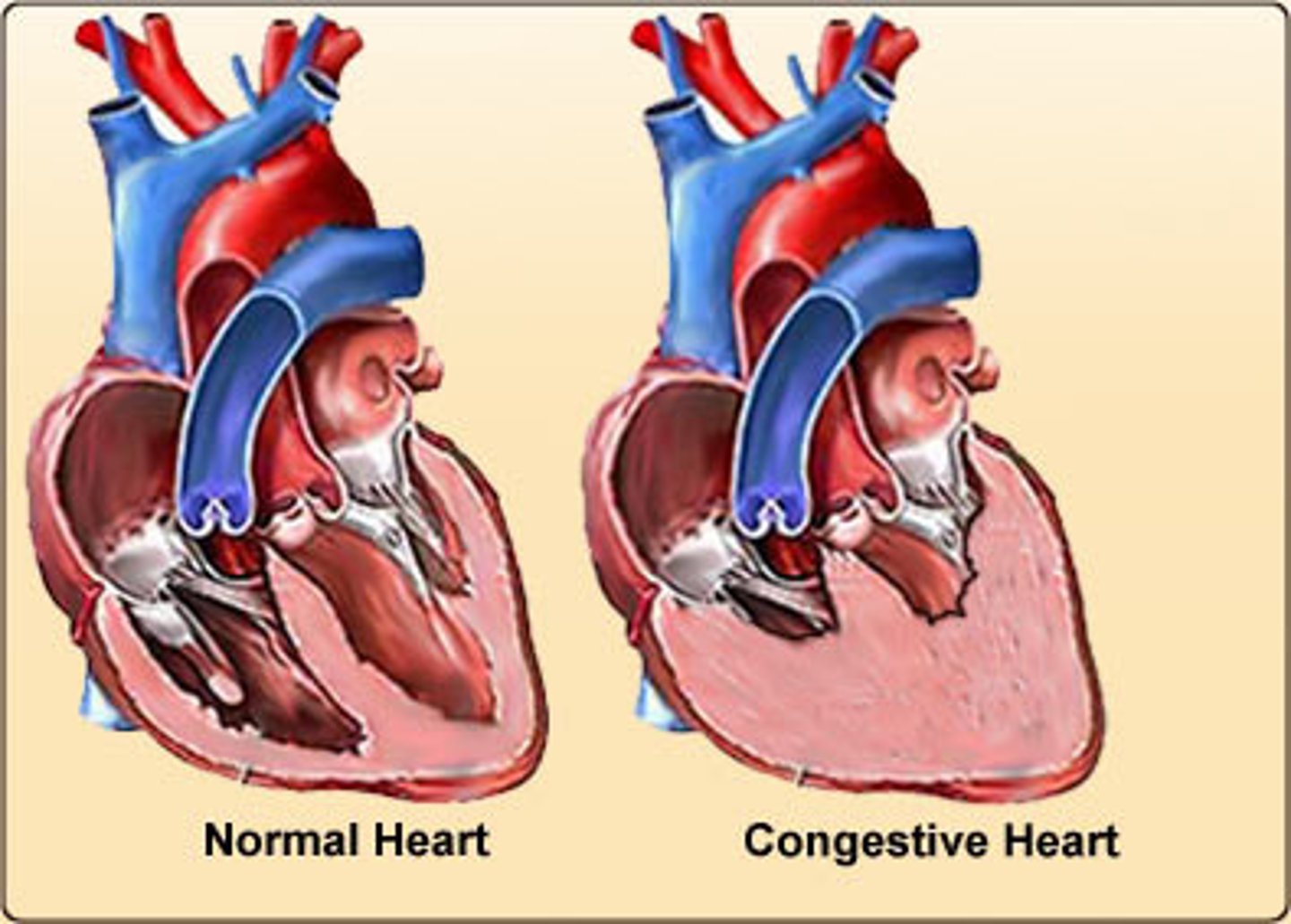
congestive heart failure
develops when the heart can no longer pump blood effectively, such as when weakened heart valves permit the back flow of blood into the chambers
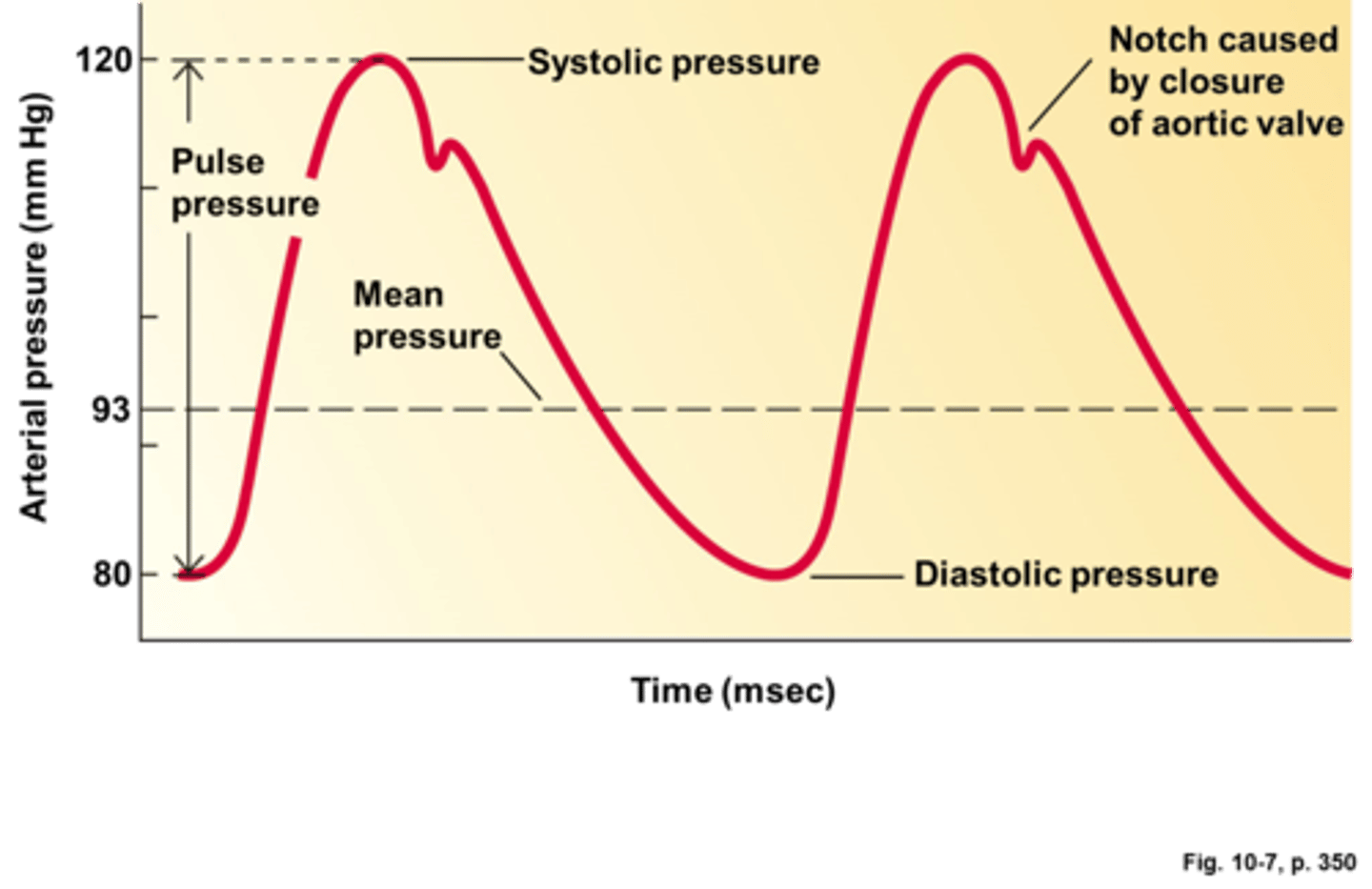
blood pressure
