Intrinsic back muscles + functional anatomy of the spine
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
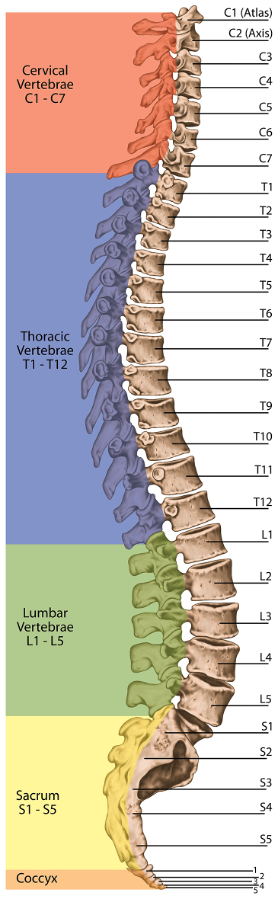
vertebral column composition
Articulating vertebrae: 24
Cervical: 7
Thoracic: 12
Lumbar: 5
Fused: 8-10
Sacrum: 5
Coccyx: 3 – 5 (fused)
Total: 32 – 34 vertebrae
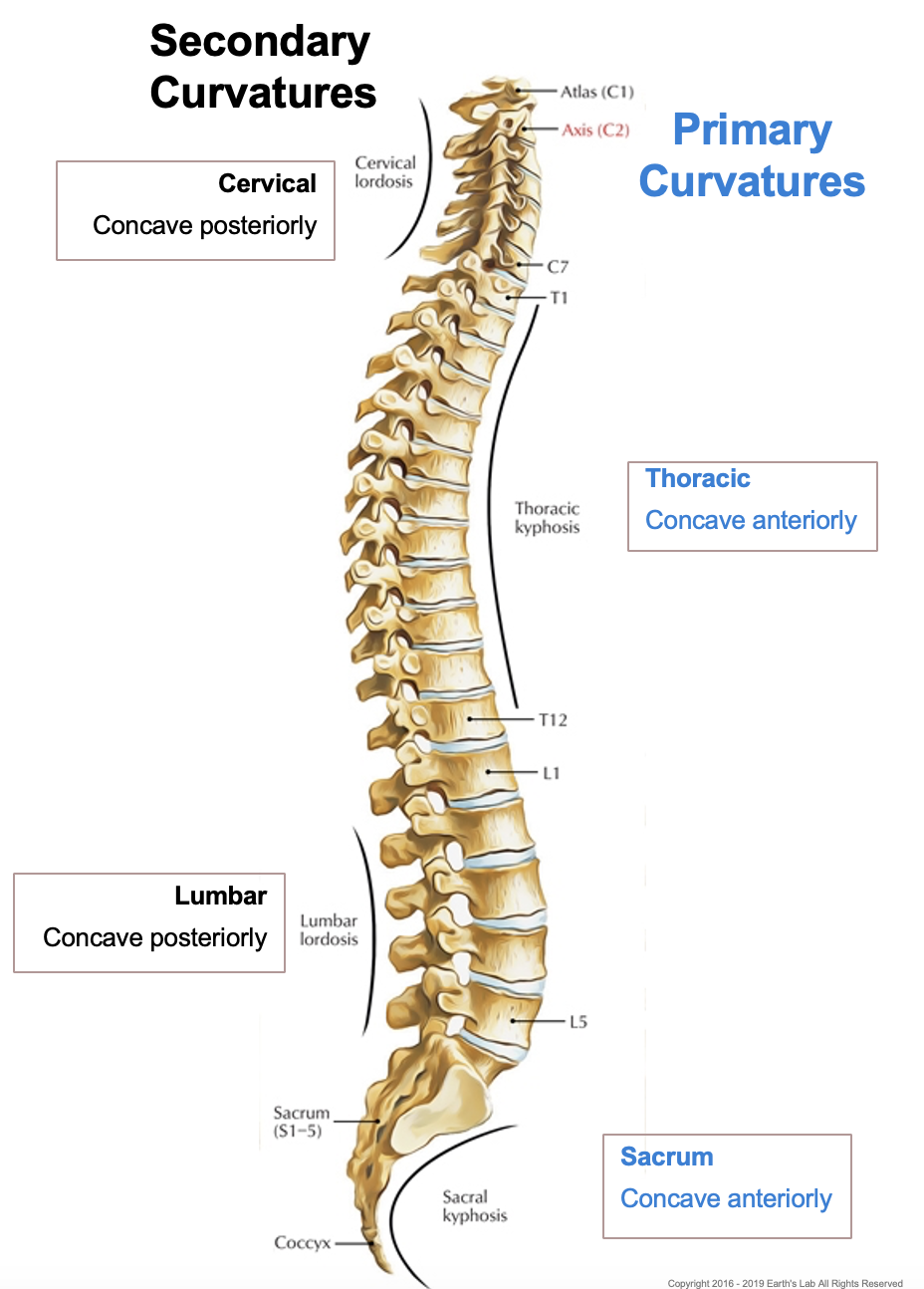
four spine curves
Primary Curvature (Kyphotic): present during foetal development, concave anteriorly
thoracic
sacral
Secondary Curvature (Lordotic): forms after birth, concave posteriorly
cervical: develops when a baby can hold up its head
lumbar: develops when a baby stands up
movements of the back
passive movement
active movement
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
bilateral contraction
ipsilateral contraction
contralateral contraction
passive movement
movement occurring without active muscle contraction
due to gravity acting on the body's mass
active movement
muscles of the back
extend
laterally flex
rotate
cervical trunk movement
flexion and extension
lateral flexion
rotation
thoracic trunk movement
lateral flexion
rotation
lumbar trunk movement
flexion/extension
(very limited rotation)
bilateral contraction trunk movement
extension
ipsilateral contraction trunk movement
lateral flexion and rotation
contralateral contraction trunk movement
lateral flexion and rotation
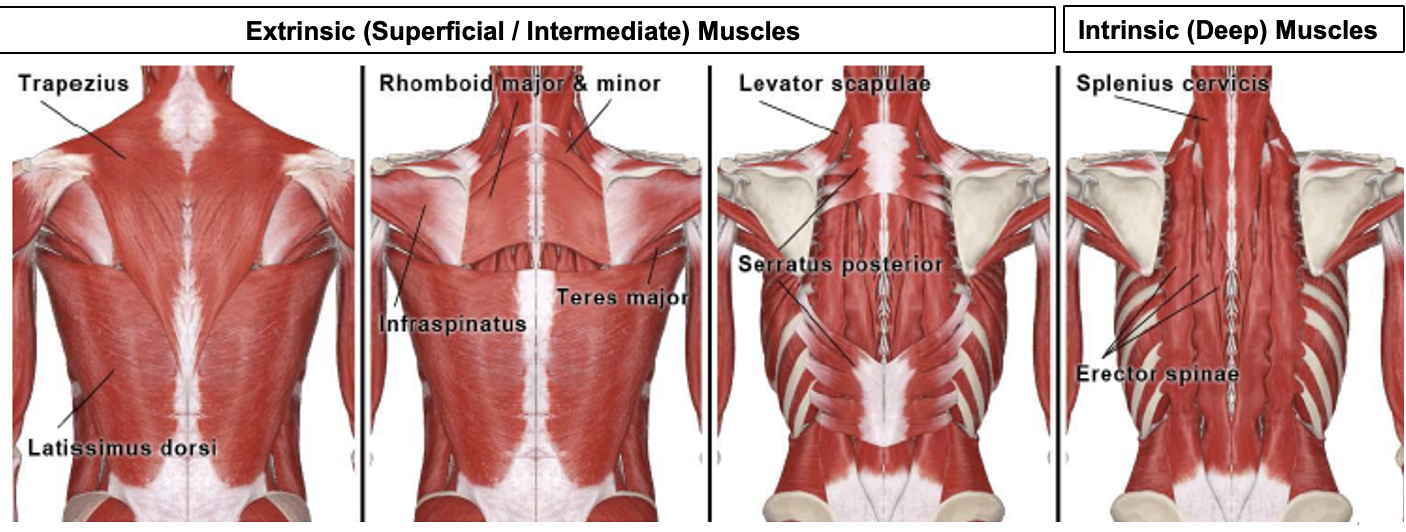
extrinsic muscles of back role
move upper limbs and ribs
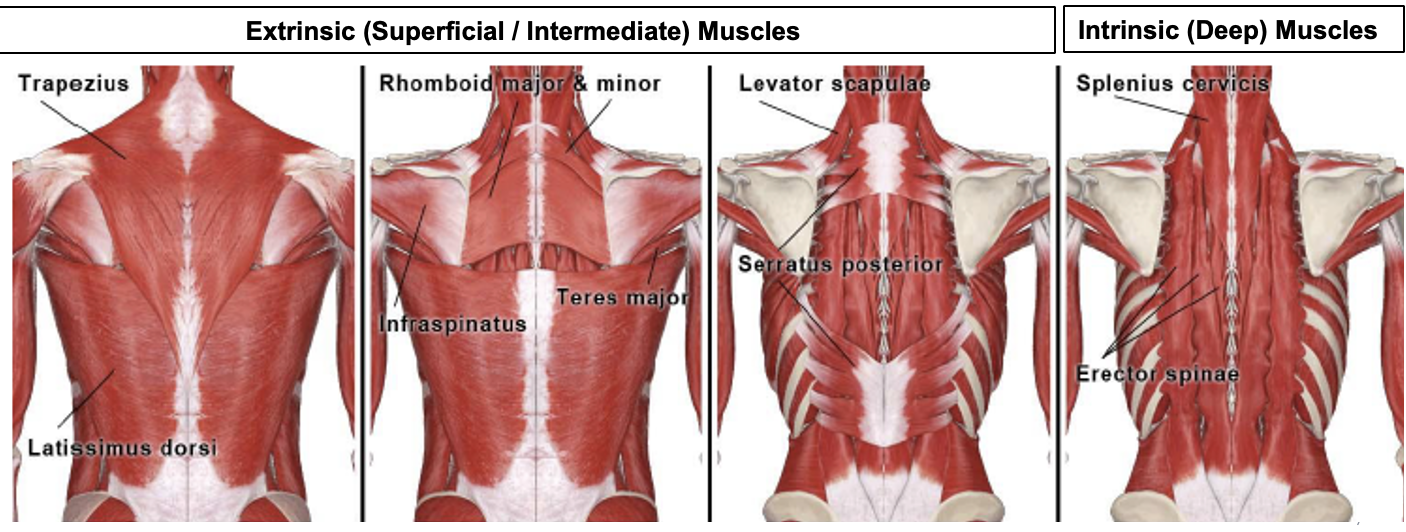
intrinsic muscles of back role
maintain posture
move the vertebral column
innervated by posterior rami of spinal nerves: proprioception
