Exam 1: Integrated Sci and Therap 1
1/176
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 1-6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
The pioneers of the modern pharmacology are?
Paul Ehrlich, John Newport and Alfred joseph clark
Pharmacokinetics is defined as
dealing with drug action, the absorption, distribution, & elimination of drugs
Pharmacodynamics is defined as
The drug effect and the Action of the chemicals on the organism
Medical pharmacology and toxicology is defined as
being aimed at understanding the actions of drugs as chemicals on individual organism
Environmental Toxicology is defined as
The effects of chemicals on all organisms and their survival in groups and as species
“Drug receptors” refers to what?
The molecular component of a cell with which the drug interacts
The concept of drug receptors interaction leads to an increase or decrease in what?
In the rate of cell’s ongoing function
Were is drug receptors located?
Typically cell surface, embedded in cell membrane
The concept of drug receptors are study through what?
Isolate and purify macromolecular component and study drug “structure-activity” relationship (SAR)
The study of receptor function in living cells are determine by what?
They are determined by amino acid sequences for proteins receptors and are cloned and express in cultured cells that are isolated from components of native cells in intact tissue
The types of binding of drugs to receptors are
van der waals attaction
hydrogen bond
hydrophobic interaction
Ionic bond
covalent bond
Drugs that do not specifically act through receptors are
Antacids, Osmotic diuretics and cathartics and chelating agents which bind heavy metals
The term “Agonist” means
A drug which causes a specific physiological effect due to direct interaction with a receptor
The term “Antagonist” means
A compound which is devoid of intrinsic pharmacological activity but blocks the actions of a specific agonist or an endogenous substance which produces the effect
The term “Allosteric modulator” means
A drug that binds to a different site on the receptor that is bound by endogenous ligands; can modulate positively or negatively
The term “Addition” means
When 2 agonists which produce the same effect are administered together, they produce an effect equal in magnitude to the sum of the effects of the individual drugs
The term “Synergism” means
When two agonists which produce the same effects are administed together, they produce an effect greater in magnitude than the sum of effects of the individual drugs
The term “potentiation” means
When a drug is itself without effect, but if administered with a second drug, increases the effect of the second drug
Quantal(all-or-none) dose-response curve is defined as
Relates drug dose to frequency of drug-induced “all-or-none” pharmacological effects
The term “Tolerance” means
When repeated administration of a given dose of the drug
produces a decreased effect, or conversely, larger doses must be
administered to obtain the same effect observed with the original dose
The term “Tachyphylaxis” means
A very rapidly developing tolerance; decreasing effect
of a drug following consecutive doses given at short intervals
The term “Supersensitivity” means
A heightened state of pharmacological responsiveness
of a tissue or organ, leading to an exaggerated effect of an agonist
The term “Desensitization” means
A reduced state of pharmacological responsiveness of
a receptor due to continuous presence of the agonist at that receptor.
Ligand occupancy leads to activation of what
to activation of the receptor and functional response
In the ligand effect efficacy is independent on what
of the slope or position of the dose-response curve
In the ligand effect the slope is another what
Another important parameter when 2 drugs are compared
Drugs in the body past through first
Transport with the lipid bilayer with protein embedded
Polar, ionized groups of molecules are located where
On the surfaces
Hydrophobic, non-polar lipid side chains oriented towards what?
towards the inside of the membrane bilayer
Most drugs must cross the membrane by diffusion through it, how?
They must dissolve in the lipid layer
Factors that determine drug diffusion across the membrane are
Concentration gradient (Fick’s law)
Lipid solubility of drug i.e its lipid: water partition coefficient
Ionized (charged) forms of drugs are what?
Are polar and exhibit low lipid solubility
Non-ionized (uncharged) drugs are what?
Not as polar and exhibit greater lipid solubility
Weak acids are unionized and ionized at what kind of pH?
At low pH weak acids are unionized and at high pH they are ionized
Weak bases are unionized and ionized at what kind of pH?
At high pH weak bases are unionized and at low pH they are ionized ionized
The “Henderson-hasselbatch equation” can be used to determine what?
It can be used to determine the proportion of ionized to unionized drugs ar a given pH
The term “Weak acid ” means
a neutral molecule that can reversibly dissociate into an anion (a negatively charged molecule) and a proton (a hydrogen ion).
The term “Weak base” means
a neutral molecule that can form a cation (a positively charged molecule) by
combining with a proton.
In alkaline urine weak acid are usually what?
are usually excreted faster in alkaline urine; weak bases are usually excreted faster in acidic urine
Other process which can mediate drug transport are
Carrier-mediated membrane transport
Facilitated transport
Bulk flow through intercellular pores
Facilitated transport is done by what physiologic function?
Norepinephrine reuptake from the synapse, serotonin reuptake from the synapse, and transport of dopamine and norepinephrine into adrenergic vesicles in nerve endings.
Active transport is done by what physiologic function?
Transport of many xenobiotics out cells and leukotriene secretion
factors that modify drug absorption are?
