Lecture 10: Coating, Extended Dosage Forms and Capsule
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Coating
a process by which an essentially dry, outer layer of coating material is applied to the surface of a dosage form in order to confer specific benefits that broadly range from facilitating product identification to modifying drug release from the dosage form
What are reasons for coating? (6)
➢ Protect drug from surrounding environment - improving product stability (moisture, light, air)
➢ Taste masking - Bitter or unpleasant taste (clarithromycin, chloramphenicol)
➢ Ease of swallowing
➢ Improving product identity - In case of batch to batch differences.
➢ Ease of handling - By improving flow and mechanical strength when high-speed automatic filling and packing equipment is used
➢ Modifying the release of drugs - enteric coating, repeat action and sustained release products
Tablet coating reduces...
cross contamination
Tablet coating chart
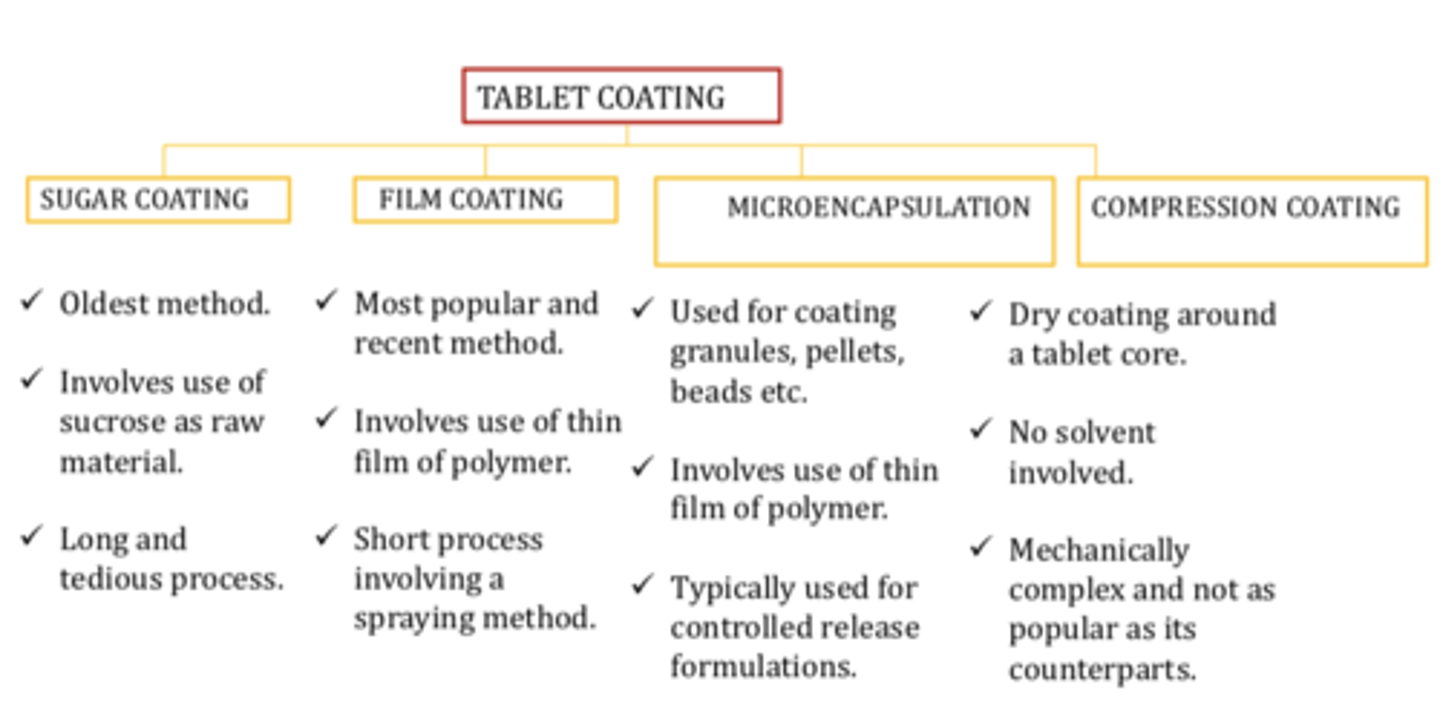
Sugar coating
➢ Oldest method.
➢ Involves use of sucrose as raw material
➢ Long and tedious process
Film coating
➢ Most popular and recent method
➢ Involves use of thin film of polymer
➢ Short process involving a spraying method.
Microencapsulation
➢ Used for coating granules, pellets ,beads etc
➢ Involves use of thin film of polymer
➢ Typically used for controlled release formulations
Compression coating
➢ Dry coating around a tablet core
➢ No solvent involved
➢ Mechanically complex and not as popular as its counterparts.
Why is film coating preferred over sugar coating?
Film coating
- retains ________________
- 2-3% _____________ due to coating
- ______________ possible
- coating of multiparticles can be performed for _______________
- contour of original core
- weight increase
- breaklines possible
- modified release
Why is film coating preferred over sugar coating?