5 categories of back pain (conditions)
traumatic
degenerative
inflammatory
oncologic
infectious
traumatic back pain
injury to:
spine
intervertebral discs (IVD)
soft tissues
acute lower back pain = lumbago
pain/strain to quadratus lumborum
or
paraspinal muscles/IVD herniation
degenerative back pain
MSK structures weaken
causes:
aging
overuse
pre-existing pathology (e.g. disc herniation)
inflammatory back pain
infection of malignancy
e.g. ankylosing spondylitis and sacroiliitis
oncologic back pain
caused by cancer or its treatment":
pathologic fractures (bone weakened e.g. due to cancer)
lytic lesions to the spine (areas of bone destruction causing holes in the bone)
cancers of the marrow
infectious back pain
from direct inoculation (IV drugs, spinal procedures e.g. lumbar puncture) or another source
infections can occur:
spine
discs
soft tissue (forming abscesses)
source of back pain
lower back muscles
back muscles causing headaches
upper back muscles
movement with high risk of back muscle damage
eccentric contraction
back muscles sensory input
back muscles are mainly proprioceptive
mostly provide sensory information about the position & movement of the spine
contributes significantly to its postural stability and fine control
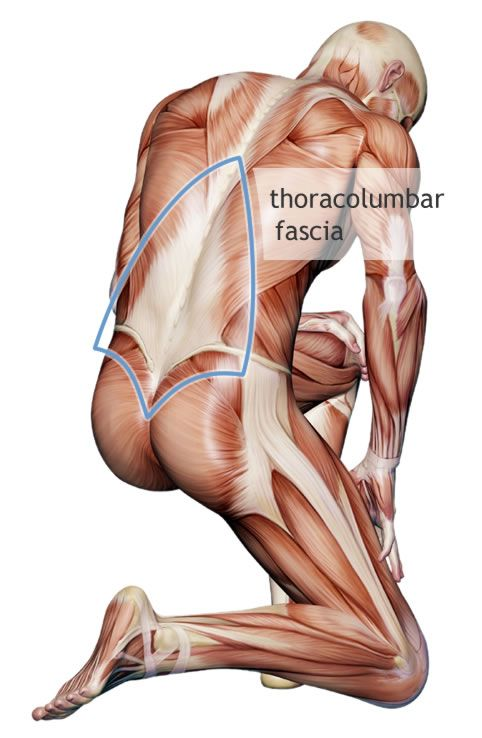
thoracolumbar fascia
sheet of connective tissue that runs along the lower back
separates paraspinal muscles (erector spinae) and the posterior abdominal wall muscles (quadratus lumborum, and psoas major)
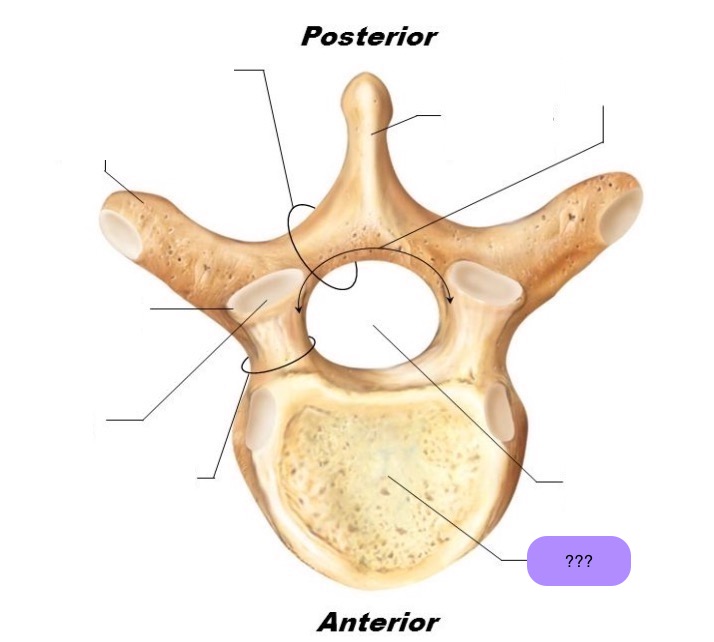
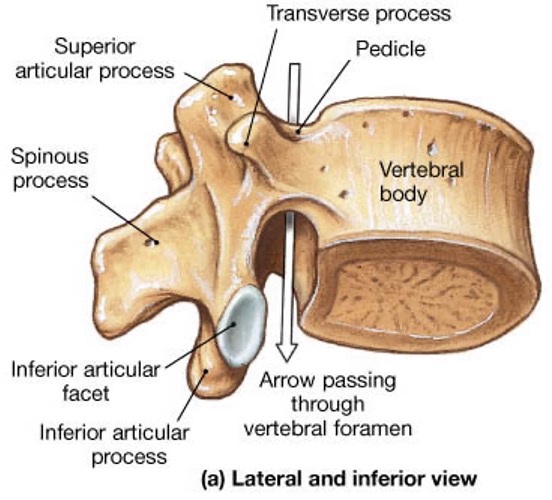
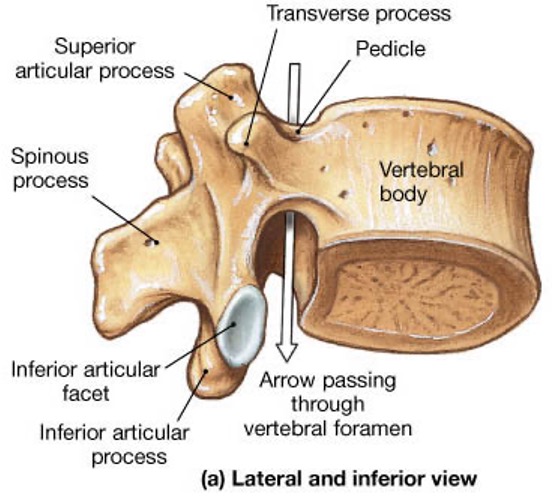
