Cell structure
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Function of nucleus
contains the genetic material
Function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Transport and synthesis of lipids, carbohydrates, and steroids
Function of lysosome
contain hydrolysing enzymes
Function of ribosome
protein synthesis
Features of mitochondria
surrounded by double membrane with the inner membrane folded to form cristae
contains enzymes needed for aerobic respiration, producing ATP
small circular pieces of DNA
Ribosome also found in the matrix for replication
similar size to mitochondria
Role of mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration for ATP
Features of Chloroplasts
double membrane
membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids containing CHLOTOPHYLL stack to form structures called grana
Grana joined by lamellae (thin and flat thylakoid membranes)
contain small circular DNA, ribosomes (synthesise proteins needed in chloroplast replication and p/s)
Functions of chloroplast
site of photosynthesis:
light dependent stage takes place in the thylakoids
light independent stage takes place in the stroma
Roles of cytoskeleton
mechanical strength
support the cell
maintaining cell shape
movement of cilia and undulipodia
cytokinesis
movement of vesicles
How organelles work together to produce and release the protein molecules from the cells
Nucleus that contains gene for proteins is the site of transcription
The ribosomes in RER is the site of protein synthesis and translations occurs
Proteins are transported in the vesicles
to Golgi apparatus where it processes, modifies and repackages the proteins into secretory vesicles
vesicles move along the cytoskeleton
Vesicles fuse to the cell surface membrane
secretion by exocytosis
Role of Golgi apparatus
Modifies proteins and lipids
repackages into vesicles
make lysosomes
exocytosis
define magnification
number of times larger the image is compared to object
define resolution
ability to distinguish between two separate points
resolution of a light microscope
50-200nm / 0.05-0.2 um
resolution of a transmission electron microscope
0.05-1.0nm
roles of membranes inside cells
isolation of contents of organelles
form organelles e.g. mitochondria, ER, nucleus, lysosomes, golgi, chloroplast
site for attachment of enzymes
How vesicles are moved from one organelle to another
cytoskeleton
provide pathways for movement
vesicles move along microtubules
microtubules extended and uses ATP
How are proteins ensure that a vesicle is transported to the correct target organelle.
receptors only on target organelle
protein has a specific shape that is complementary to the receptor.
how extracellular enzymes are secreted from the cells
exocytosis
vesicles fuse to the cell surface membrane
why the nuclear envelope contains pores
to allow movement of substances in and out of nucleus
preparing slide
how to stain the sample
use pipette to place blood on slide
place blood near one end of slide
put cover slip to spread blood across slide
coverslip at an angle
use pipette to place a drop of stain onto slide
place coverslip
ensuring there are no air bubbles
why staining
to be able to see more easily
to increase contrast to make nuclei visible
ribosomes in Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic cells- 70S ribosomes
Eukaryotic cells- 80S ribosomes
Features of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
found in plant and animal cells (Eukaryotic)
surface covered in ribosomes
formed from continuous folds of membrane continuous with the nuclear envelope
Roles of the membrane in the RER
separating proteins from cell cytoplasm
Hold ribosomes in place
Means of cell division
Animal- cytokinesis
Plant- cytokinesis
Yeast- budding
Bacterium- binary fission
structural features of mitochondria
have double membrane
with the inner membrane folded to form cristae
circular pieces of DNA
ribosomes
mitochondria
respire aerobically
produces more ATP
ATP used for active transport
increases the rate of metabolism
process and organelles involved in the translation of proteins from RNA
mRNA transported out of nucleus
to ribosome
Translation/ protein synthesis occurs at the ribosome
tRNA brings specific amino acid
Peptide bond forms between adjacent amino acids
Polypeptide protein processed through Golgi apparatus (transported in the vesicle)
ways in which tubulin (movement of cell) is essential to protein synthesis and protein secretion in eukaryotic cells
movement of vesicles from RER to golgi
Movement of secretary vesicles from golgi to plasma membrane
how does cytoskeleton moves organelles around the cell
move by protein motors/ using microtubules
function of the nuclear pores
allow communication between nucleus and cytoplasm
function of vacuole
take up water
Microscopes
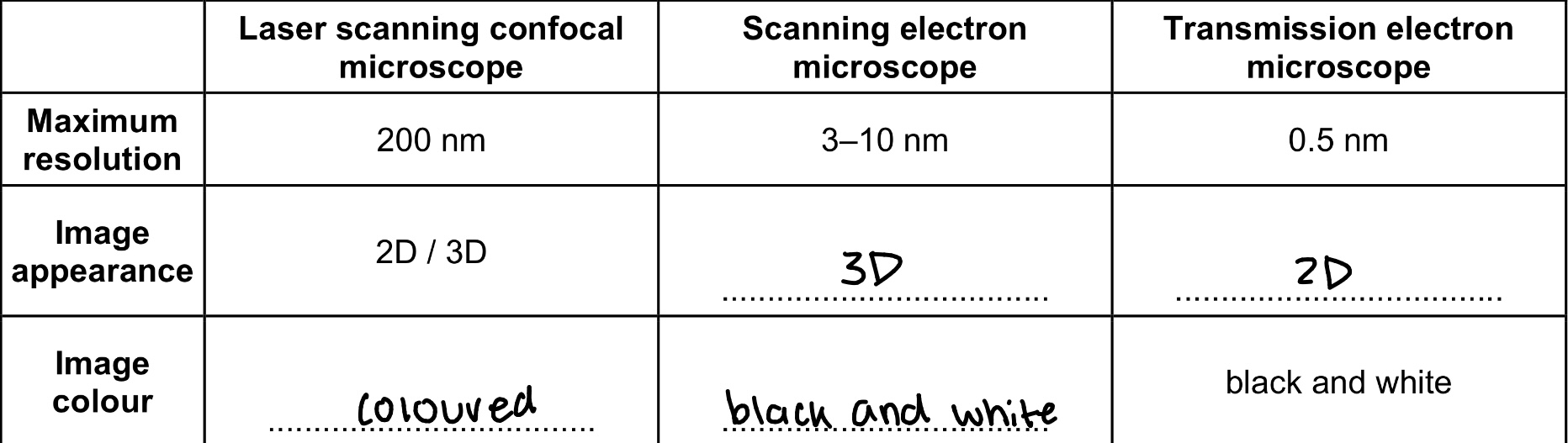
laser scanning confocal microscope vs electron microscope
LSCM has a lower resolution than EM
Explain how to measure the diameter of the nucleus of one of the white blood cells when observing the cells through a light microscope
use eyepiece graticule
calculate graticule using stage micrometer
measure the diameter of nucleus in epu
take repeat measurements and calculate a mean diameter
use calibrated epu to calculate the diameter in um
benefits of using stains
increase contrast
more internal structures visible
because organelles bind to stain
explain why it is important to use a differential stain when examining a blood smear under the microscope
to identify cells
to identify organelles
RBC visible without stain due to haemoglobin
in contrast, WBC needs staining to be visible