Sugar coating
- ________ with high degree of __________
- 30-50% ________________ due to coating
- breaklines __________________
- difficult to coat ________________
- rounded with high degree of polish
- weight increase
- breaklines nor possible
- difficult to coat multiparticles
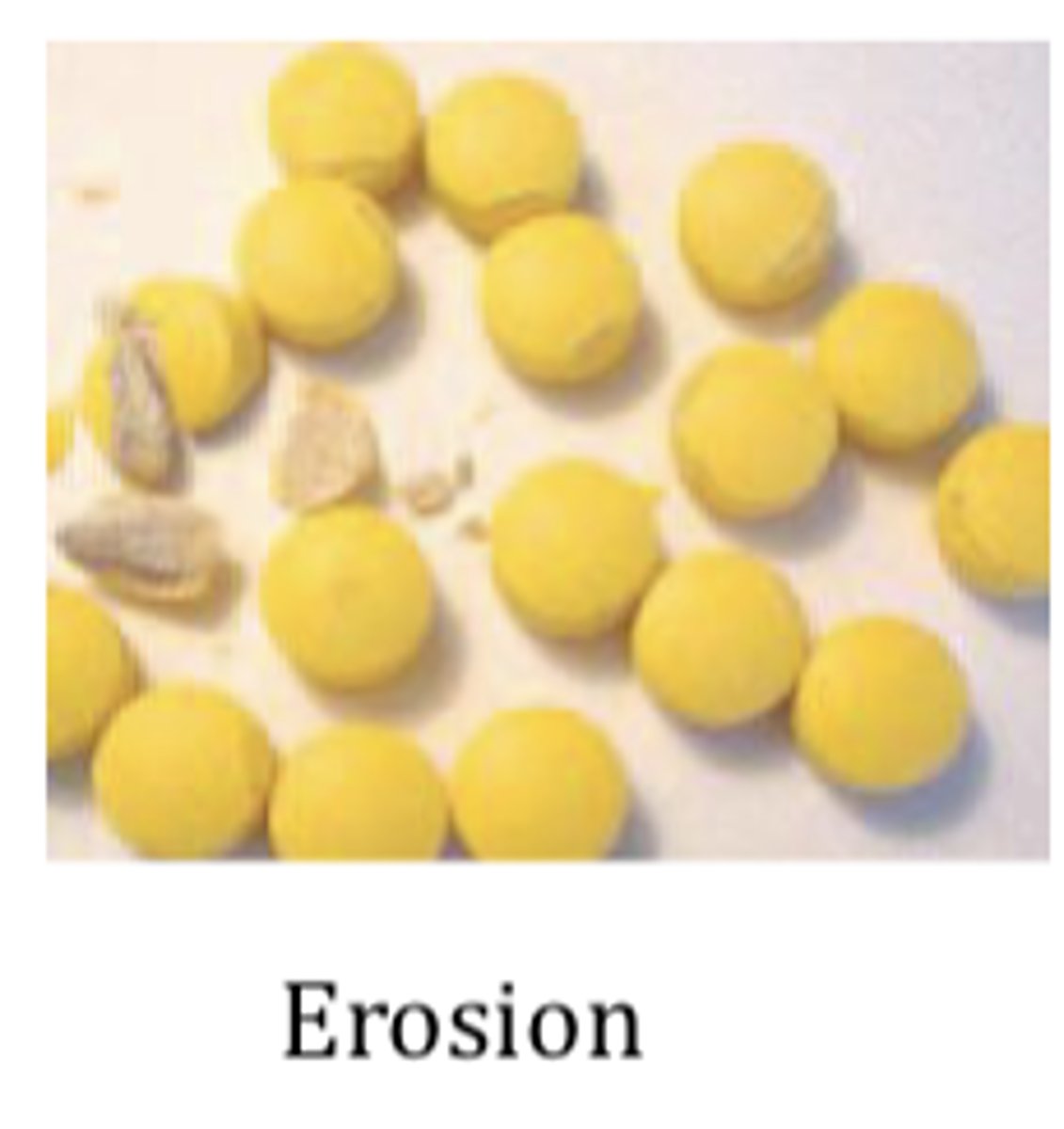
Coating problems and defects: Erosion
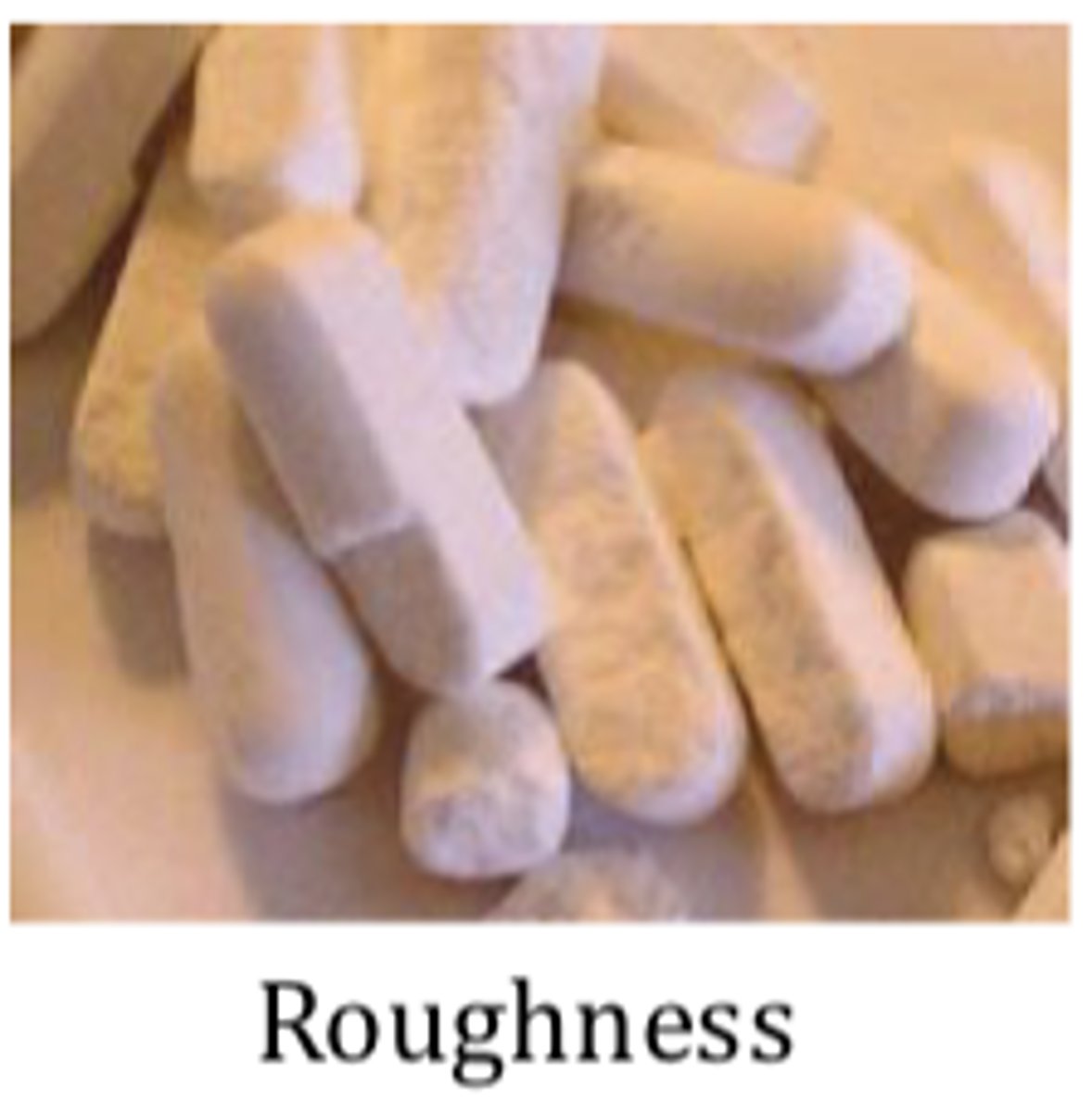
Coating problems and defects: Roughness

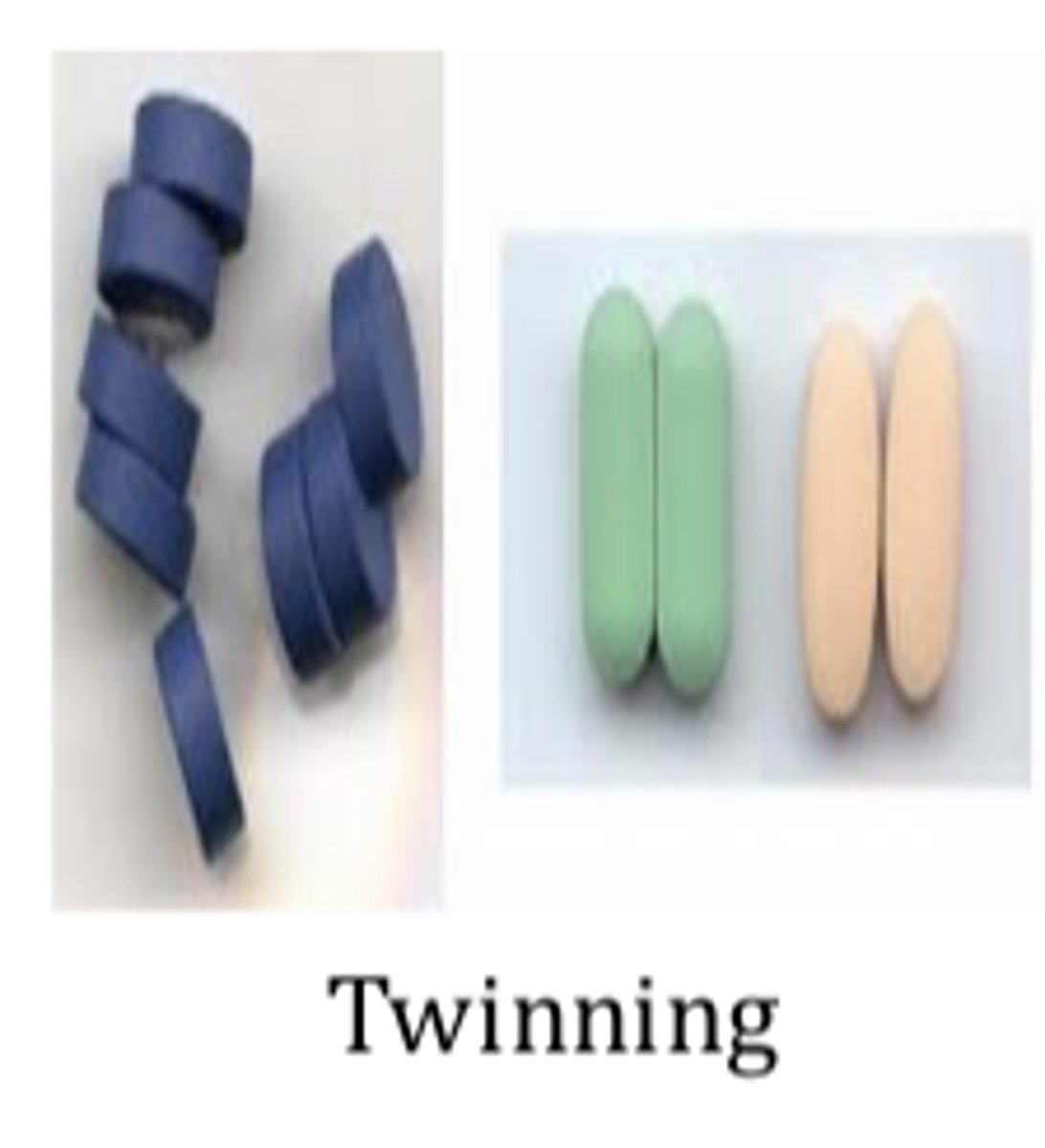
Coating problems and defects: Twinning