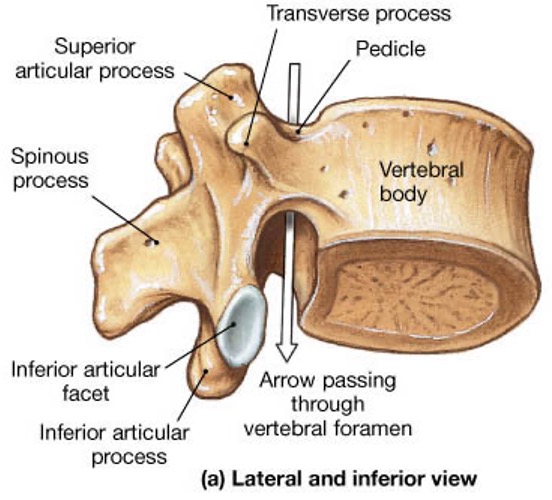
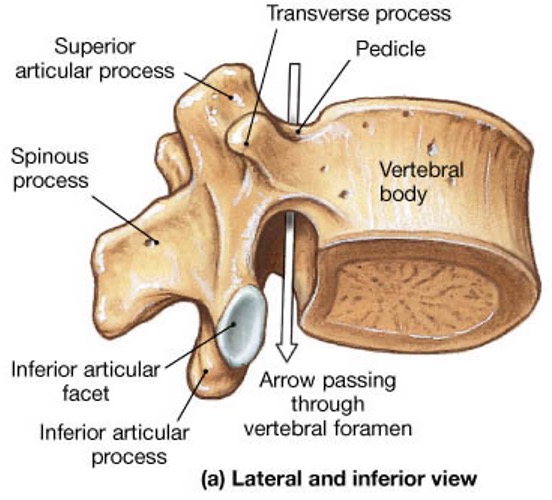
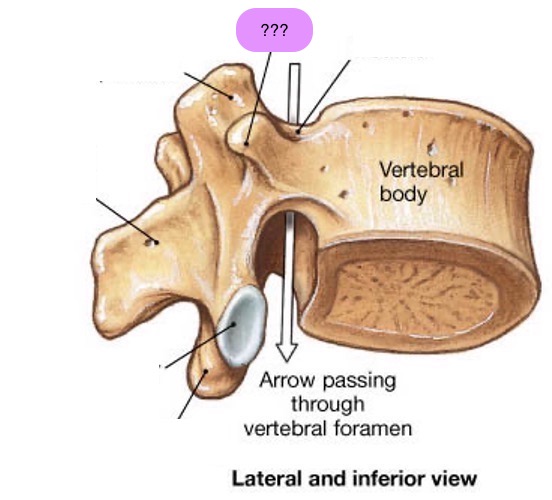
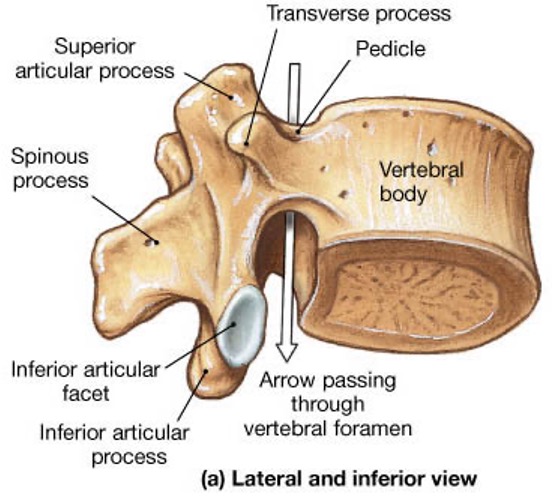
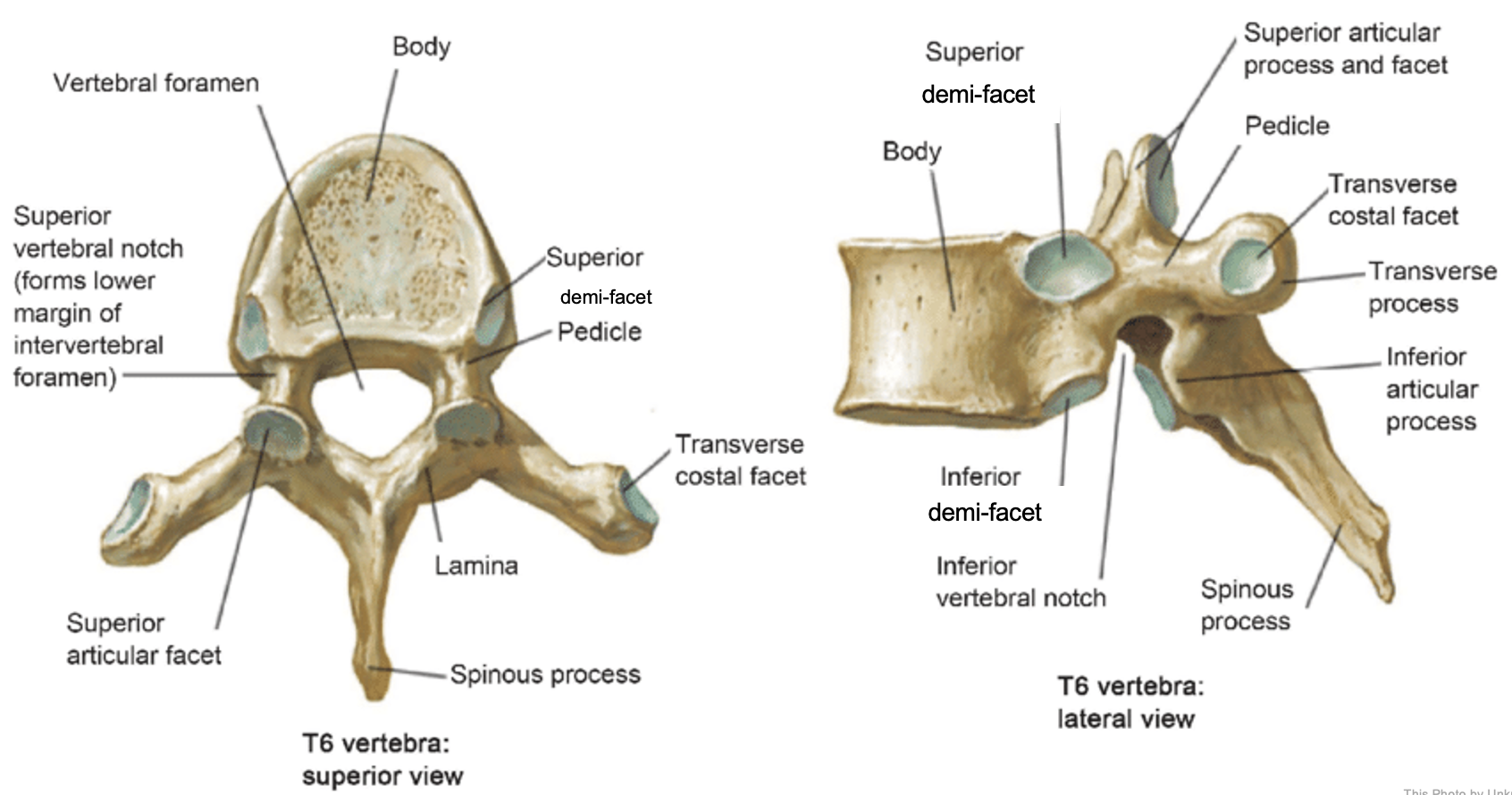
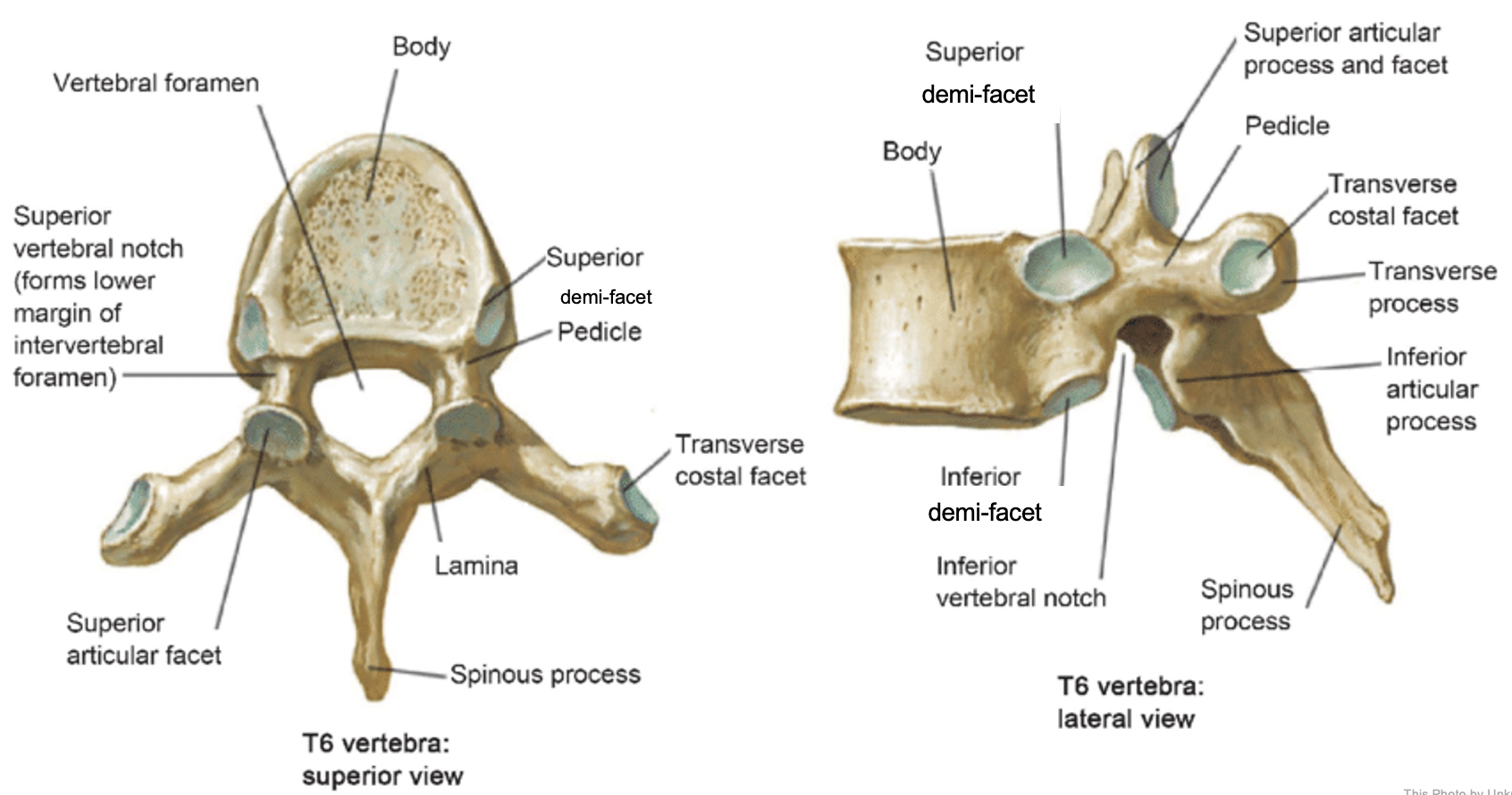
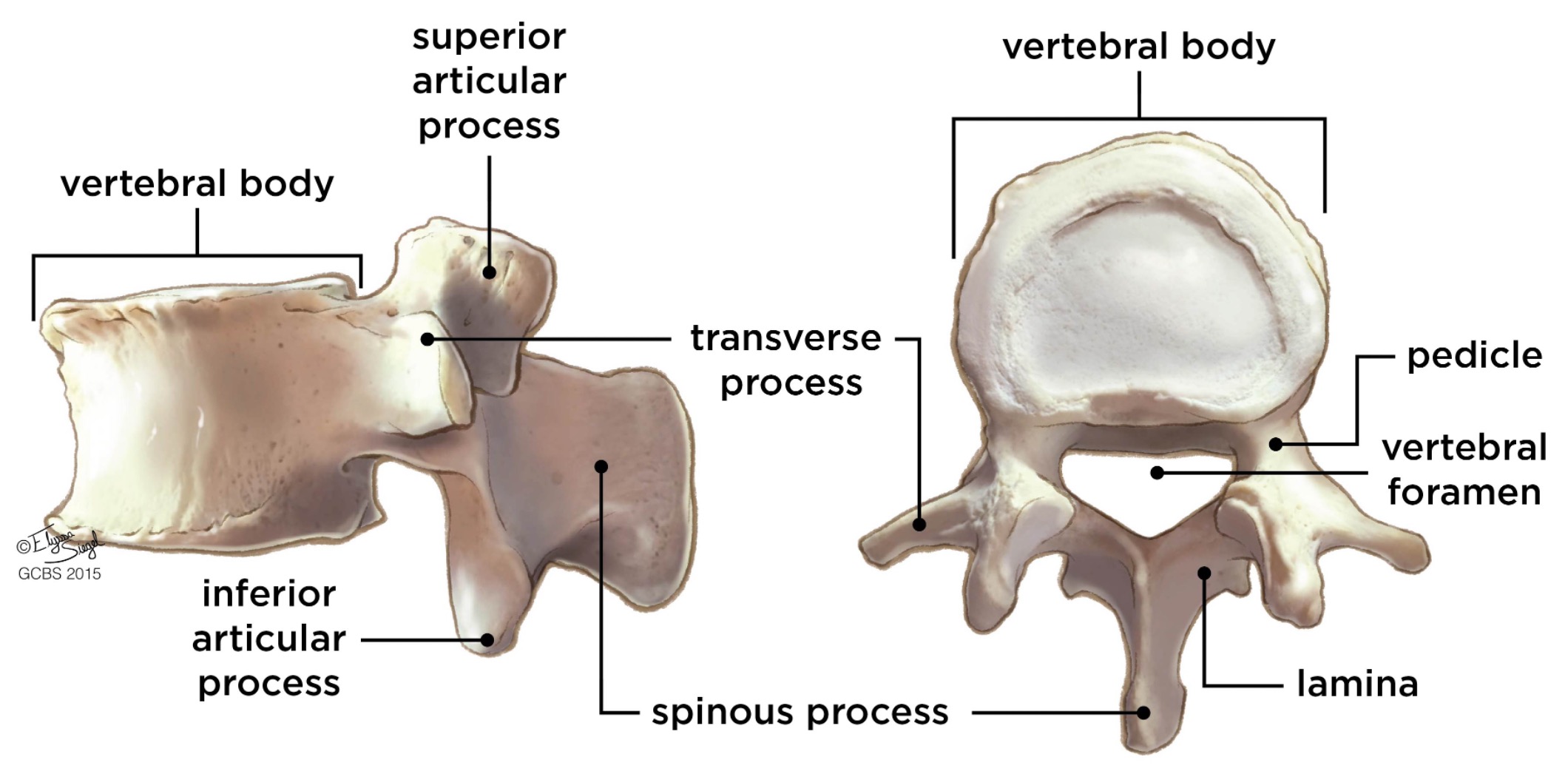
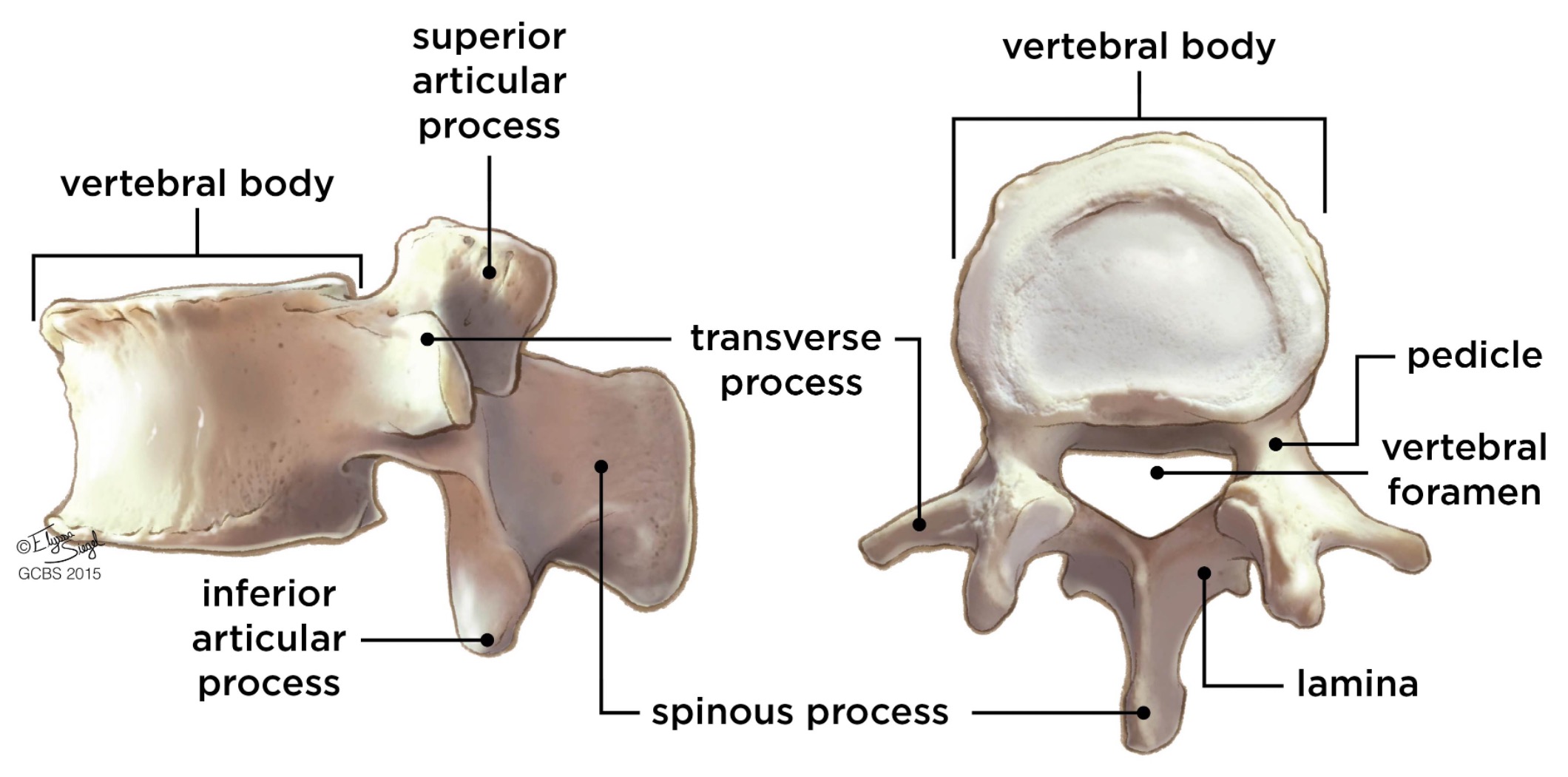
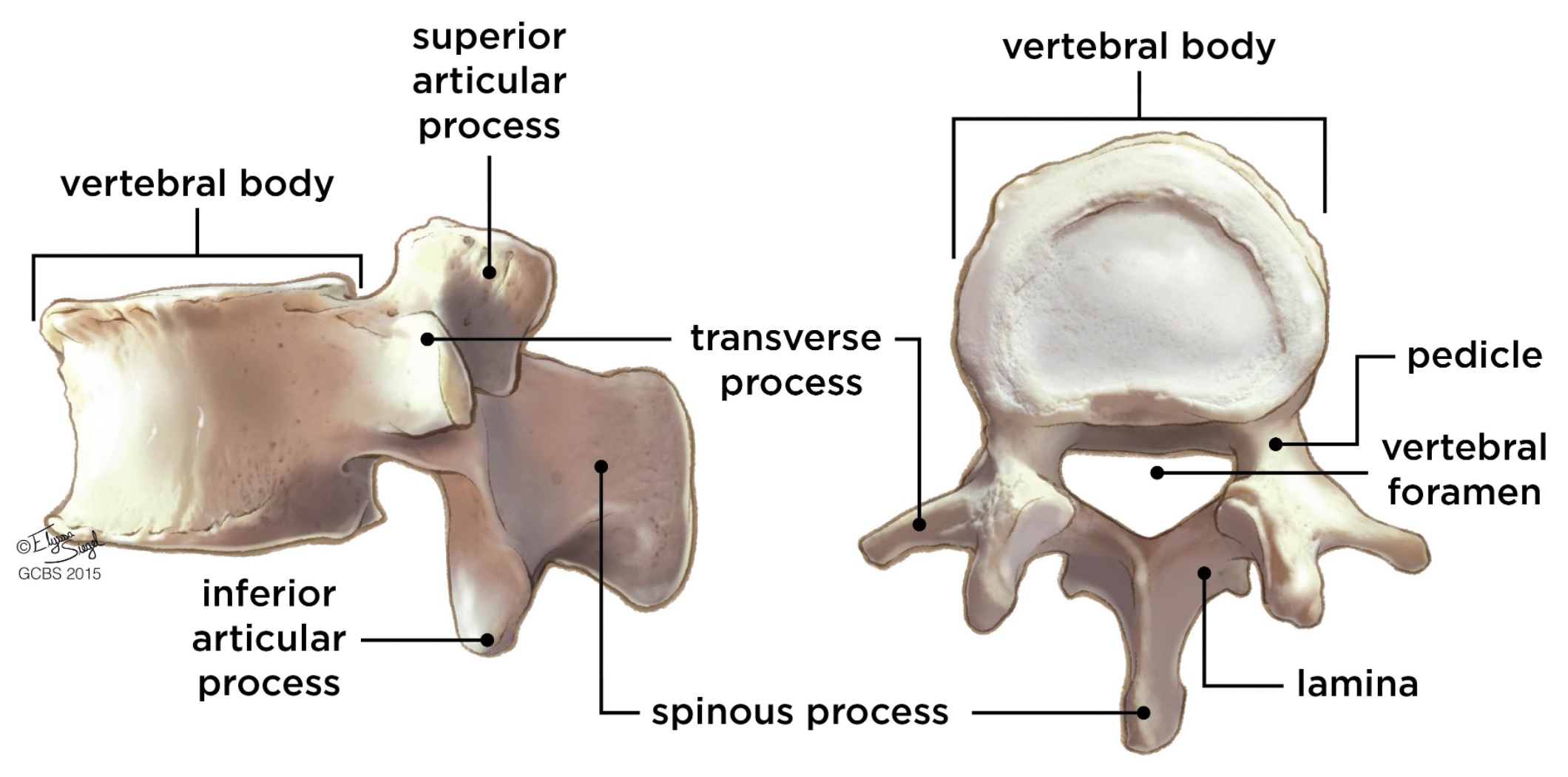
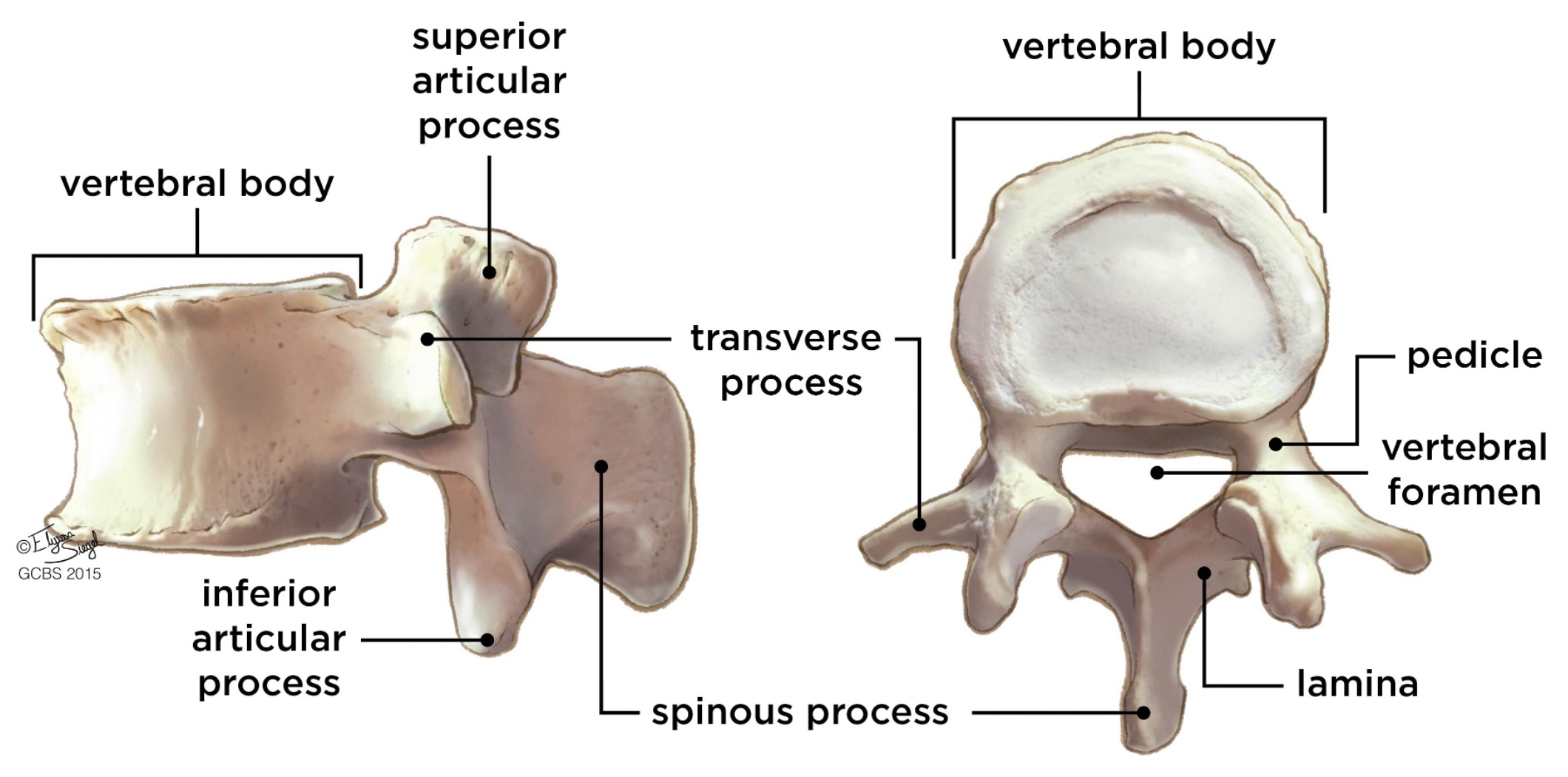
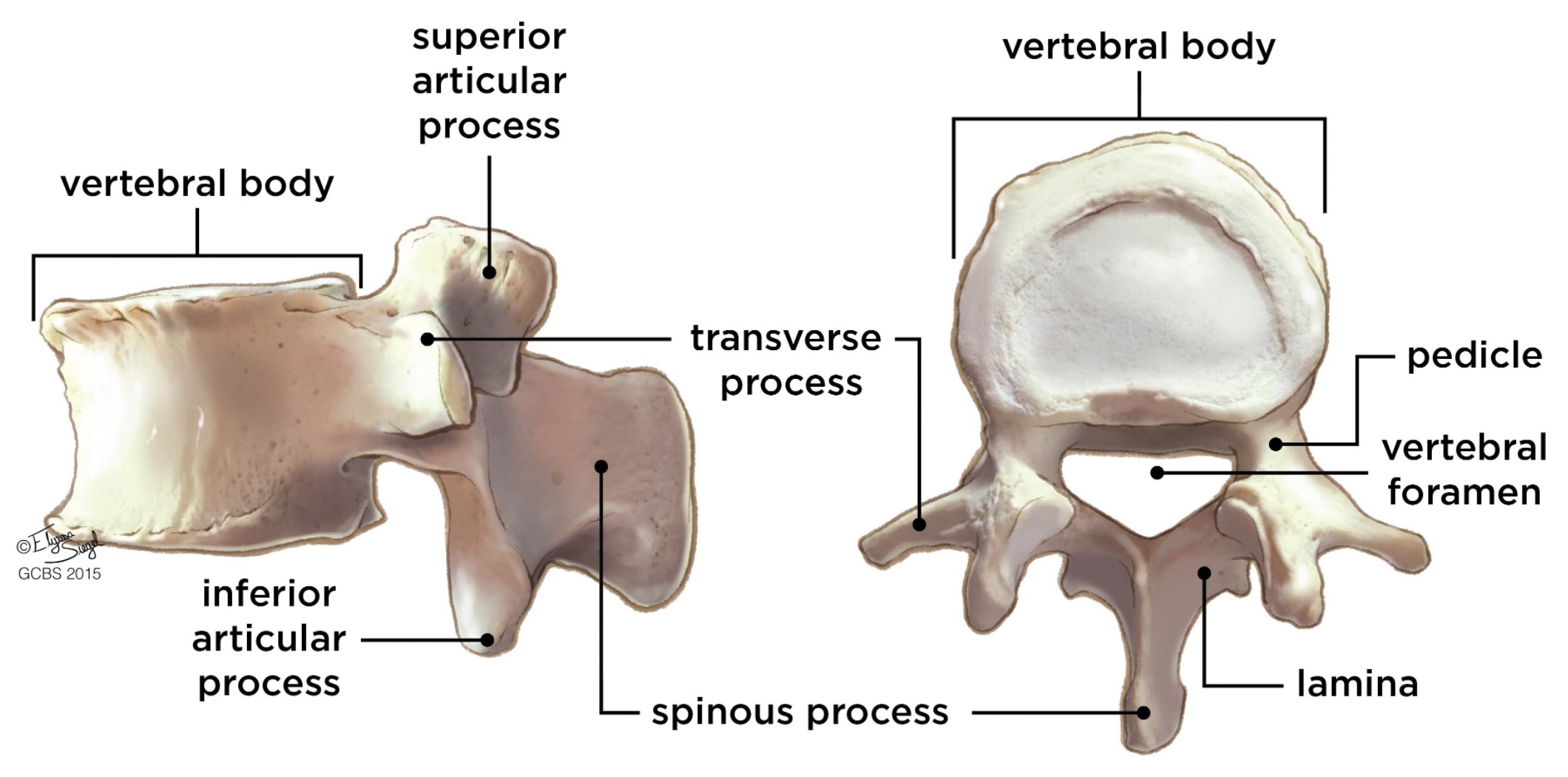
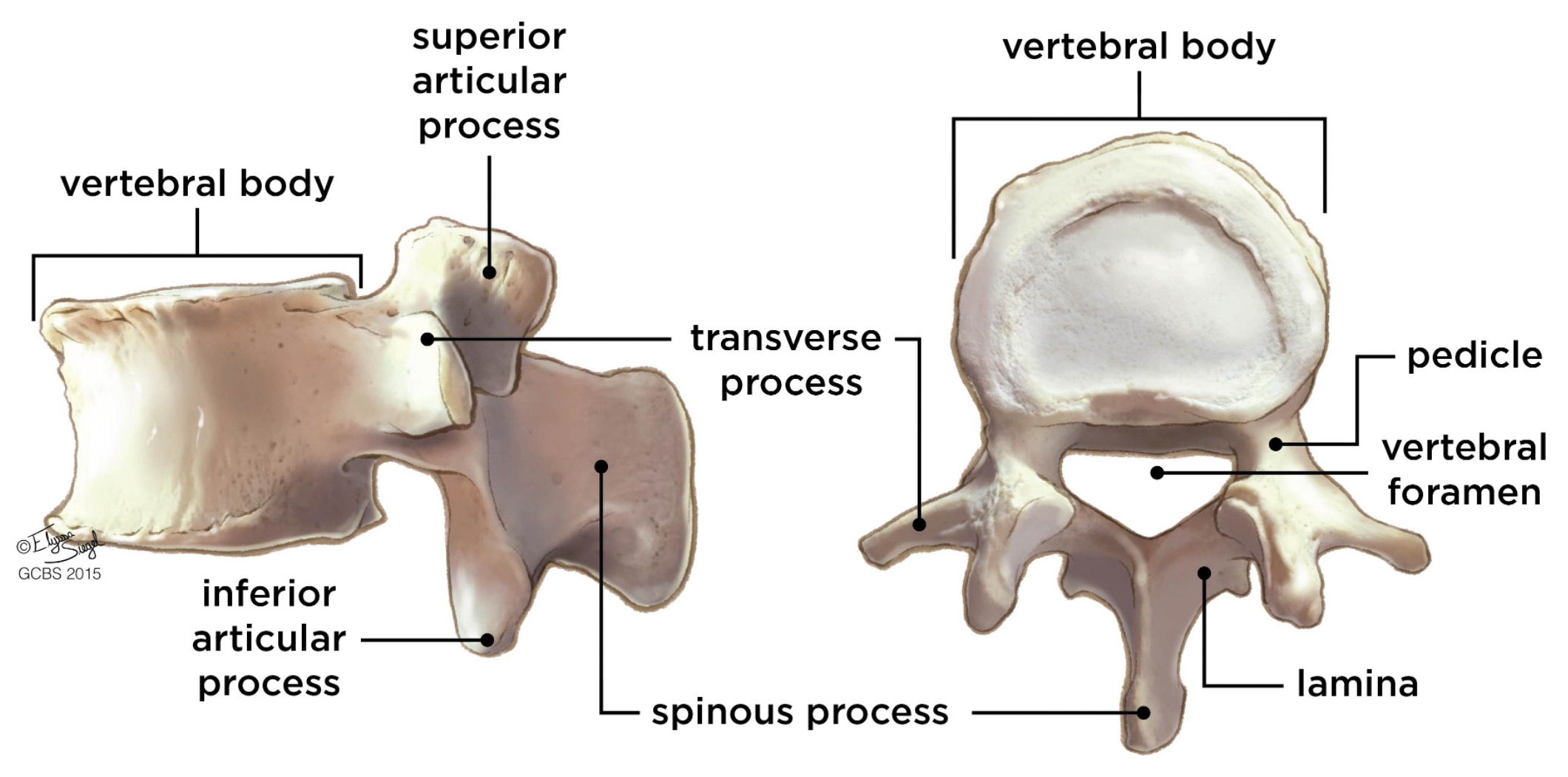
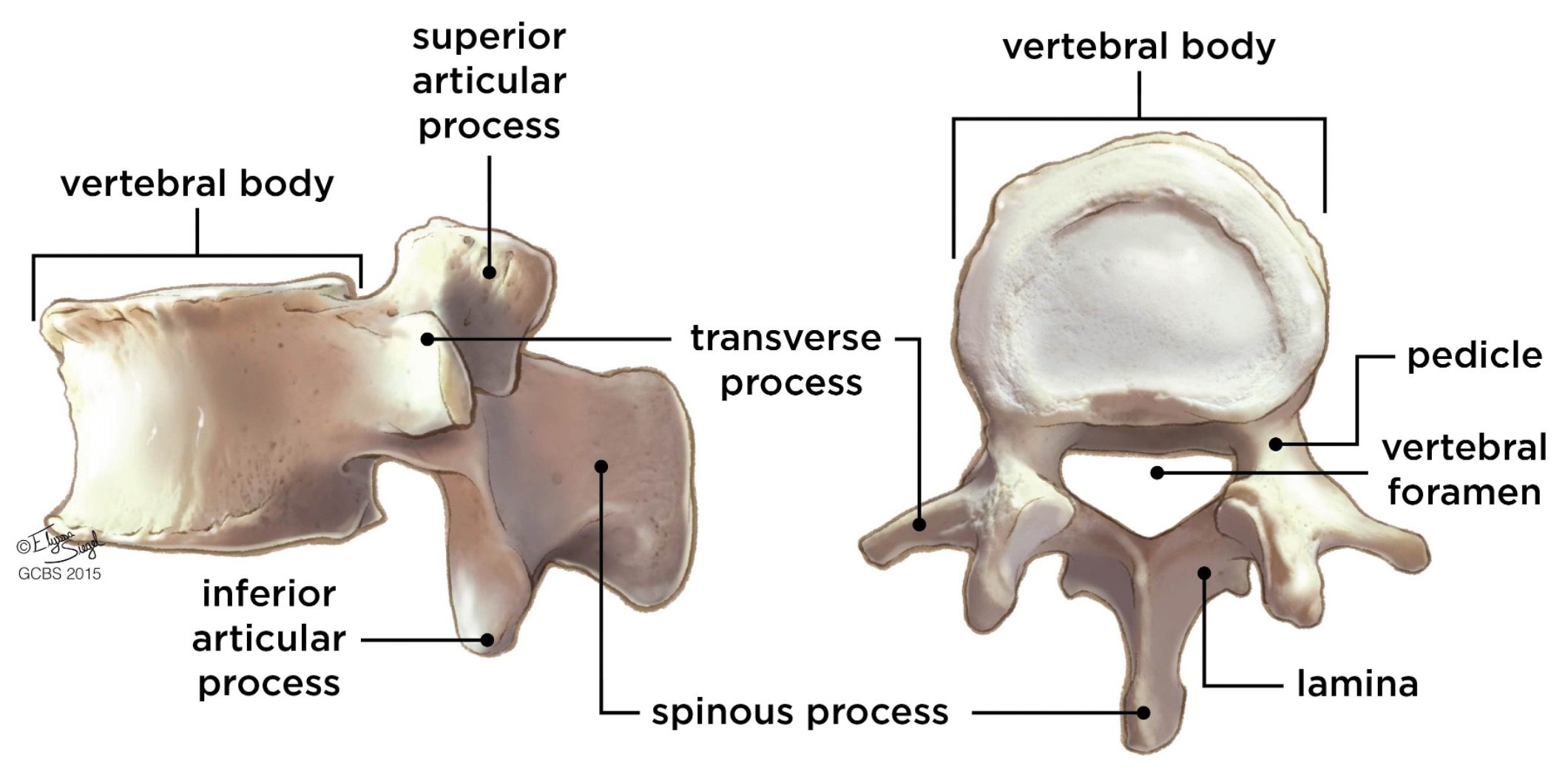
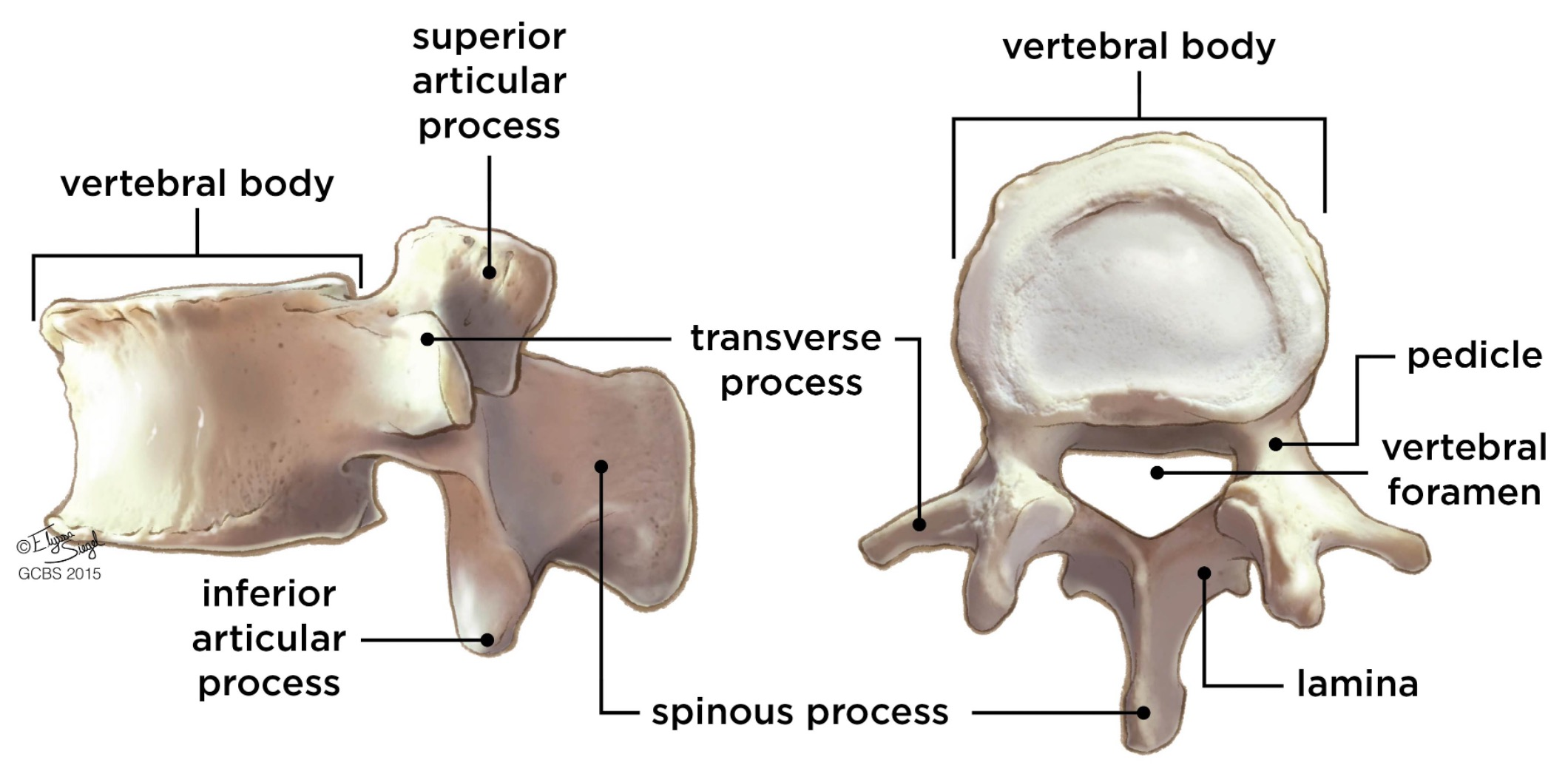
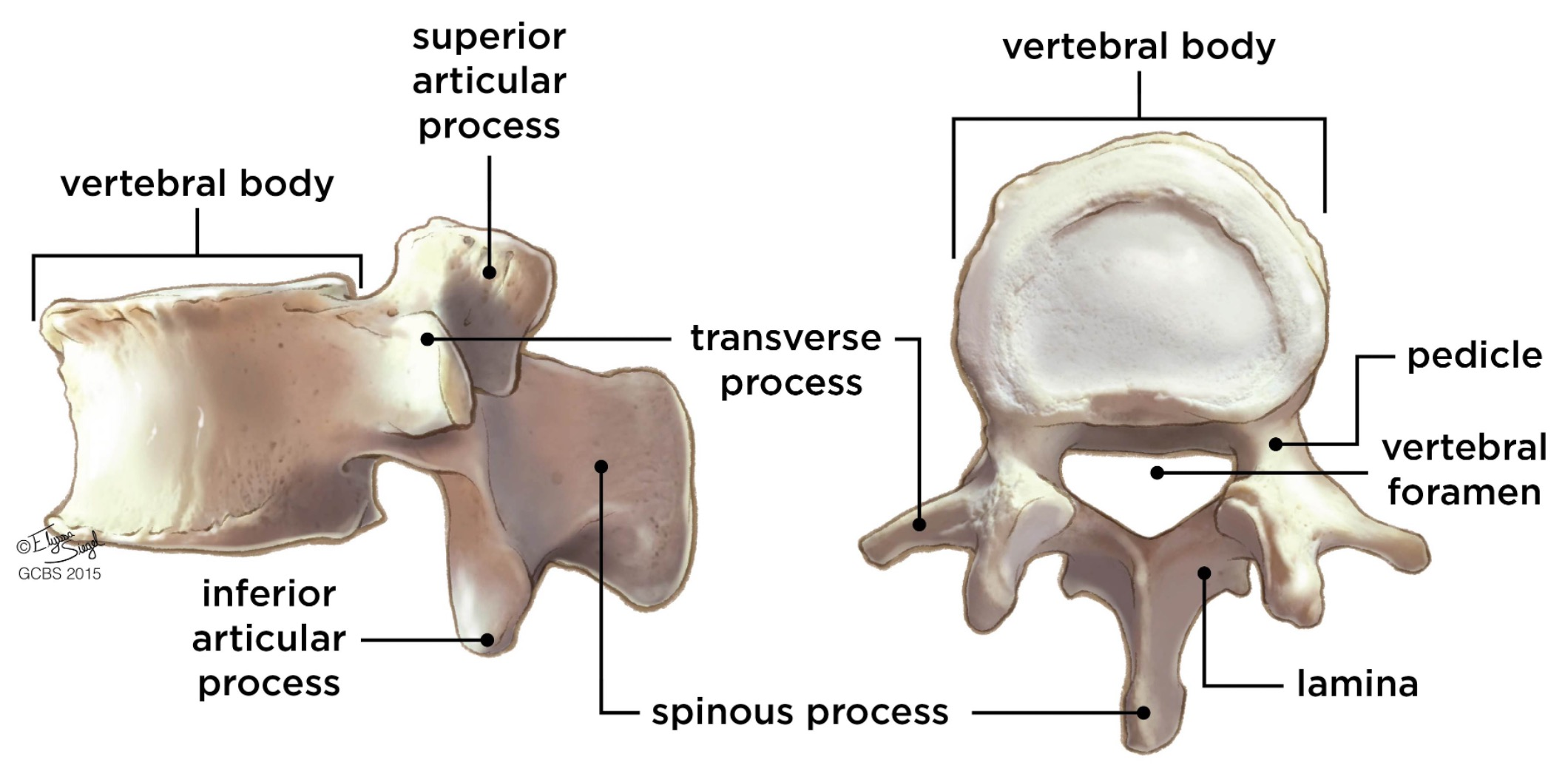
vertebral body
weight bearing
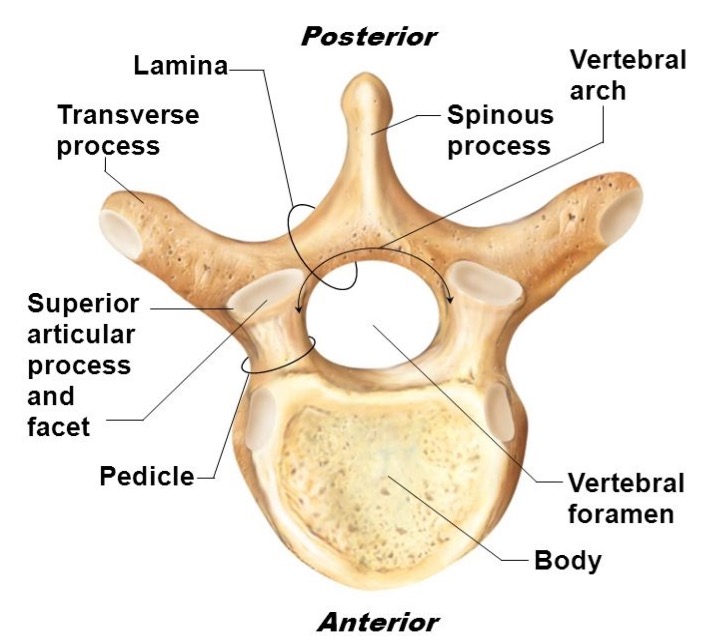
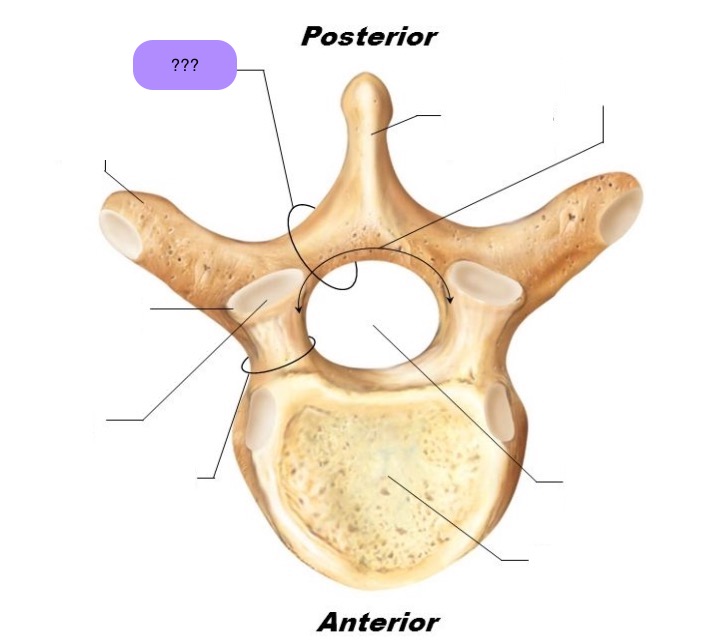
lamina
connects spinous and transverse processes
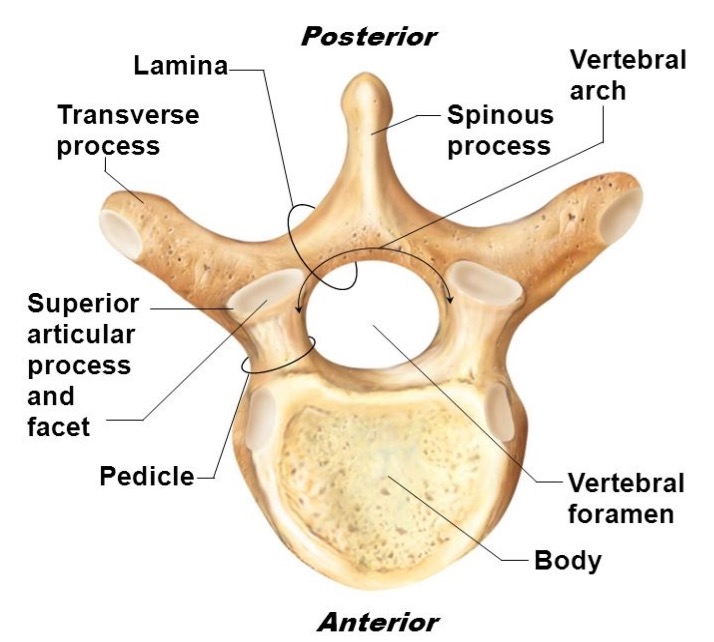
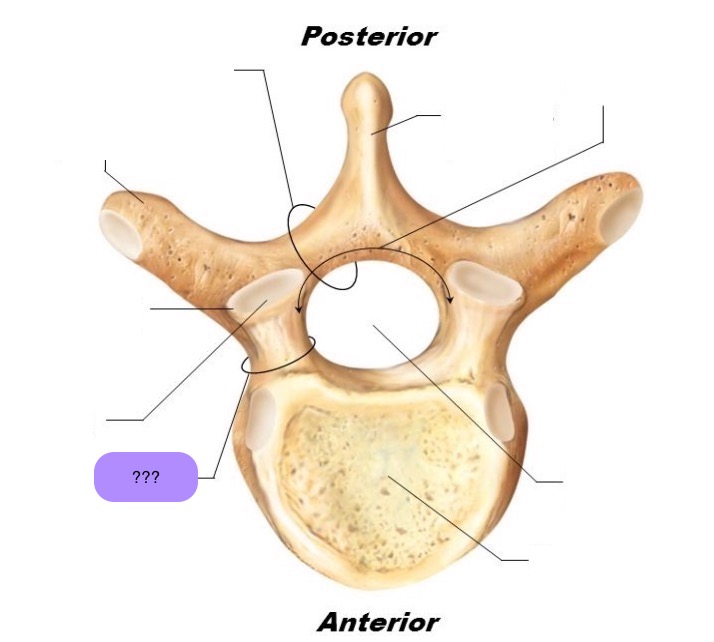
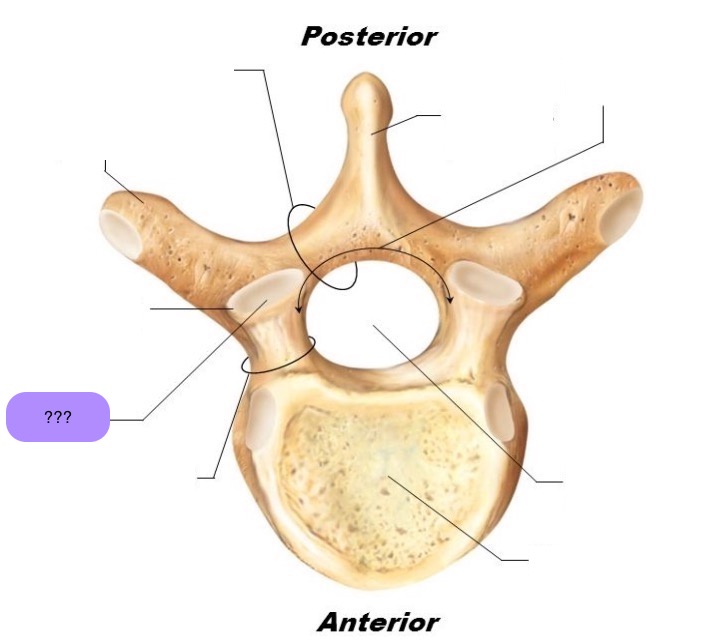
pedicle
bony pillars attaching arch to body
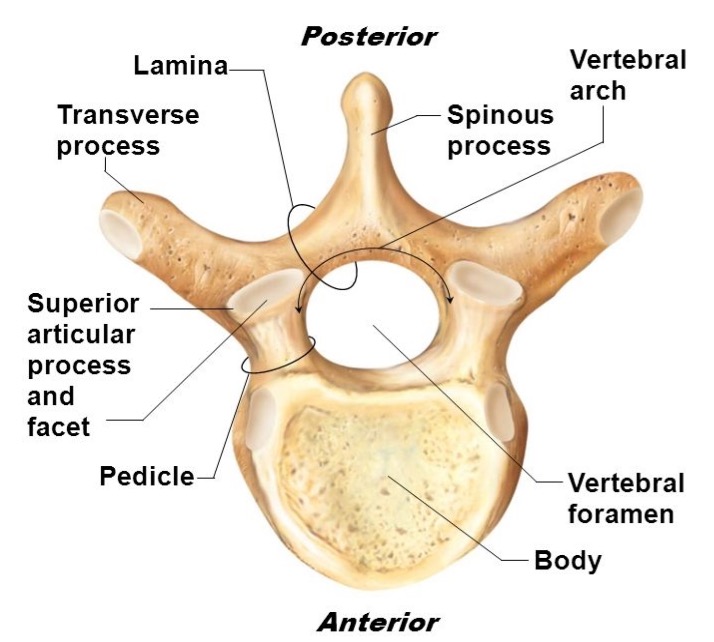
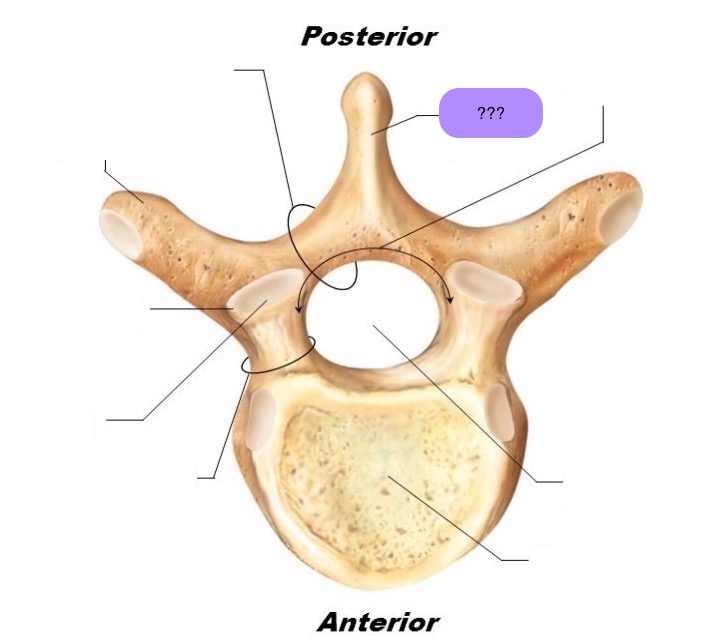
spinous process
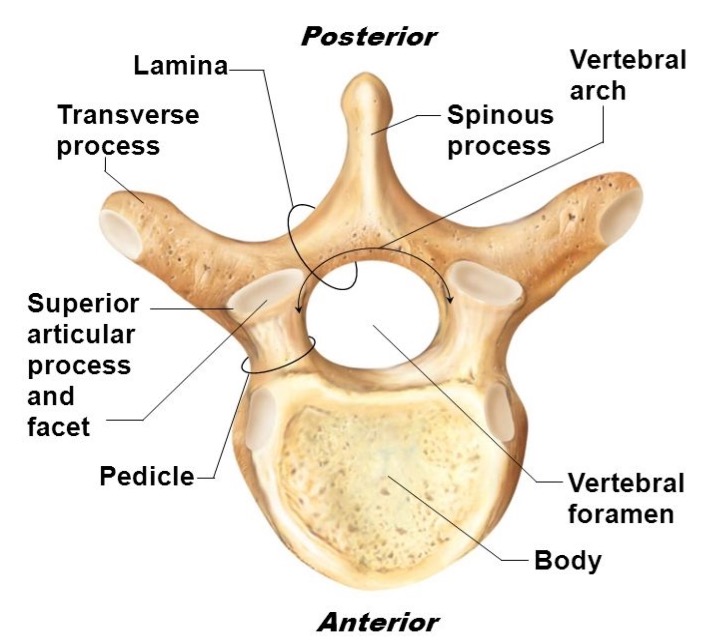
superior articular facet
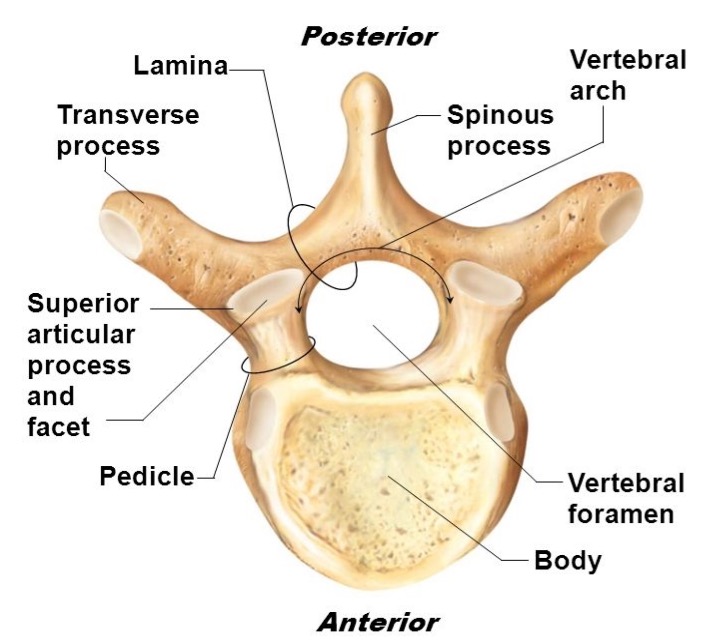
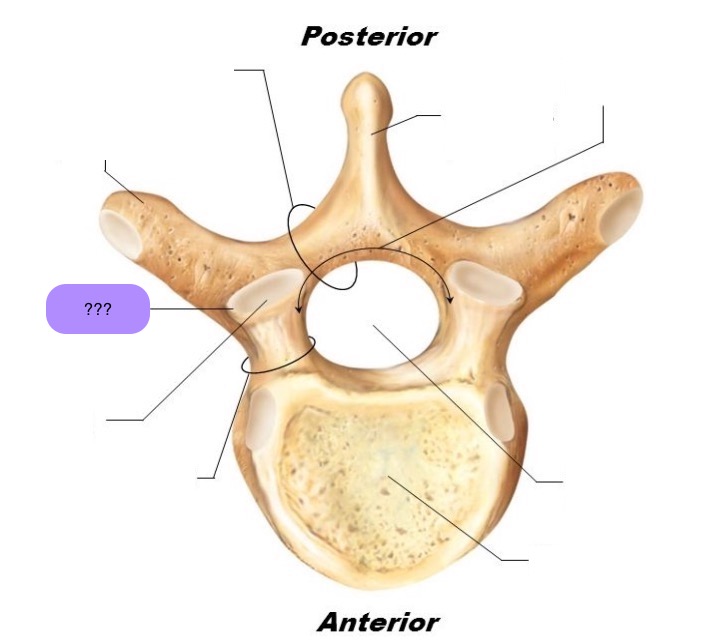
superior articular process
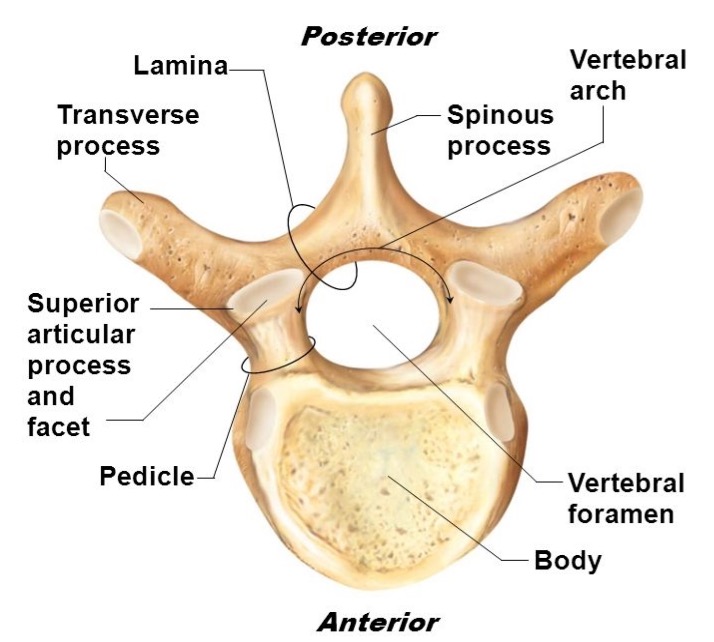
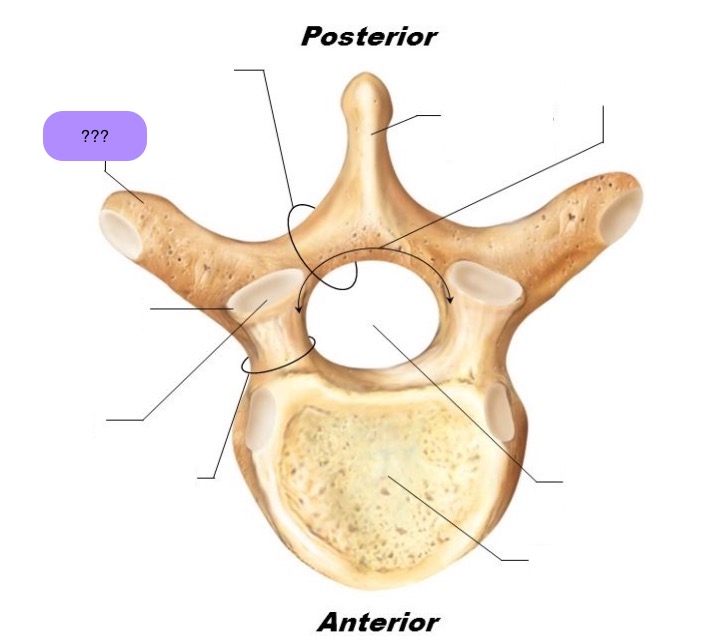
transverse process
lateral/posterior projection
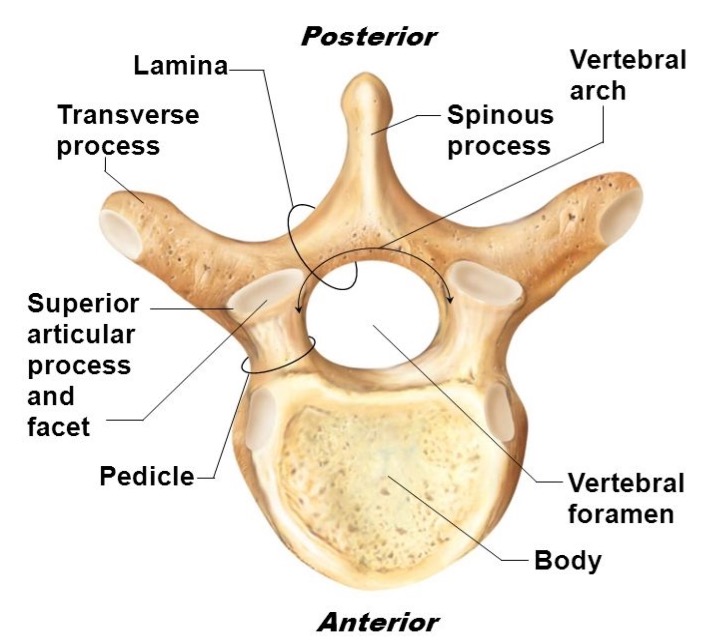
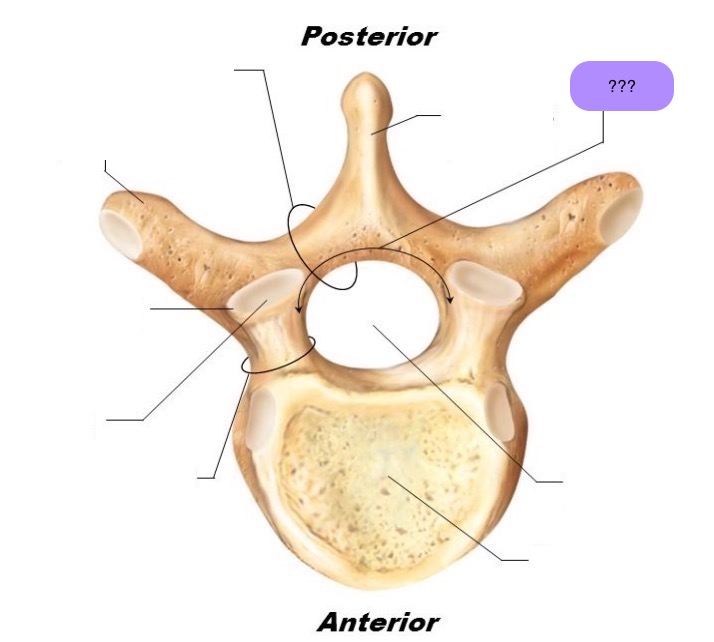
vertebral arch
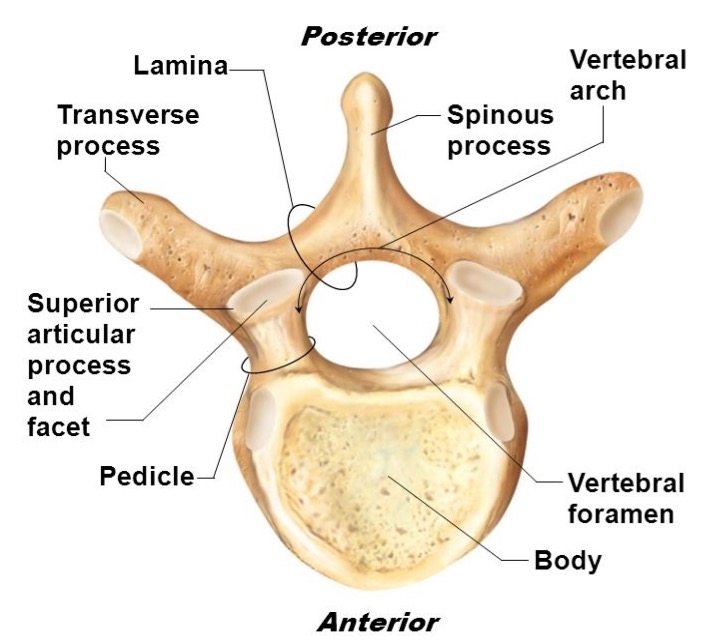
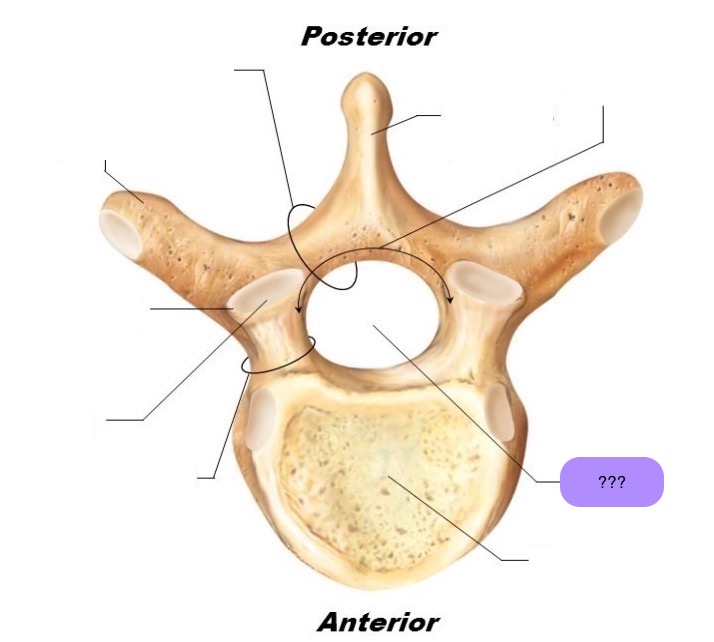
vertebral foramen (spinal canal)
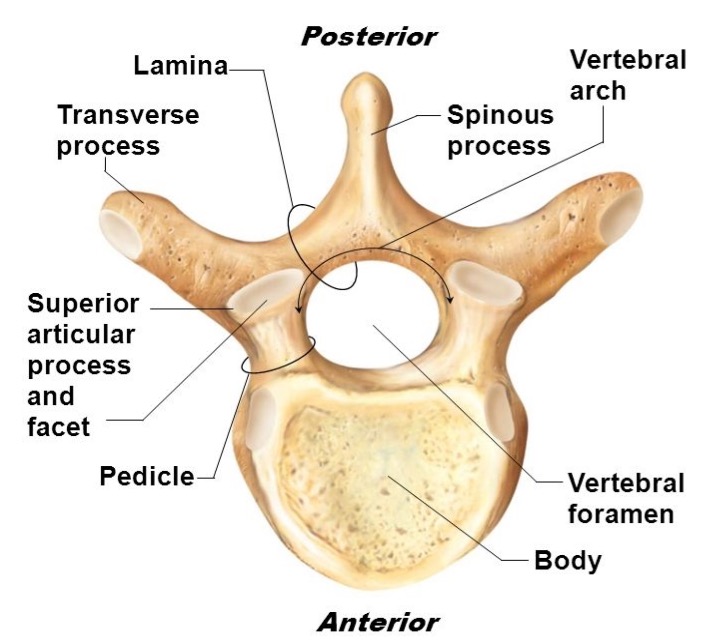