-the pressure of the blood in the circulatory system
-has 2 numbers (ex: 120/80) which reflect the different pressures that occur at systole and diastole
-blood pressure is maintained by adjusting cardiac output and vascular resistance
-if blood pressure begins to increase, the medulla will signal the heart to beat slower
-if the blood pressure begins to drop, the heart rate will increase to adjust
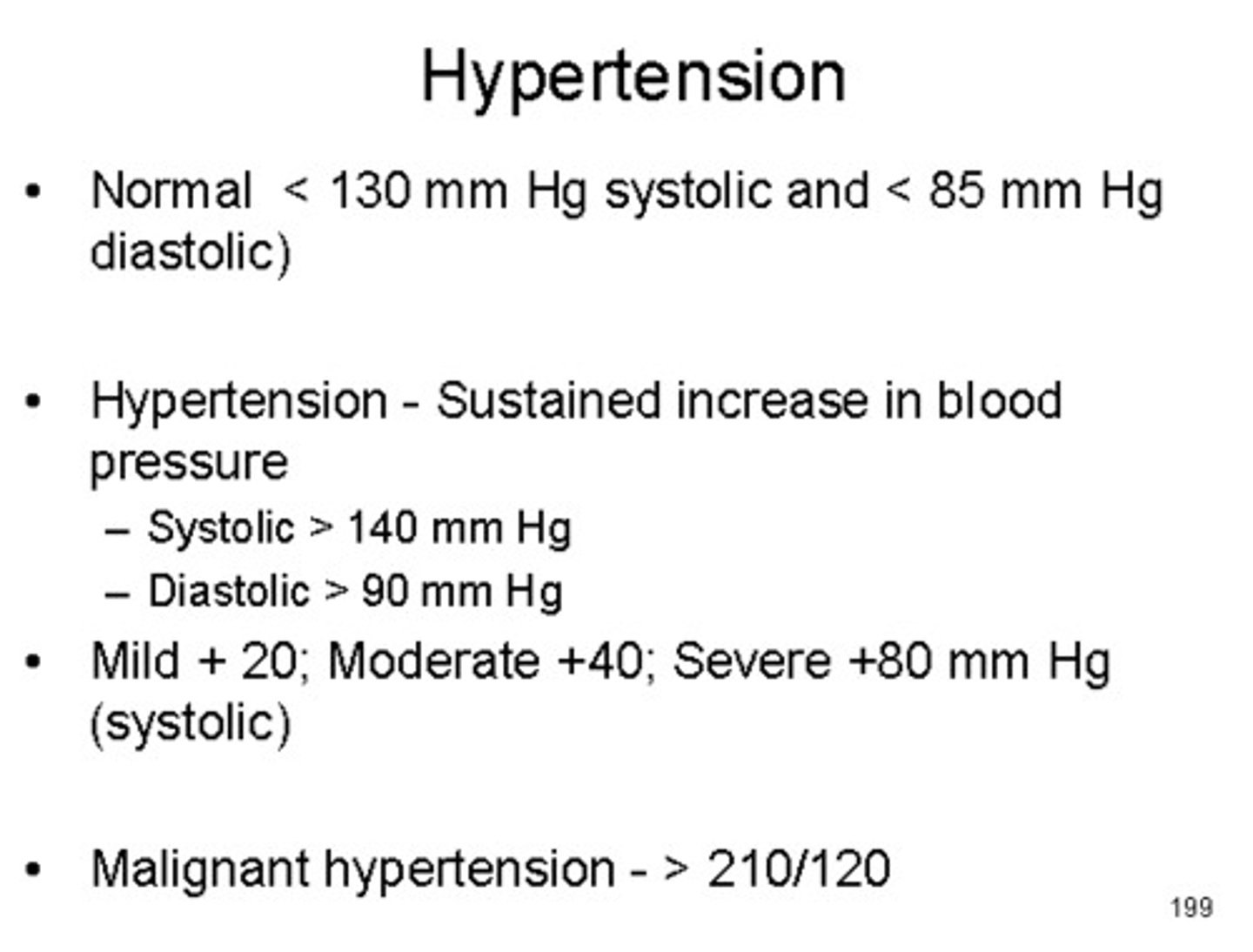
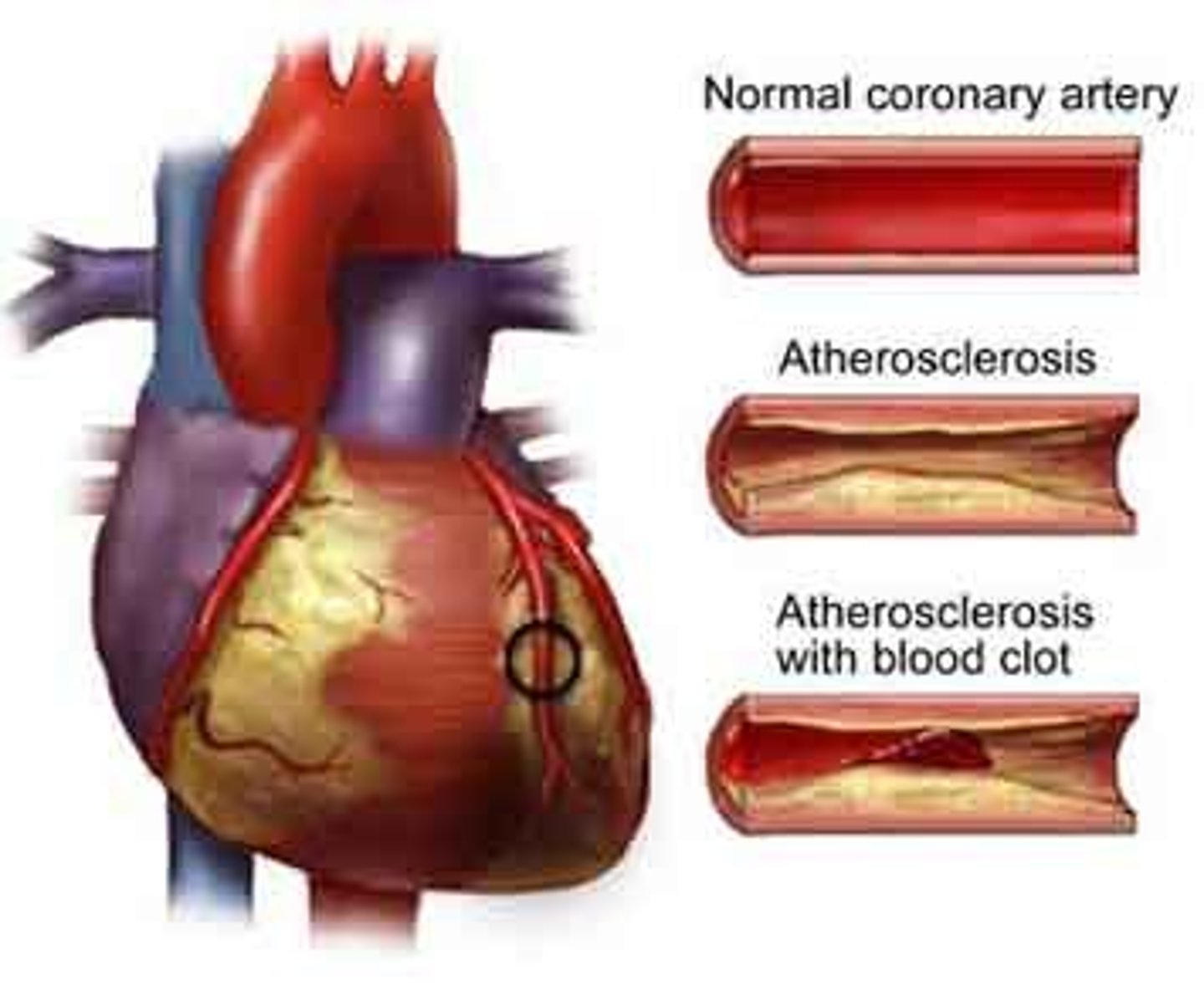
hypertension
-chronic high blood pressure
-can result from multiple factors, such as atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup), increased