AP US History Period 1, APUSH Period 1 (copy)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
maize cultivation
The growing of Indian corn, a staple of many Indians diets, leading many nomadic tribes to settle and develop great civilizations such as the Aztecs incas and Mayans.
hunter-gatherer economy
A nomadic way of life with no agriculture focused on following food sources including animals and wild plants
western hemisphere
The Americas
west africa
A area of Africa that was previously unreachable until the invention of the caravel by the Portuguese, leading to exploitation of the region for its gold and slaves

plantation-based agriculture
Large scale agriculture worked by slaves
capitalism
Economic system based on private investment and possessions
Cultural autonomy
Freedom of a group to express ones own culture without outside control i.g. The Christianization of the natives took away there Cultural autonomy
great basin
Desert area with no drainage to the ocean
agricultural economy
economy based on the production of crops
spanish exploration
Colonization of the Americas by the conquistadors in search for gold, glory and god
encomienda system
A government system where natives were given to colonists to work in return for converting them to Christianity.
empire building
The Spanish increasing their empire through grafting their culture onto the natives and taking over the land
white superiority
The European idea they were superior to other cultures/ races and needed to enforce European culture/religion on them
great plains
The open plains of the Midwest where the natives adapted to roming the prairies on horseback
permanent villages
The settlements of Indians tribes based on the spread of agriculture
Portuguese exploration
Due to advancements in sailing technology the Portuguese were able to sail down the coast of Africa and open trade of gold and slaves, settle and make plantations and eventually find the way around Africa to the indies
slave labor
Forced labor of people considered property by the people in charge
feudalism
A political, economic, and social system based on the relationship between lord and vassal in order to provide protection
political autonomy
the ability of a state to govern themselves without outside control
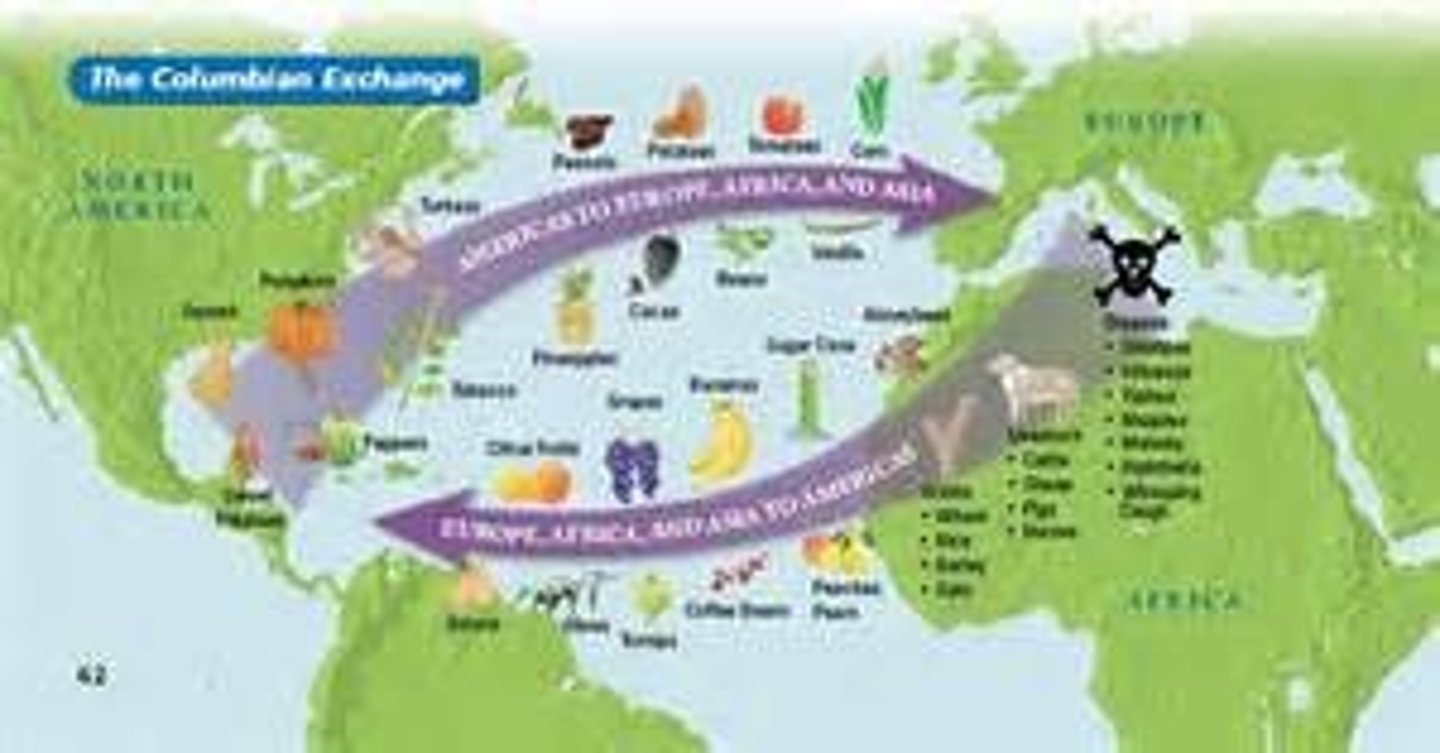
Colombian exchange
the exchange between the new world and the old world consisting of the old world bringing wheat, cows, horses, sheep, pigs, sugar, rice, coffee, smallpox, malaria and yellow fever. while the new world sent gold, silver, corn, potatoes, tobacco, and syphills
What happened as settlers migrated and settled across the vast expanse of North America over
time?