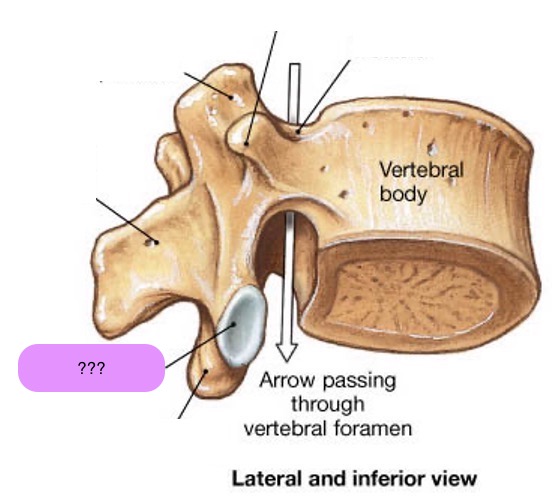
inferior articular facet
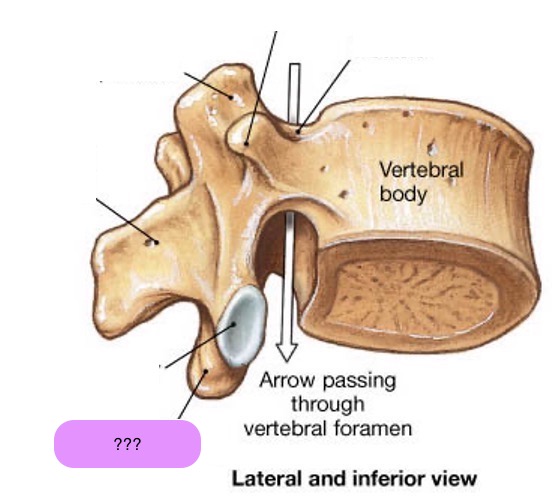
inferior articular process
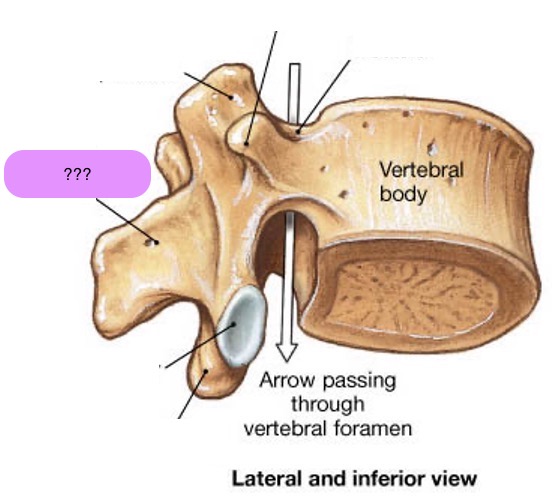
spinous process
posterior projection
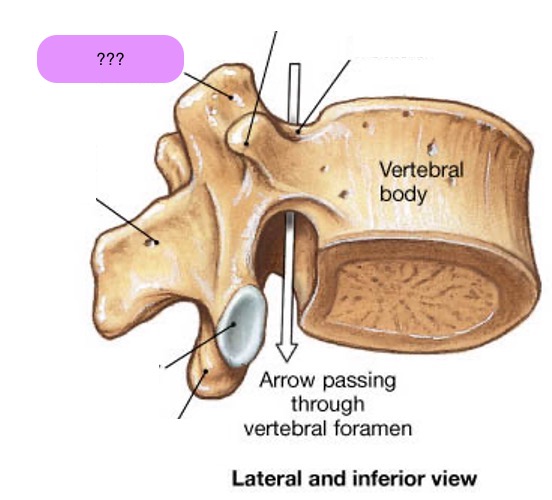
superior articular process
transverse process
lateral/posterior projection
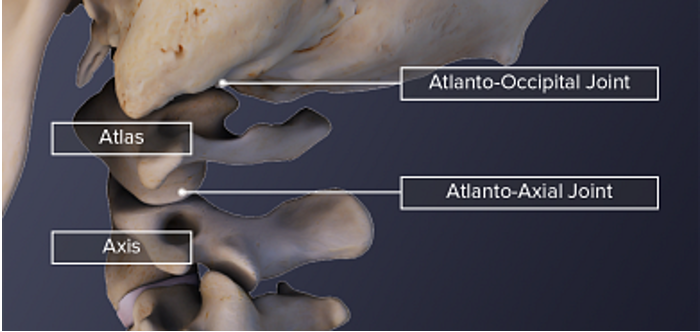
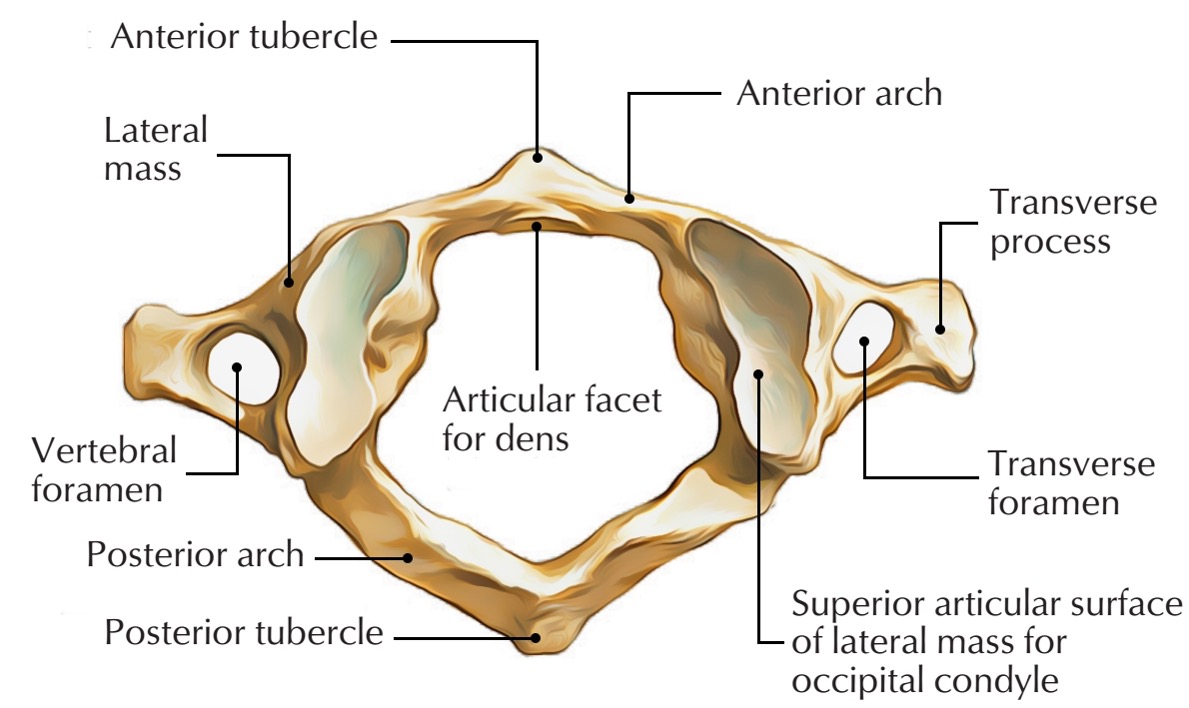
atlas vertebra
C1 (cervical 1)
no vertebral body
no spinous process
has a vertebral foramen for vertebral artery
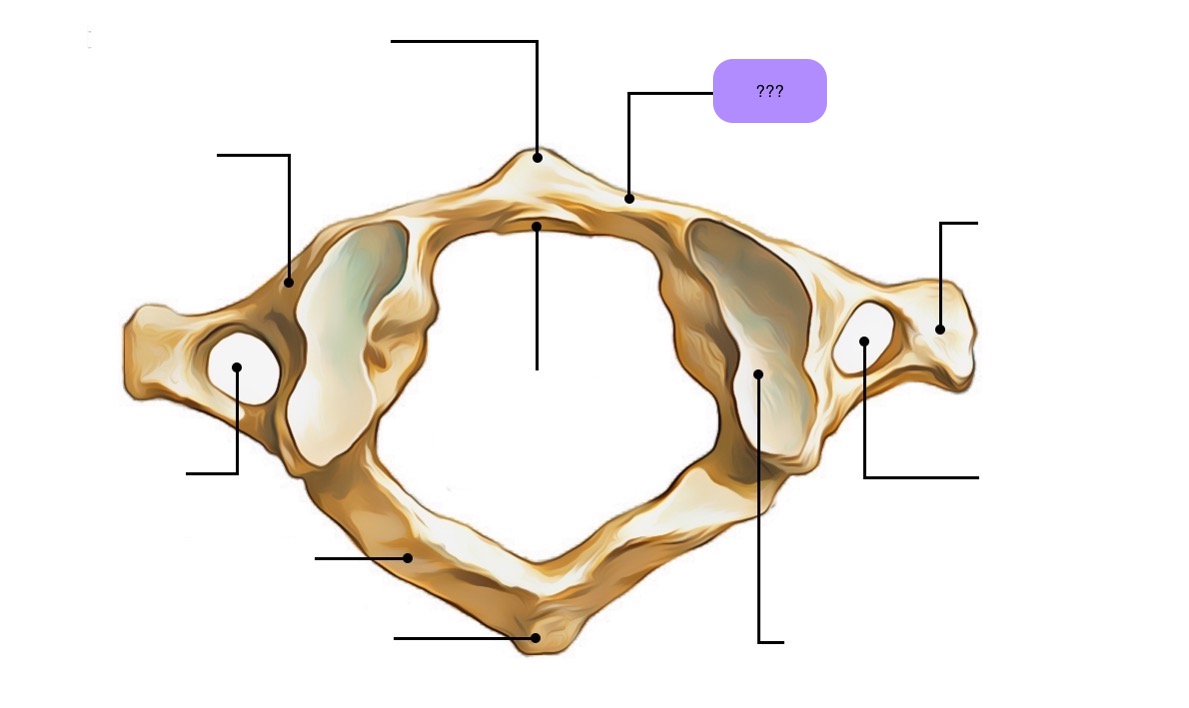
anterior arch (C1)
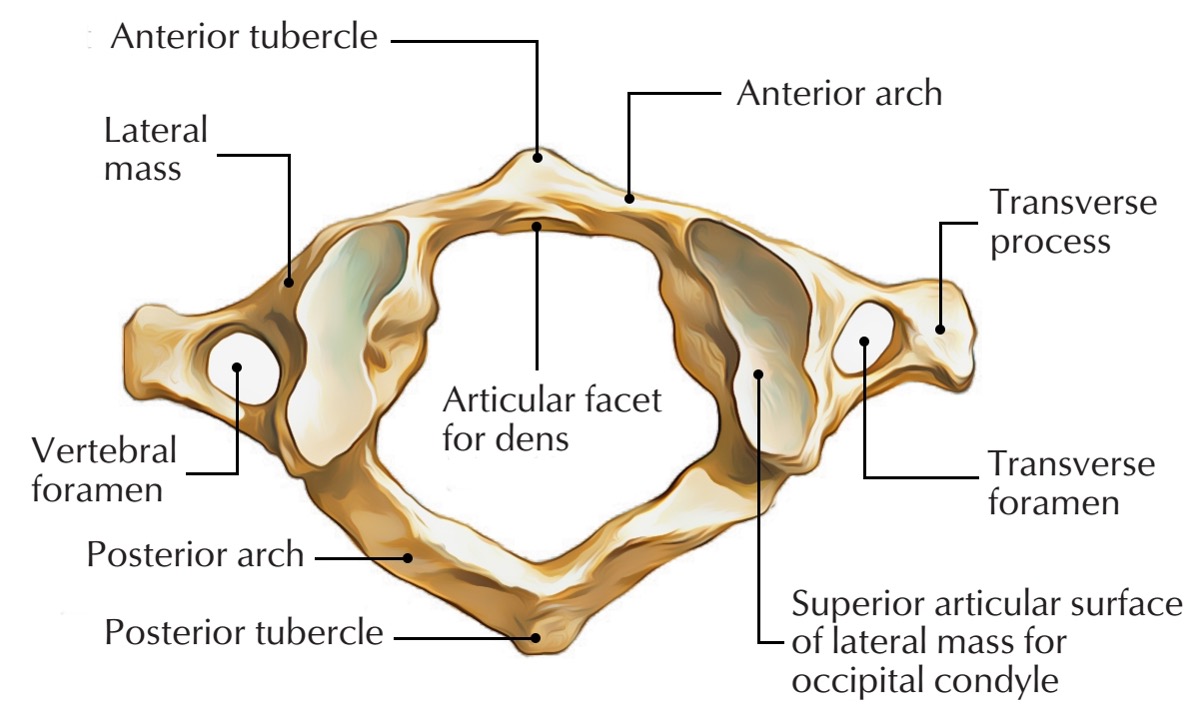
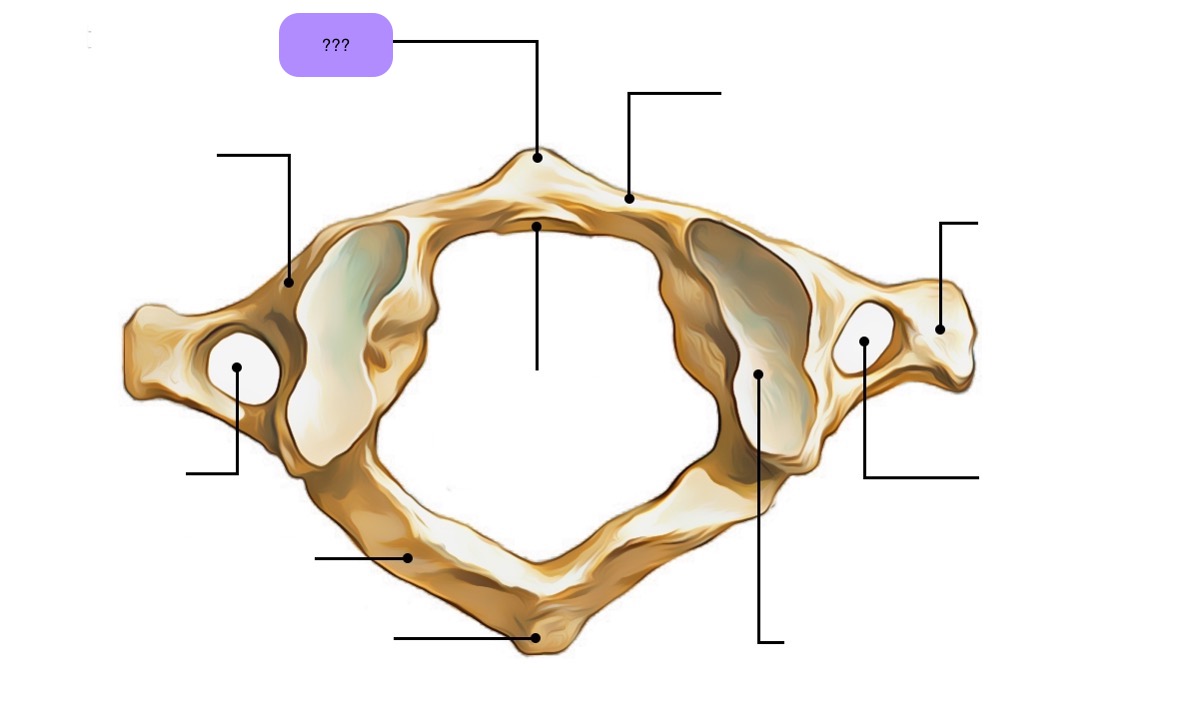
anterior tubercle (C1)
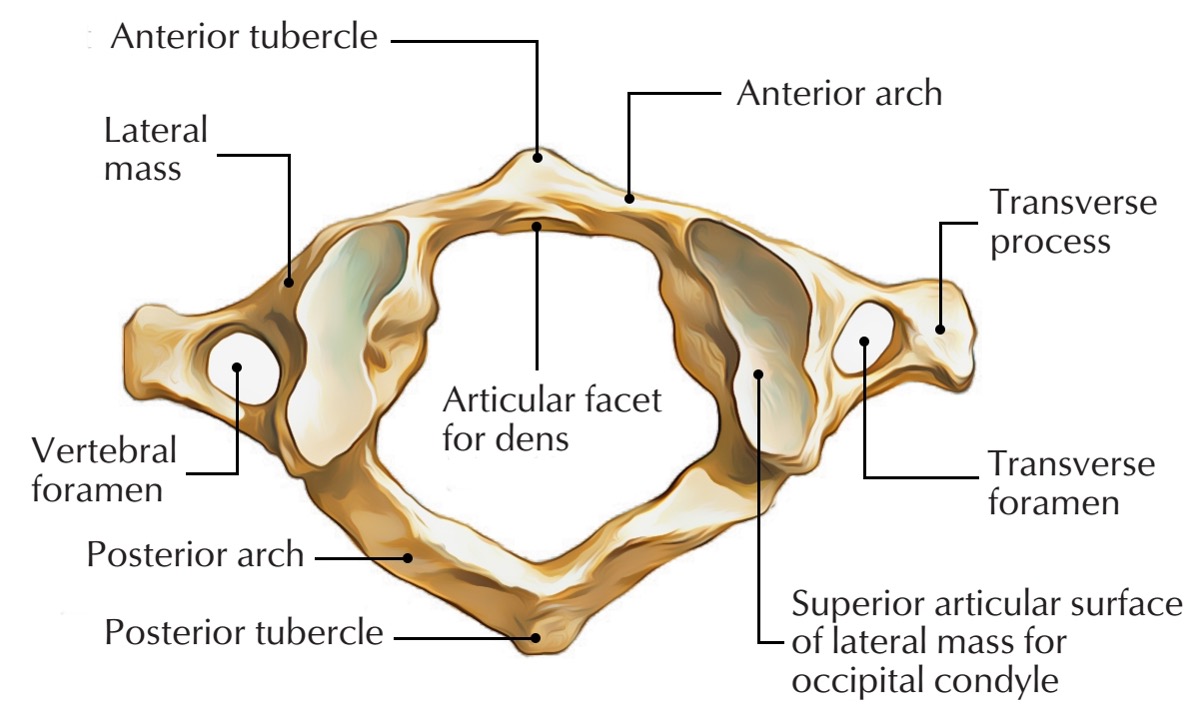
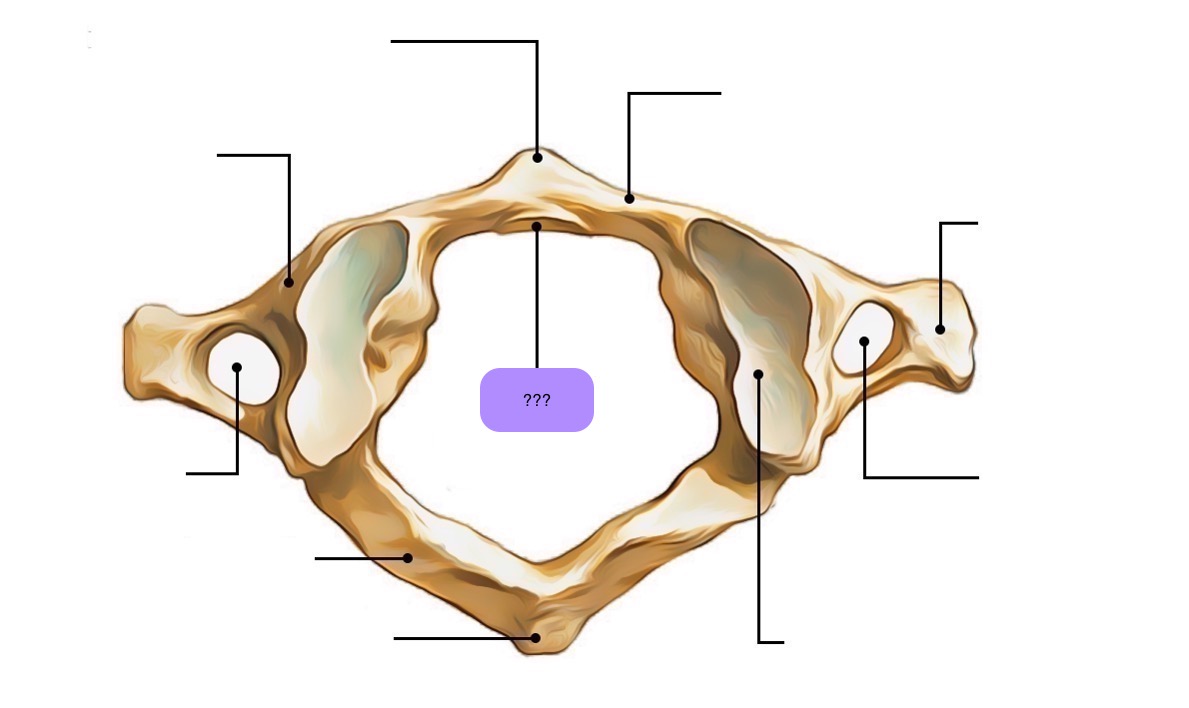
articular facet for dens (C1)
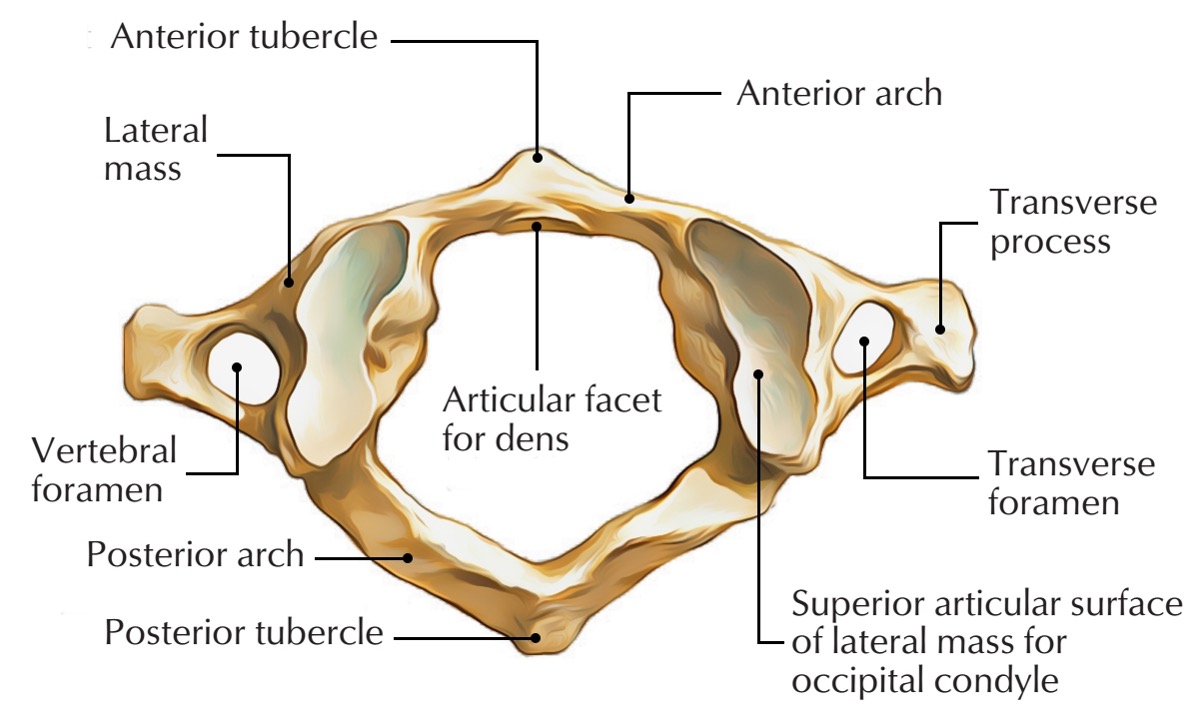
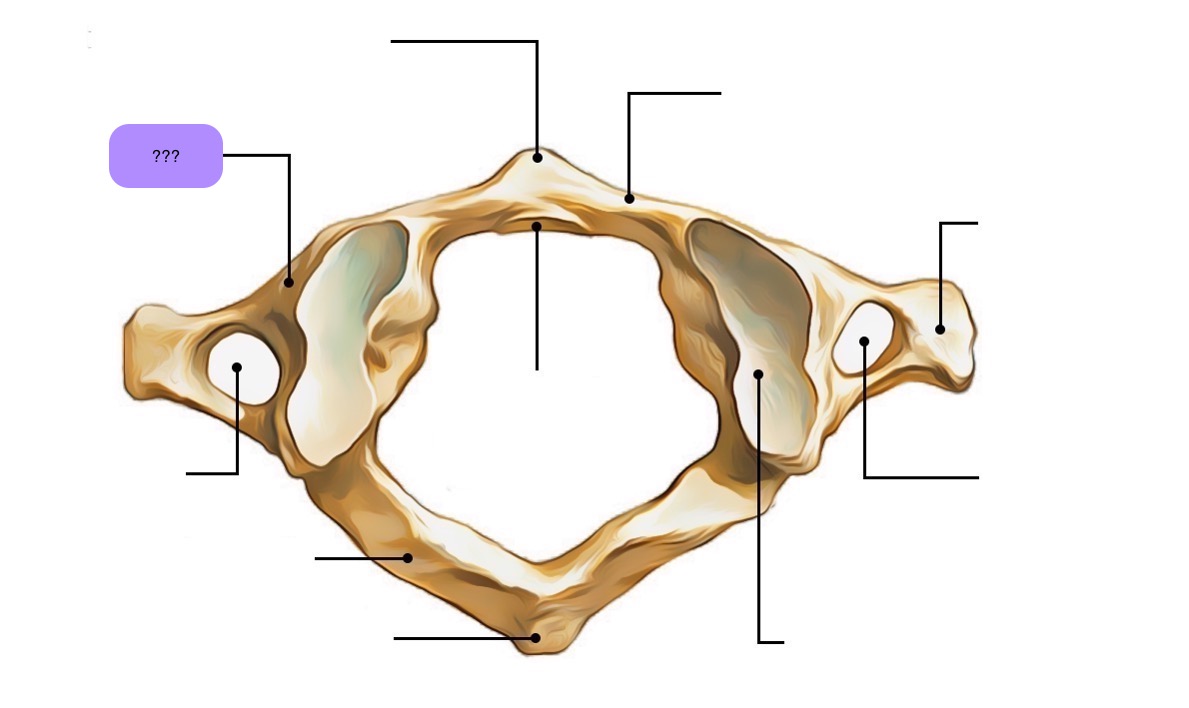
lateral mass
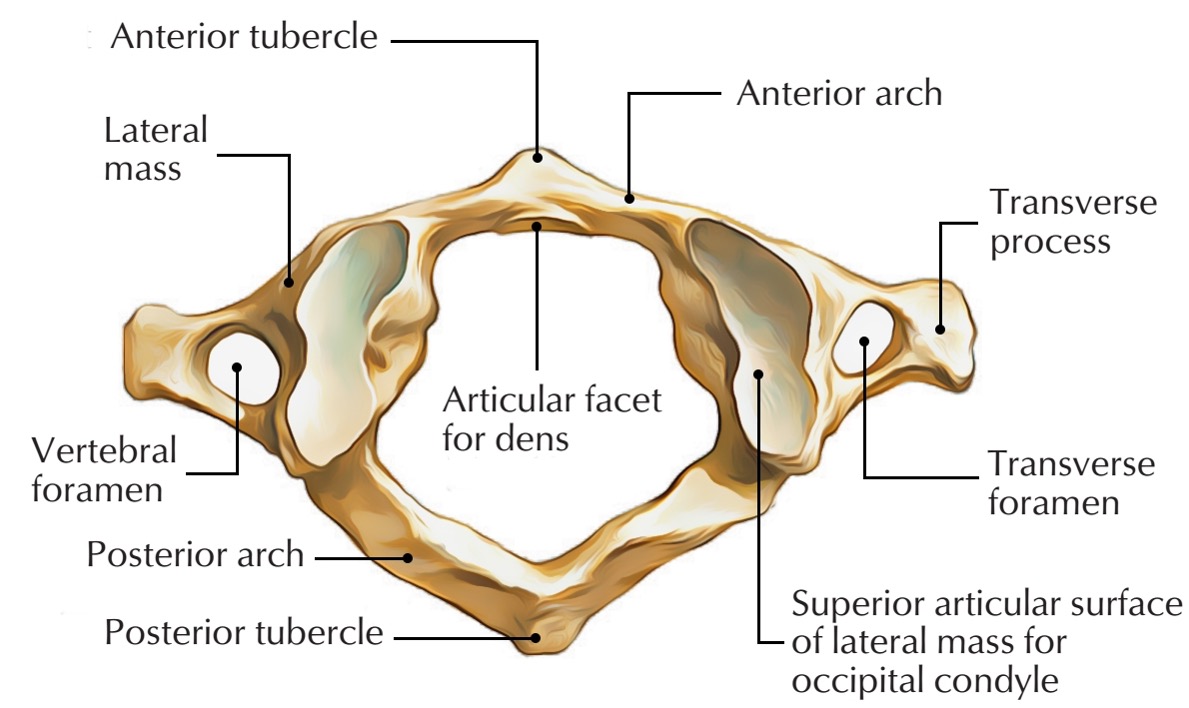
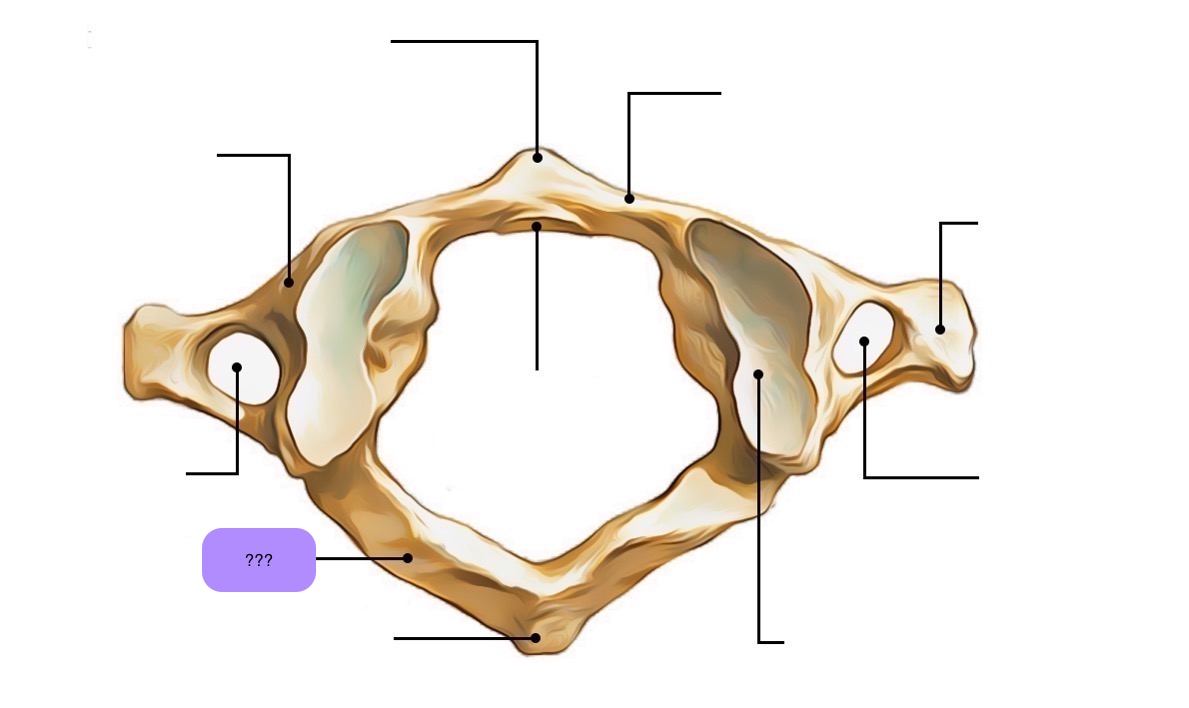
posterior arch (C1)
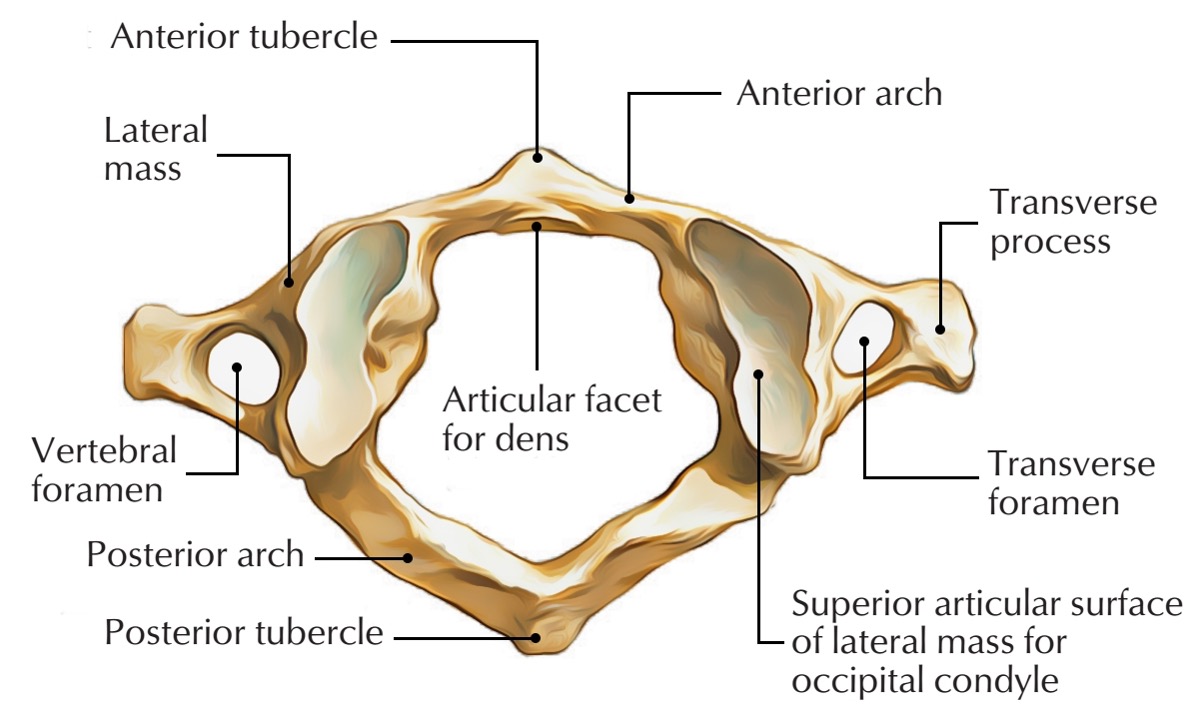
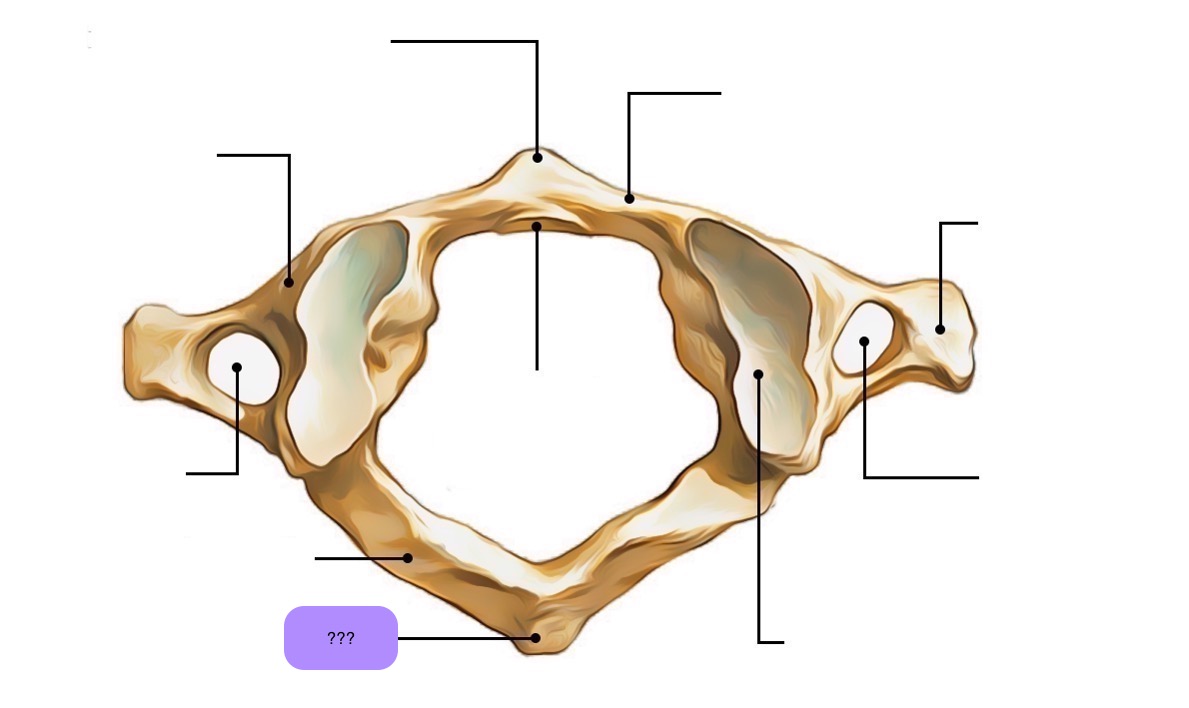
posterior tubercle (C1)
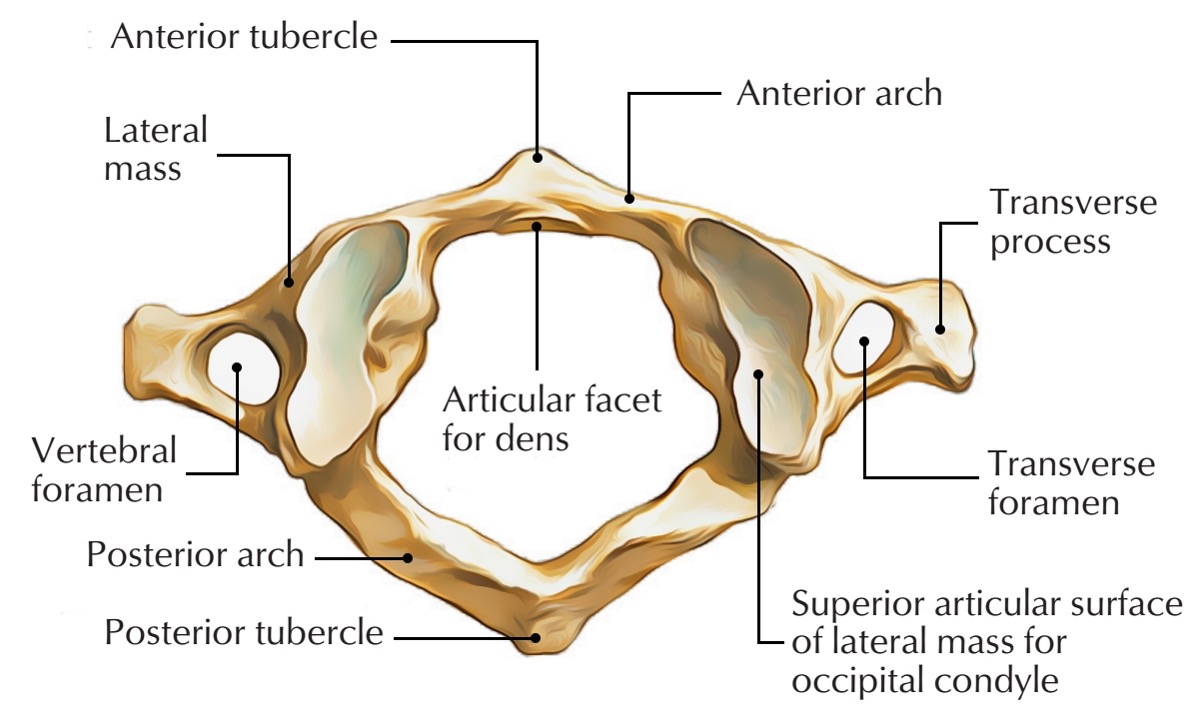
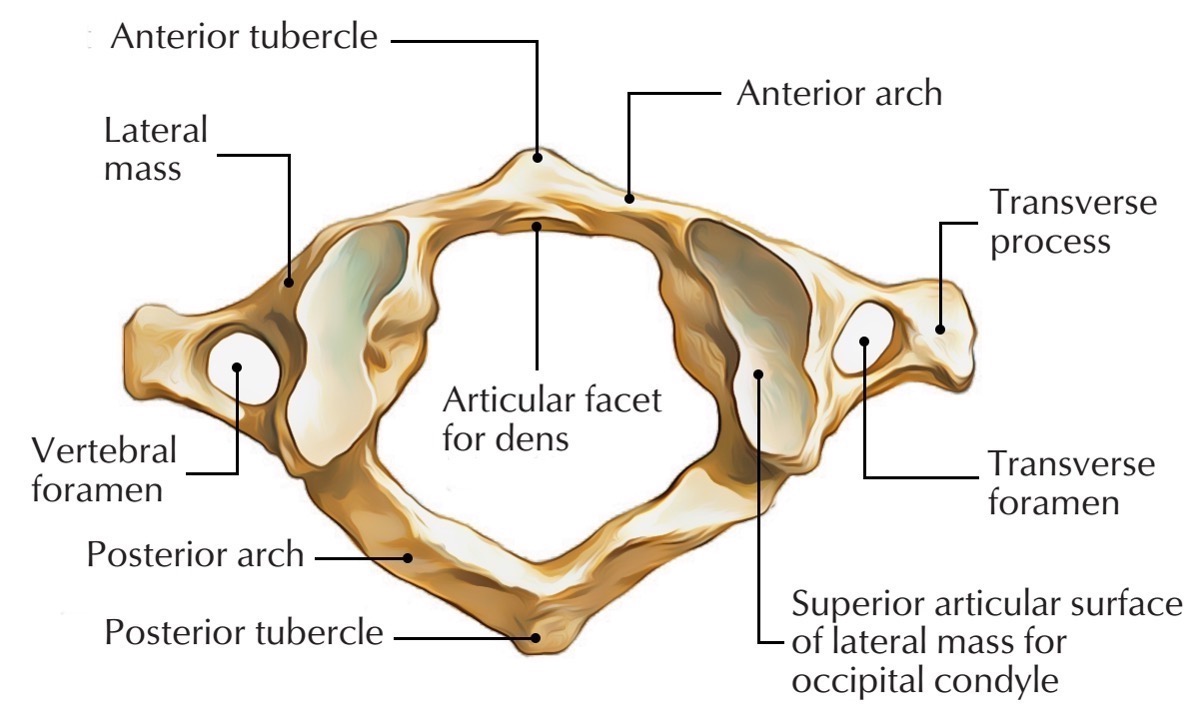
superior articular surface of lateral mass for occipital condyle (C1)
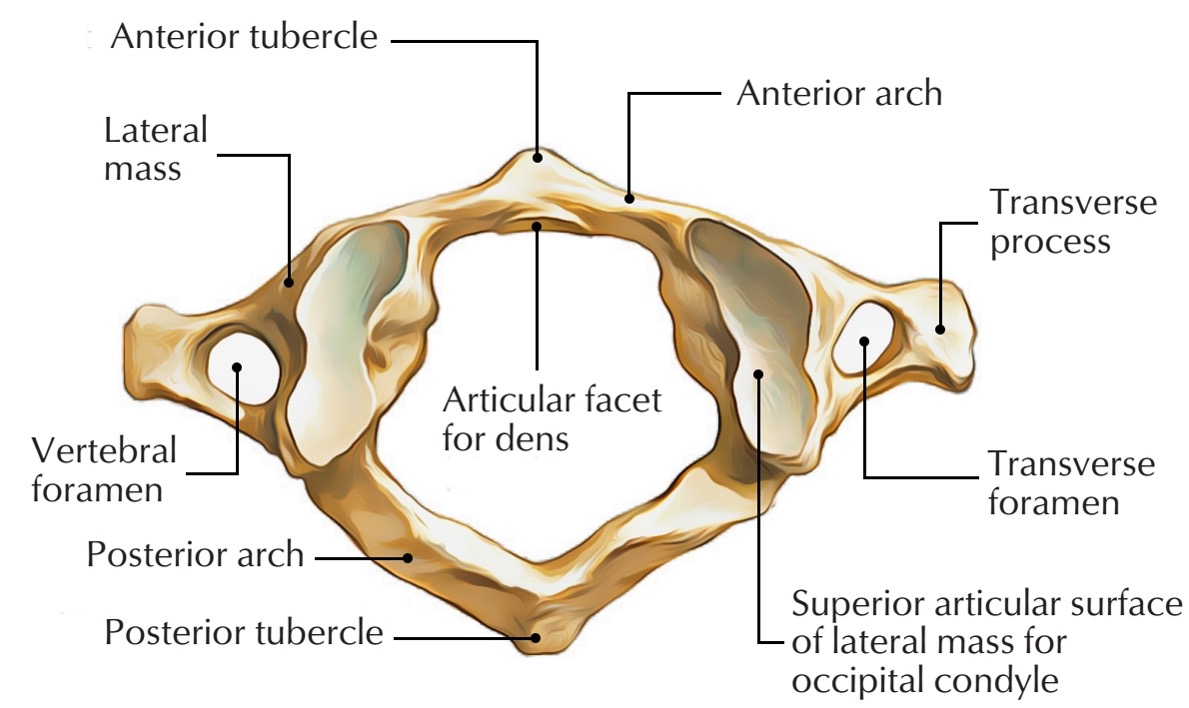
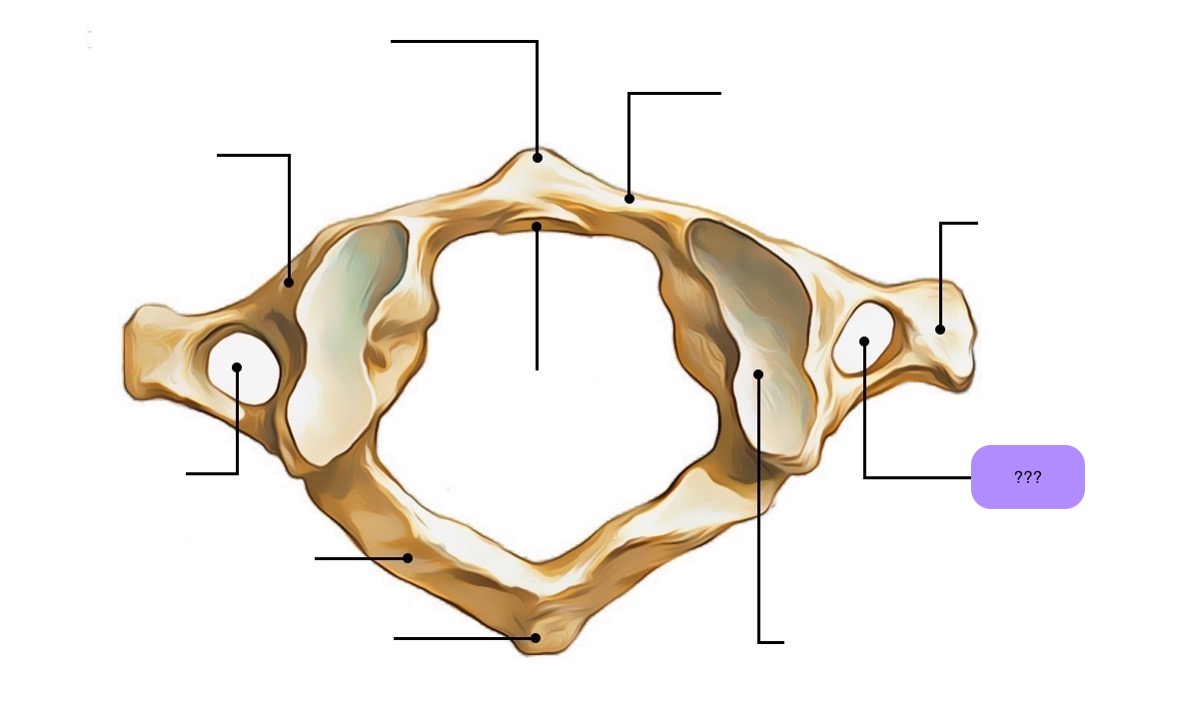
transverse foramen (C1)
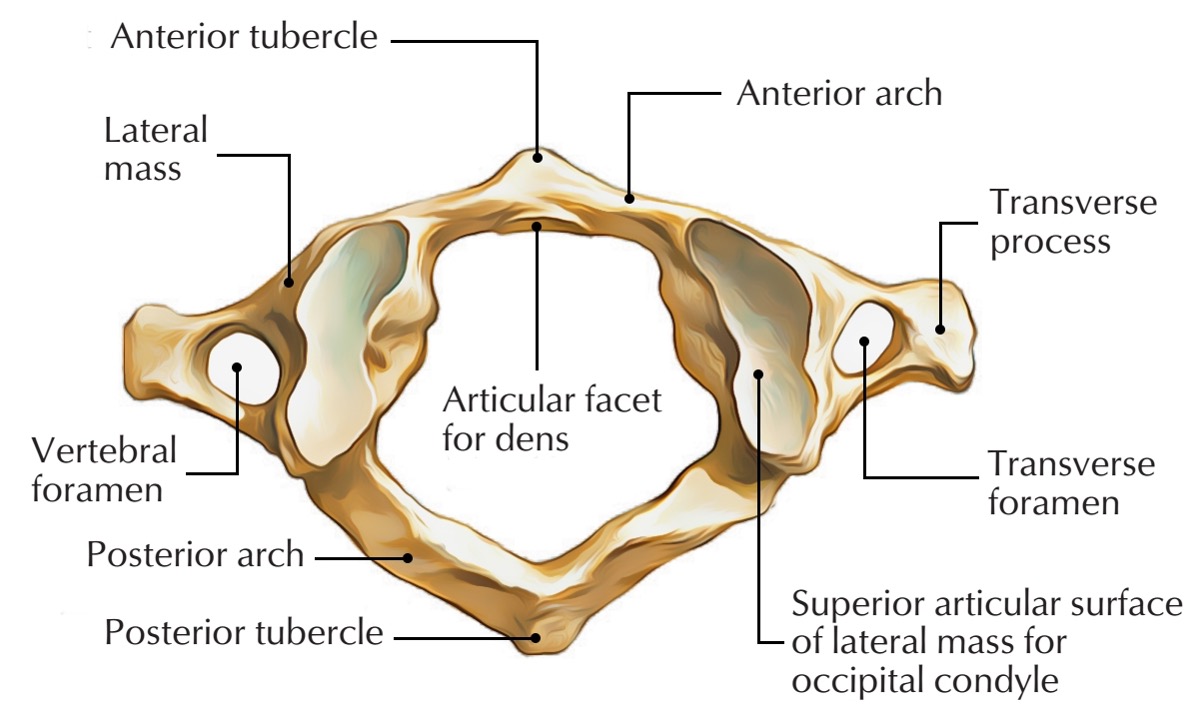
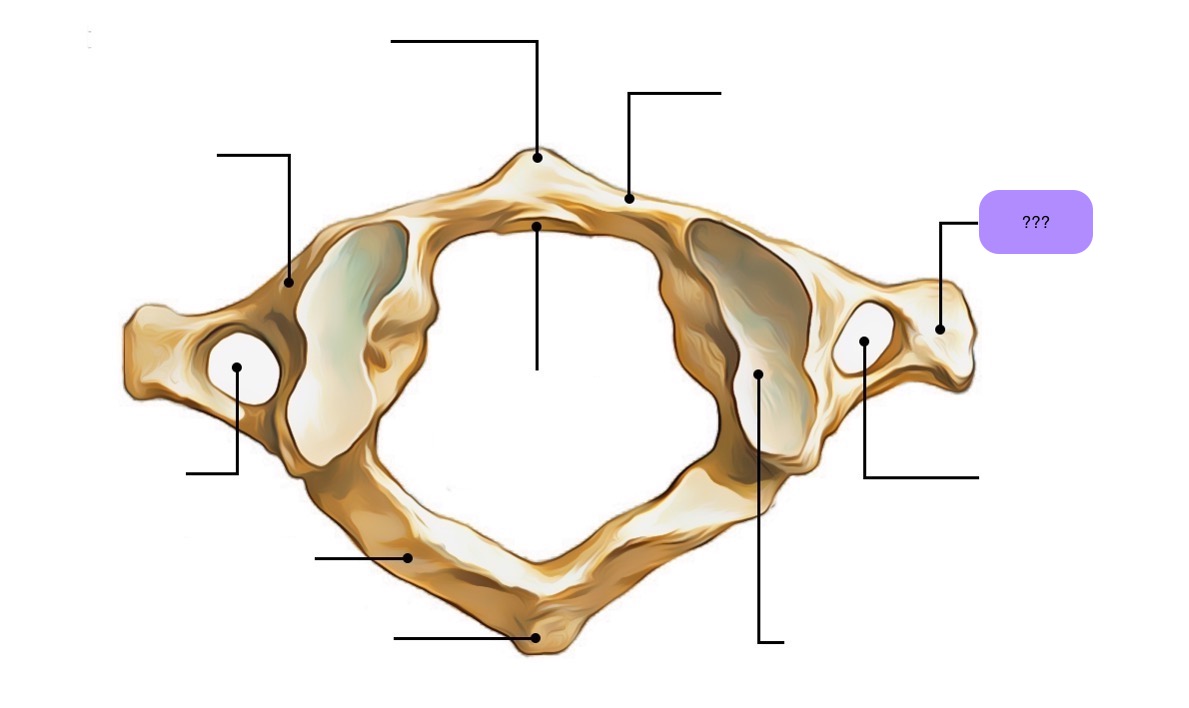
transverse process (C1)
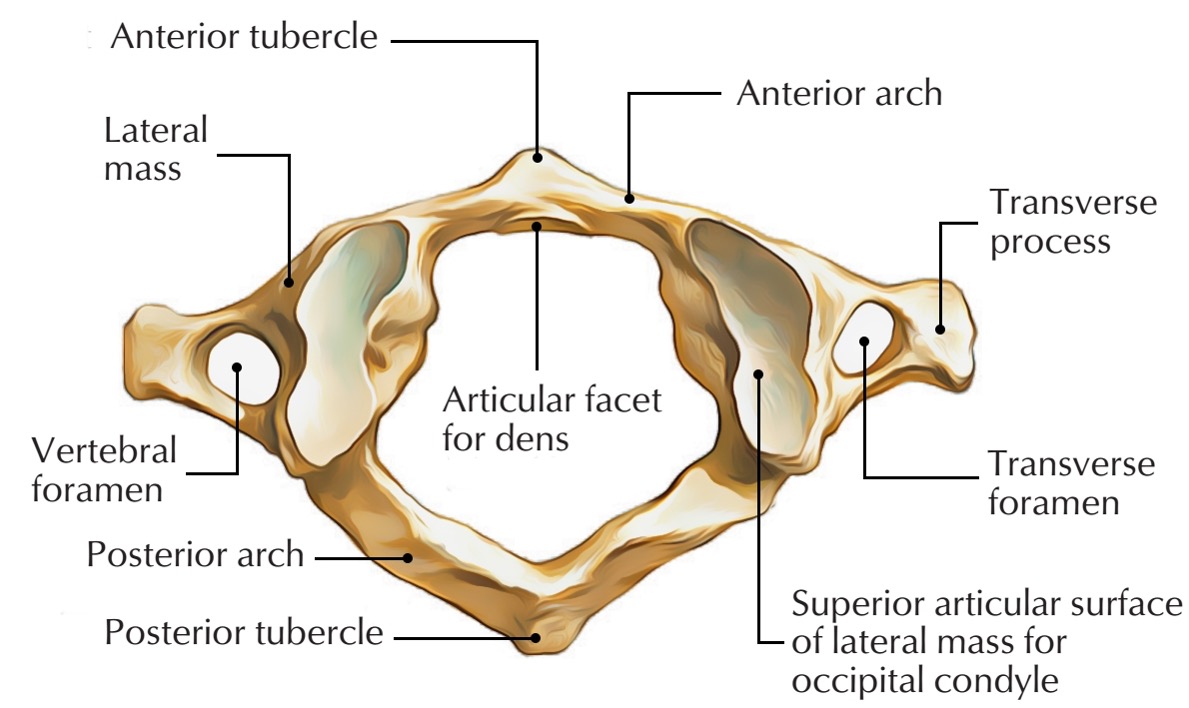
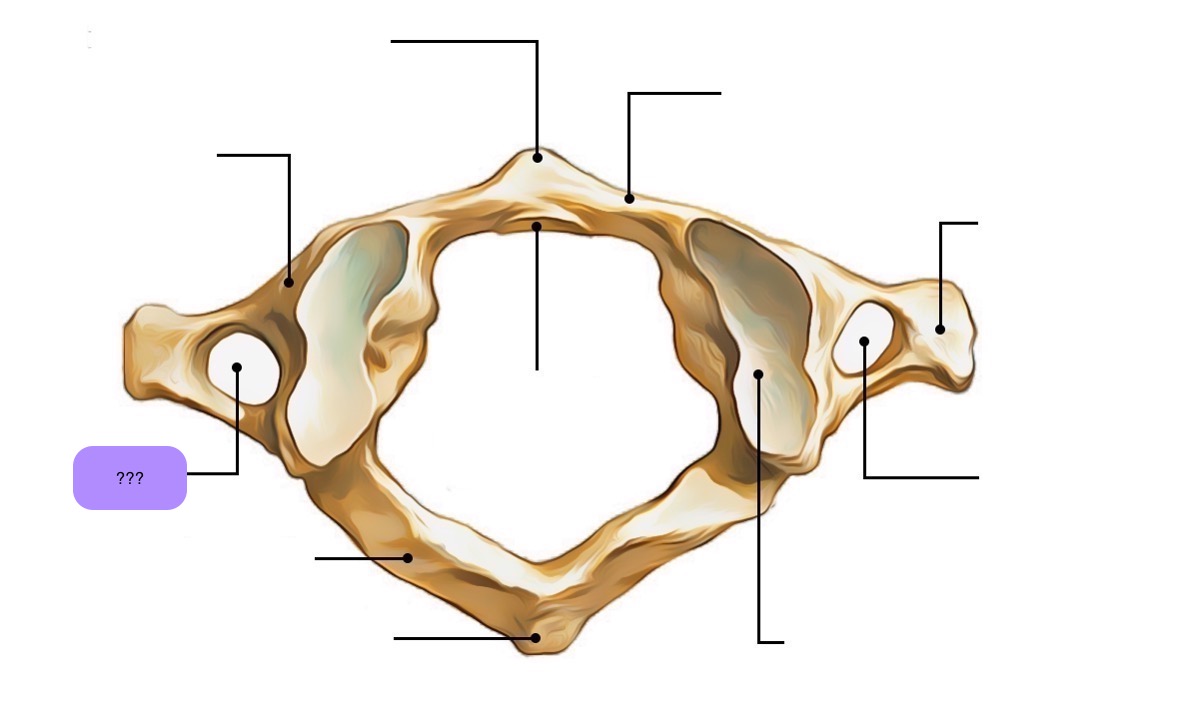
vertebral foramen (C1)
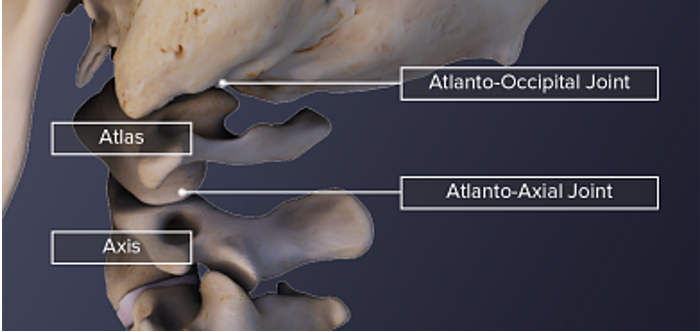
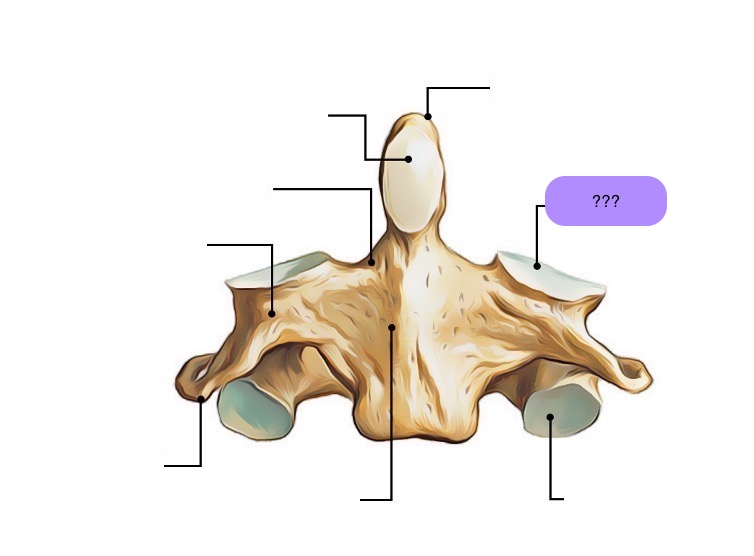