blood viscosity (such as if the blood contains high levels of cholesterol), and heart disease
-can cause rupture of smaller arterioles & capillaries, possibly leading to stroke.
atherosclerosis
narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup
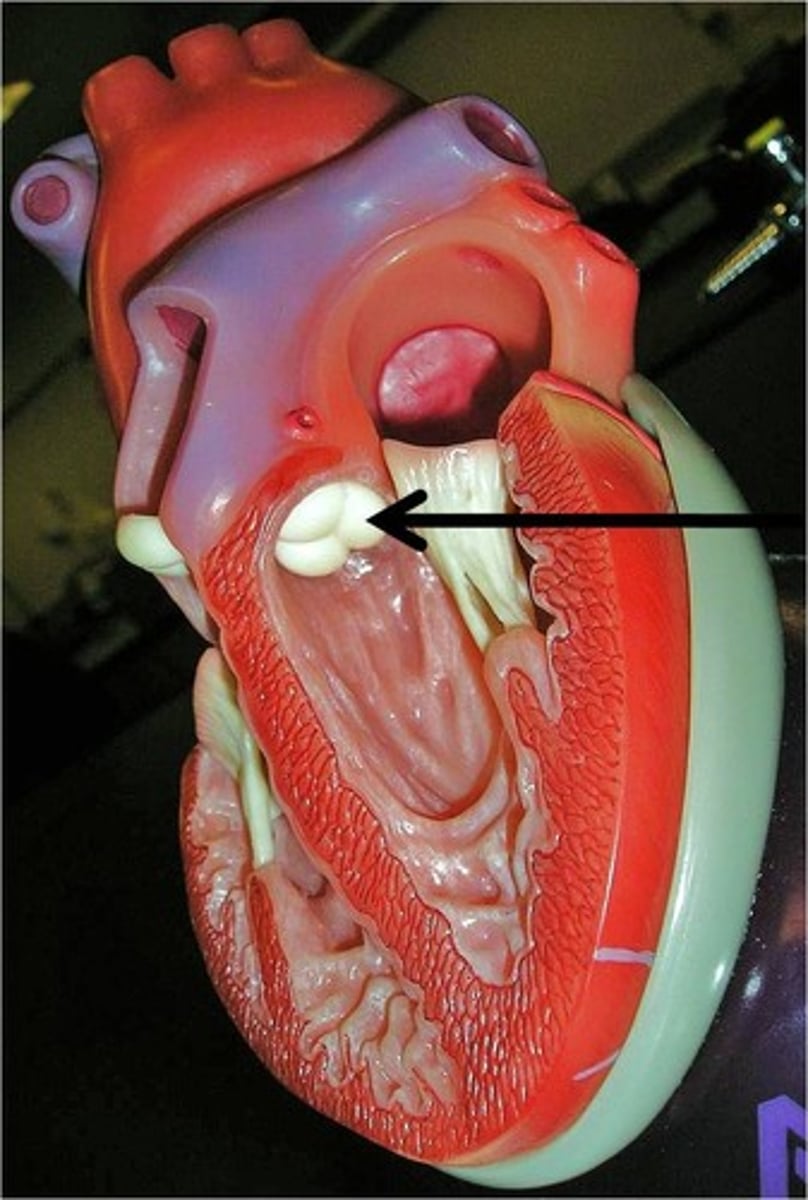
pulmonary semilunar valve
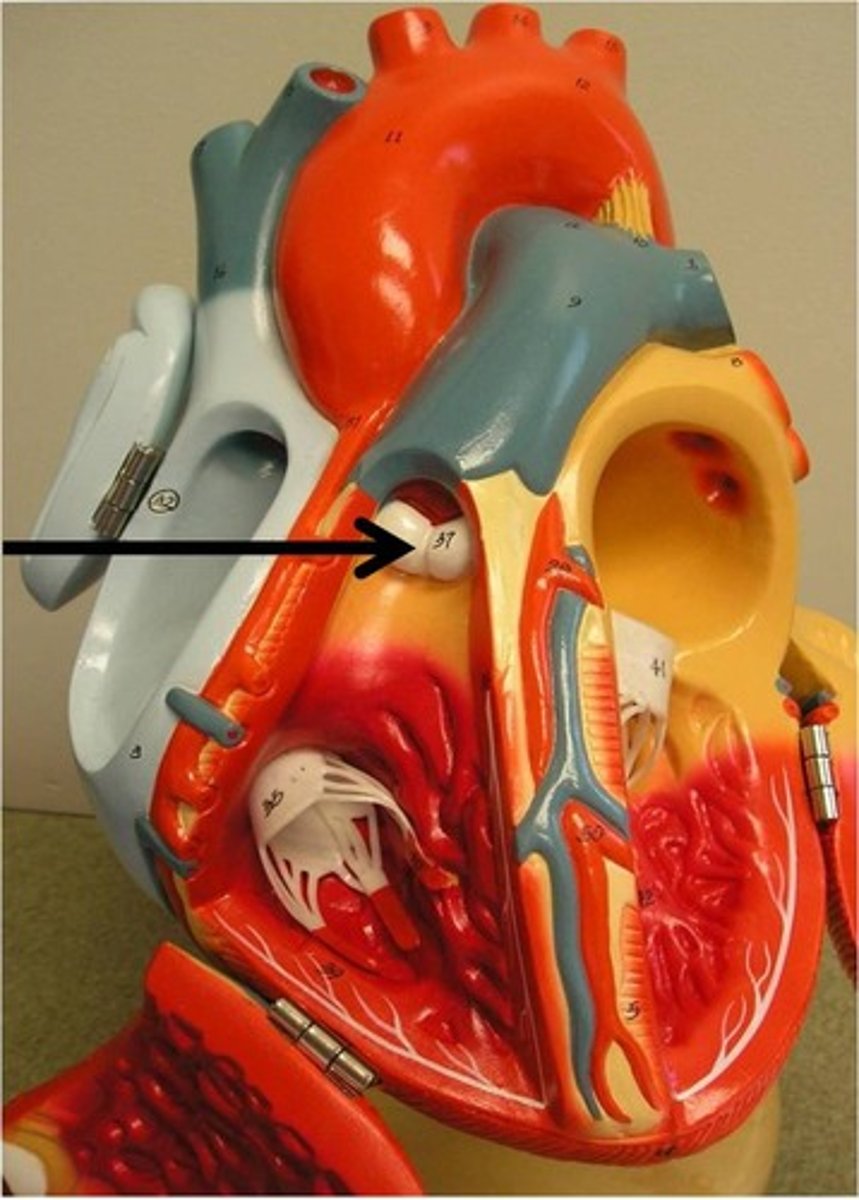
aortic semilunar valve
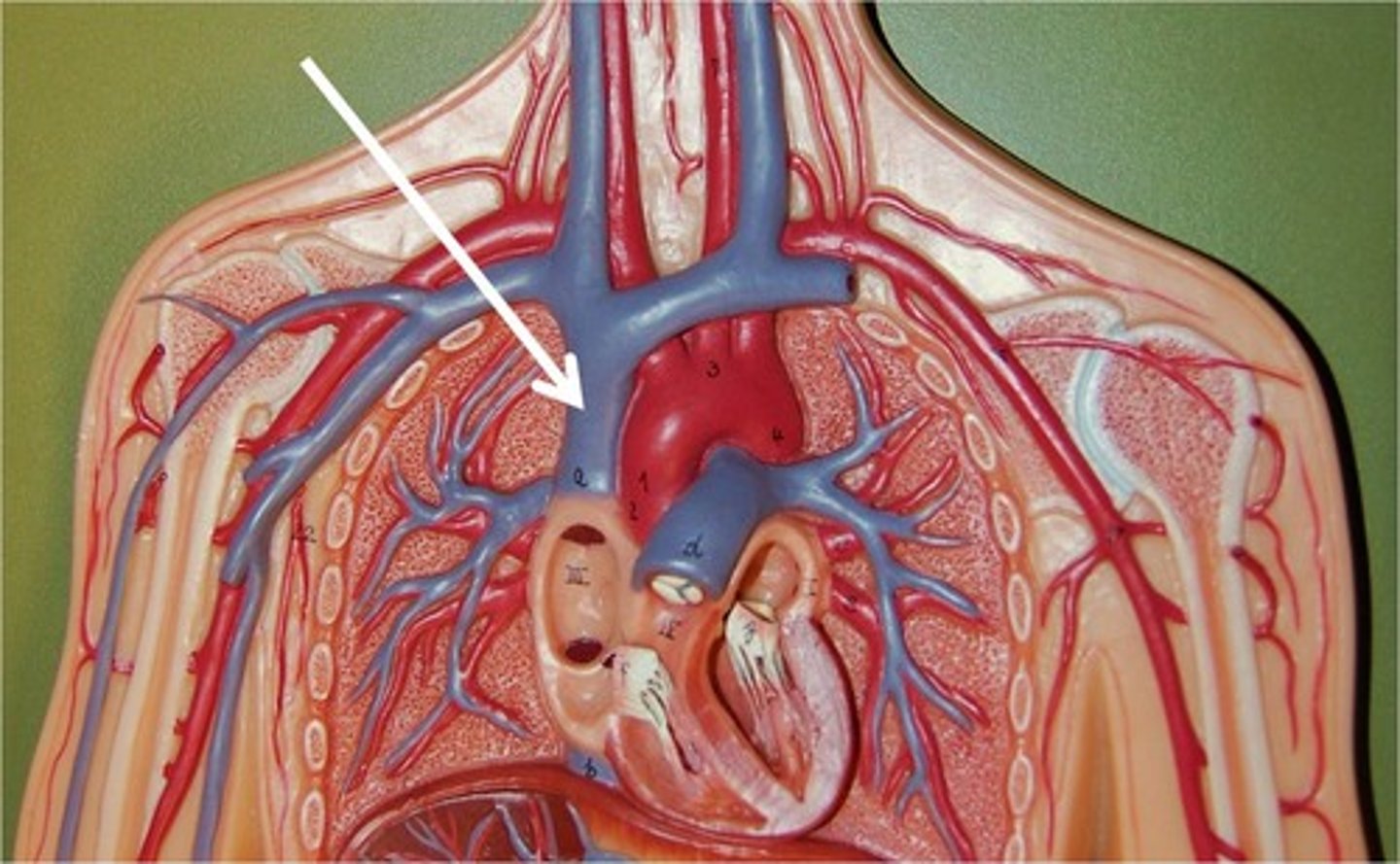
superior vena cava
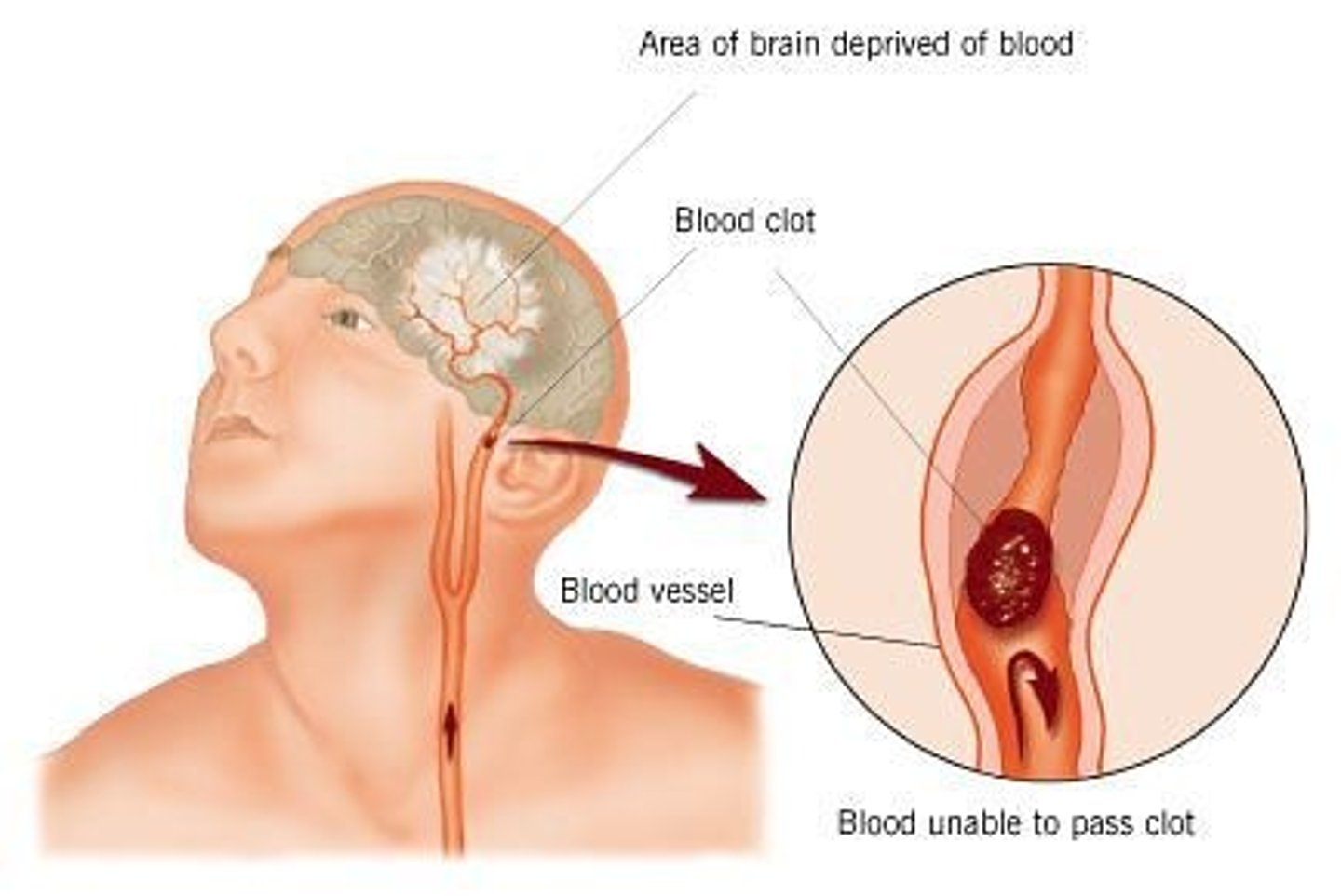
stroke
normal blood flow to brain is stopped either by blockage or