Lipid solubility and degree of ionization
Dissolution rate- solubliity at absorption site
concentration at site of absorption
Circulation to site of absorption
Area of absorptive surface
Molecular size
Drugs that past through Oral absorption what are the advantages?
safest, most convenient, most economical, requires no special device or clinical intervention for administration
What are the disadvantages of drugs that pass through oral absorption?
nausea, possible destruction of drug by low pH or enzymes food can alter absorption rate, patient compliance, absorption sometimes unpredictable
Weak acids are best absorbed where
In the stomach
Weak base are best absorbed where
From the intestine
Other factors effecting oral absorption are?
gastric emptying time, presence of food in stomach and dosage preparation
The term “Intravenous” means
circumvents absorption
The term “Intramuscular” means
rapid absorption from aqueous solution; slow absorption from oils or
other vehicles
The term “Subcutaneous” means
absorption controlled by same factors as i.m. (blood flow, surface area)
The term “Drug bioavailability” means
A measure of the fraction (or percentage) of an administered dose of drug which reaches the systemic circulation
Diffusion across capillary wall can occur in either of 2 ways, which are?
lipid soluble drugs diffuse through endothelial membrane and lipid insoluble drugs are “filtered” through intercellular pores
The term “Drug reservoirs” means
compartments in which drug accumulates and from which it can be
released back into circulation as active drug
The term “Drug redistribution” means
Secondary phase(s) in drug distribution due to mobilization of
drug from tissue reservoirs, gradual redistribution to sites of
low blood flow
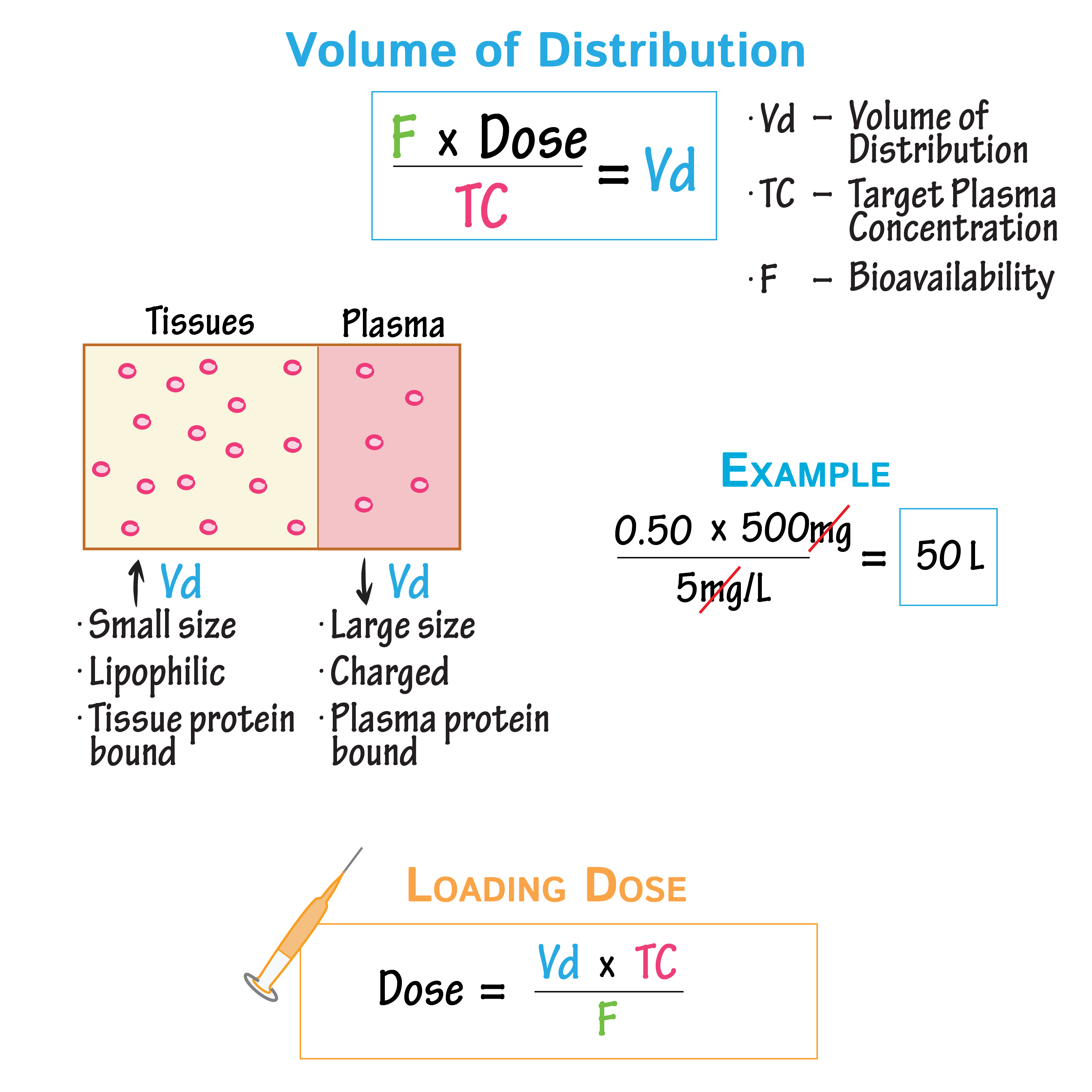
Drug distribution equation:
Three processes involved in kidney’s excretion are
glomerular filtration, Active tubular secretion and passive reabsorption
Renal excretion is one of the major routes of elimination that
drugs eliminated in urine and Ionized, polar form of drug eliminated better than unionized, lipid-soluble form
Other major routes of elimination includes
Fecal excretion, Elimination of drug from lung and elimination into milk
“if dosing rate exceeds elimination capacity, steady state cannot be achieved:
The concentration will keep on rising as long as dosing continues. This pattern is called what?”