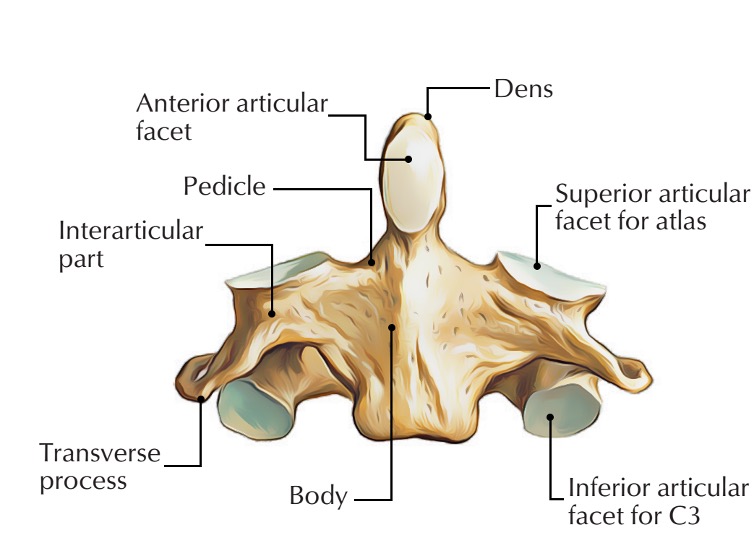
axis vertebra
C2 (cervical 2)
Extended vertebral body
Odontoid process (Dens) extends superiorly
Articulates with atlas
Atlantoaxial joint
Provides an axis (pivot) for atlas
No intervertebral disc between C1 & C2
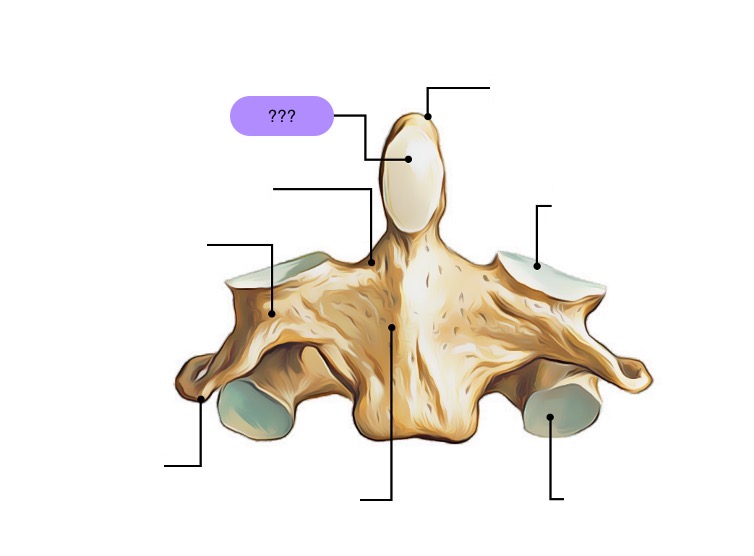
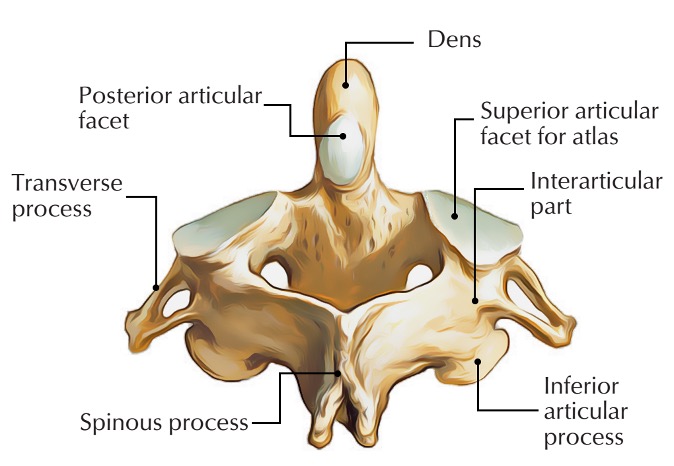
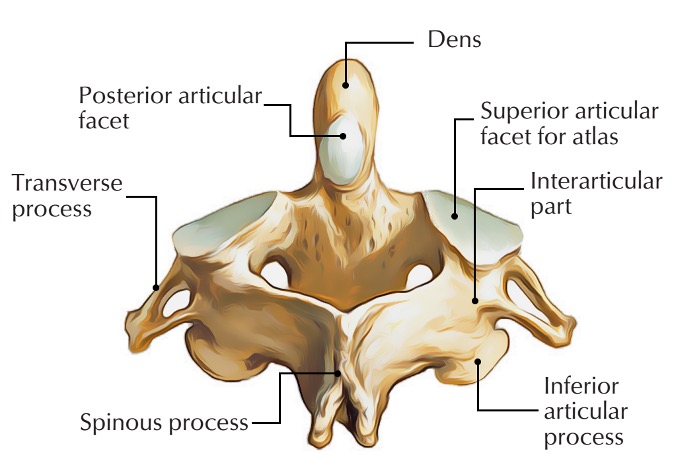
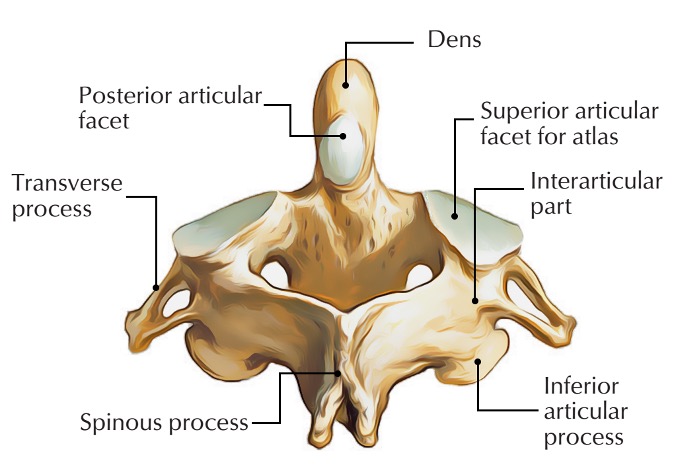
anterior articular facet (C2)
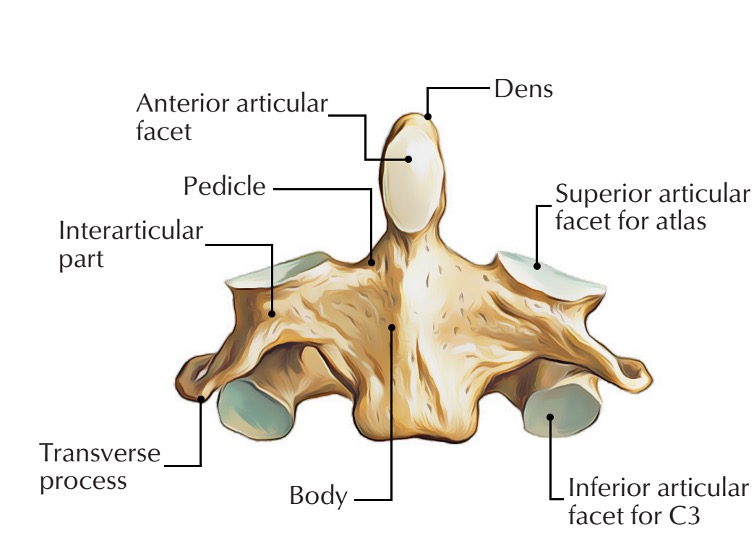
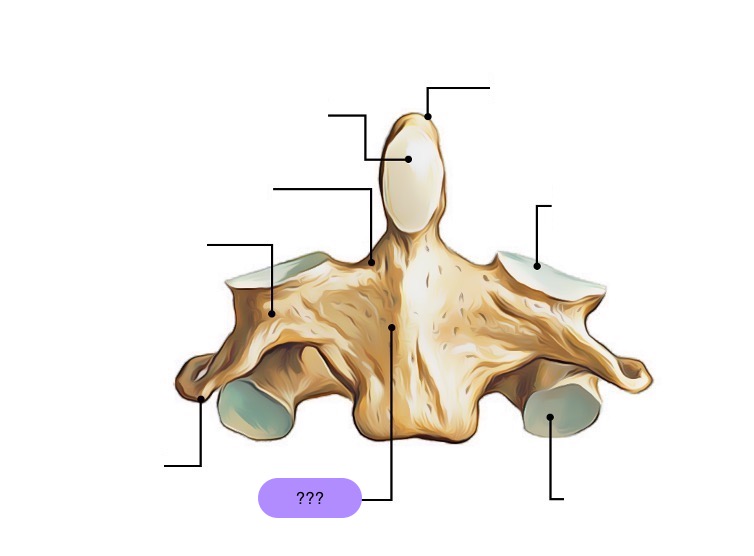
vertebral body (C2)
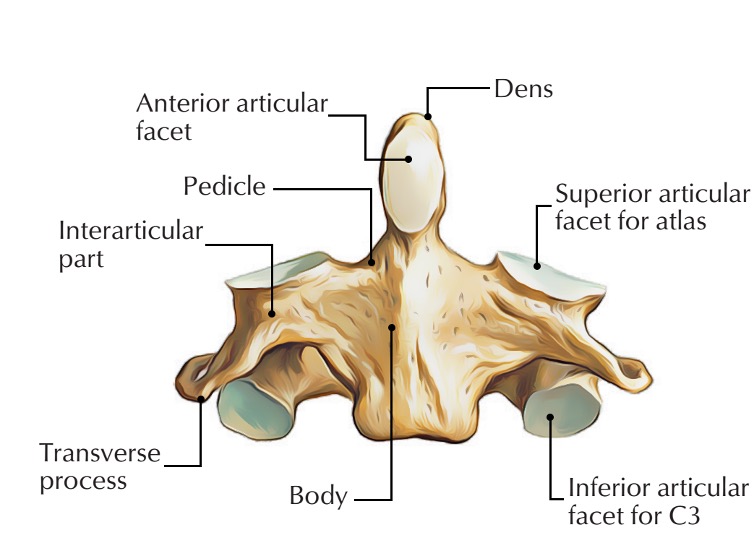
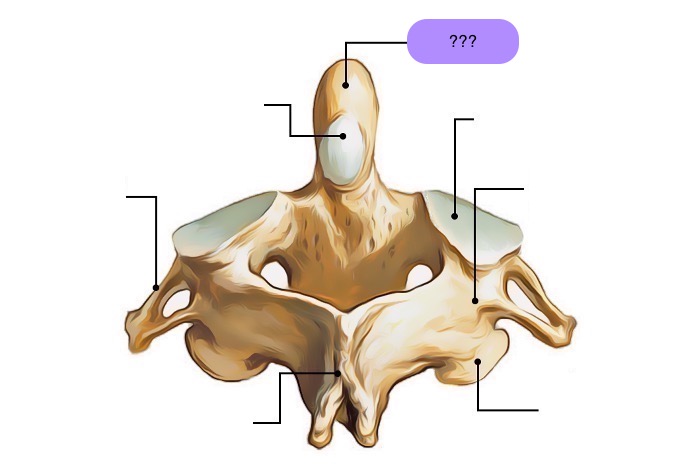
dens (C2)
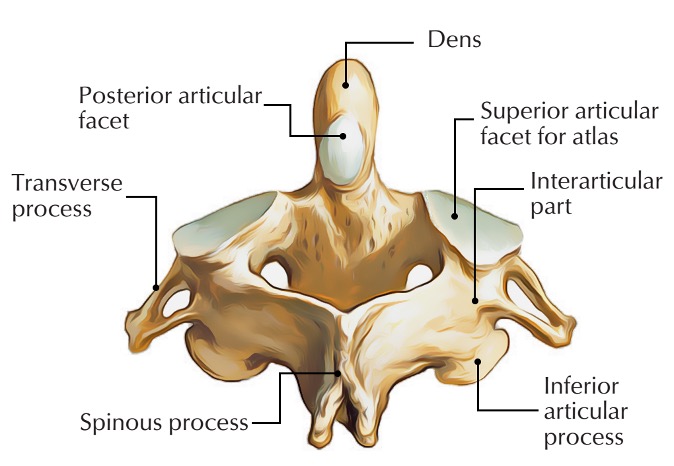
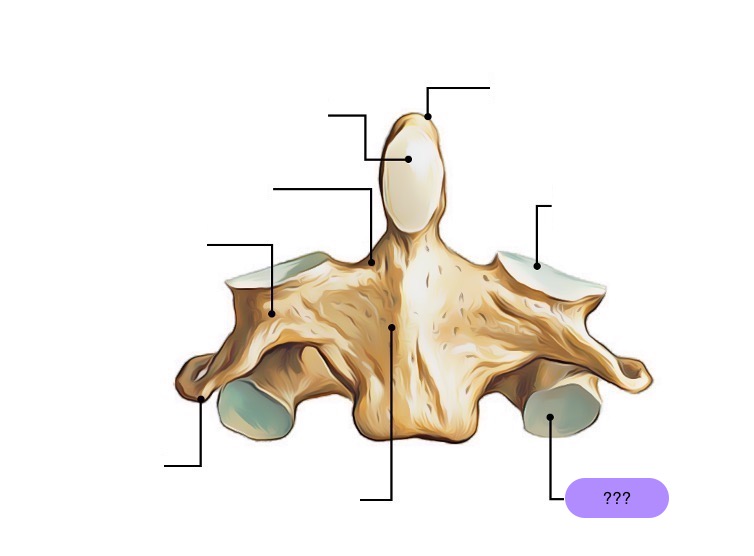
inferior articular facet (C2)
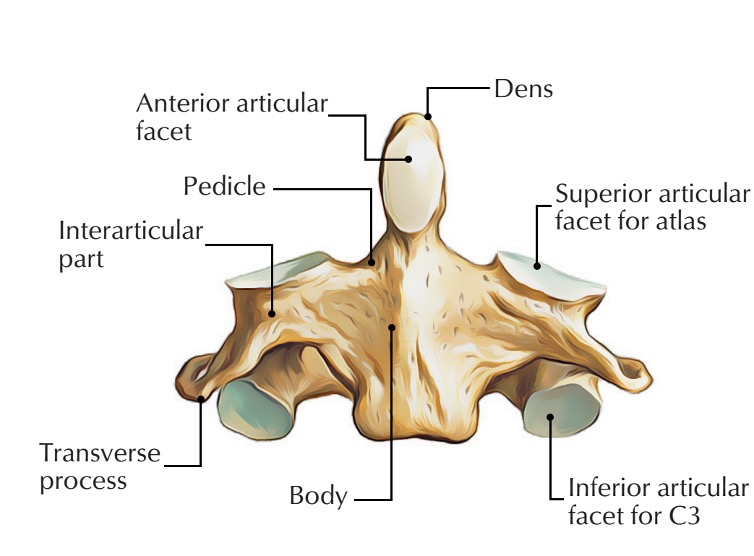
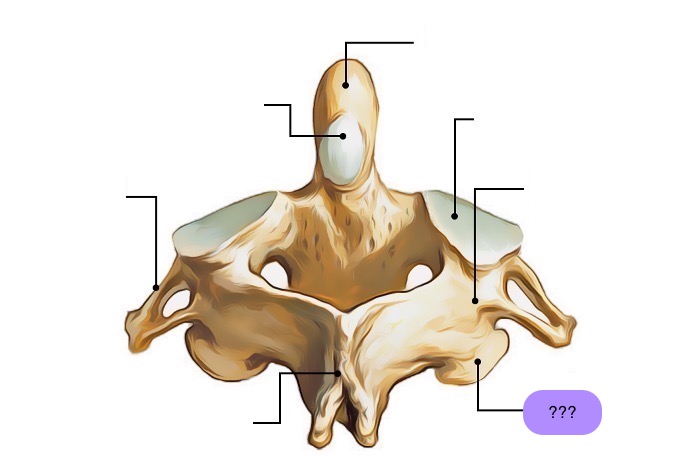
inferior articular process (C2)
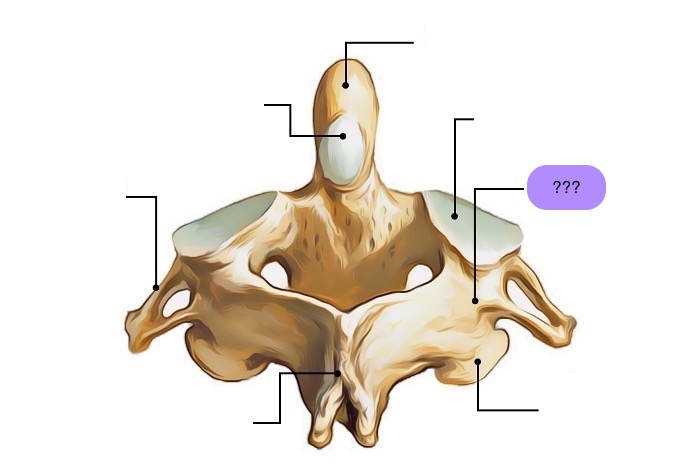
interarticular part (C2)
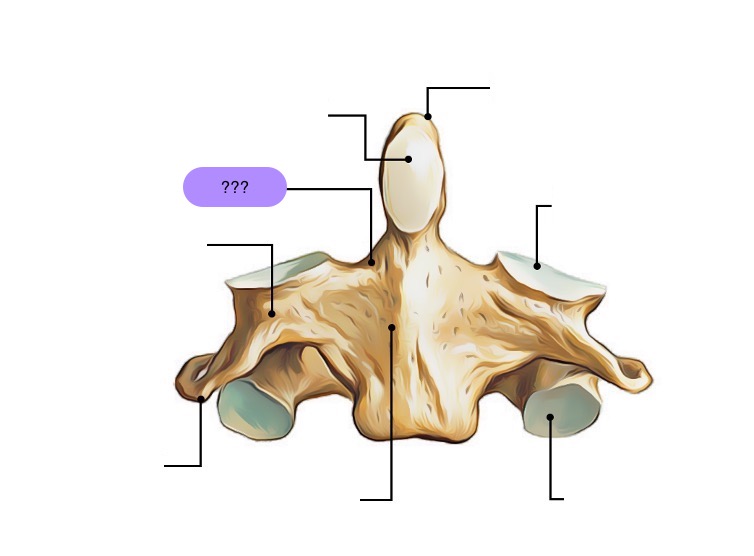
pedicle (C2)
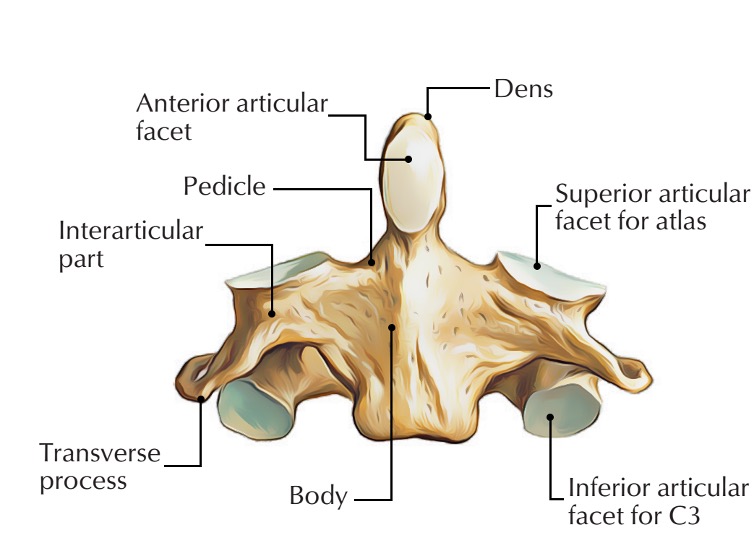
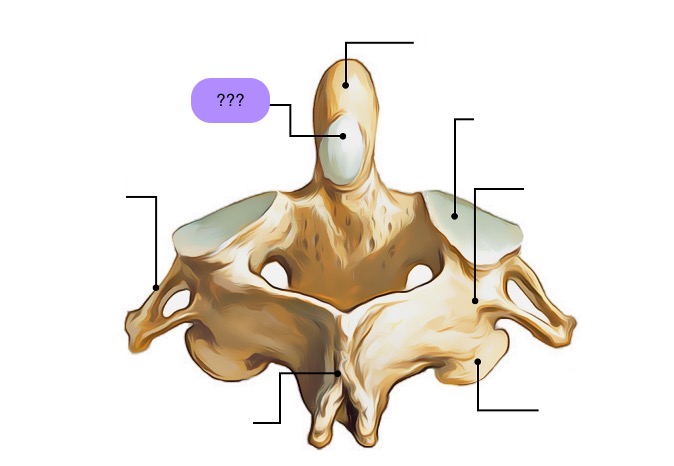
posterior articular facet (C2)
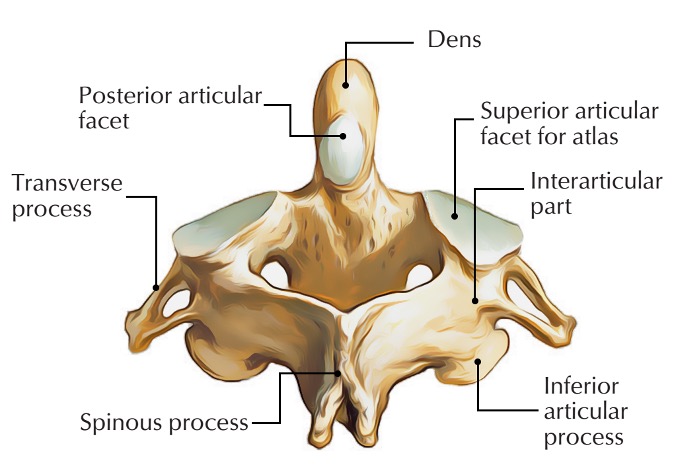
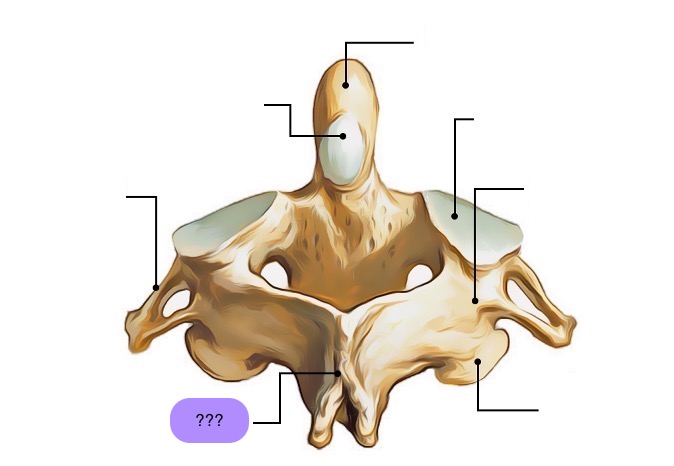
spinous process (C2)
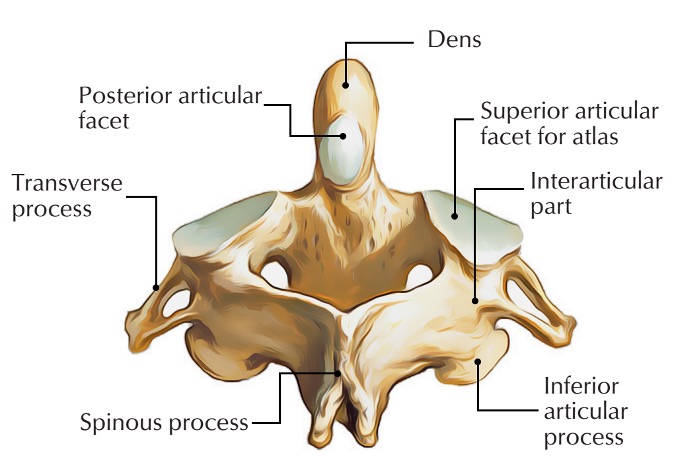
superior articular facet (C2)
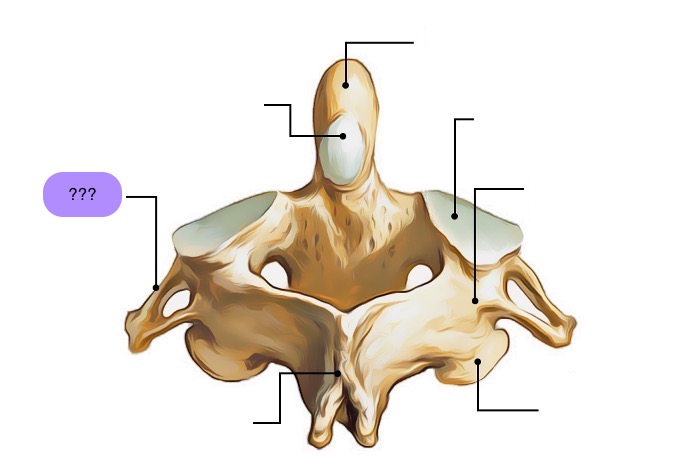
transverse process (C2)
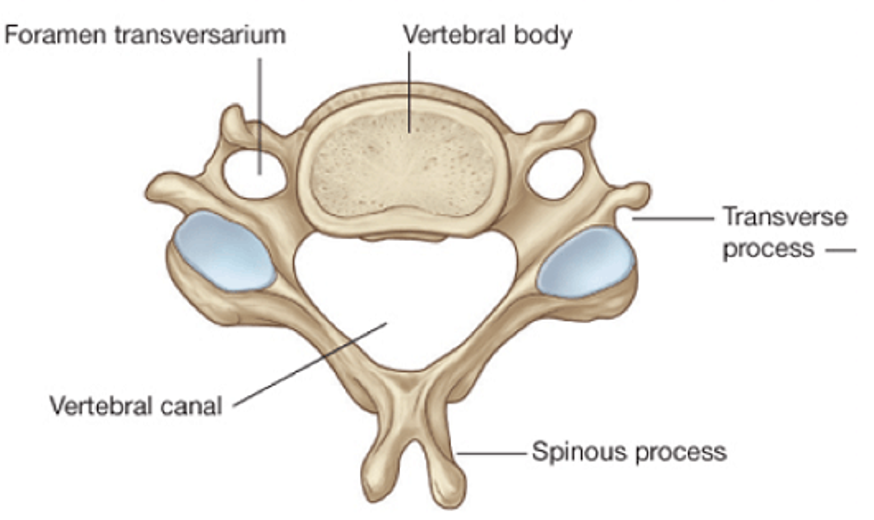
cervical vertebrae (C3-C7)
Transverse foramina (for vertebral arteries)
Large triangular vertebral foramen
Bifid spinous process
Exception: C7 single prominent spinous process (vertebra prominens)
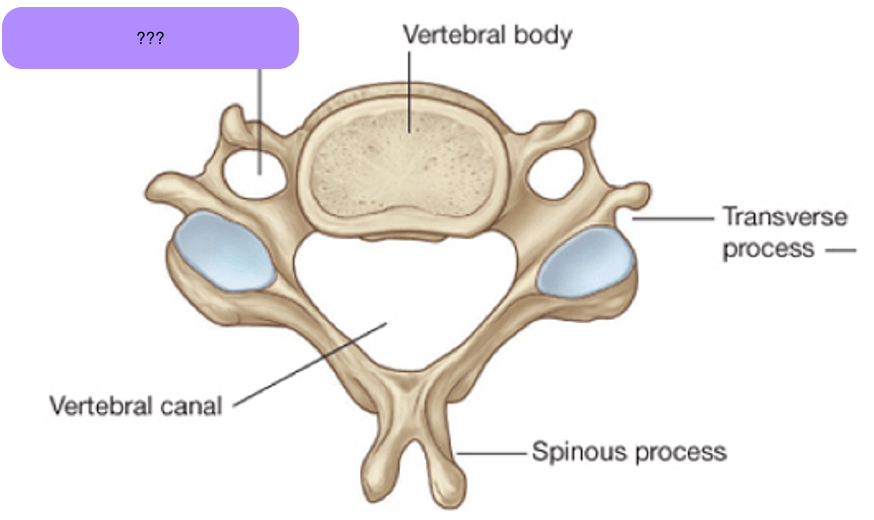