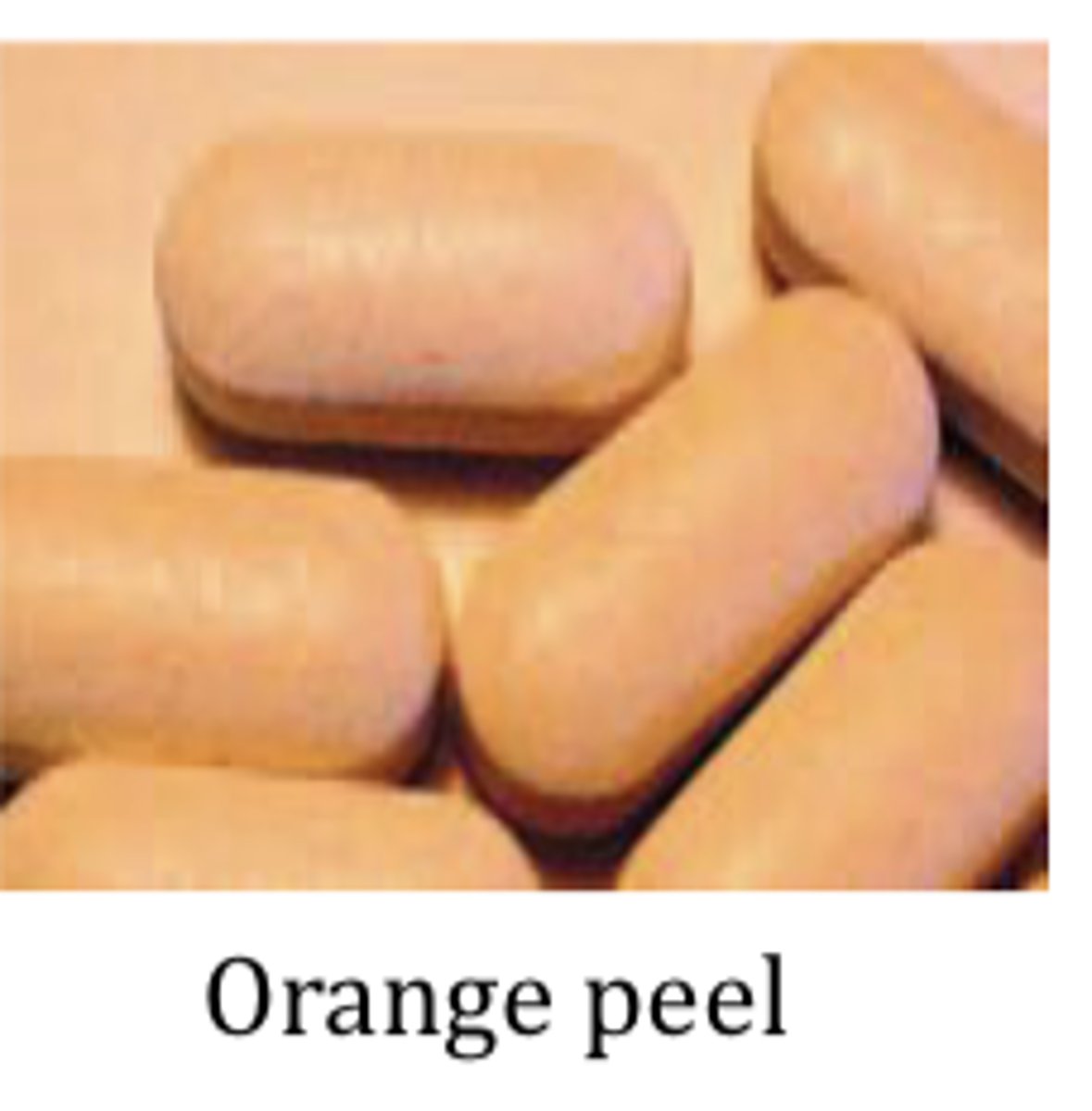
Coating problems and defects: Orange peel

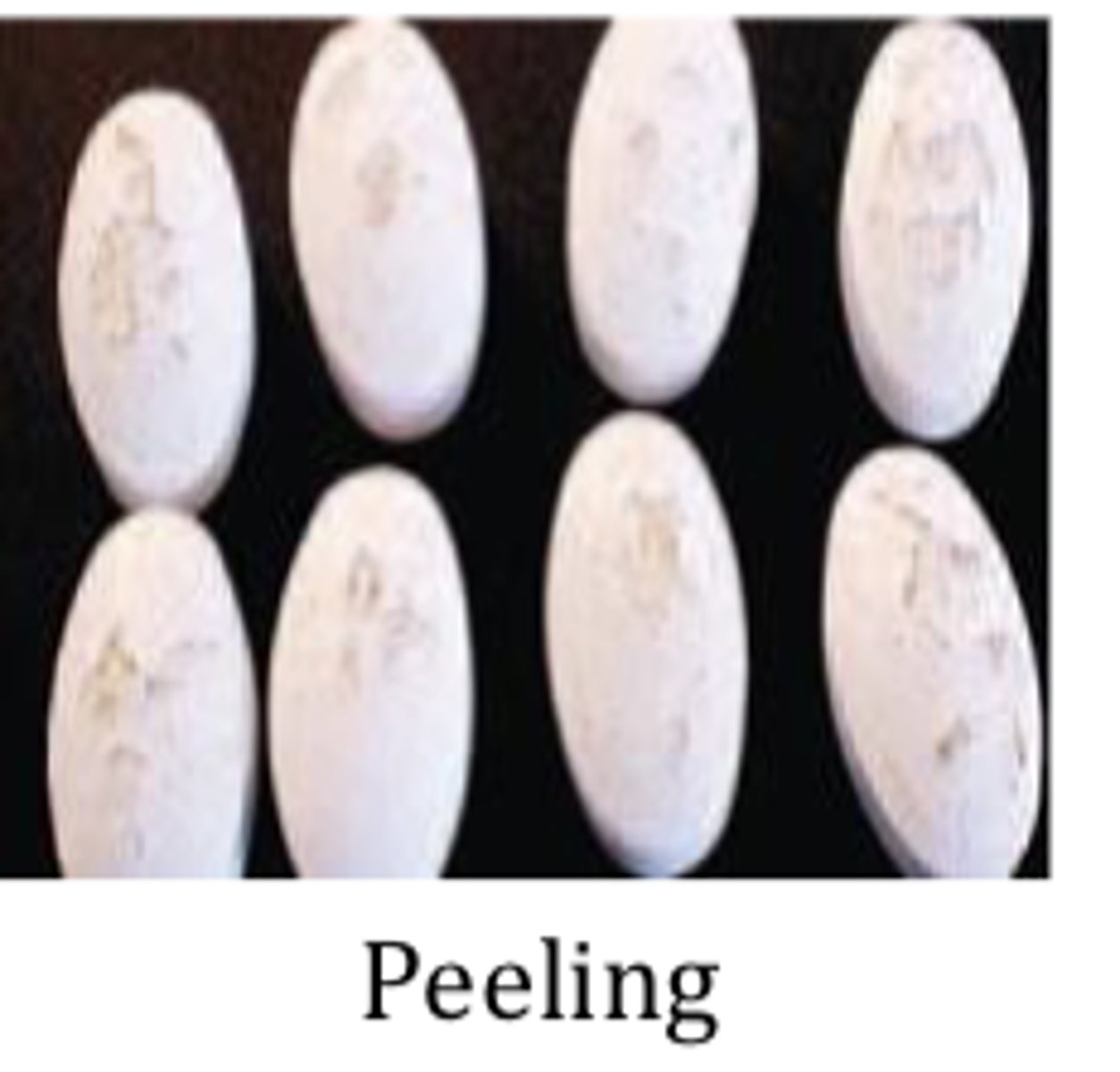
Coating problems and defects: Peeling

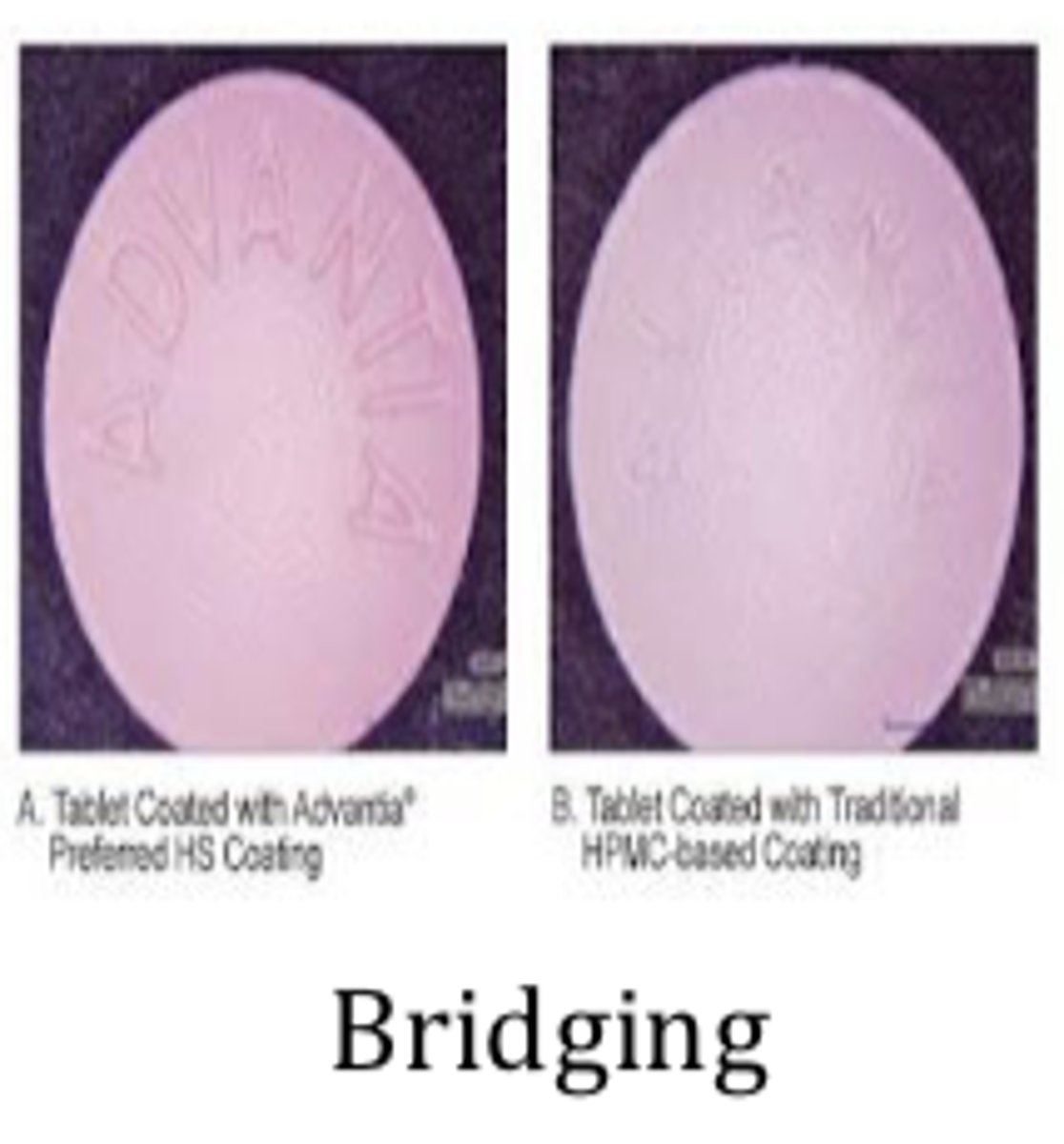
Coating problems and defects: Bridging
Modified release film coatings
1. Delayed release products- enteric coating
2. Sustained-release products
Enteric coating remains intact in ________ but will dissolve and release contents in _________________
- stomach
- small intestine