“capacity-limited elimination.”
the elimination rate is almost independent of
concentration—a state of what?
“pseudo-zero order”
The term “volume of distribution” means
the amount of drug in the body to the concentration of drug (C) in
blood or plasma
The term “Clearance” means
is the factor that predicts the rate of elimination in relation to
the drug concentration (C)
In cumulative effects, the intermittent dosing scheme produces much higher peak concentrations. What does this result in?
It saturates an uptake mechanism into the cortex thus, total aminoglycoside accumulation is less toxic
Understand maintenance dose calculations
Understand Loading dose equation
Nuclear receptors reside in either what part?
The cytoplasm or nucleus, in a complex with chaperone proteins and upon binding agonist the chaperones dissociate and receptors dimerize either with themselves (homodimers) or another nuclear receptor (heterodimers)
The term “Hormone-responsive elements” means
The specific sites on DNA that bind dimer receptors and facilitate binding of other transcription factors
Receptor tyrosine kinases is a major class of what?
Metabotropic receptors and key mediators of hormones and growth factors
The first substrate is
Autophosphorylates
What are the four human epidermal growth factor receptors?
EGFR, HER2, HER3, and HER4
The term “Etanercept” means
Is a fusion protein that works as a TNF alpha inhibitor and treats arthritis
The term “Infliximab” means
Antibody that neutralizes TNF alpha and treats Crohn’s disease
The term “TNFa” means
Blocking agents alone were sold for almost $30 billion in 2013
The term “Adalimumab or Humira” means
The human monoclonal antibody in rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease
Different between Ligand-gated ion channels and voltage-gated ion channels
LGIC is activated by ligands whereas VGIC is activated by changes in the electrical membrane potential
The similarity between Ligand-gated ion channels and voltage-gated ion channels
They both pass ions across the membrane to change membrane potential that can lead to electrical events such as action potential or neuronal firing.
Benzodiazepines are positive what?
Allosteric modulators that enhance the effect of GABA at the GABAa receptor
Benzodiazepines have sedative what?
Hypnotic(sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties
Barbiturates are used for what?
used for anxiolytics and hypnotics, but have been largely replaced by benzodiazepines which have less potential for lethal overdoses
G. protein-coupled receptors have how many transmembrane domains
7
Gi and Gs regulate what?
The Adenylate Cyclase/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway
Norepinephrine/Epinephrine can inhibit what?
(Gi) or activate (Gs) adenylyl cyclase
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of a chain of amino acids
What is the building block of a protein?
What is the chemical nature of a peptide bond?
Peptide bond is what type of functional group
An amide
Recognize the charged amino acids (D, E, K, R, H),
serine (S) and cysteine (C):
Aspartic Acid Asp (D)
3.7 pKa of side chain and is negatively charged
Glutamic Acid Glu (E)
4.2 pKa of side chain and is negatively charged
Lysine Lys (K)
10.7 pKa and is Positively charged
Arginine Arg (R)
12.1 pKa and is positively charged
Histidine His H
6.0 pKa and is positively charged
Serine Ser (S)
(S) Polar uncharged
Cysteine Cys (C)
(C) is a special class with a pKa 8.3
What functional group does a cysteine have in the side chain?
What types of interactions may exist between a drug and its target protein? Compare their relative strengths
Intermolecular bonding forces: Ionic interaction:
Strongest noncovalent ligand-receptor interaction (20-40 kJ mol-1)
➢ Taking place between functional groups with opposite charges
➢ The strength of the ionic interaction is inversely proportional to the
distance between the two charged groups
➢ Stronger interactions occur in hydrophobic environments
How does the distance separating two opposite charges affect their interactions? Is the water phase a favorable environment for strong
ionic interactions?
Captopril, an
antihypertensive, binds to angiotensin-
converting enzyme (ACE). What is the
interaction between its carboxylic acid
and the side chain of lysine 1 087
residue?
When a carboxylic acid interacts with a lysine 1087 residue, the most likely interaction is a salt bridge due to the opposite charges: the negatively charged carboxylate ion of the carboxylic acid forms an electrostatic attraction with the positively charged amino group of the lysine side chain, helping to stabilize the protein structure