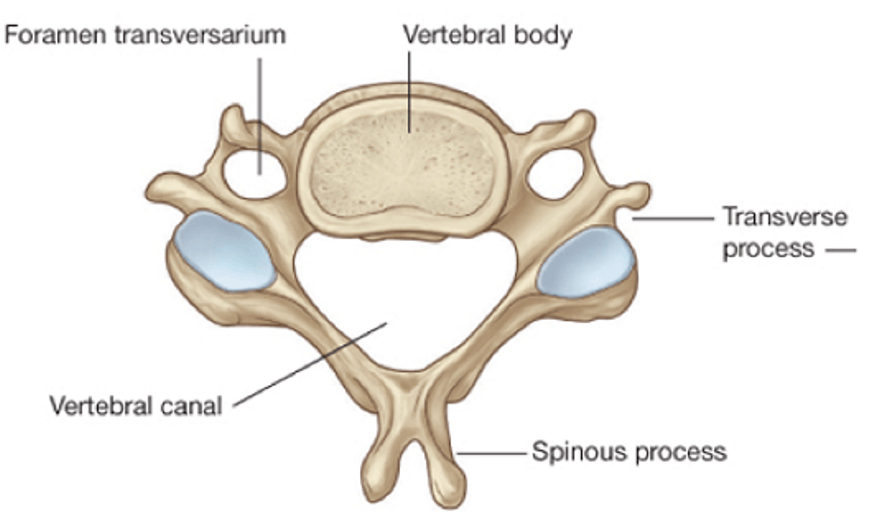
transverse foramen
characteristic of cervical vertebrae
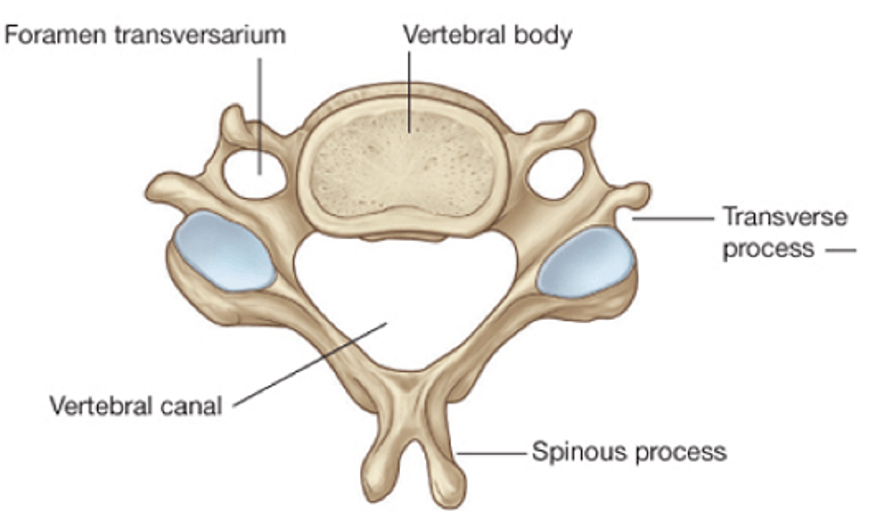
bifid spinous process
characteristic of cervical vertebrae (except C7)
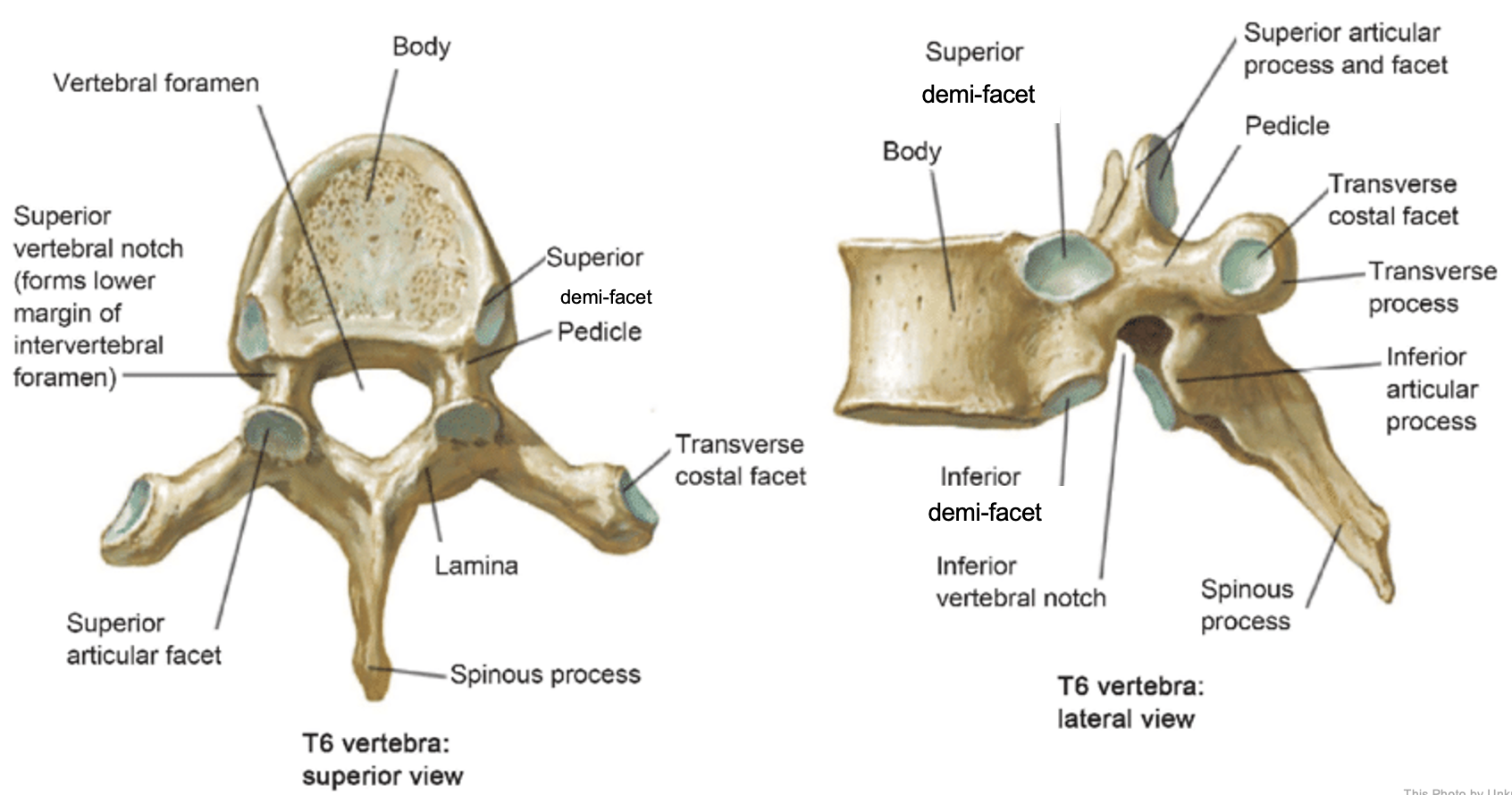
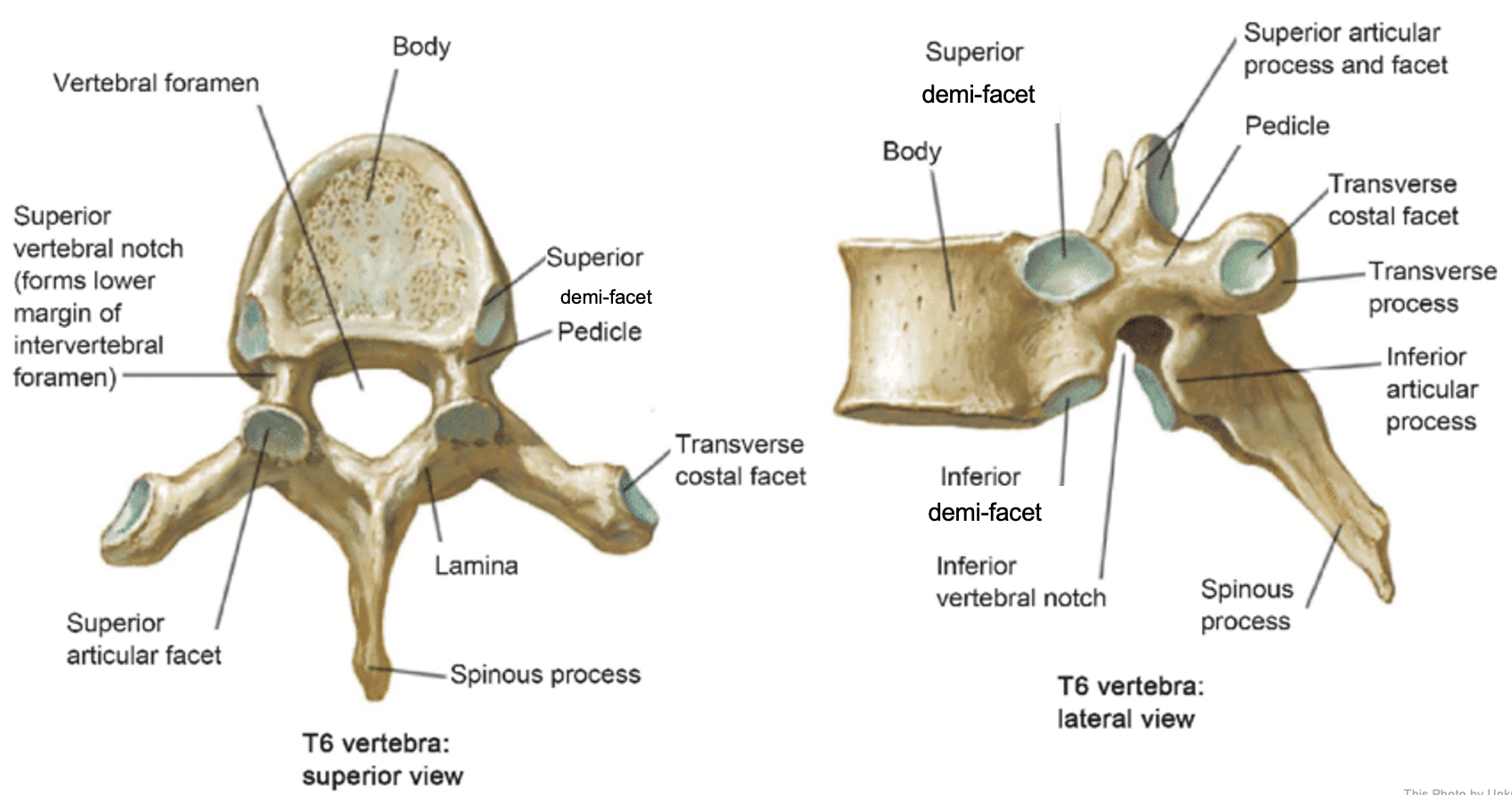
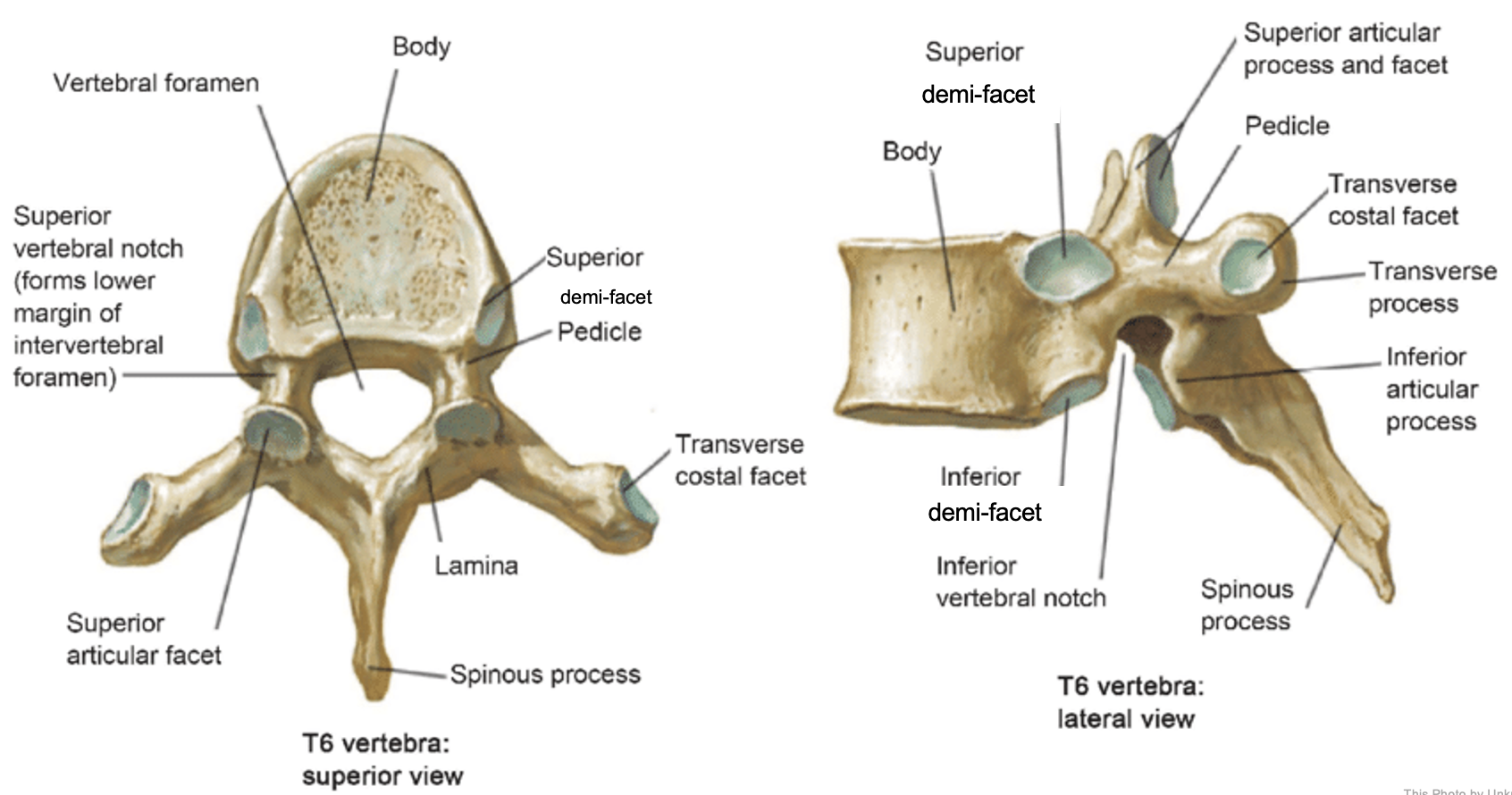
thoracic vertebrae
T1-T12
heart-shaped vertebral body & rounded vertebral foramen
Costal Facets: on body or transverse processes, articulate with tubercles of the ribs
Demi-facets: articulate with heads of the ribs (ribs 2-9)
Spinous processes:
long and slant inferiorly
Increase protection to spinal cord
Prevents objects from entering spinal canal
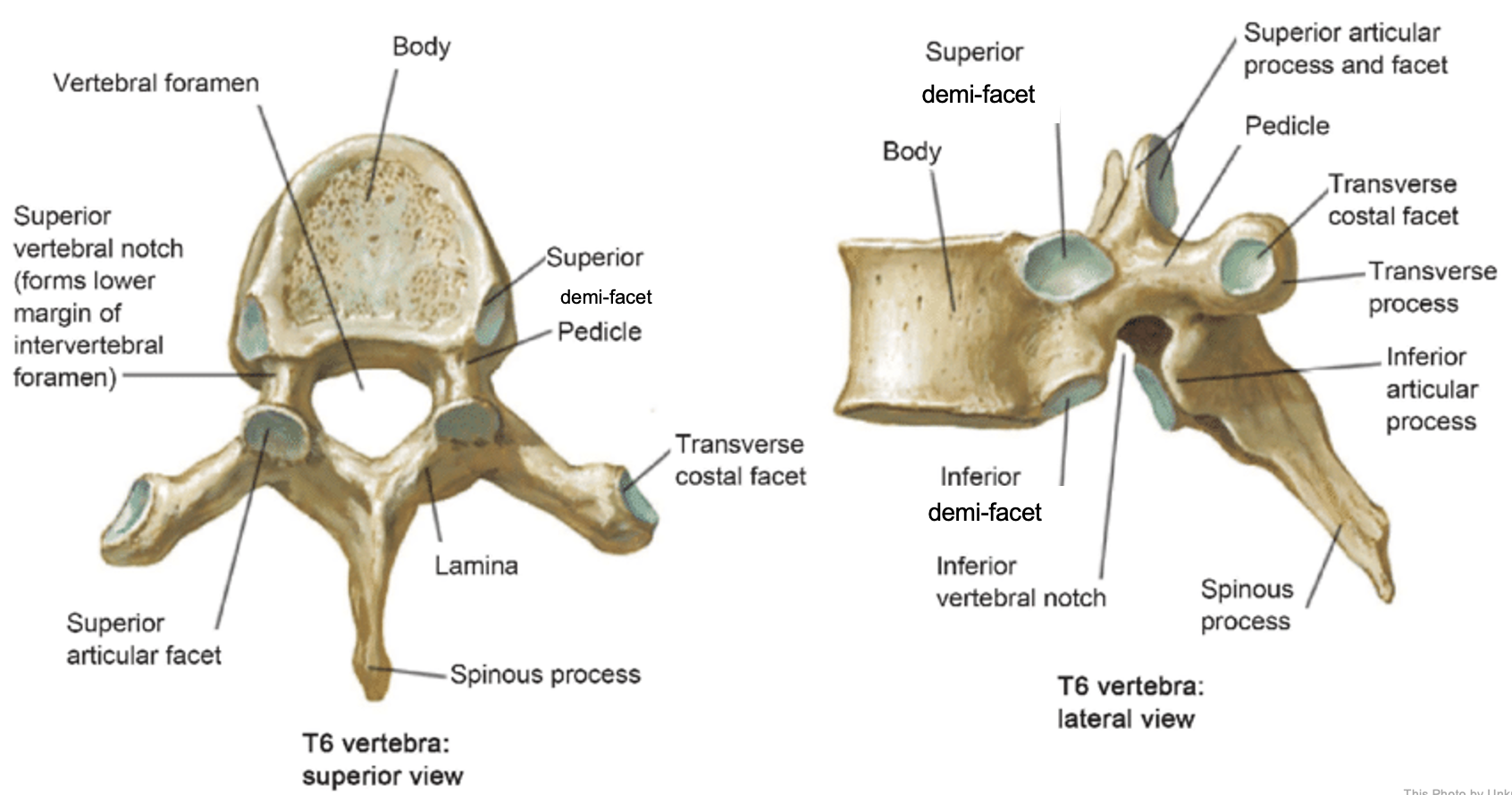
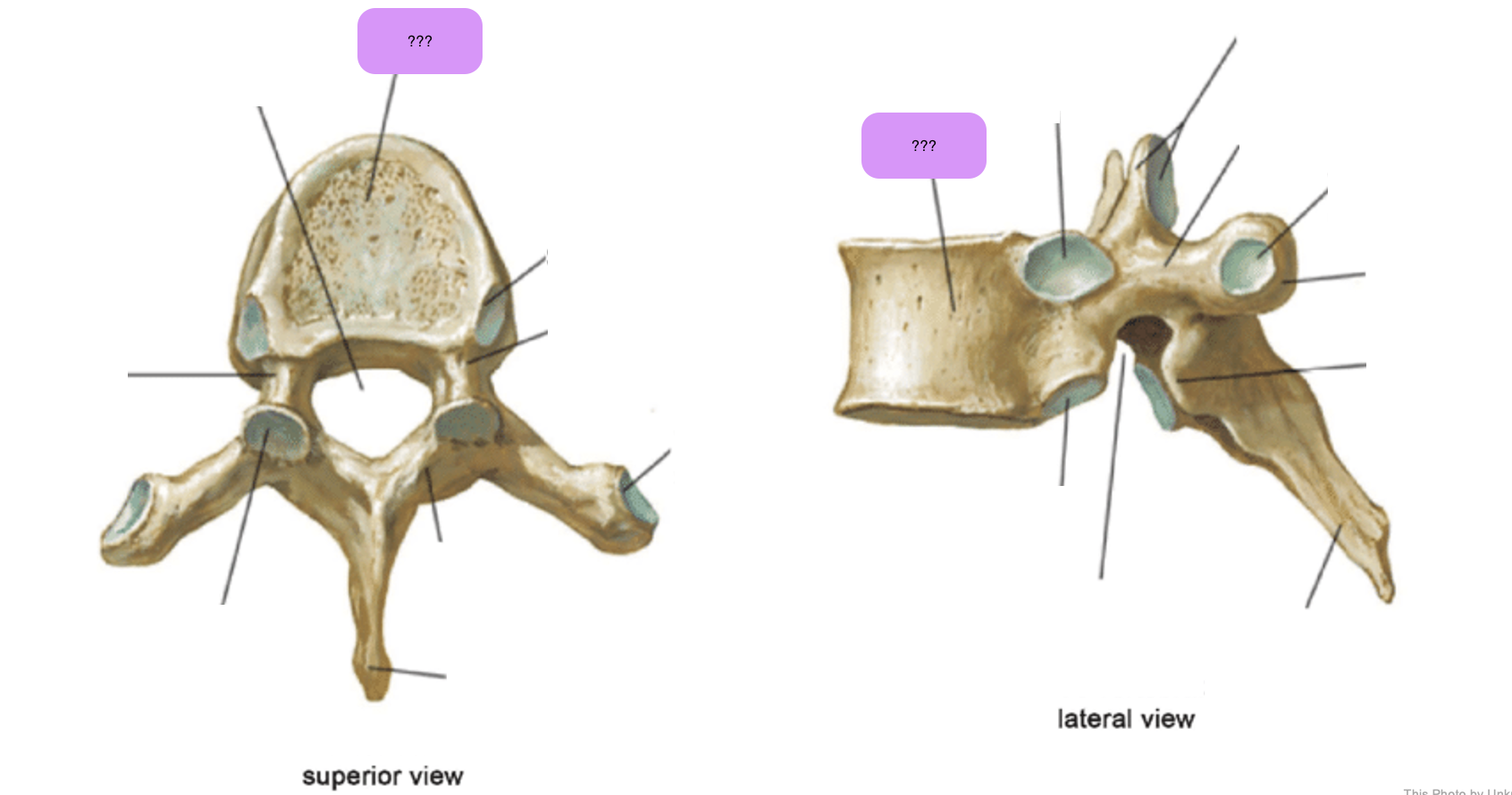
vertebral body (thoracic)
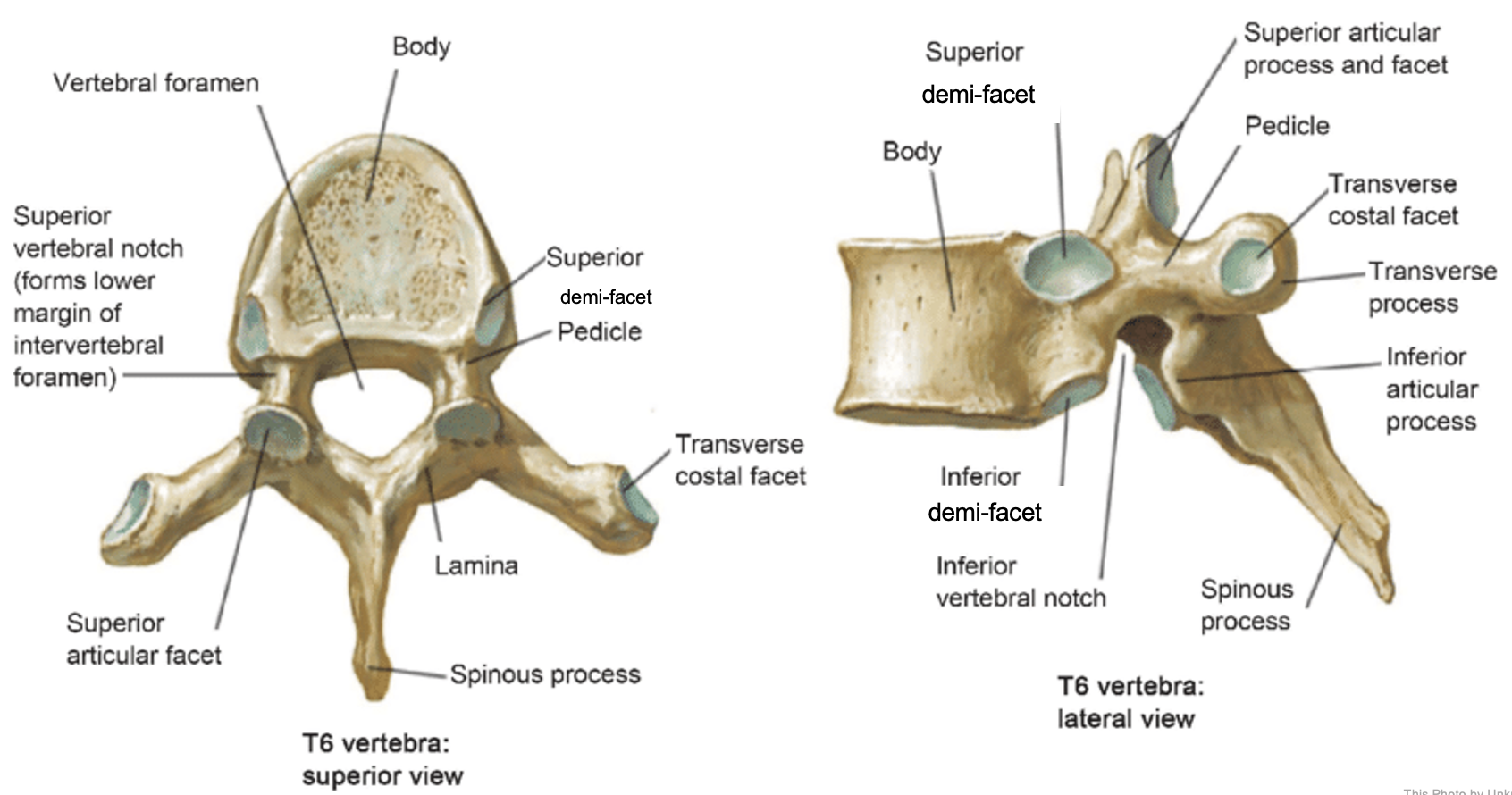
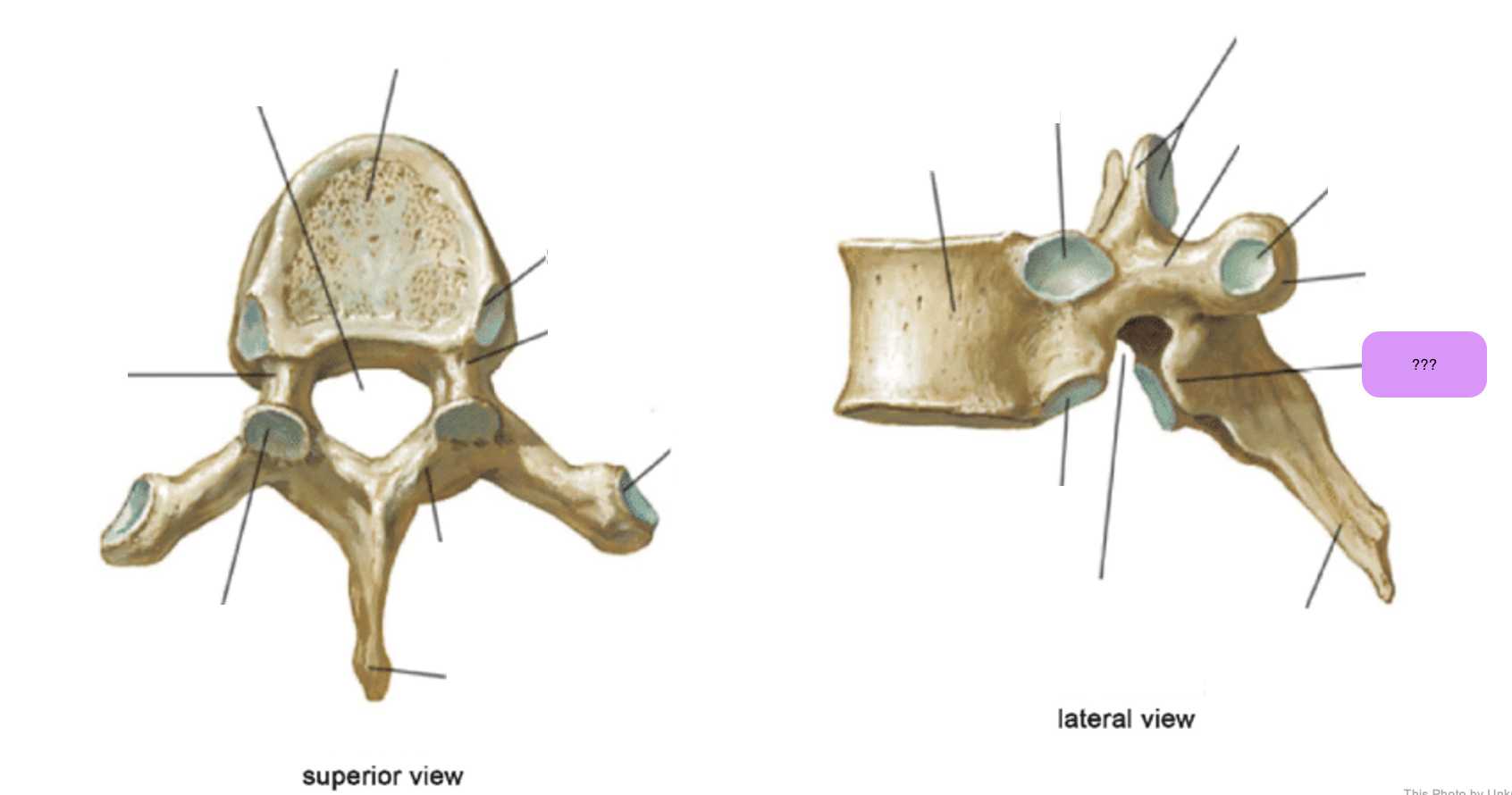
inferior articular process (thoracic)
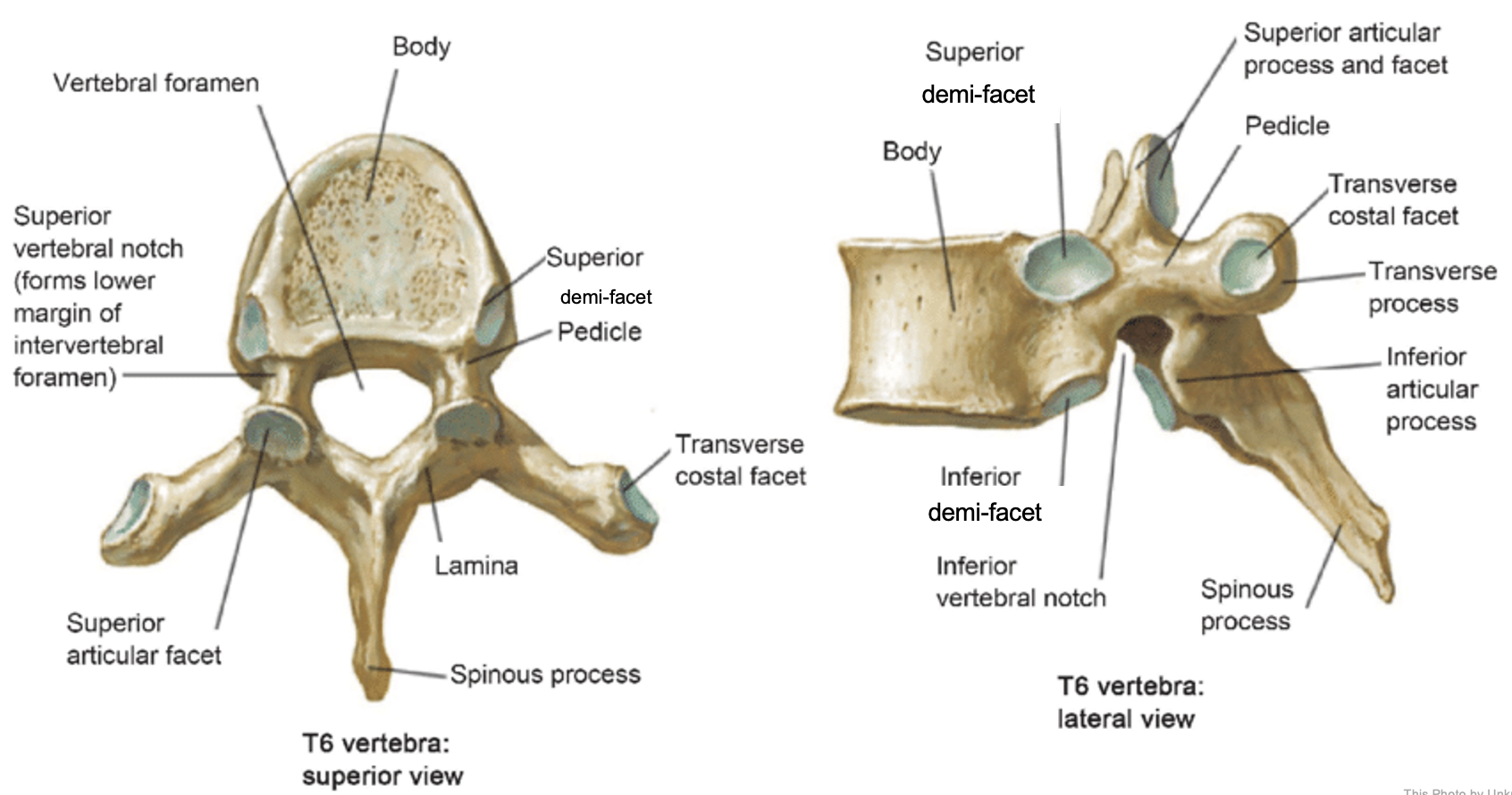
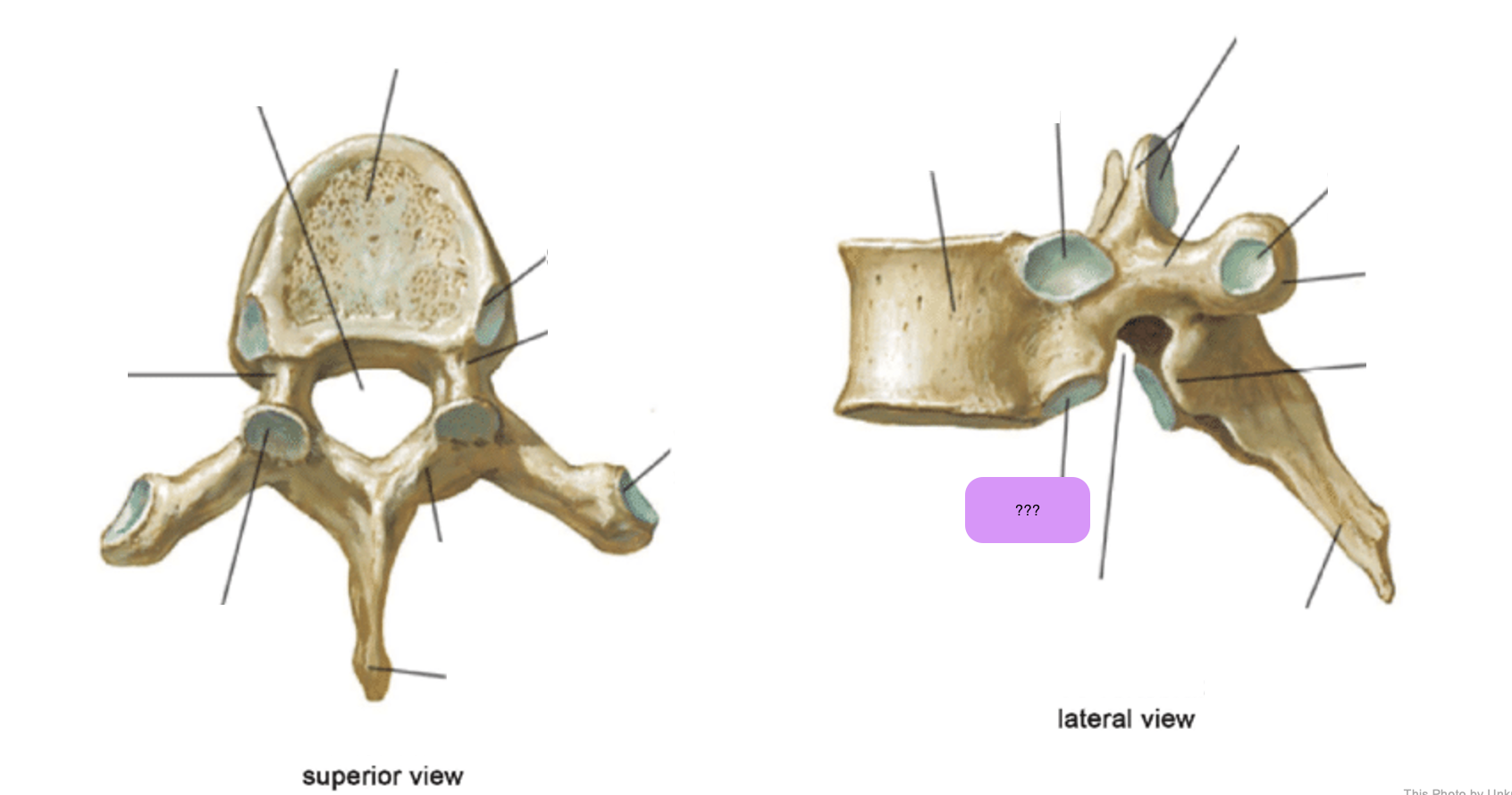
inferior demi-facet (thoracic)
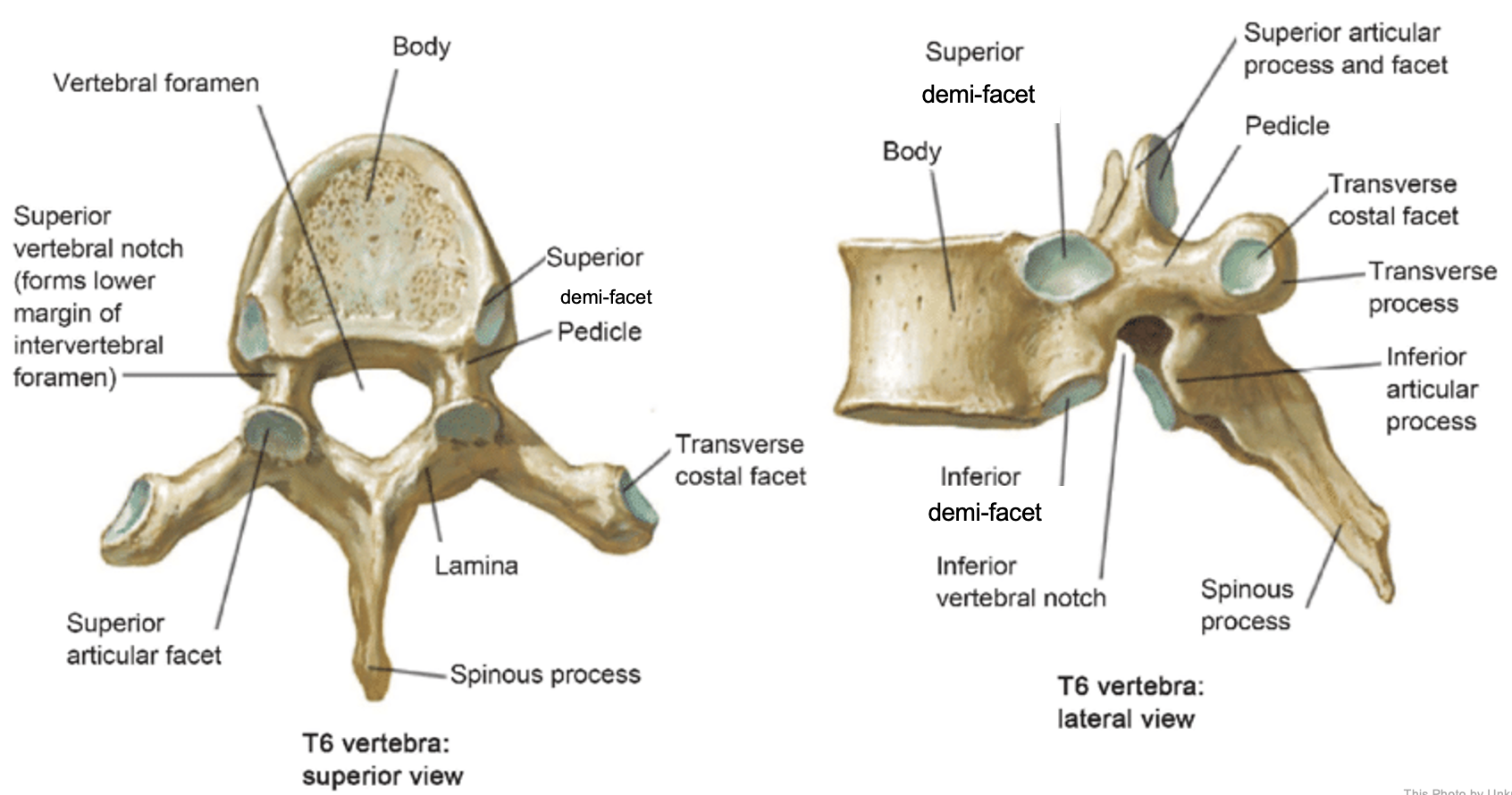
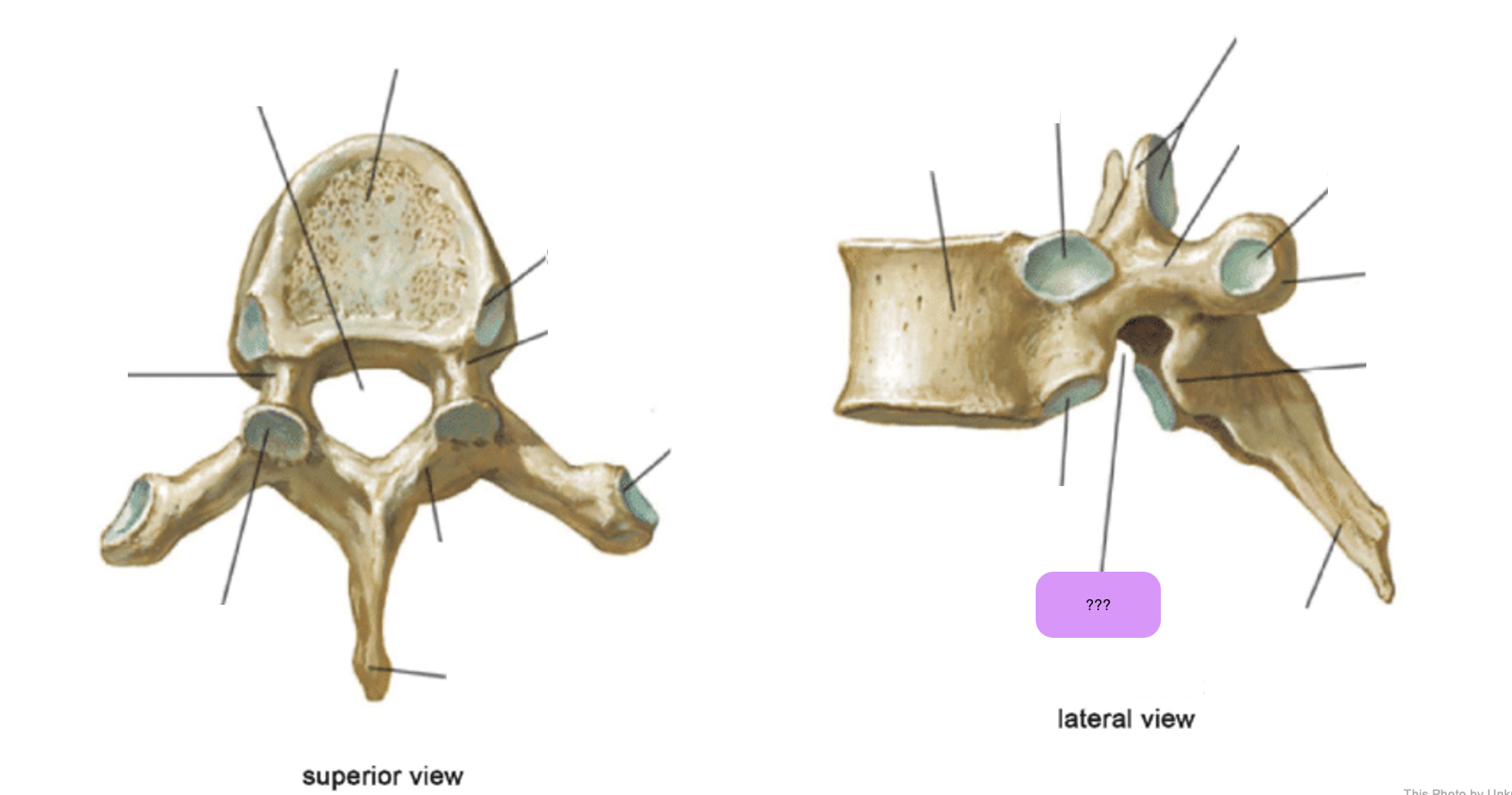
inferior vertebral notch (thoracic)
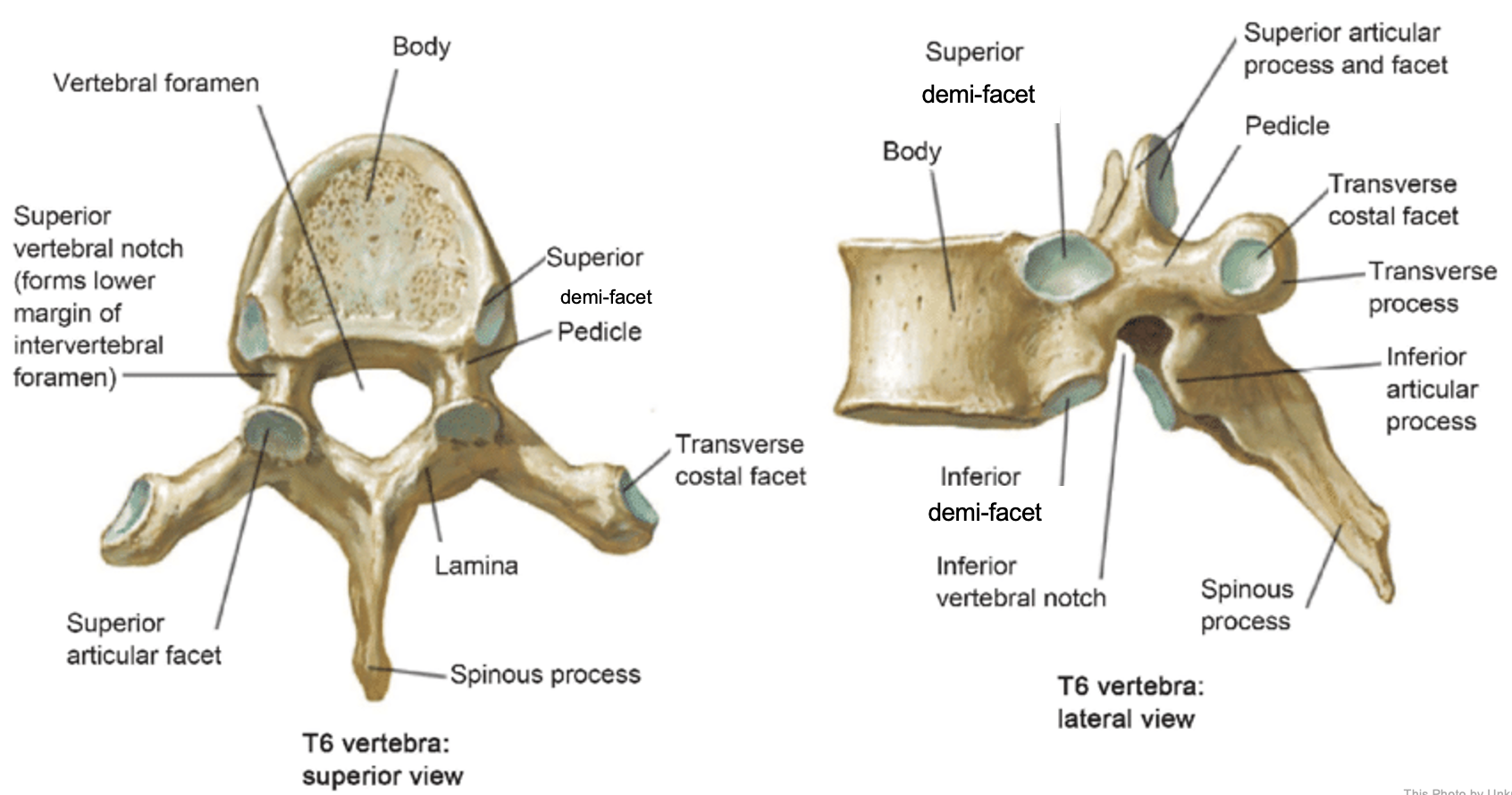
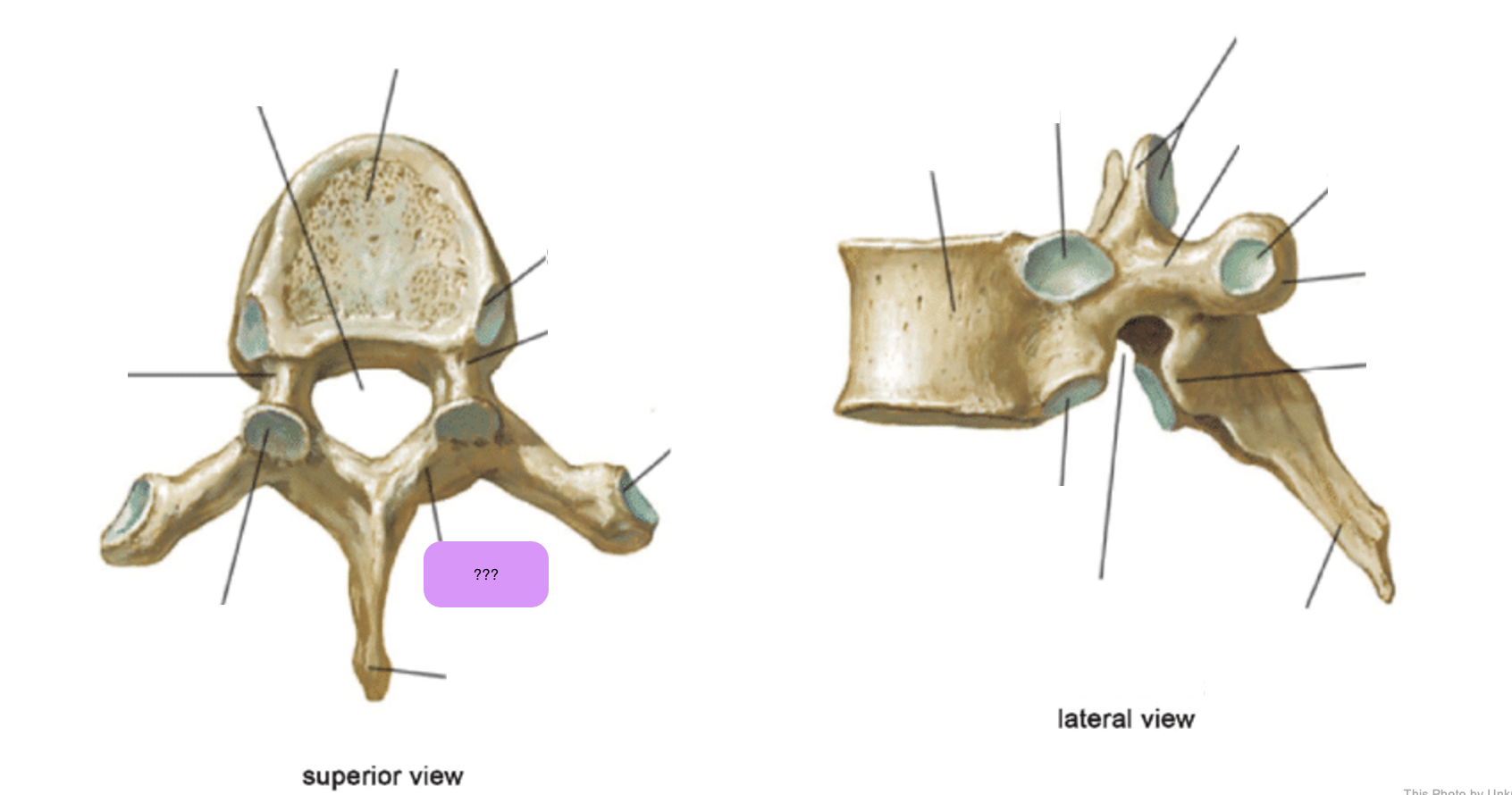
lamina (thoracic)
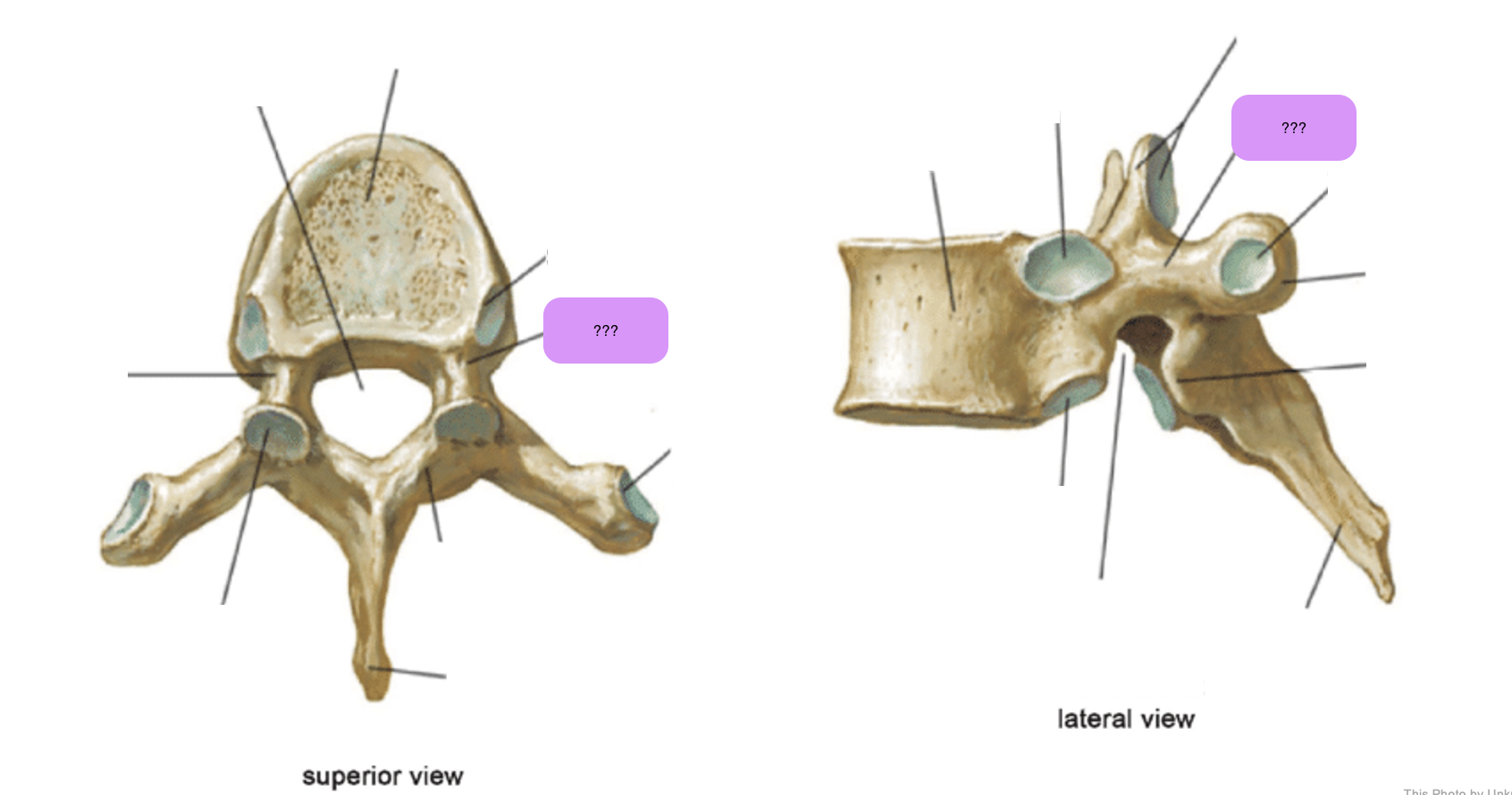
pedicle (thoracic)
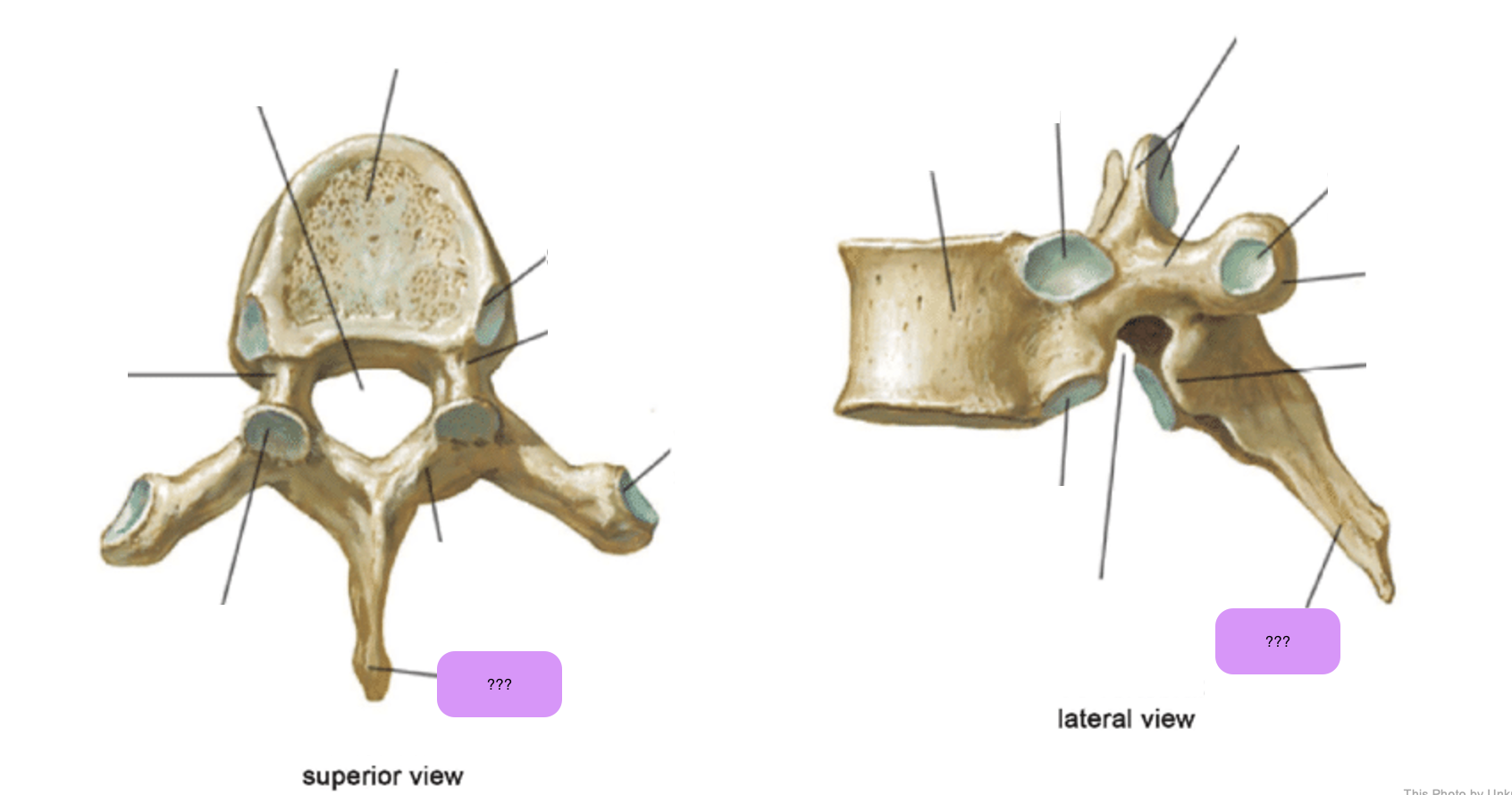
spinous process (thoracic)
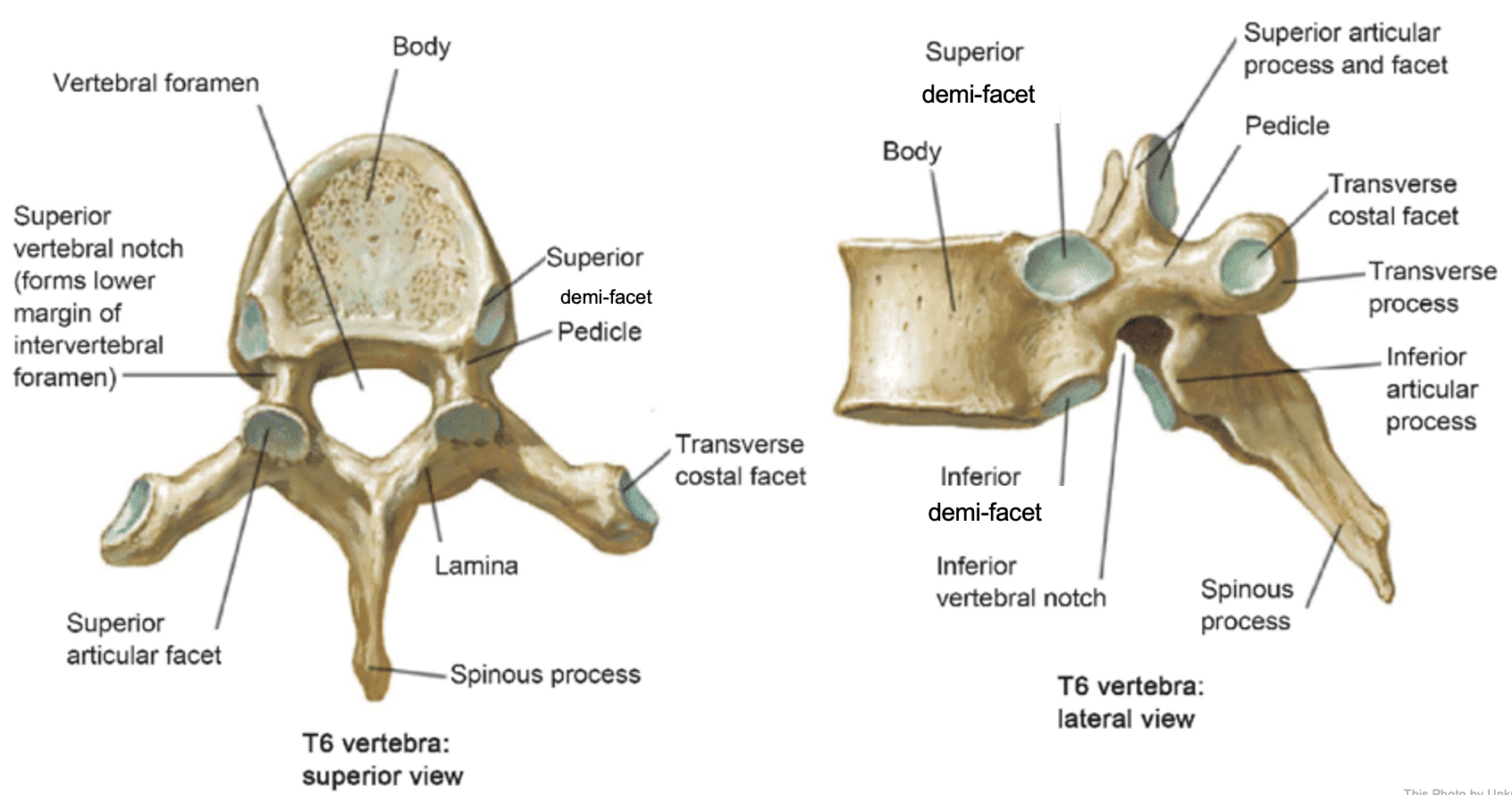
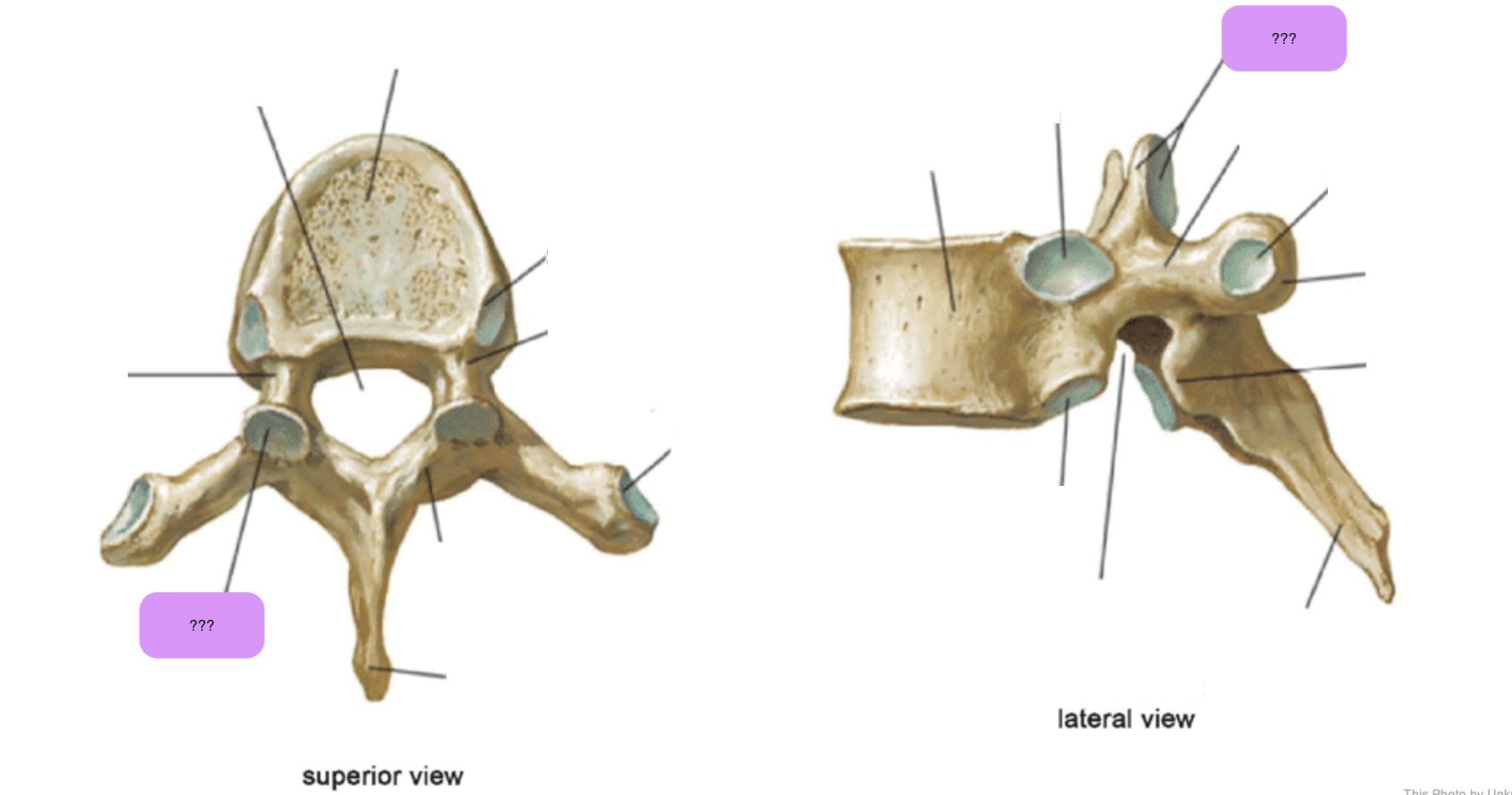
superior articular process and facet (thoracic)
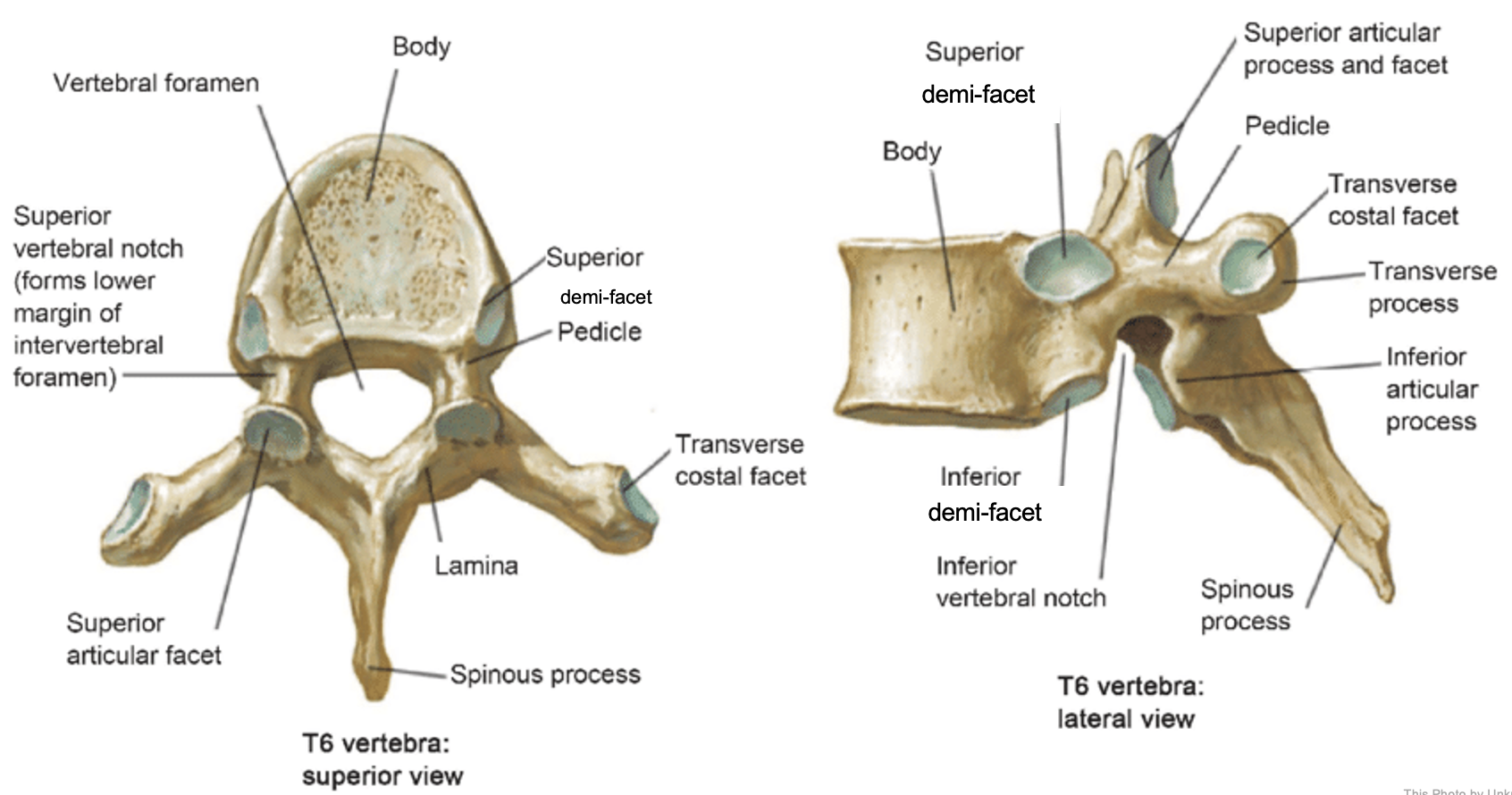
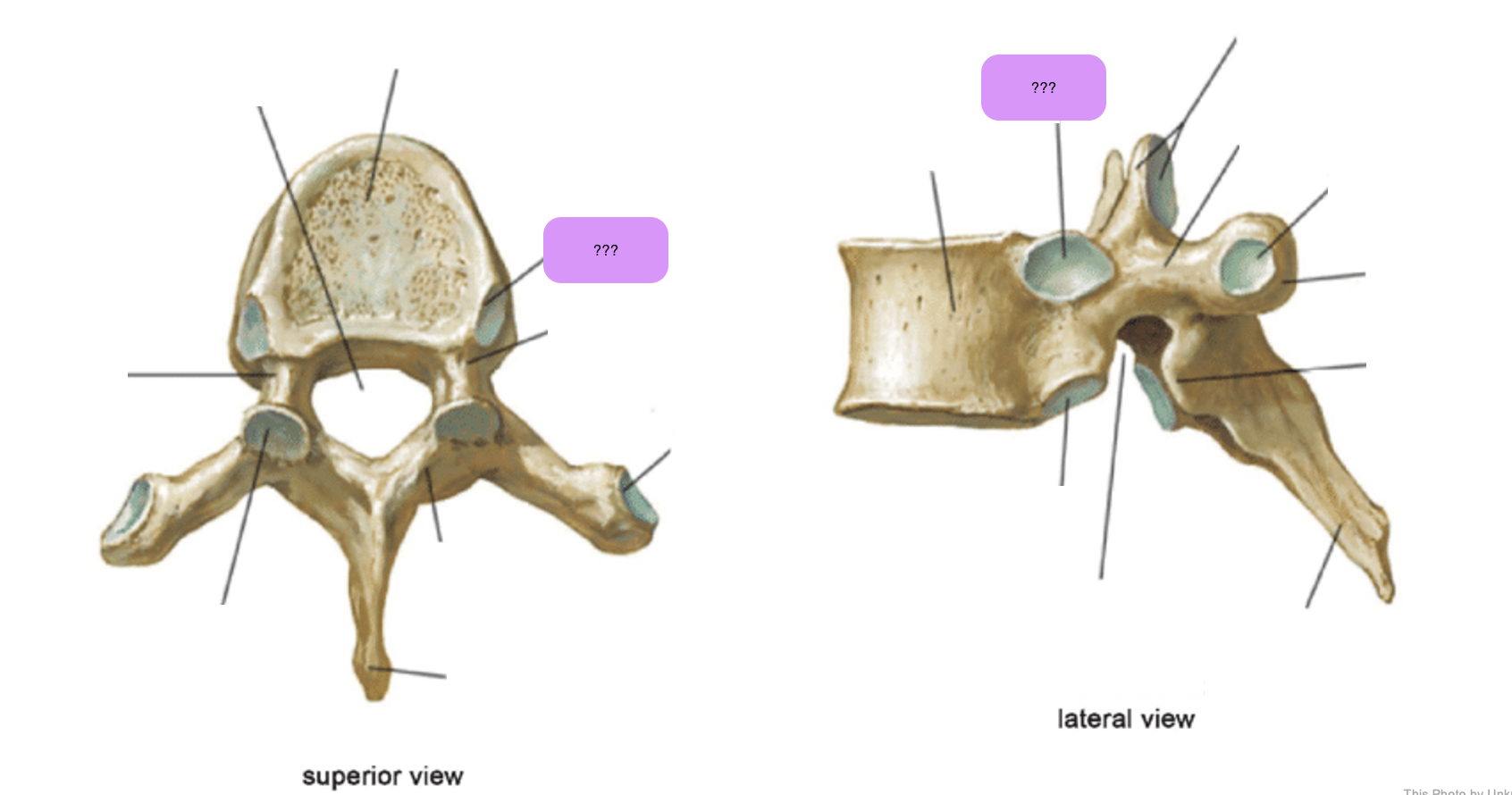
superior demi-facet (thoracic)