What is the purpose of enteric coating?
- delay release of drugs which can be inactivated by stomach pH and contents (pancreatin, erythromycin ,omeprazole)
- delay release of drugs that may cause nausea or bleeding irritating the gastric mucosa (aspirin, steroids)
Most currently used enteric coatings are ___________________ that remain ____________________ in low (acidic) pH of stomach and ionizes when pH is about _____
- weak acids
- undissociated
- 5
Cellulose Acetate Phthalate
most popular enteric coating polymer
- ex: poly vinyl acetate phthalate, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose phthalate
Materials used for sustained release coatings:
➢ Mixtures of waxes - Beeswax, Stearic acid etc. Provide coatings that are dissolved slowly in GI tract
➢ Shellac and zein
➢ Ethylcellulose - diffusion controlled products
➢ Acrylic resins - Similar to ethylcellulose
➢ Silicone elastomers
Multi-particulates of sustained-release products
➢ Granules
➢ Drug-loaded beads or nonpareils
➢ Drug crystals
➢ Drug/ion-exchange resin complexes
➢ Tablets - Minitablets
Membrane dissolution systems:
Drug release occurs in 2 steps:
1. Liquid dissolves the membrane
2. Solid drug is exposed to the liquid and subsequently dissolves
Factos affecting the rate of dissolution
1. Membrane properties
2. Applied compression force
Membrane properties affecting the rate of dissolution
- thickness- thicker membrane leads to slower/faster dissolution rate
- composition- hydrophilic/hydrophobic membranes
- porosity
Implants are sterile...