Result? (pp. 1-35) - Native populations often resisted the European advances, but
millions of Indians were killed through disease, war, and slavery. Land was taken by European settlers. In
Spanish America, Catholicism spread quickly through missions and forced conversions.
What impact did the spread of maize cultivation have on the American southwest?
Maize and other food crops led to large, more permanent agricultural societies with
larger populations. Europeans discovered that corn was a valuable agricultural staple
because it was relatively easy to grow and very useful
What was the impact of the lack of natural resources
Some native peoples had difficulty farming their land and focused on hunting and
gathering. A lack of natural resources also led to conflicts among Native peoples.
How did the development of permanent villages in the northeast impact native
tribes?
Some tribes in the northeast were able to form some loose alliances based on language and other
factors.
What did Spanish and Portuguese exploration and conquest lead to?
Spread of smallpox and other diseases which decimated huge numbers of American Indians. The Spanish
and Portuguese often employed violent and brutal tactics in their search for gold, silver, and other
riches. This led to many conflicts between Native peoples and the Spanish and Portuguese and the
deaths and subjugation of many, many Native people
What impact did Spanish and Portuguese traders have on West Africa?
Spanish and Portuguese traders dominated the slave trade, especially as demand for labor in the
colonies increased. In particular, slaves were desired for growing sugar. Some African tribes
participated in the slave trade in order to receive European goods, especially guns, and to weaken their
African rivals.
What was the impact of new crops and livestock in the Americas?
New crops (bananas, sugar) and domestic livestock (pigs, sheep, and cattle) had a huge impact on the
Americas. Horses, in particular, changed the way of life in the Americas. Disease, though, had the largest
impact, killing millions.
What was the encomienda system and why was it replaced by slave labor?
The encomienda system gave Spanish settlers land and the ability to force local Native
Americans to work on this land. Since so many Indians were dying from disease, the Spanish and
Portuguese looked to African slaves to work as laborers.
Impact of Christianity?
The Protestant reformation and the break with the Roman Catholic church created different
sects and groups of Christians. Puritans sought to purify the Anglican Church. Some of these dissenter
groups looked towards distant lands for some autonomy. Even in the colonies, divisions within the
Puritan community helped lead to the creation of Rhode Island and Pennsylvania, for example.
What was the impact of new crop and mineral wealth?
Although many early English settlers sought mineral wealth, most prosperity in the English
colonies came from agricultural commodities. Tobacco was the key crop that made English settlements,
like Jamestown, viable in North America. Sugar was the most valuable crop in the Caribbean and helped
drive the strong demand for African slaves
What was the impact of improvements in technology and better methods of international trade?
The enclosure movement in England repurposed land from fields for crops to pastures for sheep. This
displaced many poor farm workers and led to some food shortages. The increase in wool production led
to the growth of English and international trade, creating a new class of merchant capitalists. Most
European settlers had the advantage of oceangoing vessels and muskets. Indians helped teach the
European settlers about improved methods of agriculture in the Americas.
How did European expansion and sustained contact with Africans and American Indians
dramatically alter European views of social, political and economic relationships between white
and nonwhite people?