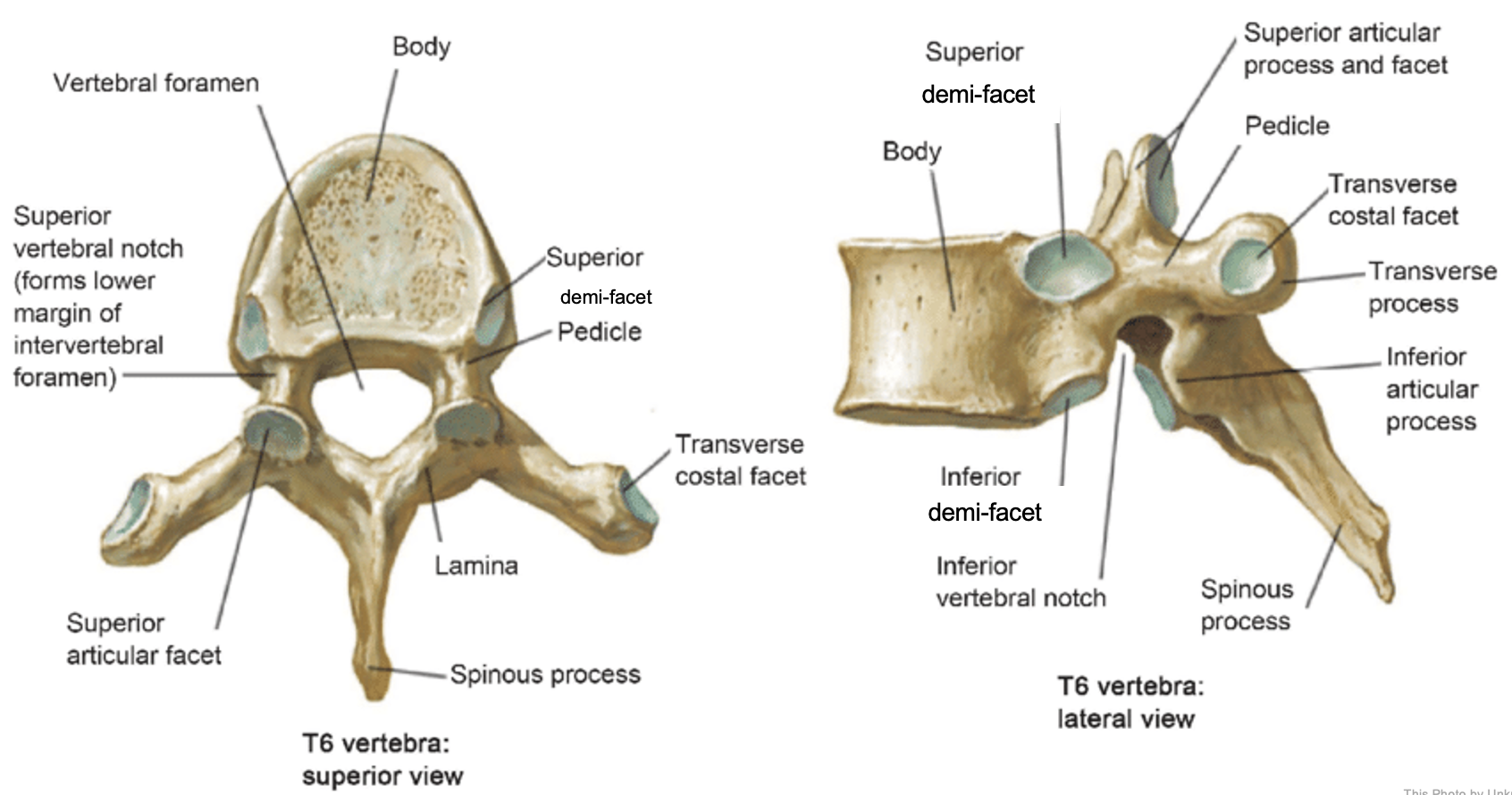
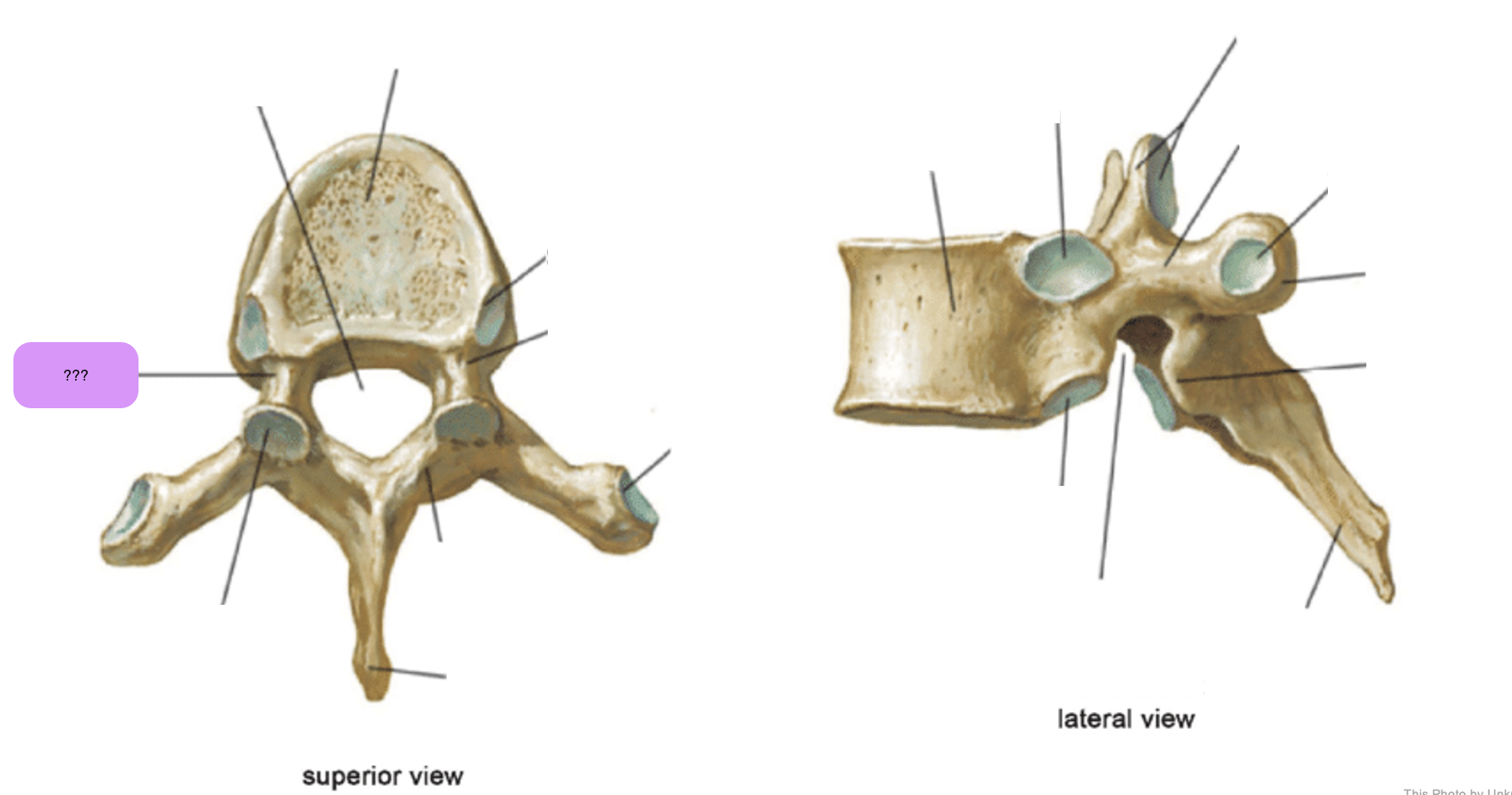
superior vertebral notch (thoracic)
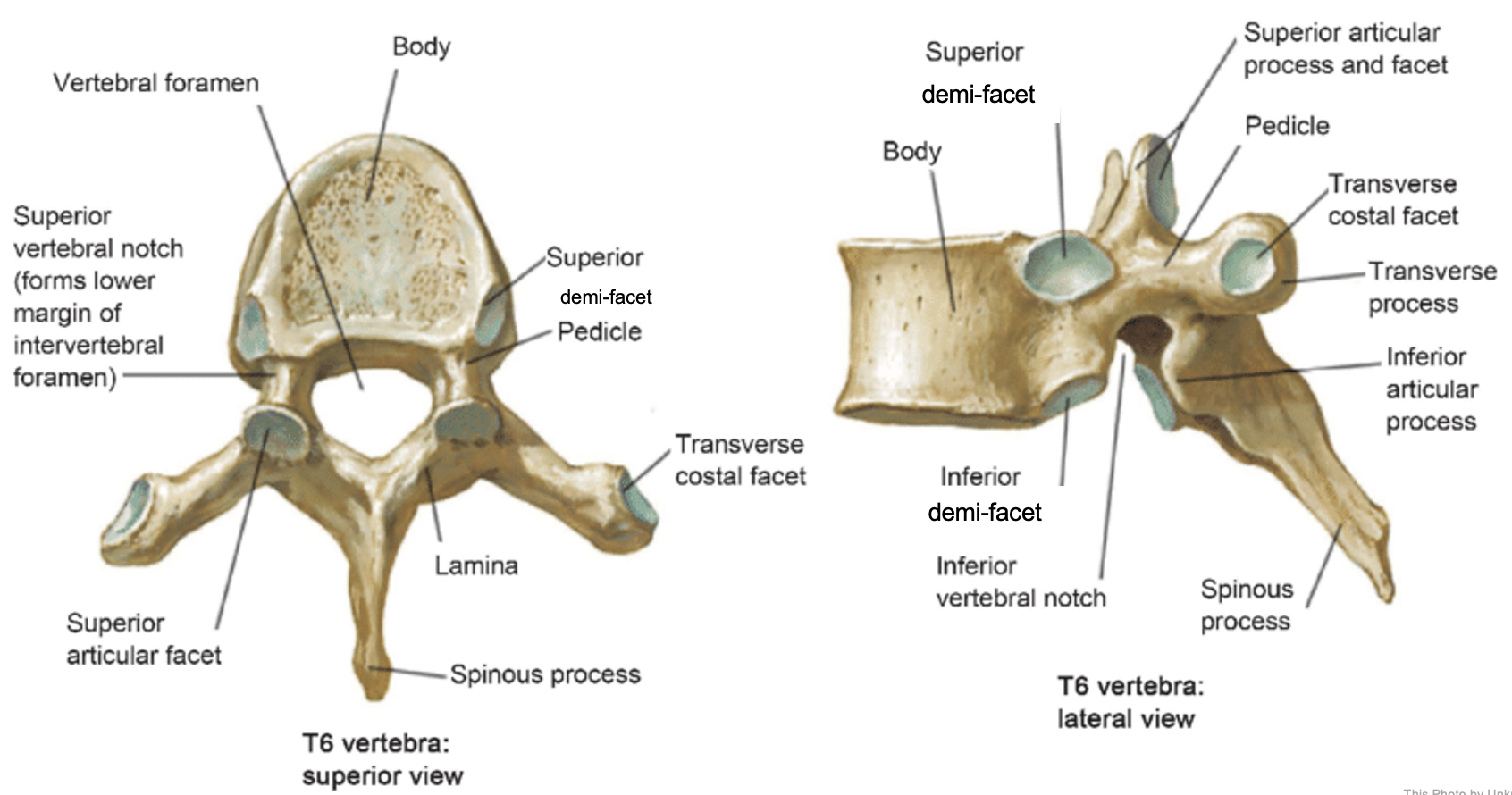
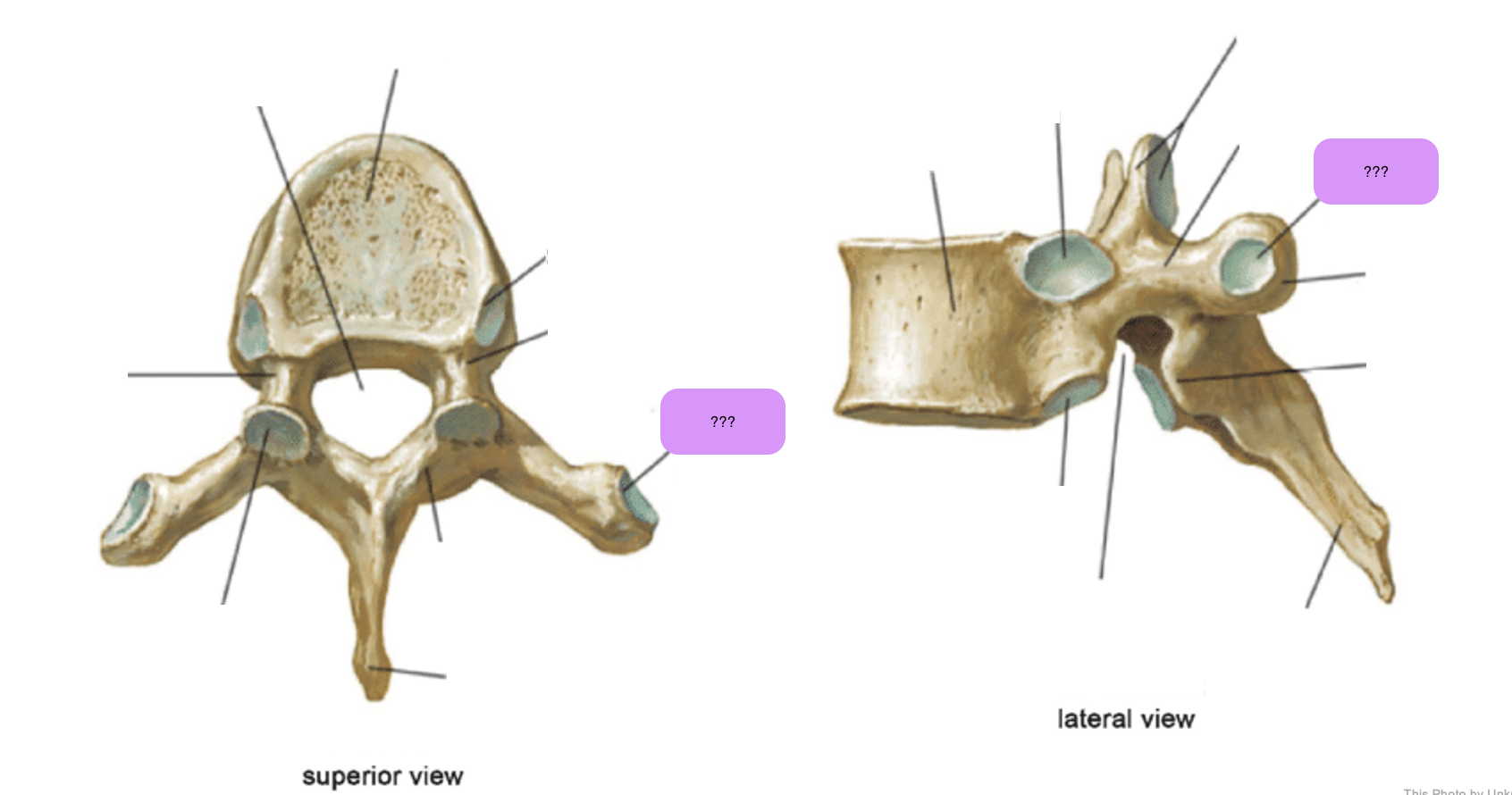
transverse costal facet (thoracic)
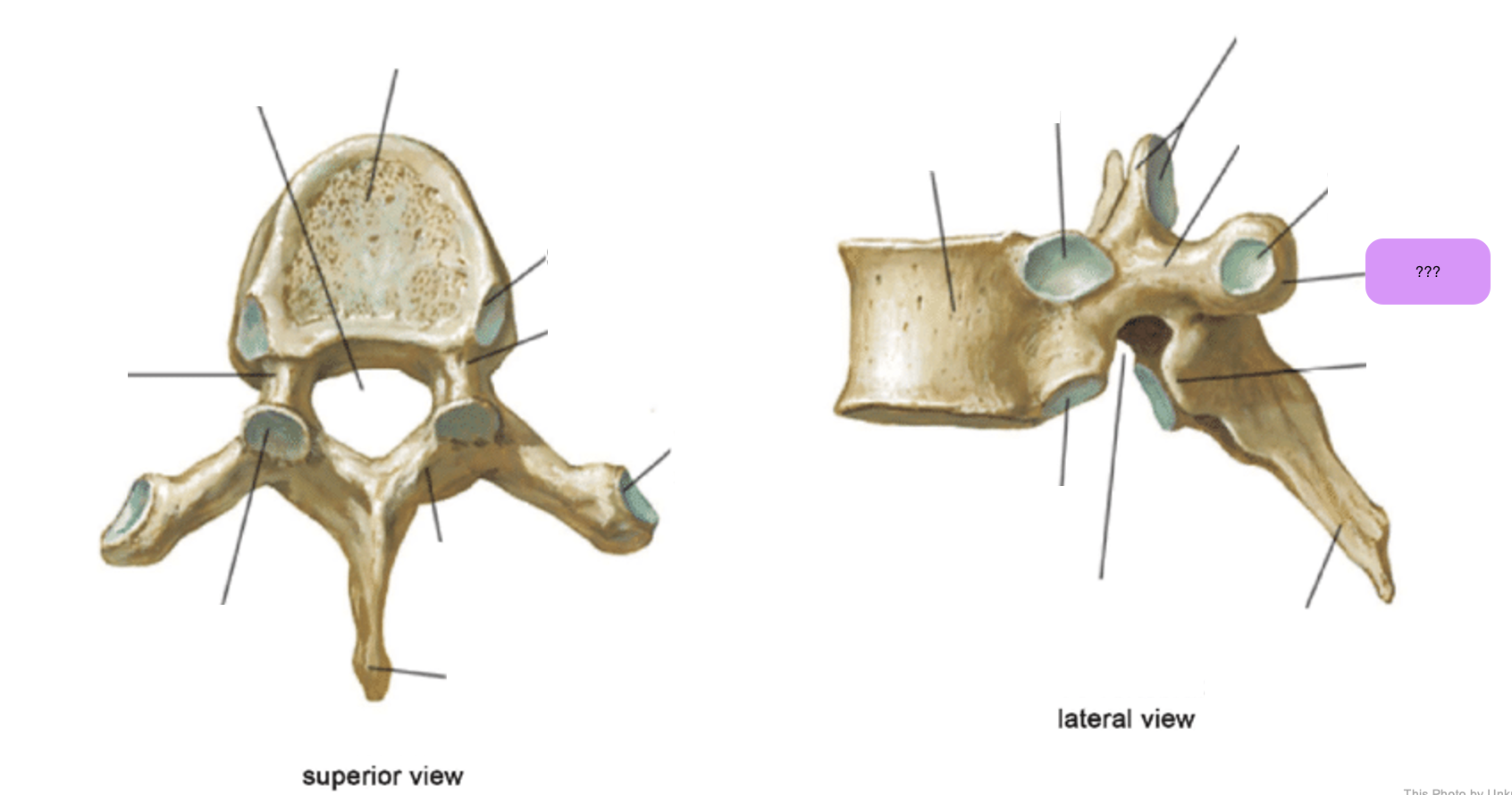
transverse process (thoracic)
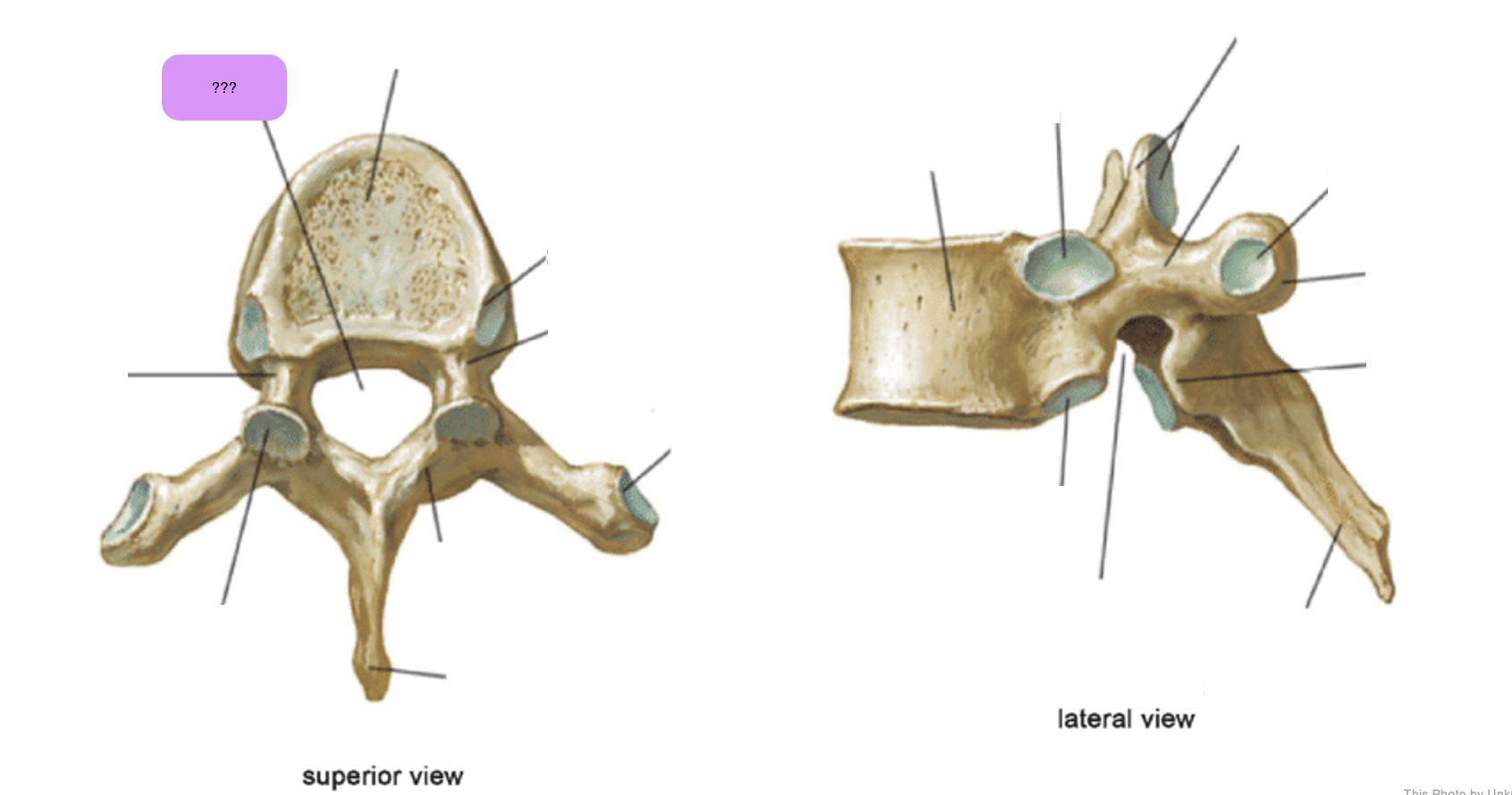
vertebral foramen (thoracic)
lumbar vertebrae
L1-L5
Large, kidney-shaped vertebral body
Short, wide spinous processes
Long, thin transverse processes (except L5)
Vertebral foramen: triangular
Sup / Inf artic. processes face inwards/outwards
NO transverse foramina
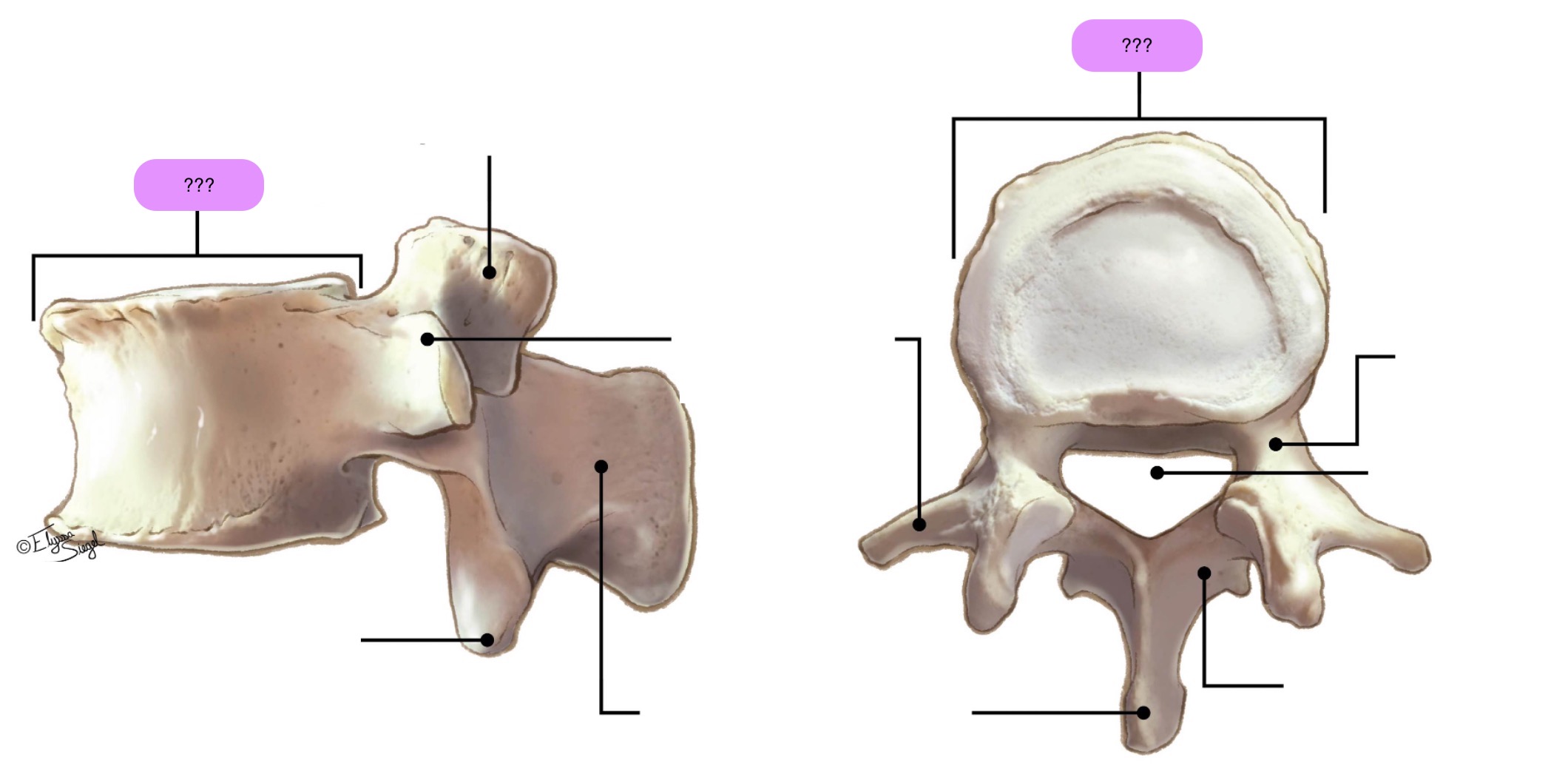
vertebral body (lumbar)
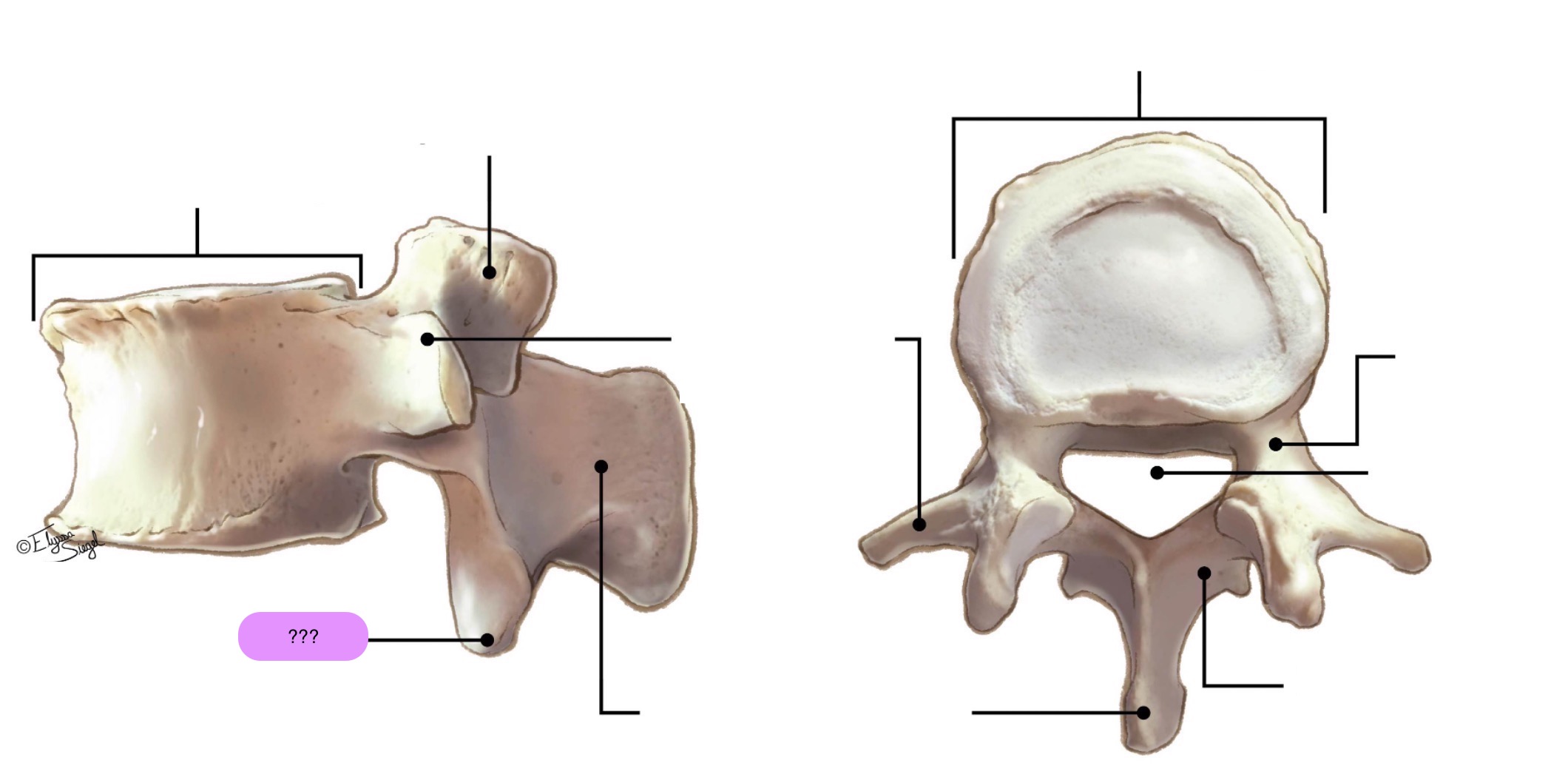
inferior articular process (lumbar)
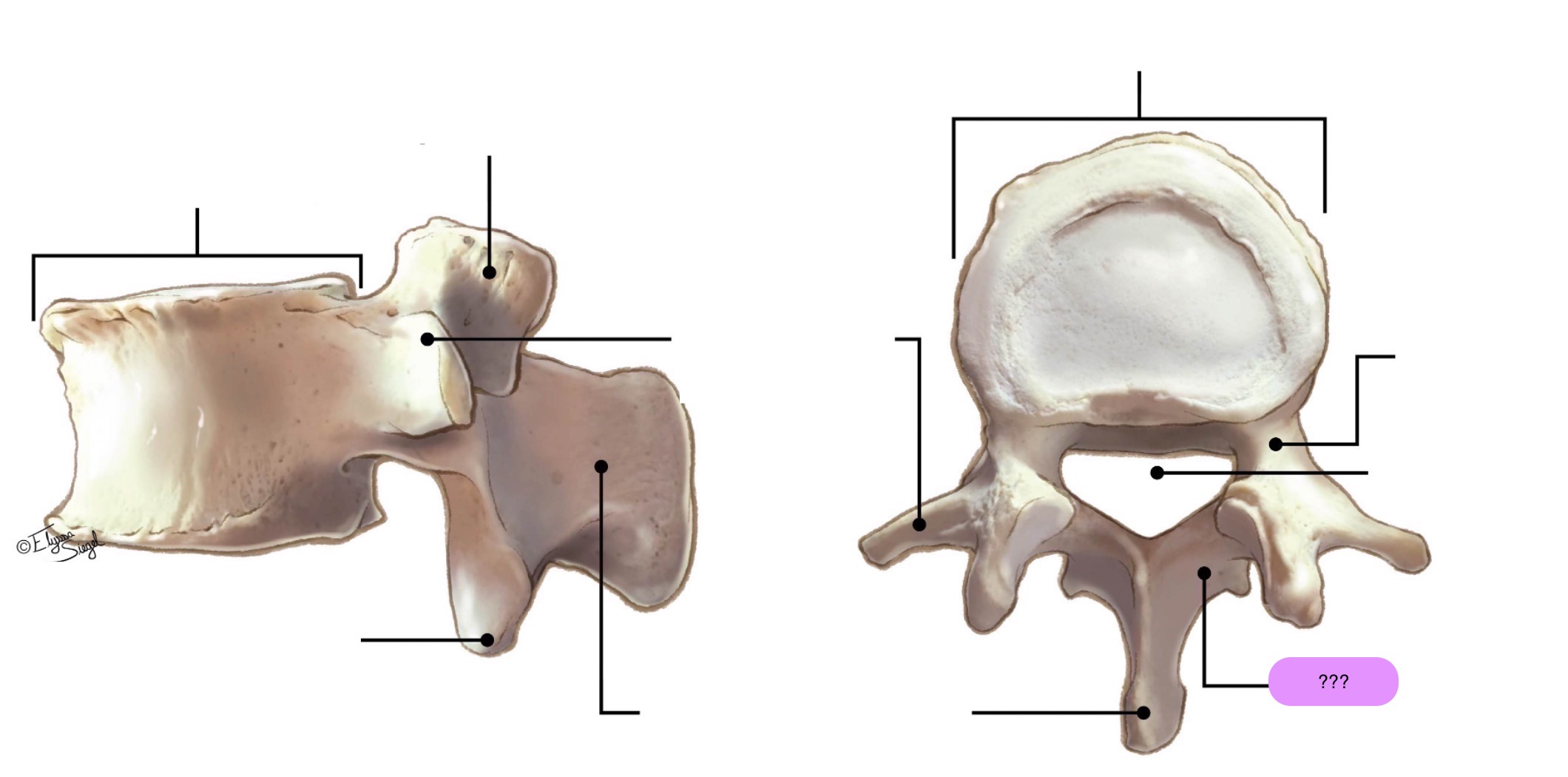
lamina (lumbar)
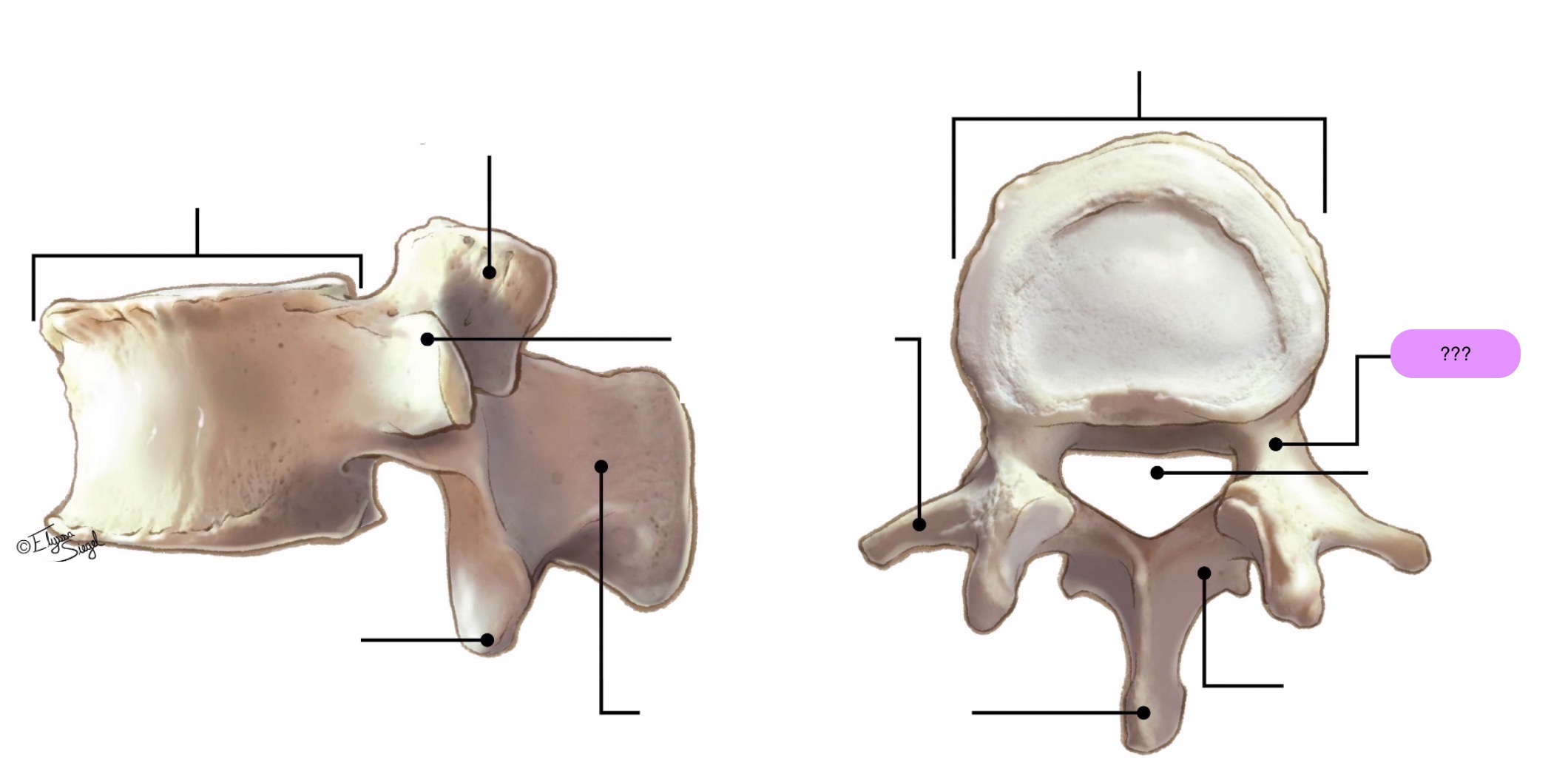
pedicle (lumbar)
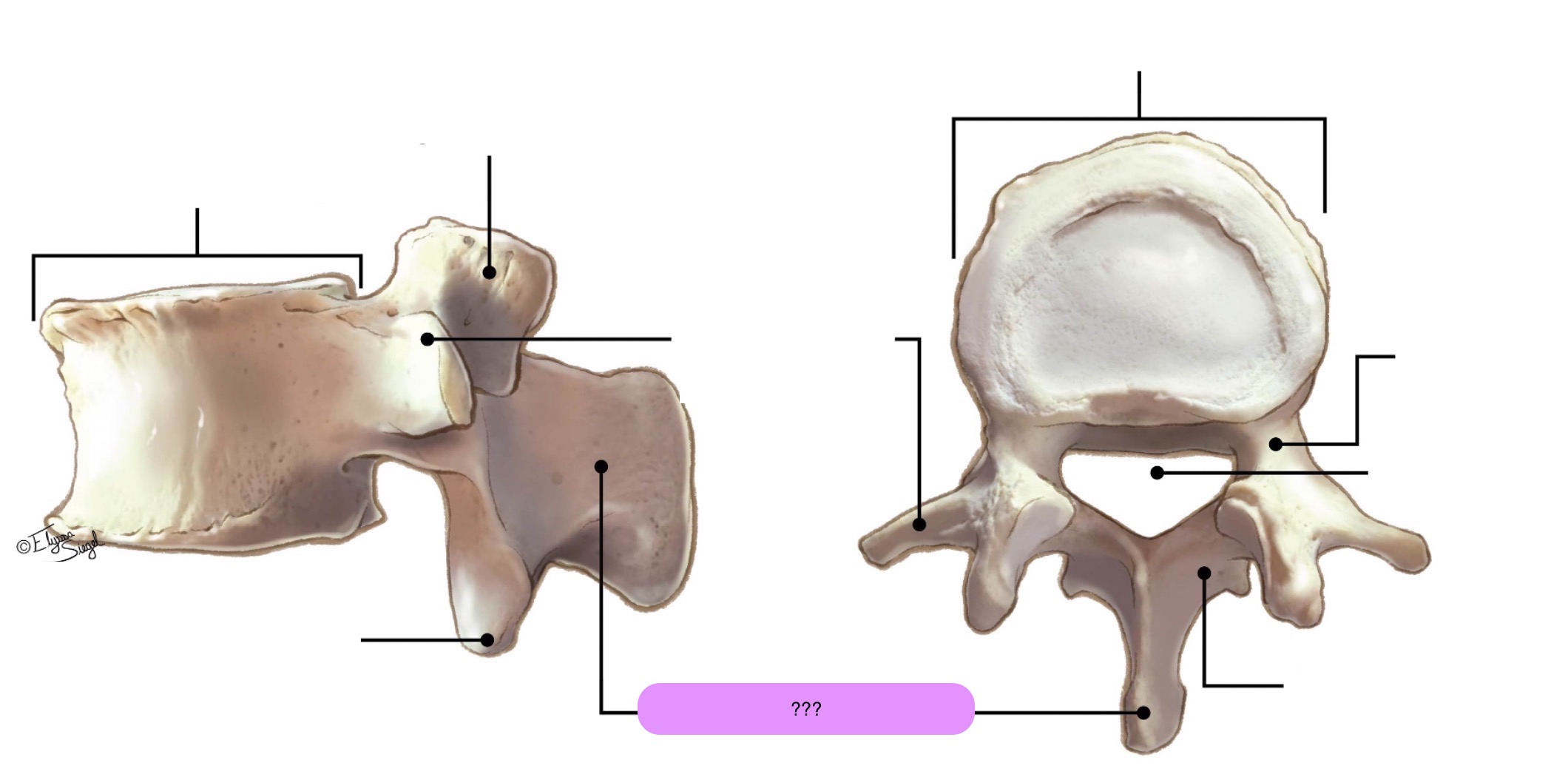
spinous process (lumbar)
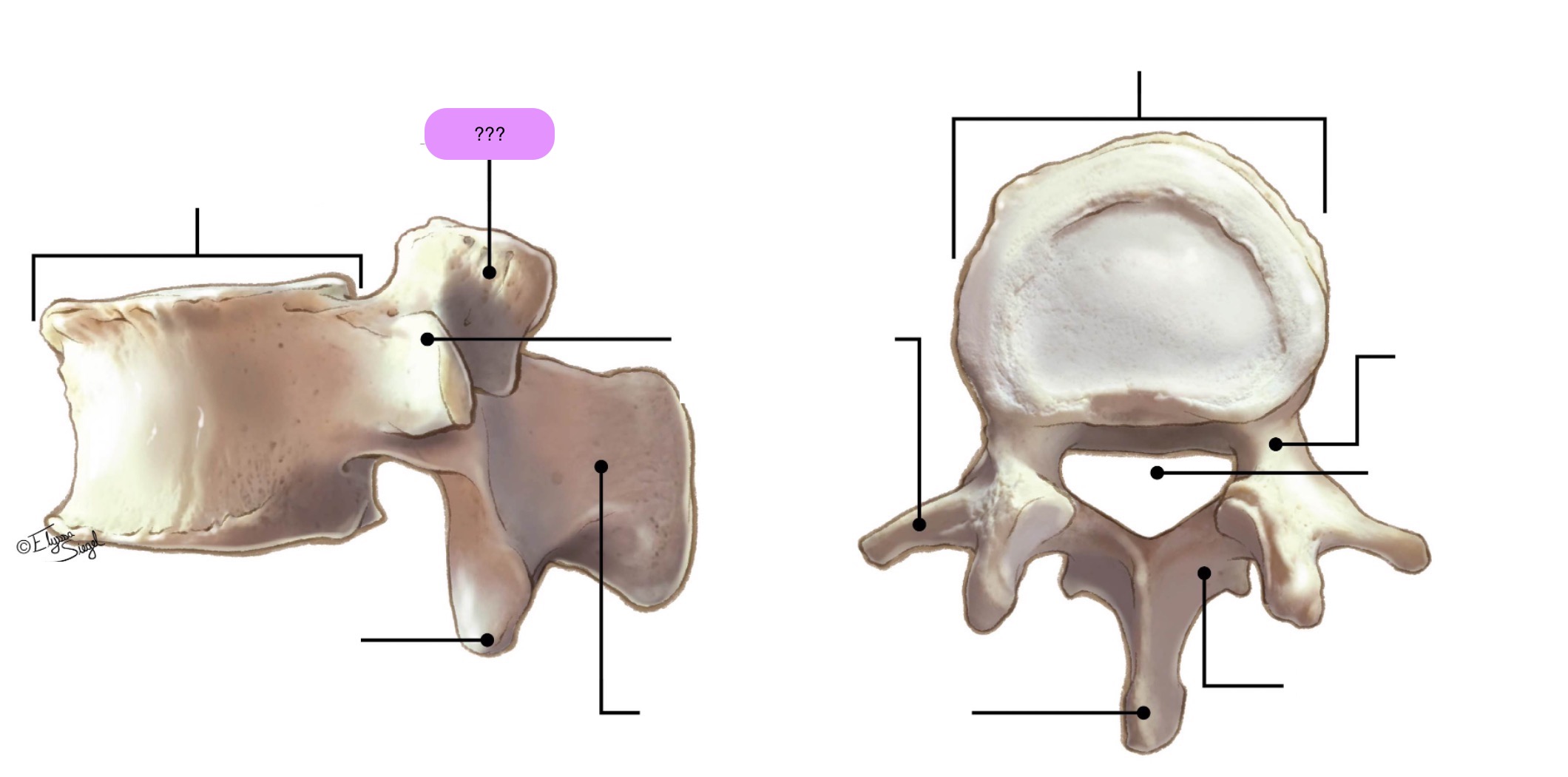
superior articular surface (lumbar)
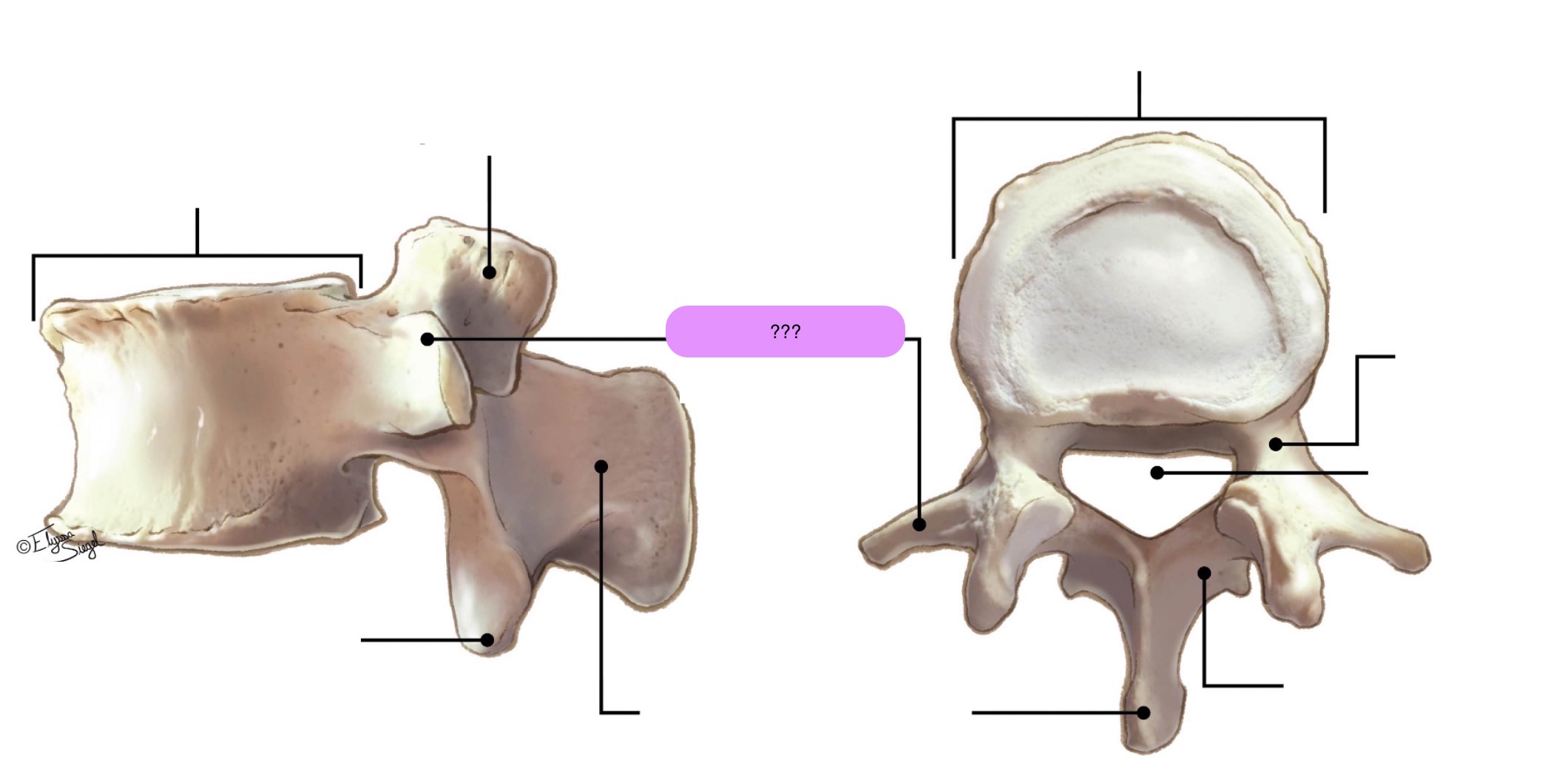
transverse process (lumbar)
vertebral foramen (lumbar)
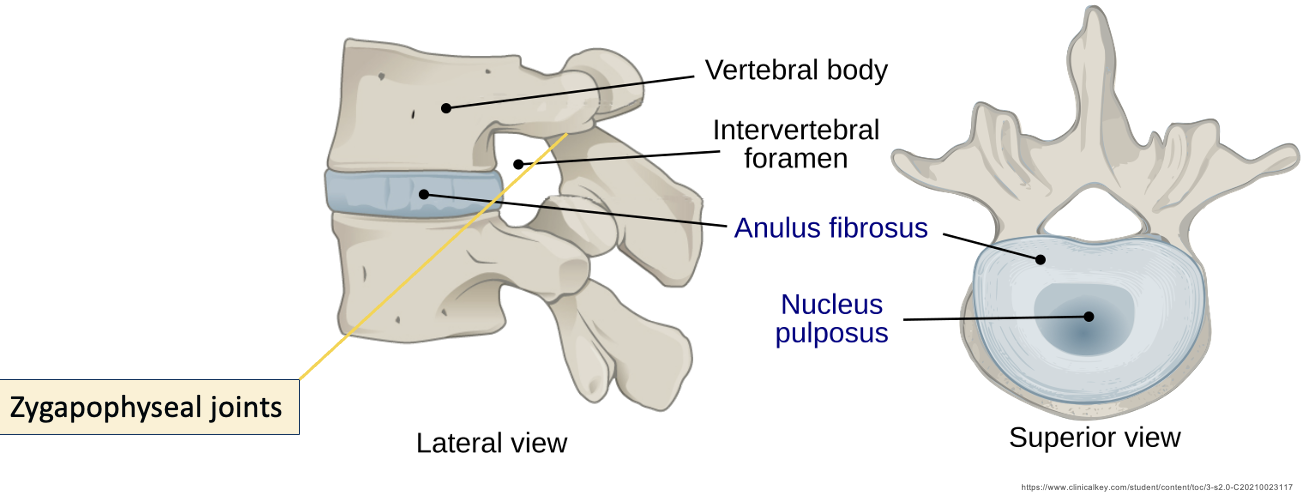
Zygapophyseal/facet joints
Synovial joints between sup/inf articular processes
allow for gliding movements
type of movement determined by its shape & arrangement
Provide strength to vertebral column, allow gliding movements & flexibility
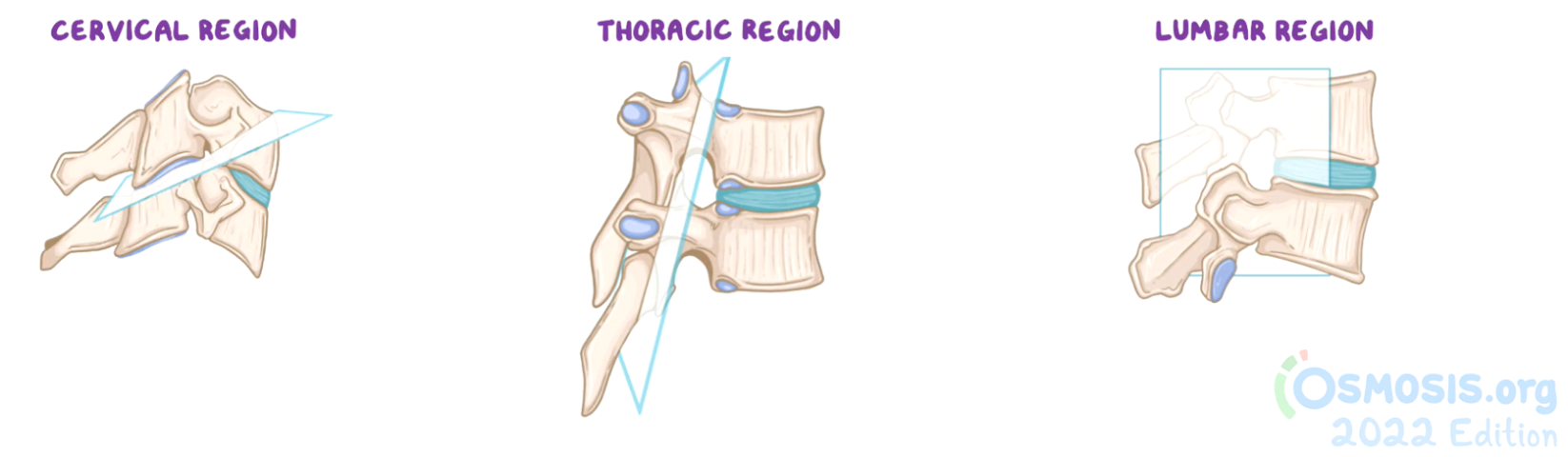
Zygapophyseal/facet joint types
cervical facet joints
thoracic facet joints
lumbar facet joints
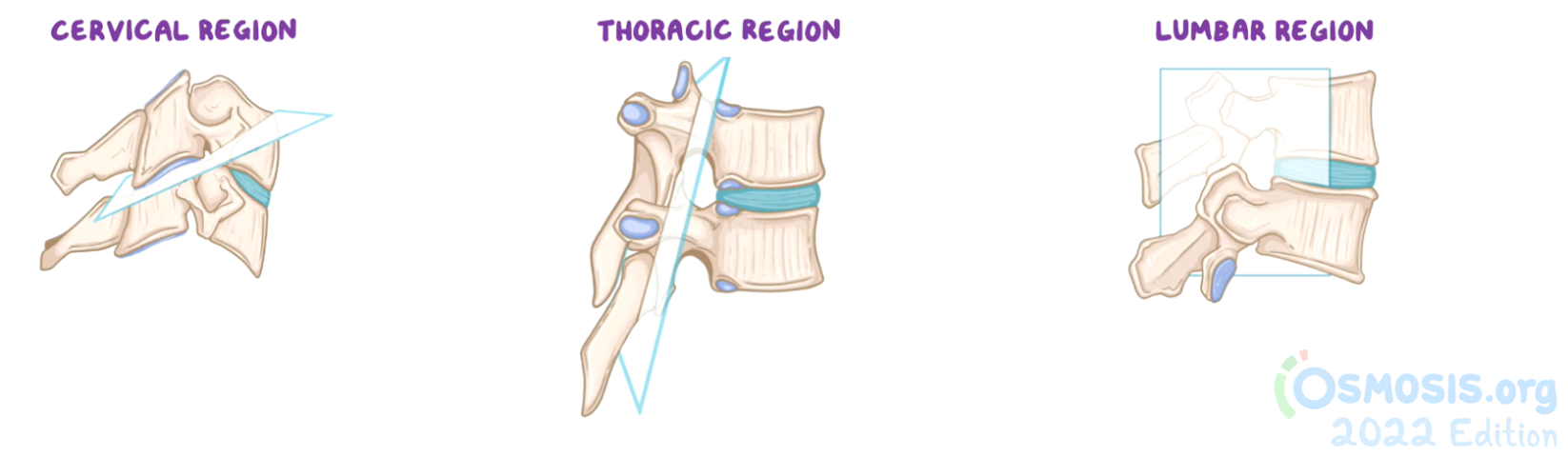
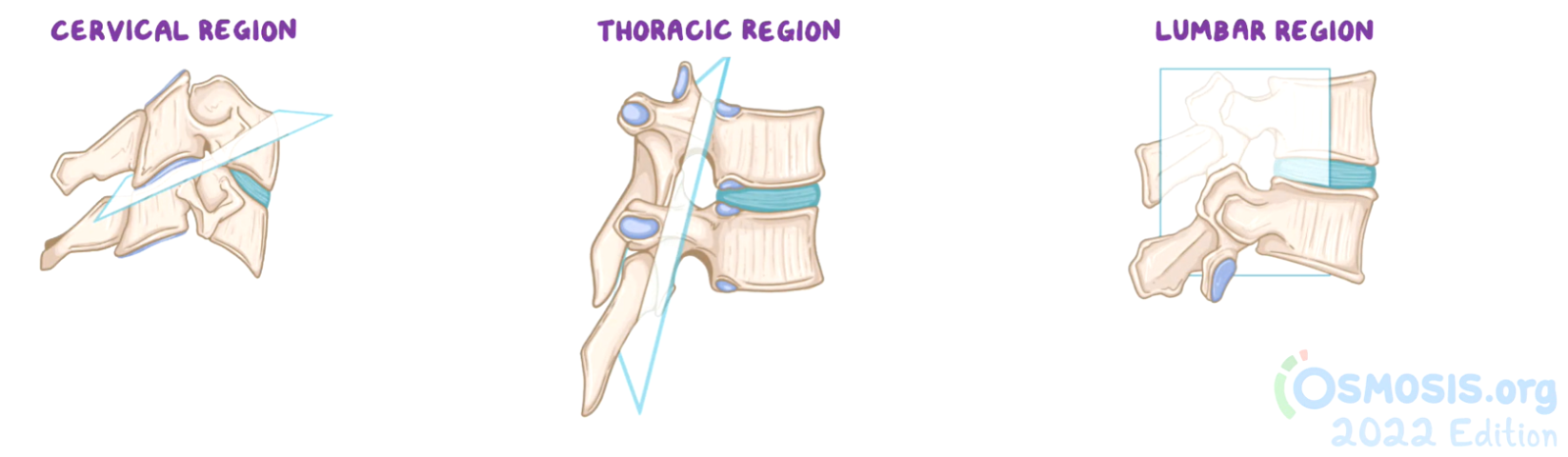