sterile solid drug products
Components of implants
- drug
- rate-controlling excipients
Implants release the drug _________ into the ________________ (subcutaneous)
- slowly
- general circulation
- potent hormones
Routes of administration for implants
- subcutaneous- upper arm, thigh, abdomen
- intravitreal
Placement of implants
- surgical incision
- special injector
Capsules
Solid dosage forms in where medicinal agents with or without excipients are enclosed in a small shell of gelatin
Types of capsules
• Hard gelatin capsules
• Soft gelatin capsules
Hard or soft gelatin capsules: One has two pieces: a longer body and a shorter cap; the other has only one piece. Which is which?
A. Hard = 2 pieces; soft = 1 piece
B. Hard = 1 piece; soft = 2 pieces
A. Hard = 2 pieces; soft = 1 piece

Characteristics of capsules
• Tasteless
• Easily administered
• Easily filled either extemporaneously or in large quantities commercially
Extemporaneous
composed, performed, or uttered on the spur of the moment; impromptu
Gelatin capsules
The primary composition material for the manufacture of capsules
Properties of gelatin capsules
• Non-toxic
• Produces a strong flexible film
• Solubility- cold water, hot water or gastric fluid
Hard gelatin capsules are manufactured in _______ sections, the capsule ________ and a shorter _______
- 2 sections
- body
- cap
Hard gelatin capsule sections...
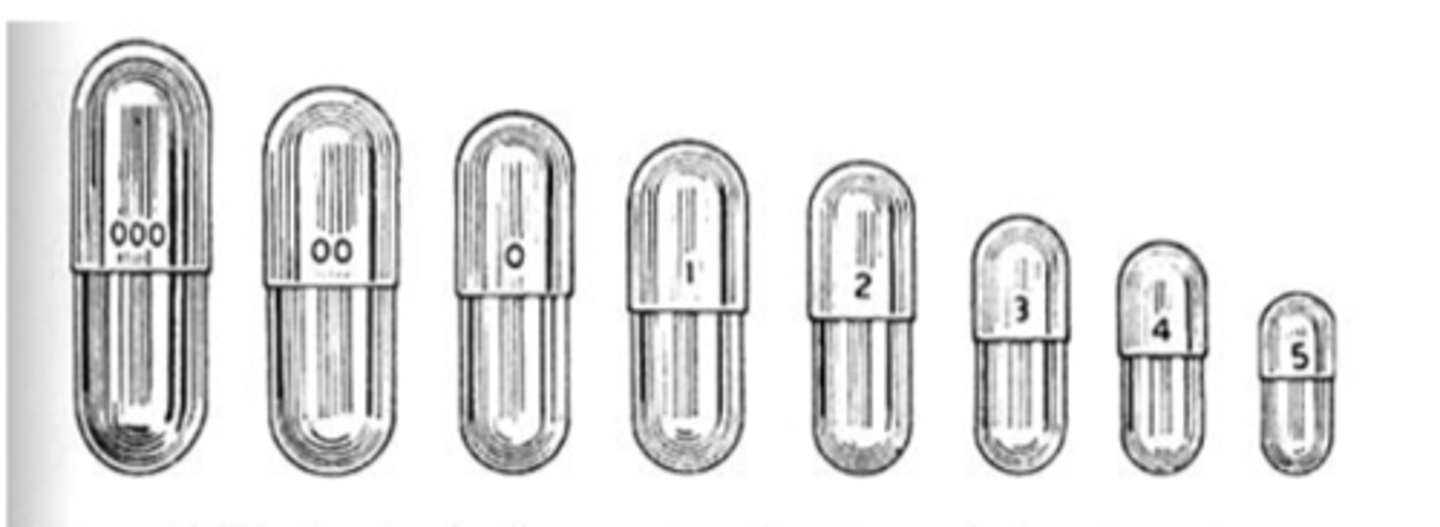
- overlap
- selection of size
Hard gelatin composition
- rim is slightly _________
- ___________ groove in shel walls
- rim is slightly tapered
- locking grove in shell walls- reliable closing, prevent splitting or denting
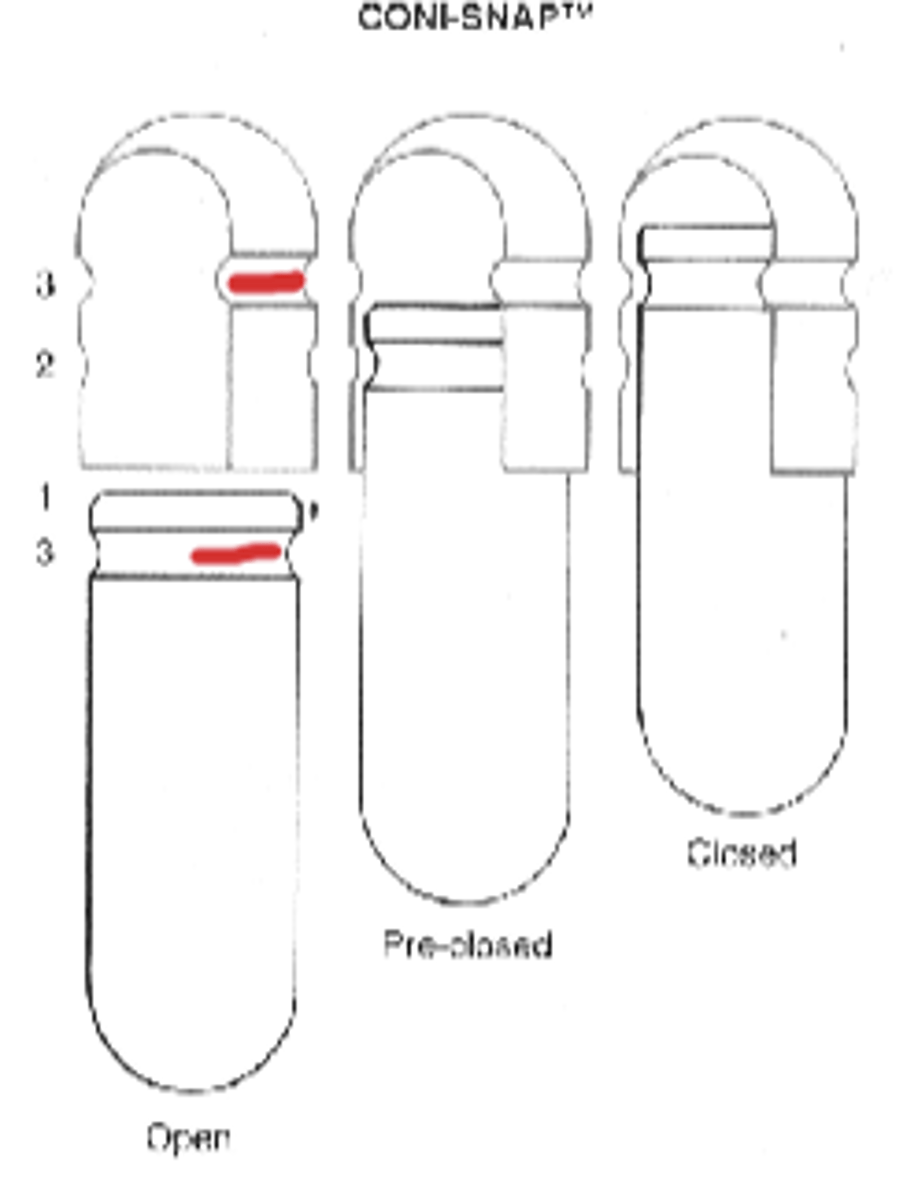
Composition of capsule shell
Gelatin
- 0.15% sulfur oxide is added to prevent decomposition during manufacture
Water (13%-16%)