rupture of blood vessel causing death of brain tissue
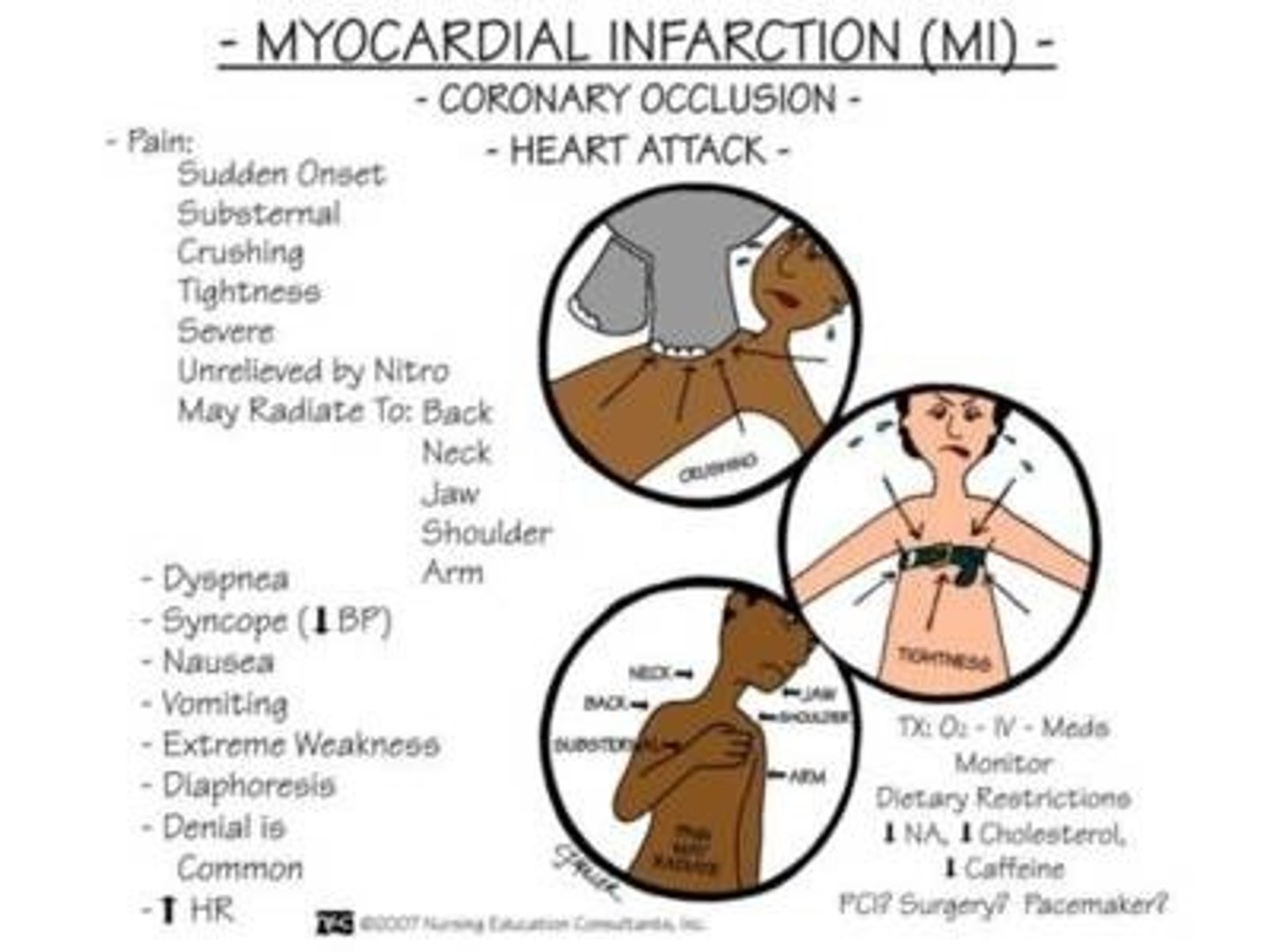
myocardial infarction
flow of blood to part of heart muscle is blocked, causing muscle tissue to die (heart attack)
Right side of heart valves
Tricuspid & pulmonary semilunar valve
Left side of heart valves
Bicuspid or mitral valve (mighty valves) & aortic semilunar valve
Where is the sinoatrial node?
SA node is in the right atria.
What is the "pub" or first sound of the heart
Ventricular systole (turbulence)
What is the "dub" or second sound of the heart?
Semilunar valve closing
Which of the following best describes the structures found underneath each rib in descending order?
a) vein, nerve, artery
b) artery, vein, nerve
c) vein, artery, nerve
d) nerve, vein, artery
c - the neurovascular structure found under each rib in descending order is the vein, artery, and nerve.