cervical facet/zygapophyseal joints
Transverse plane - slope inferior to posterior (45º)
Flexion / Extension = loose and more mobile
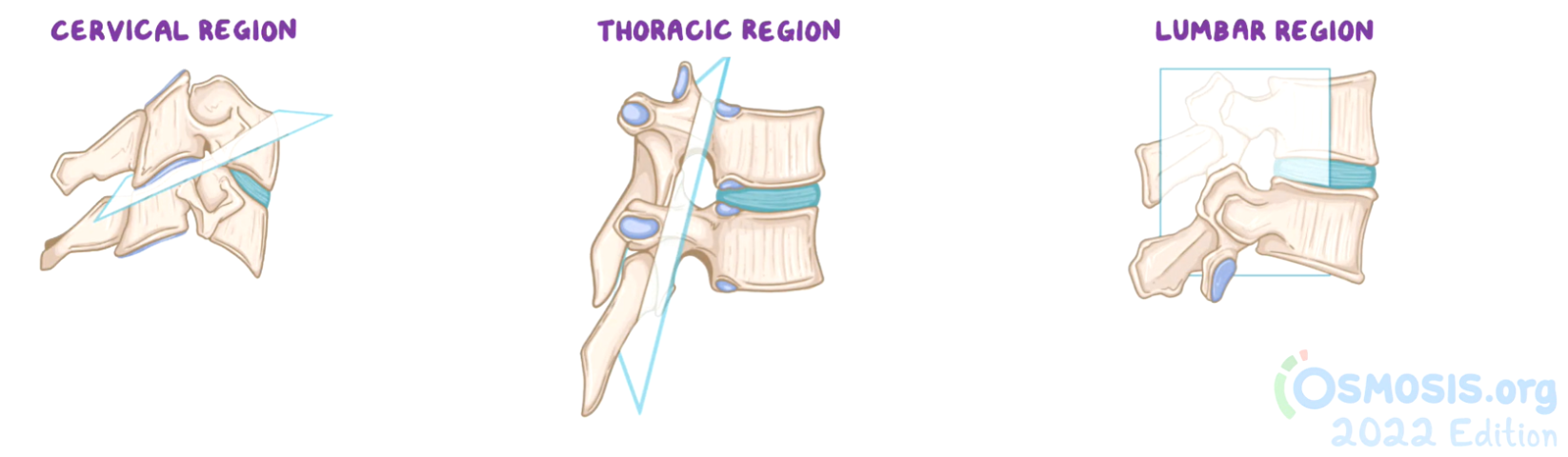
cervical region movements
flexion and extension
lateral flexion
rotation
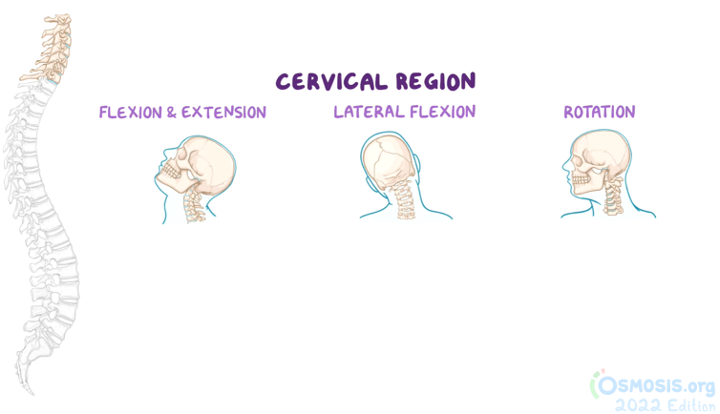
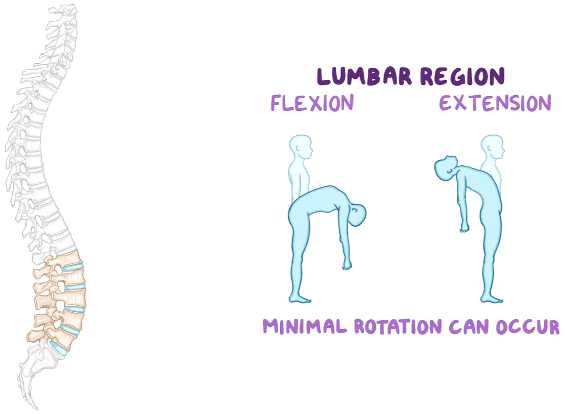
lumbar facet/zygapophyseal joints
Sagittal plane - face medially (superior) and laterally (inferior)
Flexion / Extension
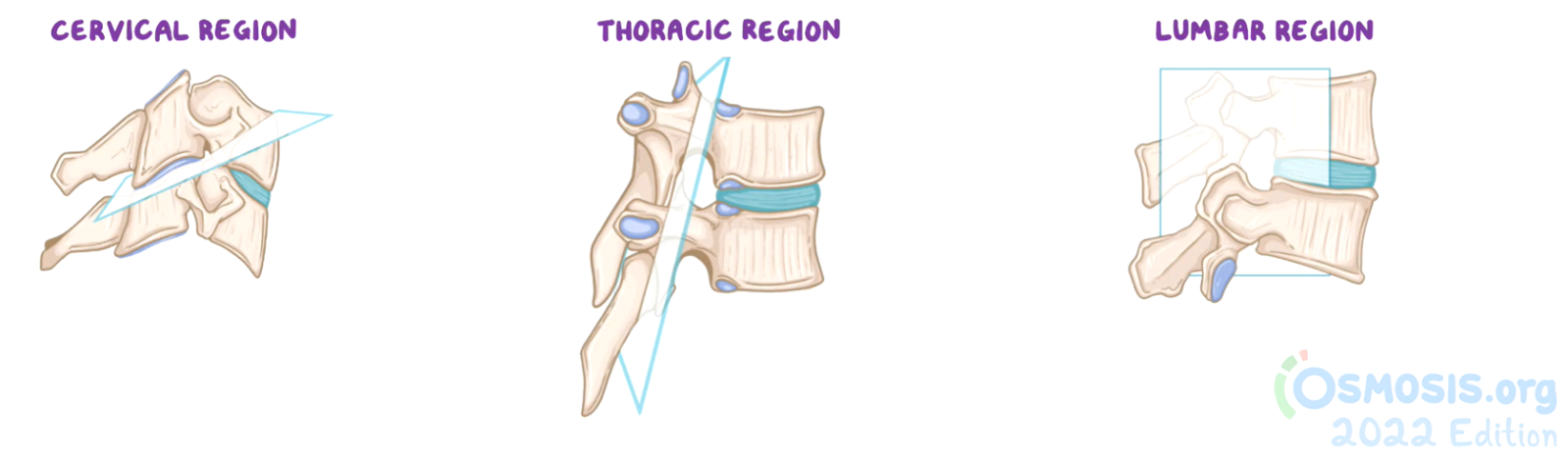
lumbar region movements
flexion
extension
(minimal rotation)
thoracic facet/zygapophyseal joints
Coronal plane - slope almost vertical (60º)
Limited movement
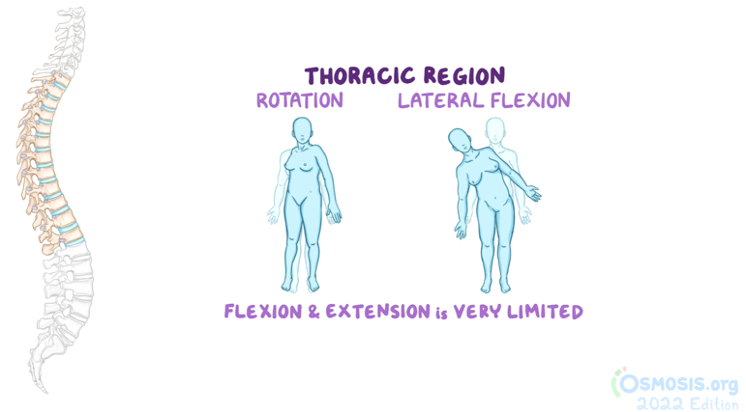
thoracic region movements
rotation
lateral flexion
(very limited flexion and extension)
Anulus Fibrosus
Allows intervertebral discs to withstand compression
Thick, tough, strong radial tire–like structure made up of lamellae
Concentric sheets of collagen fibres connected to vertebral end plates at various angles
Encloses the nucleus pulposus
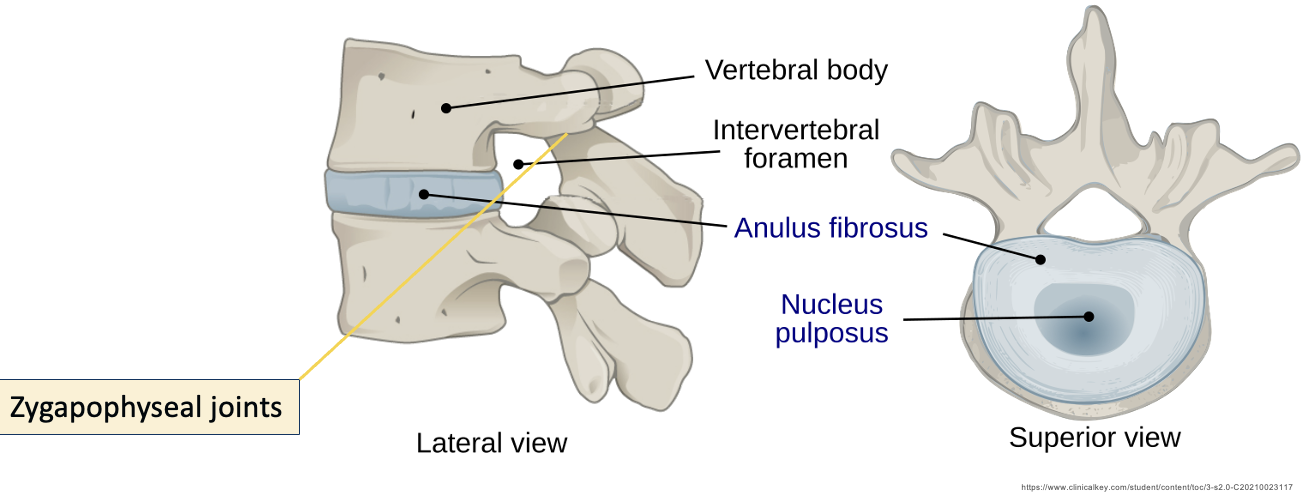
nucleus pulposus
Provides flexibility and resilience to the IVD
Gelatinous core, avascular
receives blood supply via diffusion of anulus fibrosus
Mostly H2O + primarily type II collagen & proteoglycans
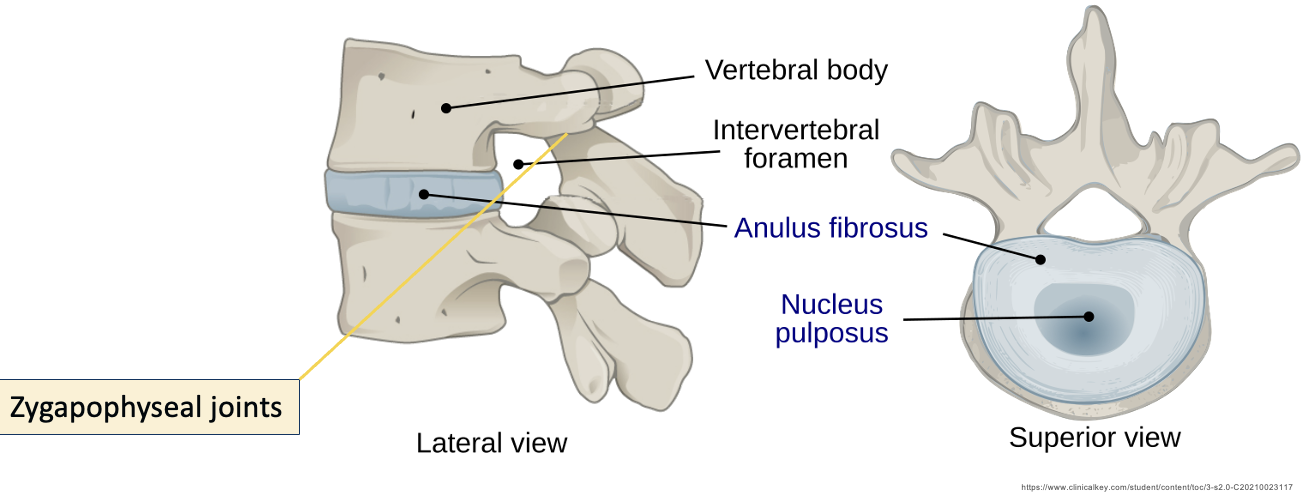
intervertebral disc function
Allows movement between adjacent vertebral bodies
Absorbs shock & transmits load
Accounts for flexibility of vertebral column
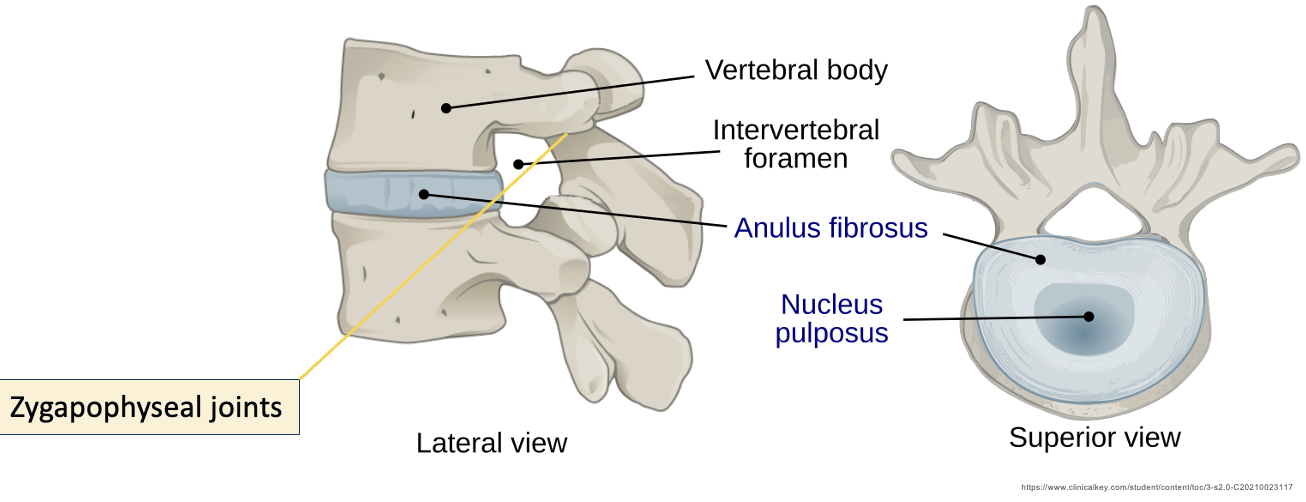
anulus fibrosus
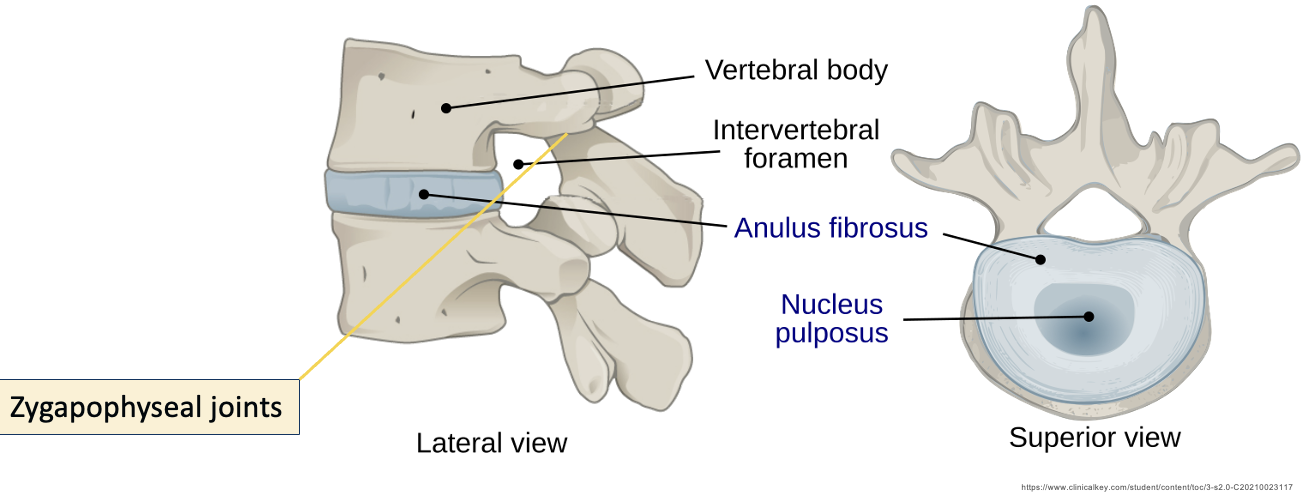
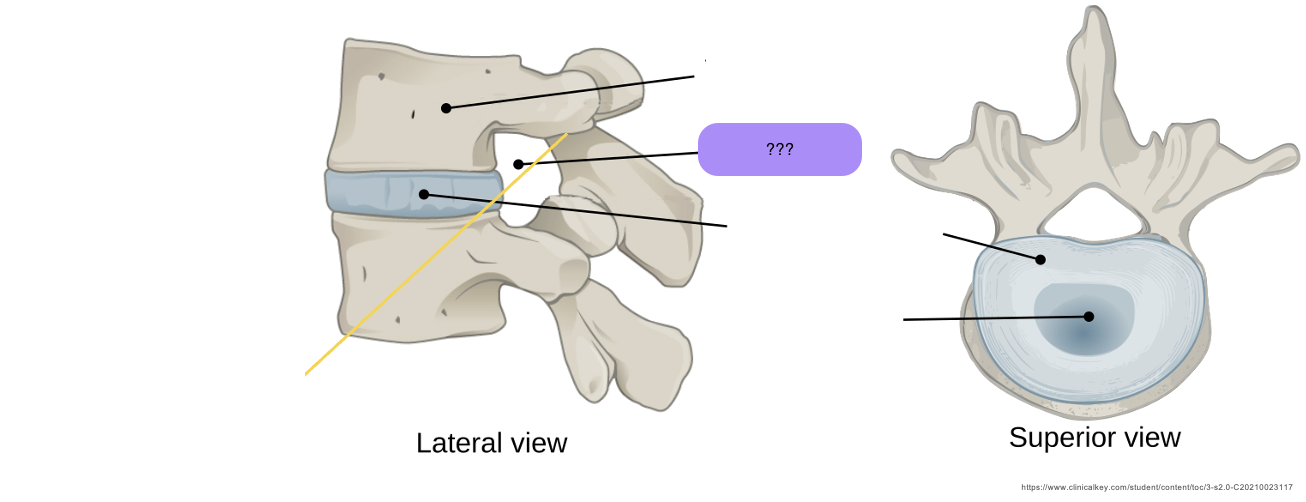
intervertebral foramen