- must be stored in an environment free from excessive humidity (>18% water) or dryness (<12% water)
Colorants
Opaquants (titanium dioxide)
Preservatives
Composition of powder mix
- active ingredients- raw ingredient
- diluent
- disintegrant
- substances to be avoided: those that interfere with the integrity of the shell (e.g., substances containing free water)
Soft gelatin capsules
- a completely sealed dosage form
- Cannot be opened without destroying the capsule
- One-piece outer gelatin shell
T/F: Liquids that do not adversely affect gelatin may be placed in both soft and hard gelatin capsules
FALSE
may be placed in soft but not hard gelatin capsules
Soft gelatin capsules: Water immiscible non-volatile liquids
Olive oil, soy oil, mineral oil
Soft gelatin capsules; Water miscible non-volatile liquids
Propylene glycol, polyethylene glycols, polysorbates
Composition of capsule shell
- gelatin
- water (6%-10%)
- pasticizer
- colorant
- opaquants
- flavorants
- preservatives- parabens
Water in the composition of capsule shell
6-10%
- ensure proper processing during preparation and encapsulation
Plasticizer in composition of capsule shell
- softens gelatin shell
- e.g. glycerin, propylene glycol, sorbital, combination
Colorants in capsule shell
color of the capsule shell should never be lighter in hue than the capsulated material
Rational for selection of soft gels
▪ Safety for potent and cytotoxic drugs
▪ Oils and low melting point drugs
▪ Dose uniformity of low dose drugs
▪ Improved absorption
▪ Good stability
▪ Capsules are stable to with stand high alkaline pH of up to 12
What are uses of vegicaps soft capsules?
health and nutritional products
Vegicaps allow for encapsulation of...
- chemically aggressive fill systems with high alkalinity
- active ingredients or excipients that cross-link gelatin