Some of the original European settlers respected the American Indians and their strength, but
the impact of disease greatly weakened most Indian societies. This confirmed European beliefs
of their superiority over the Indians. The African slave trade led to the insidious social concept of
racism that seemed to justify the permanent enslavement of a race of people.
How did treatment of American Indian tribes reflect European views of their civilization? (pp. 20,
30-31, 41, 43, 47-49, 57-58)
The English attempted to create a separate society away from Indian people, believing that the
Indians were clearly inferior. The French and Spanish were much more likely to live among and
with Native people, partly because few women or families from France and Spain emigrated to
the Americas and partly because the French and Spanish settlements more often depended on
cooperation from the American Indians than English settlements did
How did the development of white superiority impact the New World? (pp. 20-21, 23, 48, 57)
The Spanish developed an elaborate racial hierarchy that valued Spanish ancestry above Indian
or African ancestry. The slave trade was justified by a belief in white superiority. Many Puritan
settlers saw Indians as savages and godless people. Some English settlers believed that the
Indians could be "civilized." Other English settlers disagreed and sought to displace or eliminate
Indian societies.
How did Native and African attempts to maintain their political and cultural autonomy fare in the
face of European challenges to their independence? (pp. 12-23, 30-33, 47-50, 55-61)
There was often Native resistance, but much of it was undermined by the devastation of disease and
warfare. Indian people on the coasts were often the first to be subjugated to European domination, but
throughout the Americas there were areas of "middle grounds" where power was shared between
Europeans and Indians and where the two societies greatly influenced one another. There were also a
number of brutal wars and conflicts between the groups. Africans also fought to maintain autonomy,
especially in the Caribbean where there were several major slave revolts. However, slavery in the
western hemisphere was often brutal and resulted in harsh control over most aspects of slaves' lives.
What European attempts were there to change American Indian beliefs and worldviews on basic
social issues? Were they successful? (pp. 16, 18-19, 20-21, 47-50, 60-61)
Europeans attempted to convert Indians to Christianity. In some cases, they were successful. In some
cases, Indians successfully resisted. Indians also impacted European agricultural practices. The French
were usually much more successful at developing trade partnerships with Indians than the English were.
How did African slaves achieve some level cultural preservation and autonomy.? (21-23, 55-58)
African slaves maintained many traditional African religious and cultural practices under slavery. Slaves
sought to marry and create families and communities in even the most difficult situations. There were at
least seven major slave revolts in the Caribbean. In addition, slaves resisted their owners in a variety of
subtle and sometimes not subtle ways. Finally, from the first African immigrants to the western
hemisphere, there was always a population of free African settlers in the Americas.
Small pox:
highly contagious disease brought by Europeans that killed millions of American Indians, who
had not been previously exposed to this disease because most American Indians had not lived with or
near domesticated animals like cattle or sheep.
Pueblo Indians:
Native people found in the American southwest who for many years resisted Spanish
encroachment on Indian land and attempts at forced conversions.
African Religions:
Traditional African religions and practices were brought to the Western hemisphere
through the African diaspora and the slave trade, often resulting in a syncretic blending with Christianity.
African immigrants and slaves worked to maintain traditional religious and social practices in their new
surroundings.
Spanish Mission System:
Series of Spanish settlements focused on converting American Indians to
Catholicism. Many of these missions (San Francisco, San Diego, etc.) were key to economic and social
development of the American southwest.
Bartolome de Las Cases:
Spanish priest who wrote about the many atrocities he witnessed the Spanish
commit against the Indians.
Columbian Exchange:
the trade pattern that developed between the Americas and Europe/Asia. Named
after Columbus. Bananas, sugar, cattle, horses, small pox, etc., were brought to the Americas. Chocolate,
tomatoes, corn, tobacco, etc., were taken to Europe and Asia.
Encomienda System:
a land and labor distribution system that gave Spanish settlers land and the ability
to force local Native Americans to work on this land.
Mestizo and Zambo
Individuals with mixed Spanish and Indian ancestry.
Zambo: Individuals with mixed African and Indian ancestry.
Algonquin Indians:
Native people found in the American northeast who were close allies of the French
and participated in the fur trade. Algonquin Indians were the historic enemy of Iroquois Indians.
1542
Laws outlawed encomienda system